BIOL 1021 Lab Final
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What did the caffeine do to the heart rate of the Daphnia
Increased the heart rate
What did ethanol do to the heart rate of the daphnia
decreased the heart rate
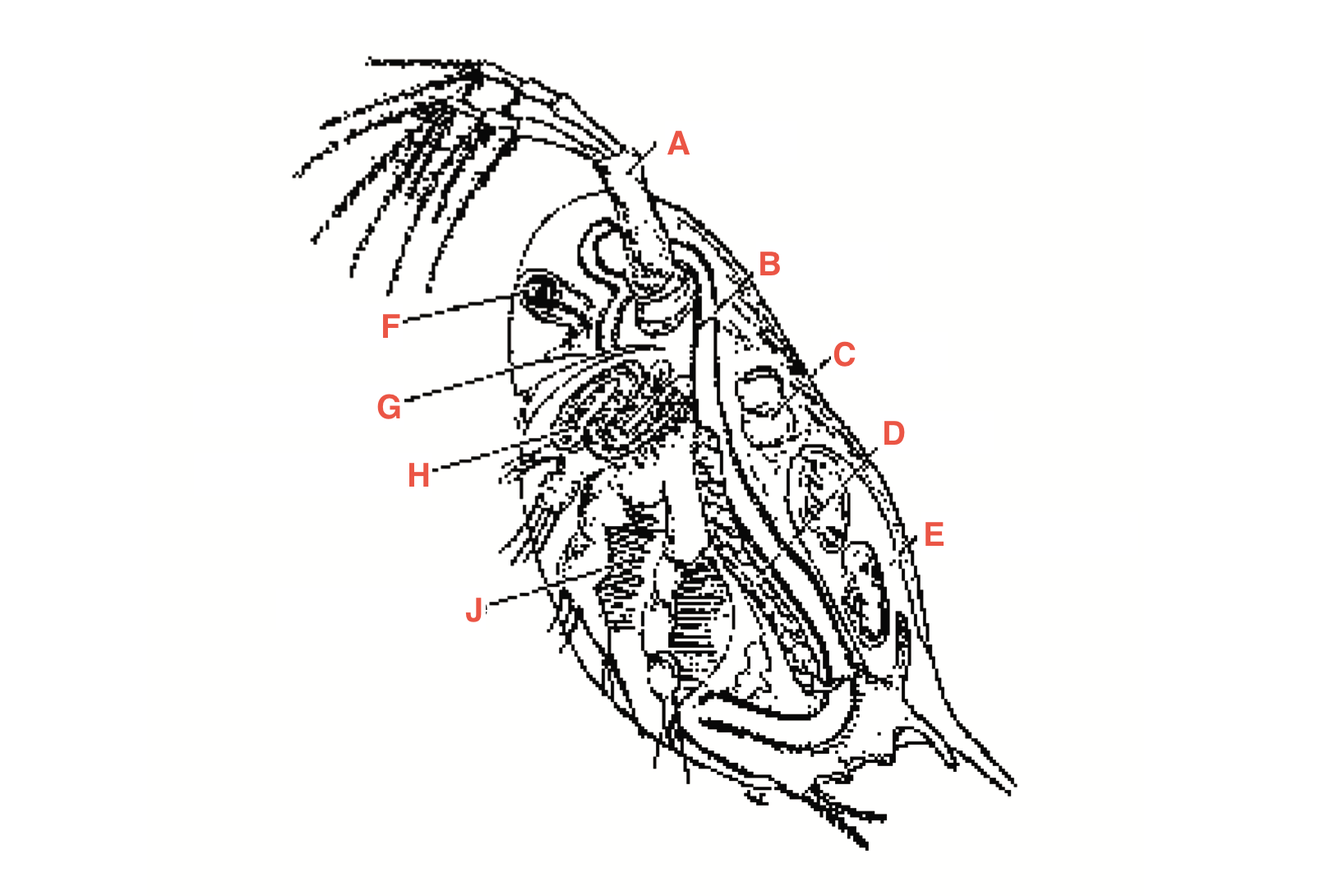
What is A
antennae
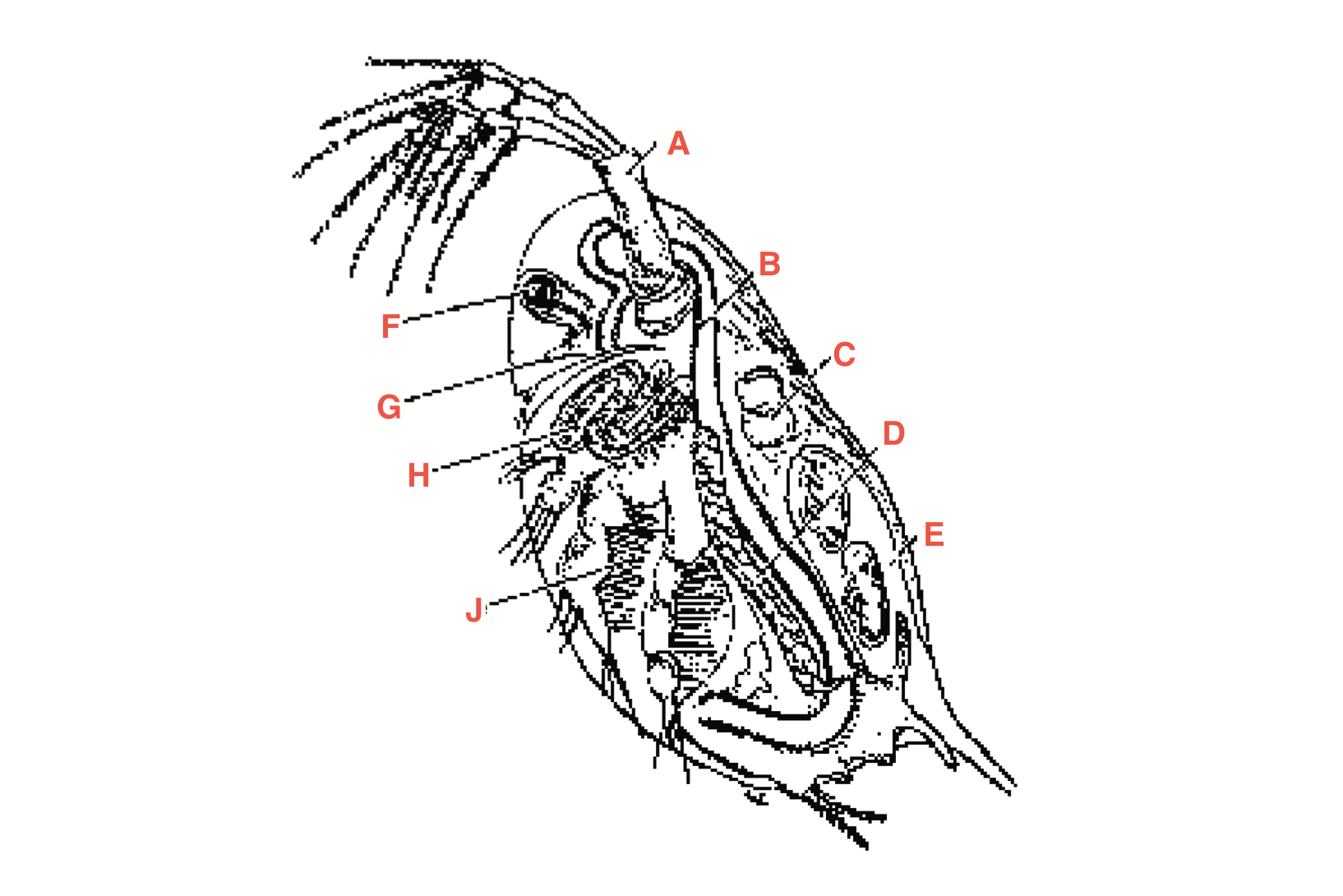
What is B
intestine
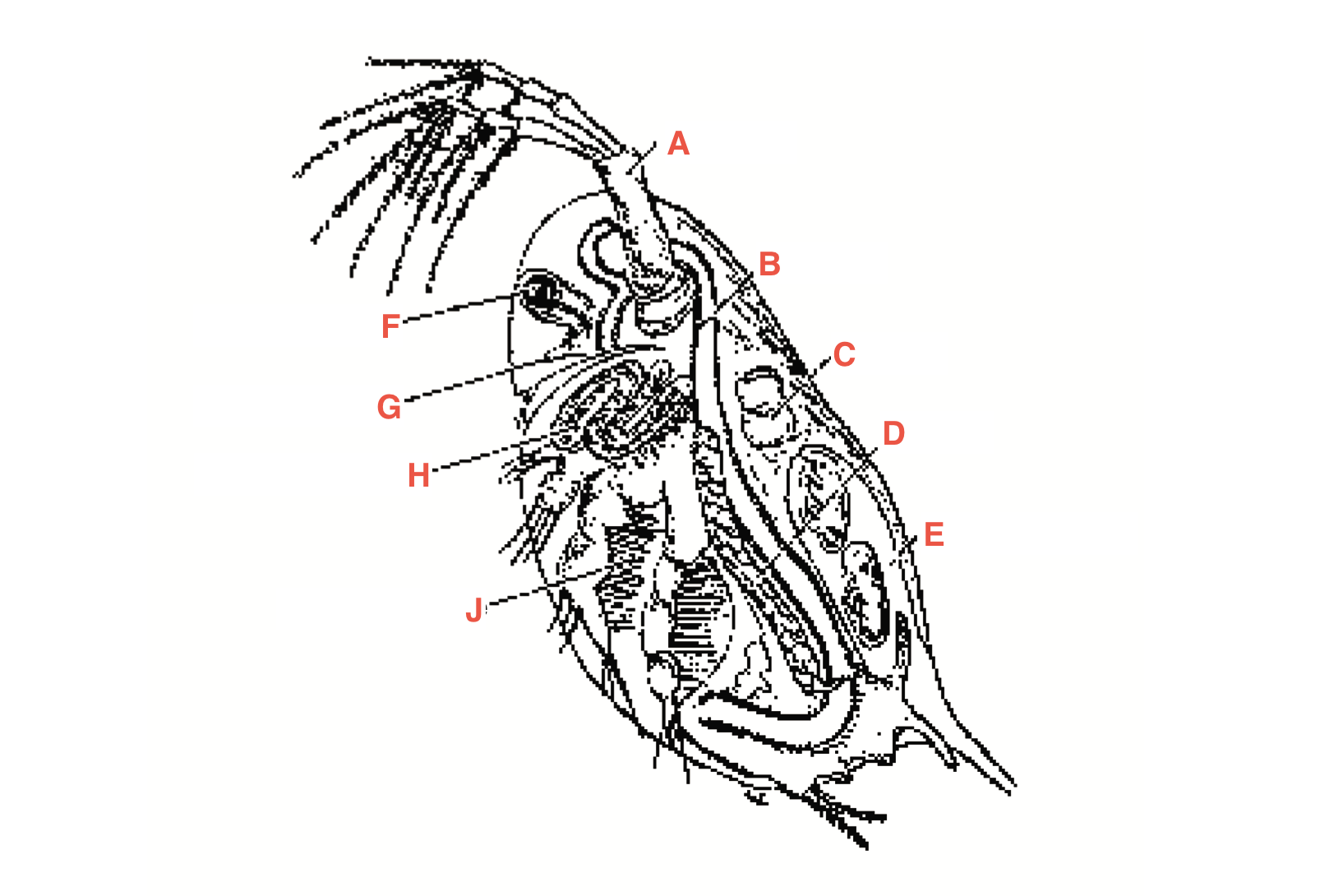
What is C
heart
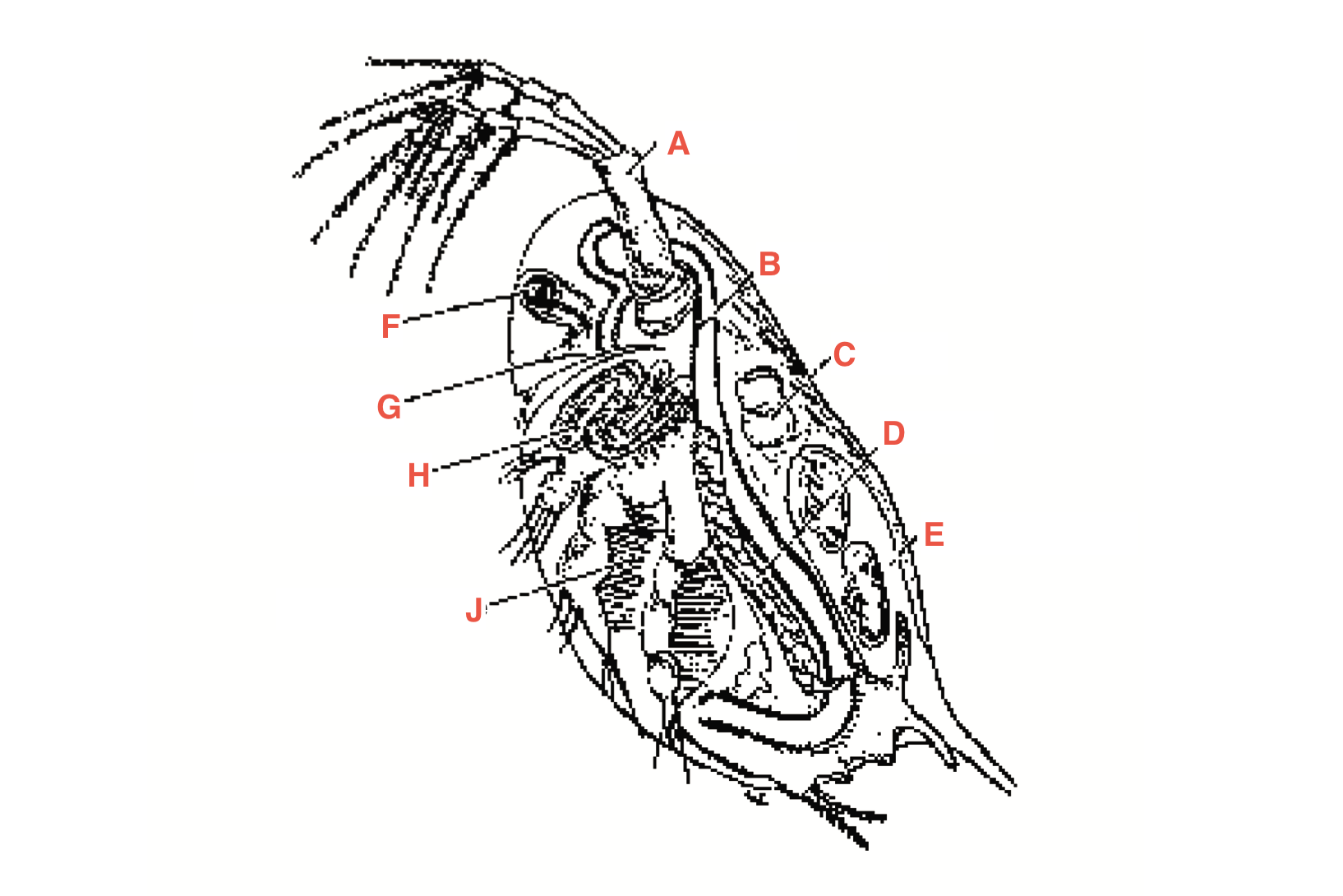
What is D?
Ovary
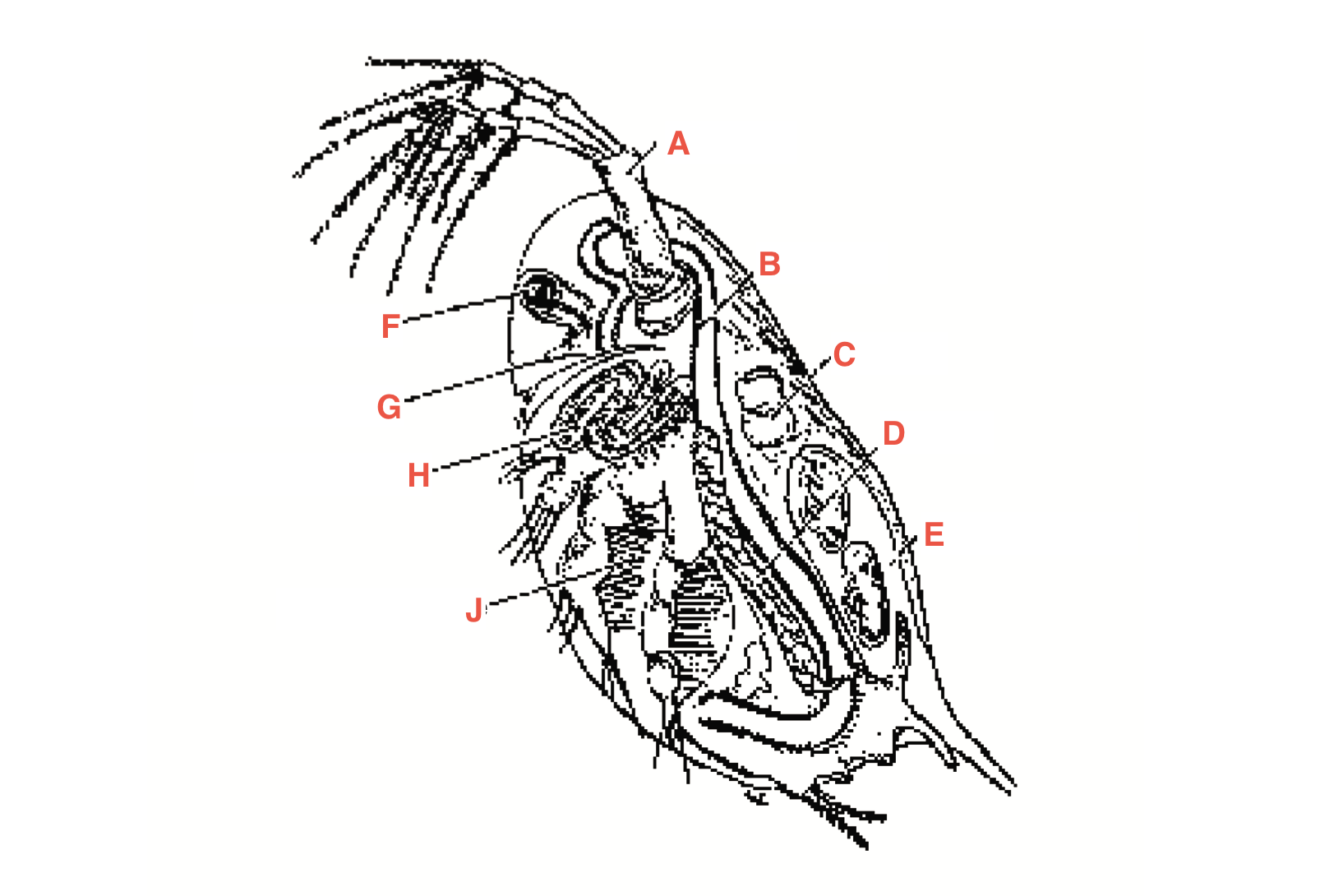
What is E?
