AP Psychology: Topic 4.3 - Psychology of Social Situations
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

35 Terms
Social norms
the unwritten rules and expectations that dictate how individuals should behave in a particular social group or society

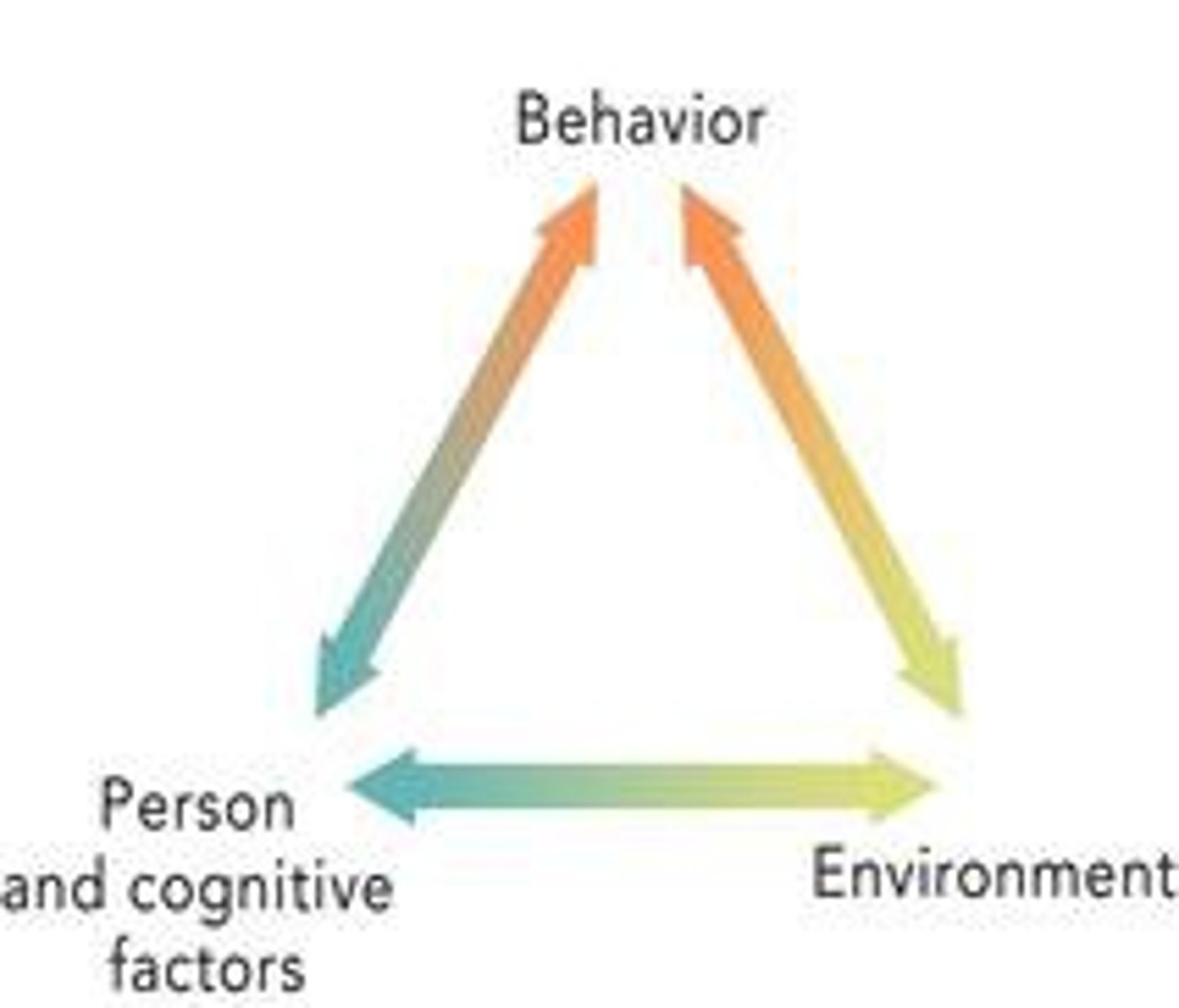
Social influence theory
the idea that a person's behavior can be heavily influenced by the ideas and actions of others
Normative social influence
factors that influence a person to conform in order to be accepted and belong to a group

