Biology Lab
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Metric System
Used in science for measurements based on powers of tens. Its is decimal based, standardized, and consistent.
Decimal based
Units scaled by multiples of 10
Standardized
Same prefixes across different types of measurements
Base unit for length
Meter m (ruler)
Base unit for mass
Gram g (Scale)
Base unit for volume
Liter l (graduated cylinder, micropipette)
Base unit for temperature
Celsius C (thermometer)
Base unit for time
Seconds s (stop watch, timer)
deci- d
-1
Centi- c
-2
Milli- m
-3
micro- u
-6
nano- n
-9
kilo K
3
mega M
6
Scientific notation
way of writing numbers in a shorter form using exponents
Meniscus
lowest margin of the water level
Celcius formula
C=(F-32)/1.8
Microscopy
fundamental technique that allows for the observation of structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
Visible light
Stereo microscope and compound light microscope
Beam of electrons
Electron microscope
40x-100x
Compound light microscope
10x-50x
Stereo microscope
1,000,000x or more
Electron microscope
200 nm
Compound light microscope
500 um
Stereo microscope
.1 nm
Electron microscope
2D
Compound light and TEM
3D
Stereo microscope and SEM
Thin, transparent specimens
Compound light microscope
Larger, opaque specimens
Stereo microscope
Very small, ultra thin, or coated specimens
Electron microscope
Simple specimens
Compound light microscope
Minimal prep
Stereo microscope
Complex specimens, must be fixed and dead
Electron microscope
Low cost and portable
Compound light microscope
Moderate cost and portable
Stereo microscope
Very expensive and stationary
Electron microscope
Compound light microscope
best for viewing small, transparent, or stained specimens like cells and thin tissues

Stereo microscope aka dissecting scope
best for examining larger, 3D objects like insects, leaves, or tools at low magnification

Electron Microscope
ideal for extremely high resolution imaging of viruses, organelles, and nanostructures- requires complex prep and expensive equipment
Magnification
making an object appear larger than it is
Resolution
ability to see objects clearly enough to tell two distinct objects apart
Eyepiece (Ocular lens)
the lens you look through, 10x magnification
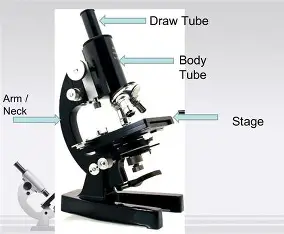
Neck
connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses
Arm
supports the neck and connects it to the base

Revolving nosepiece (Turret)
holds multiple objective lenses and allows rotation to change magnification

Objective Lenses
Usually 3 or 4 lenses (4x, 10x, 40x, 100x) that provide levels of magnification
Stage
Flat platform where the slide is placed
Stage clips
holds the slide in place on the stage
Stage adjustment knob
Moves the stage forward, backward, left, or right
Diaphragm (Iris or disc)
adjusts the amount of light that reaches the specimen
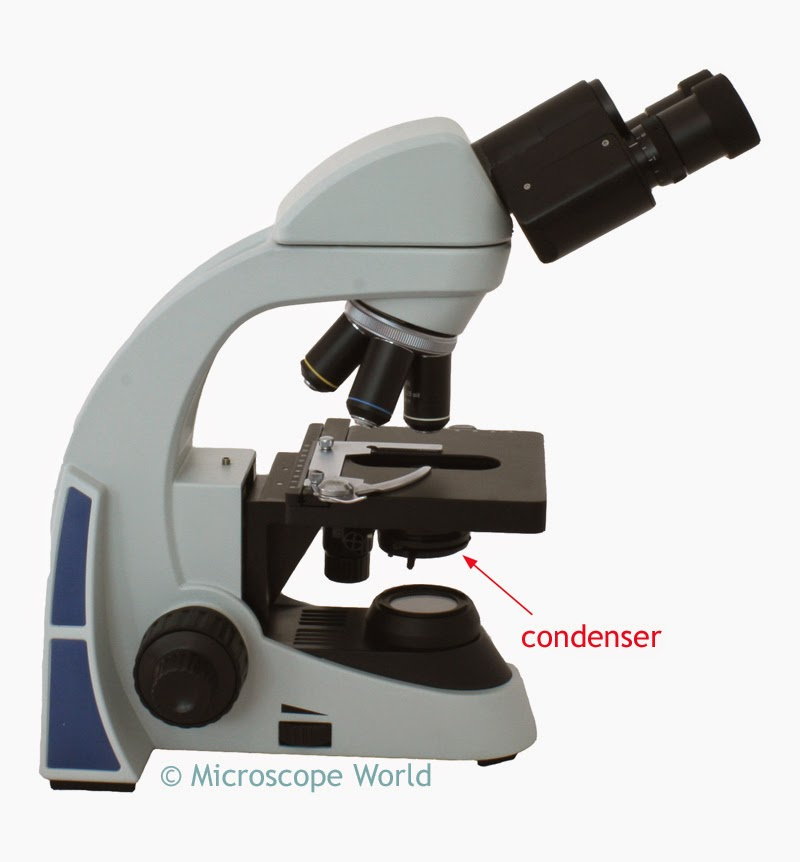
Condenser
Focuses light onto the specimen for clearer viewing
Coarse adjustment knob
moves the stage up and down for general focusing
Fine adjustment knob
fine tunes the focus for detailed viewing
Light source (illuminator)
provides the light