Blood chamber
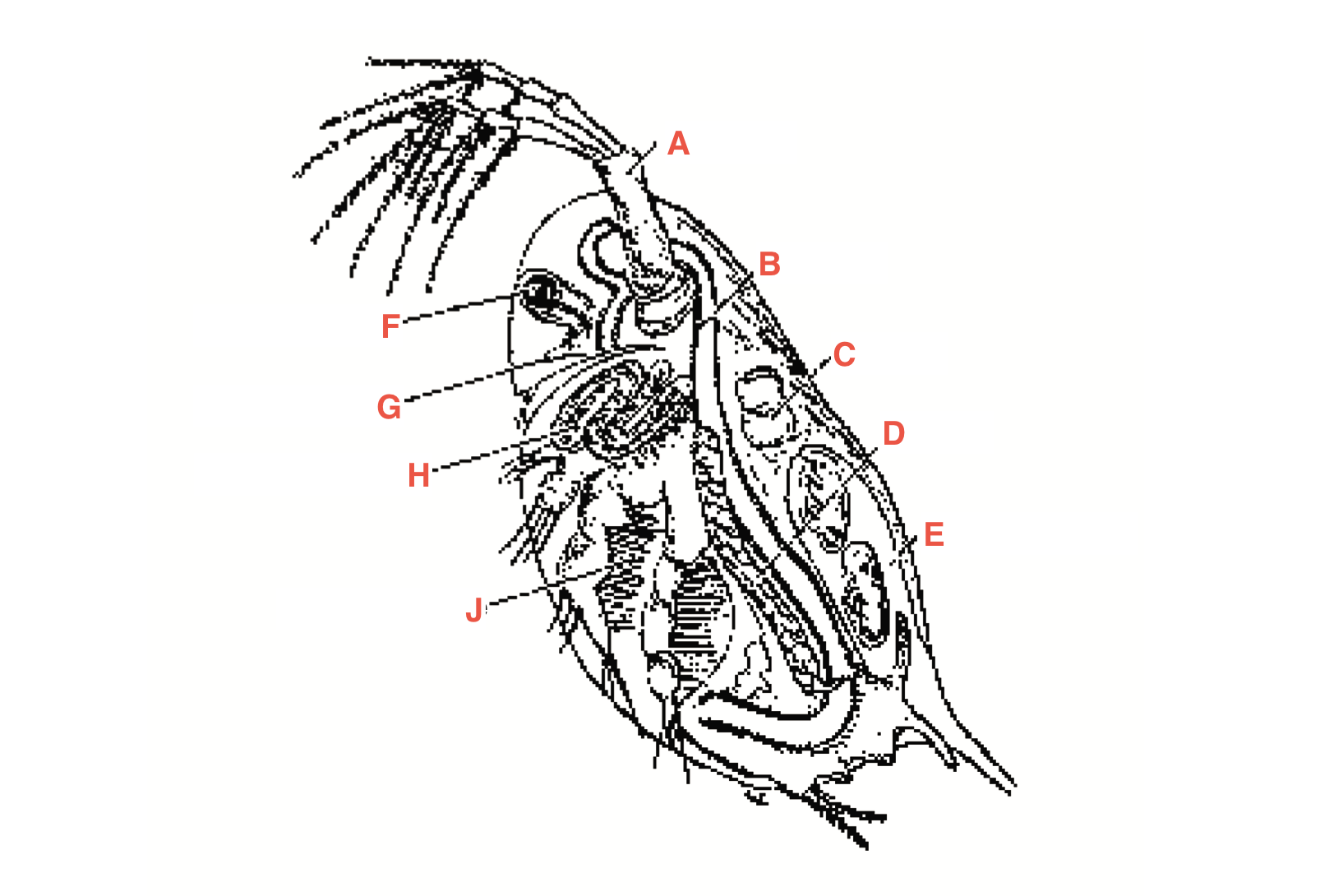
What is F
compound eye
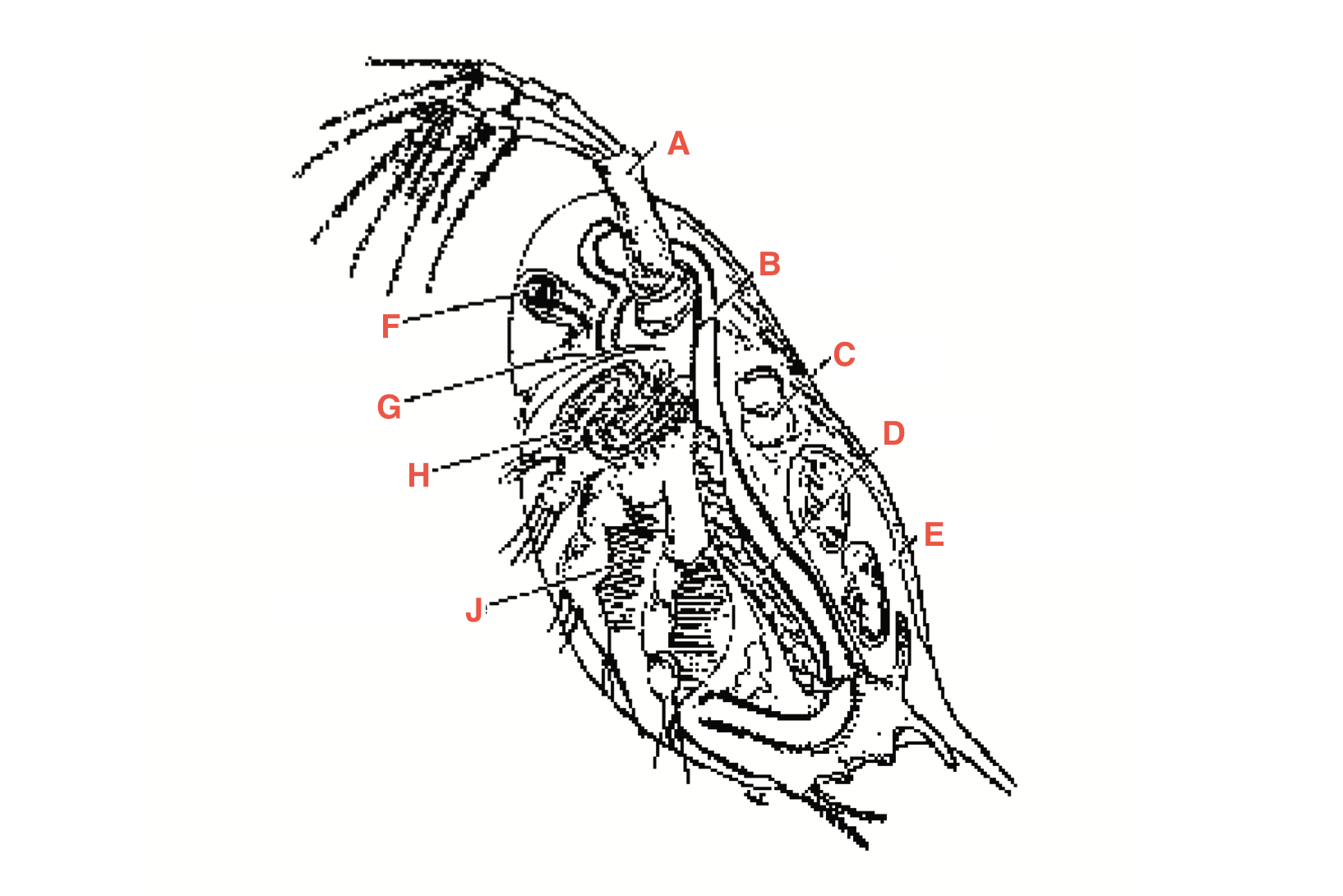
what is G
ocellus
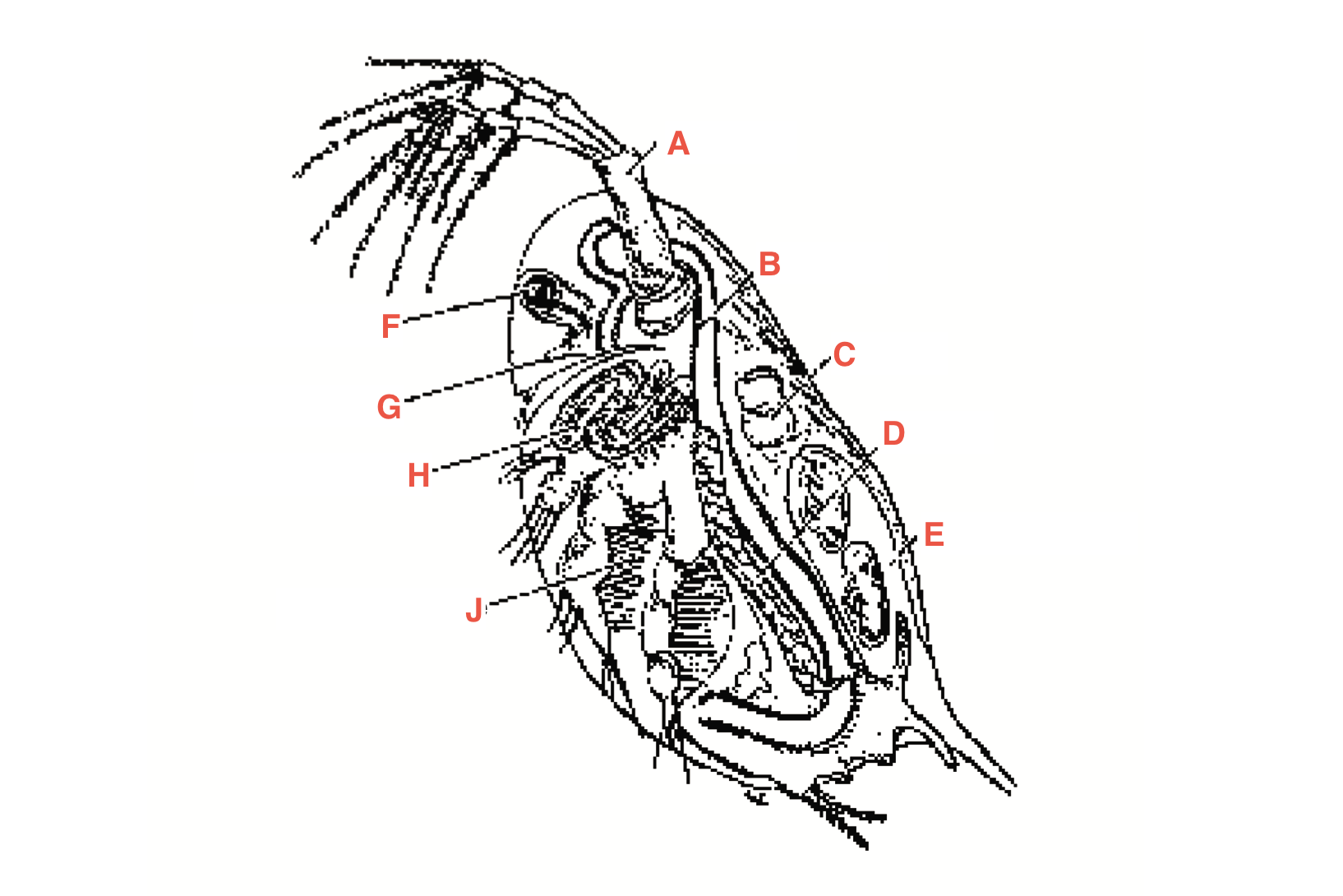
What is H
maxillary gland
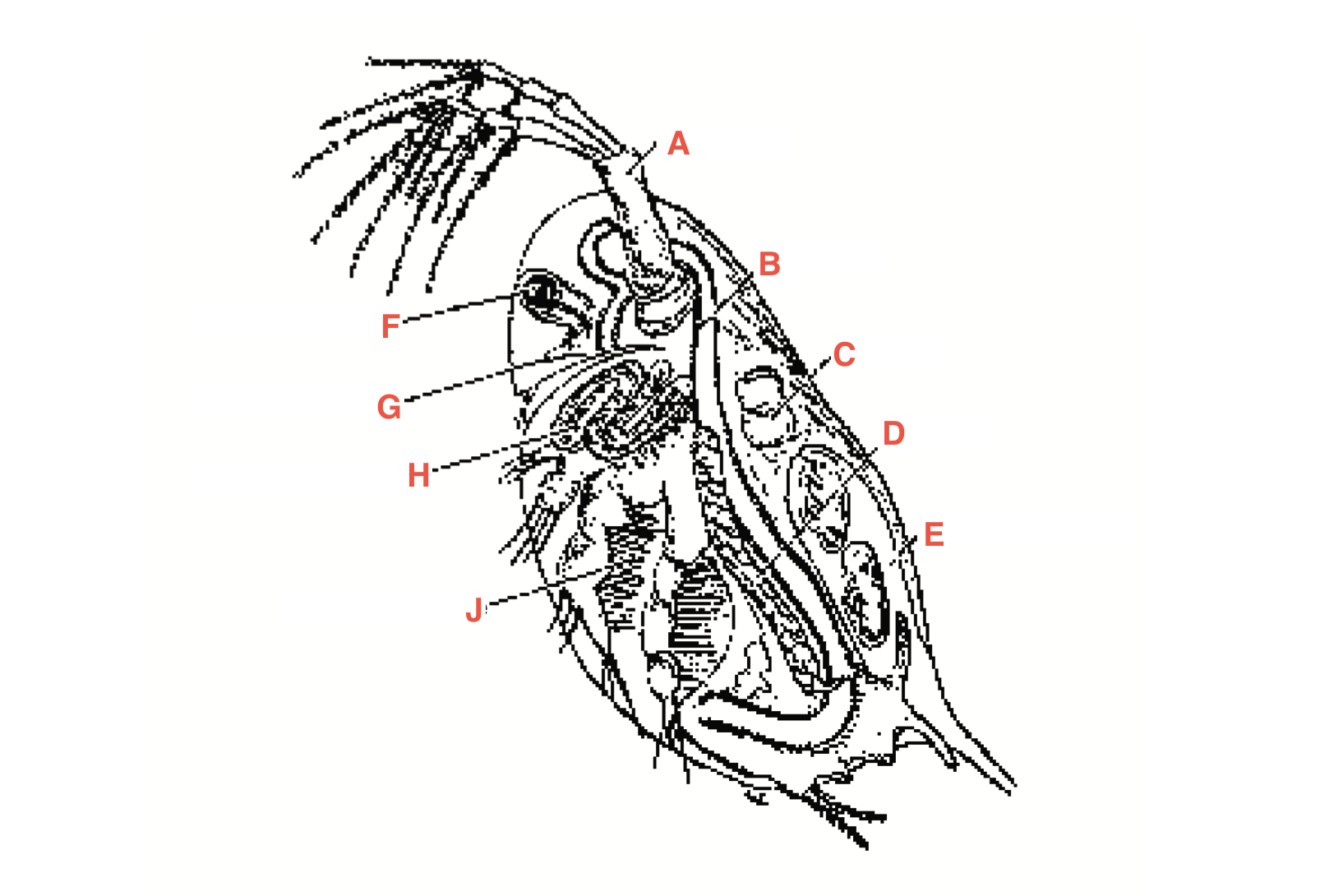
What is J?