Informational social influence
when people conform because they believe the group is competent and has the correct information, particularly when the situation is ambiguous

Persuasion
strategies used to influence someone's attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or decisions

Elaboration likelihood model (ELM)
analyzes the variables that cause long-term and short-term attitude changes to understand the effectiveness of persuasive messaging
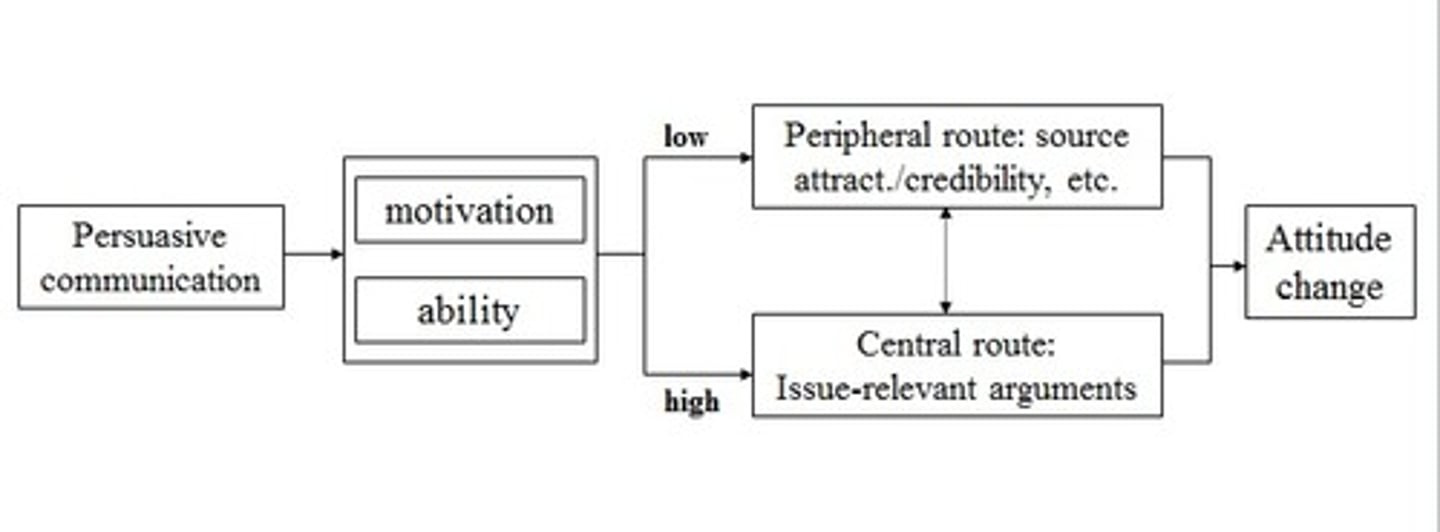
Central route
a method of persuasion that uses evidence and logical arguments to influence people, often resulting in a lasting attitude change

Peripheral route
focuses on factors other than the message itself because the recipient has little or no interest in the subject and/or has a lesser ability to process the message, often resulting in a temporary attitude change

Halo effect
the tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic
Foot-in-the-door technique
persuasive technique involving making a small request before making a bigger one

Door-in-the-face technique
persuasive technique involving making an unreasonably large request before making the small request the person is hoping to have granted

Conformity
adjusting one's behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard

Obedience
a form of compliance that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a position of authority

Individualism
giving priority to one's own goals over group goals and defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group identification

Collectivism
giving priority to the goals of a social group and defining one's identity accordingly

Multiculturalism
a situation in which distinct cultural groups in a society share equal value

