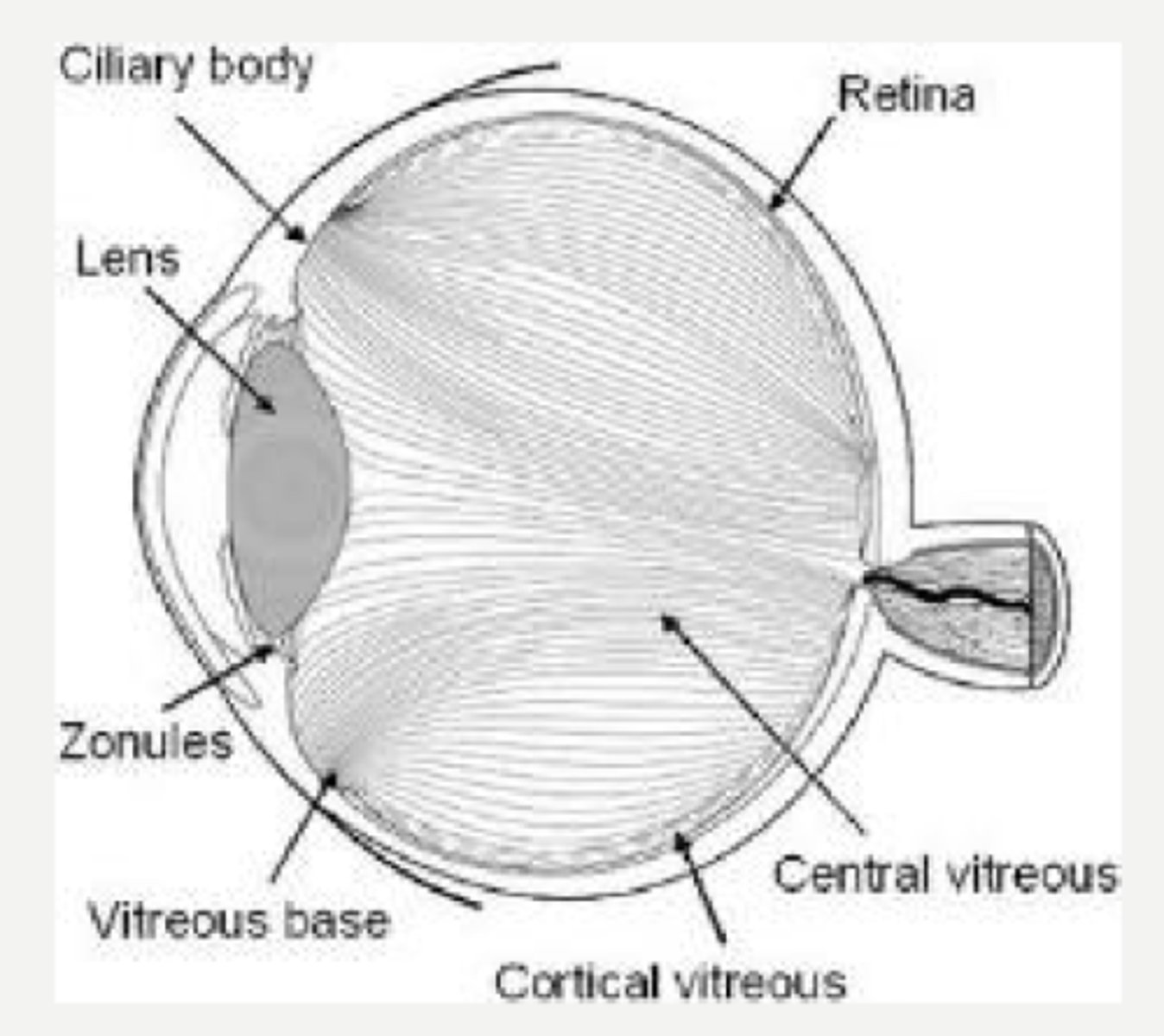
1 - Vitreous
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
75%
The vitreous makes up _______% of the ocular volume in the vitreous chamber.
water
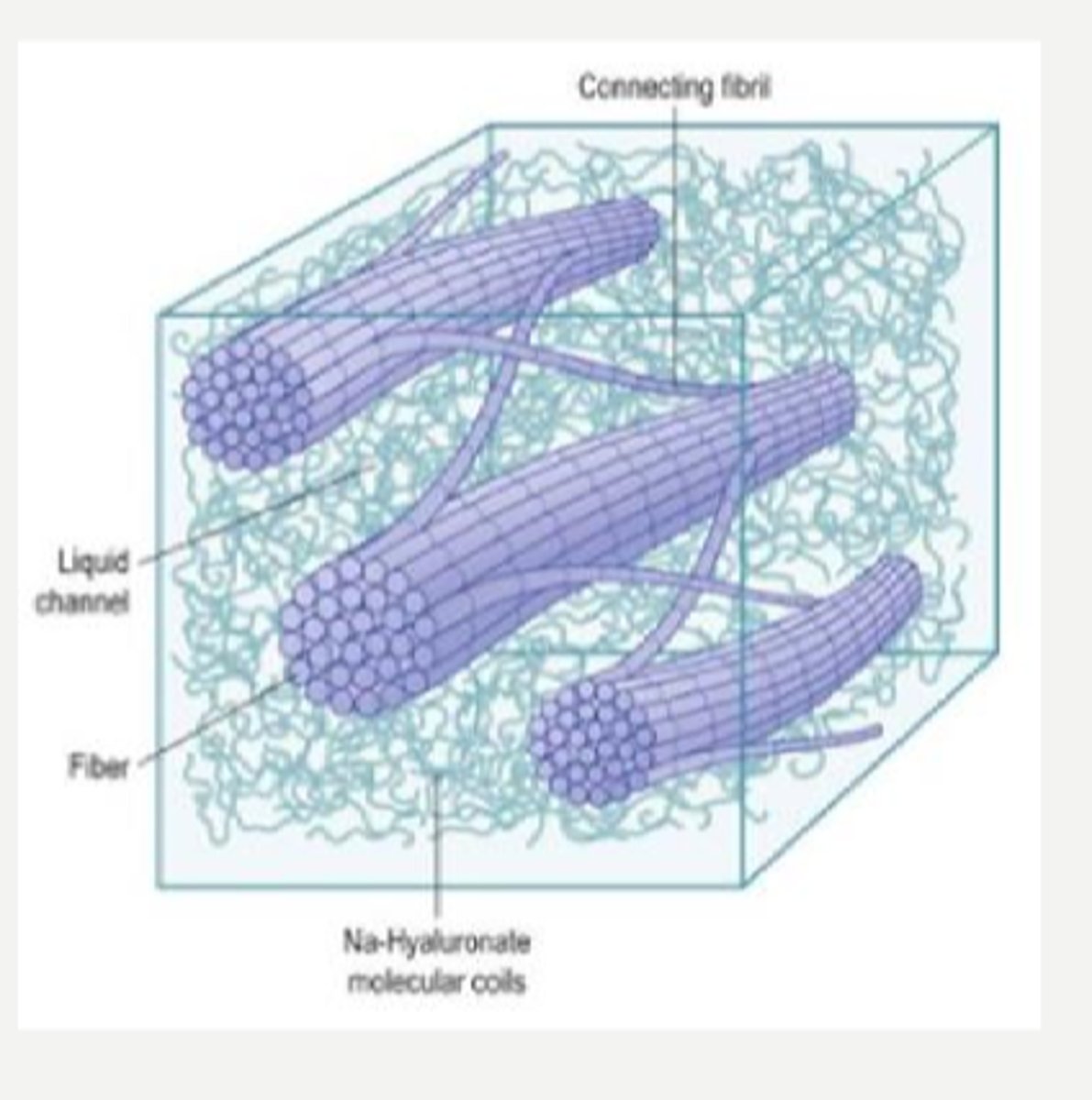
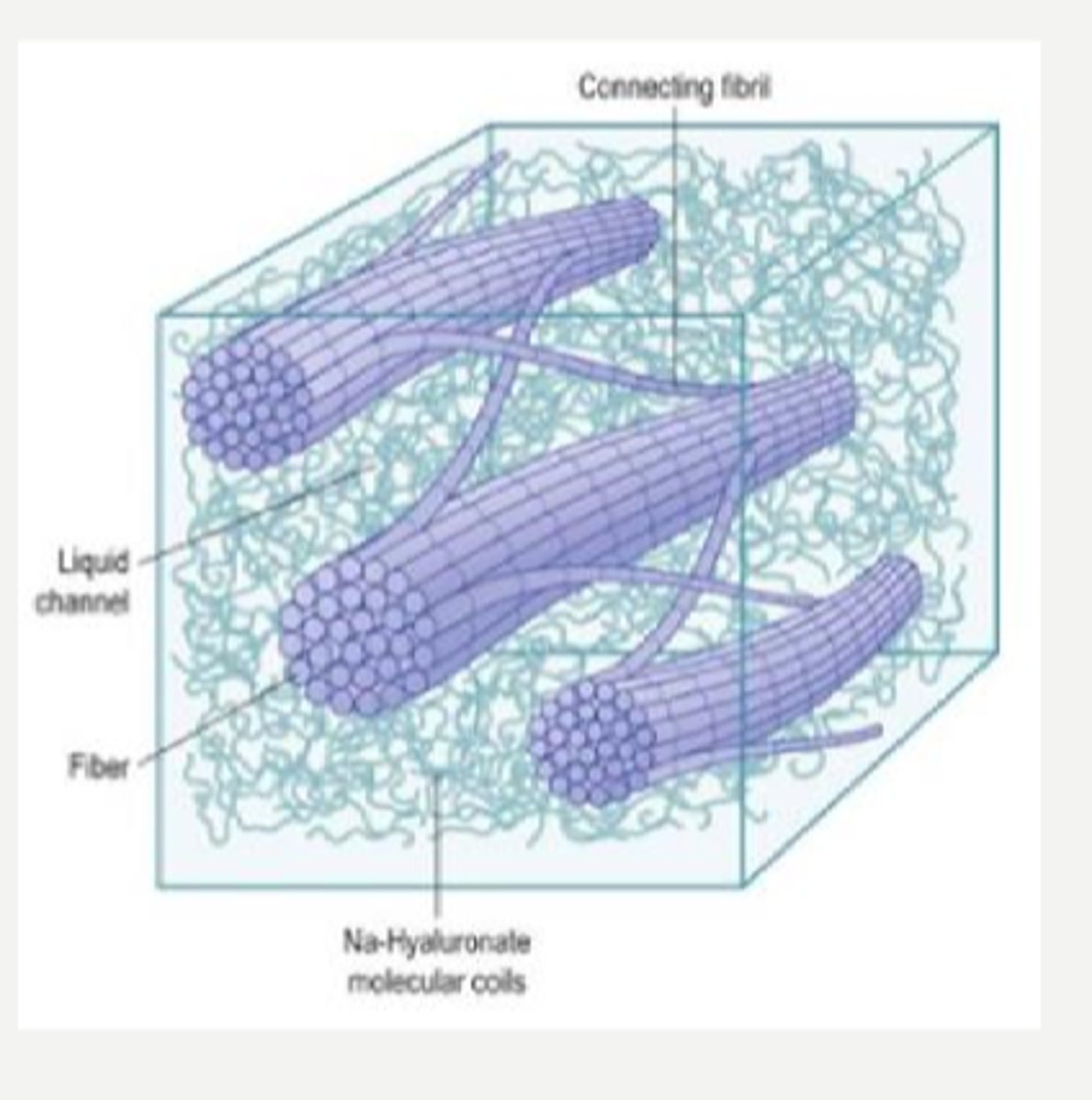
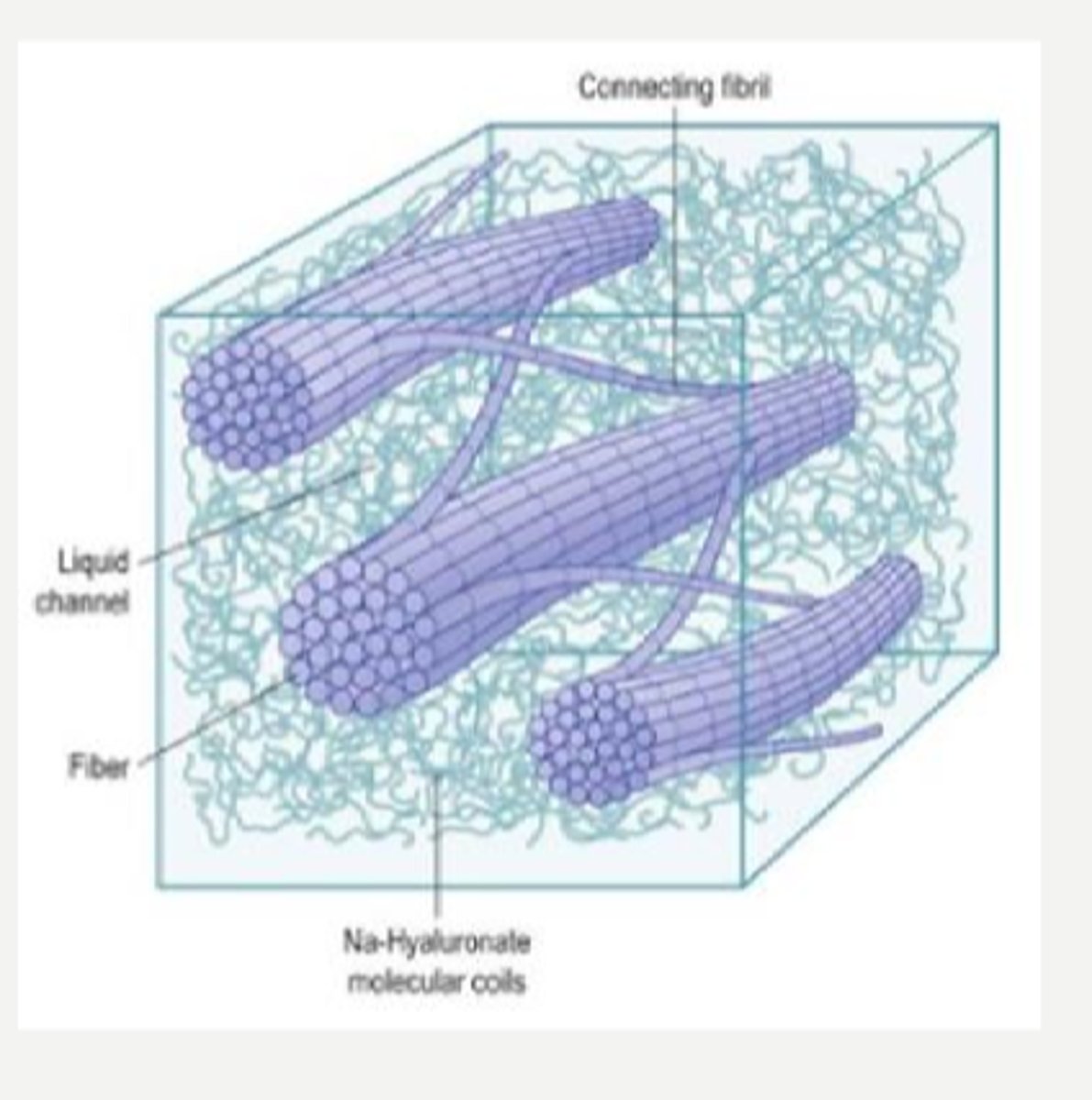
What makes up 99% of the vitreous contents?
