Fundamentals of Human Genome
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What a primary care provider should know about in Genetics
Medical paradigm is changing
Genetic disorders may be treatable
Children w/ genetic disorders often become adults w/ genetic disorders
Clinical decisions will increasingly rely on the results of genetic tests
Family history can be a clue to risk
5 common misconceptions about Genetics
Genetics deals w/ only rare disorders
Deals w/ all types of disorders
Children should not be tested for genetic disorders
Should not be tested for genetic disorders that onset as adults, should be tested for genetic disorders that onset as children
Insurance does not pay for genetic testing
Does pay for genetic testing
Genetic testing leads to discrimination
By law, GINA protects every US citizen of discrimination based on genetic information
Genetic disorders are not treatable
May not be curable, but they are treatable
Mitochondrial genome
Very efficient b/c every gene encodes for something important to the cell’s function
Know every gene in this and its function
Nuclear genome
Genes and related sequences: 25% → 5% coding DNA, 95% non-coding DNA
Other DNA: “junk,” don’t understand it’s function (75%)
Has a unique pattern → can be used for paternity test or criminal testing
Gene and related sequences
Coding DNA: codes for protein
Goes through transcription and translation
Only mRNA goes through translation (why it’s called coding RNA)
Non-coding DNA: codes for a functional RNA molecule
Does not go through translation
Nucleic acids
Provide genetic material of cells and viruses
Sugar + Nitrogenous base + Phosphate group
4 types of bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine, thymine (T) in DNA or uracil (U) in RNA
Genes
DNA segments that carry the genetic information to make proteins or functional RNA molecules within the cells
Genome
Collective term for all the different DNA molecules within a cell or organism, distributed between the nucleus and the mitochondria
23,000 to 25,000 protein encoding genes in human genome
100,000 or more proteins
Transcriptome
Total set of transcripts in an organism; expressions of the genes modified by external influences (ex. phosphorylation)
Collects all the different types of RNAs that come out of DNA, which are the end product of transcription
Proteome
Protein variation & function expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism
Metabolome
Complete set of small molecule metabolites
Metabolic intermediates, hormones, and other signaling molecules
Metabolic waste products measured in blood and urine tests: Bilirubin, urea, creatinine
Microbiome (human)
Constellation of viruses, bacteria, and fungi that colonize various human tissues
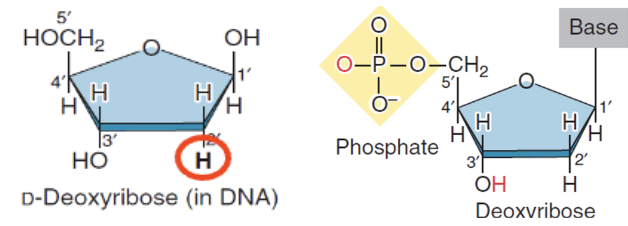
Deoxyribose sugar
Does NOT have oxygen at C2
In DNA
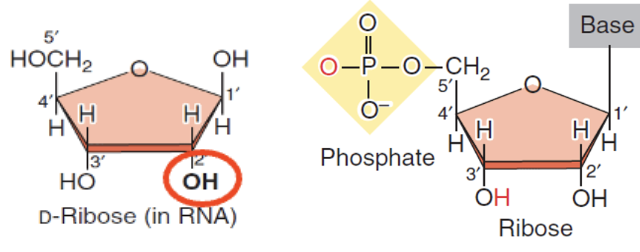
Ribose sugar
Oxygen at C2
In RNA
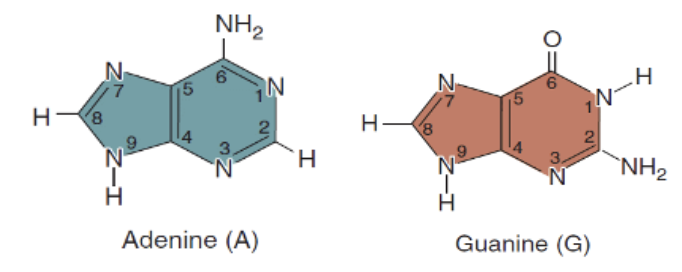
Purines
Double Ring
Adenine
Guanine
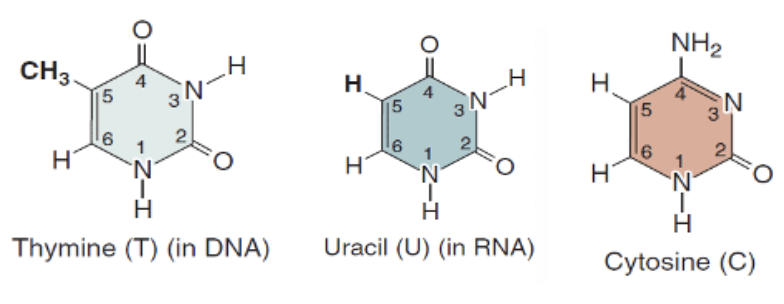
Pyrimidine
Single ring
Thymine (in DNA)
Uracil (in RNA)
Cytosine
DNA vs. RNA nitrogenous base composition
DNA: contains Thymine
Thymine is really stable → makes DNA stable
RNA: contains Uracil
Uracil is really unstable and can make unwanted bonds → makes RNA unstable
