Op-Amps
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
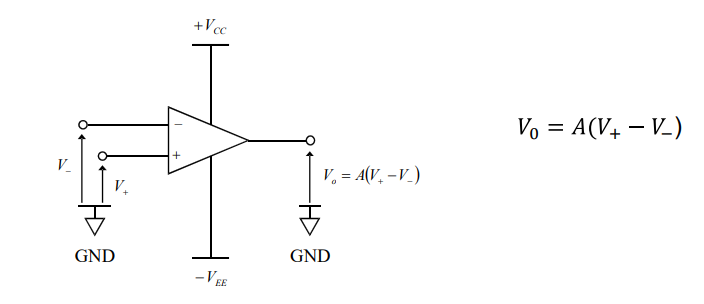
What does an Op-Amp do?
An Operational Amplifier essentially scales an input signal (Vin) to an output signal (Vout) by a factor of A.
Vin = | V- - V+ |
Key features of an Op - Amp
Active device, so has two power supplies
{+VCC and -VEE}Output signal (Vout) can only range between +VCC and -VEE.
Usually ±15V
Ideal Op-Amp Characteristics
Rin = Infinite Ohms
Leads to Iin = 0A
Rout = 0 Ohms
Open loop Gain (A) is infinite
A is independent of frequency
Ideal Op-Amp is also unaffected by temperature
Infinite slew rate
Change in Vin leads to instant change in Vout
THIS IS ONLY FOR IDEAL OP AMPS
Virtual Short
For an ideal Op-Amp:
A → Infinity
Vout → Finite Value
V+ = V- {Signifies a virtual short}
Types of Amplifiers
Inverting Op-Amp
Summing Op-Amp
Transresistance Op-Amp
Integrator
Differentiator
Voltage Follower
Non-Inverting Op-Amp
Transconductance Op-Amp
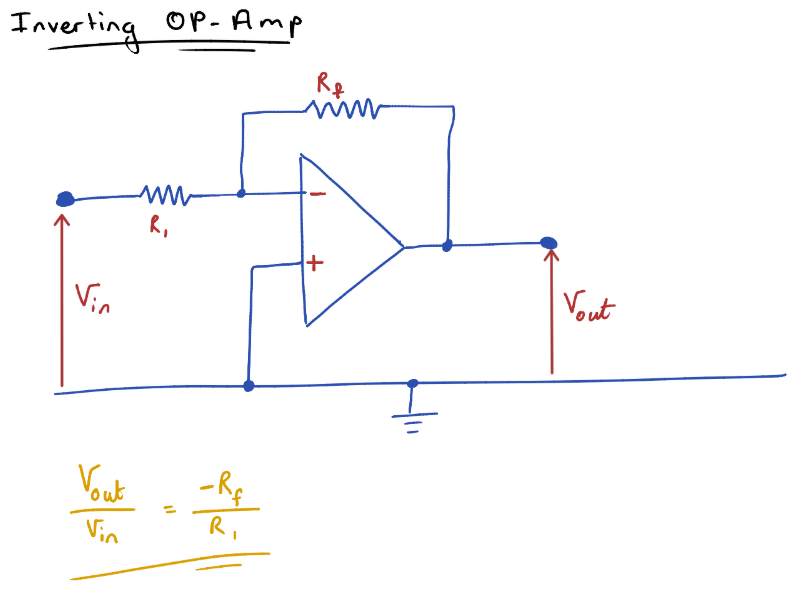
Inverting Op-Amp
Inverts the polarity of an input voltage
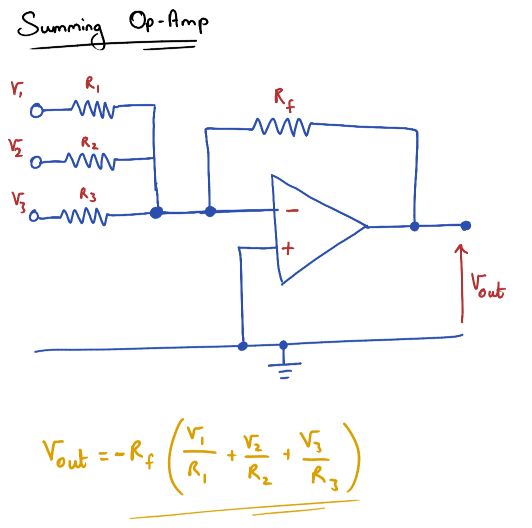
Summing Op-Amp
Sums multiple input voltages together
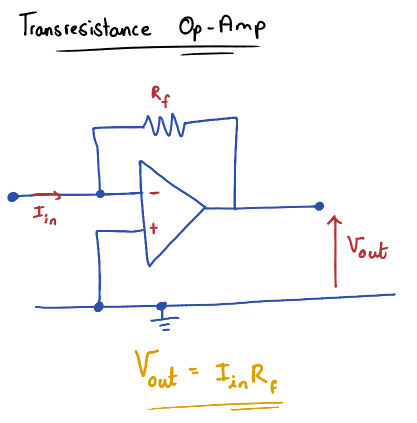
Transresistance Op-Amp
A Current-to-Voltage converter
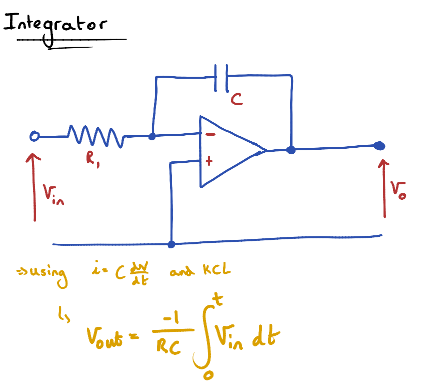
Integrator
Output voltage is the integral of input voltage
-1/RC is a constant
Also acts like a lowpass filter
