Properties of Substances and Mixtures (AP Exams) — Complete Study Guide
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
London Dispersion Forces (LDFs)
The weakest type of IMF exists between all atoms and molecules.
Dipole-Induced Dipole Interactions
Occur when a polar molecule induces a dipole in a nonpolar molecule by distorting its electron cloud.
Dipole–Dipole Interactions
Occur between two polar molecules with permanent dipoles. Molecules align positive end to negative end.
Ion–Dipole Interactions
Occur between an ion and a polar molecule.
Molecular Dipole Moment
A measure of net polarity in a molecule; vector sum of all bond dipoles.
Hydrogen Bonding
Special case of strong dipole–dipole interaction. Occurs when H is bonded to N, O, or F and attracted to a lone pair on another N, O, or F atom.
Solids
They have strong particle attractions, fixed shape, and volume.
Liquids
They have fixed volume, variable shape, and moderate IMFs.
Ionic Solids
Have high melting point, hard, and brittle
Covalent Network Solids
Atoms held by covalent bonds in a continuous network. They are very hard, have high melting points, and poor conductors.
Molecular Solids
Made of discrete molecules held by IMFs (not covalent or ionic bonds). They have low melting points, soft, and poor electrical conductors.
Metallic Solids
Consist of metal cations surrounded by a sea of delocalized electrons. They are malleable, ductile, and Electrically/Thermally Conductive.
Unit cells
They are the smallest repeating unit.
PV = nRT
What is the formula used for the Ideal Gas Law?
Boyle’s Law
Which law forms this type of graphical presentation?
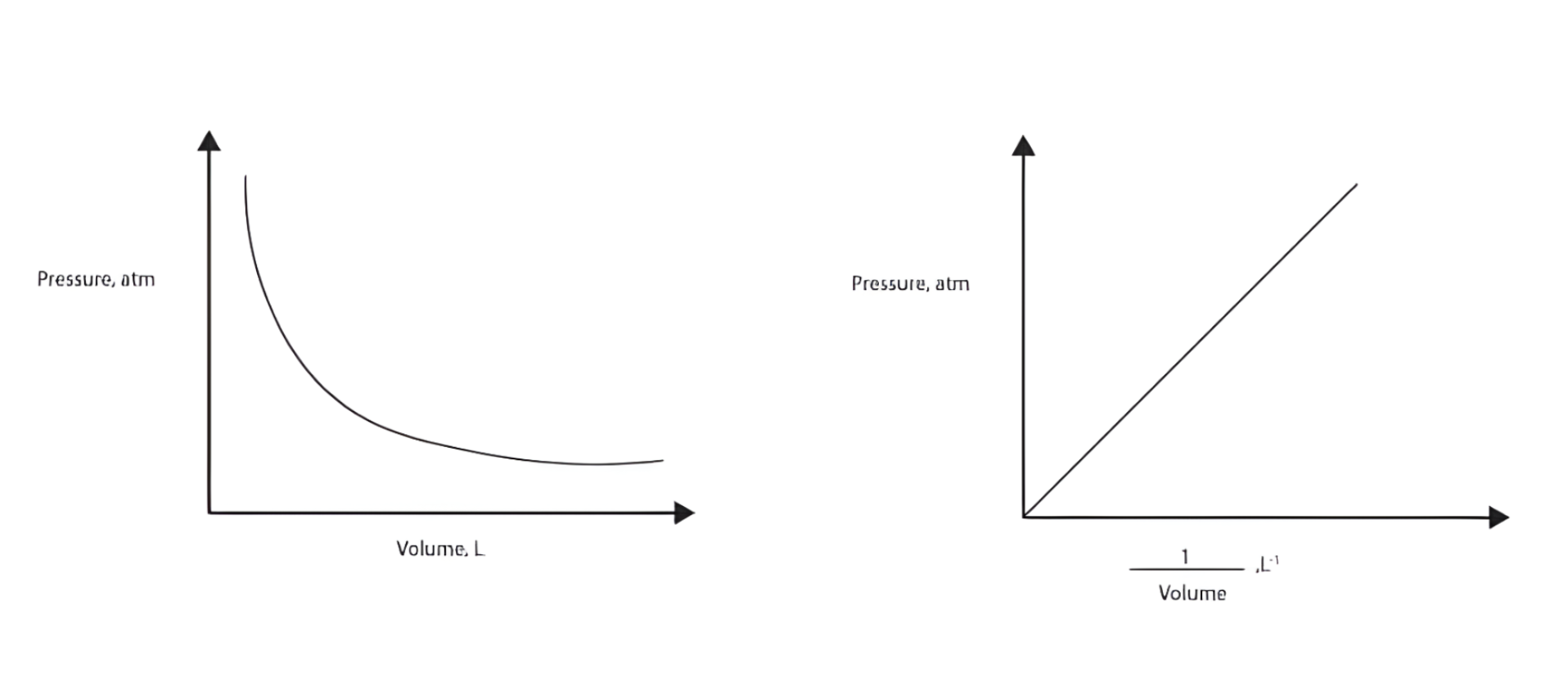
Charles’ Law
Which law forms this type of graphical presentation?
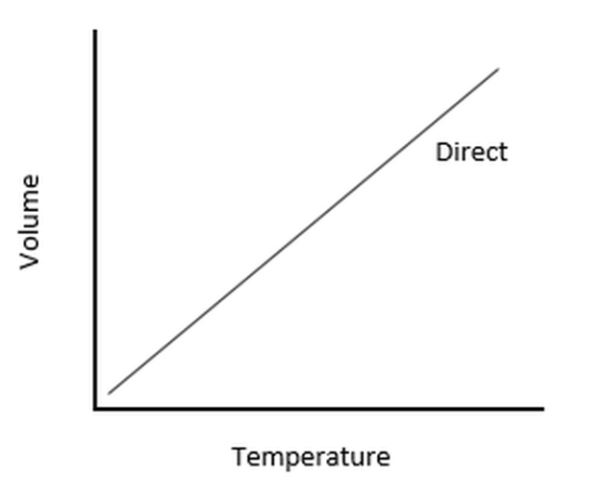
Avogadro’s Law
Which law forms this type of graphical presentation?
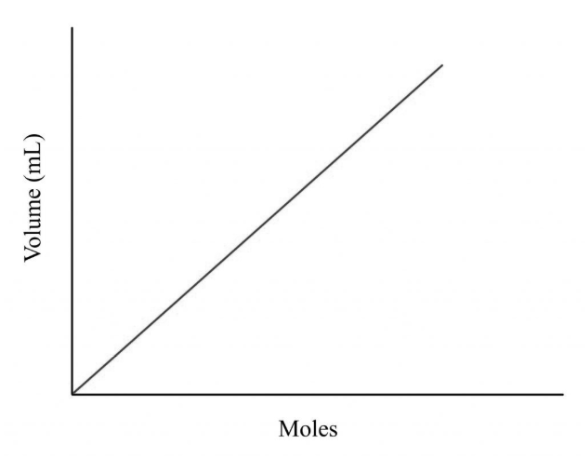
Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT)
Gas particles are in constant random motion. Volume of individual molecules ≈ negligible. Collisions are elastic (no energy loss). Average kinetic energy ∝ temperature (Kelvin). Explains pressure as particle collisions with container walls.
The Maxwell–Boltzmann Distribution
Describes range of molecular speeds in a gas sample. At higher temperatures: Distribution broadens and average kinetic energy increases. Lighter molecules move faster on average.
Non-Ideal Behavior of Gases
Deviate from ideal gas law at high pressures or low temperatures. Attractive forces lower pressure; finite volume reduces free space.
Molarity
Fill in the blank
________ (M): M = moles solute / liters solution.
Molality
Fill in the blank
________ (m): m = moles solute / kg solvent.
Heterogenous mixtures
Fill in the blank
Homogeneous mixtures: uniform composition (solutions).
______________________: non-uniform, distinct phases (suspensions, emulsions).
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
It moves from shorter wavelength to higher energy.
Gamma
Fill in the blank
Radio → Microwave → Infrared → Visible → UV → X-ray → _______.
Photoelectric effect
Light of sufficient energy ejects electrons from metal surface.
nonpolar
If polar dissolves polar, a nonpolar dissolves?
ion–dipole
Ionic compounds dissolve via these type of interactions.
titrations
Fill in the blank
Molarity is important for __________ and reaction concentration control.
dipole–dipole or hydrogen
Molecular solutes dissolve via these types of bonding.
Beer–Lambert Law
Higher concentration → higher absorbance (linear relationship).
Heterogenous
What type of mixture is sand in water?
Homogeneous
What type of mixture is air?