Unit 11: Chemical Reactions - Key Terms and Definitions for Engineering Studies
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Endothermic
A chemical reaction that absorbs heat. Feels cold to the touch.

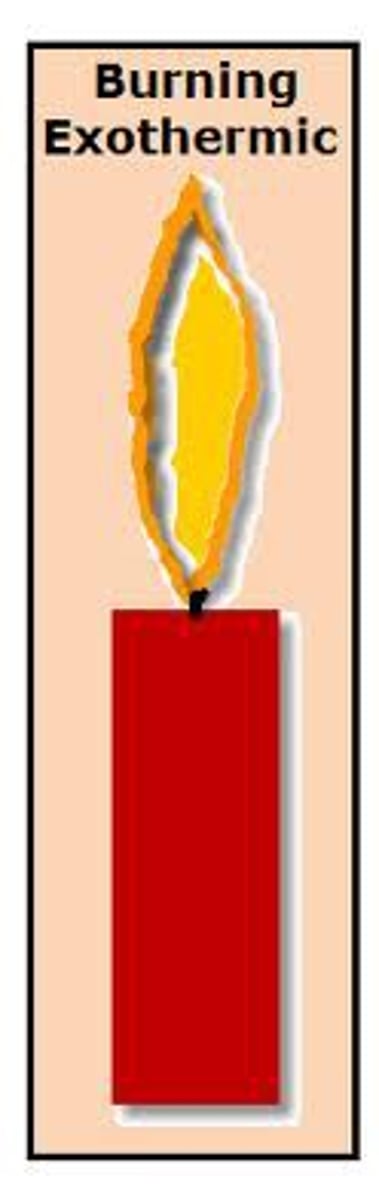
Exothermic
A chemical reaction in which energy is released. Feels warm to the touch.
Subscript
The smaller number in a chemical formula representing the number of atoms of a particular element in that element or compound.
