IPFC 1 - Non-hormonal Contraception
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Which of the following contraceptive methods has the highest failure rate in individuals who have previously given birth?
a) Internal (formerly female) condom
b) External (formerly male) condom
c) Cervical cap
d) Coitus interruptus (withdrawal method)
c) Cervical cap
Using the "Standard Days" method (a fertility awareness-based method), when would an individual with a regular 28-day cycle abstain from intercourse to avoid pregnancy?
a) Days 13-14
b) Days 12-16
c) Days 10-17
d) Days 8-19
e) Abstain until 4 days after appearance of abundant cervical mucus
d) Days 8-19
Which of the following could be used for contraception when a cisgender female partner has a latex allergy?
I. External latex condom
II. Internal condom
III. External polyurethane condom
a) I only
b) III only
c) I and II
d) II and III
e) I, II, and III
II. Internal condom
III. External polyurethane condom
Unsafe sexual behaviours may lead to:
- Unplanned pregnancies
- HIV and other STIs
- Infertility
Natural contraceptive methods
– Coitus interruptus (withdrawal)
– Fertility awareness-based methods (FABMs)
• Calendar methods
• Basal body temperature method
• Cervical mucus methods
• Lactational amehorrhea method
• Fertility monitors/ovulation prediction tests
Barrier methods
- Diaphragm
- Cervical cap
- Contraceptive sponge
- Internal (formerly female) condom
- External (formerly male) condom
Coitus interruptus
Penis is withdrawn before ejaculation occurs
Coitus interruptus Pros and Cons
Pros:
– No cost
– Always available
– No interaction with healthcare professional
Cons:
– May be hard to discern when ejaculation will occur
– Difficult to perform consistently
– HIV infection may still occur
Fertility Awareness-Based Methods (FABMs) aka natural family planning
Rely on understanding how signs and symptoms vary throughout the menstrual cycle to predict when most fertile
• Abstain from intercourse during time when most likely to be fertile
Calendar methods:
Calendar rhythm method
standard days method
Standard days method
• Used for individuals with regular cycles, 26-32 days in
duration
• Most fertile days 8-19, so abstain on those days
Calendar rhythm method
Record length of cycle for 6-12 months and identify longest and shortest cycle length
– Earliest day of fertility: length of shortest cycle minus 18
– Latest day of fertility : length of longest cycle minus 11
– Ex. If shortest cycle was 28 days and longest was 30), highest fertility would be days 10-19, so abstain these days
Basal body temperature method
– Temp is stable in follicular phase but drops slightly 12-24 hours before ovulation, followed by sharp rise due to progesterone release
– After 3 days of sustained temp elevation, ovulation has likely occurred, so now in post-ovulation infertile time period
• Abstain from day 1 of menses until 3 days after elevated temperature
– Use basal thermometers with wide calibration set to see slight variations in temperature
– Temperature taken orally, rectally, or vaginally before getting out of bed in the morning
– Many factors can affect temperature
• Ex. Illness, talking, drinking, smoking, travel, etc.
Cervical mucus methods
Cervical mucus changes from being opaque, white, viscous and sticky to being clear, thin, and stretchable (like egg white) and more voluminous as ovulation approaches
- TwoDay method
- Billings ovulation method
TwoDay method (cervical mucous)
Did I have cervical mucus today? Yesterday?