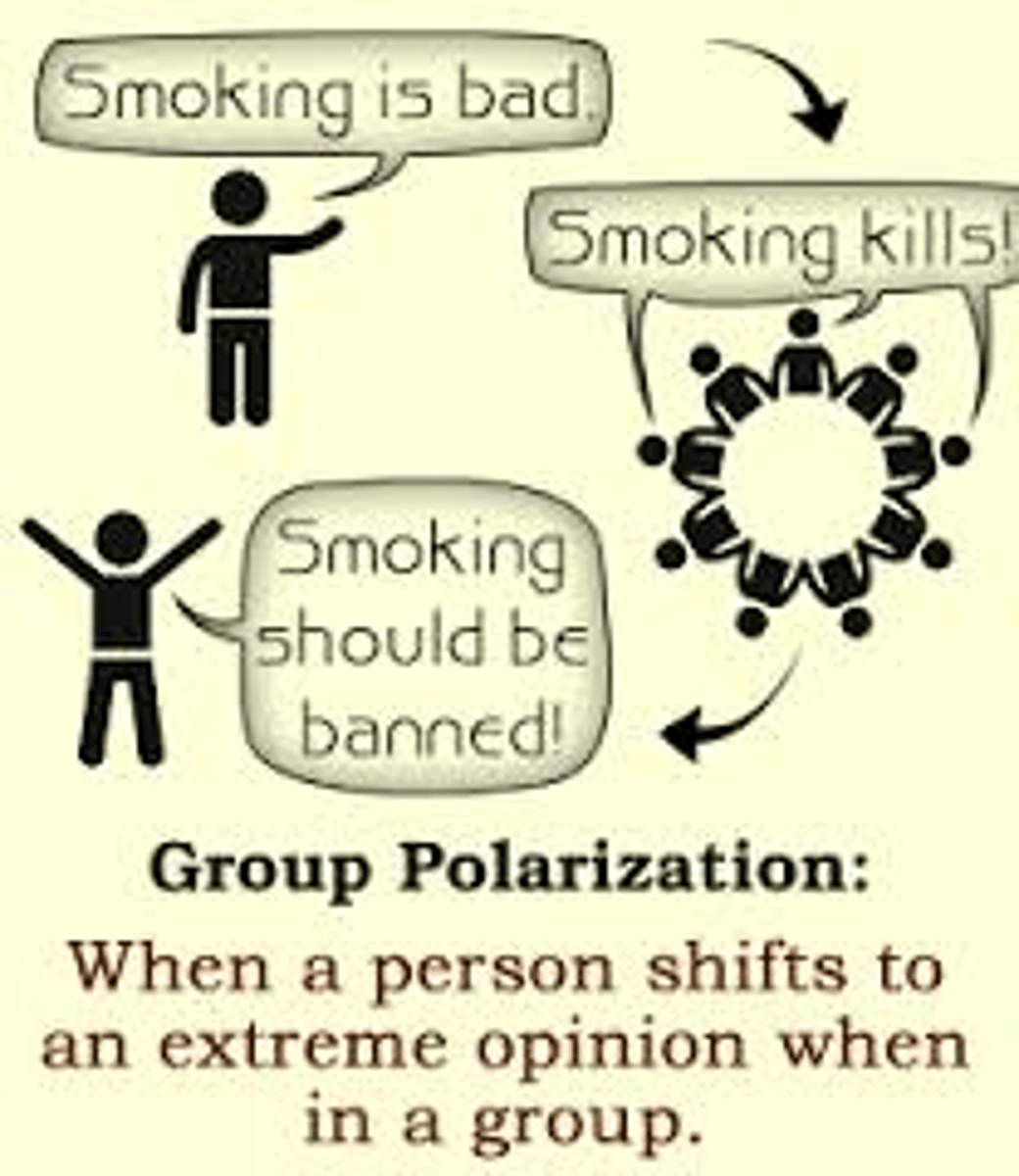
Group polarization
when a group's decision making process results in a more extreme decision than its members would have made if deciding on their own
Groupthink
when members of a group conform to majority opinion to maintain group harmony rather than stating their own views
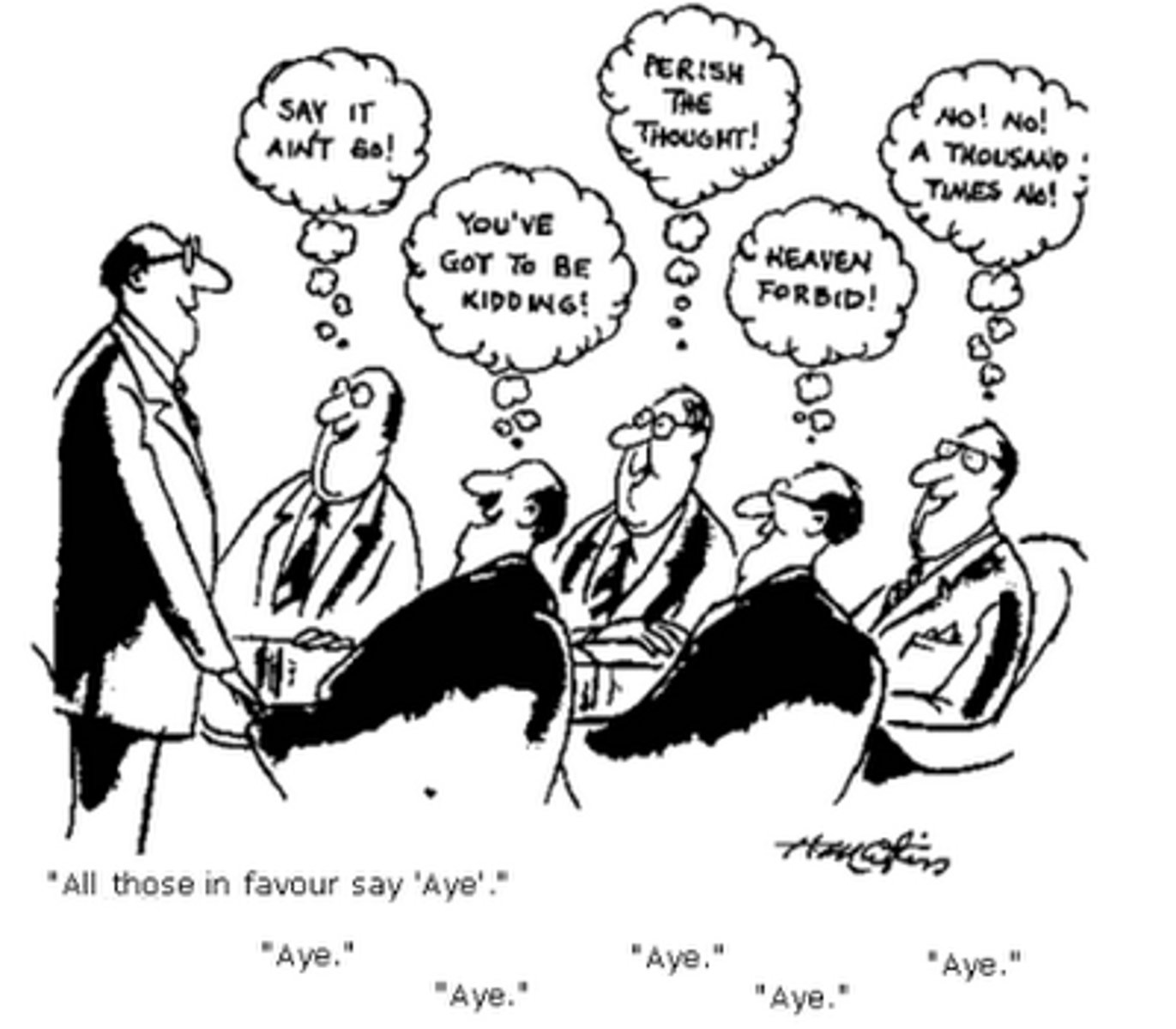

