Veterinary Anatomy #3
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
Name/state common features of endocrine glands
- The endocrine system differs from other in that the component organs/glands are not in direct continuity
• Hormone synthesis is a common function for
all endocrine glands
• Extensive blood supply
• Absence of secretory ducts
• Deliver their secretory products (hormones) into the blood, lymph or tissue fluid.
• Collaborate with nervous system to maintain the homeostasis.
• Hormones effect are slow compare with nerve system but last longer.
Name/state the primary endocrine organs
- Hypophysis (Pituitary gland)
• Pineal gland (formerly epiphysis)
• Thyroid glands
• Parathyroid glands
• Adrenal glands
Identify the hypophysis conformation and position in the cranial cavity
Occupies a central depression of the sella turcica of basisphenoid, known as the hypophyseal fossa
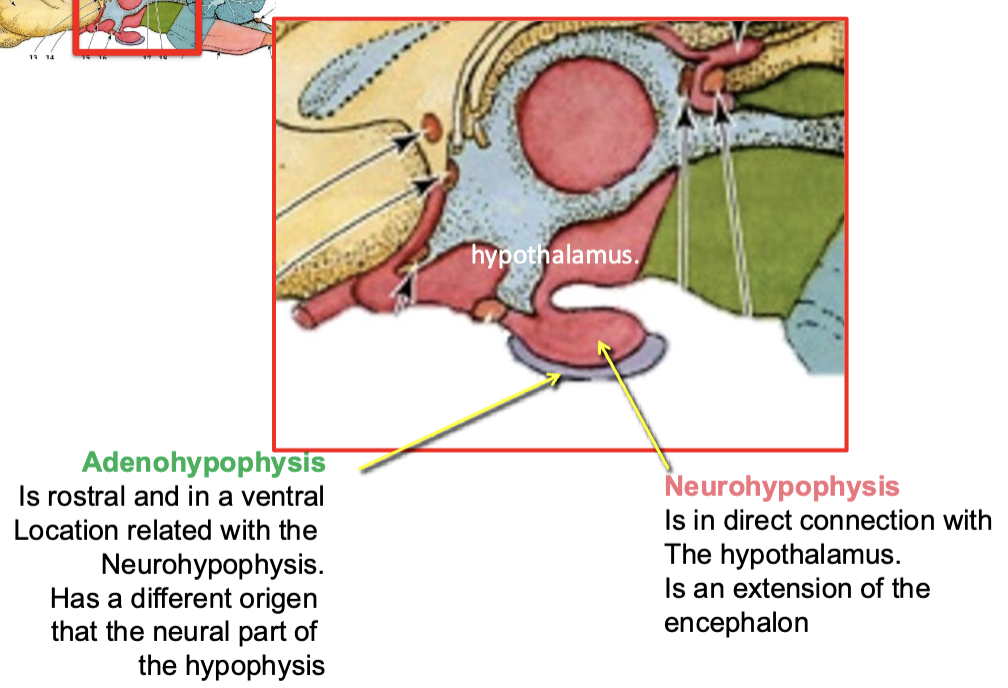
Formed by two parts: Adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis
Define sella turcica and hypophyseal fossa
Saddle-shaped depression in the basisphenoid bone of the skull that houses the pituitary gland
Hypophyseal fossa is a sunken central part of the sella turcica where the pituitary gland is physically located
Describe the communicating routes among hypothalamus and adenoohypophysis and neurohypophysis
Hypothalamus and adenohypophysis are connected by a hypophyseal portal vascular system
Hypothalamus and neurohypophysis are connected by a neural stem
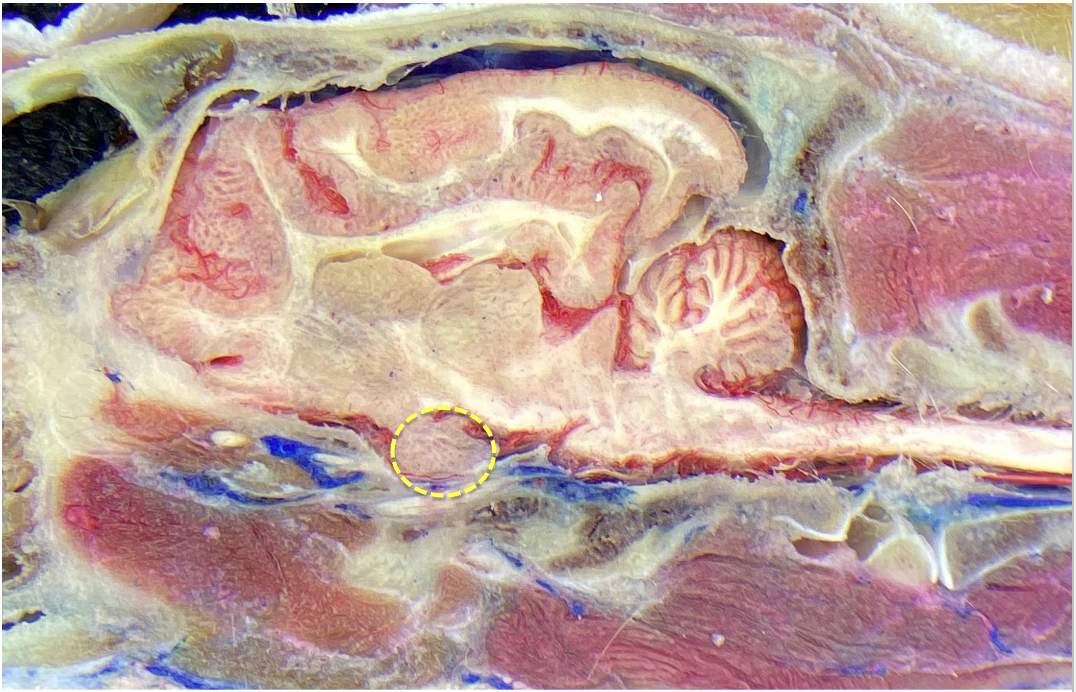
what is circled in this image
hypothalamus