Filtering setae
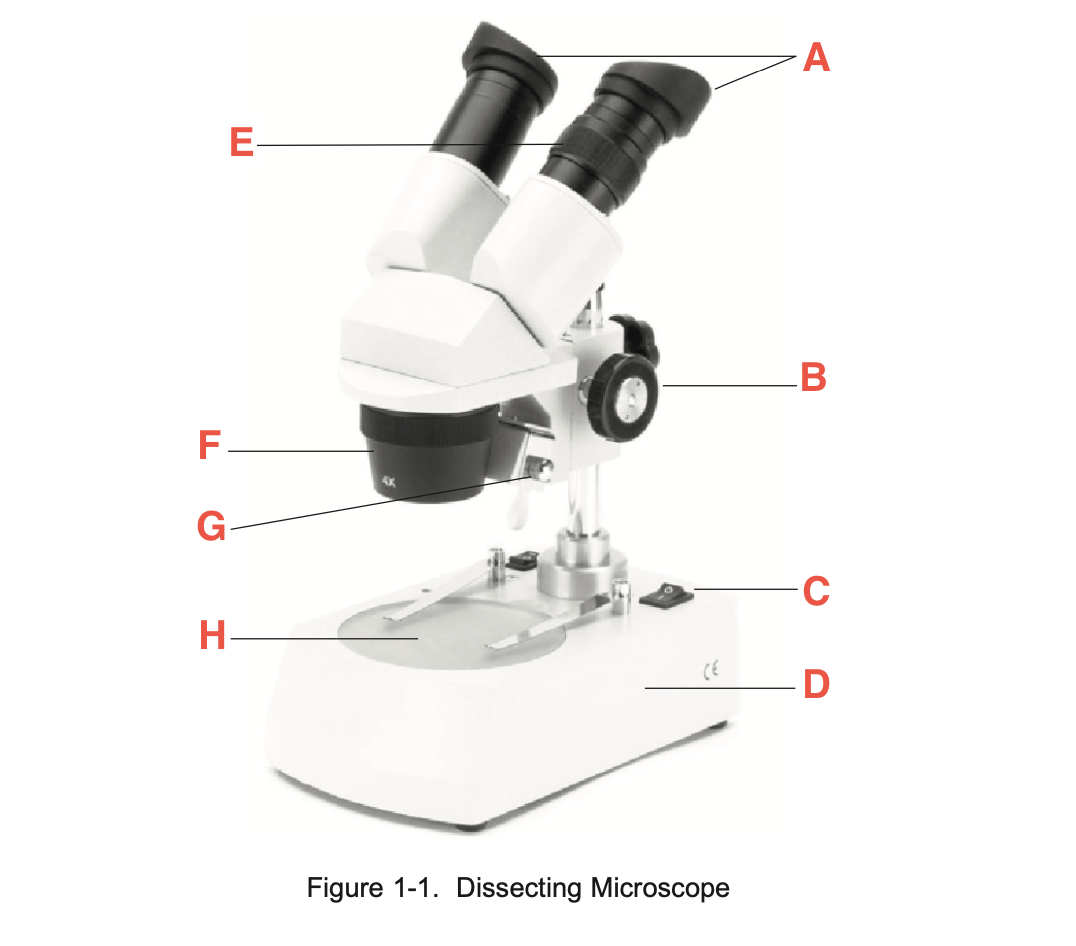
What is A
eyepieces
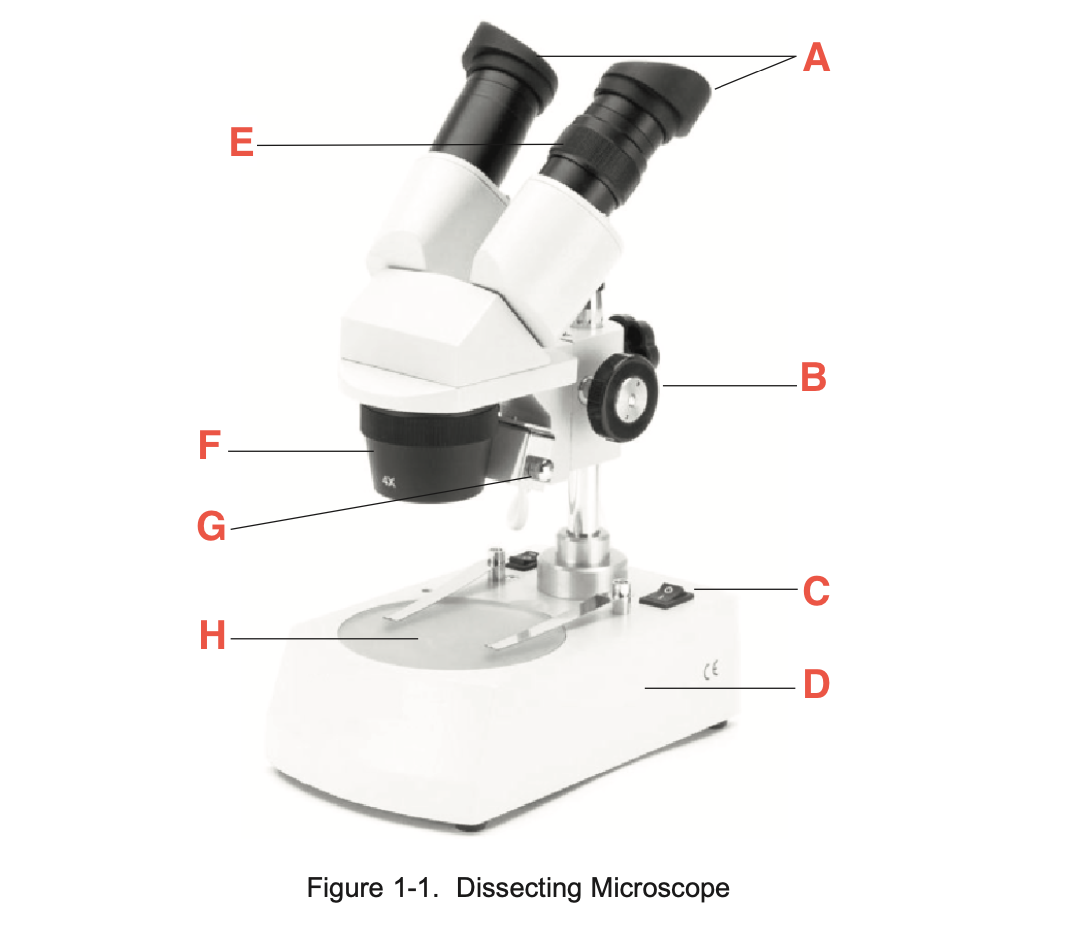
What is B
focusing knob
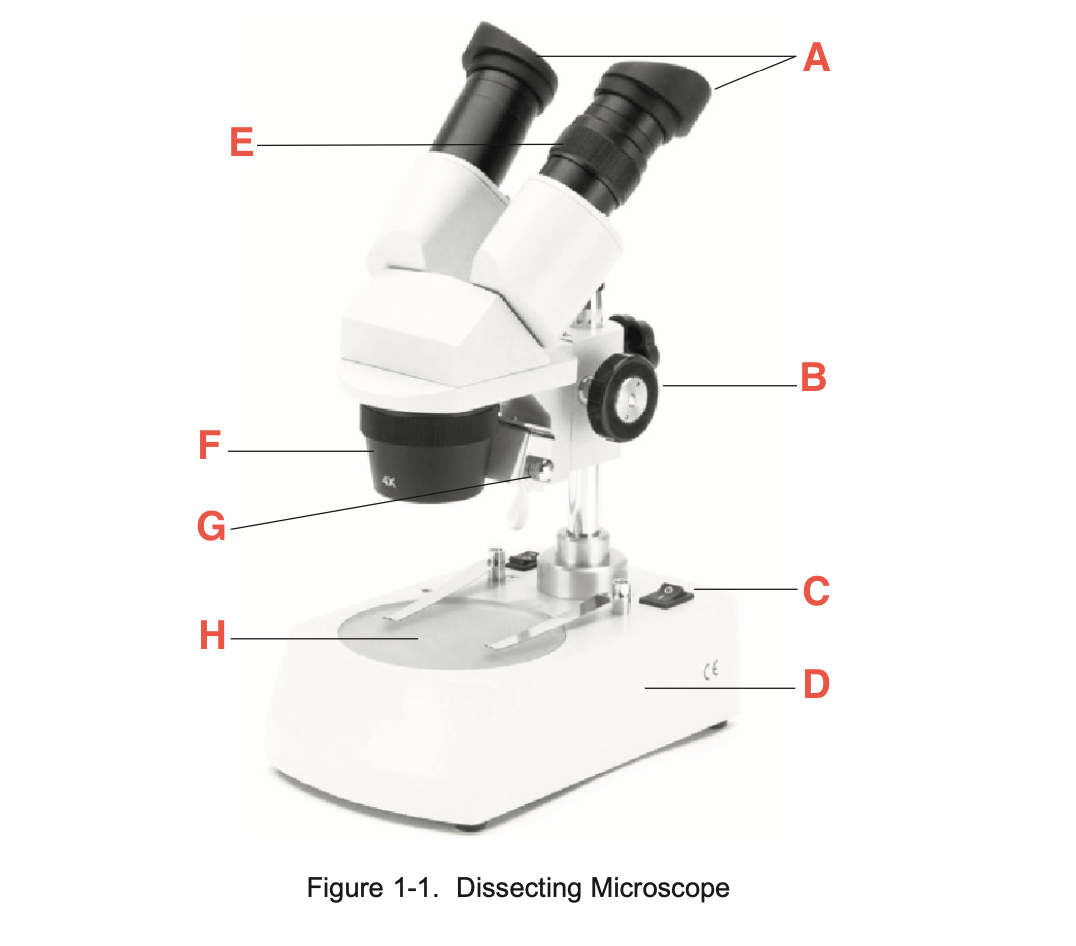
What is C
Illuminator switch
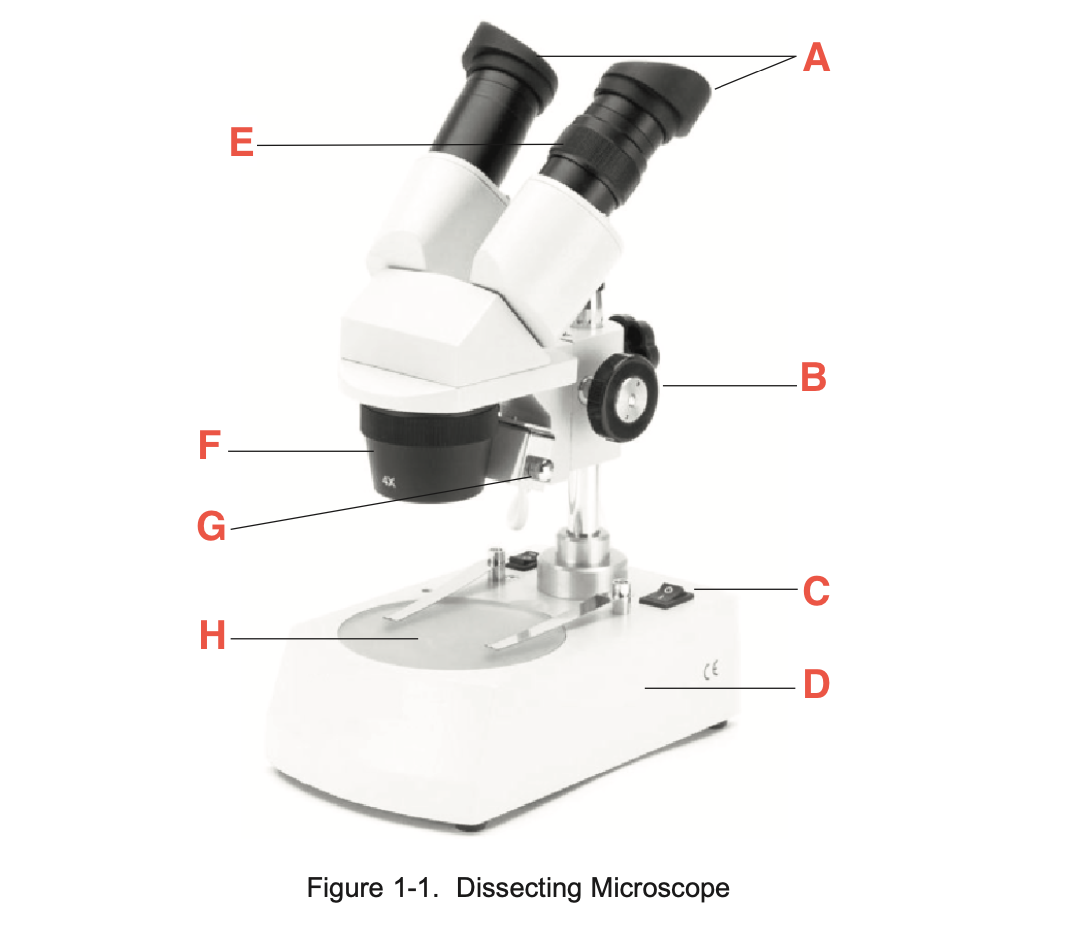
What is D
Base
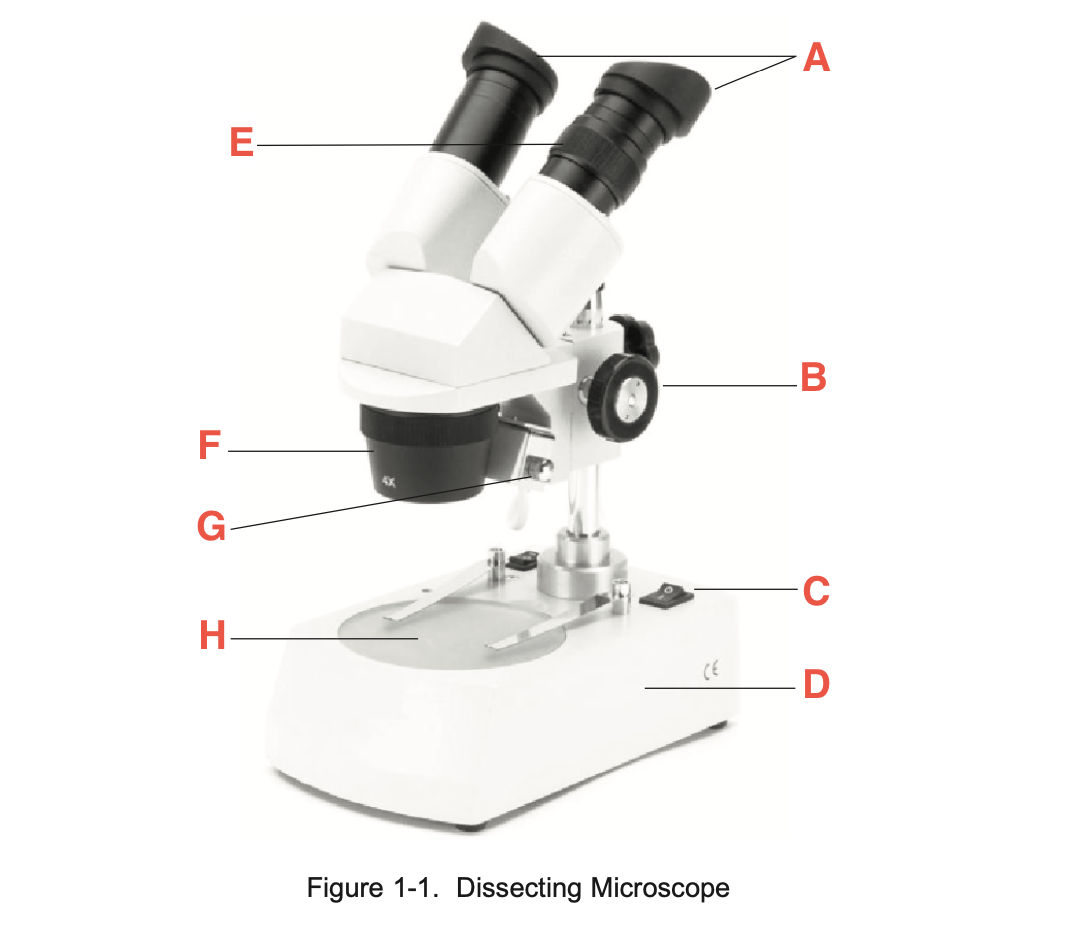
What is E
Knurled Ring
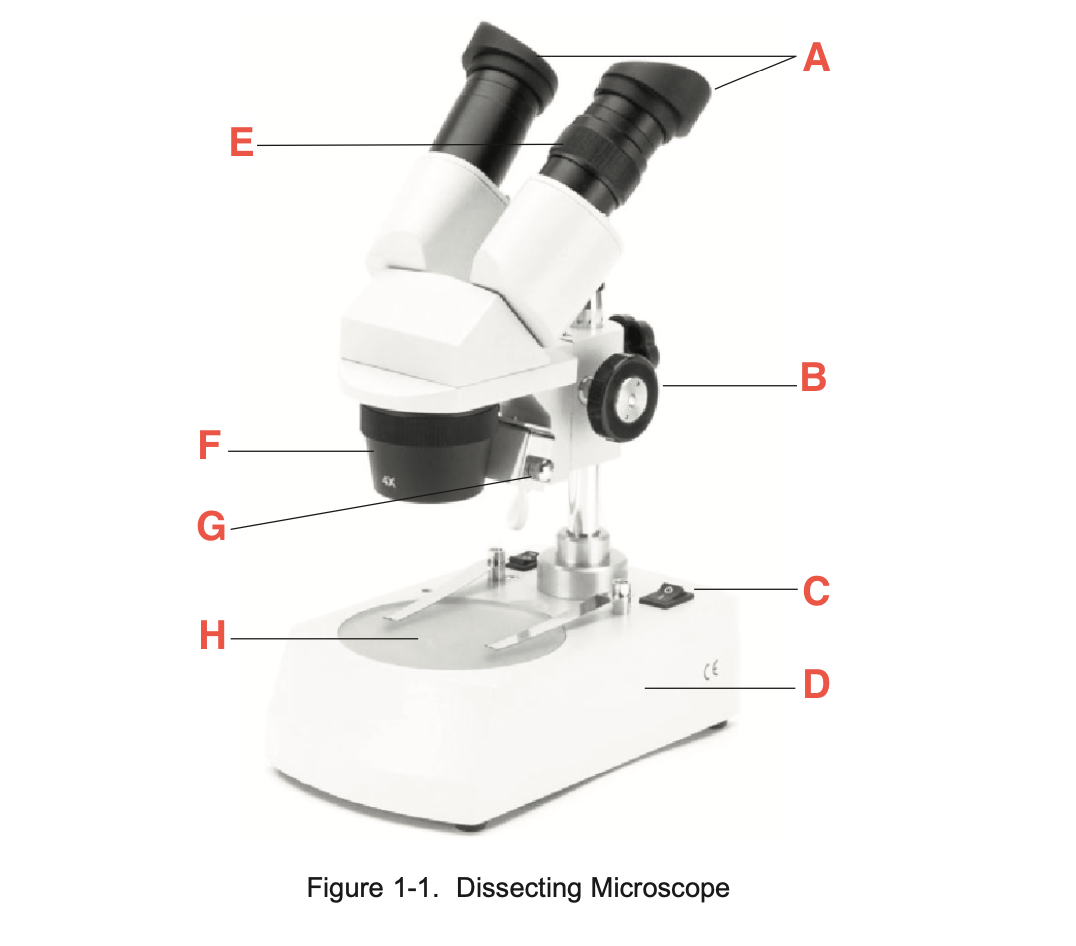
What is F
Objective
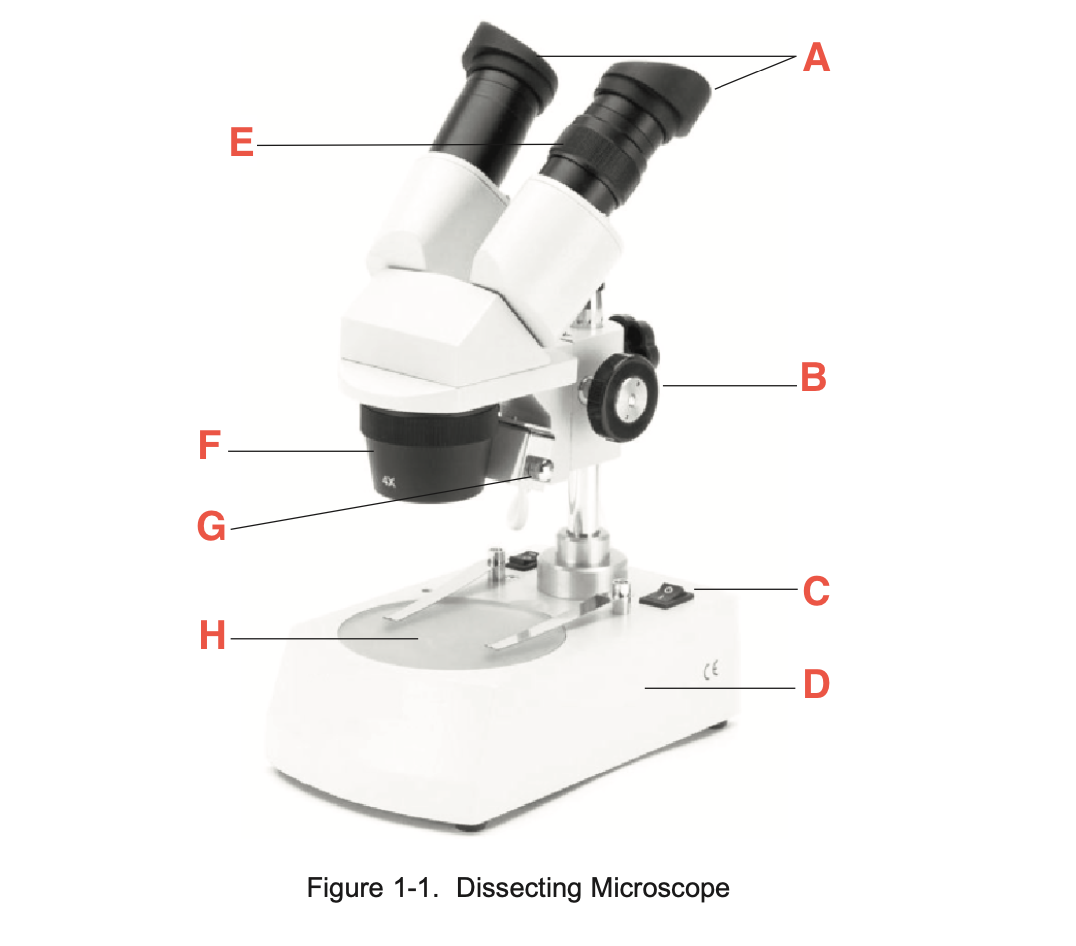
What is G
Illuminator
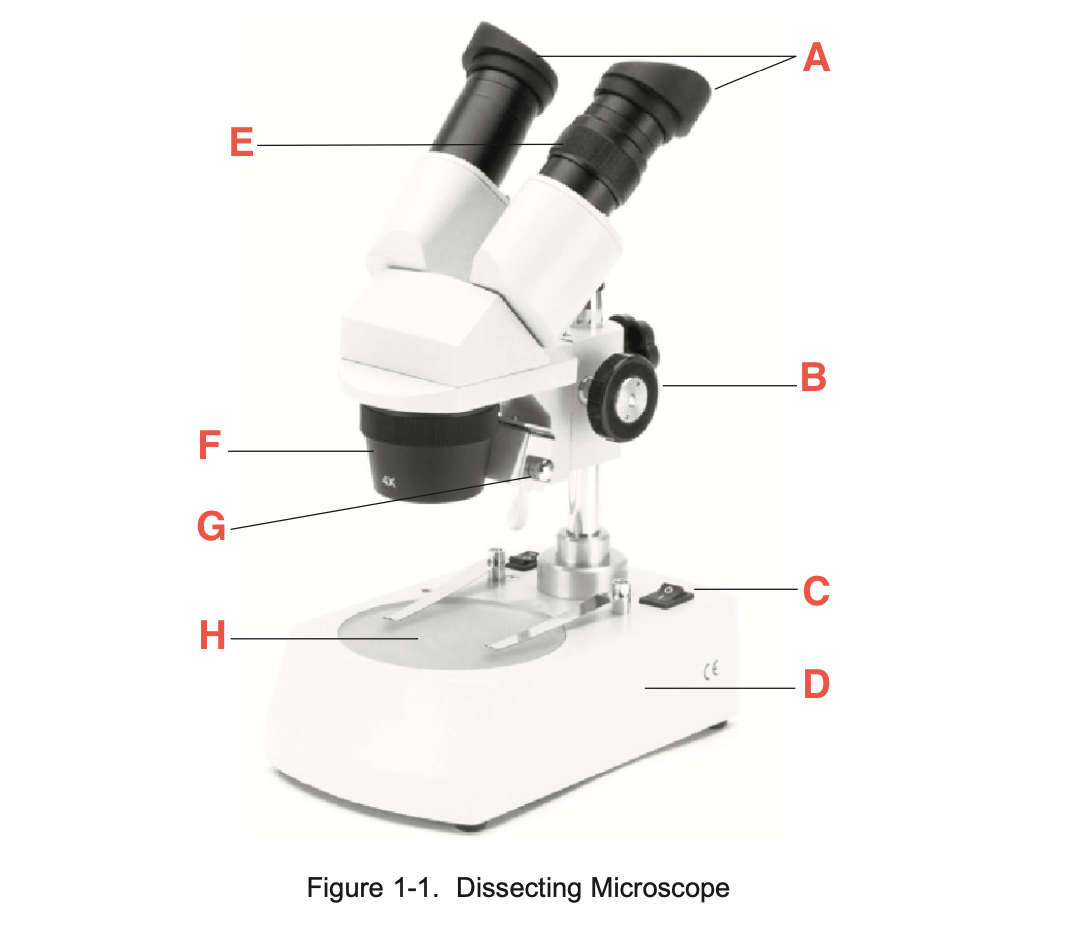
What is H
stage
Mean
Average
Mode
number that appears the most
Median
Middle number in set of numbers
Range
highest number - lowest number
To test for reducing sugars we used
