chapter 11 of anatomy and physiology mcgraw hill questions
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
what are the three meninges?
dura, arachnoid, pia
the cerebrum is the ______ of the mature brain.
a) earliest formed part
b) smaller part
c) largest part
c) largest part
Ventricles are cavities found in the _____ and are filled with _____.
a) brain ; cerebrospinafluid
b) brain; blood
c) spinal cord; blood
d) spinal cord ; cerebrospinal fluid
a) brain; cerebrospinal fluid
the neural centers and pathways that coordinate muscular movements are located in the ______.
a) venticles
b) spinal cord
c) brain
d) various ganglia throughout the body
c) brain
what is the brainstem composed of?
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
within the brain, the major area that is responsible for intelligence and personality is what?
cerebral cortex
what are the cavities within the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid?
ventricles
what are some general functions of the brain?
it issues motor commands, it is responsible for perception of sensation, it regulates visceral activity.
from where does the sensory areas of the cerebrum receive and interpret?
receptors
what are the areas on the cerebral cortex that interpret sensory impulses an handle reasoning and judgement?
association areas
what is the name for the large cells in the motor cortex of the cerebrum?
pyramidal
the neural centers and pathways that coordinate muscular movements are located where?
brain
which area of the cerebrum function to receive input from receptors, producing sensations?
sensory areas
what kind of matter does the basal nuclei consist of?
gray matter
what are the functions of association areas int he cerebral cortex?
analyze and interpret sensory experiences
the pre central gyrus of the frontal lobe contains what functional area?
a) wernicke’s area
b) broca’s area
c) sensory interpretive area
d) primary motor area
d) primary motor area
what is the area of the brain, where it is located between the cerebral hemispheres, superior to the brainstem, and surrounding the third ventricle?
diencephalon
which areas of the cerebrum function to receive input from receptors, producing sensations?
a) somatic
b) motor
c) sensory
c) sensory
the pons, medulla oblongata, and midbrain are subparts of what part of the brain?
the brainstem
what is the general name of the areas of gray matter found deep in the white matter of the cerebrum (including caudate and putamen)
basal nuclei
the brainstem connects the ___ to the ____.
brain ; spinal cord
the diencephalon is located between two cerebral _____ and superior to the ______.
hemispheres; brainstem
what part of the nervous system is responsible for sensation and perception, issuing motor commands, personality, and regulating visceral activity?
the brain
what is the name of the large mass of tissue that is located inferior to the occipital lobe and posterior to the pons?
cerebellum
the spinal cord ends near the intervetebral disc that seperates the ______.
a) fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae
b) eleventh and twelfth thoracic vertebrae
c) third and fourth lumbar vertebrae
d) first and second lumbar vertebrae
d) first and second lumbar vertebrae
the spinal cord consists of 31 segments. Each segment gives rise to a pair of what?
spinal nerves
all the basic components of a reflex are collectively known as a reflex _____.
arcs
the nervous tissue that becomes the spinal cord leaves the cranium through the ?
foramen magnum
how many segments are in the spinal cord?
31
a reflex arc begins with a sensory receptor at the dendritic end of a(n) _____.
a)sensory neuron
b) motor neuron
c) efferent neuron
d) interneuron
a) sensory neuron
what structure functions to conduct nerve impulses between the peripheral body and the brain and also acts a sa reflex center?
a) the reticular formation
b) the cerebellum
c) the spinal cord
c) spinal cord
a ______ is a nerve pathway that begins with a _____ receptor and ends with an effector. These nerve pathways are very simple and can contain as few as two neurons.
reflex; sensory
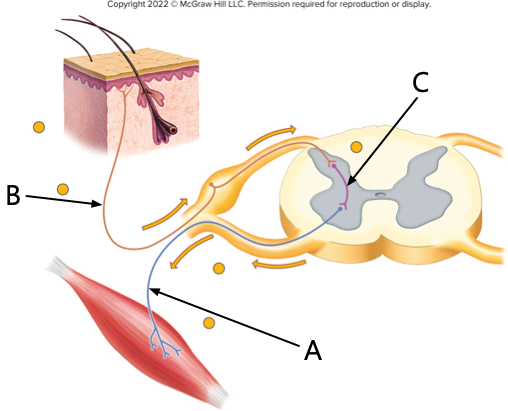
arrow b is pointing to the _____; arrow a pointing to is the ____.
sensory neuron; motor neuron
what is a reflex?
an automatic, involuntary response to a specific stimulus
carries sensory information, what type of neuron is this?
afferent neuron
relays signals within the CNS, what type of neuron is this?
interneuron
carries impulses to effectors, what type of neuron is this?
efferent neuron
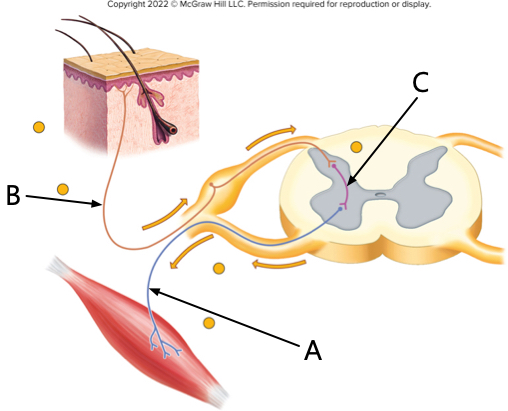
which arrow is pointing to the interneuron?
C
because it only uses two neurons, the patellar reflex is an example of a?
a) viscera reflex
b) monosynaptic reflex
c) bysynaptic reflex
d) bineuronal reflex
b) monosynaptic reflex
a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus Is called?
reflex
what is the name of the tracts of the spinal cord which carries sensory information to the brain?
ascending tracts
what is the name of the tracts the carry motor impulses from the brain to the periphery?
depending tracts
what nervous system consists of all the nerves that branch from the CNS?
peripheral
the spinal cord is a center for spinal _____ an conducts impulses to an from the brain.
reflexes
what is a monosynaptic reflex?
a flex that involves two neurons only
are reflex voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary
which tracts in the spinal cord carry sensory information?
ascending tracts
what structure functions to conduct nerve impulses between the peripheral body and the brain and also act as a reflect center?
the spinal cord
a _____ is composed of numerous nerve fibers (fascicles) bound together by connective tissue.
nerve
true or false: the cranial nerves serve parts of the head, neck, and also some structures of the trunk,
true
cranial nerves I and II are associated with the cerebrum while the remaining cranial nerves originate from the ____?
brainstem
cranial nerves and spinal nerves are part of the ____ nervous system?
peripheral
in the most generalized way, nerves can be defined as bundles of _____.
axons
the nervous system has twelve pairs of ____.
cranial nerves
what areas of the body do cranial nerves innervate?
head, neck, and some parts of the trunk
which cranial nerve contains only sensory nerve fibers and transmits impulses associated with the sense of smell?
olfactory nerve
most of the cranial nerves (cranial nerves III-XII) arise from the ___.
brainstem
what is the name of the cranial nerves II?
optic
what is the name of cranial nerve III?
oculomotor
what is the name of the cranial nerve IV?
trochlear nerve
the superior oblique muscles in the eyes is controlled by which cranial nerve?
trochlear
what is the name of cranial nerve V?
trigeminal
what is the name of the three large branches of the sensory component of the trigeminal nerve?
maxillary division, opthalmic division, mandibular division
when a physician moves a finger in front of a patients face, asking them to follow its movement with their eyes, they are testing the function of which nerve?
trochlear
it controls muscles of the pupil to adjust the amount of light entering the eye, it controls muscles that move the eye, it controls muscles that raise the eyelid. Which nerve is this describing?
oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve III)
which cranial nerve is known as the facial nerve?
cranial neve VII
what are the effectors of the motor fibers of the facial nerve?
salivary glands and tear glands; muscles of facial expression
what is the cranial nerve number for the abducens nerve?
cranial nerve VI
what is the effectors for the4 motor fibers of the trochlear nerves?
the superior oblique muscles in the eyes.
a bundle of descending lower spinal nerve roots that extend below the end of the adult spinal cord within the vertebral canal, this is describing?
cauda equina
motor signals leave the spinal cord through the ____ roots. Sensory signals enter the spinal cord through the ____ roots.
a) posterior;anterior
b) anterior; posterior
c) posterior; posterior
d) anterior; anterior
b) anterior; posterior
how do spinal nerves exit the vertebral column?
through the intervertebral foramina
as the lumbar and sacral nerves extend inferiorly beyond the end of the spinal cord, they form the _____.
cauda equina
what type of fibers are found in the anterior root of a spinal nerve?
the axons of motor neurons
what are the functions of the cervical plexus?
supply motor impulses to muscles of the neck, transmit sensory information from the skink of the neck to the CNS.
Nerves arising from the ______ plexus innervated the upper limbs.
brachial
what plexus give rise to a number of nerves that control the muscles of the thighs, legs, and feet?
lumbosacral plexus
the anterior roots consists of _____ fibers (axons) while posterior roots consists of ______ fibers (axons).
motor; sensory
the ____ plexus give rise to nerves that innervates the upper limbs.
brachial
what type of fibers are found in the anterior root of a spinal nerve?
the axons of motor neurons
what are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
parasympathetic and sympathetic
the autonomic nervous system maintains homeostasis and controls visceral activities by regulating the actions of ?
cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, anf several glands
an autonomic motor pathway consists of what two fibers?
postganglionic fiber and preganglionic fiber
what is the origin of the sympathetic preganglionic fibers?
a) the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord
b) the brainstem and the cervical regions of the spinal cord
c) the brain stem and the sacral regions of the spinal cord
a
what are the origins of parasympathetic preganglionic neurons?
the brainstem and the sacral regions of the spinal cord
sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic fibers both release which neurotransmitter?
acetylcholine
the division of the PNS regulates visceral activities and maintains homeostasis is called _____ nervous system
autonomic
the preganglionic fibers of the ____ division of the autonomic nervous system arise from the thoracic an upper lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
sympathetic
autonomic regulation of visceral functions, such as body temperature hunger, and thirst, occurs in what area of the brain?
the hypothalamus
typically, if the sympathetic vision of the autonomic nervous system activates an organ, the parasympathetic division _____.
a) doe snot innervate it
b) inhibits it
c) also activates it
b
what is true about apoptosis in the brain?
if it fails, disease like schizophrenia may result and it is a normal natural occurrence
when does stimulation at cholinergic receptors end?
when acetylcholine is broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft