bio 106 midterm vocab
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
induction
specific observation to broad generalizations and probable conclusions
hypothesis
deduction
broad generalization and princples to specific conclusions with certainty
hypothesis
replication
process of creating an exact copy of DNA, cells, etc
The duplication of genetic material.
Control untreated; used in experiments to compare with
the variables
control
a group/set that has ordinary conditions
no changes/experiment
used to have a standard resultfor comparison in experiments.
allele
different forms of genes (mendels units, particles or factors)
gene
a sequence of nucleotides coding for a protein; trait
genotype
the genetic constitution of an organism
a combination of alleles that they possess for a specific gene
homozygote:
alleles that have both dominant or both recessive
diploid organism that has two copies of the SAME allele
heterozygous:
alleles that have one dominant and one recessive
contains two different alleles at a given locus
gamete:
mature reproductive/ sex cell that are haploids
23 chromosomes
egg - female
sperm - male
dominant
an allele whose trait is expressed when in heterozygous condition
trait that will mostly likely show uo
3/4 chance of appearingr
recessive
trait will not appear/suppressed in heterozygous condition
trait will only appear if no dominant allele
¼ chance of allele showing
phenotype
observable traits/physical appearance of an organism trait that we can measure
haploid
single of set of chromosomes
23 chromosomes
diploid
two sets of chromsomes
46 chromosomes
all organisms are diploids
chromosomes
In bacteria and viruses, the DNA molecule
that contains most or all of the genetic information of the