Chemical Formula
A symbolic representation of a compound. Examples: NaCl (table salt), and H2O (water)

Chemical Reaction
A process that involves breaking of bonds in the reactants and forming new bonds in the products. (like baking or burning)
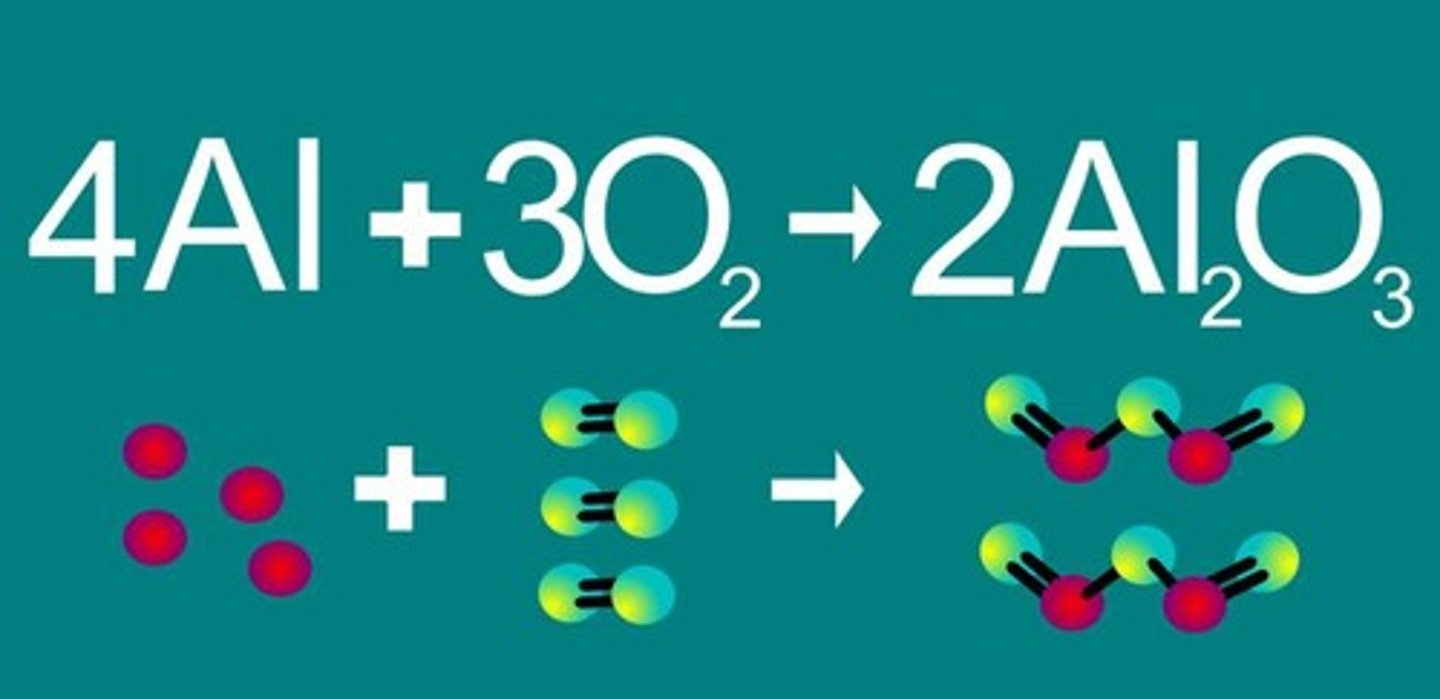
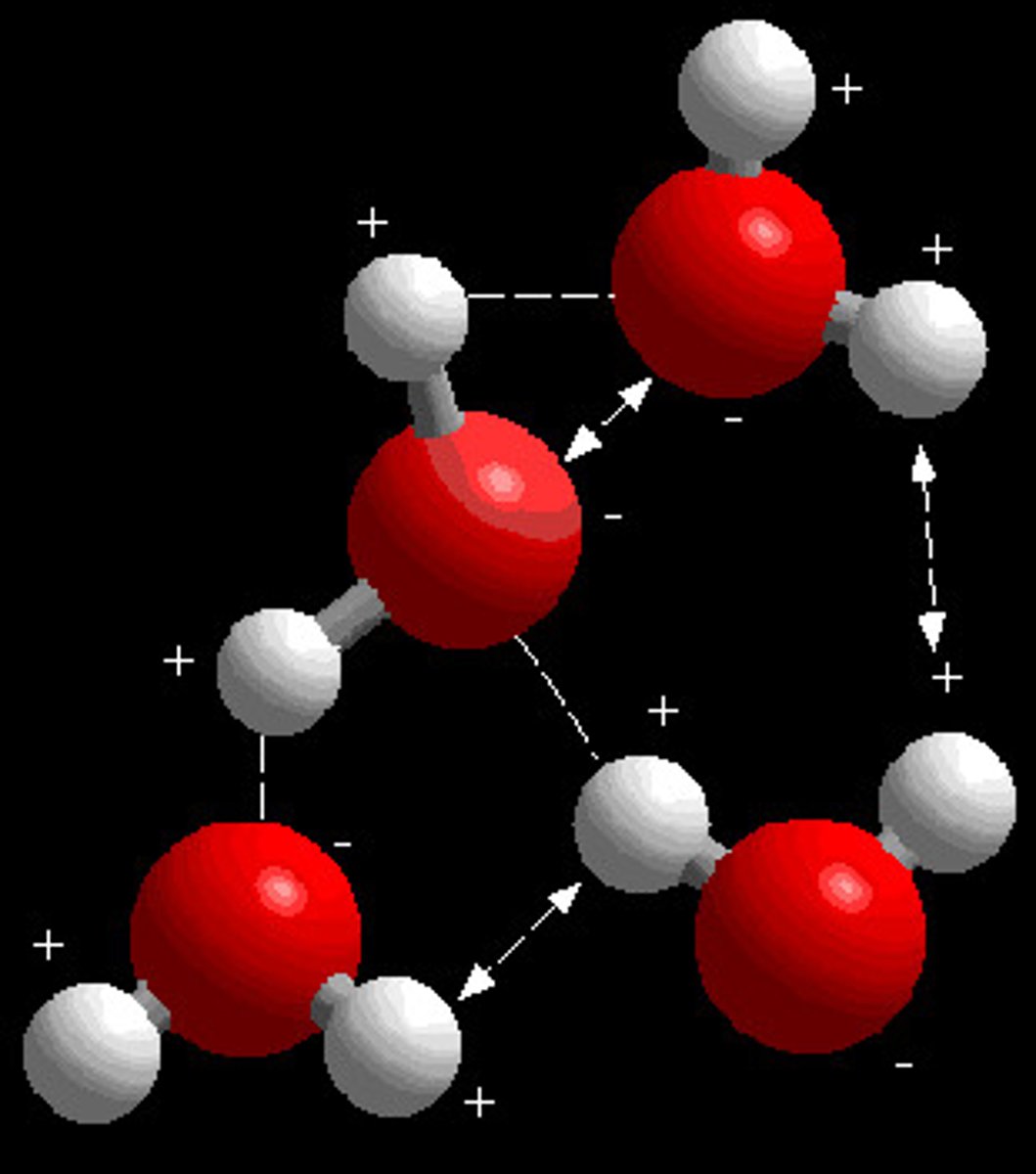
Chemical Bond
Holds two or more atoms together in a molecule.
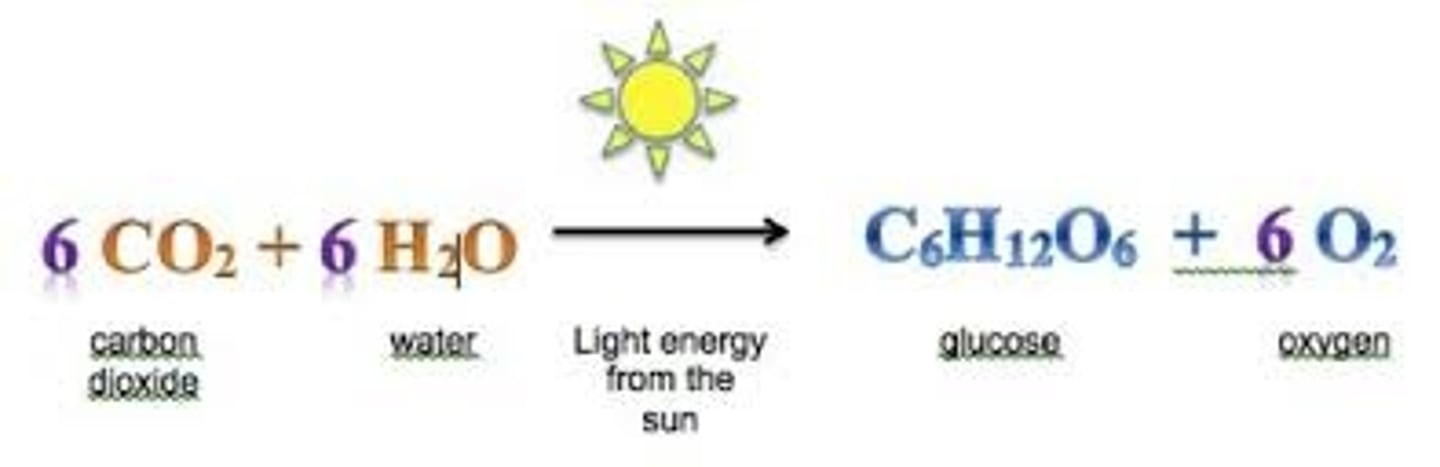
Chemical Equation
A representation of a chemical reaction that uses symbols to show the relationship between the reactants and the products.
Reactants
The substances or molecules that participates in a chemical reaction. Found on the left side of a chemical equation.

Products
The newly formed substance(s) as a result of a chemical reaction. Found on the right side of a chemical equation.
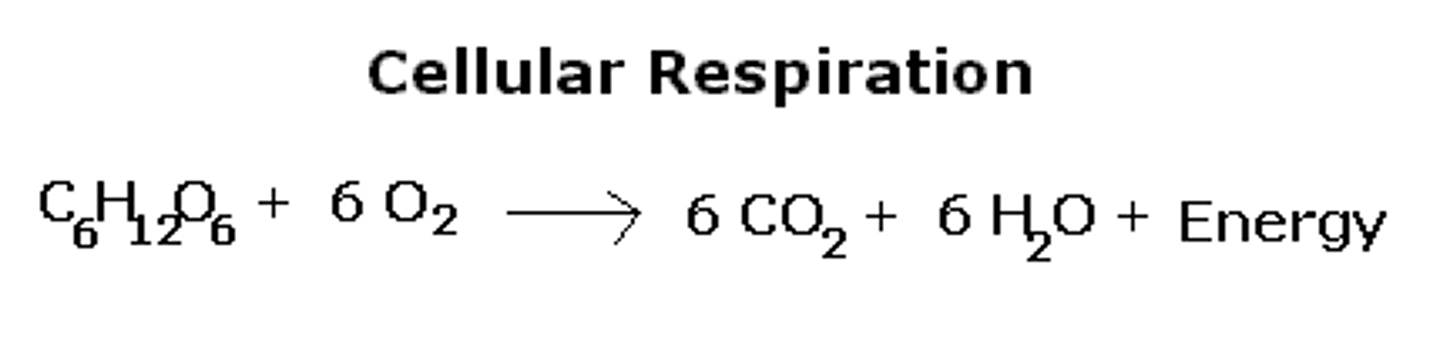
Coefficient
The larger number placed in front of a formula in an equation to indicate the amount of that substance.
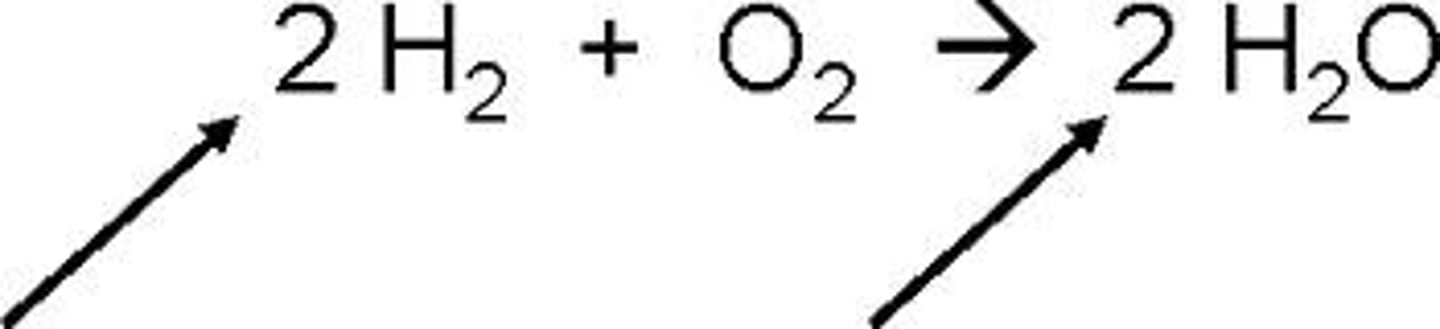
Catalyst
This is something that helps a reaction get started and speeds it up. It is NOT one of the reactants.
Balanced Equation
This occurs when both sides have the same number of atoms.
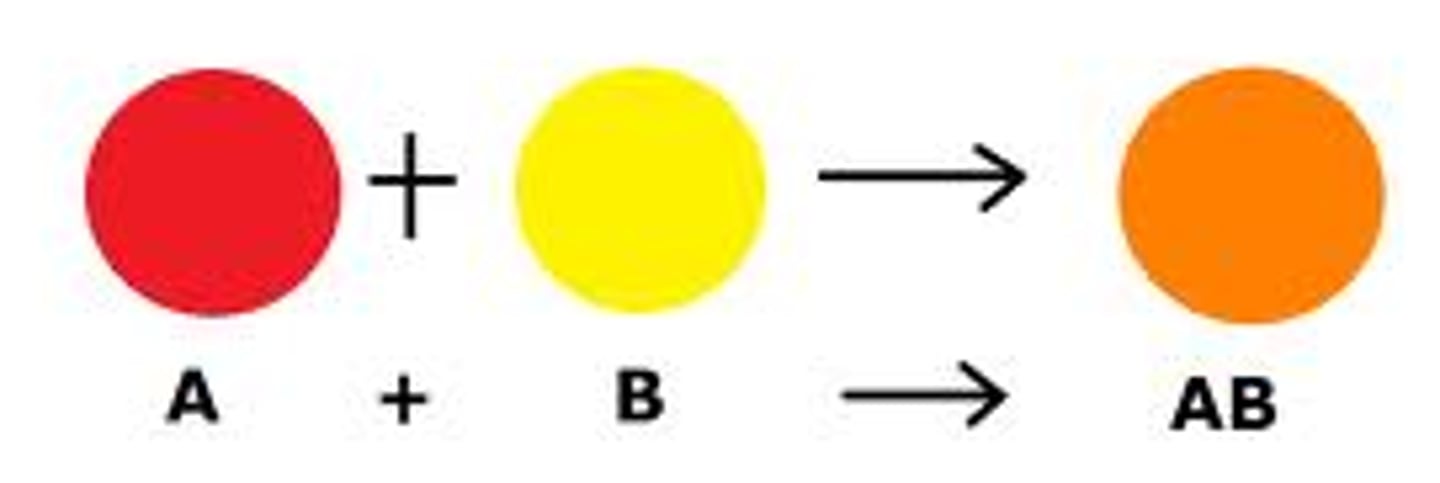
Synthesis
Two or more substances combine to form another substance.