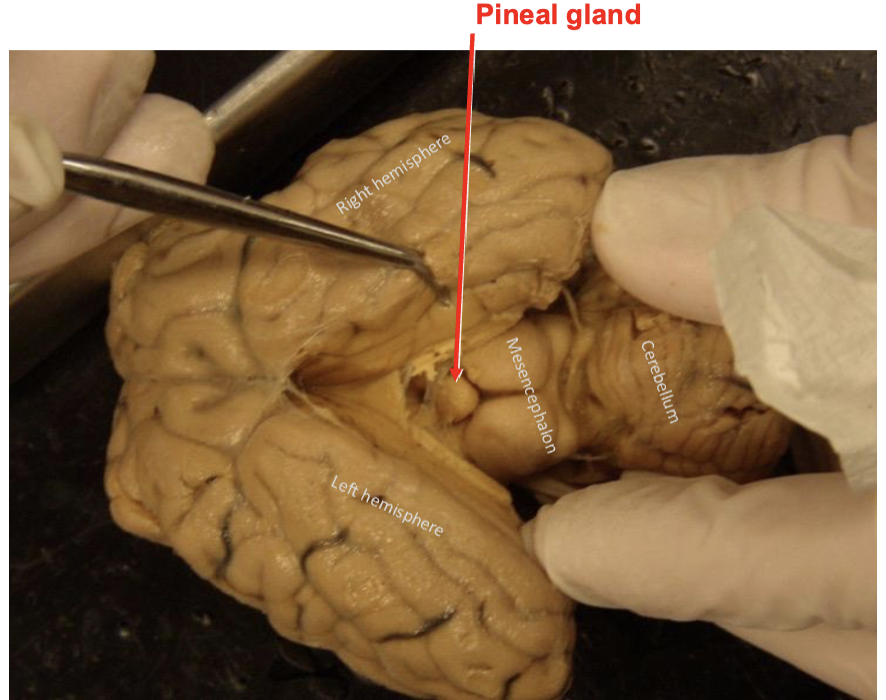
Describe the pineal gland
Produces melatonin, a hormone that modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles
Shape of the gland resembles a pine cone
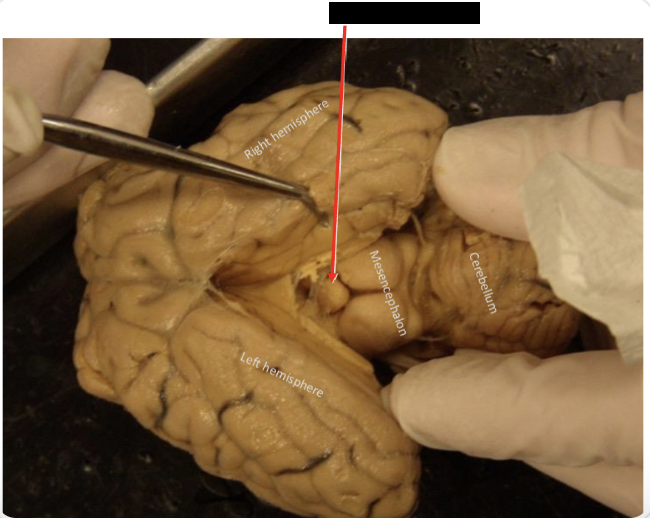
Identify its position in the encephalon
Located in the middle of the encephalon. In the area known as diencephalon. Caudo-dorsal to the thalamus
Describe the conformation and location of the thyroid glands
• Produce thyroxine hormones T3 & T4
• In most dogs is a paired gland (right & left)
nevertheless each gland can be referred as a lobe.
• Lies lateral to the trachea caudal to the larynx (sometimes overlapping the larynx)
Describe the location of parathyroid glands, be able to differentiate it from thyroid gland tissue
• Produce parathyroid hormones
• Normally four, 2 in each side
• In dogs and cats normally are embedded in the thyroid gland
• Frequently scape notice during a dissection.
• Parathyroid glands are pale contrasting with the red-brick color of thyroid glands,
Adrenal glands produce what critical hormone? and regular hormones
Cortisol
Aldosterone
Epinephrine
Androgens
Cortisol effects with body system/organ
Muscle
bone
skin
immune system
vascular system
central nervous system
liver
kidney
Adrenal gland location
Retroperitoneal
Craniomedially to kidney’s cranial pole
Small size compared to kidneys
HIDDEN BY FAT
Conformation of adrenal glands
Capsule
Cortex
Medulla
Exocrine glands function?
Exocrine glands release (secrete) substances through opening (ducts) onto your body external surfaces or within cavity surface
Sweat