Diffusion of responsibility
the more onlookers there are, the less personal responsibility individuals will feel to take action
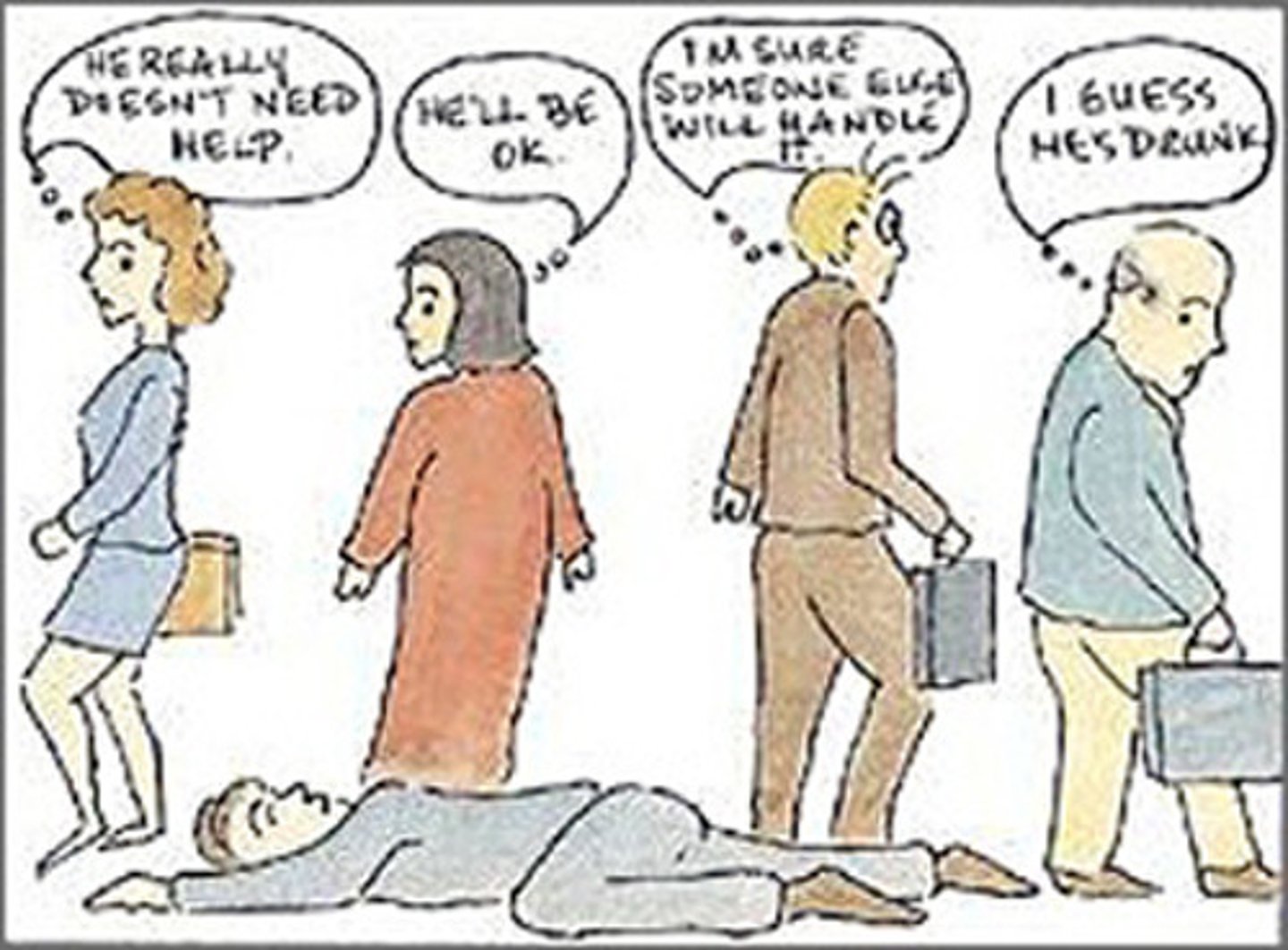