cell or virus.
chromatid:
A newly replicated chromosome, from the time
molecular duplication occurs until the time the centromeres
separate (during the anaphase of mitosis or of meiosis ).
centromere
The region where sister chromatids join.
genetic drift: Changes in gene frequencies from generation
to generation as a result of random (chance) processes.
founder effect
a type of genetic drift that occurs when a small group of individuals establishes a new population, leading to a loss of genetic diversity and a higher frequency of certain alleles compared to the original population
the reduced genetic diversity which results when a population is descended from a small number of colonizing ancestors
Random allele changes that happen when a small group starts a new population
bottleneck effect
Effect which occurs when the number of
individuals in a larger population are drastically reduced by
a disaster
when population decreases from natural disaster
By chance, some alleles may be overrepresented and
others underrepresented among the survivors
• This reduces variety and adaptability in the gene pool
male-mal competition
males compete with one another to attract females, part of sexual selection
female choice:
females chooses mate based on behavior, appearance, and smell
females actively select their desired mate
adaptive radiation
When one ancestral species evolves into many related species, each adapted to different environments.
gives rise to many descendant species
a series of evolutionary events that result in an array (radiation) of relating species that live in a variety of environments, differing in the characteristics each uses to exploit those environments
reinforcement
When natural selection strengthens reproductive barriers between already diverging populations, increasing their isolation
won’t breed together anymore → forming separate species
The evolution of enhanced reproductive
isolation between populations due to natural selection for
greater isolation
reinforcing the separation of species
allopatry
When a physical barrier (like a river or mountain) separates a population, leading to two new species
The formation of two species from one whenreproductive isolation occurs because of the interpositionof (or crossing of a physical geographic barrier, such as arive
sympatry
speciation due to reproductive isolation without any physical separation of the subpopulation
occurs in same geographic area
can be due to
behavioral differences
ecological differences
genetic changes
taxon
a biological group (typically a species or a clade) that is given a name
must be monophyletic
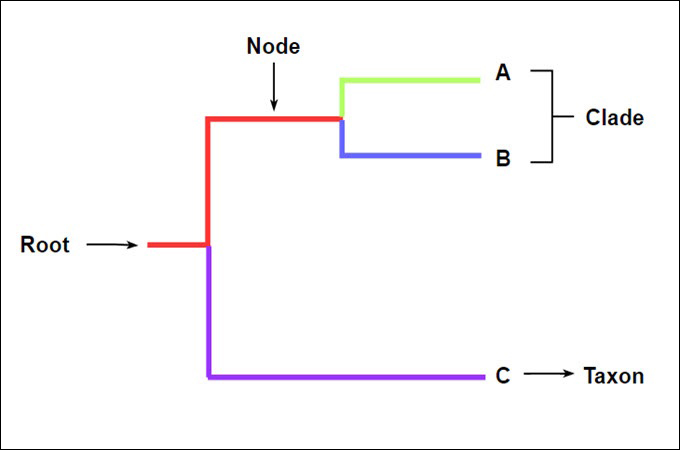
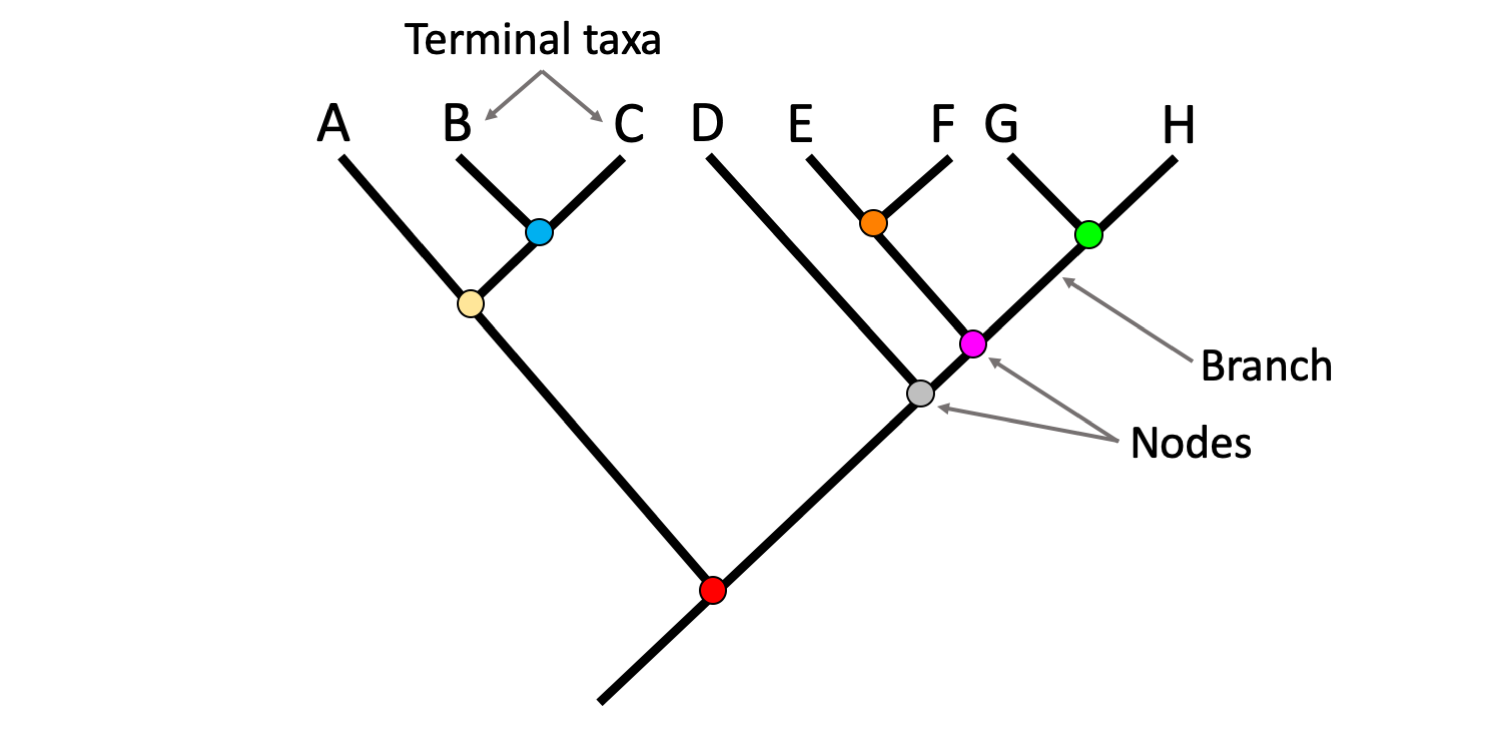
node
each branching point on a phylogenetic tree
tip
end point of a branch
represents a group (species or larger taxon) that is living today or ended in extinction
terminal node
clade
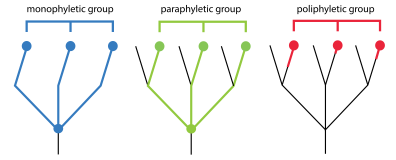
a monophyletic group made up an ancestor and all of its descendants
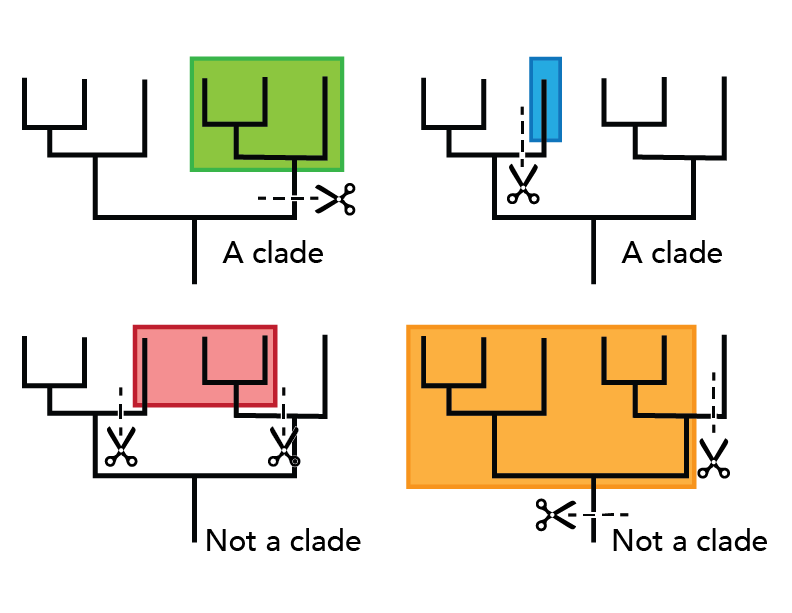
monophyletic
a group that consist of an ancestor and all of its descendants
a clade
one ancestor + all of its descendants
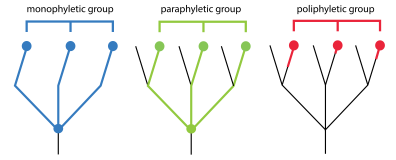
polyphyletic
pertaining to a group that consist of multiple distantly related organisms, and DOES NOT include the common ancestor of the gorup
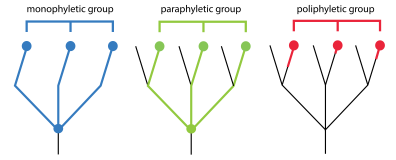