Benedict’s solution
To test for Polysaccharide (starch) we used
Iodine
To test for proteins we used
Biuret reagent
Placing samples on a brown paper bag was a test for
lipids
Lipid samples dissolve in
vegetable oil
When sugar comes in contact with Benedict’s reagent it turns the color
blue
When a polysaccharide (starch) comes in contact with Iodine it turns what color
Dark purple
When proteins come in contact with Biuret reagent it turns what color
violet
When lipids are on the paper bag
It will stay wet
When lipids undergo the solubility test
There will just be one layer
Formula for Fahrenheit to Celsius
F = 9/5 C + 32
Formula for magnification
magnification = linear magnification of the objective lens x linear magnification of the eyepiece
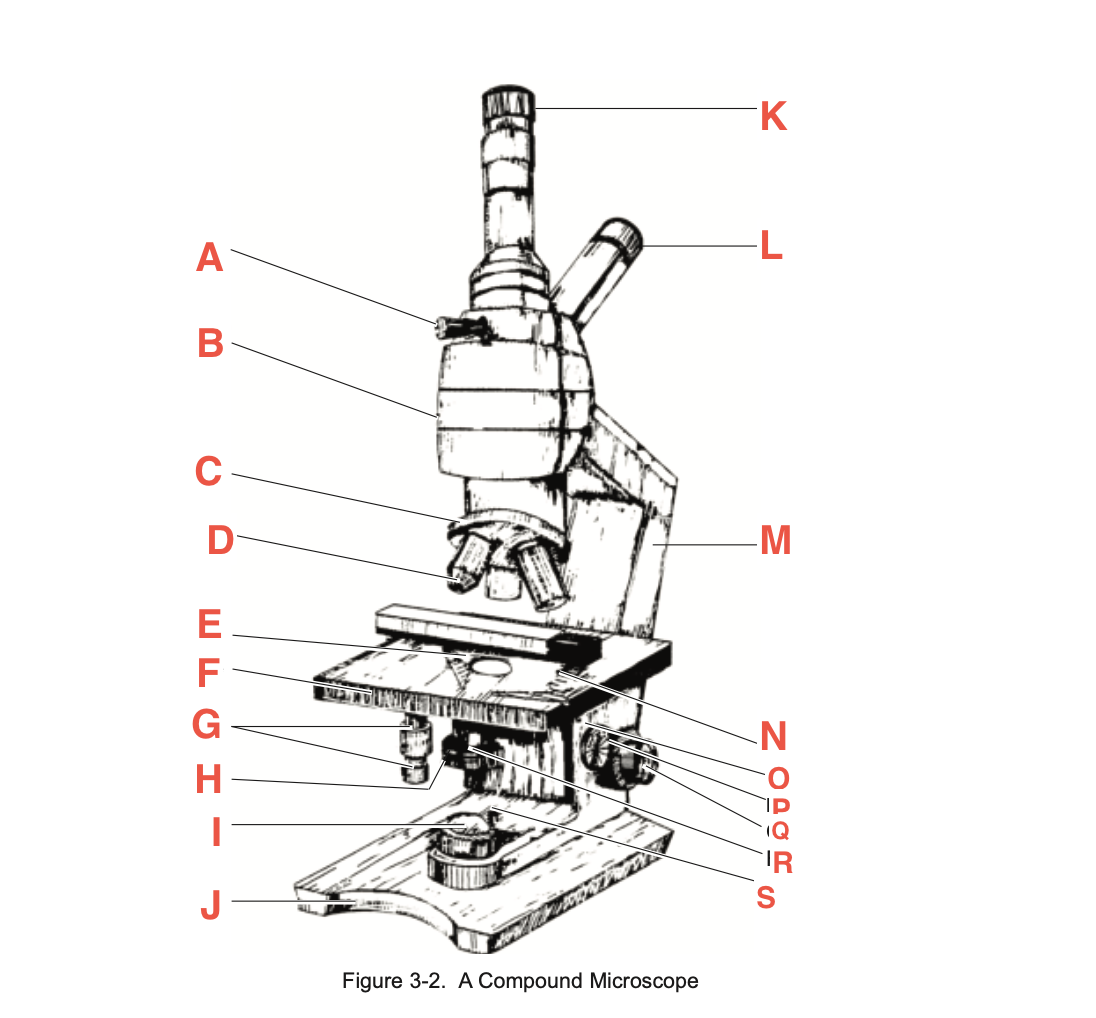
What is A
Pointer adjustment knob
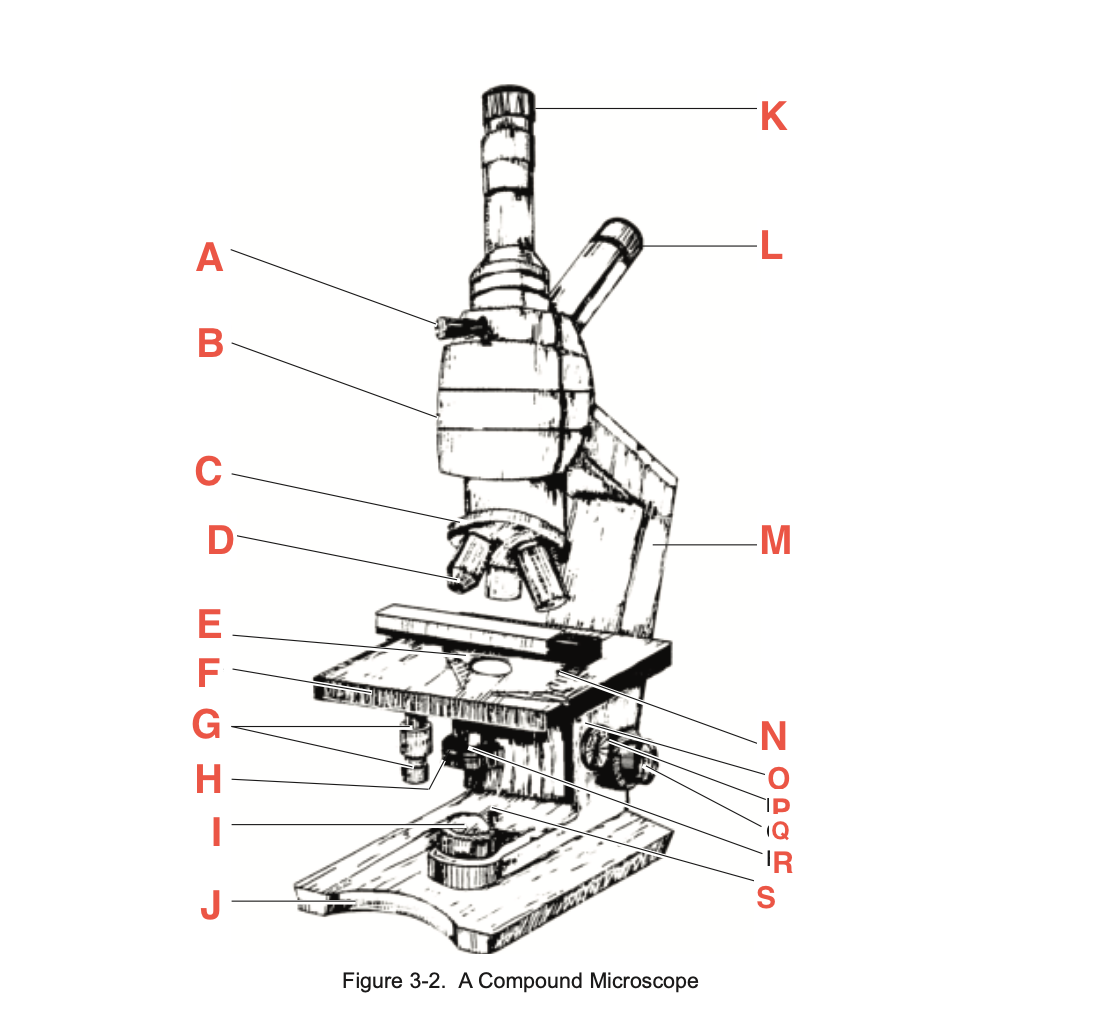
What is B
body tube
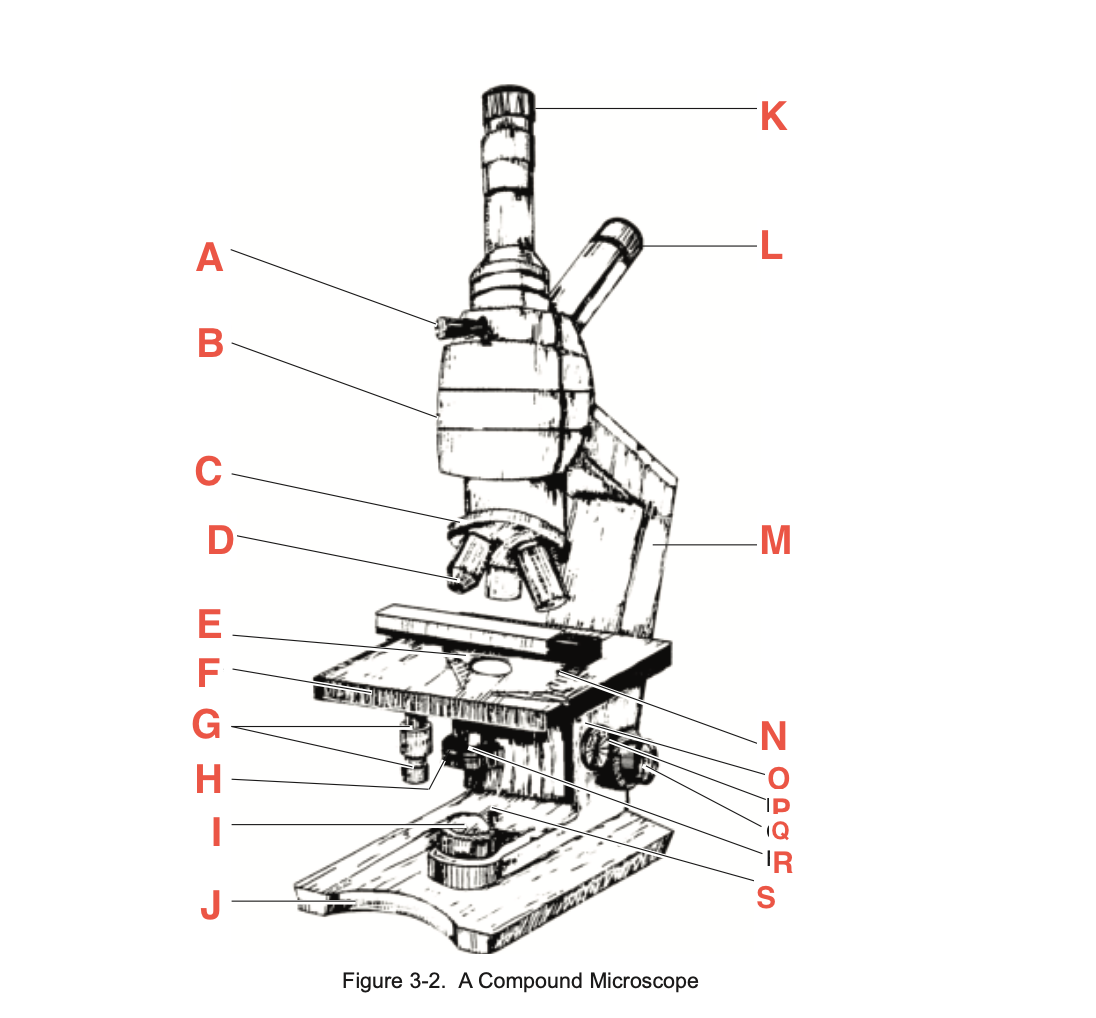
What is C
Revolving Nosepiece
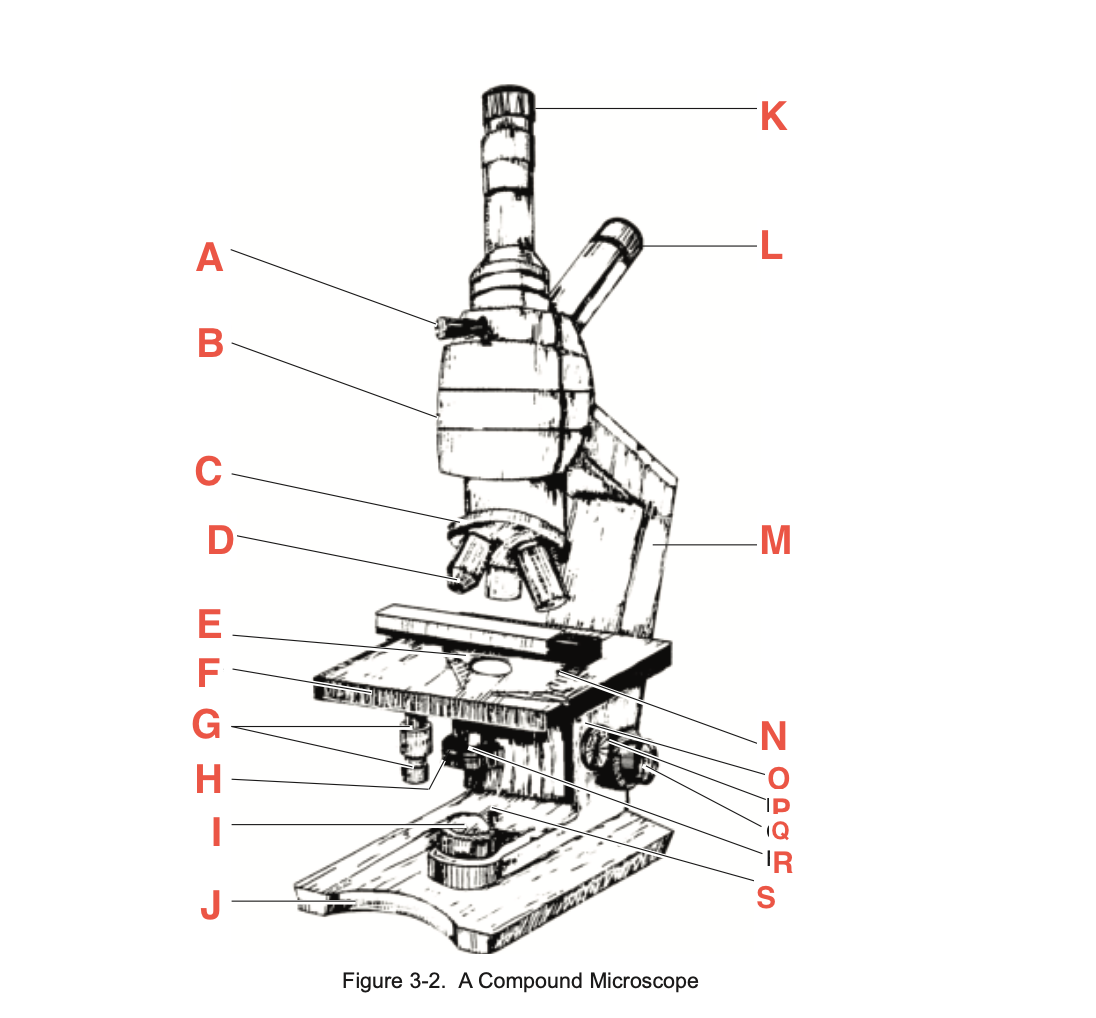
What is D
Objective
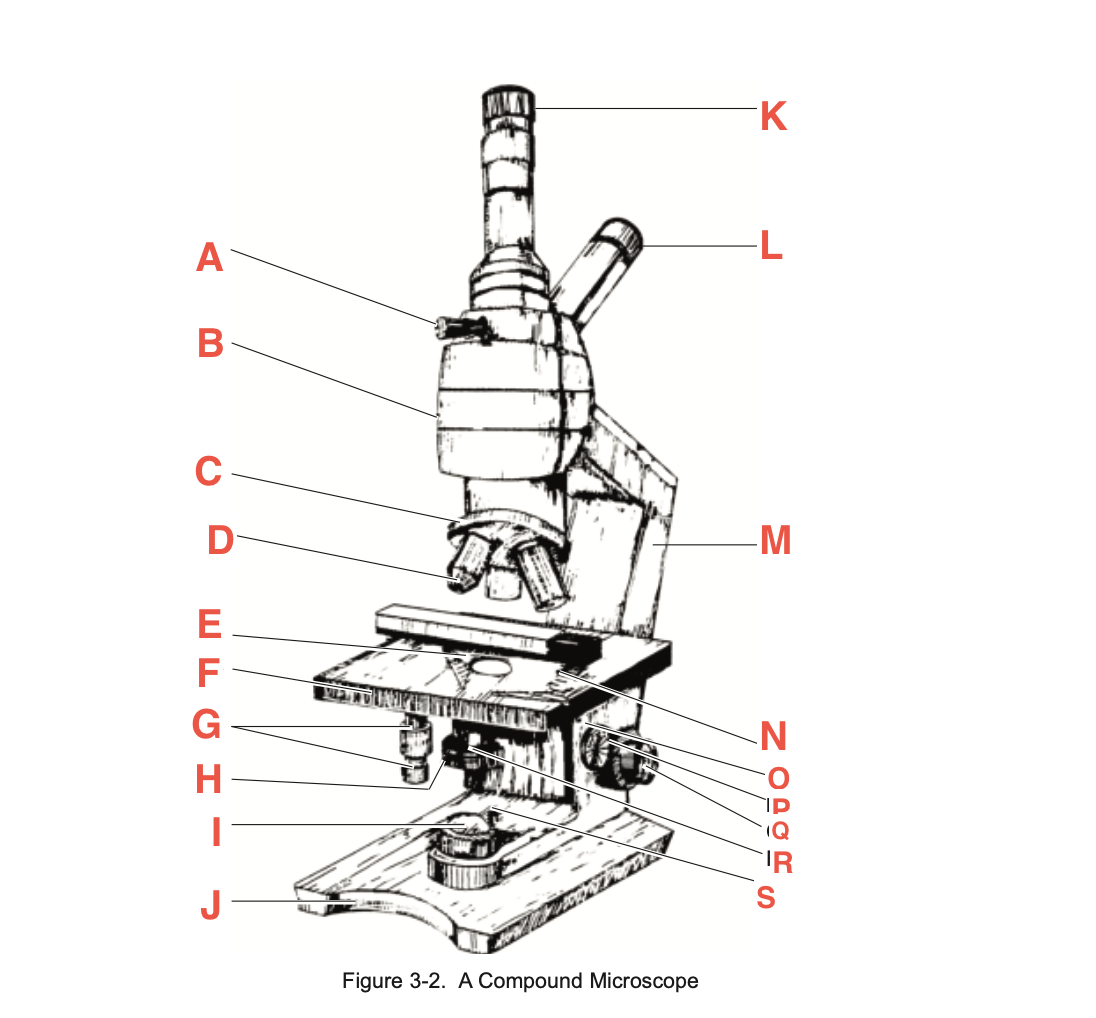
What is E
slide-holding clip
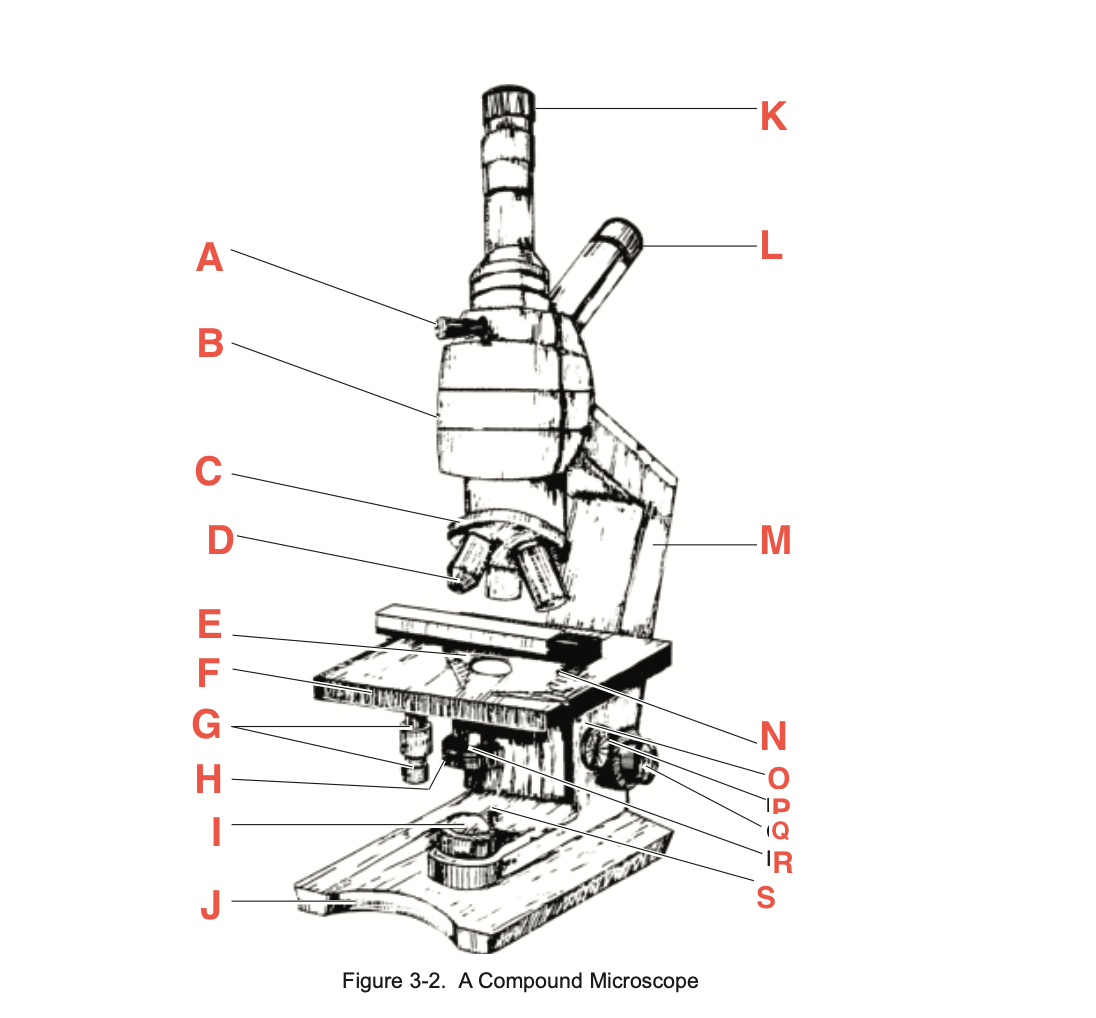
What is F
Stage
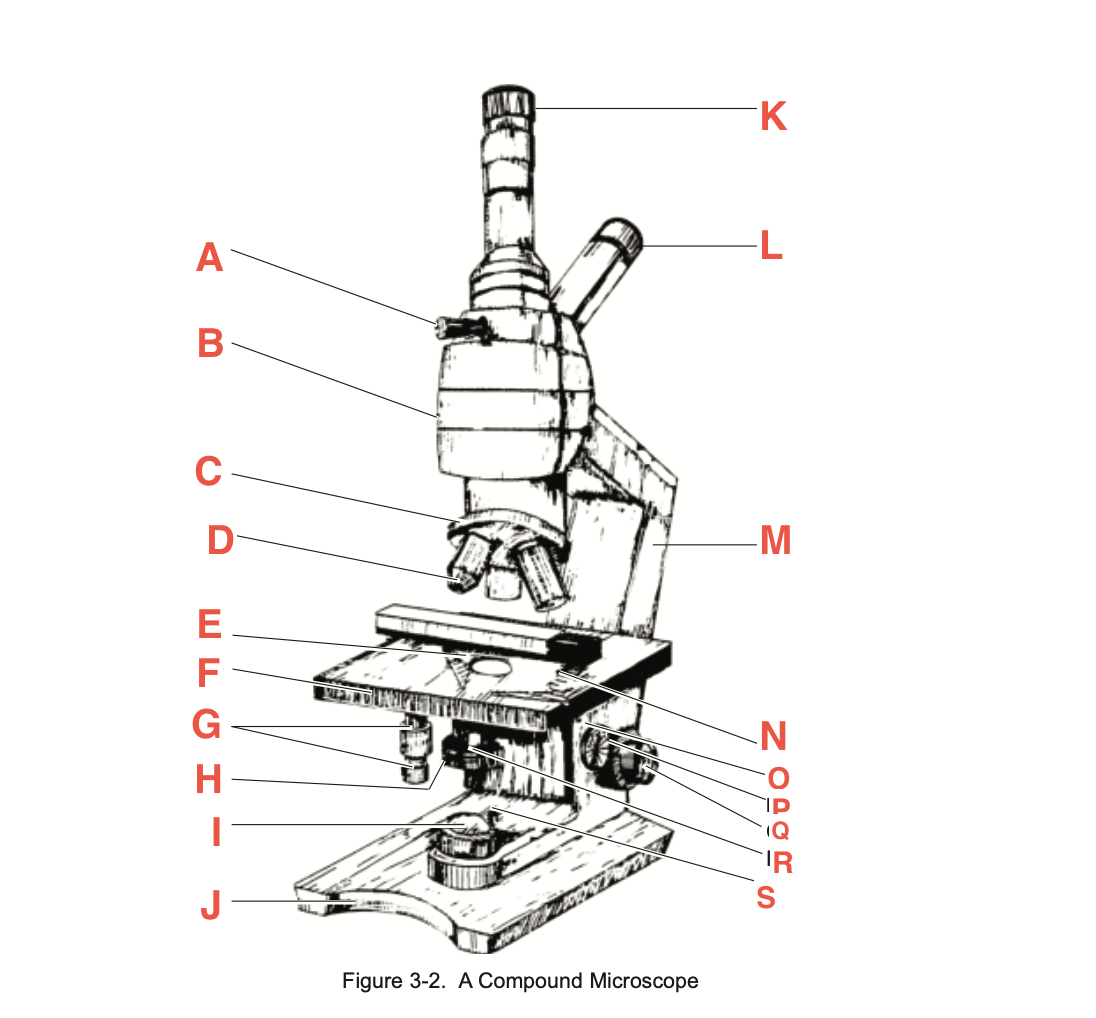
What is G
Stage adjustment knobs
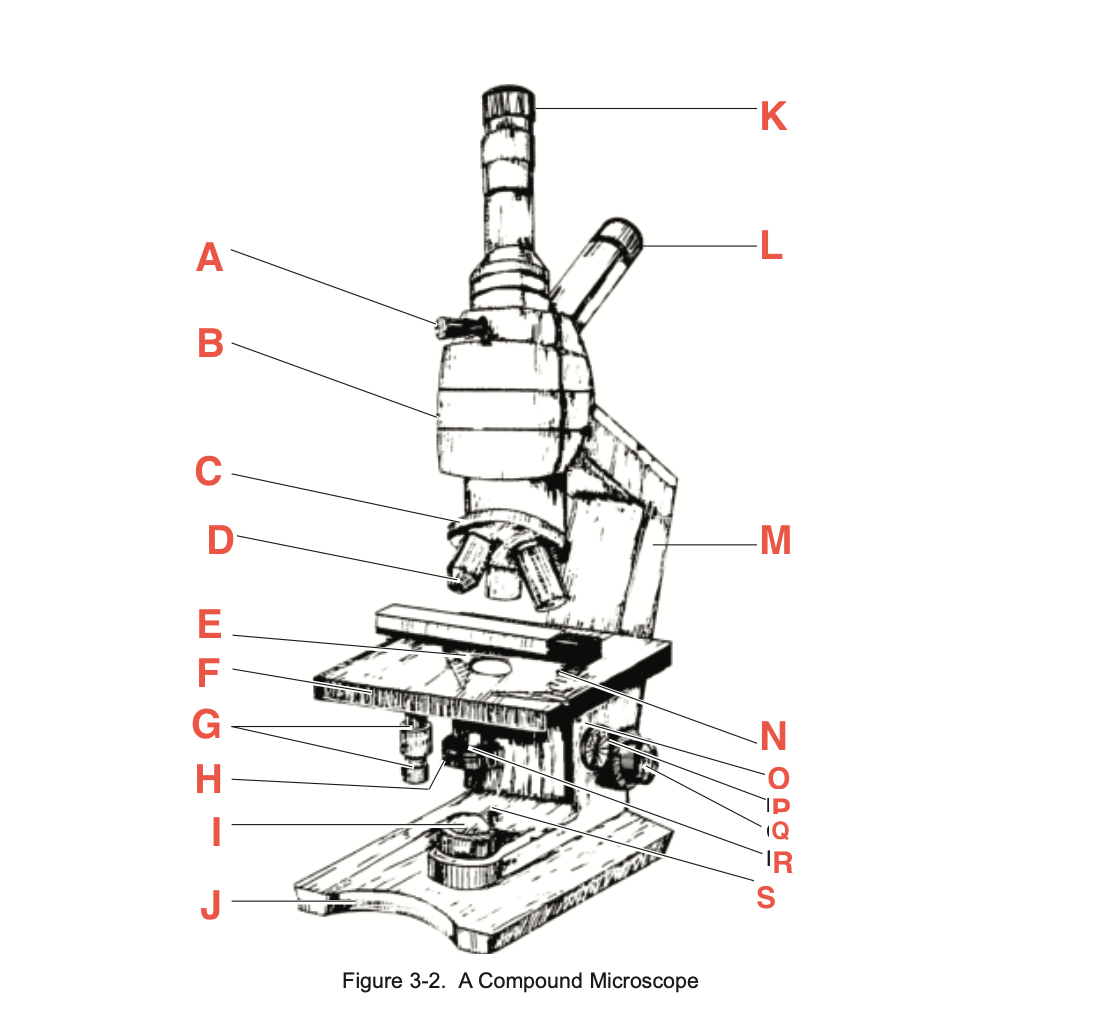
What is H
Iris diaphragm lever
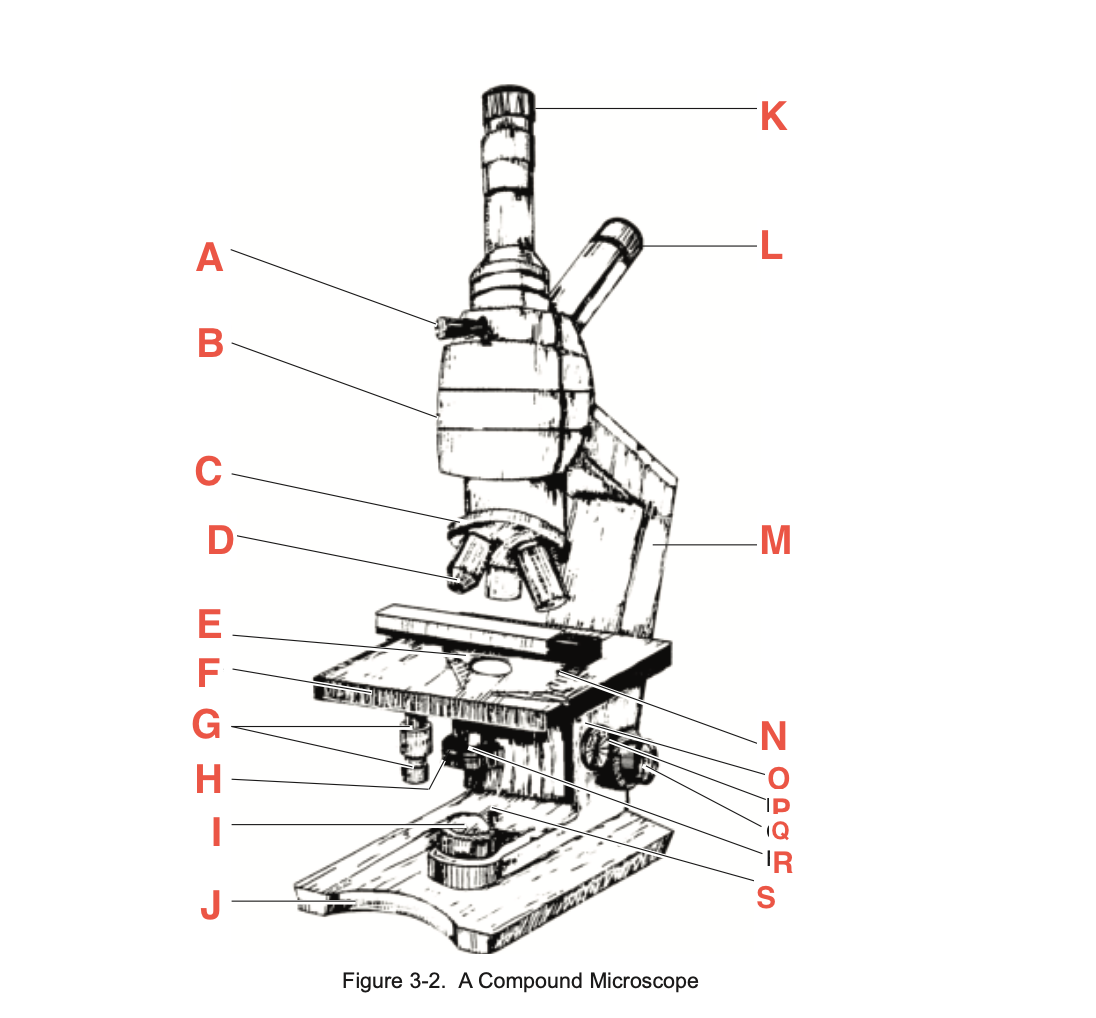
What is I?