Decomposition
One substance breaks down into two or more substances.

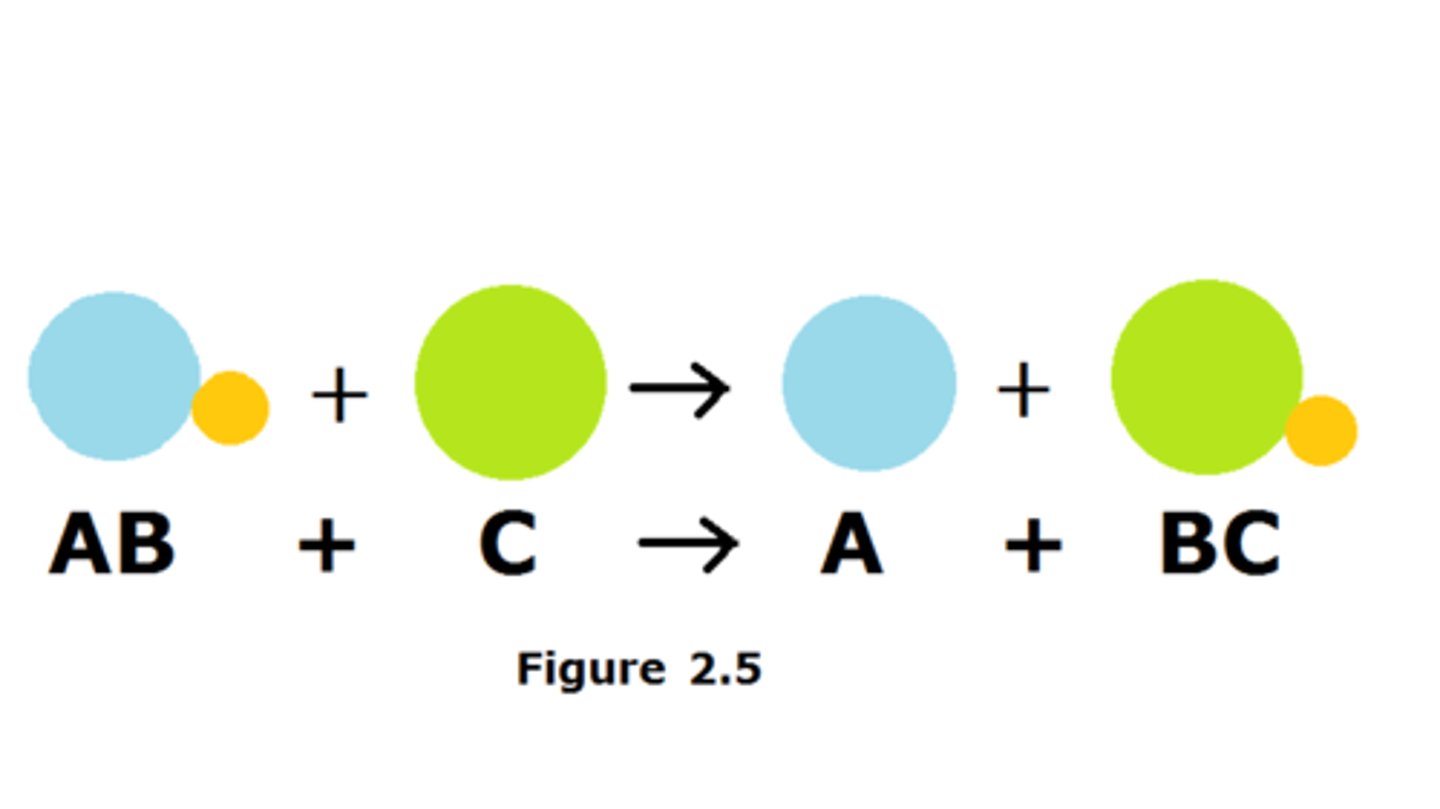
Single Displacement
One element replaces another element in a compound (single element reacting with a compound)
Chemical Change
6 signs of this are as following: change in temperature, change in odor, change in color, formation of gas (bubbles, formation of light, and formation of a precipitate (a solid formed by mixing two liquids)
Double Displacement
One element replaces another element in two compounds (two compounds reacting with each other)
Diatomic Element
An element that has 2 atoms bonded together. hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine