types of natural selection
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is selection pressure?
an environmental factor which causes selection within a population by exerting environmental pressure
examples of selection pressure
predatation, disease, temperature variation, human influence, limited light oxygen and water, competition
what is the limiting factor due to?
the phenotype, which limits reproductive success as well as selection pressure
any natural selection question:
mutation results in new allele
those new allele have the advantage of
individuals with the allele are more likely to survive and reproduce
increased frequency of this allele in a population
directional selection
what is directional selection?
shifts mean value of the phenotype in the direction that the extreme phenotype is favoured by selection.
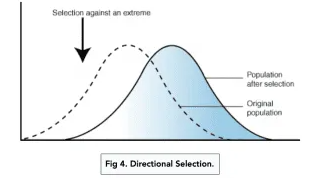
what does directional selection do over time?
individuals at one extreme may have an advantage, leading to selection to operate against the disadvantadged extreme and in favour of the other extreme, causing a shift in the population's traits - the mean and range of values shift towards the favoured extreme.
example of directional selection
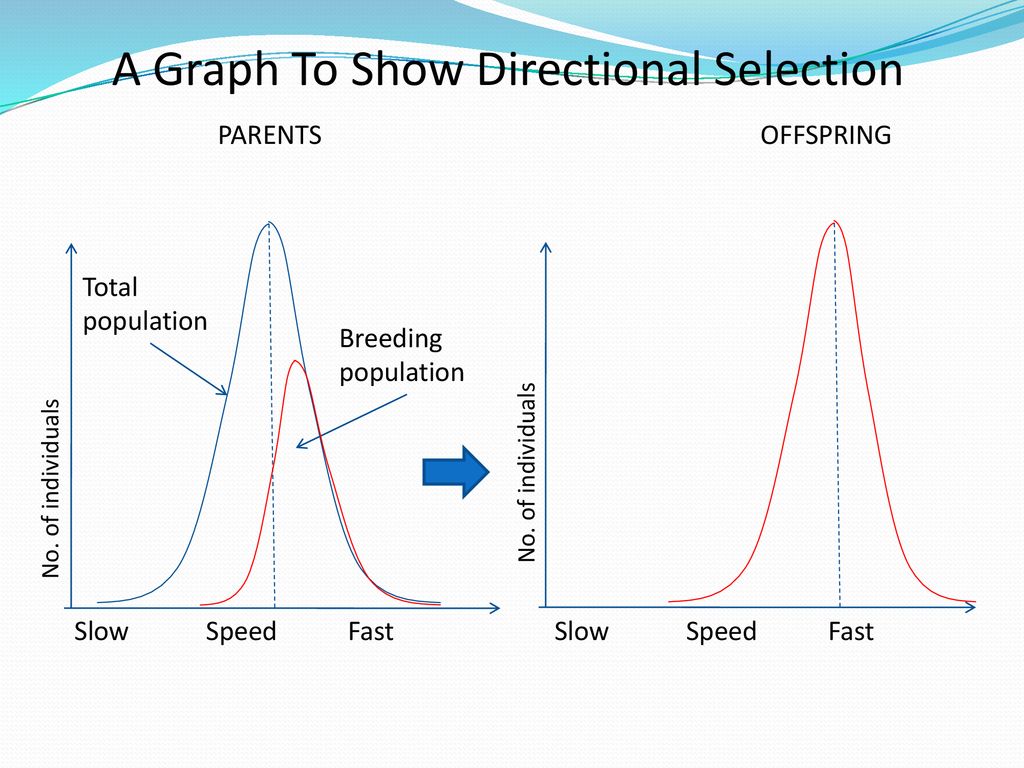
cheetahs - individuals with the speed allele more likely to catch prey than slower individuals. They have a select advantadge so they’re more likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their alleles. Over time, the frequency of alleles for high speed increases and the population becomes faster.
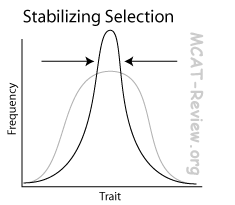
what is stabilising selection?
reduces variation but doesn’t change the mean, by favouring average phenotypes over extremes, promoting traits that are average and limiting the prevalence of extreme traits, to make it more uniform.
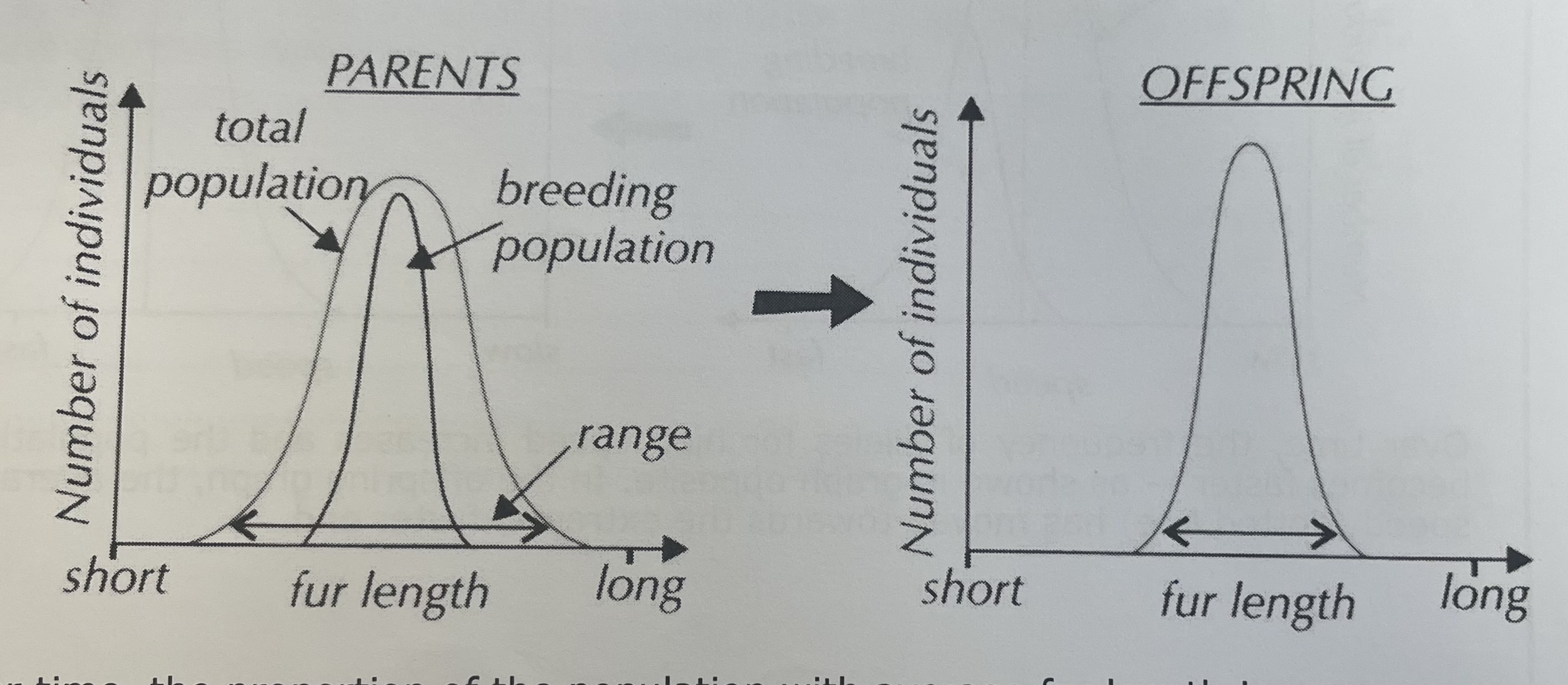
example of stabilsiing selection

occurs when there is no change in environment
Human birth weight, where infants of average weight have higher survival rates compared to those that are underweight or overweight. Over time, proportion of population with average birth weight increases and range decreases, resulting in a narrower offspring graph
what happens to standard deviation as the individuals with extreme traits decrease
The standard deviation decreases (stabilising selection).
sequence of events leading to natural selection
competition
genetic variation within population - random mutations leading to stabilising selection
combinations of alleles make them better able (fitter) to survive
so more successful breeding and more offspring produced
successful reproduction means alleles passed on through generations and the frequency of adventaageous alleles increases.