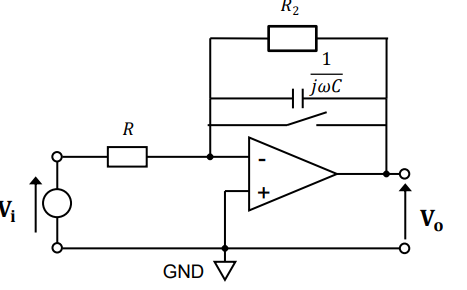
Problem/Solutions with an Integrator in real life
Problem:
At low frequencies, loop gain goes to infinity
Solutions:
Use Large values of R and C
Zero output regularly, but placing a switch across the capacitor
Add a large resistor across the capacitor
{This is now just an inverting amplifier at low frequencies, not an integrator}
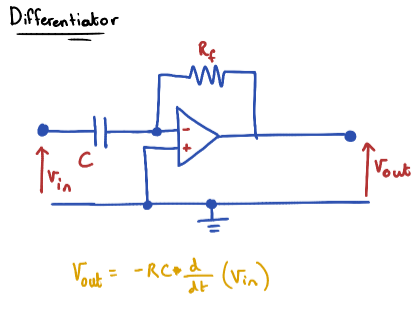
Differentiator
Output voltage is the derivative of the Input Voltage
-RC is a constant
Also acts as a highpass filter
Problem/Solution with a Differentiator in real life
Problem:
High gain at high frequencies, and can lead to unstable output
Solution:
Place a resistor in series with input capacitor
{Acts as an inverting Op-Amp at high frequencies, not a differentiator}
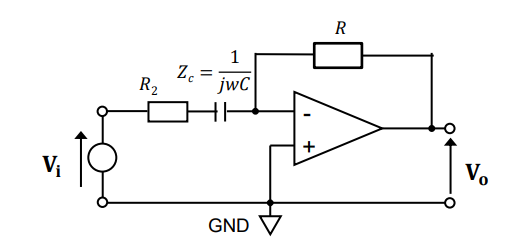
Voltage Follower
Ensures Output Voltage = Input Voltage
Acts as a buffer
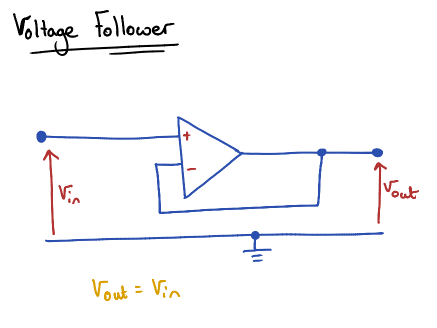
Non-Inverting Op-Amp
Output voltage is a positive multiple (A) of the Input Voltage
A is the gain
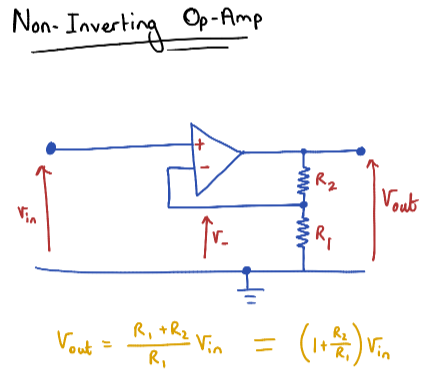
Transconductance Op-Amp
A Voltage-to-current converter
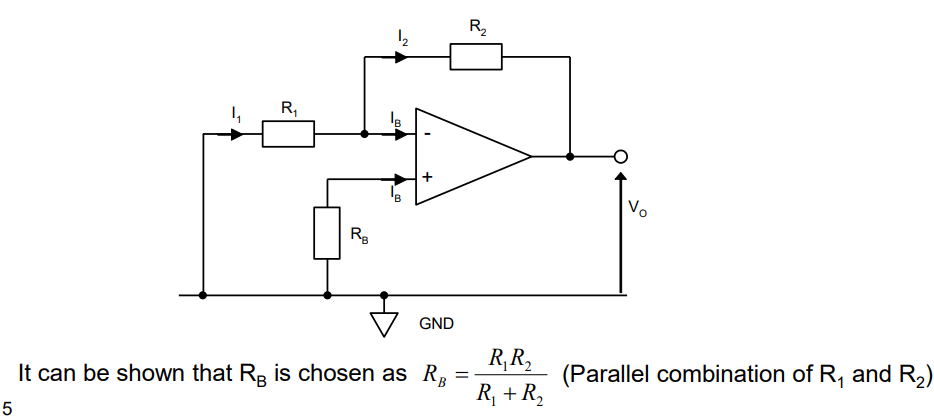
Input Bias Current
In real life, the terminals on the Op-Amps have a current flowing through them
This can be compensated by connecting a specific resistor (RB) where the input bias current goes to 0A.