paraphyletic
pertaining to a group that does include ancestor, and some, BUT NOT ALL of its descendants
convergence
independent evolution of similar features from different ancestral traits
from similar environments or ecological roles
similar selective pressures
Example: Fins in dolphins (mammals) and sharks (fish) — both for swimming efficiently
homology
a similarity between two or more features that is due to inheritance from a common ancestor
The forelimbs of humans, bats, whales, and cats all have the same bone structure (humerus, radius, ulna, etc.), showing a common evolutionary origin, even though they’re used for different things (grasping, flying, swimming, walking)
pre-zygotic isolating mechanisms
factor that prevents individuals from different species from mating
prevents mating before fertilization
example: gametic isolation - sperm and eggs are incompatible
example: temporal isolation: species breed at different times
postzygotic isolating mechanisms
a barrier that prevents hybrid zygotes from developing into viable, fertile individuals
fertilization happens → offspring cannot survive or reproduce successfully
post-fertilization barrier
reduced hybrid viability → do not develop fully or do not survive to sexual materity
reduced hybrdi fertility → survive and mature but sterile
hybrid breakdown → F1 is fertile, but next generation is not
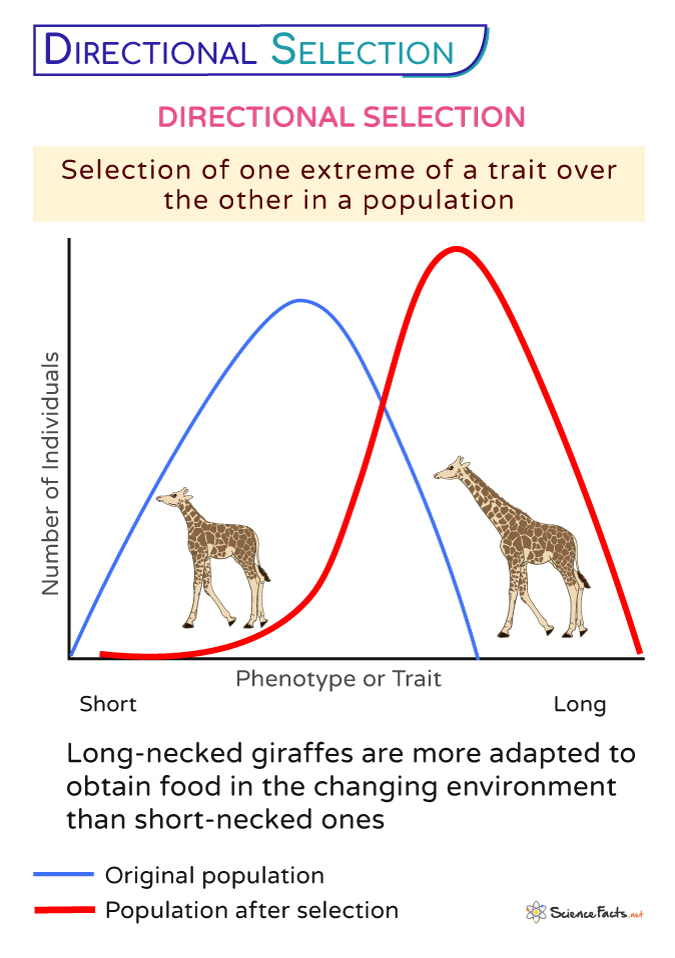
directional selection
selection in which phenotypes at one extreme of the population distribution are favored
graph shifts towards one side
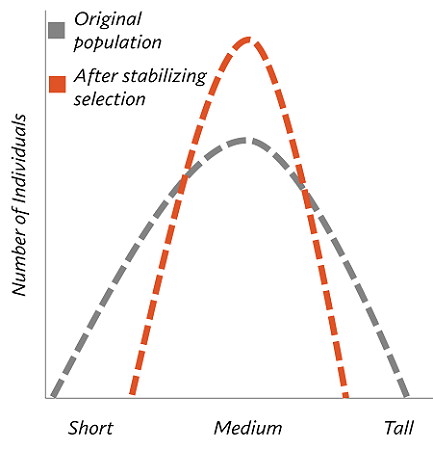
stabilizing selection
selection against the extreme phenotypes in a population so the intermediates are favored
