Working Memory and Memory Concepts
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to working memory, short-term memory, memory effects, theories of forgetting, components of the working memory model, and the impact of various disorders on memory.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Working Memory
refers to a system used for storing, maintaining, and operating on information, wherein information is constantly manipulated and changed.
Current view of memory.
Characterized as Active.
Short-term Memory (STM)
The capacity to store a small amount of information in the mind for a short period of time;
characterized as passive.
_____ Duration: Approximately 30 seconds without rehearsal.
Magical Number Seven
Miller’s theory suggesting that individuals can remember approximately 7 items, plus or minus 2.
Chunking
A method of grouping related components into memory units to enhance recall.
A ______: defined as a memory unit consisting of strongly related components.
Brown-Peterson Technique
A method to illustrate time-based decay in short-term memory through a distractor task.
Participants are presented with several items to remember, then instructed to perform a distractor task (e.g., counting backwards by 3s from 63) before testing memory on the items.
The purpose of the distractor task is to disrupt rehearsal (repeating items to self silently), thus illustrating time based decay of memory.
Serial Position Curve
U-shaped curve indicating that recall is influenced by an item's position in a list, consisting of the primacy and recency effects.
can be explained by the modal model:
Primacy effect correlates with early items being transferred to long-term memory.
Recency effect is associated with later items still being present in short-term memory.
Primacy Effect
Enhanced recall of items at the beginning of a list due to better consolidation into long-term memory.
Recency Effect
Enhanced recall of items at the end of a list as they remain in short-term memory at the time of recall.
Decay Theory
The theory that memory traces disintegrate over time, leading to forgetting.
Interference Theory
The theory suggesting that other memories disrupt retrieval, leading to forgetting.
Types of Interference
Proactive Interference: Difficulty learning new material due to interference from previously learned material.
Release from Proactive Interference
Retroactive Interference: Difficulty in recalling old information resulting from new learning.
Proactive Interference
Difficulty learning new material due to interference from previously learned material.
Example Sequence: Learn A, Learn B, Experience memory loss for B.
release from _____: The ability to remember items more readily after switching categories of materials to be recalled.
Primacy Effect: Items at the beginning of a list are not affected by _____.
Middle Items: These items are affected by both forms of interference.
Retroactive Interference
Difficulty recalling old information due to new learning.
Ex: new address, phone number
Recency Effect: Items at the end of the list are not affected by _____.
Middle Items: These items are affected by both forms of interference.
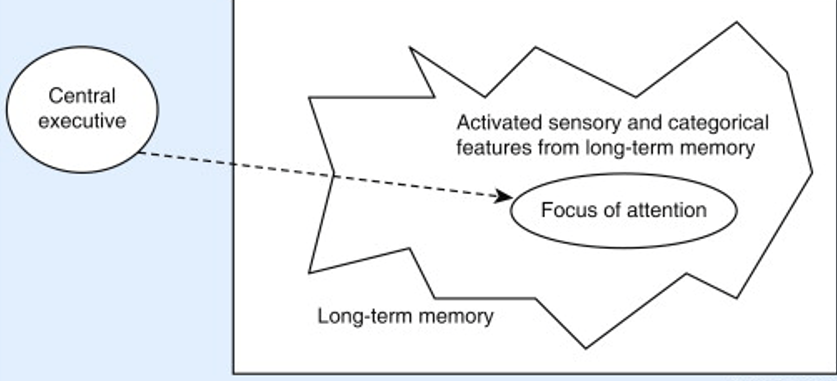
Central Executive
Subsystem of working memory that is responsible for integrating information from various subsystems and plays roles in attention, planning, and coordinating cognitive activities (does not store information).
Visuospatial Sketchpad
The subsystem of working memory responsible for processing visual and spatial information.
Phonological Loop
Subsystem of working memory model. Manages a limited number of sounds (including language) for a brief period
activated during reading.
Episodic Buffer
Subsystem of working memory model. Holds and combines information from other subsystems and long-term memory, serving to bind information together.
Word Length Effect
The tendency to remember more short words than long words due to time constraints in articulation.
Corsi Block-Tapping Task
A measure of visuospatial working memory that requires participants to tap a sequence of blocks, increasing the number of blocks until performance declines.
Operation Span
A task that involves recalling letters after solving math problems, adjusting the number of letters until performance declines.
Dual N-Back task
A working memory training task that involves recalling items presented multiple trials back.
The challenge is to remember both the position of the square and the letter that was presented a certain number of steps back (denoted as "n").
At each step, a square lights up in a specific position on a grid, and a letter is spoken simultaneously.
Participants must track both the position of the square and the letter, identifying when either matches the one presented "n" steps earlier.
Major Depression
Characterized by feelings of sadness, fatigue, and hopelessness impacting memory performance.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Chronic excessive worry that overloads working memory, affecting concentration.
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
A condition characterized by inattention and hyperactivity, affecting central executive functions.
Fidget Toys
Items used by individuals with ADHD to enhance cognitive performance through increased physical activity.