Social loafing
the tendency for people to put in less effort when working on a task as a group, compared to when working alone

Deindividuation
when individuals lose self-awareness and self-restraint in group situations and engage in impulsive, deviant, and sometimes violent acts
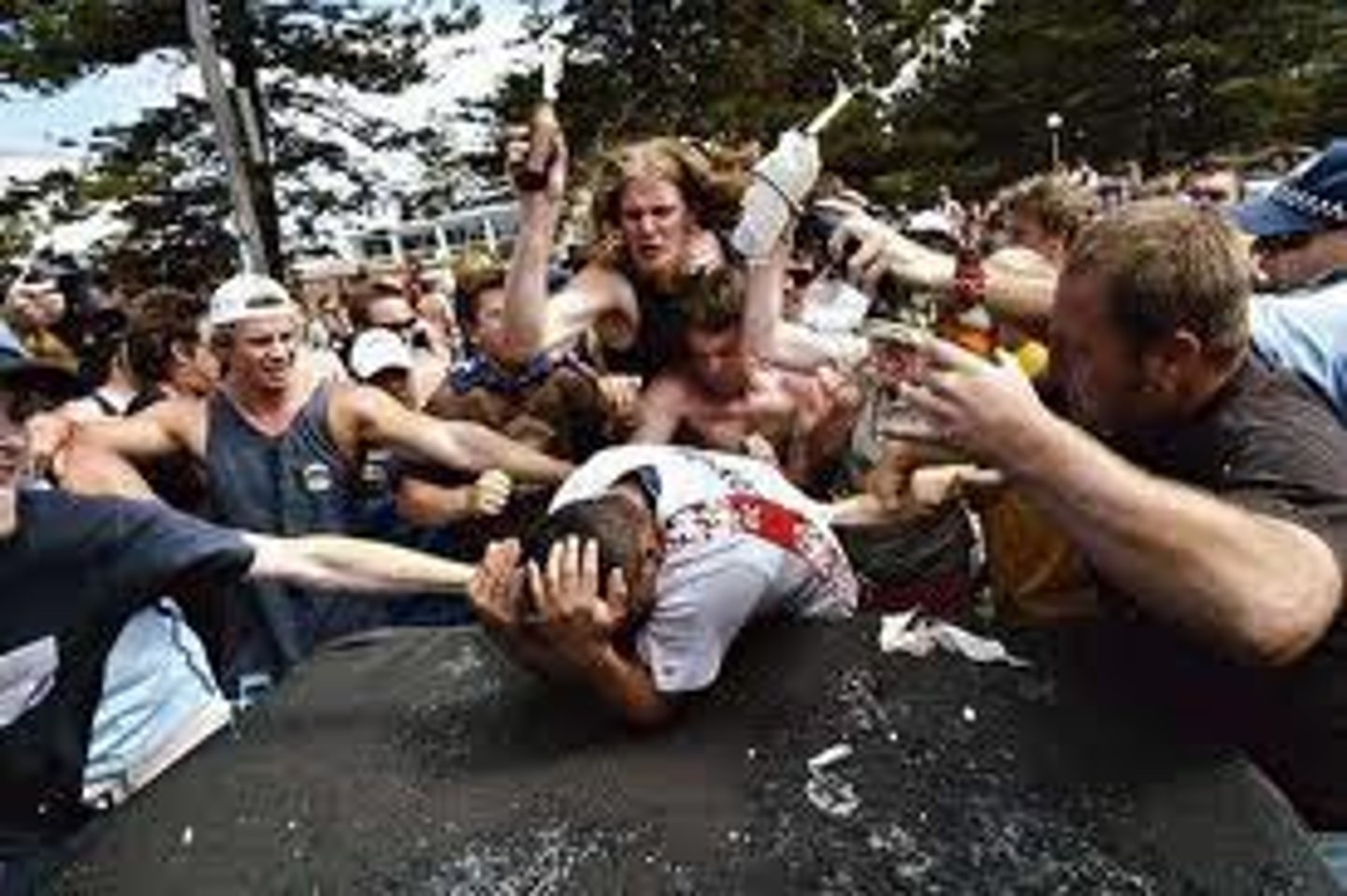

Social facilitation
a phenomenon where people show increased levels of effort and performance when in the presence of others

False consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share one's own beliefs and behaviors

Superordinate goals
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation

Social traps
decisions by individuals or groups that seem good and produce a short-term benefit, but that hurt society in the long run

Industrial-organizational (I/O) psychologists
researchers and practitioners who use the principles of social psychology to improve the workplace (e.g., job satisfaction, employee retention, productivity)

Burnout
a state of physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion created by long-term exposure to a stressful situation (e.g., a demanding job) and accompanied by lowered performance and motivation

Altruism
unselfish concern for the welfare of others

Prosocial behavior
positive, constructive, helpful behavior (the opposite of antisocial behavior)

Social debt
when people act in a prosocial way because they have been helped by others in the past (paying it forward) or by feeling responsible for the common good of society (doing my part)

Social reciprocity norm
the idea that a person is motivated to do good things because others have shown acts of kindness to them in the past

