DH101 Dental Hygiene I Quiz #4 Module #6
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
The clinical crown is the part of the tooth below the attached periodontal tissues. B) The clinical root is the part of the tooth below the base of the gingival sulcus or periodontal pocket.
False, True
In ______ of cases, cementum overlaps the enamel at the CEJ.
60%
In ____ of cases, there is a gap between enamel and cementum, exposing dentin.
10%
What are the two parts of the periodontium?
Gingiva, and the attachment apparatus
That portion of the tooth that is visible in the oral cavity
Clinical crown
The part of the tooth below the base of the gingival sulcus or periodontal pocket. It is the part of the root to which periodontal fibers are attached.
clinical root
It is made up of enamel
Anatomical crown
portion of the tooth covered with cementum
Anatomical root
The function of cementum is to:
seal the tubules of the root dentin and supports the tooth along with the alveolar bone by provide attachment for the periodontal fiber groups
The gingival sulcus is the:
crevice between the free gingiva and the tooth (1-3mm in health)
What is the function of the junctional epithelium?
Provides a seal at the base of the sulcus to attach gingiva to the tooth.
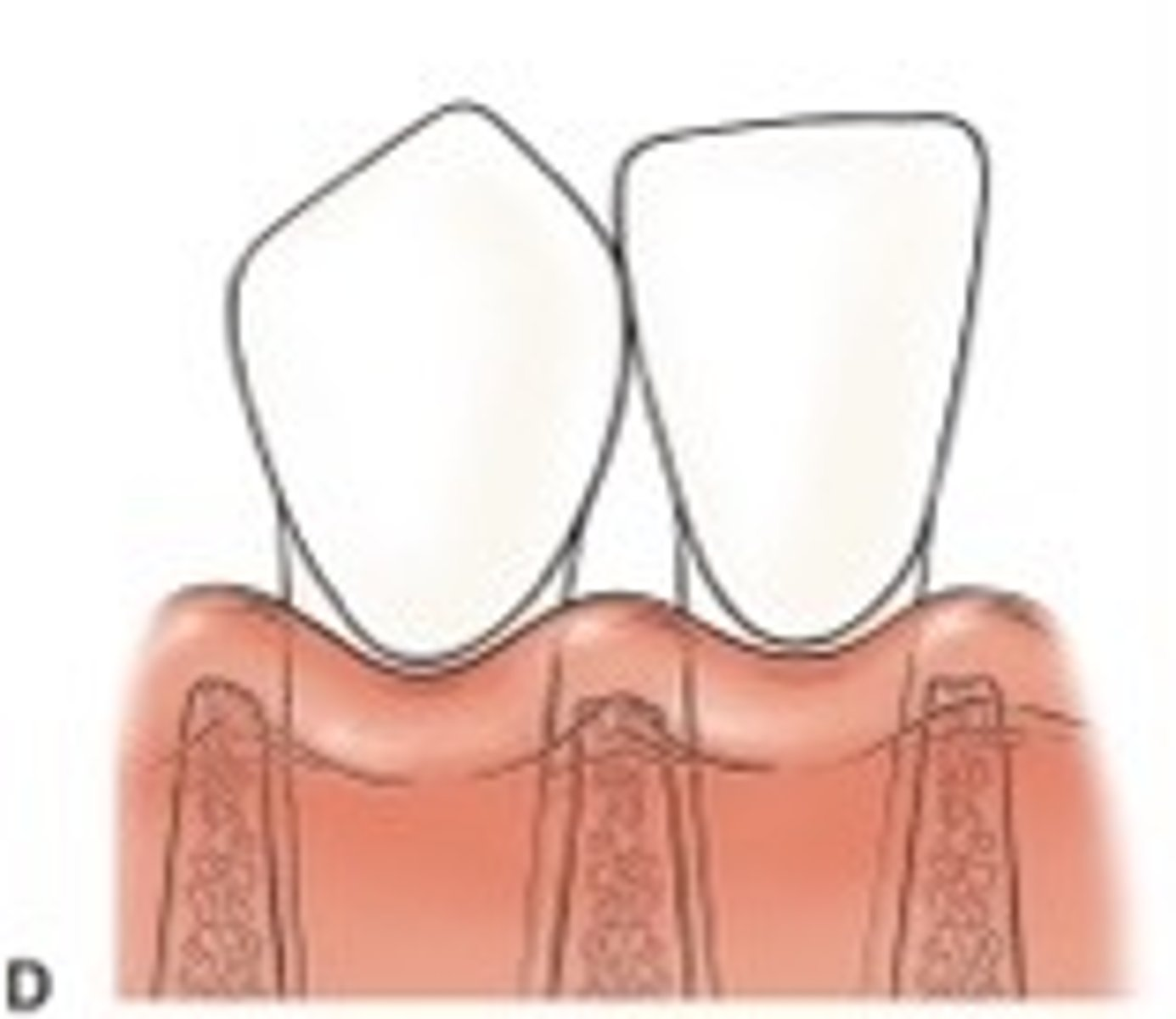
What is a Class I embrasure?