Chargaff’s rule
n(G) = n(C)
n(A) = n(T)
Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and ribose sugar are connected by ___
Covalent bonds
Phosphate and sugar is connected by a ___
phosphodiester bond
Sugar + nitrogenous base is connected by ___
glycosidic bond
DNA Replication (S phase)
Two strands of the double helix are unwound, and each strand is used to make a new complementary DNA copy
Semi-conservative b/c, at the end of DNA replication, the newly produced DNA strand has one strand from the parent and one newly synthesized strand
Simple: makes DNA copies that are transmitted from cell to cell and from parent to offspring
Key player in DNA replication
DNA poly III: enzyme that attaches new DNA nucleotides
High fluidity enzyme that rarely makes a mistake
Exonuclease usually fixes any mistakes that occur
Failure of exonuclease → DNA repair mechanisms kick in
If exonuclease and DNA repair mechanisms fail → apoptosis and cell death → live birth w/ disease
Transcription
Genes are used to make a single-stranded RNA copy that is complimentary in sequence to one of the DNA strands
Simple: produce RNA copy of a gene
Translation
Coding sequence of mRNA are used to make the polypeptide chain of a protein
Simple: produces a polypeptide using the information in mRNA
mRNA: temporary copy of a gene that contains information to make a polypeptide
Polypeptide: becomes part of a functional protein that contributes to an organism’s traits
Exons
Coding sequences; required for protein coding
Often contain a small amount of coding DNA
Introns
Noncoding DNA sequences; “useless”
Have some function but not needed for protein coding → usually gets spliced out b/c they are not wanted part of the code
5’ methylguanosine cap and 3’ poly-A tail function
Stability of the primary transcript
Protect mRNA from degradation by exonucleases
5’ methylguanosine cap not added = RNA easily destroyed by the nucleases present in the nucleus
Transportation of the primary transcript from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
Transcription happens in nucleus
Translation: ribosomes come and bind to start the protein synthesis (translation) process in the cytoplasm
Spicing
Process when introns are cleaved and the exons are tied together; cleaving the RNA transcript at the junctions b/w transcribed exons and introns
Removes introns, covalently link exons to create mature mRNA
Mature mRNA does not contain intron, only contains exons
Occurs after transcription in the nucleus
Spliceosome
Biomolecule that performs RNA splicing
Alternate splicing
Process of mix-matching exons to make alternate transcripts from the same gene
Creates multiple variants using different splicing patterns
Depending on how exons are attached together, you can make different proteins
What allows the 25k genes to make more than 100k different proteins
Posttranslational modification: Chemical modification
Additional of functional group to the protein chain
Ex. acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.
Posttranslational modification: Folding
Proper 3D structure (hydrophilic outside, hydrophobic inside)
Misfolded protein → increase ER stress → apoptosis
No apoptosis → accumulation of misfolded protein, causing cystic fibrosis, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, etc.
Posttranslational modification: Cleavage and transport
Transport to correct cellular location
Intracellular or extracellular locations
Cleavage: cutting the polypeptide chain after it has been synthesized like tailoring
Posttranslational modification: Binding of multiple polypeptide chains
Ex. Hemoglobin is made of 2 alpha and 2 beta chain, which are produced separately but are bound together b/c Hgb is a polypeptide w/ 4 lobes
Function of Hgb
Carry oxygen
Normal shaped RBCs
Bi-concaved disc → helps RBCs squeeze through tiny vasculature w/o getting clogged
Sickle Cell Disease
RBCs are sickle shape → clog and stop blood supply in the artery, causing painful crisis
Cause of SCD
Point Mutation in beta-globin (glutamate → valine) → Hgb crystallize in low O2 → Pleiotropy (MI, Stoke, Anemia)
Mutation is in the beta globin chain of the Hgb, NOT RBCs
Pleiotropy: single gene mutation that can result in a variety of clinical manifestations
SCD protects against ___
falciparum malaria
Rate and degree of sickling depends on 3 things
Mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
Higher MCHC = more crowded sickle Hb molecules → more likely to bump into each other and polymerize → faster and more severe sickling
Intracellular pH
High acidity/low pH = more sickling
Hgb releases more O2 readily in acidic conditions which makes it in the deoxygenated state for a longer amount of time
Transit time of RBCs through microvascular beds
Longer/slow transit time = more time spent deoxygenated → more sickling
Clinical features of SCD don’t develop until the baby is ___
6 months old
Clinical Features of SCD
Vasoocclusive crisis → pain crisis (bones, lungs, liver, brain)
Pain crisis depends on the blood vessel that is blocked
Acute chest syndrome, priapism, stroke
Retinopathy/blindness
“Autosplenecotomy”: spleen self infarction
Sickle cells obstruct blood supply to spleen and it can fall off and be detached
Chronic hypoxia → generalized impairment of growth and development → organ damage affecting the spleen, heart, kidneys, and lungs
Altered splenic function → susceptibility to infections
Functional splenectomy: spleen is alive but not functioning at all b/c blood supply is partially blocked
Spleen not functioning well → prone to infection, specifically w/ capsulated bacteria
SCD Epidemiology
Most prevalent in African countries
1/13 African-descent babies have the sickle cell trait
1/365 African descent babies have sickle cell disease
People w/ SCD typically live ____
A normal lifespan, but it’s difficult to manage as the patient need multiple blood transfusions
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Rare, fatal, genetic condition of childhood w/ striking features resembling premature aging
Chances of a child w/ Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
1 in 4-8 million
Only ~100 kids live with this
Cause of Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Sporadic Autosomal Dominant mutation; LMNA gene mutation
Appears spontaneously, not inherited from parents
Happens during the process of embryogenesis
Pathogenesis of Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Abnormal lamin A (Progerin) → abnormal nuclear envelope → cumulative cellular damage → abnormal aging process
Lamin A (Progerin)
Protein produced in the cytoplasm that is responsible for the proper function of the nuclear envelope
Farnesyl group is added to guide Lamin A to the nuclear membrane → after reaching the nuclear membrane, the farnesyl group must be cleaved
If not cleaved, it causes nuclear envelope instability → disrupt gene transcription → Progeria
Diagnosis of Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome happens around ___
2 years old
At birth, the baby appears normal
People w/ Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome typically pass away as a ___ d/t ___ or ____
teen d/t stroke or heart disease
Treatment of Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Farnesyl inhibitor stopping farnesylation
NOT ideal
May not reach the nuclear envelope b/c farnesylation is required for it to reach the nuclear envelope
Extends lifespan anywhere from 3 months-2 years
Clinical Features of Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Progressive atherosclerosis and associated cardiovascular abnormalities → life-threatening complications
Old people symptoms: bald, cataract (clouding of eyes), lose elasticity of skin, osteoporosis, arthritis
Other Conditions w/ Lamin A Mutations:
Emery-Dreifuss MD/Skeletal myopathy
Progressive AV block and atrial arrhythmias
Worst prognosis when you have a LMNA mutation and DCM (dilated cardiomyopathy)
LMNA mutation w/ DCM is worse than just DCM by itself
Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Most common lethal inherited disease in Caucasians
Cause of CF
Defect in the CFTR gene leading to misfolded proteins, causing abnormalities of cAMP-regulated chloride transport across epithelial cells on mucosal surfaces
Inability to conduct chloride properly
Importance of Chloride Channels
Required to maintain the fluid nature of your secretions → flowing freely, liquidy = no obstruction
Defective → secretions become thick → obstructions → does not reach place it needs to do its function
Chloride ions not getting into secretion → sodium and water is also not getting into the secretion → secretions become thick
In all tissues, the chloride channel conducts the chloride from inside the cell to the outside (lumen) of the cell
Except sweat glands are the opposite
Inheritance of CF
Autosomal recessive
Organs affected in CF
Lungs (primary), pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestines
Effect on Lungs: ↓Cl- transport, ↑Na2+ absorption, ↑H2O absorption, ↓ciliary clearance
GI Symptoms of CF
Abdominal distention and Intestinal obstruction
Not enough water content → abdominal distention, intestinal obstruction, paste-like feces
Increased frequency of stools
Failure to thrive
Flatulence or foul-smelling flatus, steatorrhea (lipid in the poop)
Lipase stuck in pancreas → lipid not metabolized → steatorrhea
Recurrent abdominal pain
Jaundice
Gallbladder is not able to secrete bile → bile accumulation, backing up into the blood → hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice)
GI bleeding
Pancreatic secretions are required to neutralize the acid
Acid not neutralized → erode the membrane → GI bleeding
Genitourinary symptoms of CF
Undescended testicles or hydrocele
Delayed secondary sexual development
Amenorrhea (absence of menstrual cycle) in females
Infertility in males
Super thick mucus stops sperm motility
Respiratory Symptoms in CF
Major cause of death in CF → respiratory infection leading to respiratory failure (lung has a lot of secretions that can invite infections)
Cough
Recurrent wheezing
Recurrent pneumonia
Atypical asthma
Dyspnea on exertion
Chest pain
Epidemiology of CF
40-50k Americans live w/ CF
1/2500 live births in North America have the disease
Typically die around 30-40s d/t respiratory depression
MODY (maturity onset diabetes of the young)
Mutation in HNF4A gene –defective transcription→ degradation of mutated transcripts → defective pancreas and beta-cell function → MODY
Inheritance of MODY
Autosomal dominant, Monogenic
Cause of MODY
HNF4A gene mutation → quantity of beta cells and ability to secrete insulin affected
HNF4A: maintains the pancreatic beta cell mass and function; maintains the proper quantity of beta cells and secrete insulin
MODY is typically suspected in patients ____ years old w/ ___
<30 years old w/ diabetes
Prevalence of MODY
2-5% d/t it being largely undiagnosed d/t not much clinical practitioners knowledge of MODY
T2D
Mutation in PPARa/ABCC8/KCNJ11 gene → defective insulin secretion/sensitivity → Type II DM
PPARa: transcription factor required for maintaining insulin sensitivity
ABCC8/KCNJ11: potassium channels required for insulin secretion
Onset of T2D
>40 years old in Caucasians
Inheritance of T2D
Polygenic
T1D
Autoimmune, lack of insulin
Onset of T1D
20s (<30 years old)
Young onset, No autoimmune antibodies in blood test = ___
MODY
Inheritance of T1D
Polygenic
Metformin
Reduce gluconeogenesis, increase insulin sensitivity, reduce insulin resistance
Metformin, which improves insulin sensitivity, is less effective in MODY as the primary problem is insufficient insulin secretion
Treatment of MODY
Most MODY patients have issues with insulin release rather than insulin resistance, making sulfonylureas more effective
Use sulfonylureas to start production of insulin before starting use of insulin in their 20s
Give insulin = chance of hypoglycemia
Prevented through giving an oral meds like sulfonylureas as long as they do not have a sulfur allergy