collagen, mostly type 2 = fibrils are mostly bound in a gel structure
GAGs = hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate
cells
inorganic salts
small organic molecules
soluble proteins albumin and globulin
Aside from water, what other things make up the vitreous?
transparency
spacing between fibrils
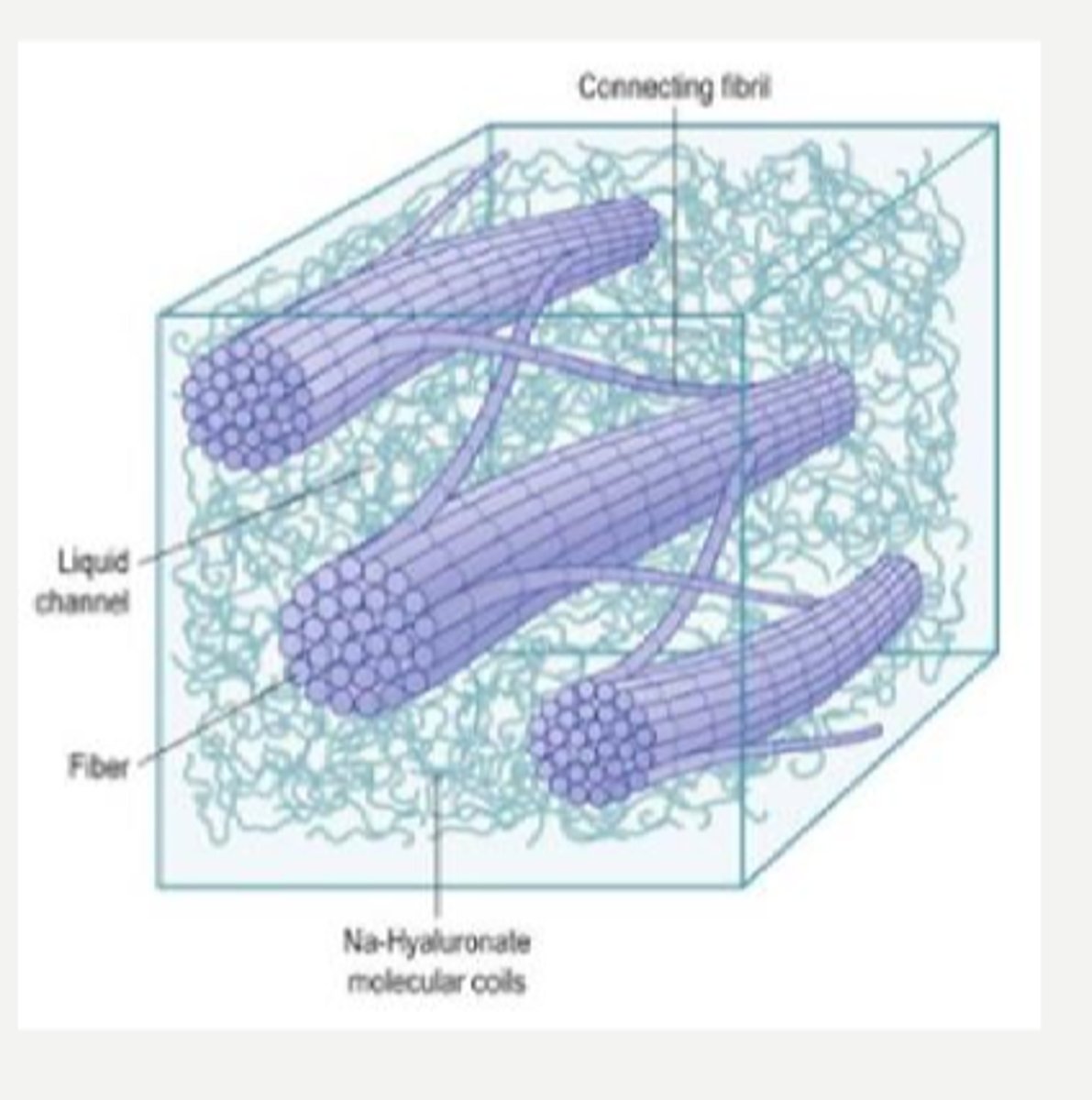
What are the 2 main functions of the GAG hyaluronic acid?
spacing between fibrils
NOTE: lower [ ] than hyaluronic acid
What is the main function of the GAG chondroitin sulfate?
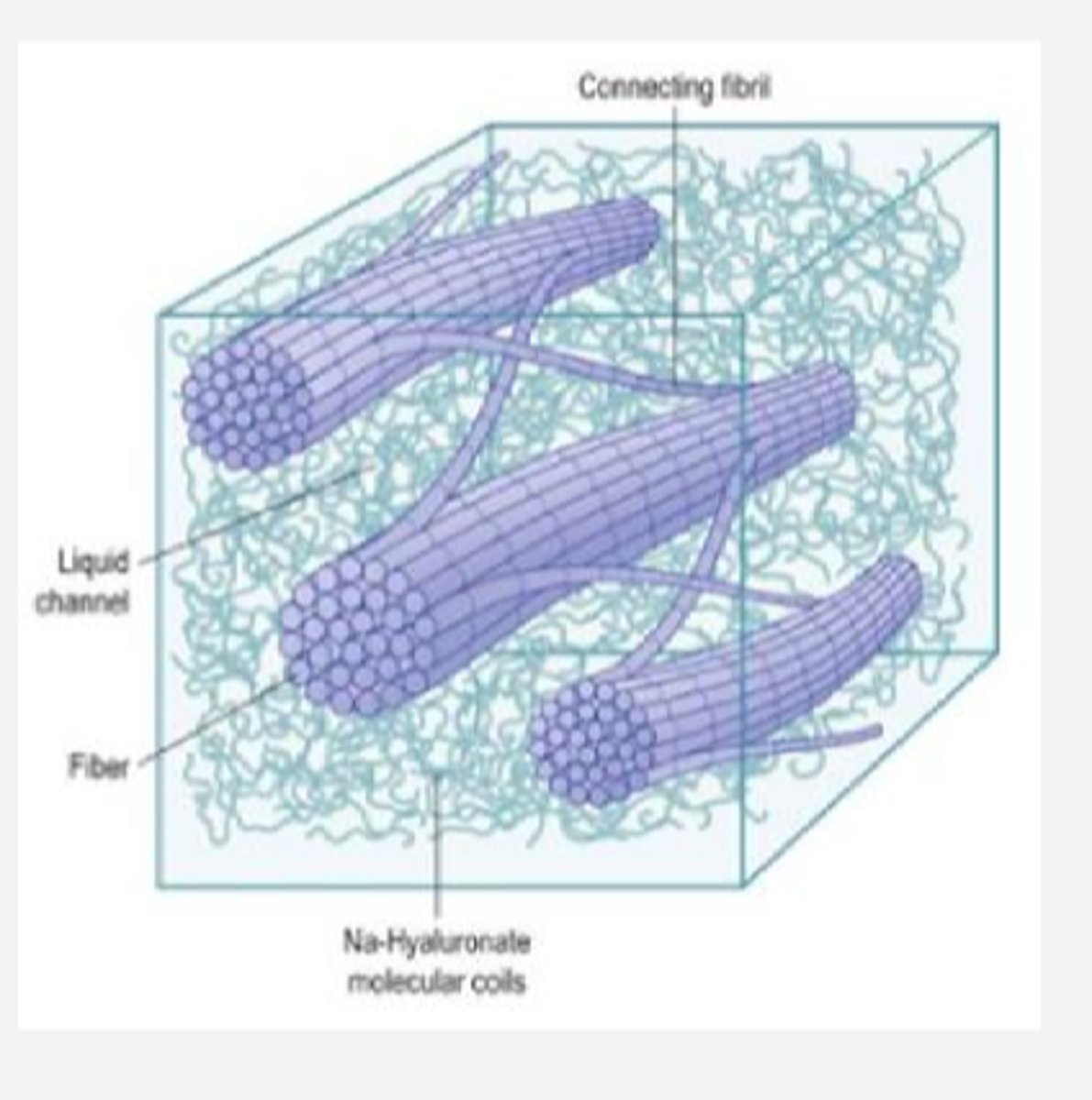
hyaluronic acid and vitrosin
What 2 things create an elastic property in the vitreous?
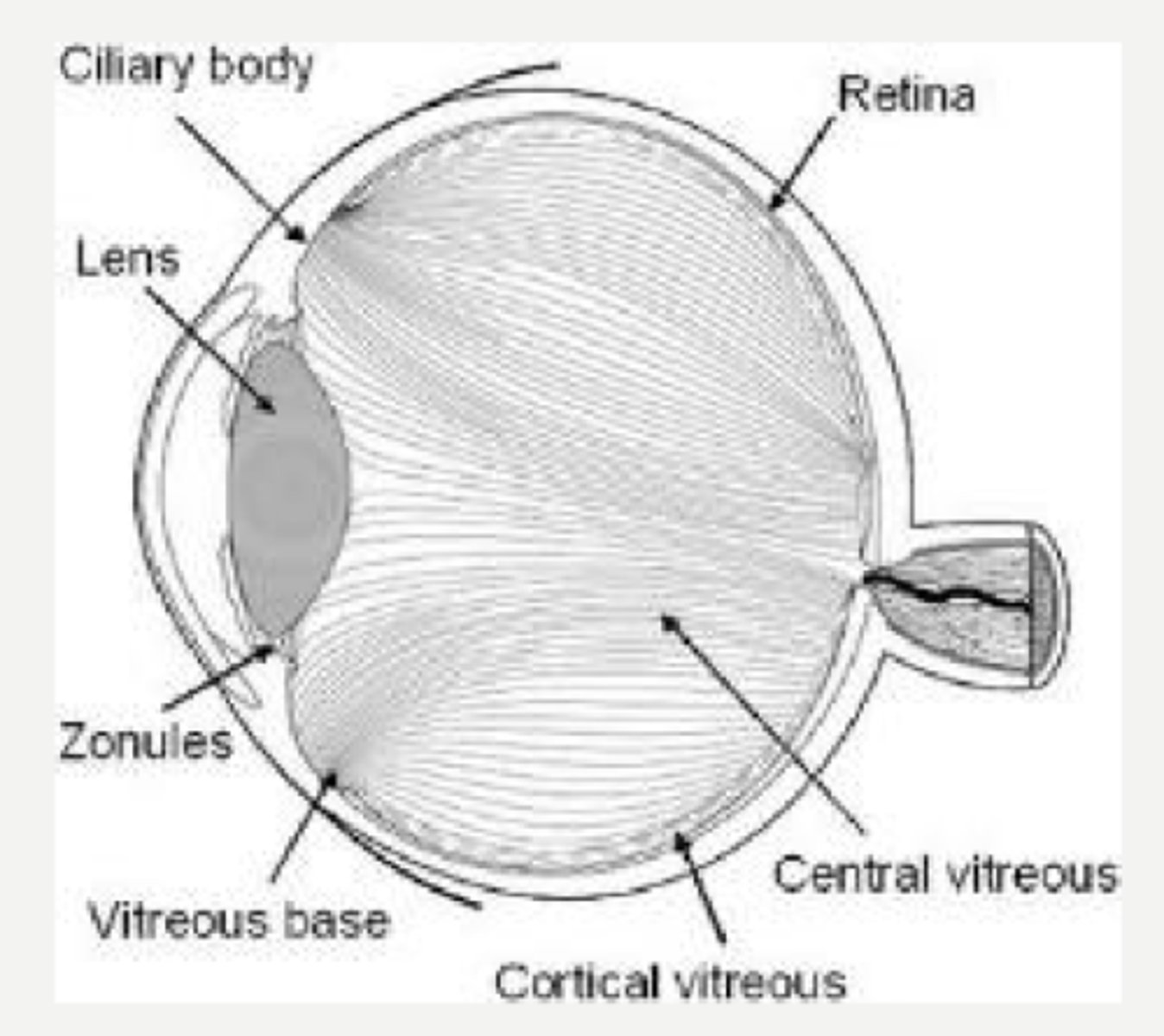
anterior to posterior, being densest around the edges
Explain the pattern that the collagen fibrils run in the vitreous
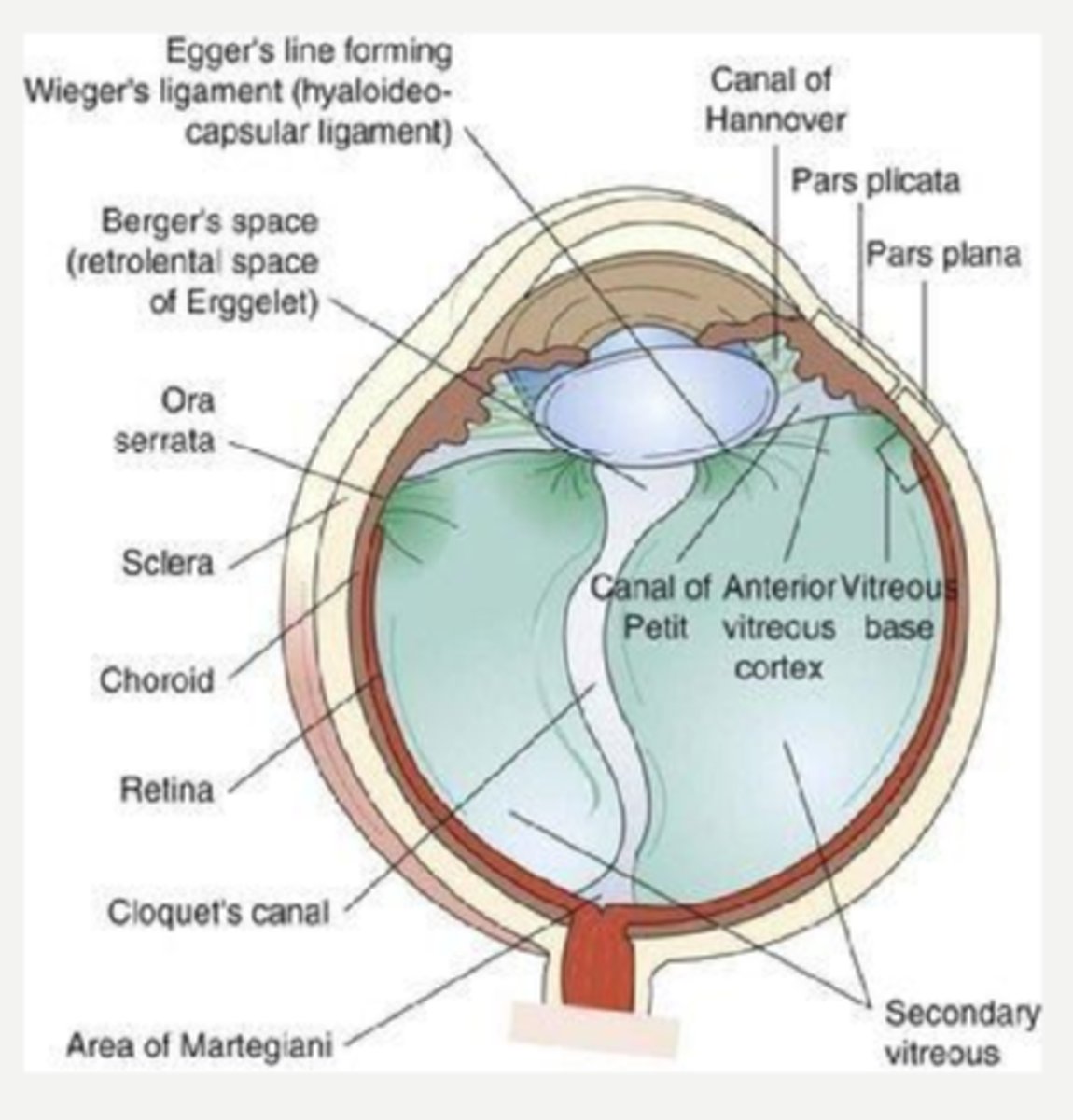
STRONG
vitreous base near ora
Wieger's ligament on posterior lens (forms Egger's line)
ONH
macula
retinal BV
WEAK
Rank the adhesion locations of the vitreous cortex from strongest to weakest.
area between the attachments at Wieger's ligament
What forms Berger's space
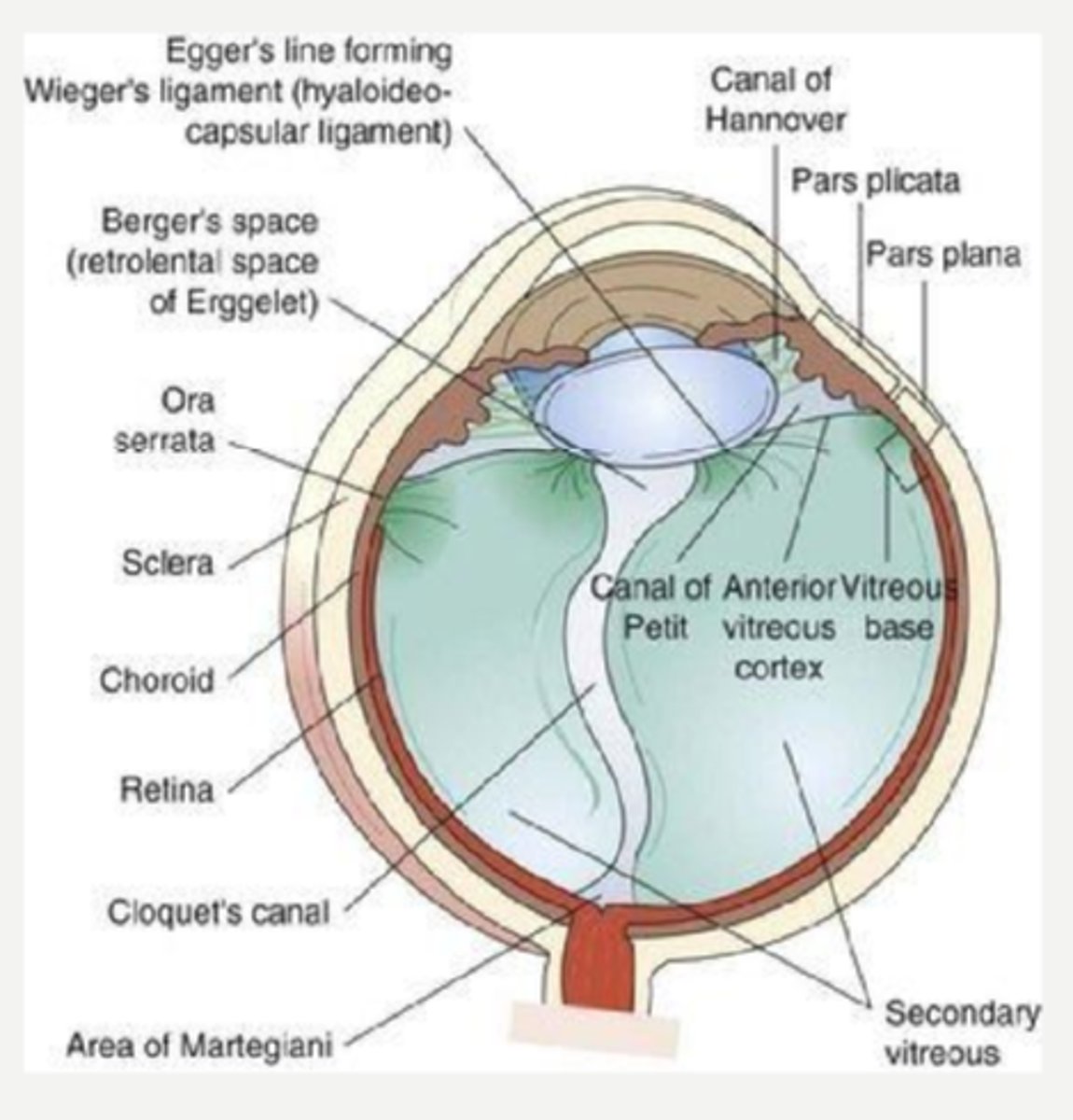
condensation of collagen fibrils
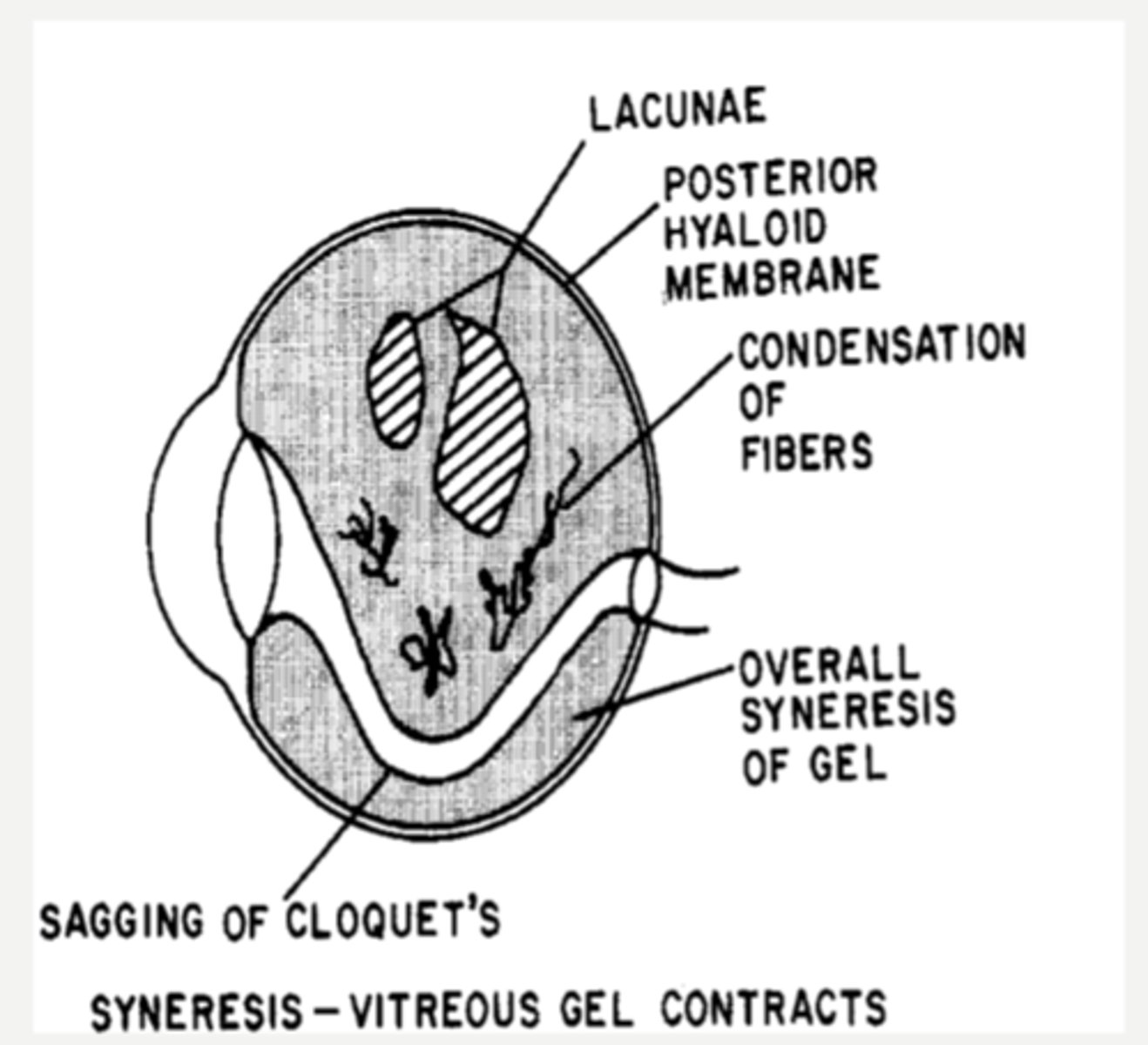
What causes floaters in the vitreous?
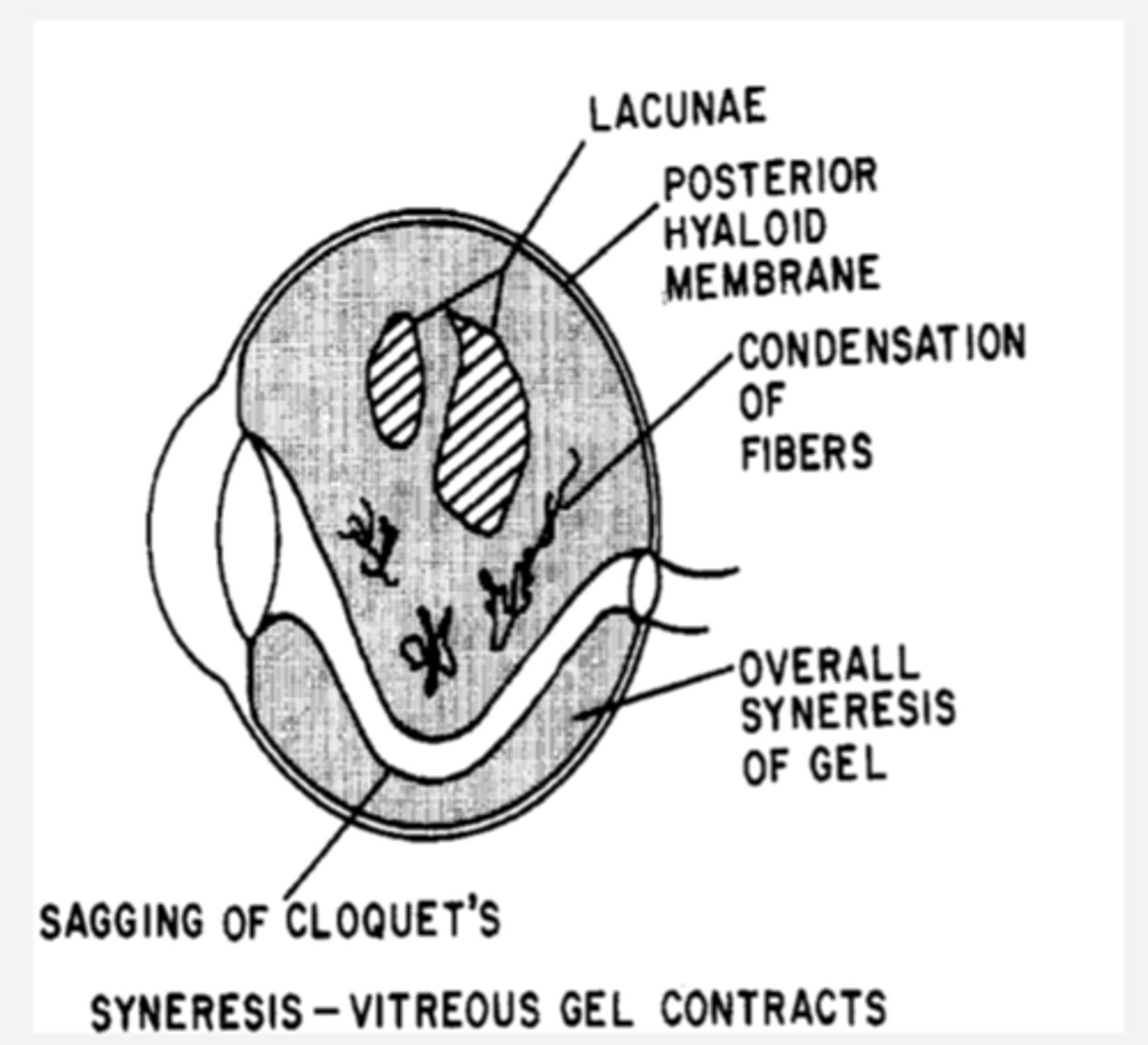
hyaluronic acid depolymerizes = breaks down the gel = vitreous liquefaction, fibril condensation, lacunae (liquid pockets) form
What causes synchysis senilis in the vitreous?