- Answering yes indicates fertility; therefore abstain
Billings ovulation method (cervical mucous)
• Individual is fertile when any cervical secretions are noted, until the fourth day past the last appearance of abundant, clear and stretchy secretions
– Abstain during these times
Sympto-thermal method
Uses both changes in cervical mucus and changes in
basal temperature to assess fertility
Lactational amehorrhea method
Exclusive breastfeeding provides natural contraception
- Reduced effectiveness if supplemental bottle feeding is provided, food supplements introduced, baby is 6 months old
- Use other method of contraception when menstruation resumes
- works well with progestin-only contraceptives
Advantages of Fertility Awareness-Based Methods (FABMs)
- No device required
- No pharmacologic agents
- No ADRs
- May be better for some religious groups
- Can also be used to know fertile period If conception is the goal
Disadvantages of Fertility Awareness-Based Methods (FABMs)
- Needs motivation and discipline
- may need to track cycle for a long time
- abstinence needs to be consistent during fertile periods
- No protection from STIs
- Methods may be impacted by factors like illness (BBT), douching/lubricants (cervical mucous)
Spermicides
Non Rx
• Usually contain nonoxynol-9, which acts on the sperm cell membrane to make it permeable to moisture
– Causes membrane to swell and be destroyed
• Used alone or with barrier methods
• Do NOT reduce HIV/STI transmission
– Cause irritation/lesions, which increases infection risk
Spermicidal foam (ex. VCF® Vaginal Contraceptive Foam) How to use
– Shake container
– Insert applicator deep into vagina while lying down and push plunger
– Intercourse should take place within 30-60 minutes
No douching for at least 6 hours after
Spermicidal film (ex. VCF® Vaginal Contraceptive Film)
– Insert 15 minutes to 3 hours before intercourse
– Insert high in the vagina against the cervix
• Gel acts as barrier to sperm entering the cervix
No douching for at least 6 hours after
Pros of spermicides
- Non Rx
- easy
- best when combined with other methods
Cons of spermicides
– Apply repeatedly (before each act of intercourse)
– Messy
– Irritating
– Spermicide plus diaphragm may increase UTI risk
– Do not prevent STI; may actually increase HIV
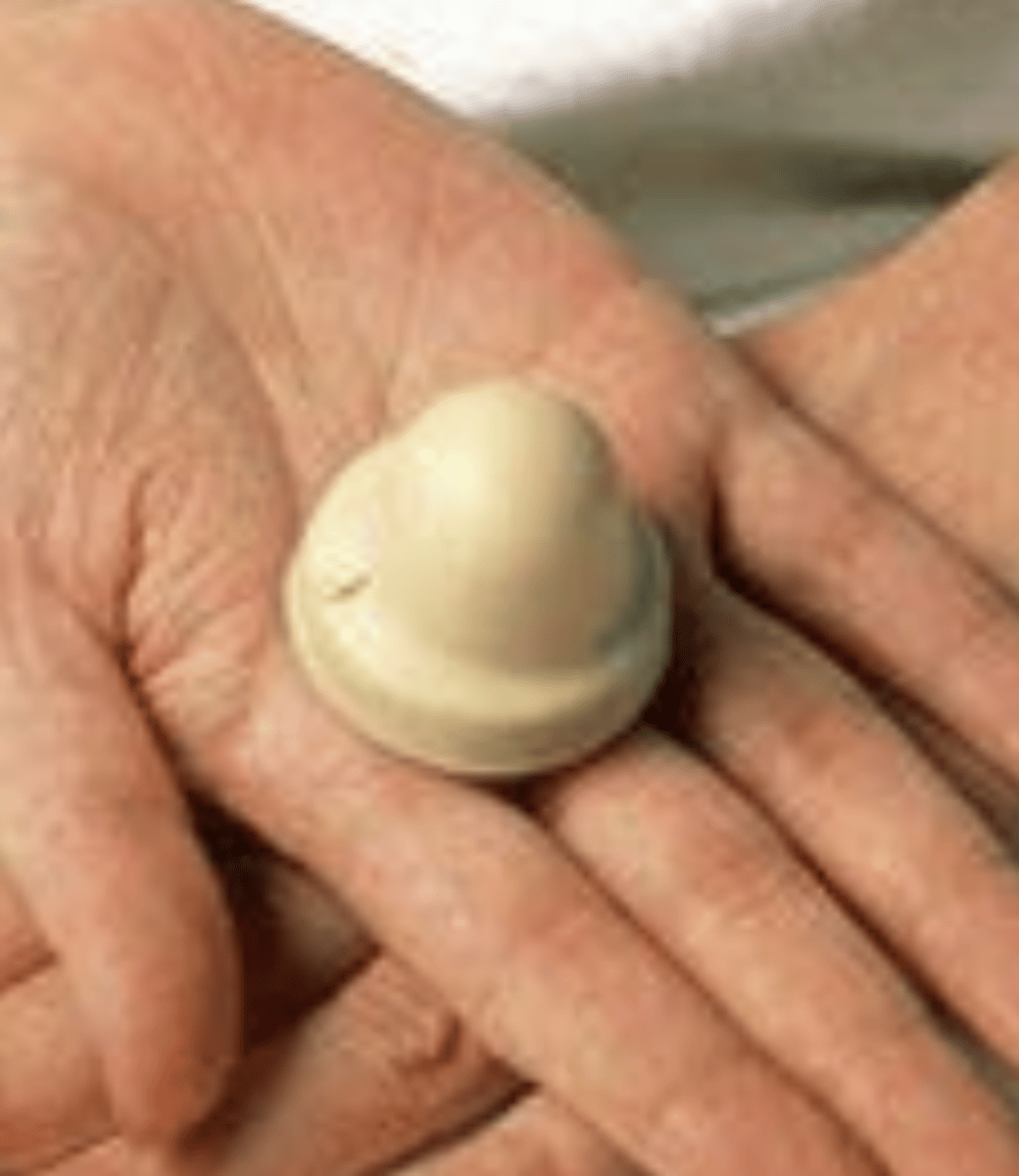
Diaphragm (barrier methods)
• Latex or silicone dome that covers the cervix
• Requires proper fitting
• Can be filled with spermicidal gel
• Can be inserted up to 6 hours before intercourse
• Must remain in place 6 hours after intercourse (24 hours maximum)

Diaphragm Pros and Cons
Pros:
– Can be inserted in advance (to not interfere with sexual encounter)
Cons:
– Hard to insert
– Can get dislodged during sex
– Require refitting after childbirth
– Not used for STI/HIV protection
– Use with spermicide may increase UIT risk, toxic shock
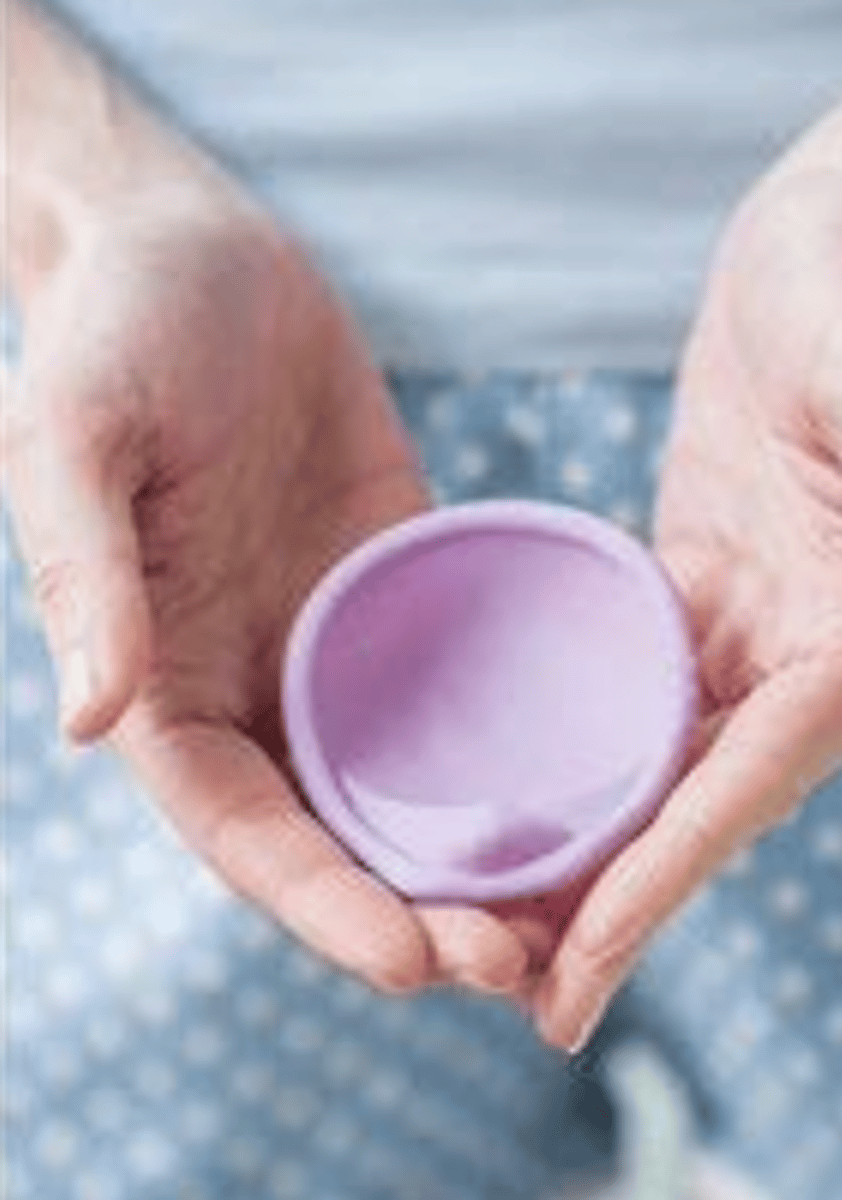
Cervical cap (barrier methods)
• Similar to diaphragm
• Can use with spermicide
• Fits snugly over the cervix
• Size chosen based on history of pregnancy/vaginal birth
• Suction is produced when it is inserted
• Leave in place for at least 8 hours after intercourse

Cervical cap (barrier methods) Pros and Cons
Pros
– Can be left in place up to 48 hours, allowing spontaneous intercourse
Cons
– Hard to insert
– Can become dislodged during intercourse
– No STI/HIV protection
– Risk of toxic shock syndrome
– Less effective after vaginal birth
Contraceptive sponge (barrier method)
• Soft foam filled with spermicide (Ex. Today Sponge)
• Provide a physical barrier and have spermicidal activity
• Single-use, disposable
• Can insert any time before intercourse, and can be used for repeated acts of intercourse within 24-hour period
• Leave in place at least 6 hours after intercourse, up to 24 hours total

Contraceptive sponge Pros and Cons
Pros:
– Easy to use snd carry; small and comfy
- Today sponge - 24 hour protection even with repeated intercourse
Cons:
– High failure rate when used alone
- May be hard to insert/remove
- No STI/UTI prevention
- Risk of TSS
Internal (formerly female) condom
• Single-use barrier product
• Provides protection against STI/HIV
• FC2 is second-generation internal condom made from nitrile
• Lubricated
• Rings at each end to hold it in place
– Closed end is inserted into the vagina and covers cervix, open end stays outside the vagina
• Use new condom for repeated intercourse
• Don’t use with external (formerly male) condoms
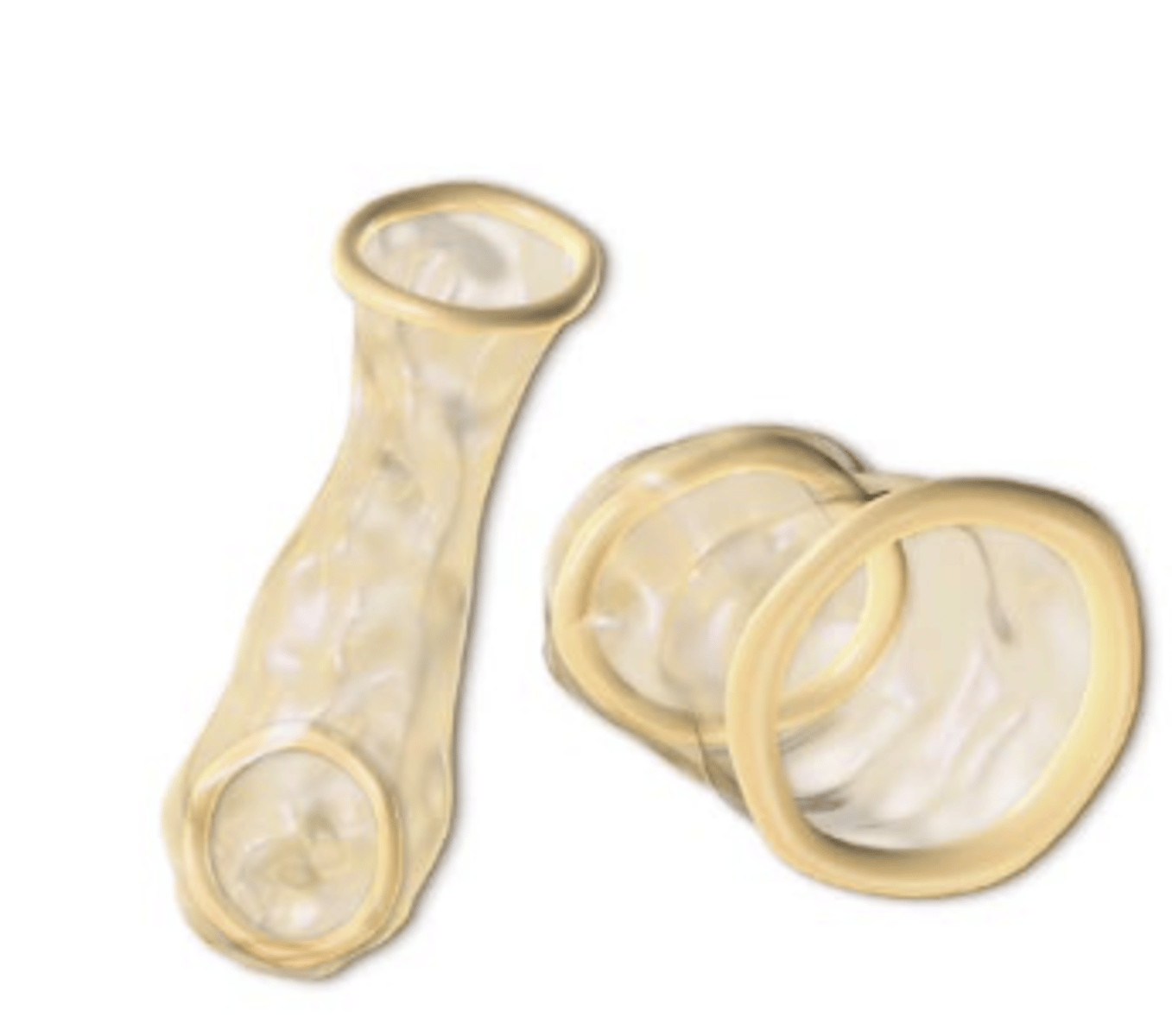
Internal condom pros
– Women have more control
– Can be inserted several hours in advance
– Can use any type of lubricant (not latex-based)
– STI/HIV protection
– Hypoallergenic
– Can be used with latex allergy
Internal condom Cons
- may be hard to use
- noise during intercourse
External (formerly male) condom
• Made of lambskin, latex, polyisoprene, or polyurethane
• Failure may occur due to breakage (0.5-2.5%) or slippage (0.6-2%)
What may increase risk of external condom failure
• Opening package with sharp objects
• Unrolling the condom before putting it on
• Lack of education/experience
• Lengthy/intense intercourse
• Lubricant use (increased slippage in vaginal intercourse)
• Alcohol/drug use
• Failure also results from inconsistent use
– Ex. reduced sensation, interruption of sexual activity
Latex condoms
– Effective at preventing STI/HIV
• Condoms are only partially effective against infections transmitted through skin/mucous membranes Ex. Herpes simplex, human papillomavirus
– Several types available – ex. Reservoir end, lubrication, spermicide, ribbed, etc.
– Never used with oil-based lubricants (ex. Massage oil, vaseline) can break down material
– Can be used with water-based lubricants
– Allergy may result from repeated exposure
• Genital inflammation with redness, itching, burning, vesicles
Which condoms can be used with a latex allergy
If allergy is present – use polyurethane or polyisoprene external condom, or internal condom
Lambskin condoms
– Made from intestinal cecum of lambs
– Poor elasticity
– May slip off
– Can use with oil- and water- based lubricants
– Less protection against HIV/STI (small pores)
Polyurethane
Awesome! but more expensive
– Latex-free
– Stronger than latex
– Thinner than latex (more sensation)
– Can use with oil- or water-based lubricants
– As effective as latex for STI/HIV protection
Polyisoprene
- Made from synthetic rubber with proteins
causing latex allergy removed
- Effective for STI/HIV protection
- Softer and more resistant to breakage compared to polyurethane
Pros of external condoms
– Inexpensive, convenient
– Easy to use
– May prolong intercourse
– Some types protect against STI/HIV
– Good for infrequent intercourse
Cons of external condoms
– May be difficult to put on
– May not stay in place
– Difficulty maintaining erection in some individuals
– Embarrassment
– Reduced sensation
– Interruption of sexual encounters for putting condom on and immediate removal
– Allergic reactions
– Breakage/slippage
Which contraception methods have the highest failure rates in women who have given birth
cervical cap, contraceptive sponge, diaphragm