Base illuminator
What is J
Base
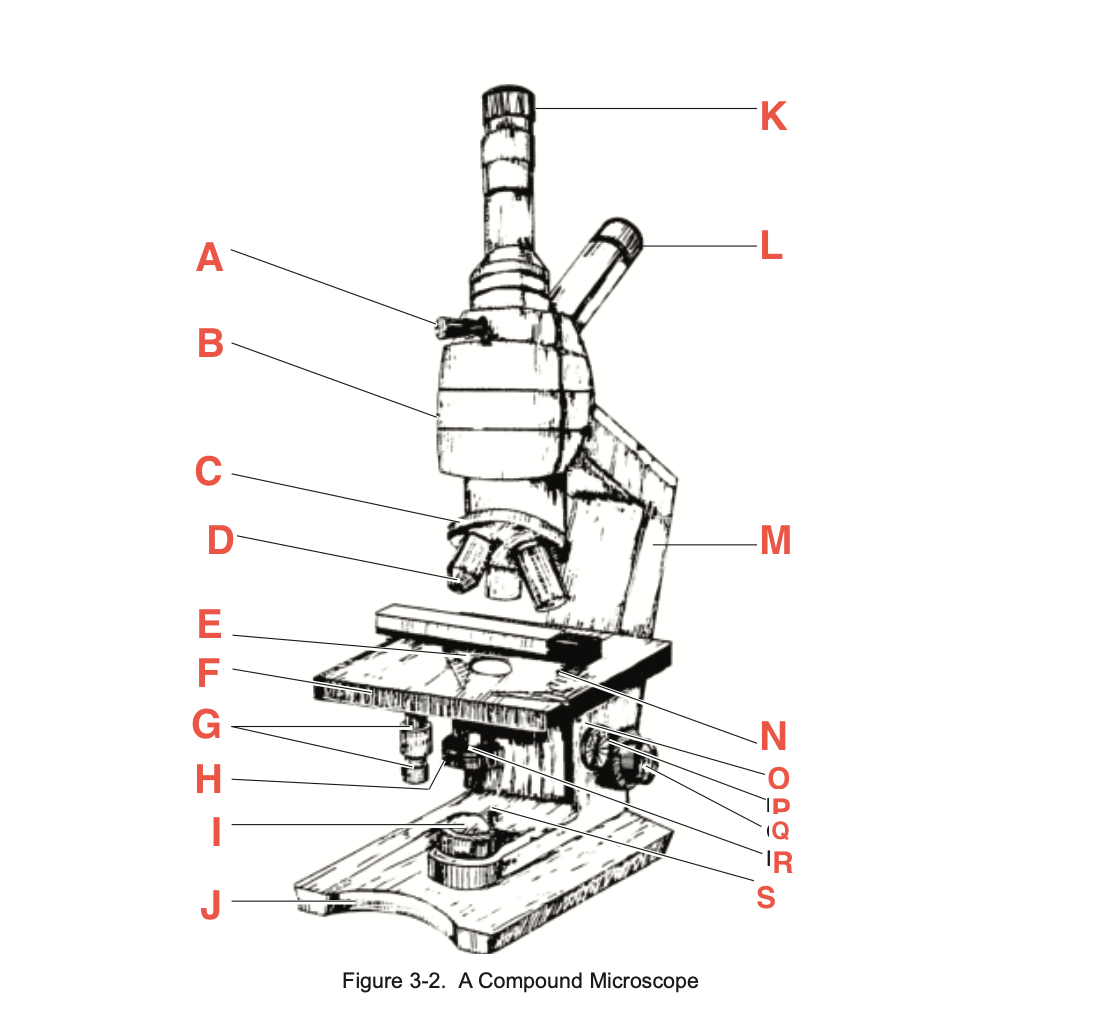
What is K
Vertical eyepiece for instructors
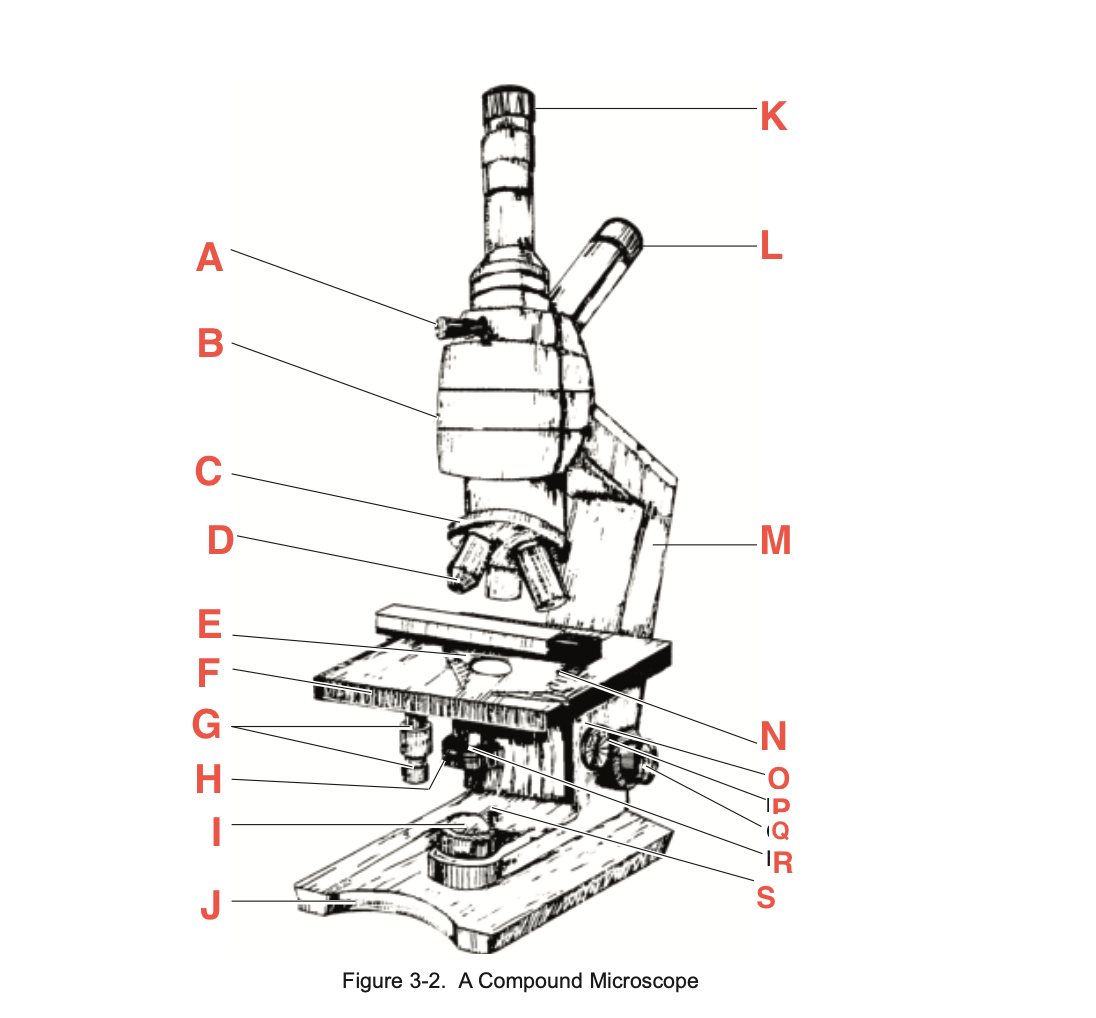
What is L
Inclined eyepiece
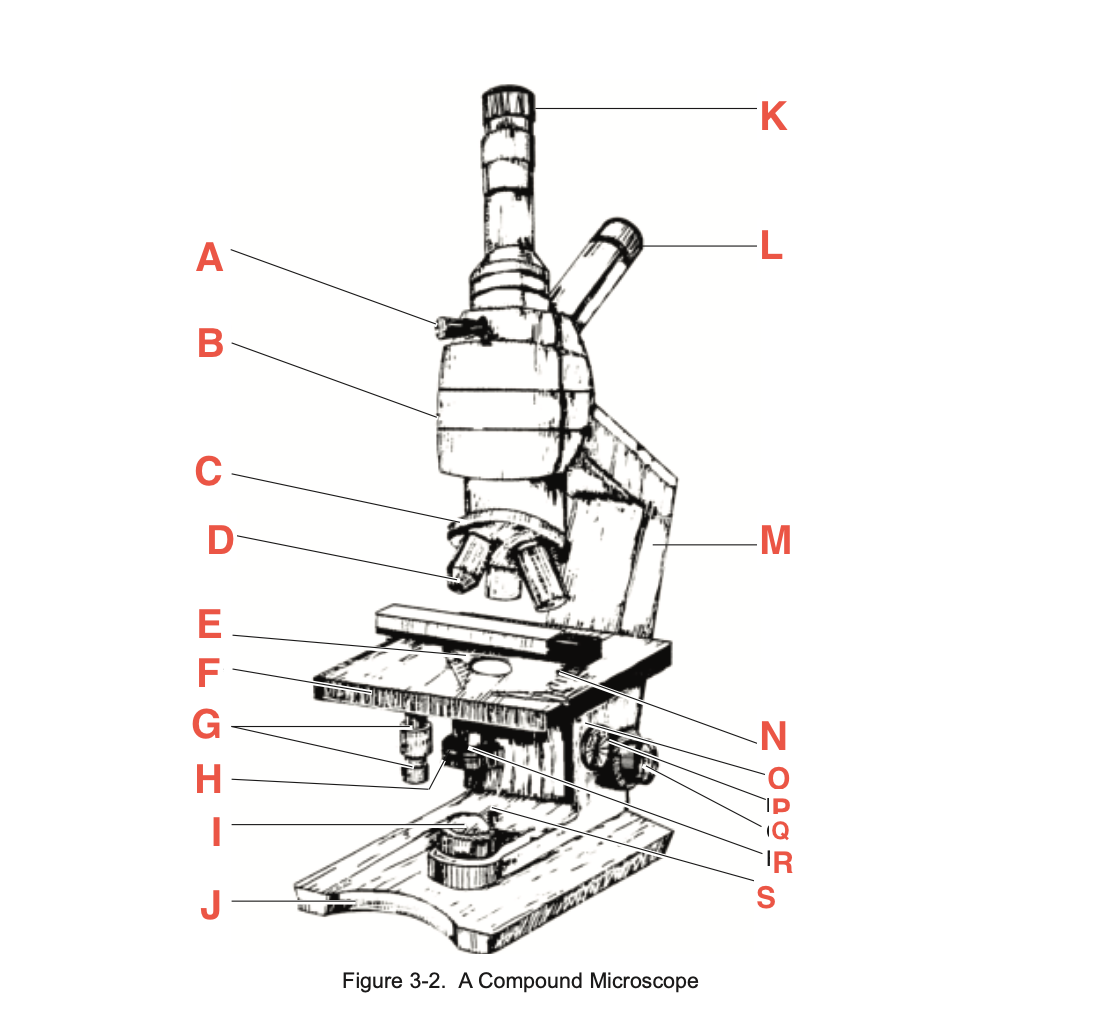
What is M
Arm
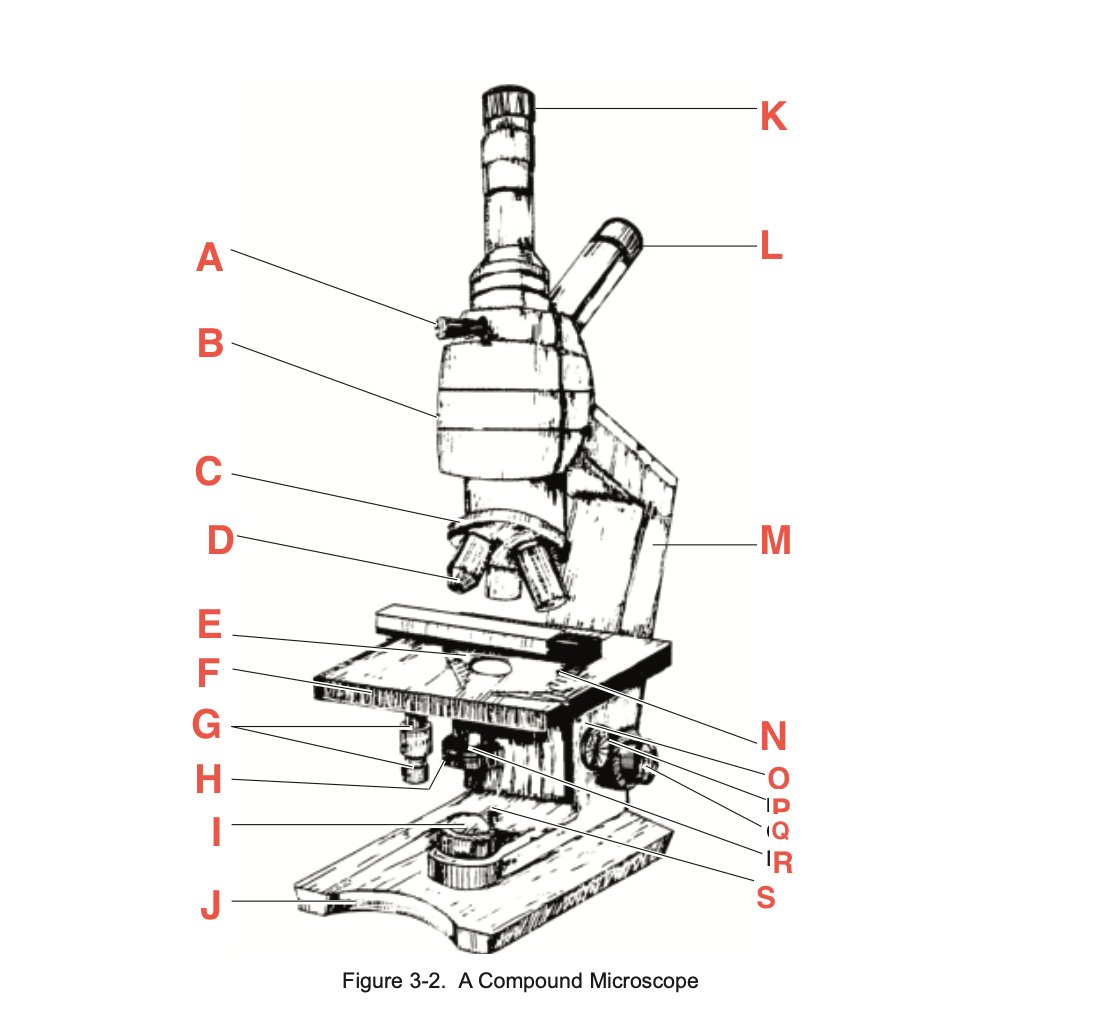
What is N
Sliding-holding clip
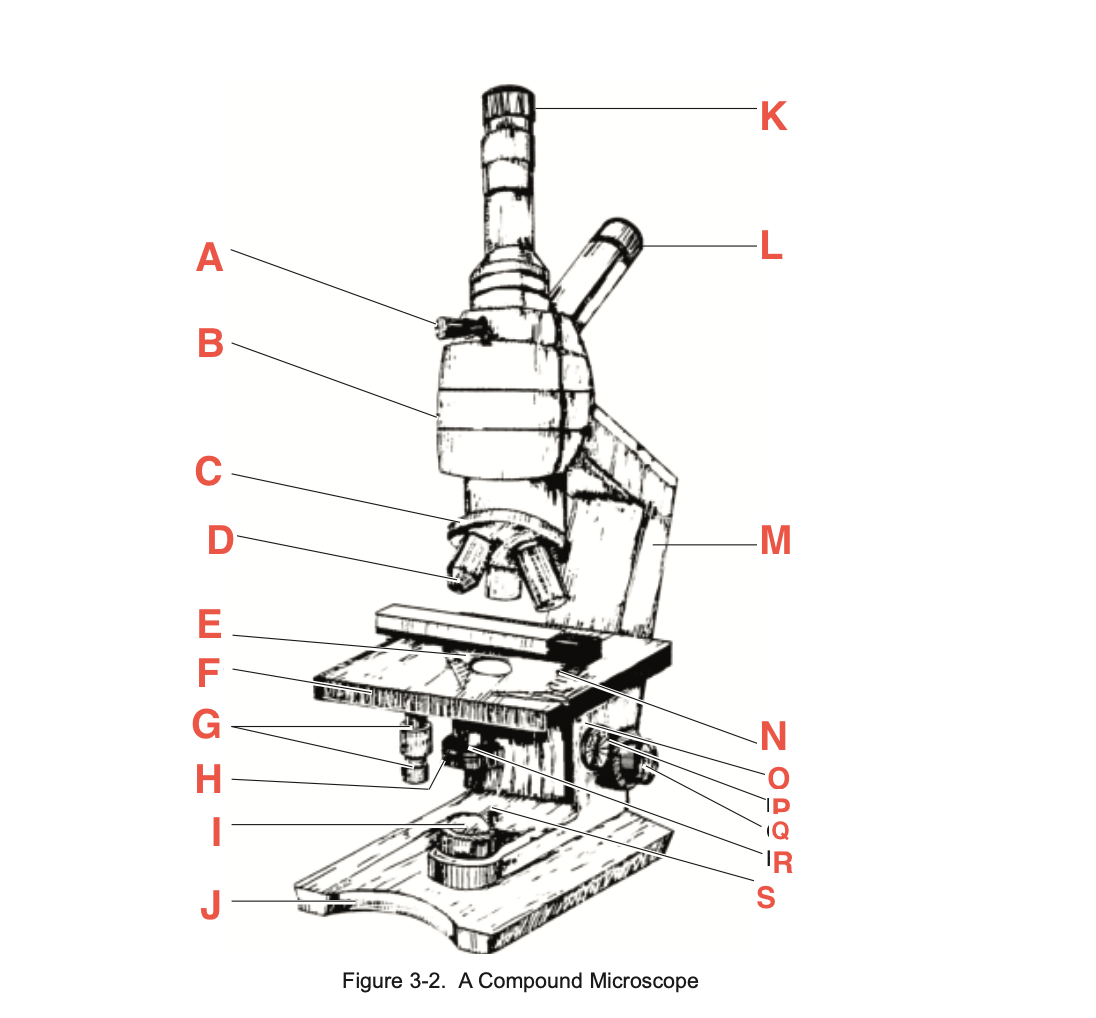
What is O
Condenser adjustment
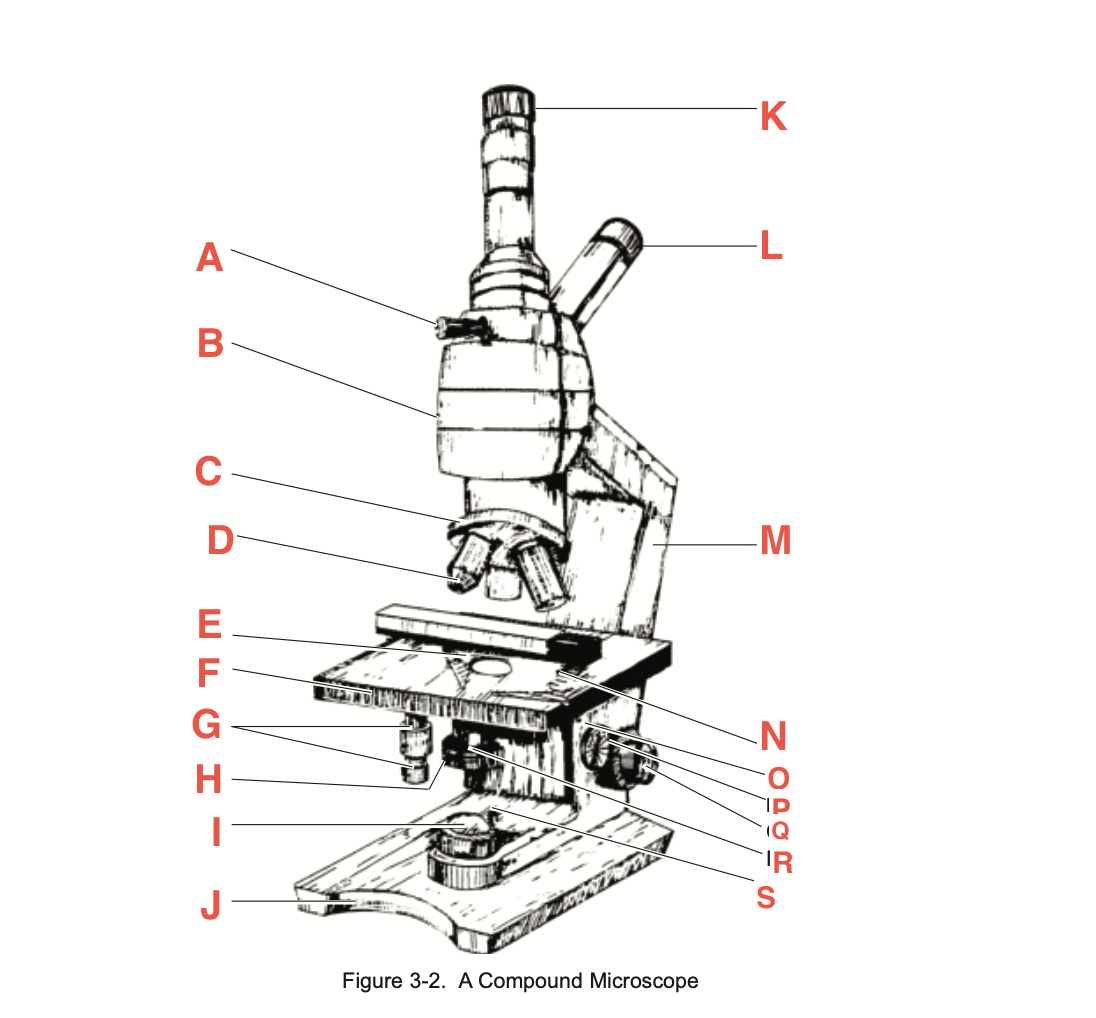