The tip of the interdental papilla is apical to the contact point of adjacent teeth, but the interproximal CEJ is not visible. Papilla fills the entire interdental space.
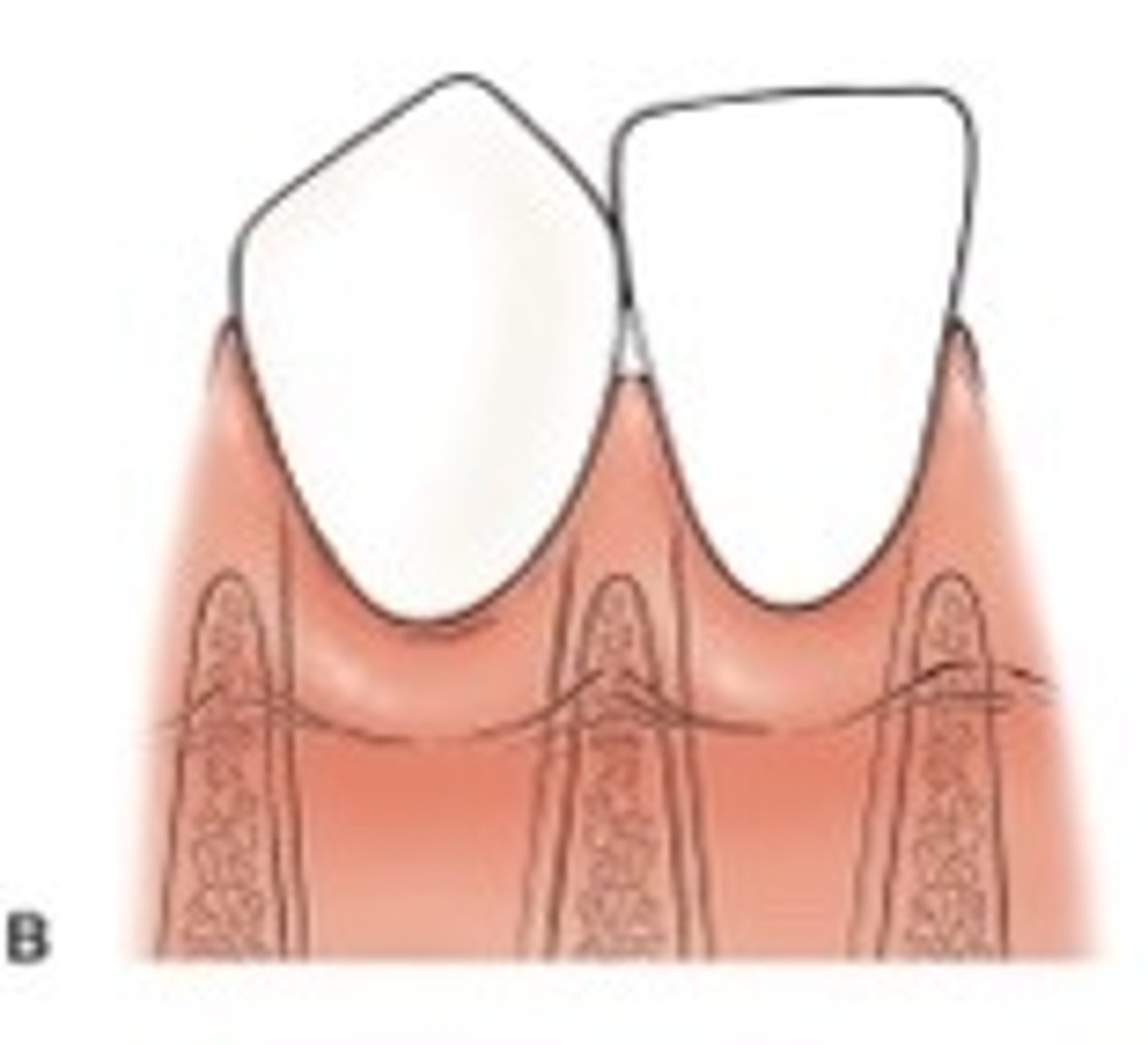
Class II embrasure
The tip of the interdental papilla is at or apical to the interproximal CEJ, but coronal to the height of the facial CEJ. Papilla is partially missing
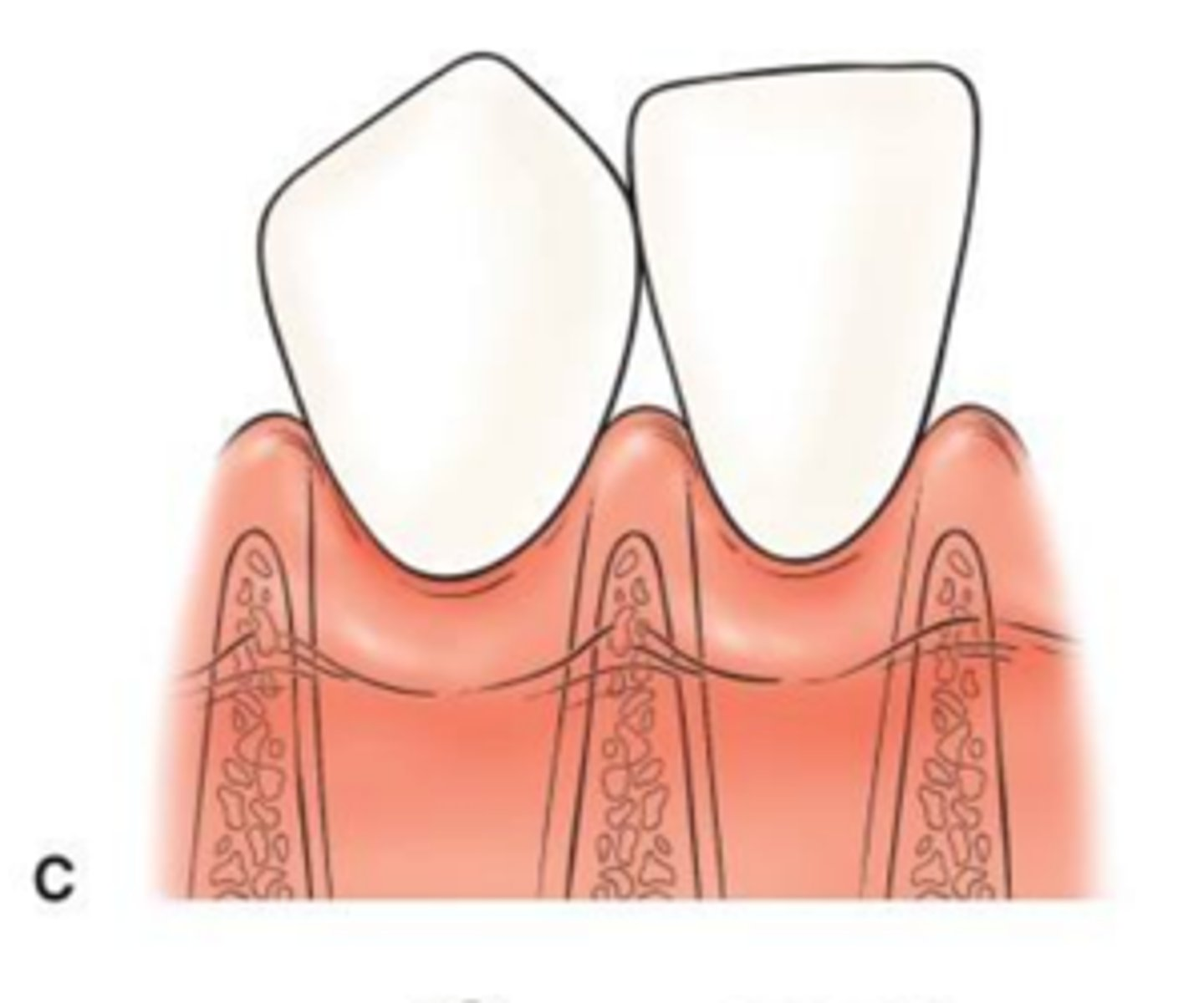
Class III embrasure
The interdental papilla is at or apical to the level of the facial CEJ. Papilla completely missing
Embrasure
Triangular space in a gingival direction between the proximal surfaces of two adjoining teeth in contact.
Which of the following should not be designated as clinically normal or clinically healthy?
Smooth, soft, and maximal sulcus depth with bleeding when probed
A) Factors that influence color are vascular supply, thickness of epithelium, and degree of keratinization. B) Chronic inflammation appears as a dark red, bluish red, magenta, or deep blue.
Both statements are true.
Signs of health in the gingiva include all of the following, except:
