Science Chapter 5
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the Lithosphere?
The outer layer of the Earth, made up of the crust and upper mantle.
What is the crust of the earth made up of?
Magma
What is the hydrosphere made up of?
All the water found on, under and above the earth's surface
What is cryosphere?
The part of the hydrosphere made up of frozen water
What is the atmosphere made out of?
Layers of gases that surround the earth.
What does the atmosphere do?
It traps heat to warm earth, create a protective layer from the Sun (ozone) and carry sound
What does the atmosphere contain?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases to trap heat
What is Nitrifying bacteria able to do?
To return nitrogen to the atmosphere
What is the 4th most abundant element on Earth?
Carbon
Are organisms carbon-based life forms?
Yes
What does carbon make up?
Carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acid- all needed for life
What is the difference between a geological carbon cycle and a biological/physical carbon cycle?
Geological carbon cycle is a long-term cycle, whereas biological/physical is short term.
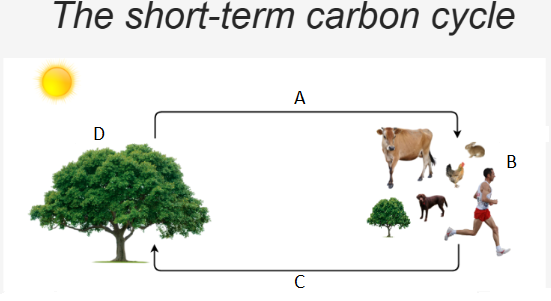
A- Glucose & Oxygen
B- Respiration
C- Water and Carbon Dioxide
D- Photosynthesis
What gases and particles are released into the atmosphere when biomass burns?
It releases Carbon dioxide, methane, monoxide and carbon particles (smoke) into the atmosphere
What do decomposers do with dead matter?
They break it down, returning carbon to the atmosphere.
How does decomposition return carbon to the air?
by breaking down organic material.
What are the two main ways carbon returns to the atmosphere?
Through fire and decomposition of dead matter.
What is a carbon sink?
A natural feature that absorbs and stores carbon, keeping it out of the atmosphere.
Give examples of major carbon sinks.
Forests, oceans, fossil fuels, rocks, soil, and shells of organisms.
What role do carbon sinks play in the carbon cycle?
They reduce atmospheric carbon by storing it long-term.
How do humans reduce carbon sinks?
By deforestation, burning fossil fuels, and destroying natural habitats.
What gases are released when fossil fuels are burned?
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄).
How does livestock farming affect the carbon cycle?
Because of the release methane, increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
What is the result of destroying carbon sinks?
Less carbon storage and more carbon in the atmosphere, worsening climate change.
What type of waves does the Sun emit?
Shortwave radiation that passes easily through atmosphere or glass.
What happens when sunlight reaches the ground?
Shortwave rays, heat the ground, which then radiates heat as longwave.
Why can’t infrared rays pass back through the glass?
Glass blocks longwave infrared radiation, trapping inside heat.
What causes the air inside the greenhouse to warm up?
Heat from the ground warms the air, which rises and spreads.
How is this process similar to Earth’s atmosphere?
Greenhouse gases act like glass, trapping heat and preventing it from escaping.
What happens to some of the heat in the greenhouse effect?
Only some escapes, however most are retained keeping the greenhouse warm.
Why is the greenhouse effect important?
It keeps Earth’s temperature suitable for life.
What happens when solar radiation reaches Earth?
It gets absorbed by the surface, warming land and oceans.
What happens to absorbed solar energy?
It’s re-emitted as infrared radiation from Earth’s surface.
What do greenhouse gases do?
They trap heat by absorbing infrared radiation and re-emitting it back to Earth.
Name the 3 main greenhouse gases:
Water vapor
Carbon dioxide
Methane
What is global warming?
The long- term rise in Earth’s average temperature.
Main effects of climate change?
Melting permafrost, rising seas, & extreme weather
What is permafrost?
Permanently frozen ground storing carbon from dead plants.
How does global warming cause extreme weather?
Warmer oceans fuel stronger storms and cyclones.
How does heat affect health?
High temperatures cause heat-related deaths and illness.
Example of deadly heat event?
2003 Europe heatwave killed about 27,000 people.
How does climate change spread disease?
Expands warm zones for diseases like malaria.
What causes smog-related illness?
Trapped warm air and pollutants cause breathing issues.
Why does biodiversity decline with climate change?
Organisms can’t adapt to fast temperature or habitat changes
What causes coral bleaching?
Warmer water stresses coral
What drives ocean currents?
Temperature and salt concentration differences.
How does melting ice affect currents?
Alters water temperature and salt balance, changing flow patterns.
What is a carbon tax?
A fee for each ton of CO₂ a business emits.
What is carbon trading?
Companies buy or sell emission allowances to meet targets.
What is geosequestration?
Capturing and storing CO₂ underground to reduce emissions.
How is methane produced?
From grass fermentation in cattle stomachs.
Why is methane increasing?
Population growth raises meat demand, increasing cattle numbers.
How can individuals reduce carbon emissions?
Use public transport, carpool, or switch off unused electronics.
What energy source helps cut emissions?
Renewable energy like solar power.