Social responsibility norm
an expectation that people will help those dependent upon them or those who need assistance even if doing so may not offer any visible reward

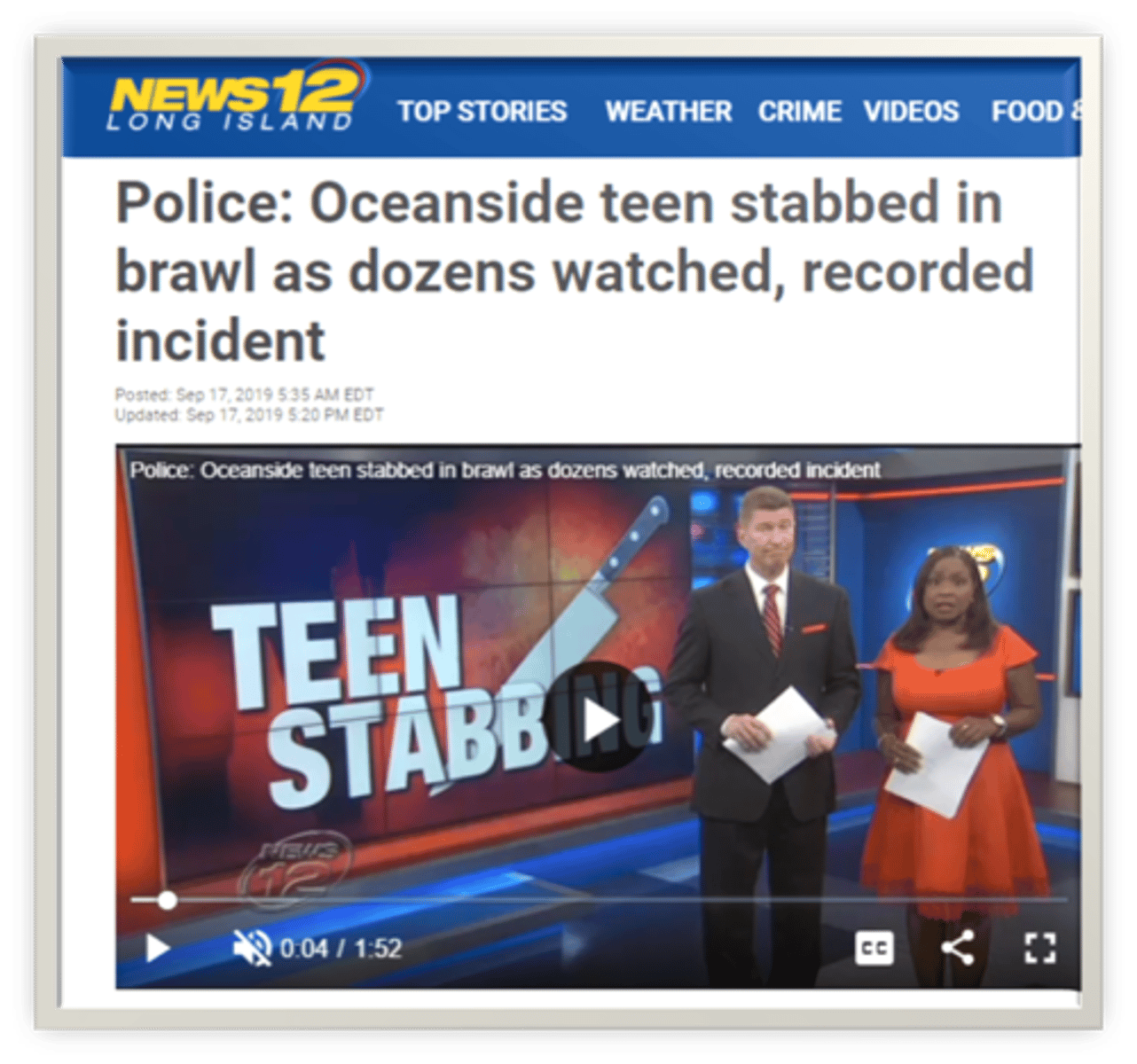
Bystander effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
Situational variables
factors in a particular context that can impact an individual's likelihood of helping another person

Attentional variables
elements of attention that can impact an individual's likelihood of helping another person