graph increases in length
range/diversity decreases
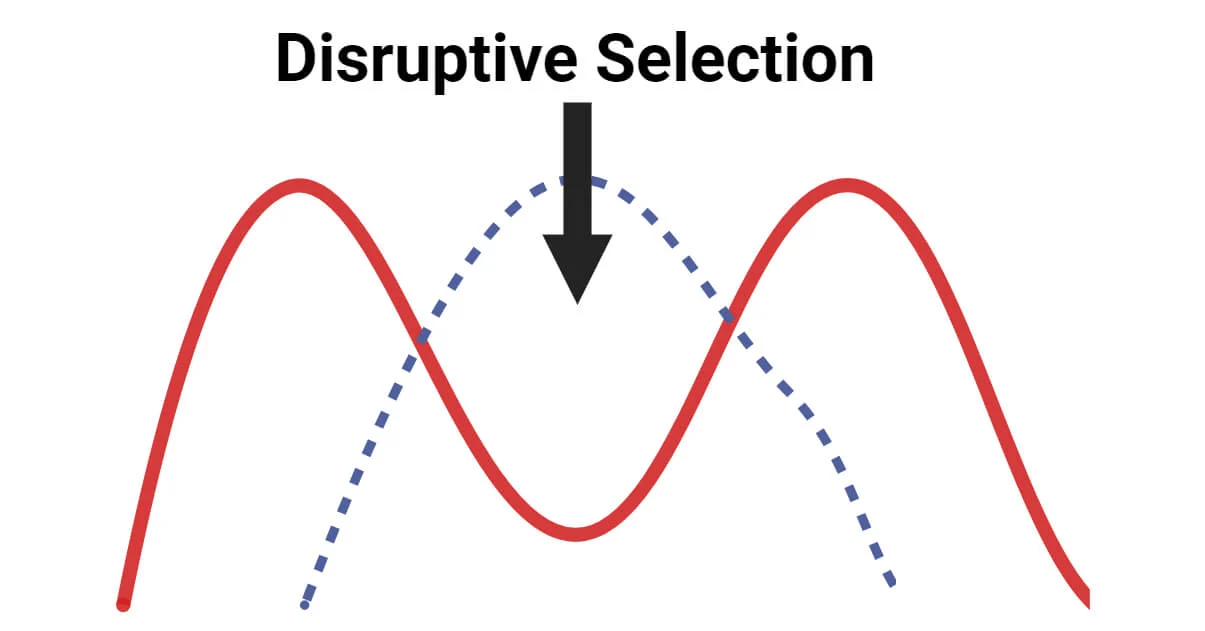
disruptive selection
selection in which phenotypes at both extremes of the population distribution are favored
both ends increase
middle dipped
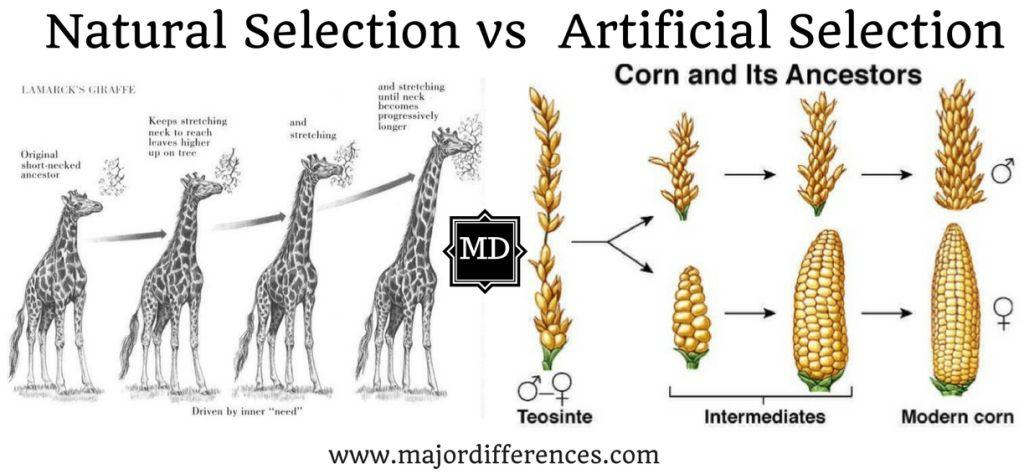
artificial:
the selection by humans, plants, and animals breeders of individuals with certain desirable traits
artificial sexual
humans put two animals together to breed to get desired offspring/traitsna
natural
the process by which traits that improve survival and reproduction become more common in a population over generations
traits that re more likely to survive and reproduce
traits are then passed on to next gen → can change allele frequency of whole population
charles darwin's theory that the features of an organism that help it survive and reproduce are more likely than other features to be passed on to subsequent generations
natural sexual
random mating between two animals
not forced
sexual
the process where traits help an individual attract or compete for mates → becomes more common over generation
An evolutionary mechanism by which traits that
increase the ability of individuals to attract or acquire
mates appear with increasing frequency in a population;
selection in which a mate is chosen on the basis of a
particular trait or traits
peacock tail feathers
deer antler fight
intersexual
indivduals of one sex choose mates based on traits
peacocok tail feathers
intrasexual selection
individuals compete with the same sex for access to mates
deer antler fight
categorical values
contain a fix set of possible categories/finite number of categories or distinct groups.
Categorical data might not have a logical order.
