2 A-level Economics Edexcel keywords
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Set 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what does PIRATES stand for
population, income, related goods, advertising, trends, expectations and seasons
what is derived demand
where the demand for one good is linked to the demand for a related good
what is composite demand
when the good demanded has more than one use
what is joint demand
when goods are bought together
what are Veblen goods
luxury goods or superior goods whose demand does not follow the typical economic laws of supply and demand e.g. goods prices rise = more demand
what are Giffen goods
a type of product that experiences an increase in demand as its price rises
what is ceteris paribus
all other things being equal
what is the demand curve
a line showing the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
what is the income effect
when price of a g/s changes the consumer can maintain same consumption for less expenditure making them feel richer
what is real income
income of individuals or nations after adjusting for inflation
what is the substitution effect
when price of a g/s falls the product is now relatively cheaper so consumers will switch from the alternative g/s
what is PED
the responsiveness of quantity to a change in price
what’s the formula for PED
% change in QD / % change in P
what is a normal good
product whose demand increases as consumer income rises
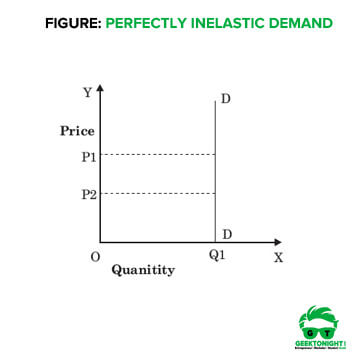
what value is perfectly price inelastic and what does it mean
0 - QD does NOT change at all when price changes
what value is relatively price inelastic and what does it mean
0 to -1 means % change in QD is smaller than the % change in P

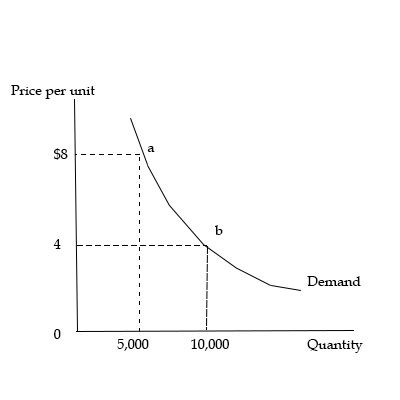
what value is unit price elastic and what does it mean
-1 and means the % change in QD is exactly the same as the % change in P
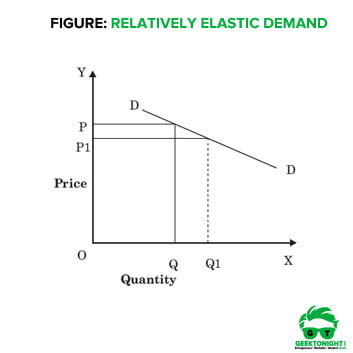
what value is relatively price elastic and what does it mean
-1 to -∞ and means the % change in QD is larger than the % change in P
what is the value for perfectly price elastic and what does it mean
QD falls to 0 if the price rises

what factors affect PED
number of close substitutes, cost of switching between products, degree of necessity , habitual consumption