bleeding on probing
A) Floss cleft is created by using the floss correctly. B) Stillman's cleft is a localized recession that may be in a V-shape that extends several millimeters toward the mucogingival junction.
False, True
Hyperkeratosis:
leathery, hard, or nodular surface
A) Gingivitis occurs frequently in children, but is usually reversible without having permanent damage. B) Periodontal disease cannot occur in children.
True, False
In the relationship of enamel and cementum at the cervical area there are ______ instances where they do not meet and there can be an area of exposed dentin.
10% to 40%
Which of the following statements best describes alveolar mucosa?
Movable tissue, smooth, shiny surface with non-keratinized, thin epithelium
Which systemic disease(s) can influence the occurrence and severity of periodontitis?
Diabetes mellitus,
Obesity, and
Osteoporosis
Why would a dental hygienist dry supragingival calculus with an air syringe?
To facilitate exploring and scaling
A pocket is:
diseased gingival sulcus
The technique used with the periodontal probe is:
walking stroke
Suppuration is the formation of:
pus; indication of infection
The center of the col area is not usually __________, and thus is more susceptible to infection.
keratinized
Sulcus
narrow groove
All of the following are factors that affect probe determinations except:
severity and extent of periodontal disease
the periodontal probe (calibration)
Placement problems ( anatomic variations)
patient age
patient age
A) A probe is a slender instrument with a rough, pointed tip designed for examination of the depth and topography of a gingival sulcus or periodontal pocket.
B) A probe has three parts: the handle, the angled shank, and the working end.
Statement A is false and statement B is true
Define the col and the significance of disease susceptibility
A col is the depression under the contact area between a lingual or palatal and facial papilla that conforms to the proximal contact areas.
The center of the col area is not usually keratinized and thus more susceptible to infection.
A pathologically deepened sulcus due to periodontal disease is
Periodontal Pocket (4mm or more)