Lecture 23 & 24 Drug Transporters and Pharmacogenomics
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1) Describe the importance of drug transporters in drug disposition. 2) Describe the role of drug transporters in managing passage of compounds through the blood brain barrier. 3) Explain the importance of P-glycoprotein, PEPT1, and OATP1B1 to the disposition of various drug substrates. 4) Understand the importance of porin channels and efflux pumps in bacteria for the activity of antibiotics. Describe genetic variation and how it affects drug response • Define pharmacogenomics • Apply the pharmacogenomic concept to specific drug dosing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is a Drug Transporter Inhibitor and what does it do to Drug Transporter Substrates
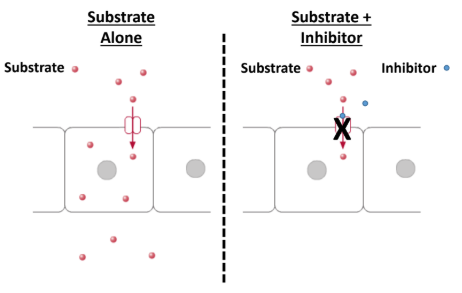
It can inhibit the drug transporter substrate and can block substrates.
causes drug-drug interactions
What is paracellular transport?
a. movement of molecules through cells
b. movement of molecules between cells
b. movement of molecules between cells
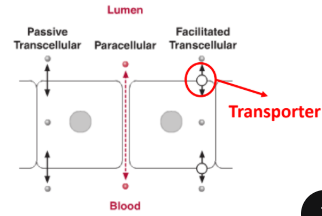
What kind of Drug Transporter is an efflux pump that works to eliminate drugs from the cell?
a. P-glycoprotein
b. OATP1B1
c. PEPT1
a. P-glycoprotein
What is P-glycoprotein (P-gp) also known as?
Multiple drug-resistant receptor (MDR1)
Why is P-glycoprotein an important transporter?
It is important for limiting drug entry through BBB
Facilitates biliary and urinary excretion of drugs
How does P-glycoprotein interact with the drug Paclitaxel in both PO and IV dosing?
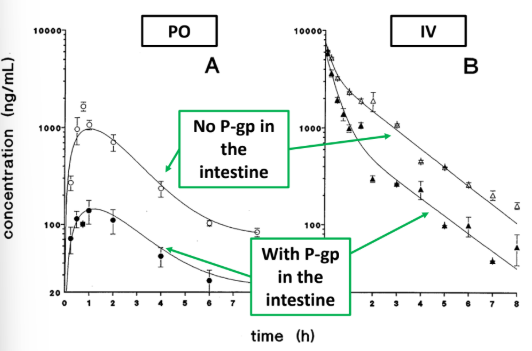
PO: P-gp reduces paclitaxel conc, by limiting uptake through intestine
IV: P-gp reduces paclitaxel conc. by secretion into intestinal lumen
How does Digoxin and a P-gp inhibitor (cyclosporine) interact with each other?
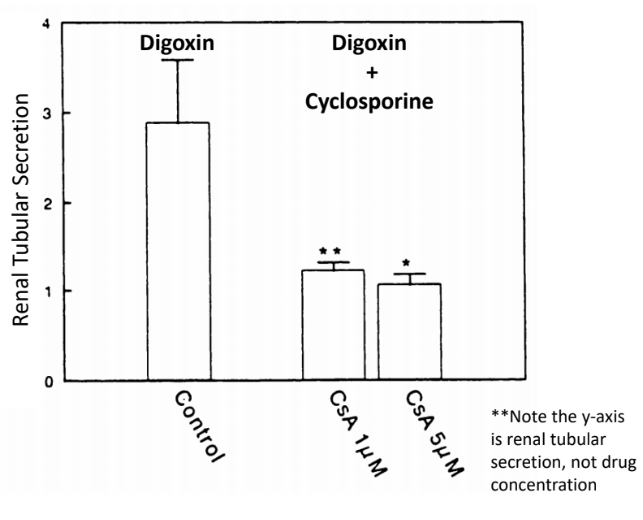
Digoxin is renally effluxed thru P-gp
P-gp —> in the proximal tubule of kidney —> secretes drug into urine
Digoxin + Cyclosporine —> reduces tubular secretion (INCREASED digoxin plasma levels)
How does Ritonavir related to P-gp and what else does it interact with?
It is a strong CYP3A4 (cytochrome P450) inhibitor and P-gp inhibitor —> unintended result —> drug-drug interactions

True or False: P-gp substrates may be returned to the intestines via biliary excretion due to the presence of P-gp in the hepatocytes.
True!!!
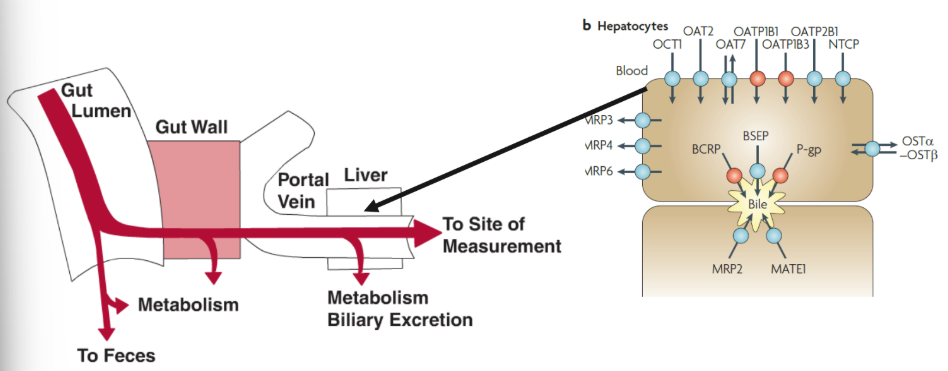
1) Which of the following would you expect to occur when you co-administer paclitaxel and cyclosporine compared to administering paclitaxel alone? Select all that apply.
A. Decreased paclitaxel concentrations in the brain
B. Decreased serum paclitaxel concentrations
C. Decreased biliary excretion of paclitaxel
D. Decreased renal excretion of paclitaxel
E. None of the above
paclitaxel —> gets reduced by p-gp (substrate)
cyclosporine —> pgp inhibitor (inhibitor)
** cyclosporine (P-GP INHIBITOR) inhibits P-gp, which allows an increase of paclitaxel conc. in brain and serum (accumulates in body):
C. Decreased biliary excretion of paclitaxel
D. Decreased renal excretion of paclitaxel
What kind of Drug Transporter is an uptake transporter contains in the sinusoidal side of hepatocytes?
transports endogenous bilirubum, bile acids frm blood —> hepatocytes
a. P-glycoprotein
b. OATP1B1
c. PEPT1
b. OATP1B1
What does OATP1B1 stand for?
Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP)
What are the substrates of OATP1B1 transporters?
Statins!
They inhibit HMG-CoA reductase (lowers cholesterol)
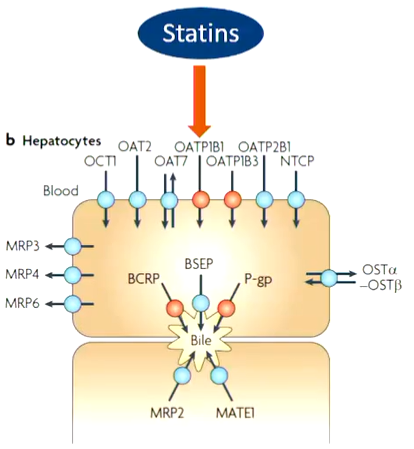
OATP1B1 has SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) that can cause variation in structures. Some can lead to a decreased transport of statins. What does this result in and give an example of an SNP!
Decreased transport of statins —> increased side effect risk —> myopathy
Example of SNP: V17A —> nonfunctional OAT1B1

Genetic polymorphisms of OATP1B1 that are associated with nonfunctional transporter activity would lead to:
A. Increased hepatotoxicity of statins
B. Decreased efficacy of statins
C. Decreased myopathy of statins
D. None of the above
B. Decreased efficacy of statins
What kind of Drug Transporter is an influx transporter primarily responsible for the absorption of peptides from the intestine?
also enables intestinal uptake of peptide-like drugs
a. P-glycoprotein
b. OATP1B1
c. PEPT1
c. PEPT1
Peptidase transporter 1
True or False: Plasma concentration of acyclovir and valacyclovir through PO is dependent on the presence of PEPT1.
True! Valacyclovir gets pumped through PEPT1 —> gets converted to acyclovir (active form of drug, less bioavailable)
How does Liver Cirrhosis affect OATP1B1 (hepatocytes) and P-gp (hepatocyte)
a. increase, increase
b. increase, decrease
c. decrease, decrease
d. decrease, increase
d. decrease, increase
think: OATP1B1 is an uptake transporter, while P-gp is an efflux. when the liver is damaged, do you think there will be more influx or efflux?
How does Inflammatory Bowel Disease affect P-gp (intestine) and PEPT1 (intestine)
a. increase, increase
b. increase, decrease
c. decrease, decrease
d. decrease, increase
d. decrease, increase
think: when you have a disease, do you think there will be more influx or efflux?
What transporter channels allow passage of certain antibiotics across the bacterial cell wall?
a. Porin channels
b. Efflux pumps
a. Porin channels
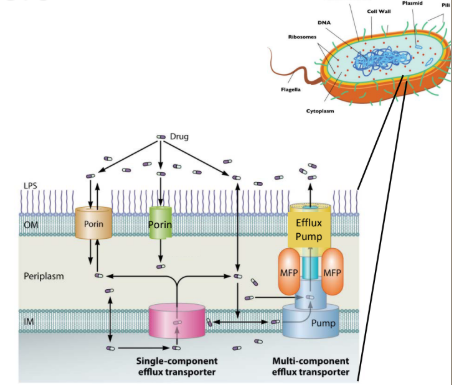
What transporter channels remove antibiotics from cell membrane (decreases intracellular antibiotic conc)l?
a. Porin channels
b. Efflux pumps
b. Efflux pumps
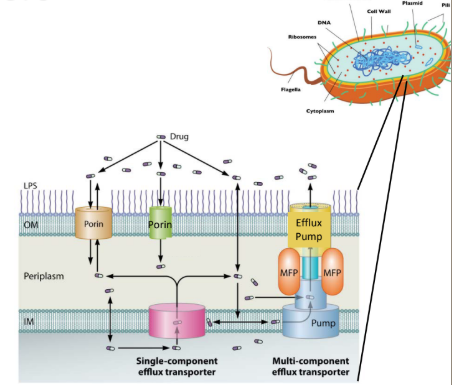
What are Porin channel mutations that can prevent uptake of substrates (causes antibiotic resistance)?
a. OmpK35, OmpK36
b. AcrB, MexAB-OprM
a. OmpK35, OmpK36
K35: cephalosporins, cephamycins
K36: cephalosporins, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones
What are some Efflux pumps that remove antibiotics from bacterial cells (mutations or loss of function)
a. OmpK35, OmpK36
b. AcrB, MexAB-OprM
b. AcrB, MexAB-OprM
AcrB: all antibiotics except aminoglycosides
MexAB-OprM: Most beta lactams
Which one of the following transporters is responsible for aiding oral absorption of valacyclovir?
A. P-gp
B. OATP1B1
C. PepT1
D. OCT1
C. PepT1
Which one of the following transporters is responsible for hepatic uptake of statins?
A. P-gp
B. OATP1B1
C. PepT1
D. OCT1
B. OATP1B1
Which of the following are associated with bacterial resistance to an antibiotic? Select all that apply.
A. Functional OmpK35 porin channel
B. Nonfunctional OmpK35 porin channel
C. Functional AcrB efflux pump
D. Nonfunctional AcrB efflux pump
E. None of the above
B. Nonfunctional OmpK35 porin channel
C. Functional AcrB efflux pump
Match the term to its definition:
Pharmacogenetics
a. effect of variability in a single gene (or a few genes) on drug response
b. effect of variability in the whole genome on drug response
a. effect of variability in a single gene (or a few genes) on drug response
Match the term to its definition:
Pharmacogenomics
a. effect of variability in a single gene (or a few genes) on drug response
b. effect of variability in the whole genome on drug response
b. effect of variability in the whole genome on drug response
Why is pharmacogenomics so important?
There is a potential to eliminate trial-and-error approach to drug prescribing.
What is the indication for Warfarin?
Atrial fibrillation
VTE treatment/prophylaxis
What is the MOA of Warfarin?
Inhibits vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKORC1) enzyme complex
Warfarin is metabolized mainly by what?
CYP2C9
CYP2C9×1 allele has the NORMAL activity
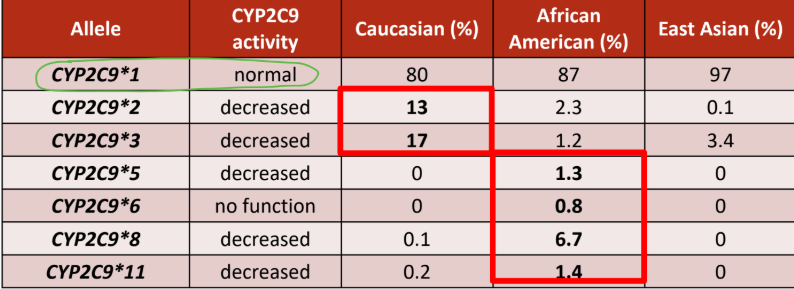
Which CYP2C9 allele is common in European descent?
a. 2 and 3
b. 5,6,8,11
a. 2 and 3
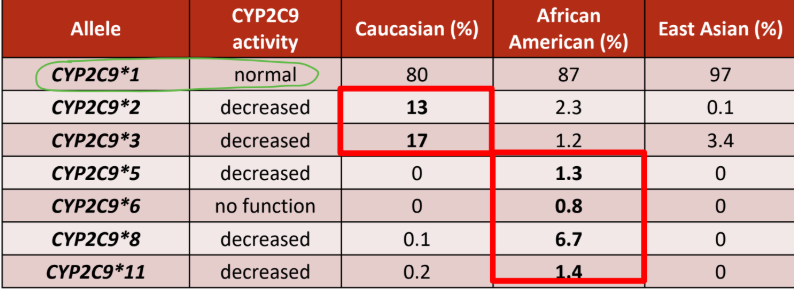

Which CYP2C9 allele is common in African descent?
a. 2 and 3
b. 5,6,8,11

b. 5,6,8,11
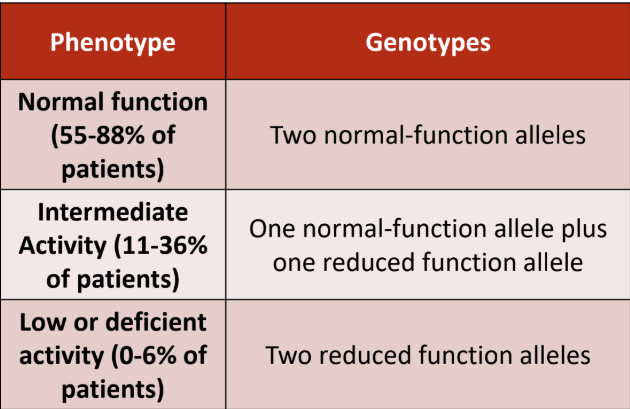
What is considered a normal metabolizer?
a. 2 normal function alleles (1/1)
b. 1 normal function + 1 decreased function (1/2) (1/3)
c. 2 decreased function alleles (2/3) (2/2) (3/3)
a. 2 normal function alleles (1/1)
What is considered an intermediate metabolizer?
a. 2 normal function alleles (1/1)
b. 1 normal function + 1 decreased function (1/2) (1/3)
c. 2 decreased function alleles (2/3) (2/2) (3/3)
b. 1 normal function + 1 decreased function (1/2) (1/3)
What is considered a poor metabolizer?
a. 2 normal function alleles (1/1)
b. 1 normal function + 1 decreased function (1/2) (1/3)
c. 2 decreased function alleles (2/3) (2/2) (3/3)
c. 2 decreased function alleles (2/3) (2/2) (3/3)
What does VKORC1 do in relation to vitamin K?
It converts vitamin K-epoxide to vitamin K (active form)
What is the normal form of VKORC1*2 allele
a. G (reduced warfarin sensitivity)
b. A (increased warfarin sensitivity)
a. G (reduced warfarin sensitivity)
What is the decreased function form of VKORC1*2 allele
a. G (reduced warfarin sensitivity)
b. A (increased warfarin sensitivity)
b. A (increased warfarin sensitivity)
What does CYP4F2 do in relation to vitamin K?
Catalyzes vitamin K metabolism to hydroxyvitamin K1 and removes vitamin K from the vitamin K cycle

If you are a patient on warfarin and you receive a
letter stating that your genotype is CYP2C9 2/3
and VKORC1 AA, what dose should you start?
a. Lower than normal dose
b. Normal dose
c. Higher than normal dose
a. Lower than normal dose
What does Clopidogrel (Plavix) do?
Antiplatelet drug that inhibits the P2Y12 class of ADP (adenosine diphosphate) receptor
prodrug
metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2C19
If you are a patient on clopidogrel and you receive a
letter stating that your CYP2C19 genotype is 2/3,
what dose should you start?
a. Extensive metabolizer, normal dose
b. Ultrarapid metabolizer, normal dose
c. Poor metabolizer, alternative therapy
c. Poor metabolizer, alternative therapy
What is Codeine
Prodrug with no analgesic activity —> morphine (Active metabolite)
metabolized by CYP2D6
If you are a patient on acetaminophen-codeine PRN
for pain and you receive a letter stating that you are
a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer, what dose should you
start?
a. Normal dose
b. Avoid codeine use due to toxicity
c. Avoid codeine use due to lack of efficacy
c. Avoid codeine use due to lack of efficacy
What is Simvastatin and what is its most common adverse effect?
It is an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor used in Hyperlipidemia and primary and secondary prevention of CAD
Most common adverse effect: muscle toxicity
OATP1B1 is encoded by Simvastatin. Which polymorphism affects its function which causes an increased risk of statin-related myopathies?
SLCO1B1, there is a single amino acid change in OATP1B1 protein (T>C)
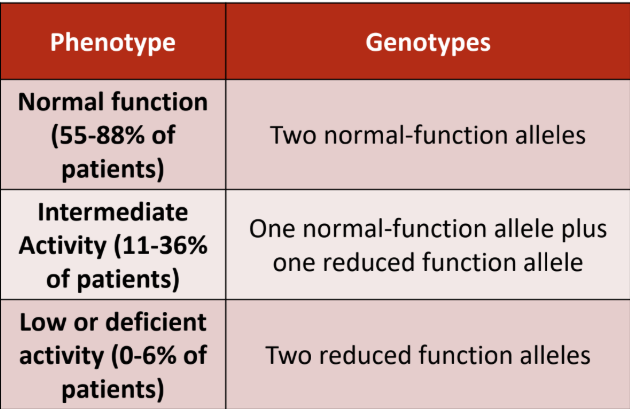
What is the genotype for normal function?
a. CC
b. TC
c. TT
c. TT
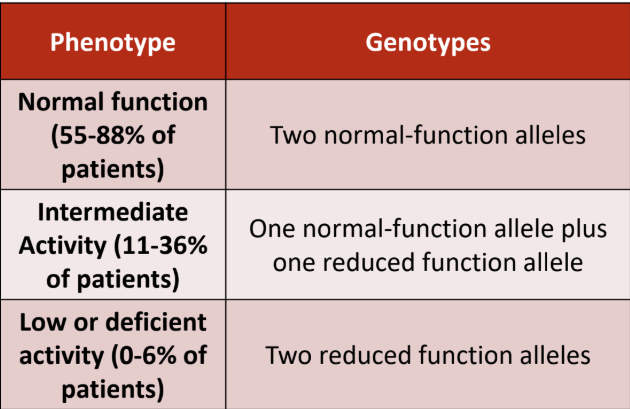
What is the genotype for intermediate function?
a. CC
b. TC
c. TT
b. TC
What is the genotype for low/deficient function?
a. CC
b. TC
c. TT
a. CC
If you are a patient on simvastatin and you receive a
letter stating that your genotype at SLCO1B1
rs4149056 SNP is CC, which of the following is true?
a. High risk to develop myopathy, alternative therapy
b. Intermediate risk to develop myopathy, use lower
dose
c. Low risk to develop myopathy, use normal dose
a. High risk to develop myopathy, alternative therapy