For example, categorical predictors
include gender, material type, and payment method
discrete variables
numerical variables that have a countable number of values between any two values
always numeric
# of customer complaints
# of defects
continuous variables
can be measured and take on any value within a given range, including infinite decimal points. These variables are measured rather than counted
A continuous variable can be numeric or date/time.
For example, the length of a part or the date and time a
payment is received
heigh , weight
dependent/response
hat you are testing or measuring; it depends on other factors
independent/explanatory
factor you can change or control to see if its affects something else
variable
thing that is being affected/changed in the experiment
synapomorphies
a trait that a group of organisms shares because they inherited it from a common ancestor
it distinguishes them from other groups
morphology
the shape, size, and structure of an organism or its parts
derived traint
new trait that evolves in a species or group and was NOT present in its ancestors
ancestral trait
present in common ancestor
homoplasises/analogous traits
similar traits that evolve independently in different lineages, not due to a common ancestor
caused by convergent evolution
not shared ancestry
evolutionary reversal
when trait reversed from derived state & back to ancestralstate
notochord
flexible- rod shaped structures found in all chordate embryos that provide support along the body’s lengths
lineage
series of ancestors and descendent population
descent with modification
the idea that organisms inherit traits from their ancestors, but changes (modifications) occur over generations, leading to diversity of lifespe
species
group of individuals that can live and breed with each other
lineage system hierarchy
domain → kingdom → phylum → class → order → family → genus → species
dear kids, please come on for goodness sake
phylogeny
history of evolution relationships among organisms or their genes
phylogenetic tree
group of evolutionary related species are presented as branches
molecular clock
method that uses the rate of genetic mutations to estimate the time since two species shared a common ancestor
scientific hypothesis is one thate
a. leads to predictions that can be tested
b. uses deduction
c. is tenetative until repeated test fail to disprove it
d. all of the above
e. a and c
e
biogeography
study of the distribution of species and ecosystems across geographic space and through geological time
neutral mutation
a change in DNA that does not affect an organism's fitness or phenotype, occurring in non-coding regions or as a "silent mutation" where the new DNA codon still codes for the same amino acid
molecular clock
tracks how long it has been since populations (or species) diverged.
measures the genetic difference between species roughly constant rate over time
more differences → longer ago common ancestors lived
cyanobacteria
first photosyntheic organism
primary endosymbiosis
The engulfment of a cyanobacterium by a larger eukaryotic cell that gave rise to the first photosynthetic eukaryotes with chloroplasts
always internal
gave rise to all of todays chloroplast
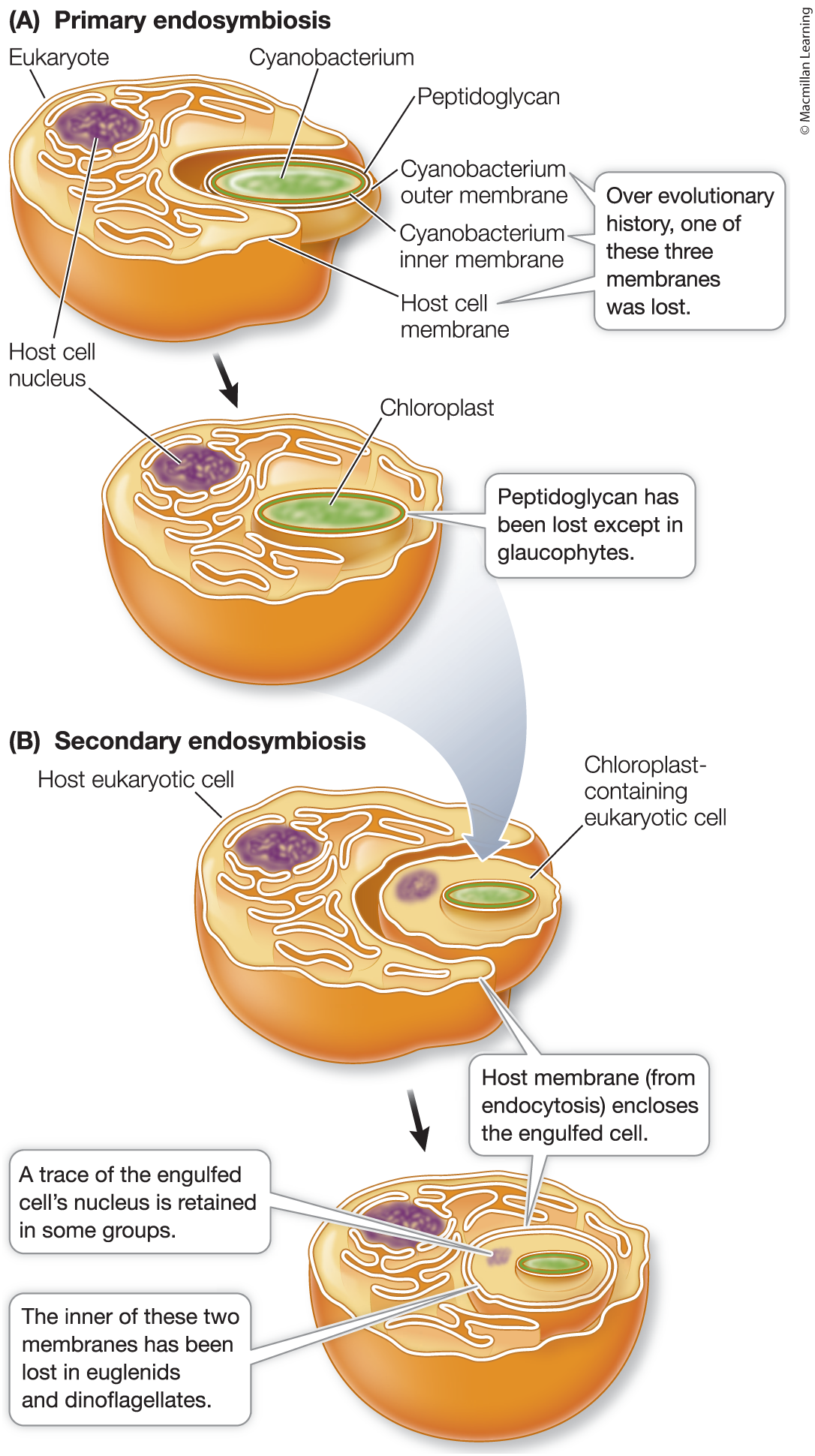
secondary endosymbiosis
The engulfment of a photosynthetic eukaryote by another eukaryotic cell that gave rise to certain groups of photosynthetic eukaryotes
symbiosis
a close, long-term interaction between two different species where at least one benefits
mutualism
biological relationship where two different species benefit from interacting with each other
ex: chloroplast and eukaryotic
phylogenesis
the evolutionary development and diversification of a species or group of organisms, or of a particular feature of an organism
phylogenetic group
sets of organisms classified according to their evolutionary relationships
Types:
monophyletic
paraphyletic
polyphyletic
coenocyte
an organism that contains many nuclei within each cell membrane
myxotrophic
microfilaments and contractile protein
commensalism
an association between two organisms in which one benefits and the other derives neither benefit nor harm
lateral and apical Meristems
meristems - region of actively dividing cells in plants
responsible for growth
Apical meristems: responsible for primary growth of plants → make tall or longer
increase in length of roots + stems
new leaves and flowers
at the tip of roots and shoots
Lateral Meristems: responsible for secondary growth → increases thickness or girth of plant
makes plant wider and stronger
along sides of stems and roots
stomata
small closeable openings in leaves and stems that are used to regulate gas exchange and water loss
tracheids
new cell type
found in vascular plants
is the principle water conducting element of xylem except for angiosperms and gnetophytes
in gymnosperm and ferns
archegonium
multicellular flask shaped female sex organ that produces a single egg
in a non-seed plant
during gamephyte stage
antheridium
male sex organ where sperm produced in big numbers
in nonflowering plants
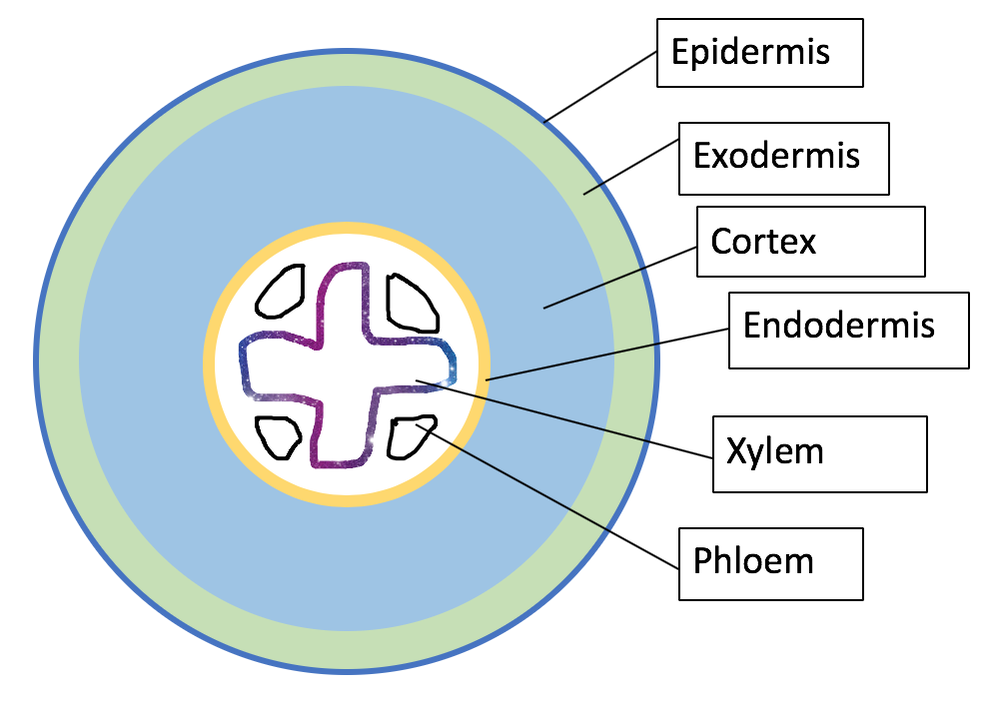
xylem
conducts water and minerals from soil/roots to aerial parts of plant
provides support against gravity in terrestrial environment
phloem
conducts the products of photosynthesis from sites where they are produced or released to sites where they are used or stored
cortex
outer layer of ground tissue between outer skin (epidermis) and vascular tissue (xylem and phloem)
sporangium
reproductive structure in plants that contain and forms spores
where mitosis takes place → produces genetically identical haploid spores
in ferns and lower plants
vascular and ground tissue
vascular tissue: plants transport system → moves water, minerals, and food throughout the plant
includes xylem and phloem
ground tissue: all plant tissue that is not vascular or part of outer layer
forms most of the body of the plant
includes parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
nonvascular land plants
lack specialized vascular tissues for the conduction of water or nutrients through plant body, and their life cycle depend on liquid water
liverworts (hepatophyta), mosses (bryophyta), and hornworts (anthocerophyta)
spores
any asexual reproductive cell capable of developing into an adult organism without gametic fusion. In plants, haploid spores develop into gametophytes, diploid spores into sporophytes
sporophyte
in plants and protists with alternation of generations, the diploid phase that produces the spores.
gametophyte
the multicellular haploid phase that produces the gametes
heterosporous
In plants and photosynthetic protists with alternation of generations, the multicellular haploid phase that produces the gamete
megaspore develops into female gametophyte → produces egg in megasporangia
microspore develops into male gametophyte → produces sperm in microsporangia
homospory
single type of spore develops into a gametophyte that produces both eggs and sperm
vascular plants
lycophytes: club mosses and allies (lycopodiophyta)
horsetails and ferns (monilophyta)
Seed plants
gymnosperms → naked seed to reproduce
cycads (cycadophyta)
ginkgo (ginkgophyta)
gneotophytes (gnetophyta)
conifer (coniferophyta)
flower plants (anigosperms) → endosperm
cryptic species
distinct species that look very similar and were previously classified as a single species