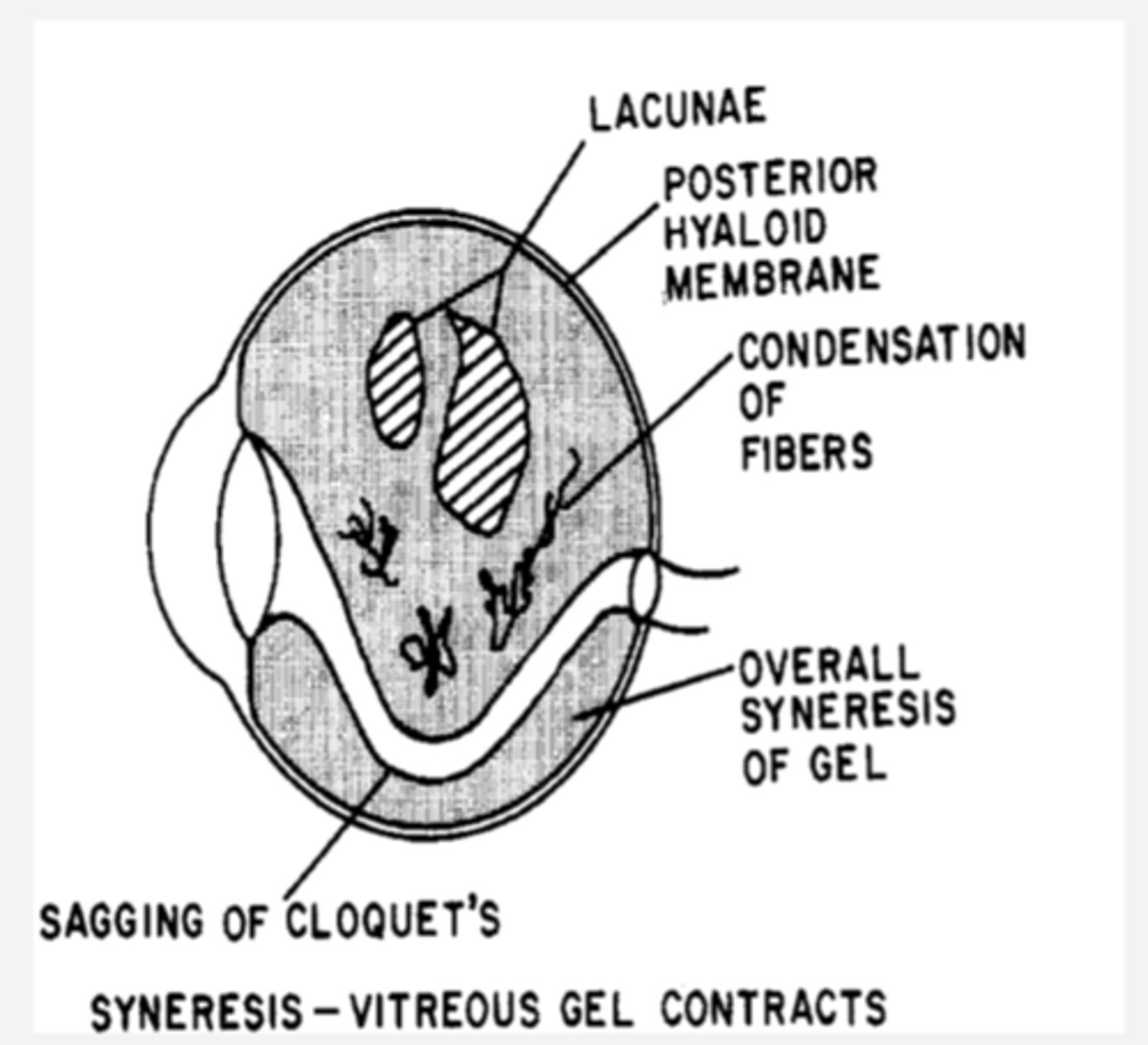
shrinkage of vitreous as solids and liquids separate
What causes syneresis in the vitreous?
before age 50 = 25% liquid
after age 60 = 62% liquid
How does the % liquid content of the vitreous change before age 50 vs after age 60?
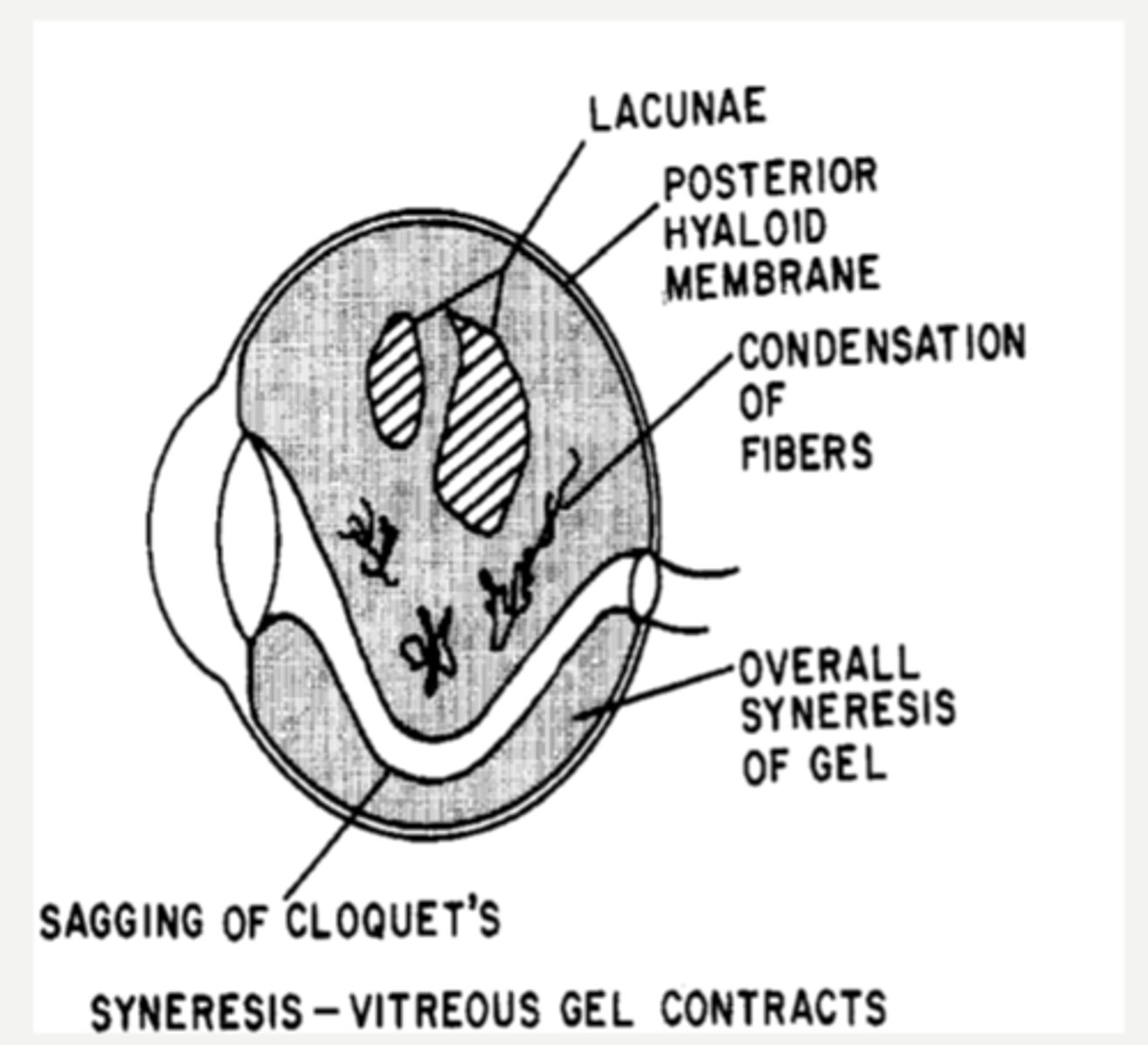
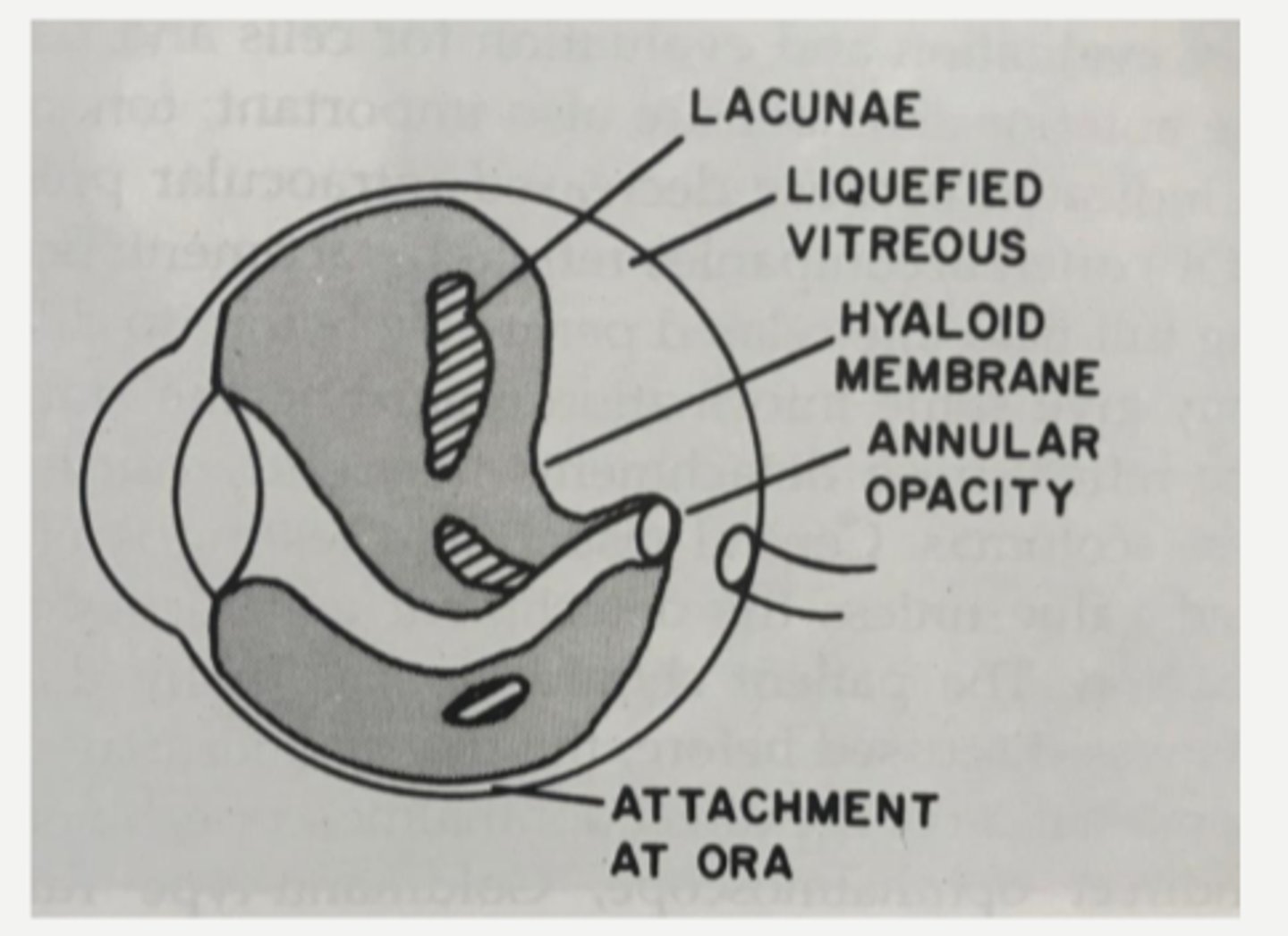
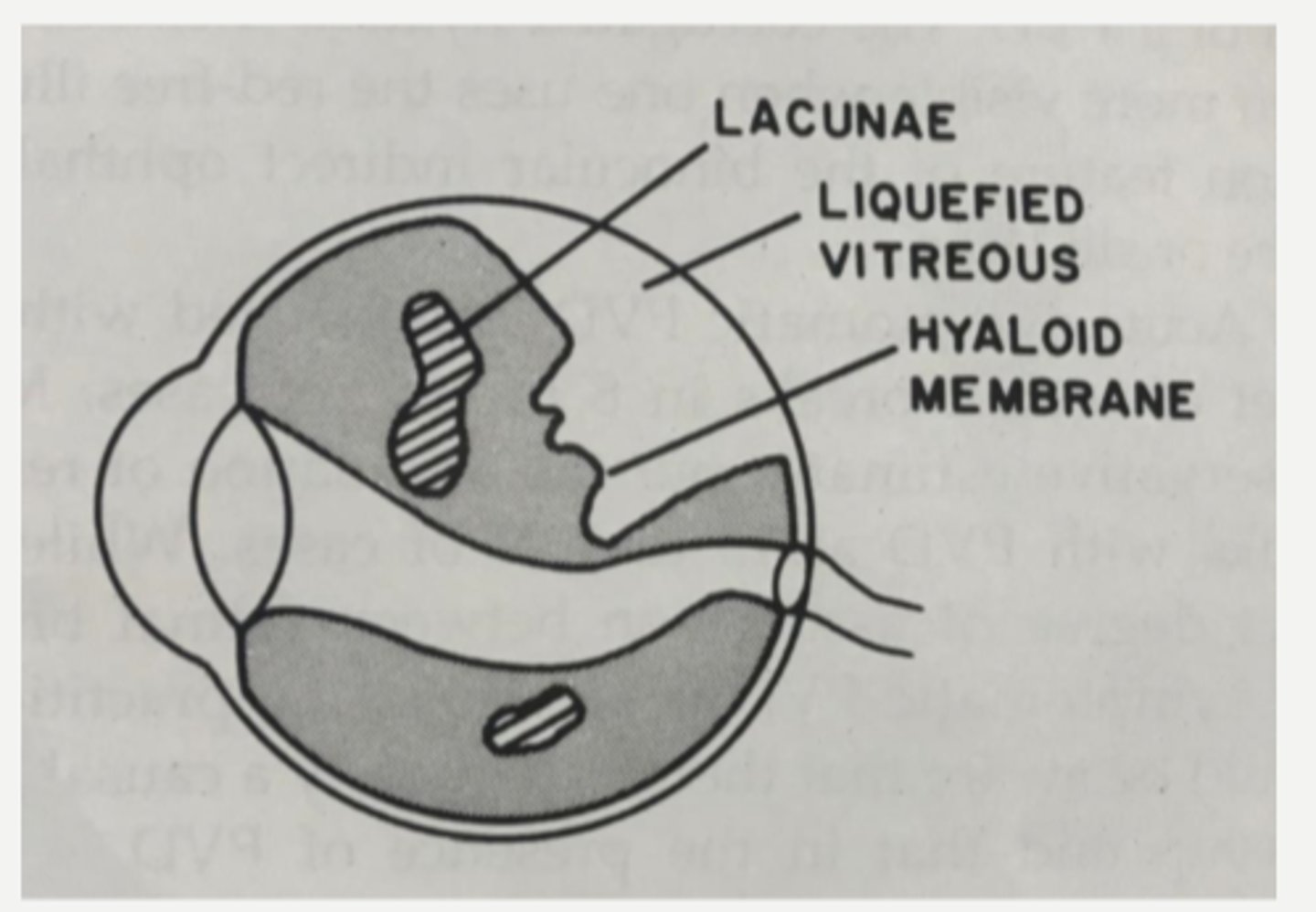