What is P
knob
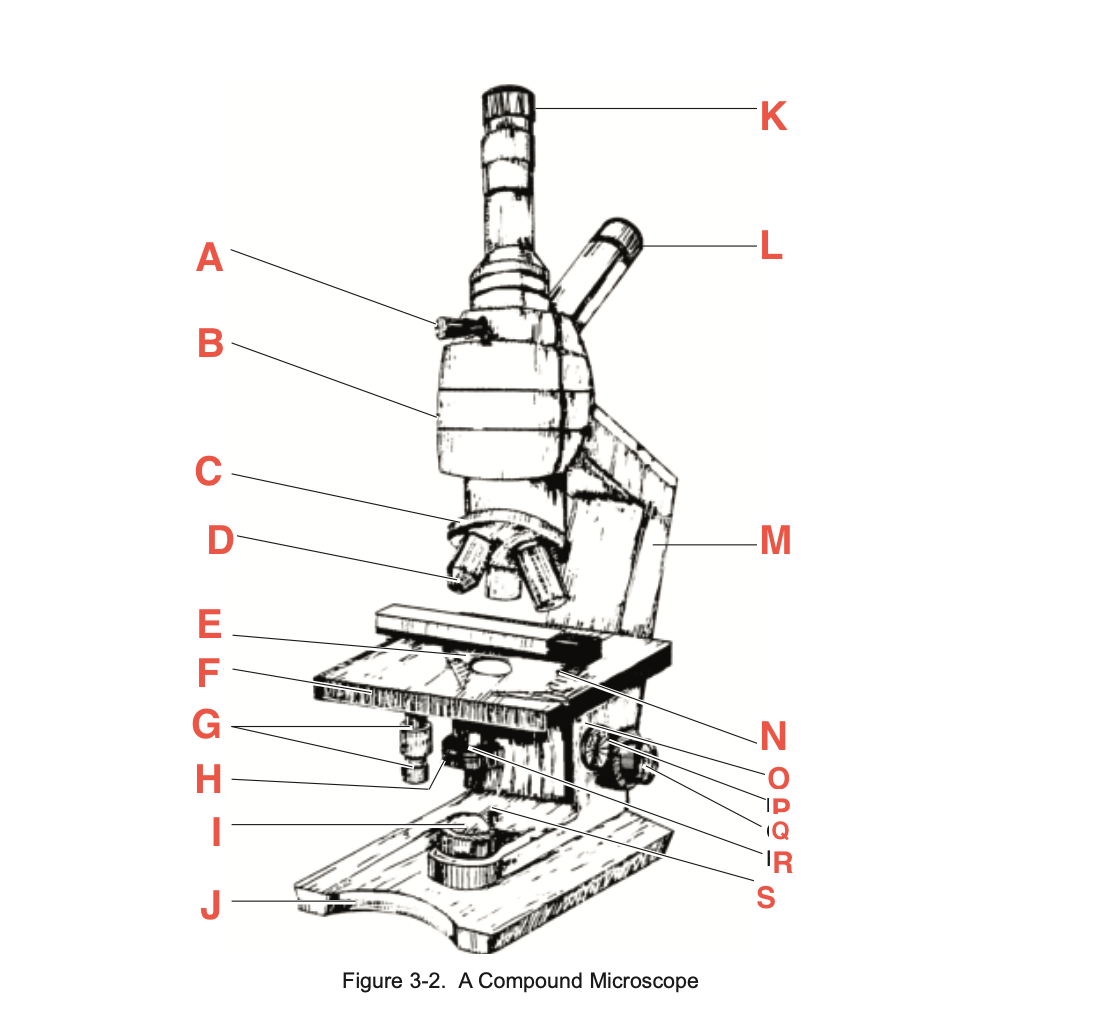
What is Q
Coarse focusing knob
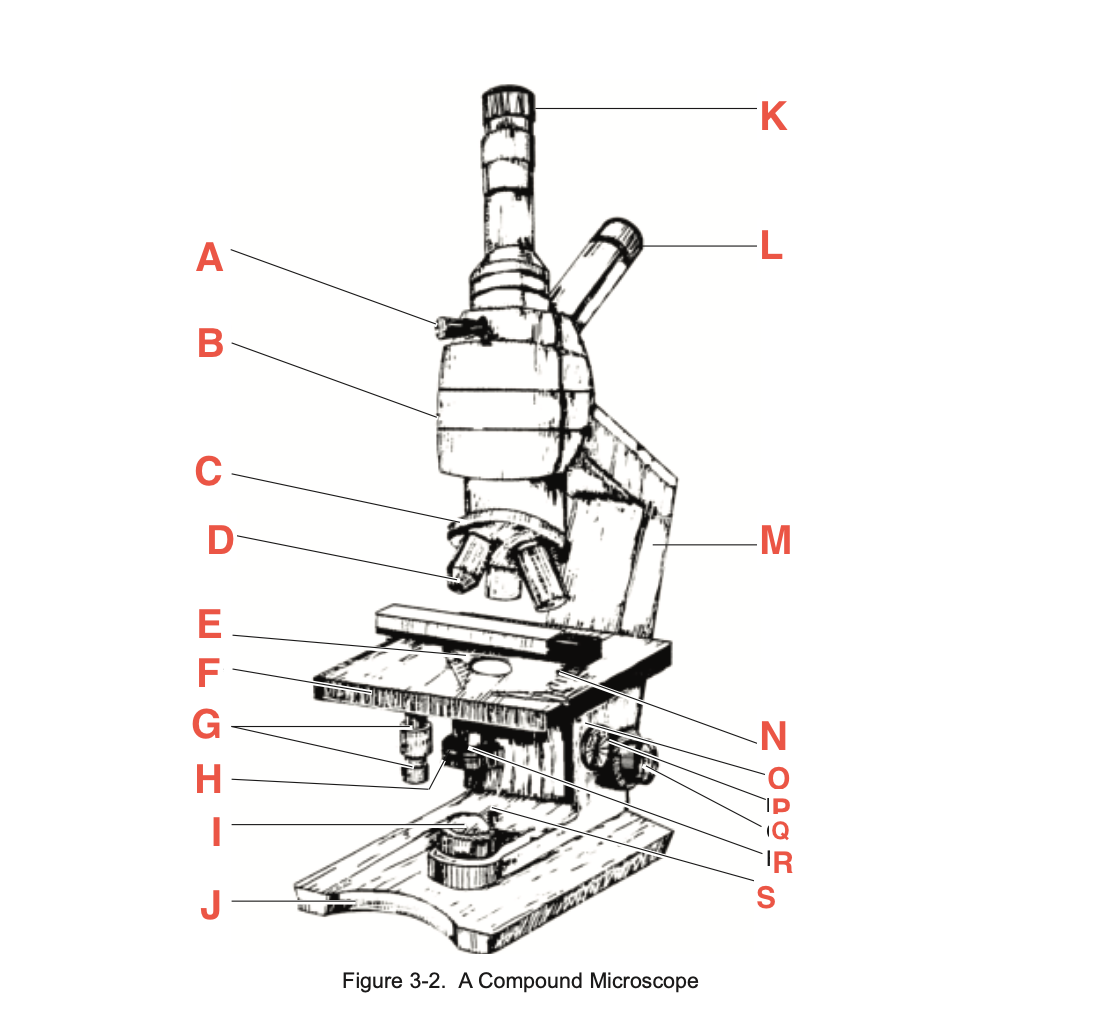
What is R
Fine focusing knob
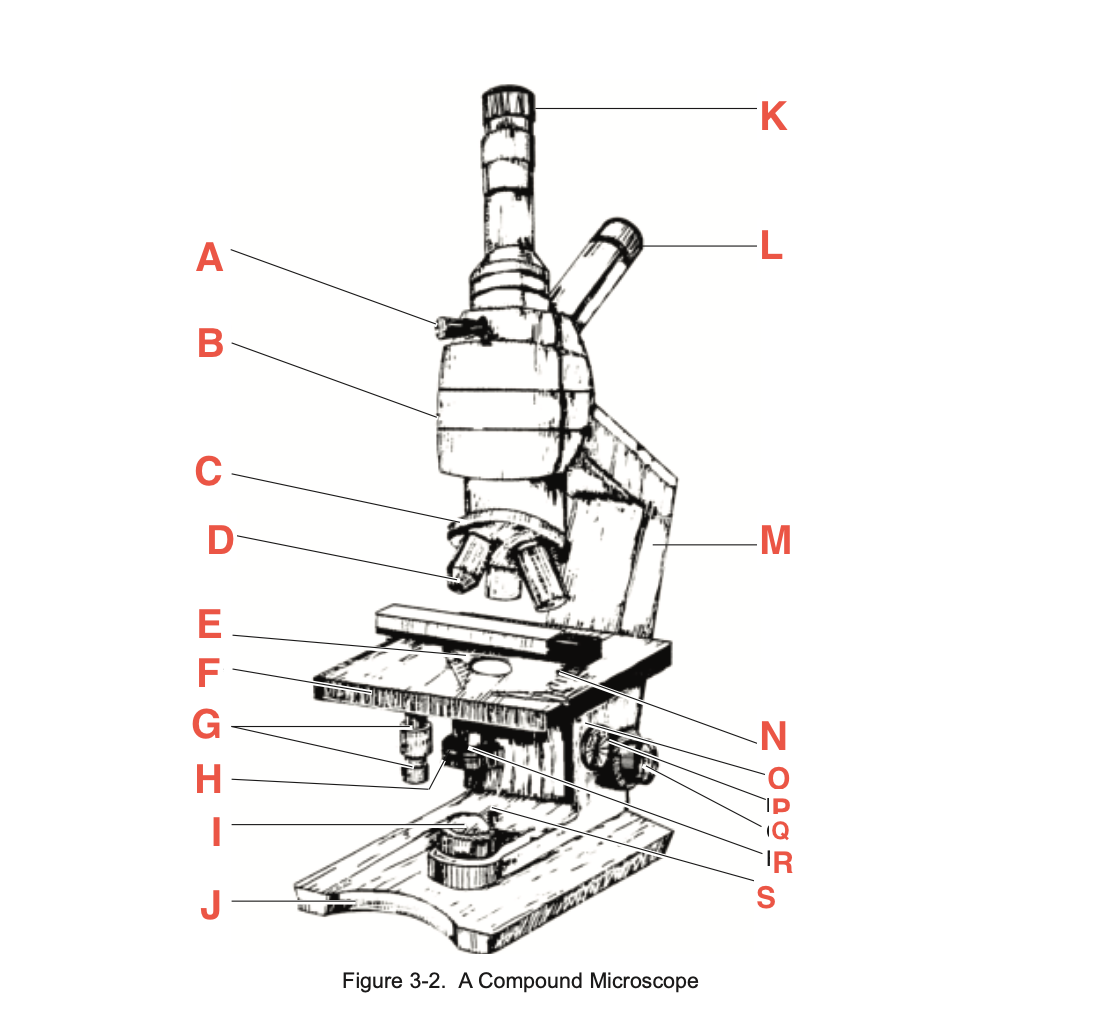
What is S
Condenser Light switch
Formula for diameter of field on a compound scope

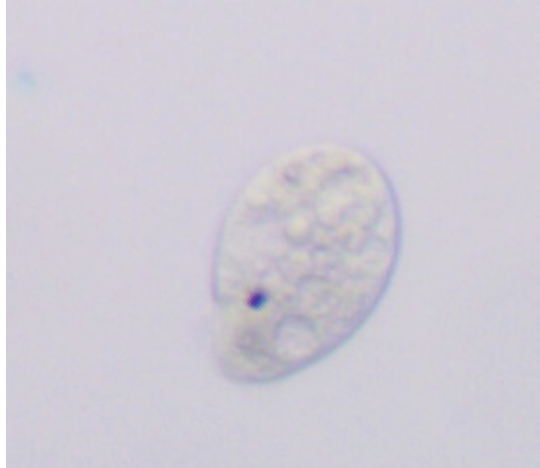
What cell is this?
Tetrahymena
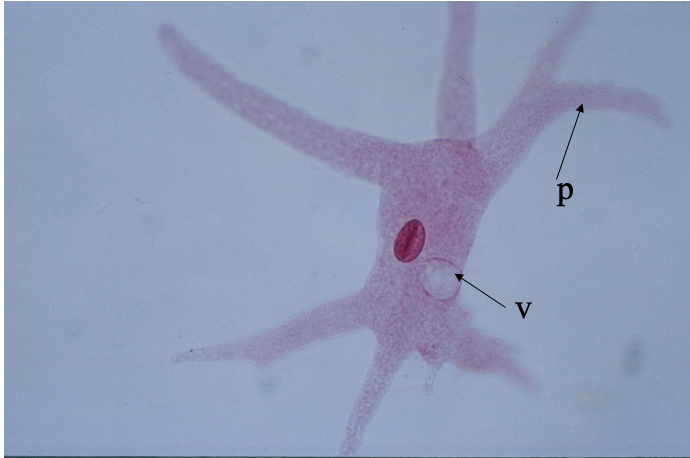
What cell is this?
Amoeba
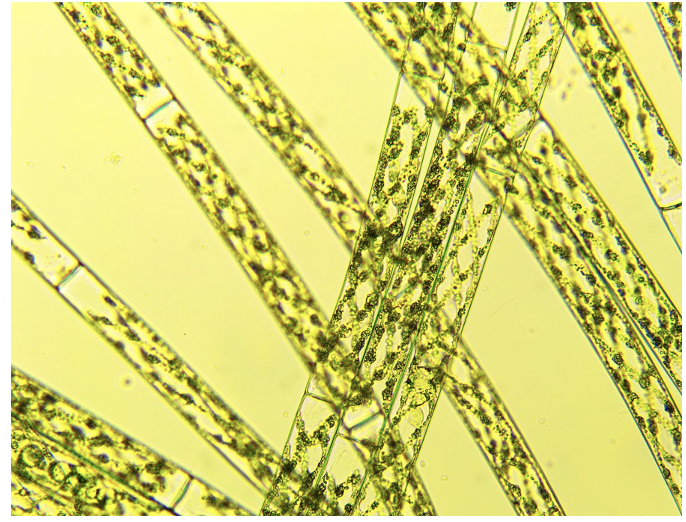
What cell is this?
Spirogyra
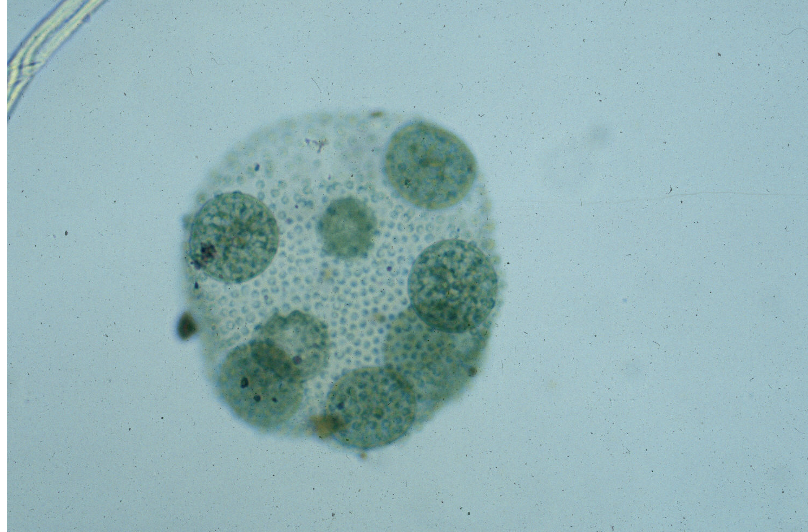
What cell is this?
Volvox
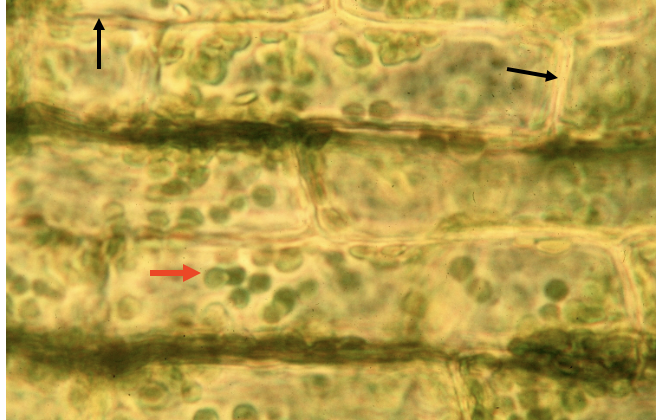
What cell is this?
Elodea
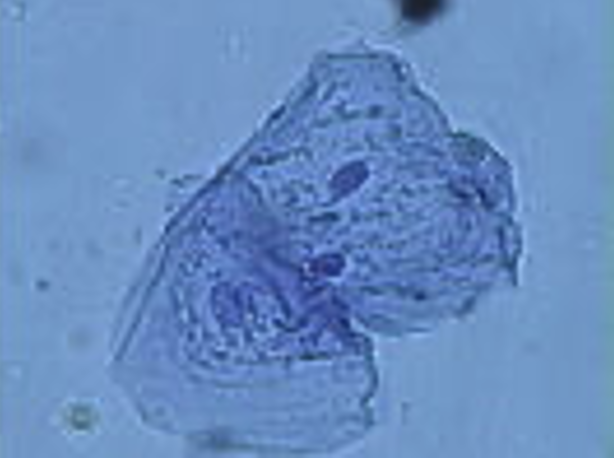
What cell is this?
squamous epithelia
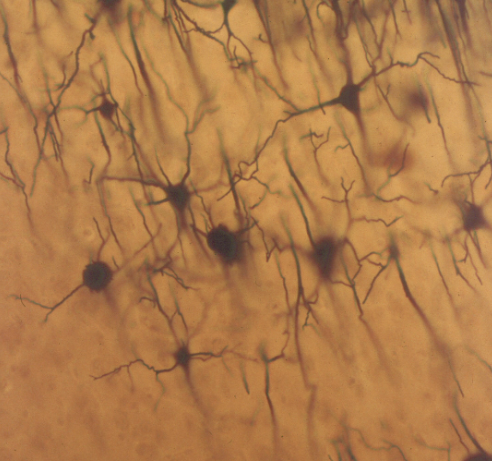
What cell is this?
Nerve
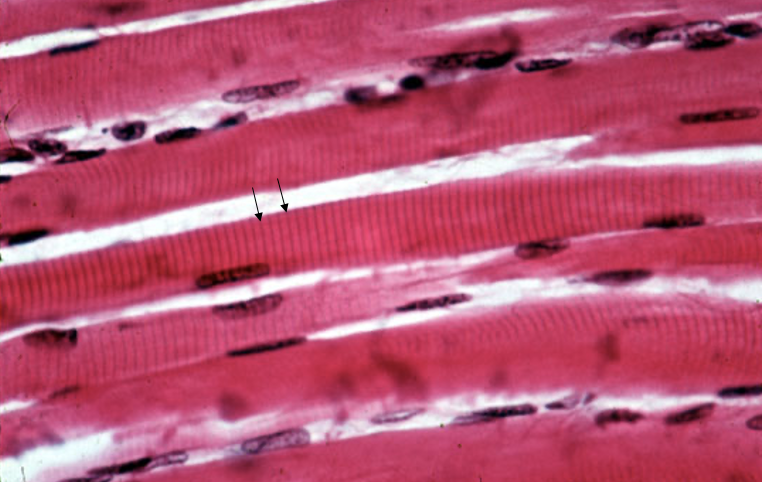
What cell is this?
Striated, skeletal muscle
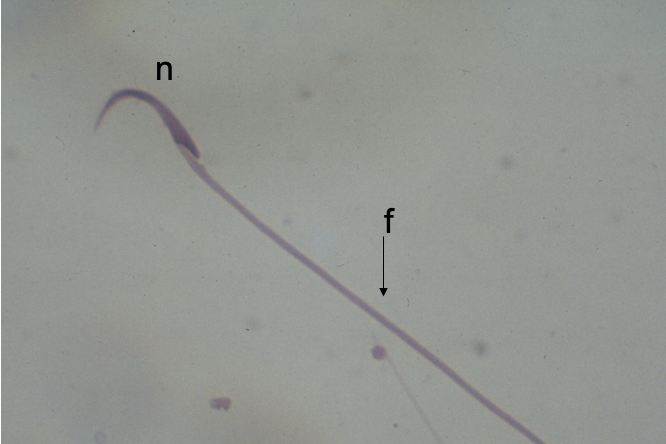
What cell is this?
Sperm
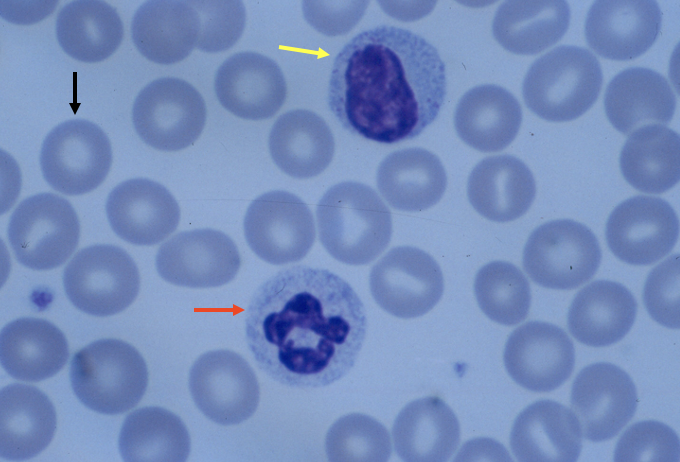
What cell is the black arrow pointing to?
red blood cell (aka erythrocytes)
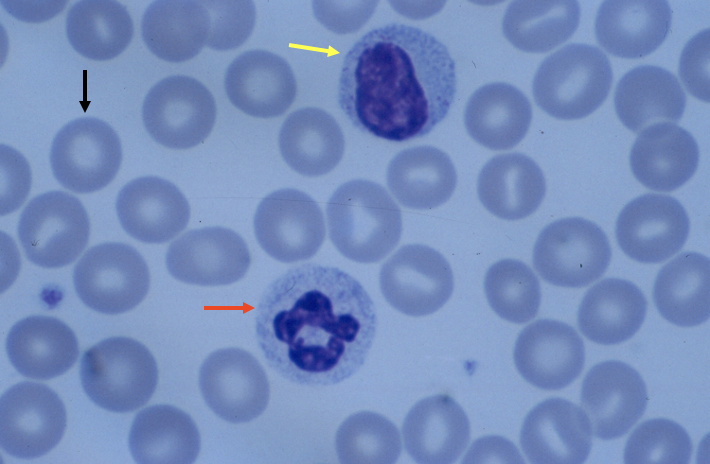
What cell is the yellow arrow pointing to?
lymphocyte
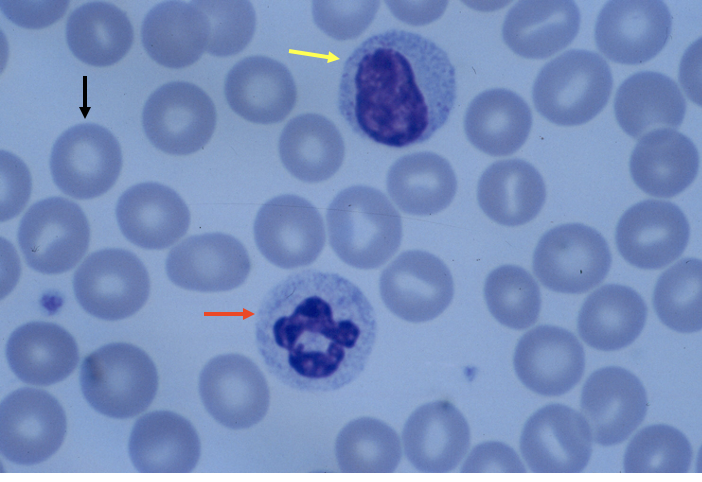
What cell is the red arrow pointing to?
neutrophil
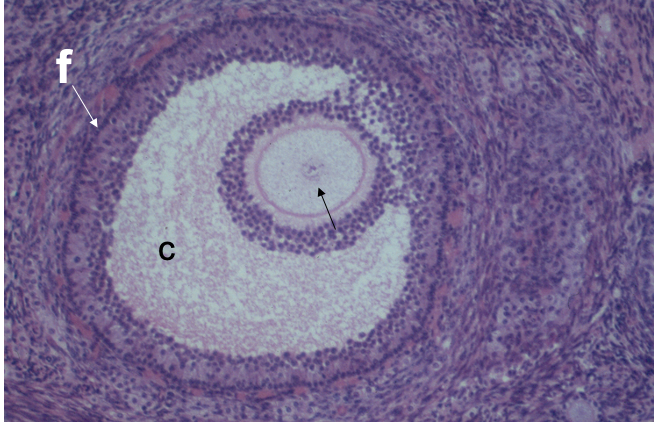
What cell is the black arrow pointing to?
Ovary egg cell
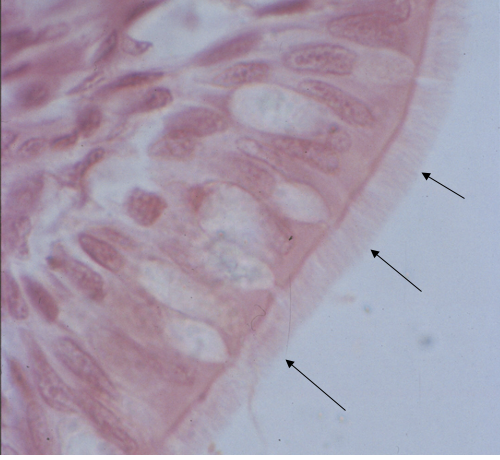
What are the black arrows pointing to?
cilia
As temperature increases rate of diffusion will
a) decrease
b) increase
c) stay the same
b) increase
The heavier the molecular weight the ___ the rate of diffusion
a) slower
b) molecular weight has no influence on rate of diffusion
c) faster
a) slower
Osmosis
net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Diffusion
net movement of particles form an area of high initial concentration to an area with a low initial concentration
Tonic
when two solutions have the same relative concentration of dissolved substances
When a solution has a higher relative concentration of dissolved substances it is
hypertonic
When a solution has a relativly lower concentration os dissolved substances it is
Hypotonic
The dialysis bags with water inside that were placed in a beaker of NaCl had a ___ in mass because they were ____.
a) decrease, hypertonic
b) decrease, hypotonic
c) increase, hypertonic
d) increase, hypotonic
b) decrease, hypotonic
The dialysis bags with NaCl that were placed in a beaker of H2O had a ___ in mass because they were ____.
a) decrease, hypertonic
b) decrease, hypotonic
c) increase, hypertonic
d) increase, hypotonic
c) increase, hypertonic
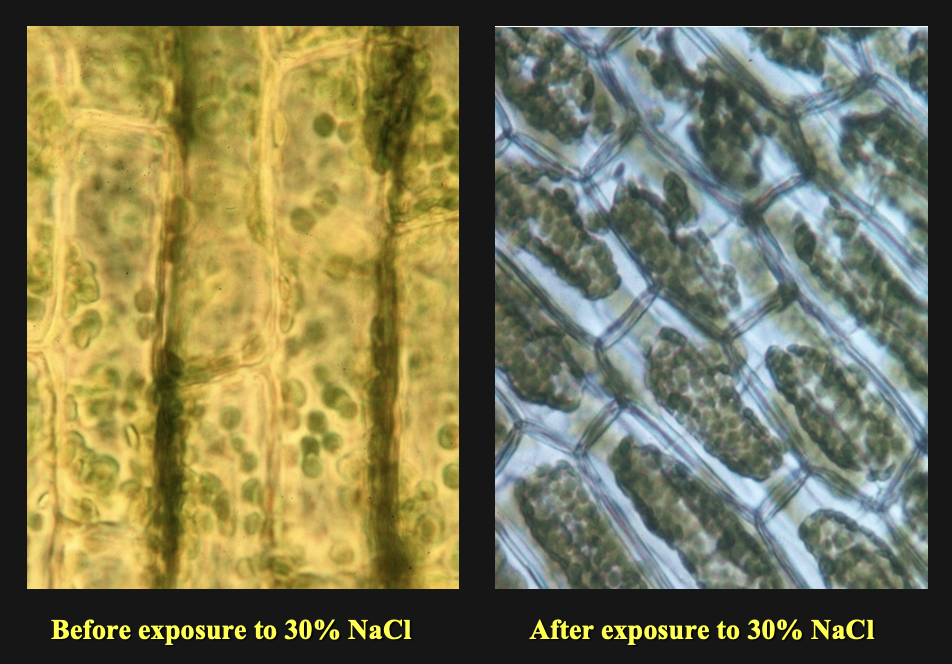
When the Eloda cells were placed in NaCl they ___ because the NaCl was ___ to the cell
a) grew, hypertonic
b) grew, hypotonic
c) shrunk, hypertonic
d) shrunk, hypotonic
c) shrunk, hypertonic
Enzyme
substance that acts as a catalyst for biochemical reactions
In lab 6 what was the enzyme used
Catechol oxidase
In lab 6 what is the substrate of the reaction
catechol, para-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and hydroquinone
In lab 6 what is the product of the reaction
benzoquinone
Why did plants have different levels of CO2 in light vs. dark in the bromothymol blue experiment
The plant grown in light turned the solution yellow due to there being more CO2 present and the plant grown in the dark turned the solution dark green due to there being little CO2 present
Chromatography
separates molecules based on thier different rates of movement through a substance due to their different chemical properties
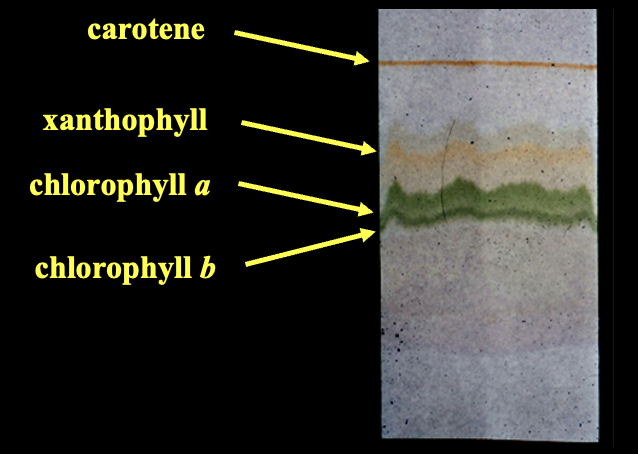
In this chromatography the carotene traveled the furthest and this means that it is the most _____ in the solution
soluble
What color is most useful for photosynthesis?
Reds and violets
What color is the worst for photosynthesis?
green
Where is starch stored in plants?
Where green pigment is
Plants grown in the dark have ___ starch storage than those grown in light
less
When extracting strawberry DNA what was the DNA extraction buffer
Soapy salt water
For extraction of strawberry DNA was caused the strawberry DNA to precipitate?
the ethanol
What does p represent in Hardy-Weinberg
Frequency of dominate allele
What does q represent in Hardy-Weinberg
frequency of recessive allele
What does p² represent in Hardy-Weinberg
Frequency of genotype AA
What does 2pq represent in Hardy-Weinberg
frequency of genotype Aa
What does q² represent in Hardy-Weinberg
frequency of genotype aa
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for two alleles
p + q = 1
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for genotypes
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
A population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium if…
The allele and genotype frequencies remain the same from one generation to the next