Lacrima
Saliva
Digestive juices
Milk
Describe the mammary glands
Subcutaneous, enlarges sweat glands
Produced colostrum and milk
Each gland is separated by a CT septa
Develop in the mammary ridges, the ridges extend from axilla to inguinal regions
Each gland secretes via a teat or papilla
Each teat can secret via one or multiple papillary ducts
Mammary glands in dogs and cats
Dogs normally have five pairs of mammary glands. Cats have four pairs
Each gland has 10-12 openings in dogs
4-8 in cats
Describe the lymphatic drainage in mammary glands
Axillary and accessory axillary lymph nodes:
Both thoracic mammary glands and cranial abdominal mammary glands
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes:
Both cranial and caudal abdominal mammary glands and inguinal mammary glands
Name the tunics (coats) of the gastrointestinal tract
Serous coat - visceral peritoneum
Muscular coat - longitudinal and circular layers
Mucous coat - most internal has glands absorbs
Submucous coat - In between muscle and mucous layer
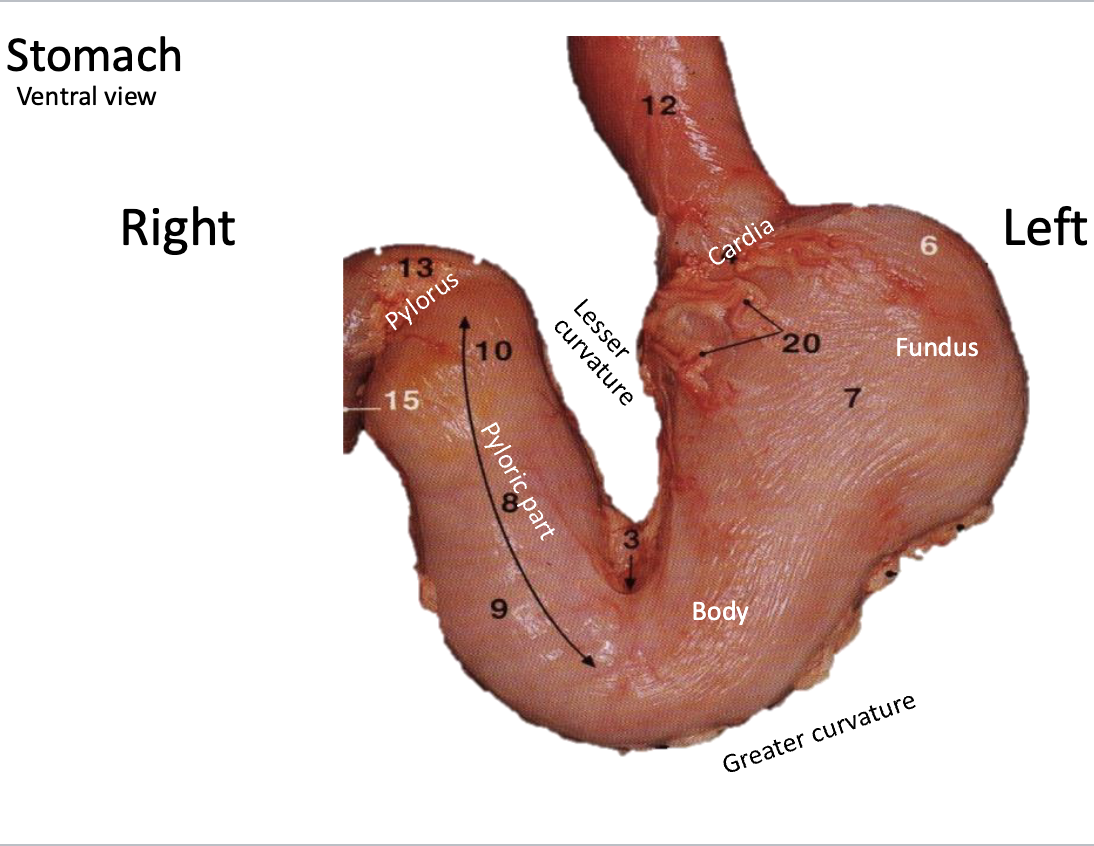
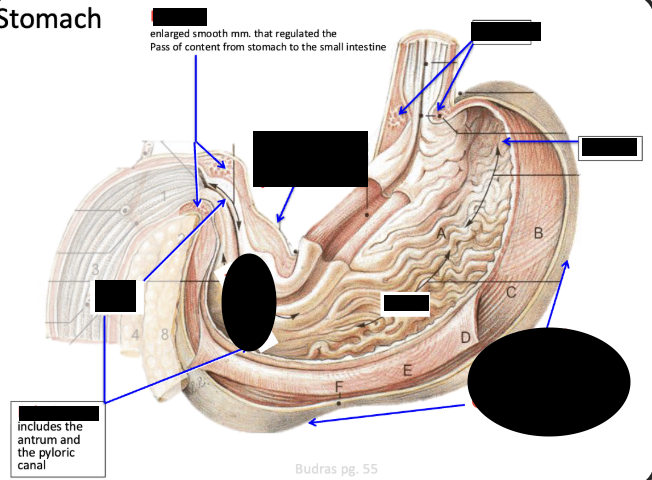
When esophagus joins with stomach in dogs it creates what structure?
Cardia sphincter - IT IS AN ANATOMICAL STRUCTURE AND NOT A FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE
What is pylorus
enlarges smooth mm. that regulated the pass of content from stomach to the small intestine
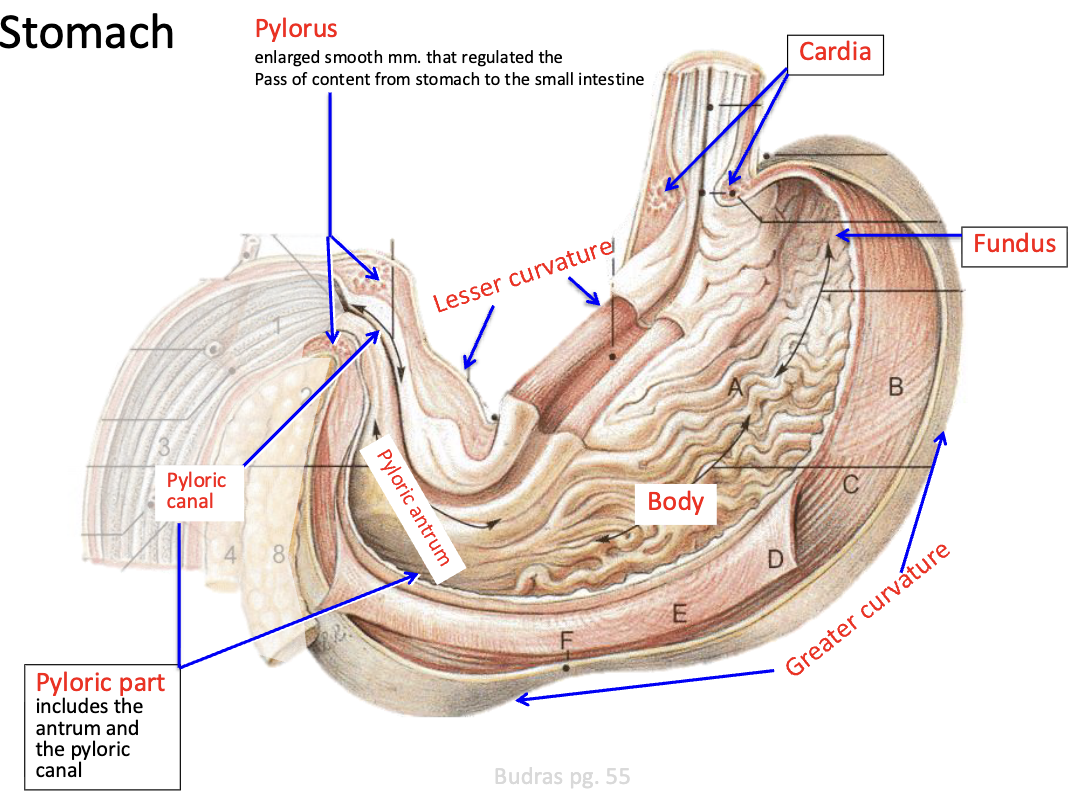
Fundus location
Very dorsal and left normally touch the spleen and walls and hypochondrium
How does gastric dilation and volvulus, also known as bloat, occur?