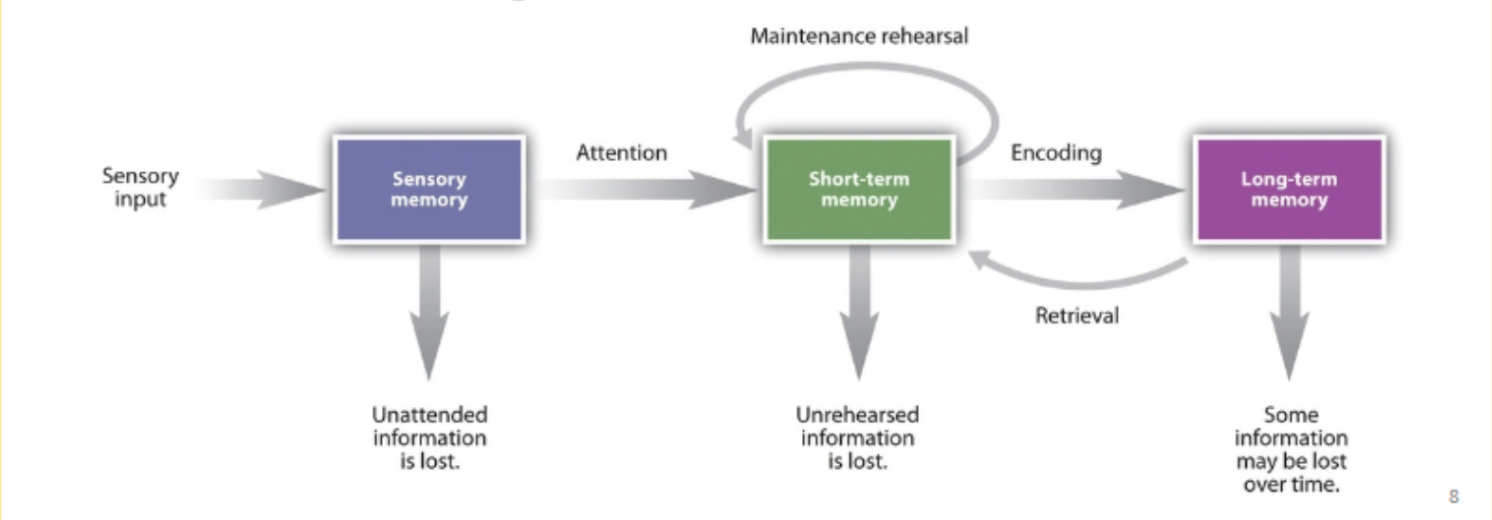
modal model
includes a short-term memory and a long-term memory and provides details on how information is encoded and later retrieved from memory
STM Duration: Approximately 30 seconds without rehearsal.
Three distinct storage areas
Sensory Memory: Large-capacity storage system that records information from each sense with relative accuracy. Unattended information is lost.
Iconic Memory
Echoic Memory
Haptic Memory
Utilizes control processes
evidence for _____
Amnesic patients show intact sensory memory and short-term memory capabilities but impaired long-term memory capabilities, validating the separation of storage systems.
Critiques of _____
Some researchers argue that sensory memory is better understood as part of perceptual processes rather than actual memory storage.
There are concerns regarding the overly simplistic distinction between long-term memory (LTM) and short-term memory (STM), particularly as STM may imply a passive memory store.
Iconic memory
A part of the modal model, specifically sensory memory. Visual sensory memory lasting about 0.5 seconds.
Echoic memory
A part of the modal model, specifically sensory memory. Auditory sensory memory lasting approximately 3-4 seconds.
Haptic memory
A part of the modal model, specifically sensory memory. Sensory memory related to touch lasting about 1-2 seconds.
control processes
Intentional strategies employed to enhance memory performance, such as rehearsal.
sensory memory
Large-capacity storage system that records information from each sense with relative accuracy. Unattended information is lost.
Release from Proactive Interference
The ability to remember items more readily after switching categories of materials to be recalled.
Tara: “As you learn a series of stimuli from the same category, memory will become less accurate; if you switch to a new category, memory will improve.”
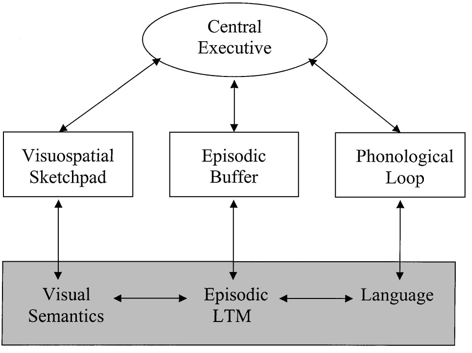
working memory approach
Components of Working Memory Model
Central Executive
Visuospatial Sketchpad
Phonological Loop:
Episodic Buffer
Evidence for Baddeley & Hitch's Model (1974)
Phonological Loop Evidence:
Acoustic Similarity Effect: People are prone to confuse similar-sounding stimuli
Articulatory Vocal Suppression Effect
Word Length Effect
Further Evidence for Baddeley & Hitch's Model
Visuospatial Sketchpad Evidence: Individuals can effectively multitask using a phonological and a visuospatial task simultaneously, but they struggle when tasked with two visuospatial tasks simultaneously as shown in studies by Baddeley (1999).
Central Executive Evidence
Disexecutive Syndrome: This syndrome is related to frontal lobe damage, leading to impaired organization, planning, and increased distractibility, while other aspects of working memory remain intact.
acoustic similarity effect
People are prone to confuse similar-sounding stimuli; for instance:
When asked to remember a sequence of similar-sounding letters (C, T, D, G, B), performance worsens compared to different sounds (C, F, M, I, H).
Articulatory Vocal Suppression Effect
Disruption occurs in memory performance when participants engage in vocal suppression while trying to remember.
inhibiting memory performance by speaking while being presented with an item to remember.
requiring an individual to repeatedly say an irrelevant speech sound out loud while being presented with a list of words to recall shortly after.
Span task
Span tasks are cognitive assessments designed to measure the capacity and efficiency of working memory by evaluating how much information an individual can hold and manipulate over a short period
Operation Span
Corsi Block-Tapping Task
Dual N-back Task
Cowan (1999)
argues that working memory is just an activated part of long-term
memory