Base
the bottom support structure of the microscope

Light dimmer knob
adjusts the brightness
Total magnification
ocular lens multiplied by the objective lens magnification
Scanning lens
x4
low power lens
x10
high and dry lens, blue
x40
oil immersion lens
x100
Field of view
what you can see when looking through the ocular lens. Diameter of the circle.
FOV formula
FOV=objective lens you measured x field of view you measure/ objective lens you want
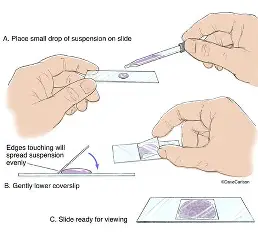
Wet mount
simple and commonly used technique in biology labs to observe living microorganisms, cells, or tissues in a liquid medium.
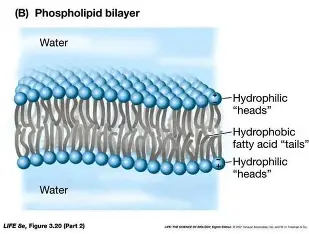
Plasma membrane aka cell membrane
a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds every cell. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, carbs, and cholesterol.
Phospholipid
Polar hydrophillic head and nonpolar hydrophobic tails
Hydrophobic tails are
fatty acid chains
where is betacyanin found in beets
the central vacuole
High temperature can
increase fluidity, denature proteins, disrupt membranes, increase permeability
what do phospholipids do when temps rise
gain kinetic energy and move more freely
Low temperatures can
decrease fluidity, reduce transport, and cause cold shock
what do phospholipids do in low temps
pack tightly
Organic solvents disrupt
the phospholipid bilayer
which is more nonpolar ethanol or acetone
acetone
Changes away from optimum pH can
denature membrane proteins, change the charge and polarity of phospholipid head groups
What happens to the membrane at low pH
excess H disrupts hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions leading to membrane destabilization
what happens to the membrane at high pH
OH can interfere but less dramatic than acidic
reagent for protein
biuret
reagent for carbs
iodine
lipids
sterols, paper towel, water
Protein subunit
amino acids
carbs
monosaccharides
regent for monosaccharides
benedicts
Lipids subunit
fatty acids, glycerol, phosphate functional group
Dehydration synthesis
water molecule is removed between 2 subunits joining them together
degradation hydrolysis
breaking the bond between subunits by adding water
controls
known solutions used to validate our experiments
positive control
contains the variable you are testing, elicits a known postive result
negative control
does not contain the variable you are testing and elicits a known negative response
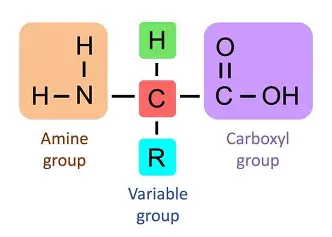
draw amino acid
H, Amino group H2N, carboxyl group, R group
Draw nucleotide
phosphate group, pentose sugar, nitrogeneous base
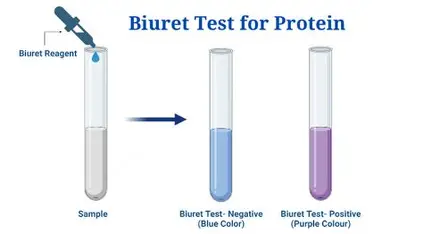
The Biuret test
detects proteins in a solution. Contains copper sulfate in an alkaline solution. When peptide bonds are present the copper ions turn violet
The iodine test
detects the presence of starch, will turn blueish black
Benedicts test
detects simple sugars. Changes redish orange in responde to copper oxide
Starch
polycaccharide that can be broken into maltose and glucose by the enzyme amylase
Sudan test
sudan is nonpolar so it dissolves nonpolar molecules, creating a red layer
Water solubility
water is polar so it will not dissolve non polar molecules, it will create 2 separate layers of insoluble fats or oils
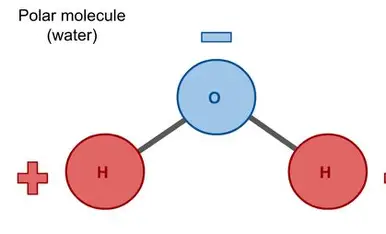
emulsifier
a way to mix insoluble materials within polar water. It contains a polar and non polar side, polar side interacts with water nonpolar interacts with fat or oil.