Since stomach doesn’t have super strong ligaments → flipping the stomach = entrance and exit twisted and vessel twisted
what does the superficial leaf contain and what does the deep leaf contain
Superficial - contains spleen
Deep - contains left limb of pancreas
what structures arises from the dorsal mesentery
Dorsal mesentery
– Dorsal mesogastrium (greater omentum)
– Mesoduodenum
– Mesojejunum
– Mesoileum
– Mesocolon
– Mesorectum
what structures arises from the ventral mesentery
Ventral mesentery
– Ventral mesogastrium (lesser omentum)
– Falciform ligament
– Median ligament of the bladder
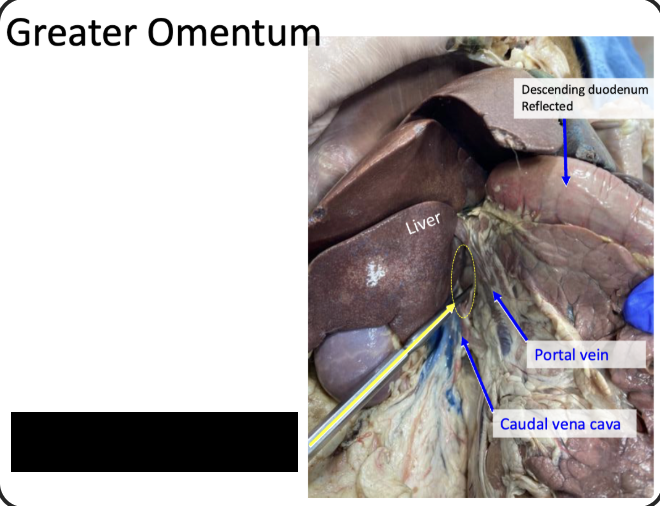
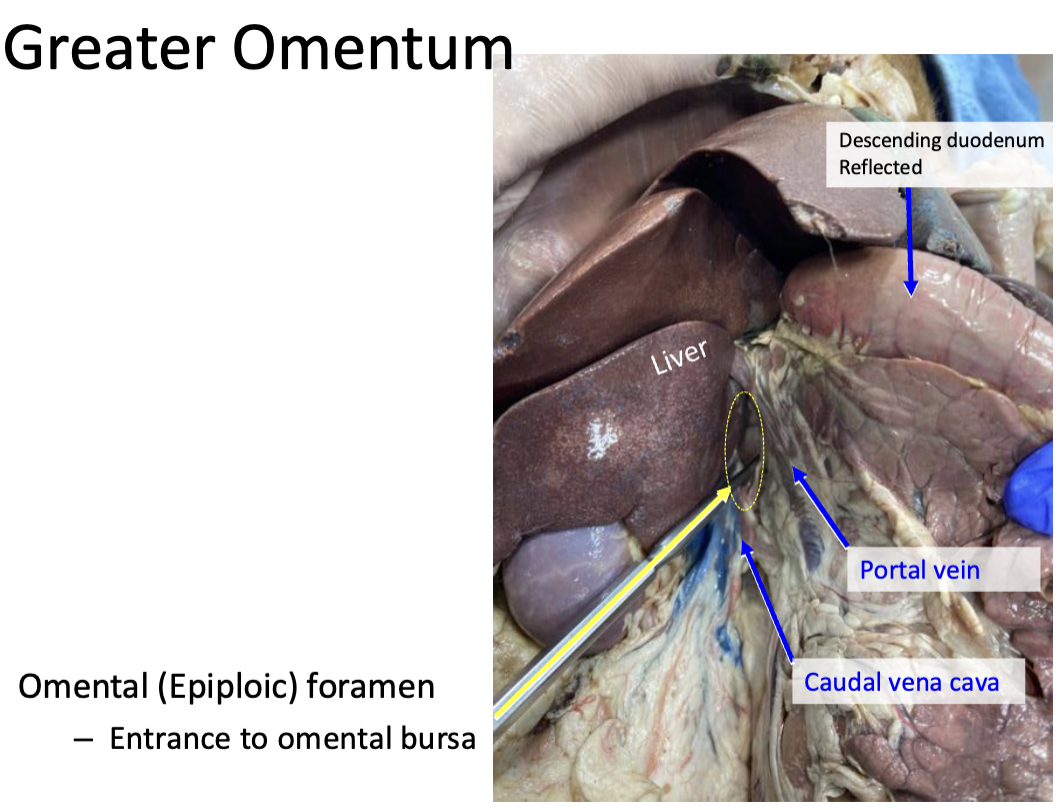
Purpose of omental foramen
Entrance to omental bursa and boundaries
IN ORDER state the structures in the duodenum
Which is the most important structure
Cranial part
Cranial duodenal flexure
Descending part
Caudal duodenal flexure
Ascending part
Duodenojejunal flexure
What makes up the small intestine?
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
What makes up the large intestine?
Cecum
Colon
Rectum
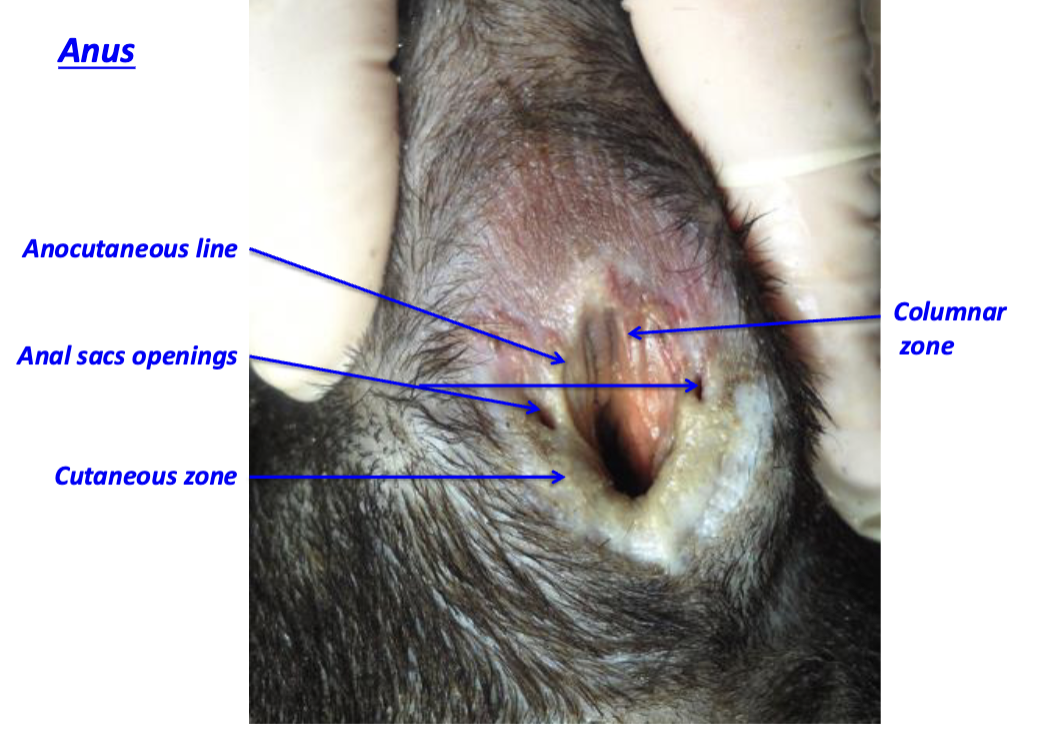
Anus
What is the greater omentum attached to?
