Applications of Differentiation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is Rolle’s Theorem?
Suppose f : [a, b] → R is continuous on [a, b], differentiable on (a, b), and f(a) = f(b). Then there exists a c in (a, b) such that f’(c) = 0
![<p>Suppose f : [a, b] → <strong>R </strong>is continuous on [a, b], differentiable on (a, b), and f(a) = f(b). Then there exists a c in (a, b) such that f’(c) = 0</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/42f44e48-ac6e-4366-9a80-d278bdf26bb6.jpg)
What is the Mean Value Theorem?
Suppose f : [a, b] → R is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then there exists a c in (a, b) such that (f(b) - f(a))/(b - a) = f’(c). (Useful for proving inequalities of the form |f(x) - f(y)| \< c|x - y|)
![<p>Suppose f : [a, b] → <strong>R </strong>is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b). Then there exists a c in (a, b) such that (f(b) - f(a))/(b - a) = f’(c). (Useful for proving inequalities of the form |f(x) - f(y)| \< c|x - y|)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b2b4698d-86cf-48c3-a665-5e3821cd47df.jpg)
How to tell if a function is constant, increasing or decreasing?
Suppose f : [a, b] → R is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b).
If f’(x) = 0, f is constant
If f’(x) > 0, f is strictly increasing
If f’(x) < 0, f is strictly decreasing
What is the Generalised Mean Value Theorem?
Suppose f : [a, b] → R is continuous on [a, b], differentiable on (a, b), and that g’(x) =/ 0 for every x in (a, b). Then there exists a c in (a, b) such that (f(b) - f(a))/(g(b) - g(a)) = f’(c)/g’(c)
What is L’Hôpital’s Rule?
limx→x0f(x)/g(x) = limx→x0f’(x)/g’(x) provided that limx→x0f(x) = limx→x0g(x) = 0 or limx→x0f(x) = limx→x0g(x) = infinity (indeterminate form)
What does it mean if a function is infinitely differentiable?
If the nth derivative, f(n) exists for all positive integers n
What is the Taylor polynomial?
Taylor series centered at 0 are usually known as Maclaurin series
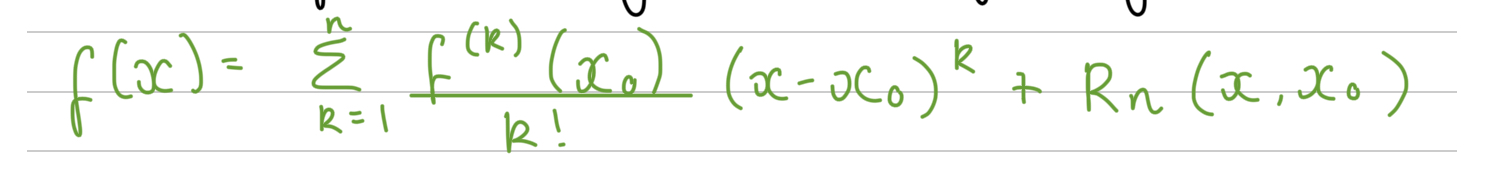
What is the formula for the error term in the Taylor polynomial?
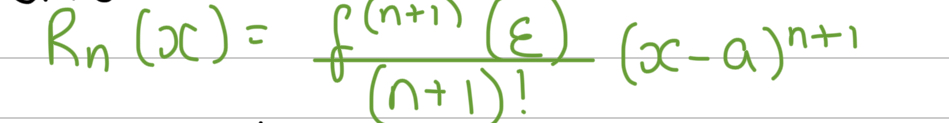
What is the Maclaurin series formula?
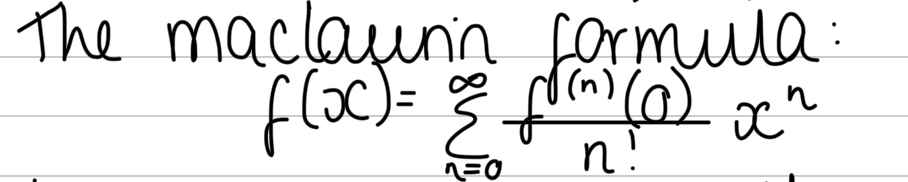
Let c belong to Dom(f) for a real function f. What is the absolute min and max of f?
f(c) is the absolute min of f on Dom(f) if f(c) \< f(x) for all x in Dom(f)
f(c) is the absolute max of f on Dom(f) if f(c) >/ f(x) for all x in Dom(f)
What are the max and min values of a function f called?
Extreme values
What are absolute min and max values sometimes called?
