Basic Nerve Anatomy: The Action Potential
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Neuron
fundamental (basic) unit of the nervous system
-nerve cell
VIIIth Nerve: Auditory Nerve
two branches: auditory and vestibular
Auditory Branch of the VIIIth Nerve
nerve fibers connected to the cochlea are routed through the habenula perforata to the modiolus
Vestibular Branch of the VIIIth Nerve
connected to the balance organs of the inner ear
What are the two basic types of neurons each branch has?
afferent and efferent
Afferent Neurons
hair cells signal to the brain
-sensory neurons
Efferent Neurons
brain signal to the hair cells
-motor neurons
Bipolar Type Neurons
-nearly all of th VIIIth nerve fiber bundle is composed of bipolar neurons
-axon on either side of cell body
-direction of chemo-electrical activity is a one-way path
Direction of Chemo-Electrical Activity is a One-Way Path
axon to cell body to axon
-a group of cell bodies is called a ganglion
Ganglion
a group of cell bodies
Action Potential
*SLIDE 4*
Dendrites
found along the basilar membrane
-they are "post-synaptic" - behind the gap (synapse) between hair cell and nerve
-they act as sensors and are stimulated by a chemical (neurotransmitter) emitted from the base of the hair cells
Axon
extends through the habenula perforata to the cell body found in the modiolus
-the axon extends from the modiolus into and through the internal auditory canal (IAC) and is part of the VIIIth nerve
-nerve fiber
Cell Body
recall that a ganglion is a mass of cell bodies
-the spiral ganglion is a mass of cell bodies found in the modiolus
Myelin
on the nerve (specifically the axon), myelin is a whitish, fatty substance coating the axon
-the "insulation" that keeps out Na+
The Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in myelin sheath
-regulate the speed of neural firing
-if the nodes are close together, the nerve cell will transmit an impulse relatively slowly
-if the nodes are far apart the impulse transmission will occur more quickly
Schwann Sheathing
covers myelin
-made up of tissue from nearby Schwann cells
-if the Schwann sheathing is damaged or malformed, the cell will misfire when stimulated
Theodor Schwann (1810-1882)
Discoverer of...
-Schwann cells on nerve cells
-Pepsin (digestive enzyme)
-Striated muscles in upper esophagus
-Embryologic process
-Coined the term "metabolism"
What is the role of Schwann cells?
to hold myelin in place
Terminal Arbor
"pre-synaptic" and precedes the synapse (gap) between it and next cell
-the terminal arbor receives the impulse that is racing down the axon
Direction of Nerve Conduction
the nerve impulse begins in the dendrites, and if the stimulation of the dendrites is great enough, it will continue down the first axon through the cell body, through the second axon and on to the terminal arbor
What are the features of the VIIIth nerve bipolar neurons?
synapse, cell interior, cell exterior
Synapse of the VIIIth Nerve Bipolar Neurons
gap between the hair cell and the dendrites of the VIIIth nerve cells
-initial axon's dendrites: post-synaptic region (sensitive to neurotransmitter)
-terminal arbor's dendrites: pre-synaptic region (produces neurotransmitter)
-Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine (ACH)
How do you count the sequence of neurons?
use the presence of a synapse to count the sequence of neurons
First Synapse
hair cell to afferent neuron
-VIIIth nerve neurons are "first order neurons"
Second Synapse
at cochlear nuclei in brainstem
-all neurons leaving cochlear nuclei are 2nd order
Cell Interior of the VIIIth Nerve Bipolar Neurons
potassium (K+) is constantly leaking from the interior
-organic negative ions
-overall the charge in the interior is negative
Cell Exterior of the VIIIth Nerve Bipolar Neurons
sodium (Na+) and CHloride (Cl-)
-more Na+ than Cl-
-overall charge in the exterior is positive
What are the types of afferent VIIIth Nerve's Neurons
radial (Type I)
outer spiral (Type II)
Radial Afferent VIIIth Nerve's Neurons (Type I)
-bipolar neurons
-90 to 95% of afferents
-all radial nerve cell dendrites connect directly
to base of IHCs
-ganglia found in modiolus
-many radial cells connect to only 3,000 IHCs
-ratio: about 20 radials-to-1 IHC
Myelinated axons (relatively fast transmission)
Outer Spiral Afferent VIIIth Nerve's Neurons (Type II)
-second type of afferent nerve cell in VIIIth nerve
-pseudo-monopolarneurons (5% of afferents)
-ratio: about 1 Outer Spiral Neuron-to-10 OHCs
-complex innervation pattern
-not all OHCs are innervated by afferents
-fibers cross floor of Corti's tunnel
-ganglia found in modiolus
-unmyelinated axons (relatively slow transmission)
Complex Innervation Pattern of Outer Spiral (Type II) Neurons
Basal turn --1st row of OHCs
Middle turn --2nd row of OHCs
Apical turn --3rd row of OHCs
Type I afferent neurons are...
inner hair cells
Type II afferent neurons are...
outer hair cells
Inner spirals and tunnel radials are the...
efferent nerve fibers
Radial and Outer Spiral fibers are the...
afferent nerve fibers
Each cochlear nucleus receives ____________________ and outer spiral fibers of the VIIIth nerve. The cochlear nucleus is the highest point in the auditory pathway that receives only ipsilateral input.
ipsilateral radial
-ipsilateral = one side
-cochlea nucleus only receives nerve fibers from the cochlea on the same side (not from the other ear)
What does the nerve cell membrane do?
separates the intracellular and extracellular fluids
Neurons at rest present...
an uneven distribution of ions across the plasma membrane
-the charges of the ions in the two fluids differ
What do the electrical differences between the intracellular and extracellular fluids produce?
an electric potential
The action potential exists for the flow of...
electric current
The electrical potential always exists (in a living subject)...
whether or not the nerve is excited
Resting Potential
the permanent electrical potential
Intracellular fluid consists primarily of...
potassium (K+) with a negatively charged ionic field
Extracellular fluid is primarily...
sodium (Na+) and has a positively charged ionic field
The overall number of positive ions is...
higher outside the cell than inside the cell (at rest)
Protein inserted in the plasma membrane function as...
ion channels
-they allow the passage of ions into and out of the plasma membrane
There are __________ types of ion channels.
various
Ligand-gated channels will open when chemically stimulated with...
a neurotransmitter (glutamate
from the inner hair cells to the afferent fibers and acetylcholine to the outer hair cells from efferent fibers)
When glutamate is released at the base of the inner hair cells...
it moves across the synapse towards the dendrites of the afferent neuron
The glutamate will cause the Ligand-gated ion channels to...
open, allowing Na+ to flow into the dendrites and K+ to flow out
There is a __________ inflow of Na+ than an outflow of K+
greater
Ligand-gated channels will open when...
chemically stimulated
Voltage-gated channels are activated by...
changes in the electrical potential difference near the channel
-they allow for rapid and coordinated depolarization in the nerve cell
Action Potential
a short lasting electrical event on the plasma membrane of a nerve cell
What is another name for action potential?
nerve impulse
The resting potential is the...
difference between the intra and extra cellular fluids (across the cell membrane)
-it is between -40 to -90 mV
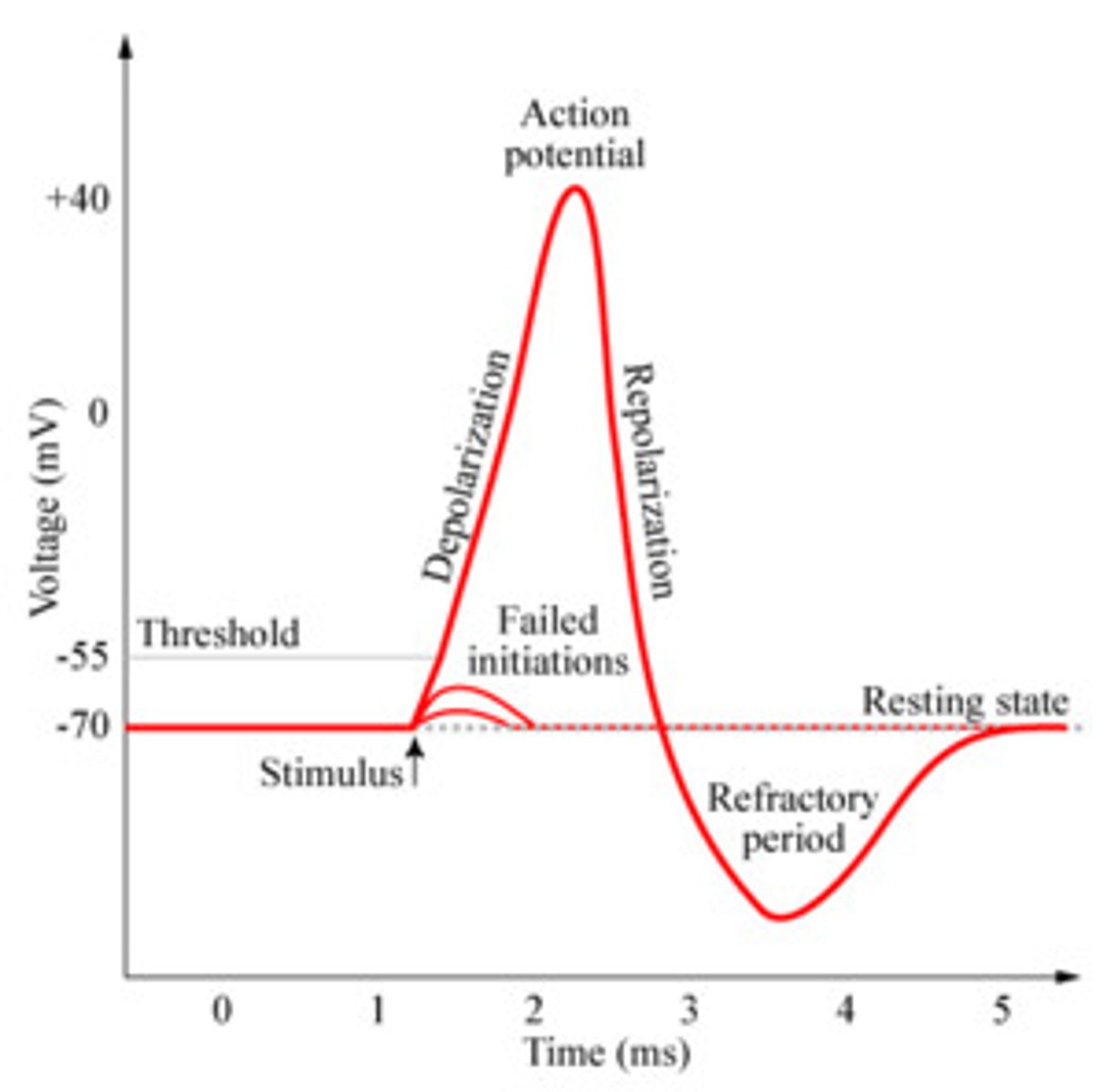
The graph shows the electrical potential change at one point along the nerve
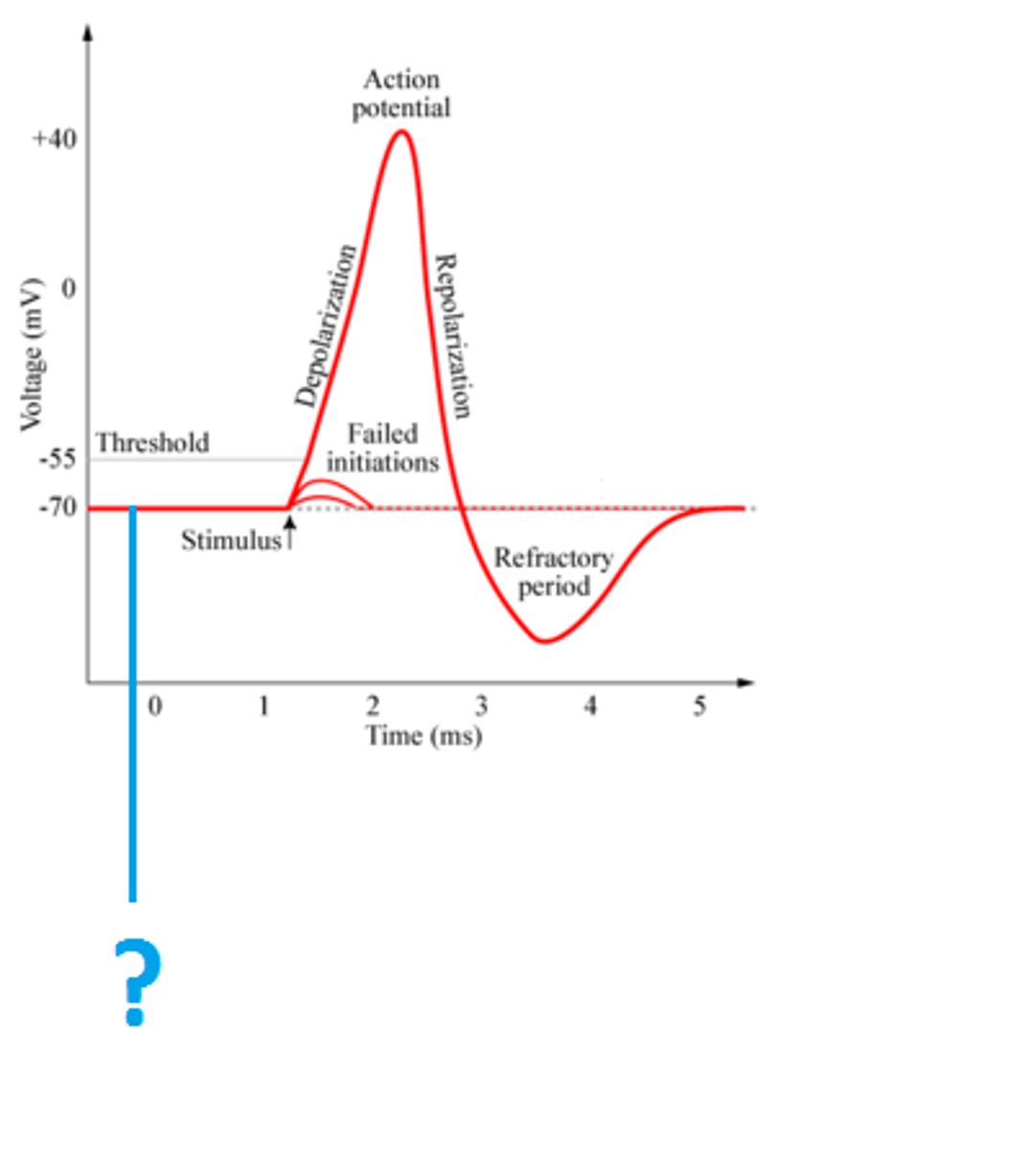
Action Potential Graph
action potential occurs at the peak
know the steps of the graph
The most widely accepted theory on the flow of an electric current through the neurons starts with a change in the...
permeability of the cell membrane to potassium and sodium as a function of excitation of the nerve
Permeability
the ability of the cell membrane to allow ions to pass through
Basic Chemo-Electrical Activity Stimulating the Nerve Cell
generator potential
Generator Potential
occurs in post-synaptic regions (specialized areas on unmyelinated dendrites)
-graduated response to a neurotransmitter
-allows localized infusion of Na+
-when the generator potential is high enough (and the nerve threshold is reached) it will generate the action potential
Some adequate stimulus changes the...
permeability of the cell membrane, allows for sodium to flow into the cell
-this causes depolarization
Depolarization
where the potential difference changes from a negative value to a positive value
If the change in potential difference does not meet the "threshold"...
no action potential will occur
If depolarization leads to a sufficient increase in the potential voltage...
an action potential will occur
What is the action potential?
the neural signal
Hyperpolarization or repolarization occurs...
as the ions move toward the resting (more negative) state
-sodium flows from the cell until the resting potential is reached
The time between the peak of the action potential and point in time for the most negative potential is called the...
absolute refractory period of the nerve impulse
-during this time no new discharge can occur
The time between the most negative potential and the re- initialization of the resting state is called the...
relative refractory period of the nerve impulse
-during this time is is difficult but possible for a new discharge to occur
Basic Chemo-Electrical Activity Firing the nerve Cell
action potential
Action Potential
the cell membrane becomes permeable to Na+ which changes the electrical polarity of the cell at that point
-these changes in electrical activity move from the first axon to the cell body and then to the second axon
Diagram of a bipolar neuron that synapses with the bases of the inner hair cell. The resting potential...
results in a more positive (+) charge outside the cell and a more negative (-) charge inside the cell
Once glutamate is released from the inner hair cells, it causes...
the Ligand-gated channels in the dendrites to open. Na+ infuses the cell in segments while K+ is removed. This is the beginning of the generator potential
If the generator potential is large enough...
the voltage-gated channels will open to allow the flow of Na+ into the cell and the flow of K+ out of the cell. This "action potential" occurs one segment at a time
Step-by-Step process through one segment of the cell at a time
-Impulse has reached a certain point
-Na+ penetrates the cell membrane through the nodes of Ranvier
-Since the rate of Na+ penetration is constant, the speed of the impulse (i.e., nerve conduction rate) is determined by the distance between nodes of Ranvier.
-Compared to other nerves, the distance between nodes on the VIIIth nerve is relatively far, implying a fast transmission rate.
-When the impulse reaches the terminal arbor, the neurotransmitter is released, which stimulates the dendrites of the next nerve in order.
Infusing the cell with sodium in step-by-step stages is...
only part of the process. The sodium also must be removed from the cell as the impulse proceeds from dendrites to terminal arbor. This occurs progressively behind the impulse
Dendrites are stimulated by...
glutamate from hair cell; dendrites admit Na+; generator potential established; interior of dendrites turns to positive charge
If generator potential is sufficiently large (lots of Na+ enters dendrites)...
then nearby portion of axon admits Na+ and action potential has begun; dendrites pump out Na+ to begin to return to negative charge
Once the action potential begins...
it is unstoppable; impulse moves to next segment of axon as areas behind it continue to pump out Na+ in order to return to a negative charge
Depolarization is followed by...
hyperpolarization
Impulse now has crossed the cell body and entered the second axon...
note that Na+ is penetrating through and exiting the nodes of Ranvier, which are gaps on axons without mylin or Schwann cell sheathing. Cell is in absolute refraction and cannot fire again until this process proceeds further
How does the nerve work?
go through the slides step-by-step
All Na+ now removed from the cell...
the interior has its original negative charge; cell is in resting potential, ready to fire at normal threshold for generator potential in its dendrites
The sequence of events (from depolarization to repolarization) occur...
sequentially across the nerve cell during the action potential
Basic Chemo-Electrical Activity: Sequence of Events
1. Resting Potential
2. Generator Potential
3. Action Potential
4. Absolute Refractory
5. Relative Refractory
6. Resting Potential
Resting Potential
ready for normal level of stimulation
Generator Potential and Relative Refractor
needs higher level of stimulation
Frequency Specific Neurons
-Individual neurons are more responsive to specific frequencies
-However, each neuron may respond to or "phase-lock" to a range of frequencies depending on the level of the stimulus (e.g., neural tuning curves and the upward spread of masking).