lacunae of liquified vitreous
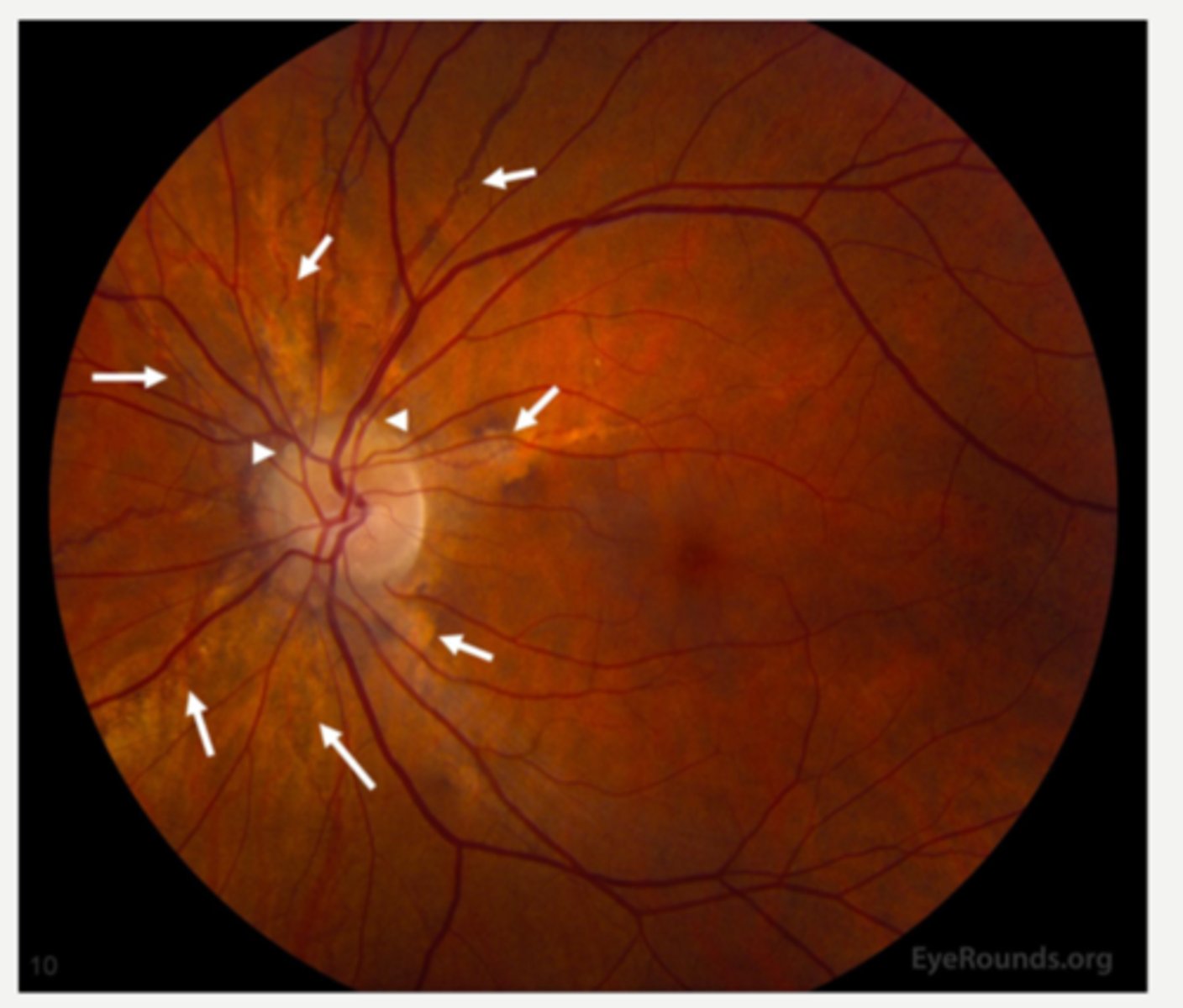
What aging change in the vitreous is shown by the stars in this image?
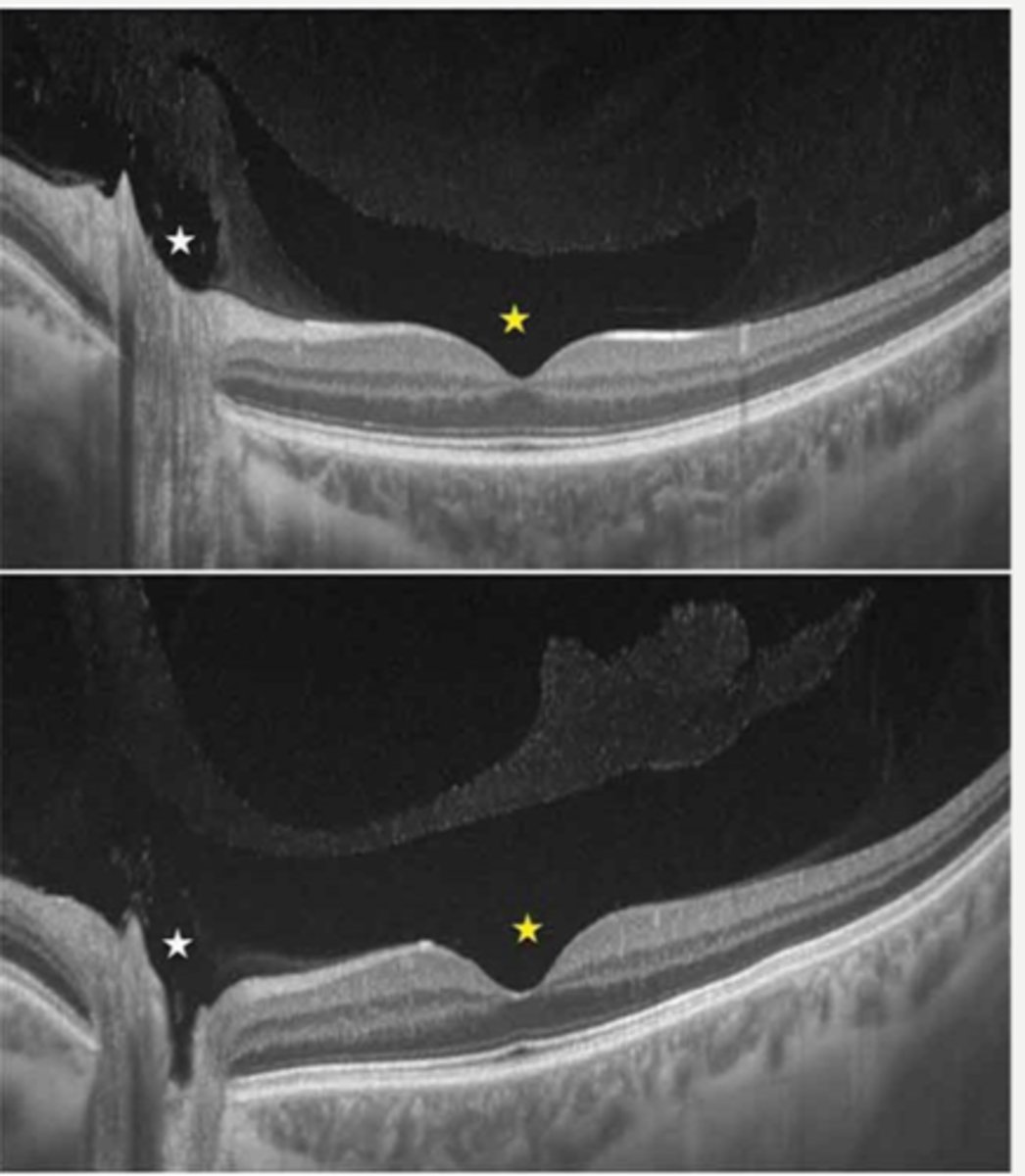
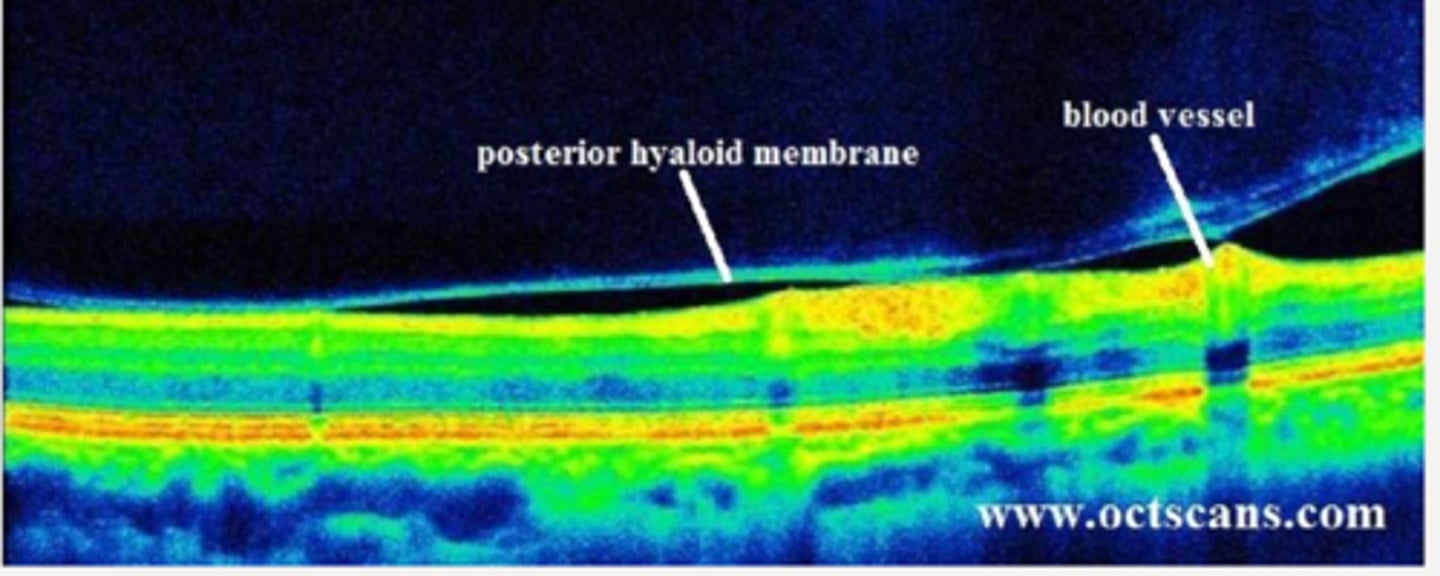
posterior vitreous detachment
What condition is shown here?
hyaloid membrane separates from retina at the area posterior to the vitreous base
What is a PVD?
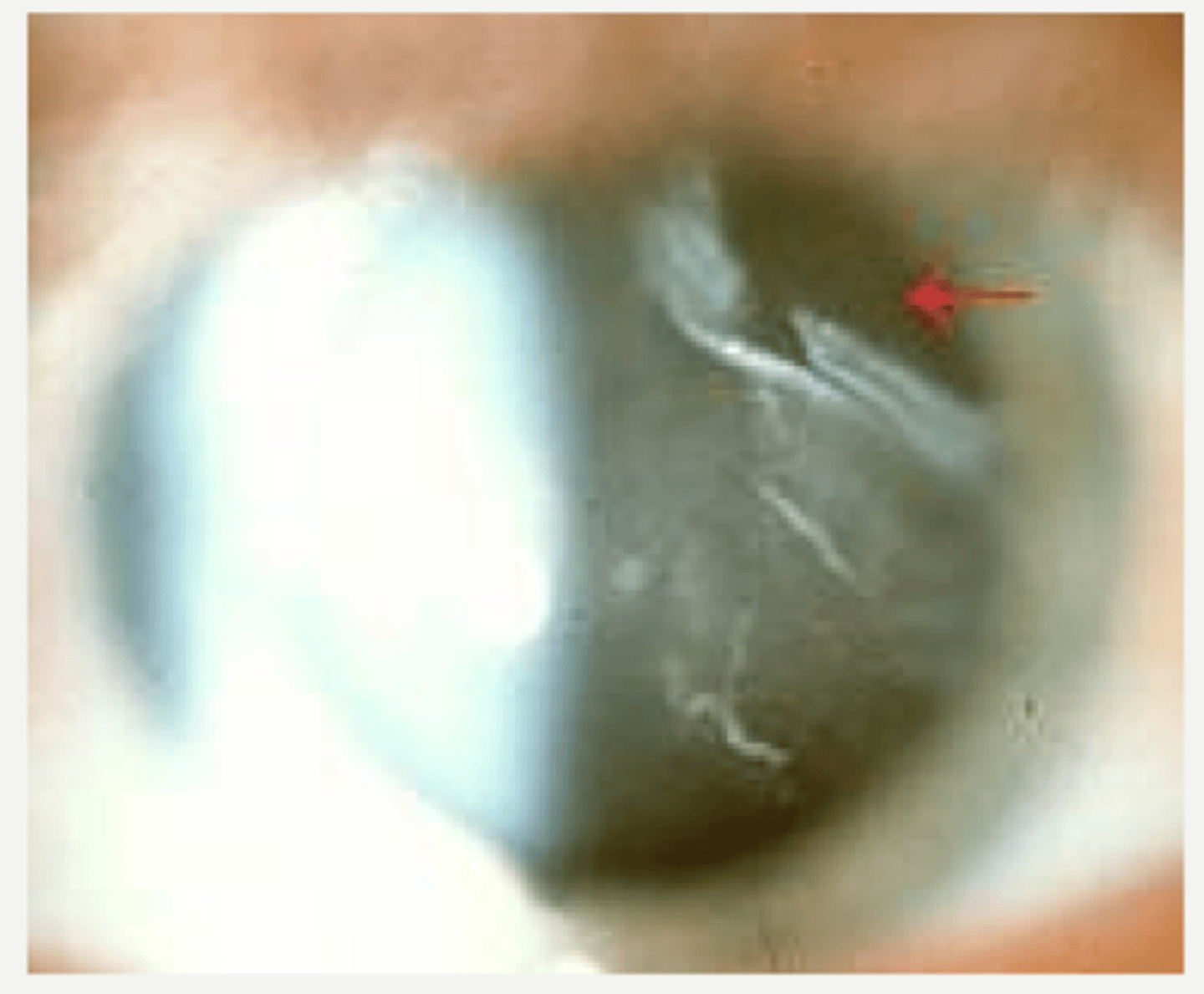
>45 years old
women
What are the demographics of who is most affected by PVD?
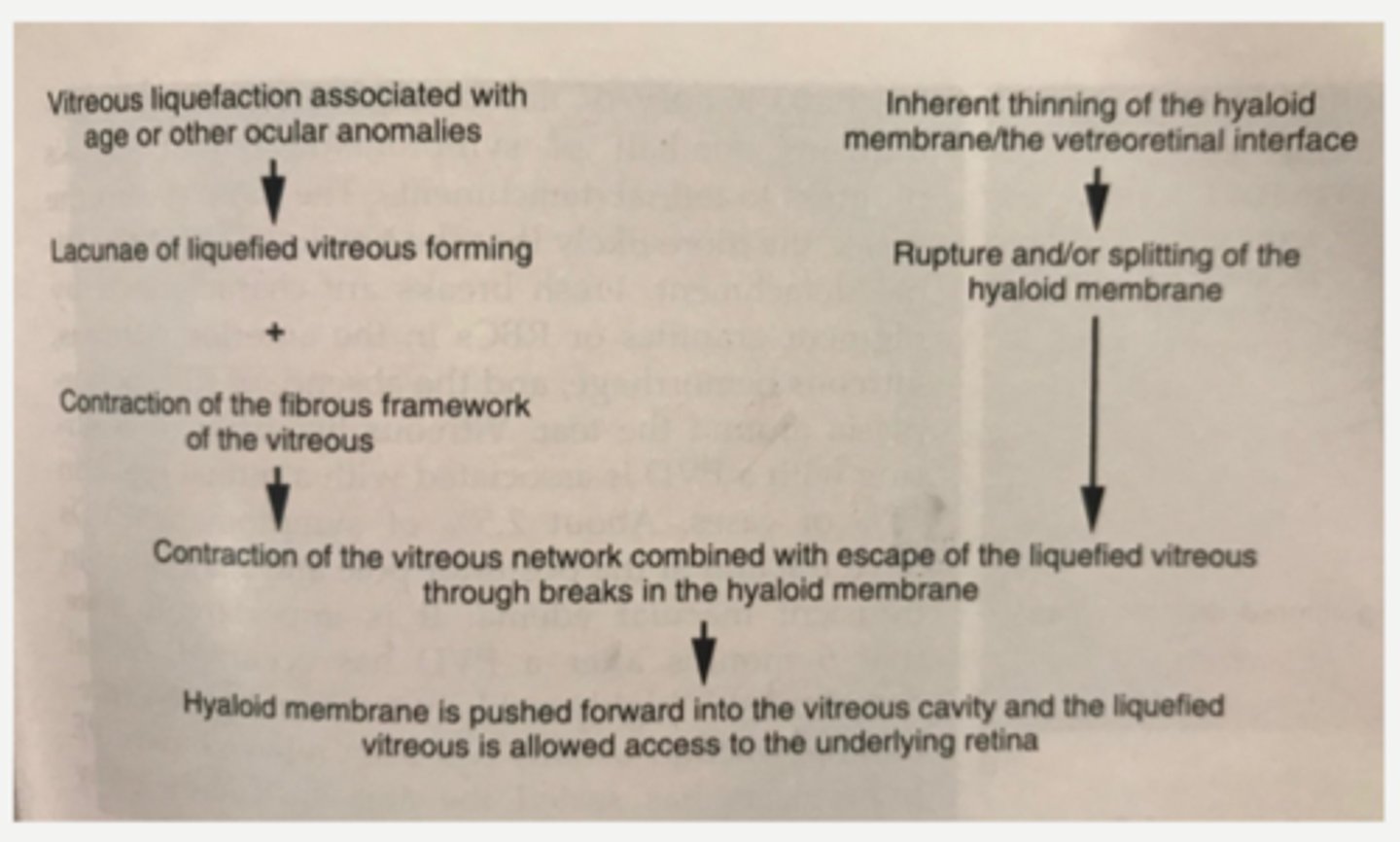
age = vitreous liquifaction, lacunae form, fibrin contraction
high myopia
trauma
inflam
aphakia
CAT surgery
vitreoretinal degeneration = thinning and splitting of hyaloid memb = vitreous fluid enters posterior space between retina and vitreous
What are some causes of PVD?
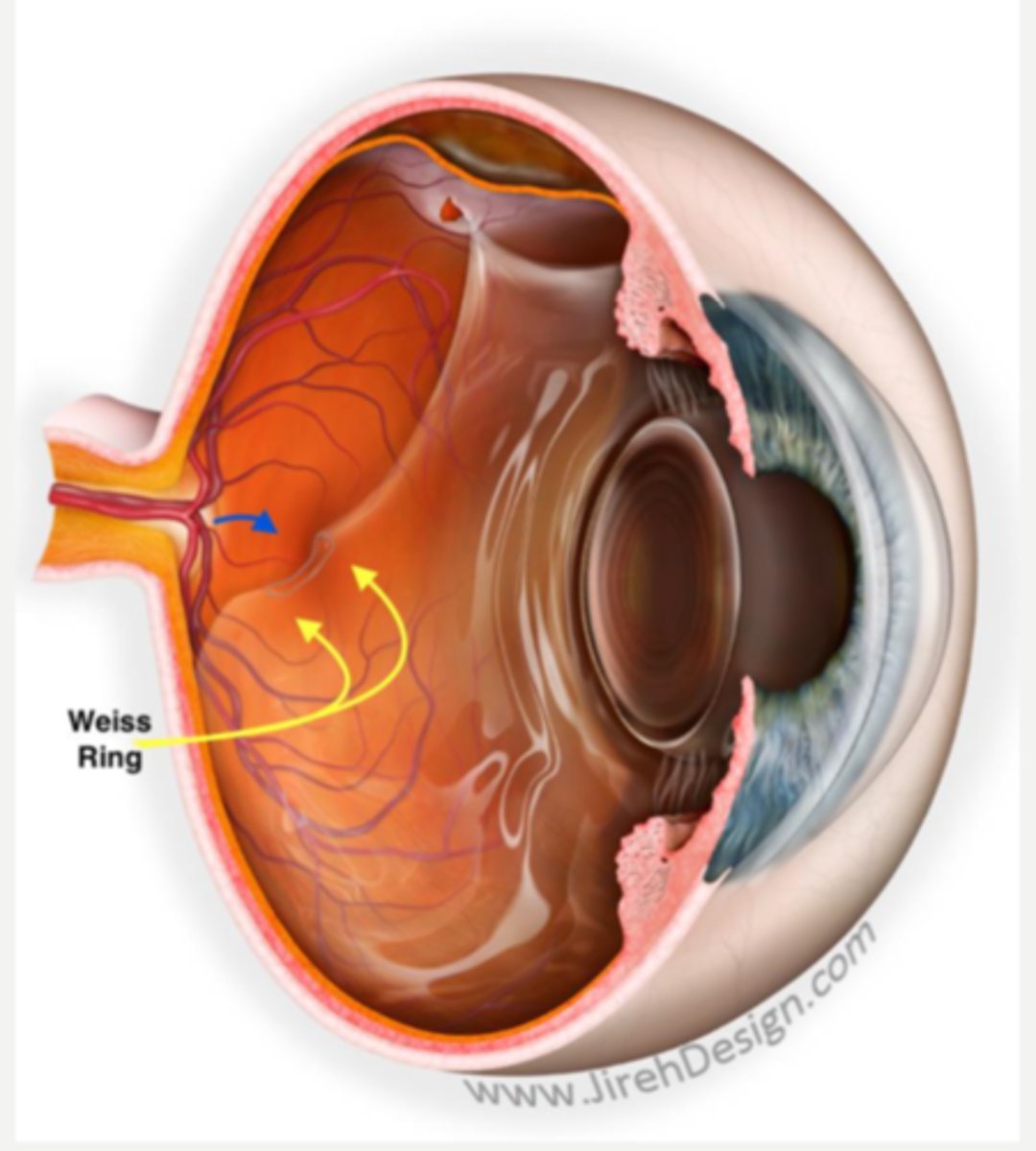
complete PVD w/ collapse of vitreous gel = Weiss ring detached from ONH
What type of PVD is shown here?
incomplete PVD w/ collapse of vitreous gel = ONH attachment still intact
What type of PVD is shown here?