Global min and max
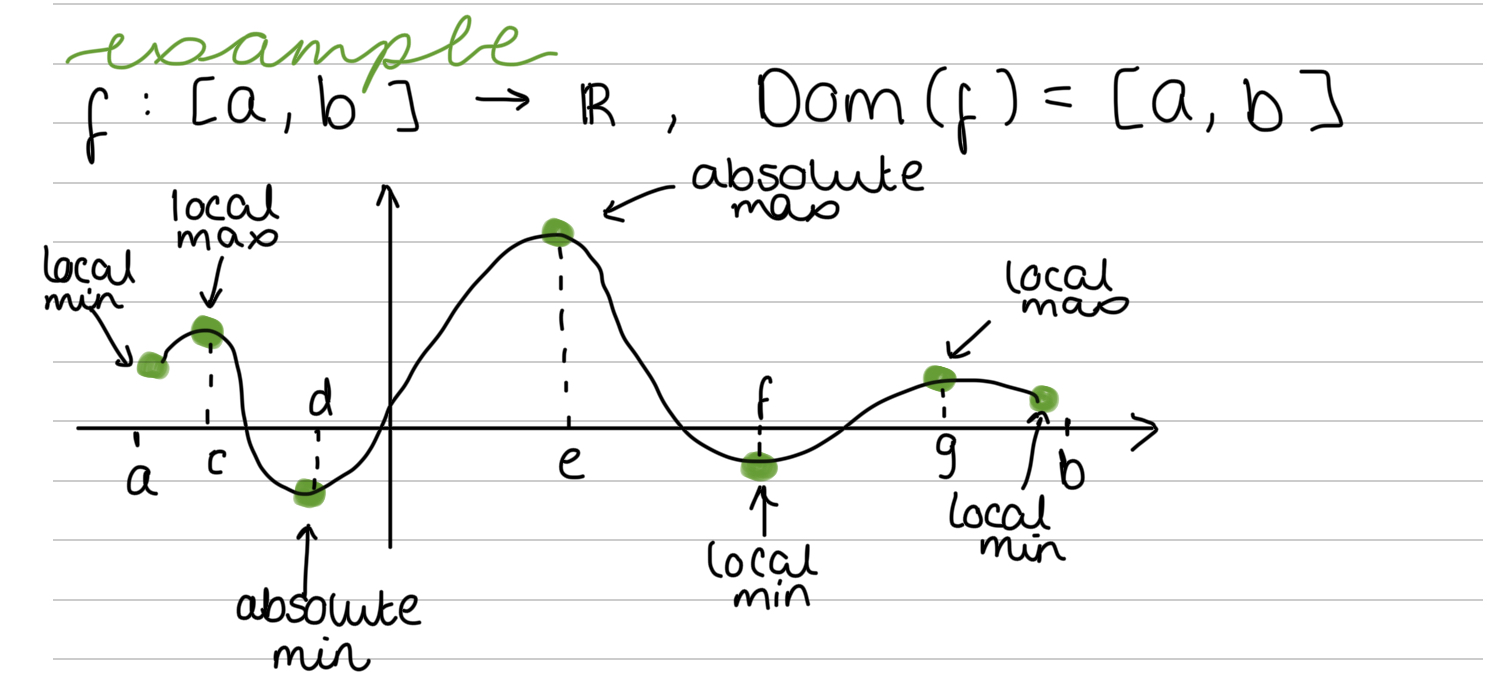
Let c belong to Dom(f) for a real function f. What is the local min and max of f?
f(c) is the local max value of f if f(c) >/ f(x) for all x close to c (i.e. there exists a δ > 0 such that f(c) >/ f(x) for every x belonging to (c - δ, c + δ) and in Dom(f))
f(c) is the local min value of f if f(c) \< f(x) for all x close to c (i.e. there exists a δ > 0 such that f(c) \< f(x) for every x belonging to (c - δ, c + δ) and in Dom(f))
What is Fermat’s Theorem?
If f has a local max/min at c belonging to (a, b)and f’(c) exists then f’(c) = 0
What is a critical point?
The number c in Dom(f) such that f’(c) = 0 or f’(c) DNE
What are the steps to finding the max/min points of a function?
Find values at critical points
Find values at endpoints
Pick the largest/smallest values from above
What is the derivate test for extreme values?
If f’(x) > 0 for x < c and f’(x) < 0 for x > c then f(c) is a maximum of f
If f’(x) < 0 for x < c and f’(x) >0 for x > c then f(c) is a minimum of f
What is the definition of a horizontal asymptote of the curve y = f(x)?
The line y = L is called a horizontal asymptote if either limx→∞f(x) = L or limx→-∞f(x) = L
What is the definition of a vertical asymptote of the curve y = f(x)?
The line x = a is a vertical asymptote if at least one of the following is true: limx→a+f(x) = ∞, limx→a+f(x) = -∞, limx→a-f(x) = ∞ or limx→a-f(x) = -∞
How to tell if a curve is concave upward?
f”(x) > 0
How to tell if a curve is concave downward?
f”(x) < 0
What is an inflection point?
Where a curve changes concavities
What are the steps for sketching a curve?
Determine domain of f using domain convention
Find intersections with axis (f(0), f(x) = 0)
Symmetry and whether it is an odd or even function
On which intervals it is increasing/decreasing (f’(x) > 0, f’(x) < 0)
Local max/mins
Concavity and inflection points
Asymptotes