Combustion
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
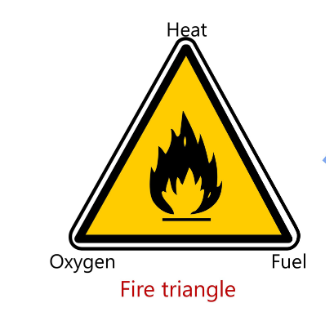
Fire triangle
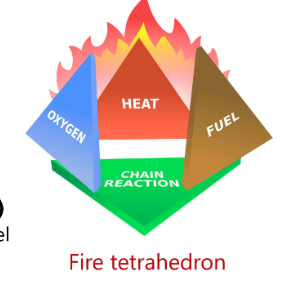
fire tetrahedron
1. Fuel – material that burns
2. oxygen
3. Heat – ignition source
4. Chemical chain reaction – sustains combustion
Open vs closed systems
· Open system:
o Oxygen is freely available from the air.
o Pressure doesn’t build up significantly.
o Common in fires and deflagrations (e.g., burning wood, gasoline fire).
· Closed system:
o Limited oxygen supply.
o Pressure can rise rapidly.
o Common in confined explosions or detonations (e.g., bomb casing).
Deflagration definition:
· Rapid combustion where the flame front moves slower than the speed of sound
detonation definition:
Extremely rapid combustion where the reaction front moves faster than the speed of sound
Analytical scheme for deflagration
- Collect → Extract/Desorb → Analyze → Interpret
o Collect: debris + ACS (activated carbon strips)
o Extract/Desorb: solvent extraction, SPME(solid phase micro extraction), thermal desorption
o Analyze: GC‑MS
o Interpret: match to accelerant patterns
- Note: it is important to understand the background because the polymeric sample may look like an ignitable liquid
Physical evidence from detonation (shrapnel)
pieces of casing, metal, or objects propelled by the blast