Greater curvature of stomach + medial surface of spleen (hilus)
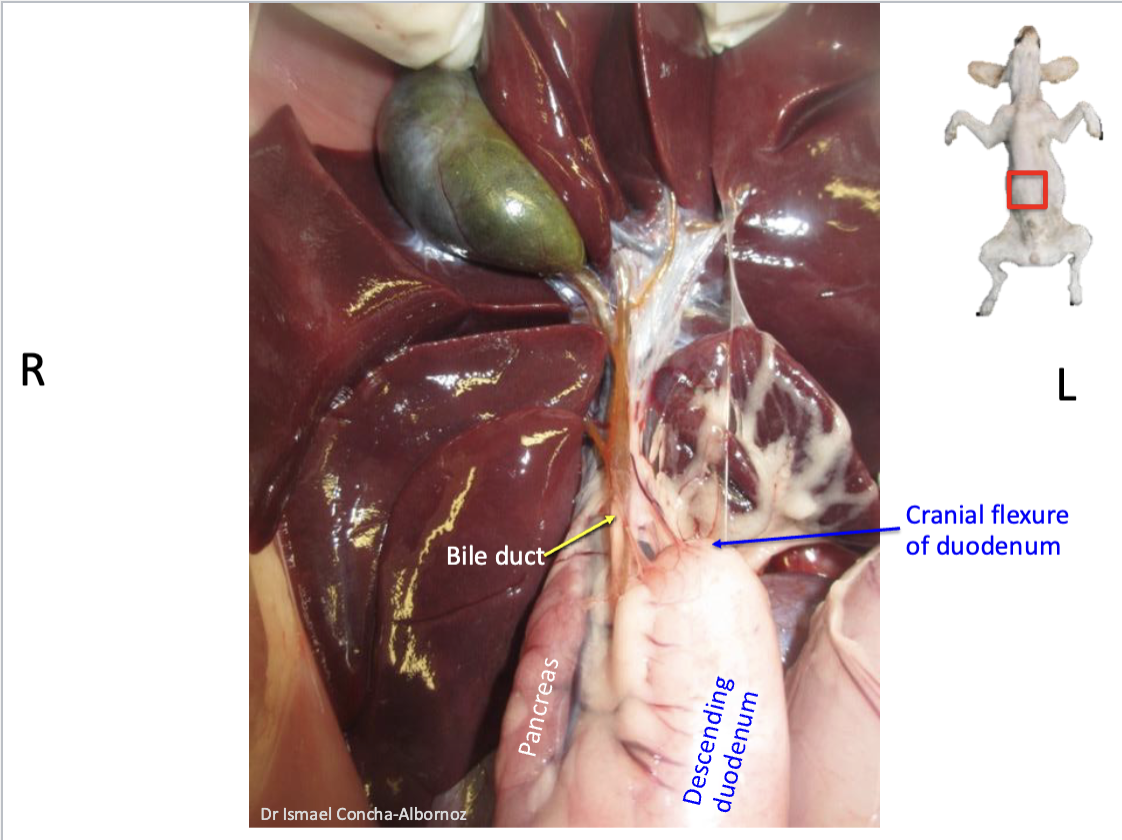
Where is the major duodenal papilla located and where duct(s) empty there
Common bile duct - Bile going towards lumen of duodenum
Pancreatic duct - Pancreatic juice towards small intestine
BOTH OPEN AT MAJOR DUODENUM PAPILLA at the descending portion
Where is the minor duodenal papilla located and where duct(s) empty there
Descending portion
Accessory pancreatic duct
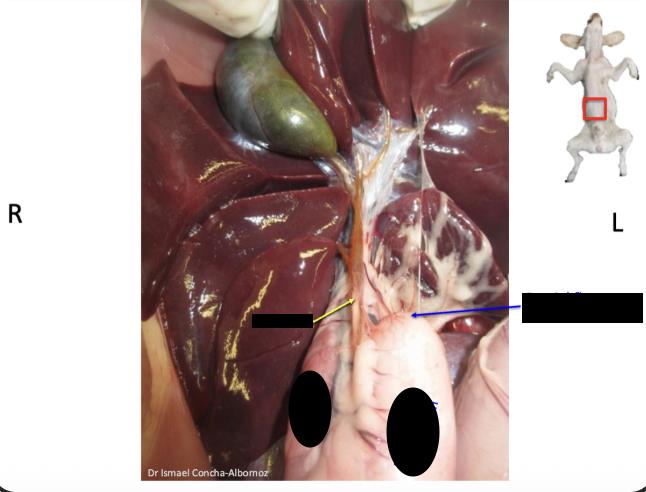
What structures help identify the ileum
define by antimesenteric ileal artery and the ileocecal fold
Ileocolic orifice
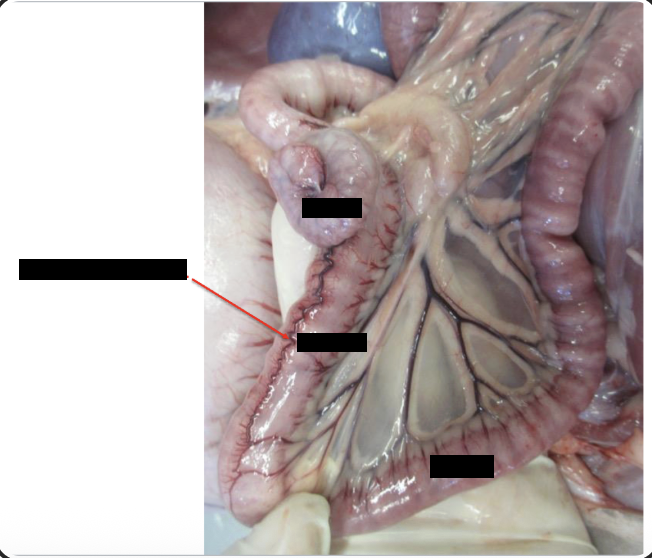
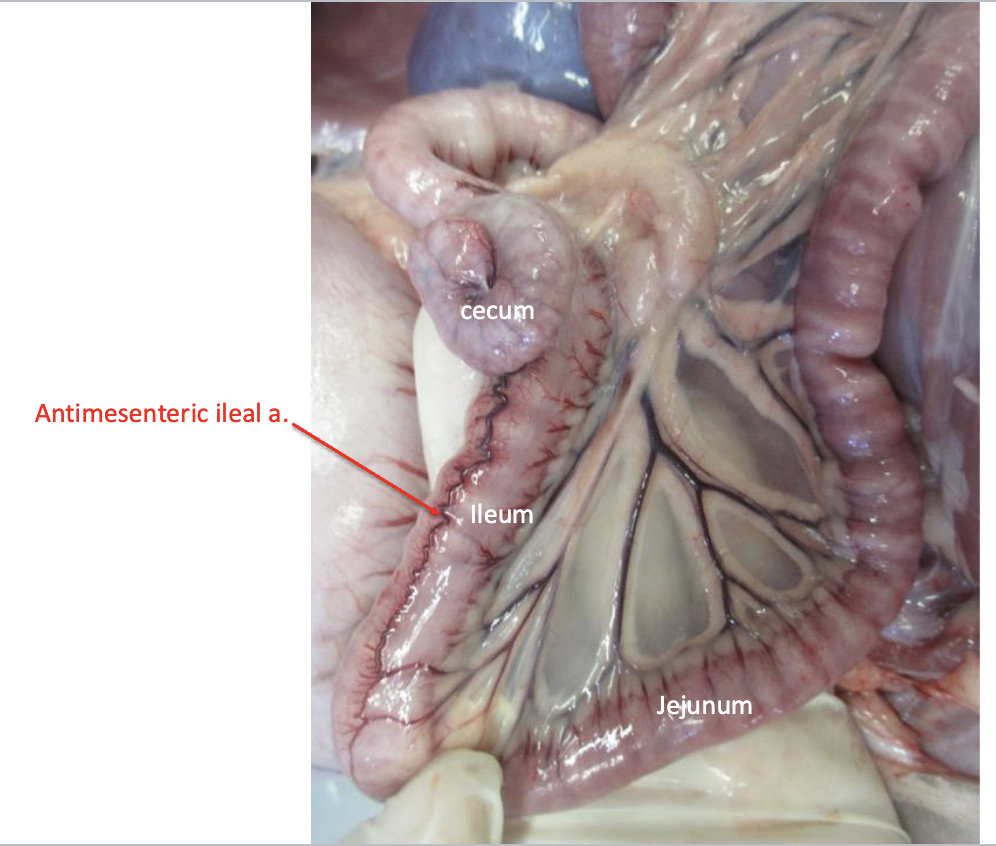
what is the cecocolic orifice?
Opening between the cecum and the ascending colon
what is the Ileocecal fold?
Plica of peritoneum between the cecum and the ileum
IN ORDER state the structure of the colon
Ascending colon
Right colic flexure
Transverse colon
Left colic flexure
Descending colon
Rectum
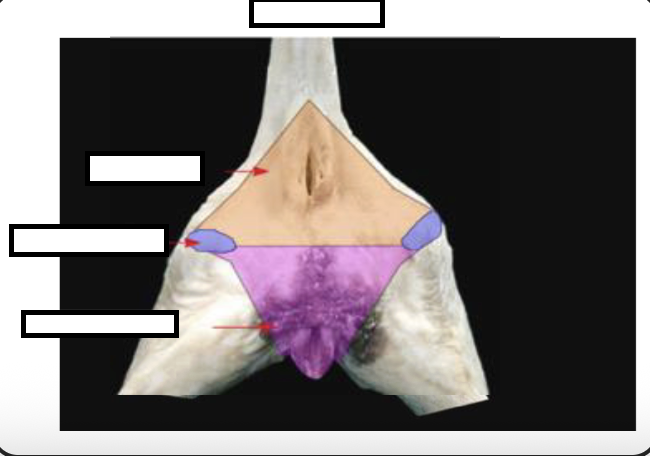
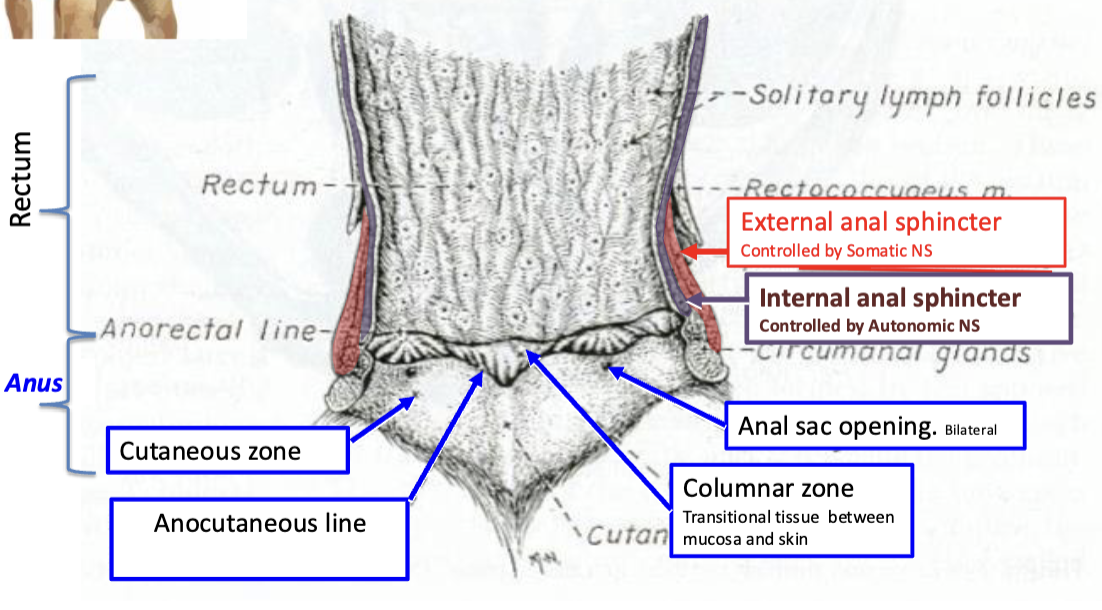
what is controlling the external anal sphincter?
Controlled by somatic NS
What is controlling the internal sphincter?
Controlled by autonomic NS
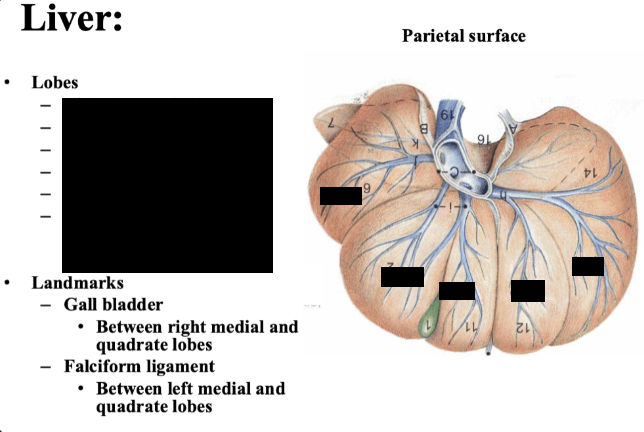
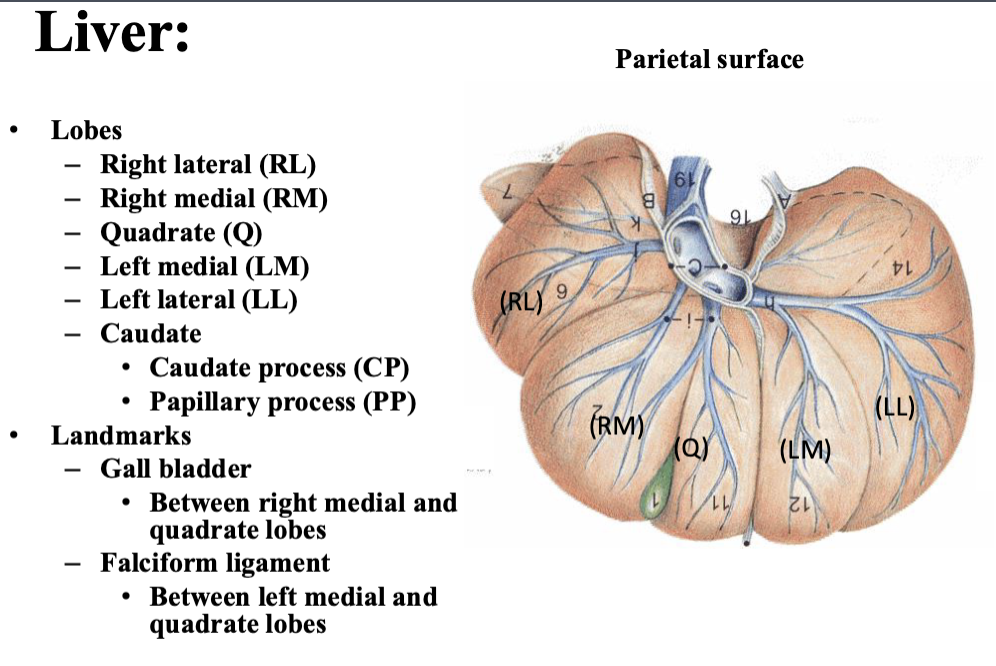
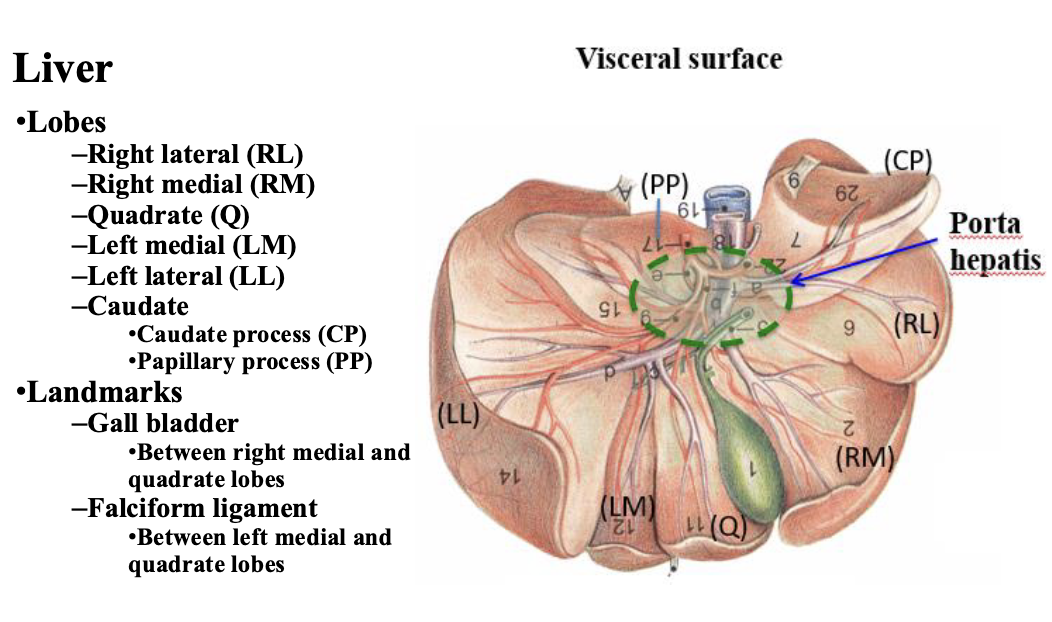
purpose of gall bladder
dispose of lipids
purpose of hepatic ducts
brings bile to the ducts
IN ORDER state the structures of biliary system
gall bladder
cystic duct
hepatic ducts
bile duct
major duodenal papilla
purpose of cystic duct
duct that connect the gall bladder with the bile duct
purpose of bile duct
duct that carries the bile to the lumen of the descending duodenum. Opens into the major duodenal papilla.
name the ligaments that hold the liver in position
Right triangular ligament
left triangular ligament
coronary ligament
location of right triangular ligament
courses from the right crus of the diaphragm to the right lateral lobe of the liver
left triangular ligament location
courses from the left crus of the diaphragm to the left lateral lobe of the liver
coronary ligament location
courses between the diaphragm and liver around the caudal vena cava and hepatic veins
pancreas function
exocrine function - to produce pancreatic juice, rich in enzyme
pancreas parts location
body
Near pylorus
right lobe
within mesoduodenum
left lobe
within deep leaf of greater omentum
spleen location
located within the superficial leaf of the greater omentum (attaches at the hilus)
what is the pelvic cavity composed of
Levator ani muscle
Coccygeus muscle
Name the pouches within the pelvic cavity (starting ventrally to dorsal)
Pubovesicle pouch
Vesicogenital pouch
Rectogenital pouch
Pararectal fossa
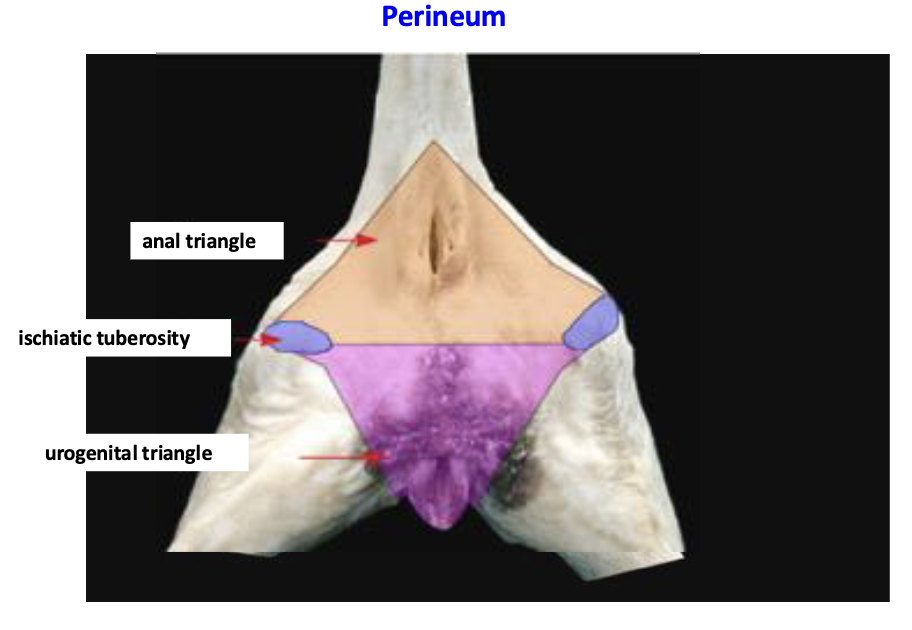
what is the perineum? what structures does it surround
Portion of the body wall that covers the pelvic outlet (caudal pelvic aperture)
Surrounds the anus and terminal parts of the urogenital tracy
How can we determine sex of an animal when they are young?
Use the anogenital distance to determine sex
distinguish the perineal body and perineal region
Perineal region is externally visible projection of the perineum on the skin
Anus, vulva
The perineal body is the internal tissue located between rectum and urogenital organs
Between the anal canal and bulb of the penis
Median fibromuscular mass b/t the anus and vulva
function of the kidneys
Filters blood to detoxify and rid the body of waste
function of the ureters
transport urine from kidneys to bladder
function of urinary bladder
temporary storage of urine
function of urethra
eliminate urine
location of kidneys dog:
Right → ventral to L1-L3 & recessed into the liver
Recessed/capped by the caudate process of the caudate lobe of the liver
Left → ventral to L2-L4
Right kidney is ~ 3x the length of L2 vertebral body
Location of kidneys cat
Kidney more mobile than the dog
Right kidney cranial to left
2.4 to 3x the length of L2 vertebral body
May be shrunken in older cats
B/c CKD
Anatomy of kidney - dog and cat (from the outside)
Convex lateral border
Concave medial border → hilus
Cranial pole
Caudal pole
Dorsal & ventral surface
Name the first outer layer of kidney
Surrounded by adipose capsule
Fibrous outer capsule - DICCT (dense irregular collagenous connective tissue)
Attaches to renal vessels and renal pelvis
location of renal sinus and its surrounding structure
Renal sinus: cavity located at renal hilus
Surrounding renal pelvis
Filled with white adipose tissue
what is the renal pelvis and purpose of the renal pelvis
Mucosa of the ureter expands into kidney, within the renal sinus
Funnel that is going to funnel urine from kidneys into ureter
what is the pelvic recesses
Diverticula of pelvis that extend into the renal parenchyma
what is the renal cortex
Reddish-brown, granular appearance
Contains renal corpuscles
OUTER MOST PORTION
what is the renal medulla
INNERMOST/DEEPEST PART OF THE KIDNEY
contains the renal crest
Renal pyramid conformation
part of renal medulla
base
apex: papilla “fits” into renal pelvis
papillary foramina on the renal crest
fused as one pyramid on midline
State where the urine flows
urine made in the renal cortex flow through renal pyramid to → renal papilla → renal crest → renal pelvis
Blood supply to the kidney (arteries)
Renal Aa → interlobar Aa → arcuate Aa → interlobular Aa → afferent arterioles → glomerulus → efferent arterioles
blood supply to the kidney (veins)
Stellate Vv → interlobular Vv → arcuate Vv → interlobar Vv → renal Vv
what unique feature on the kidneys do cats have
Subcapsular veins
Sympathetic innervation of the kidneys
from our splachnic nerves and a little bit of lumbar splachinic nerve
Parasympathetic innvervation of the kidneys
vagus nerve sends parasympathetic innervation to celiac mesenteric ganglion and plexus → down to kidney
why does the ureter enter the bladder dorsally at an oblique angle? why?
It is functional valve that is going to stop or slow the flow of the urine from the ureter into the bladder
define trigone
location of ureteral orifices and urethral orifice
what are the serosal attachments of the urinary bladder and what does each attachment contains
Lateral ligaments of the bladder
Contains umbilical around of the bladder and ureter
Median ligament of the bladder
Contains remnant of the fetal urachus
what is the urinary bladder made up of?
thick tunica muscularis
detrusor muscle - contracts urinary bladder (under ANS control)
How does the SNS and PSNS work in the urinary bladder
SNS - inhibits bladder contraction
PSNS - stimulates bladder contraction
main blood supply: urinary bladder
Branches of the vaginal/prostatic a.
Cranial vesicle (br. of umbilical a.)
Hypogastric nerve innervation of the urinary bladder
SNS
controls physiological sphincter at the neck of the urinary bladder
name/list the nerve innervation of the urinary bladder
hypogastric nerve (SNS)
pelvic nerve (PSNS)
pudendal nerve (Somatic)
Pudendal nerve innervation of the urinary bladder
Somatic
Urethralis muscle - you can choose to hold your pee
name the muscle surrounding the pelvic urethra
Surrounded by urethralis muscle
Function of urethralis muscle
voluntary sphincter