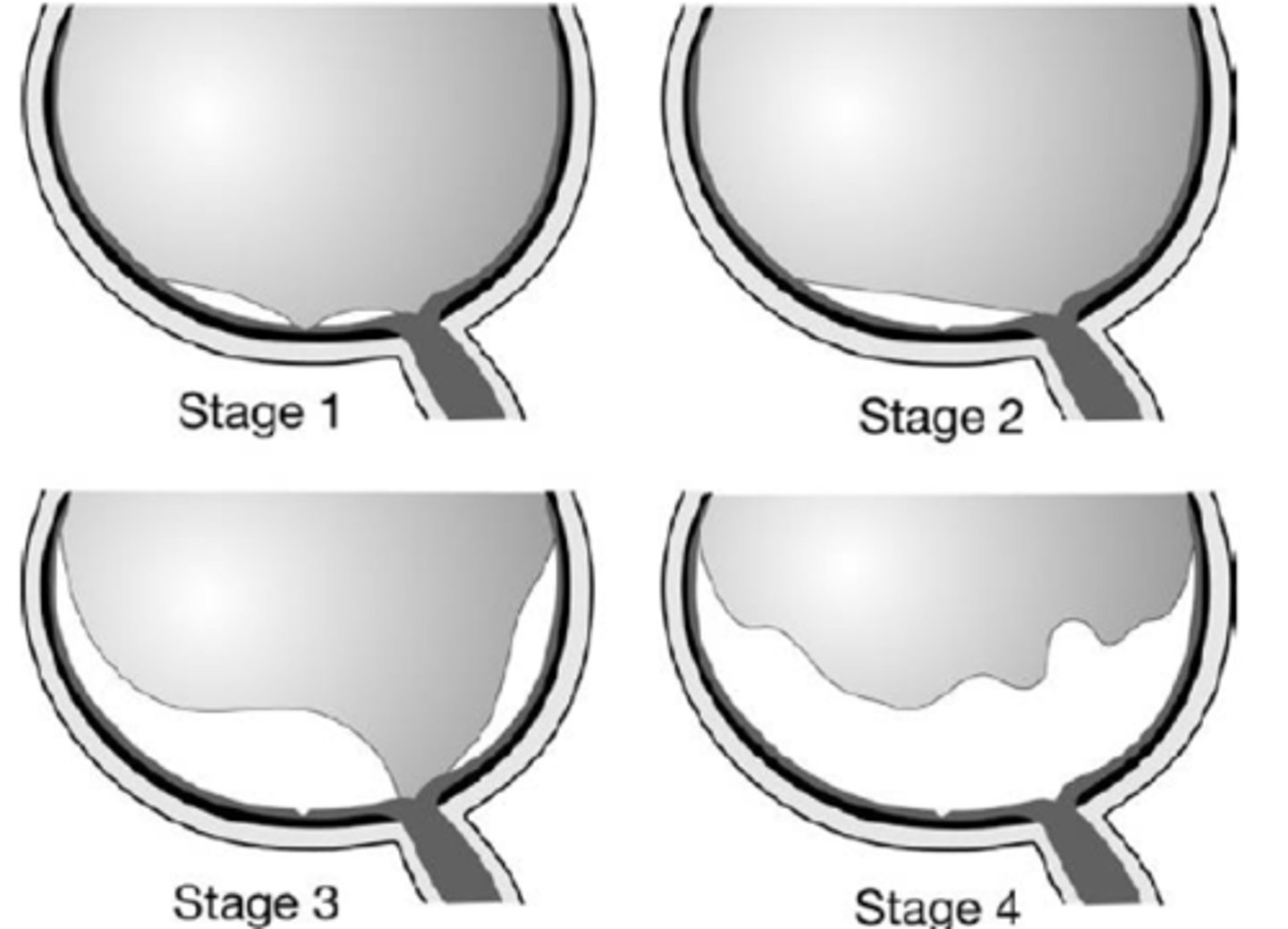
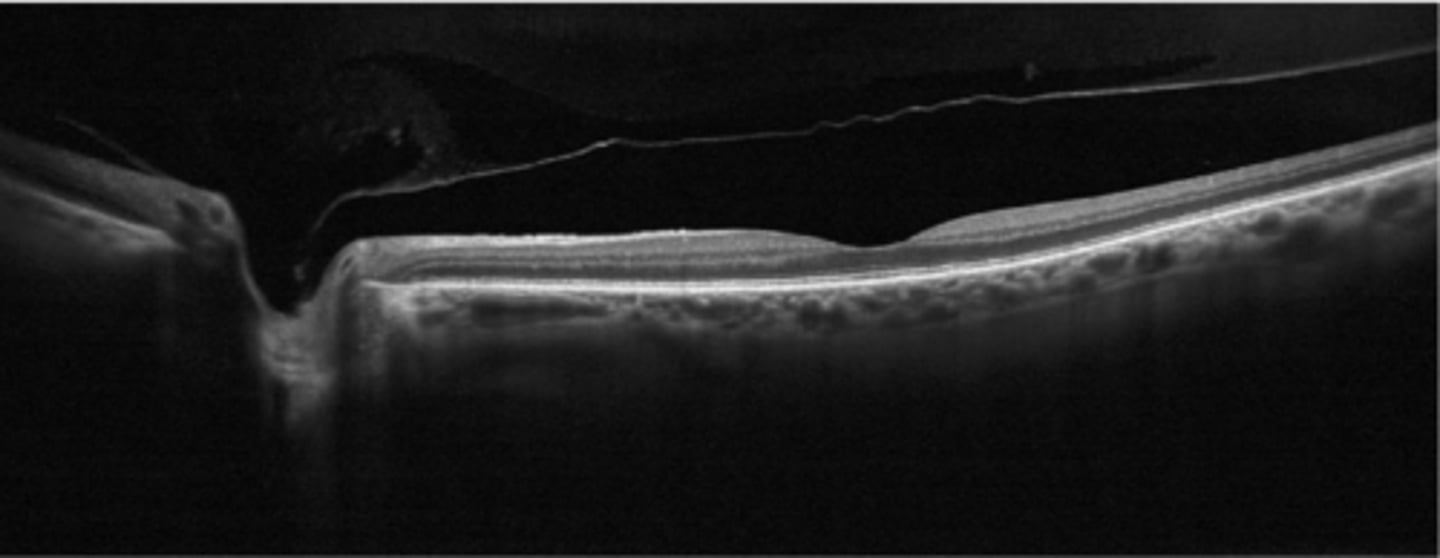
perifoveal PVD = adhesion at macula, VMT
What is shown in stage 1 PVD here?
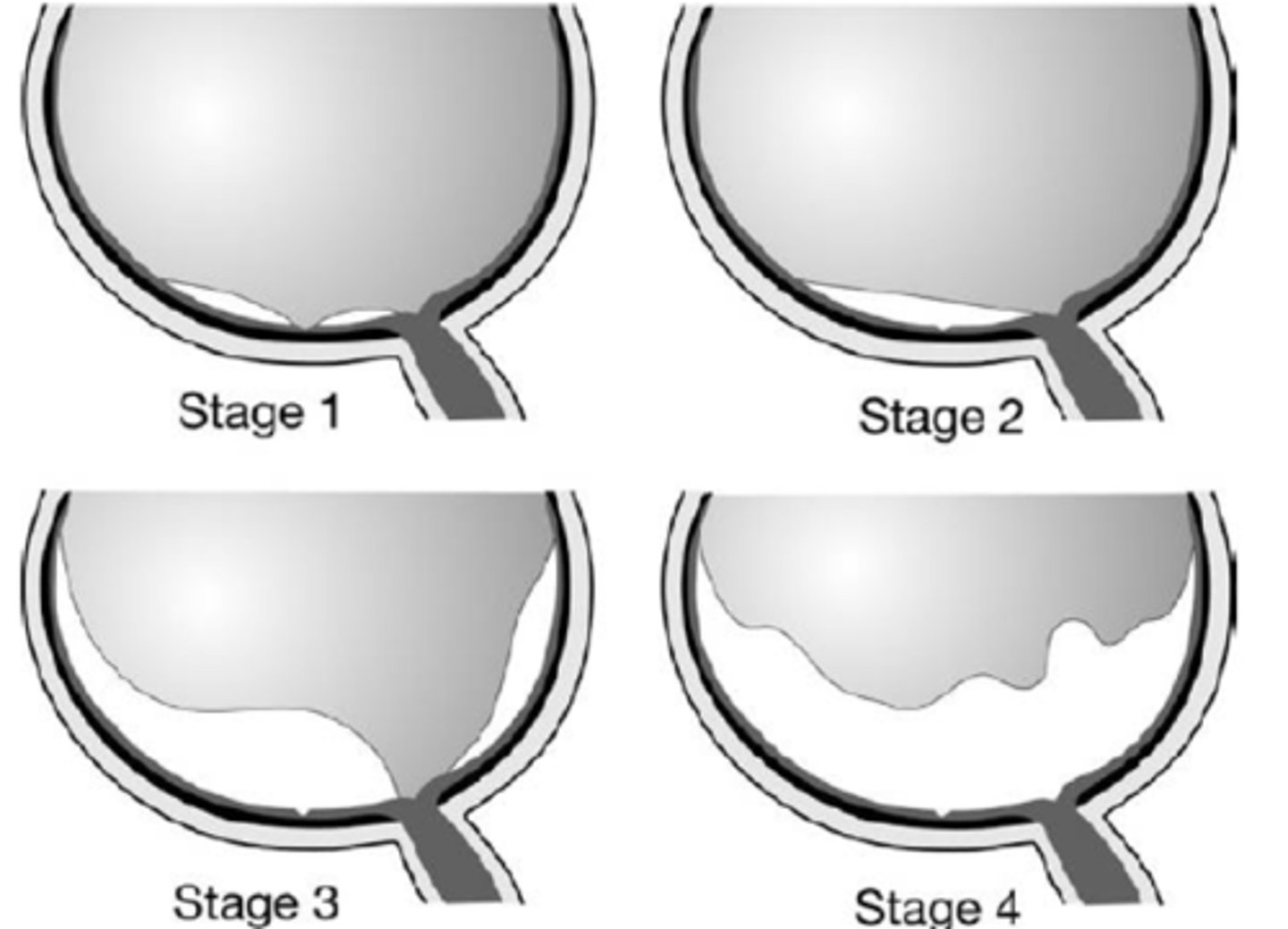
macular PVD, still attached everywhere else
What is shown in stage 2 PVD here?
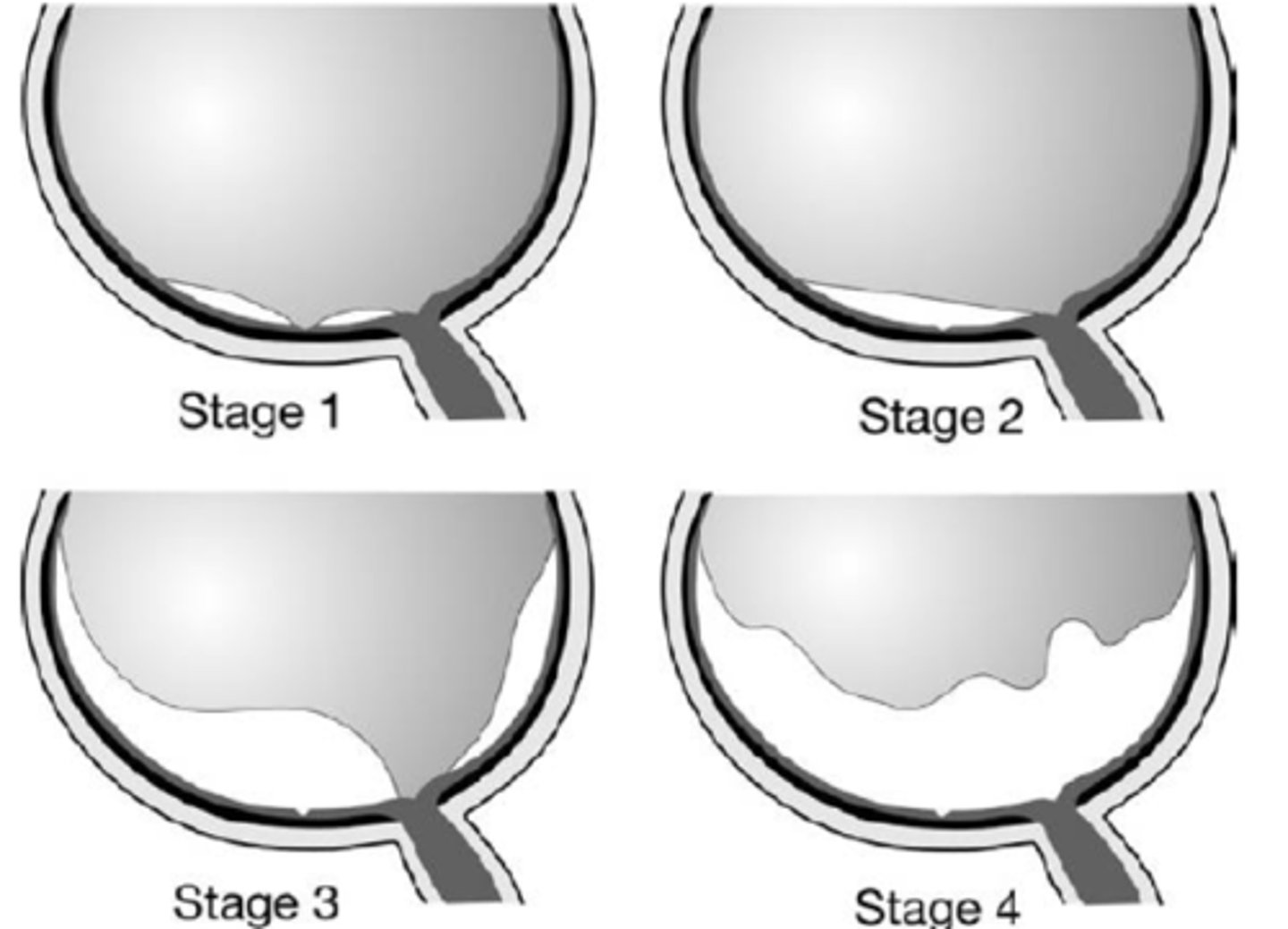
near complete PVD, still attached at ONH
What is shown in stage 3 PVD here?
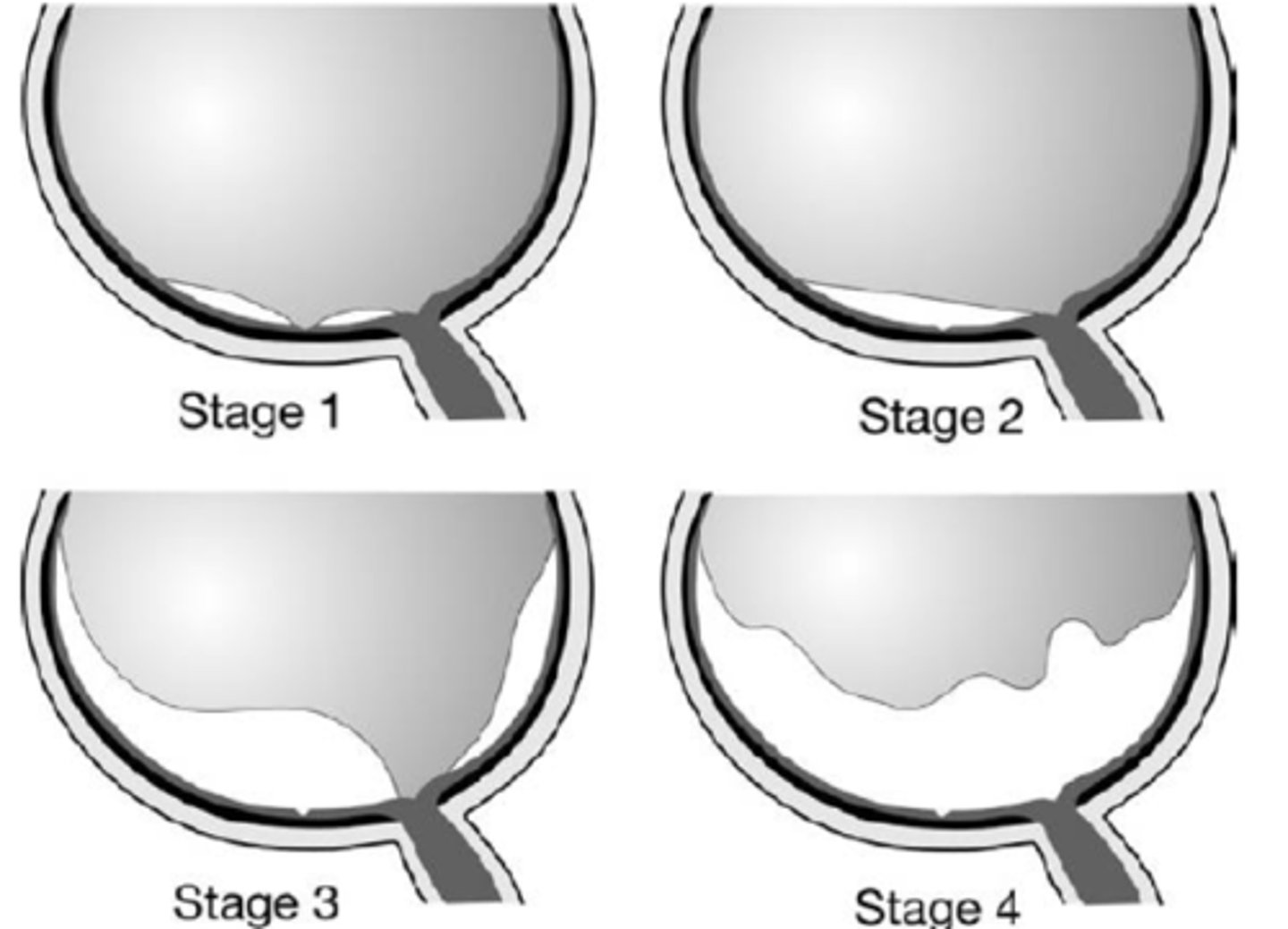
complete PVD with ONH detached
What is shown in stage 4 PVD here?
Weiss ring after a complete PVD (may collapse over time and not be this distinct)
What is shown here?
visible vitrous cortex hanging from the vitreous base
macular traction if incomplete PVD
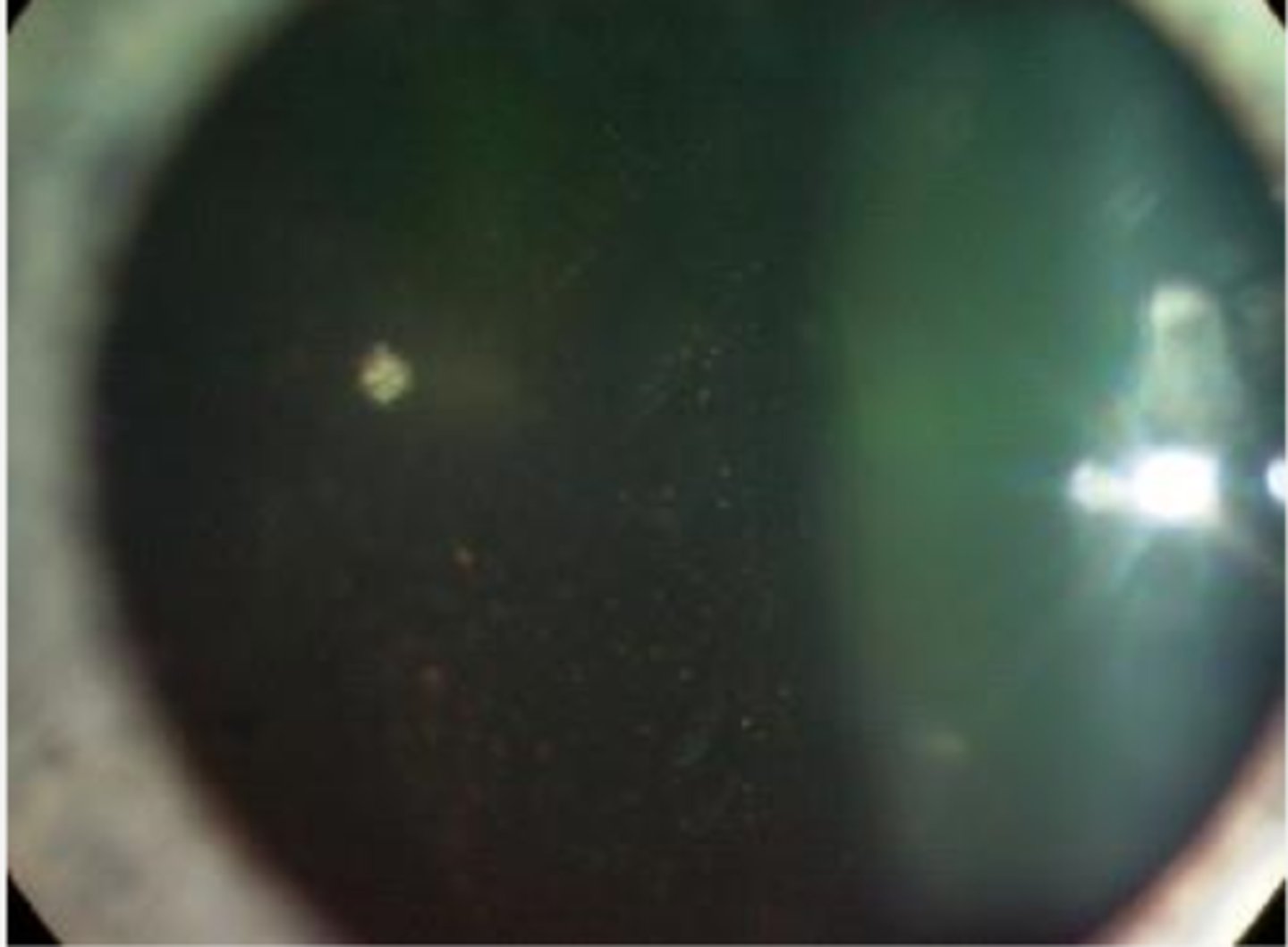
tobacco dust/Shafer sign = pigmented cells floating in vitreous
Aside from a Weiss ring, what are some other signs of PVD?
liquefied vitreous accesses retina-RPE interface = breakdown mucopolysaccharide bond (glue of RPE) = pigment cells enter vitreous, are mobile
What causes tobacco dust/Shafer sign?
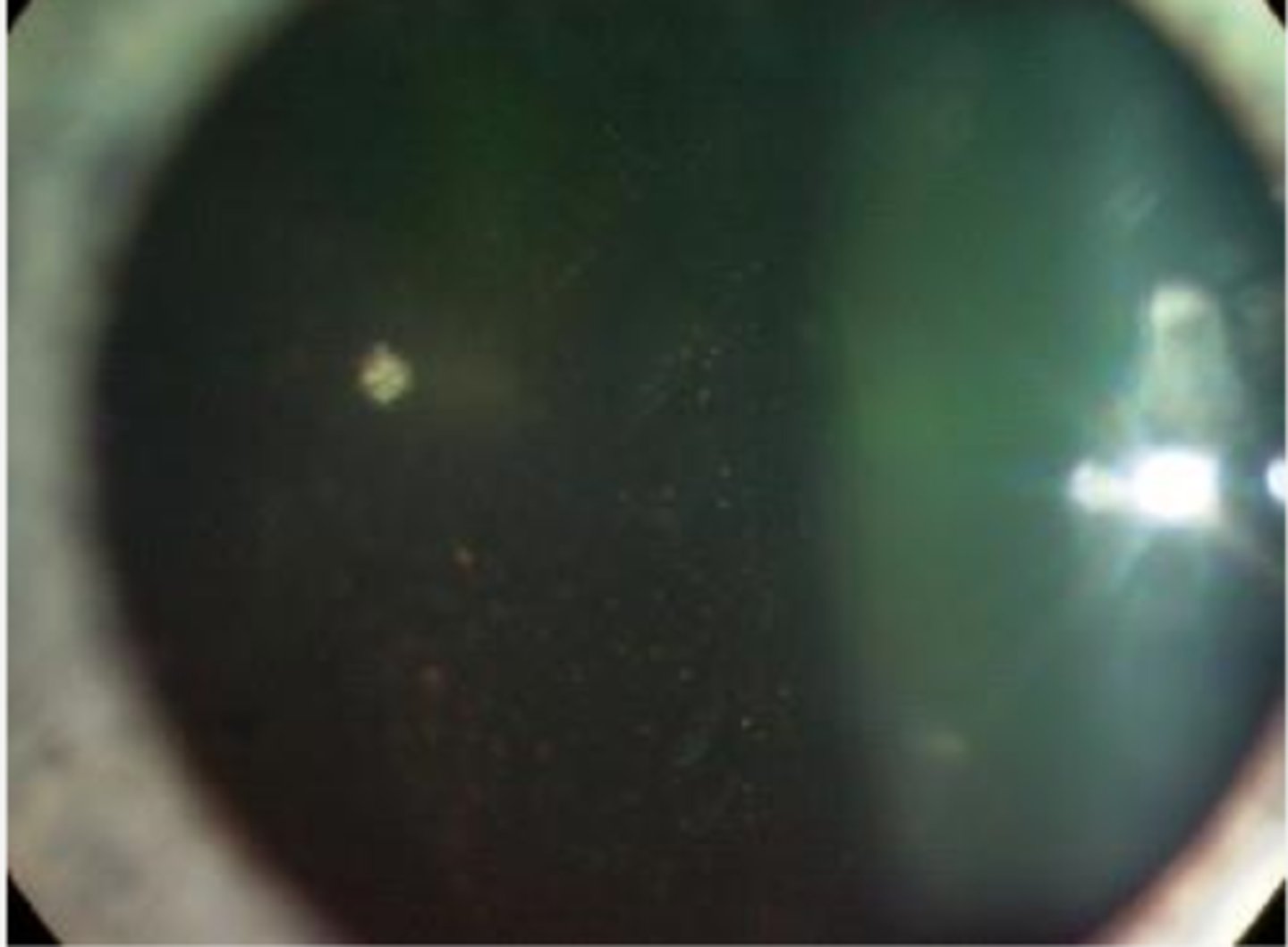
52x more likely to have an active or impending RD/break in retina
What does tobacco dust/Shafer sign mean?
visible vitrous cortex hanging from the vitreous base
What sign of PVD is seen here?
Weiss ring = complete PVD
What sign of PVD is seen here?
incomplete PVD bc still attached at ONH
Is this PVD complete or incomplete?
incomplete PVD bc still partially attached = tugs on retina
Is this PVD complete or incomplete?
floaters esp sudden onset
flashes/photopsias due to vitreoretinal traction
metamorphopsia or slightly reduced VA due to vitreoretinal traction
What are some symptoms of PVD?
macular traction, edema, hole
vitreous hemorrhage = also likely to occur with retinal break
retinal break/RD
retinal hemorrhage
What are 4 potential complications of a PVD?
DFE with scleral depression
3M gonio
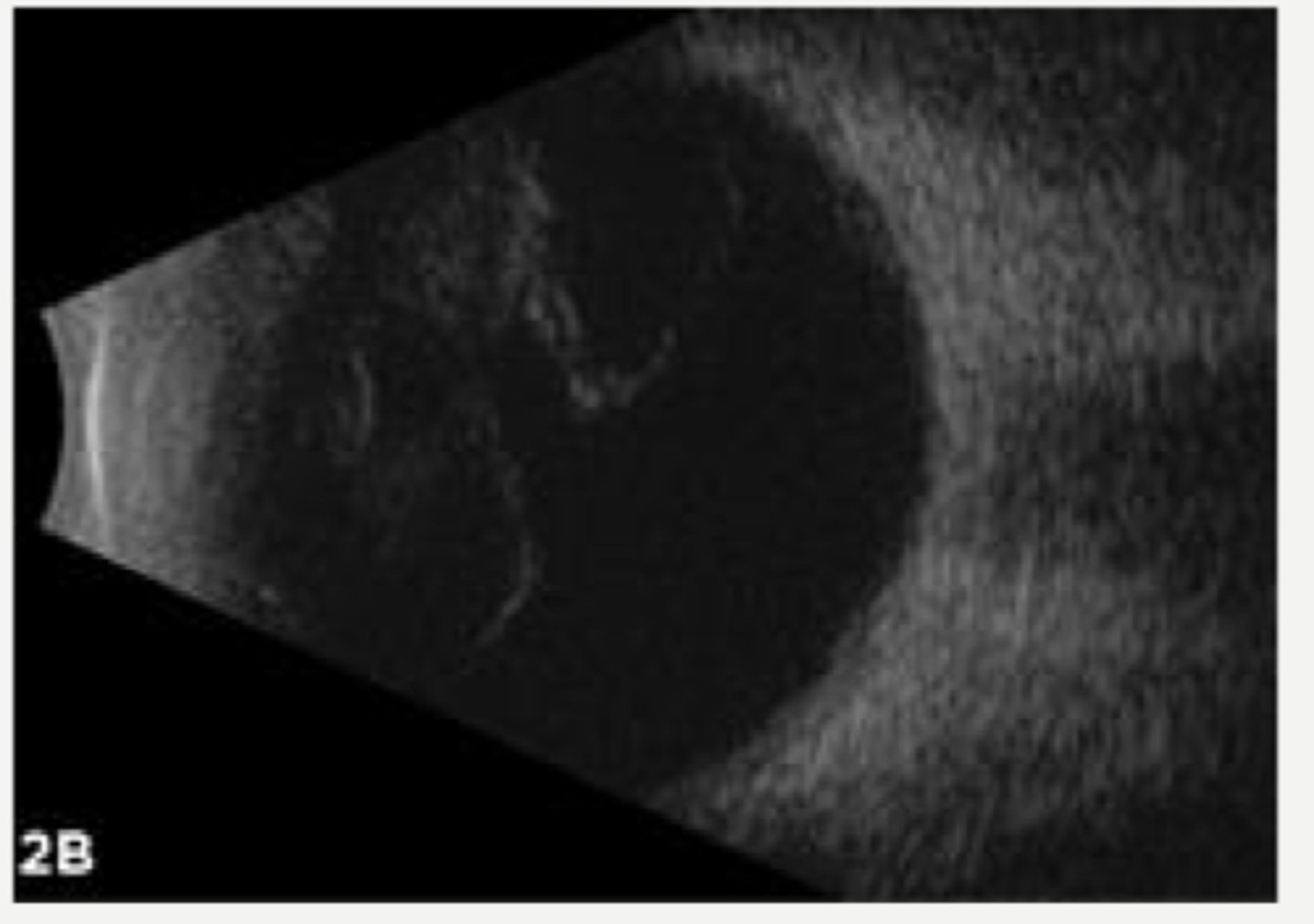
B-scan ultrasound if cloudy media
What are some alternative ways to evaluate a PVD?
educate on S/S of RD
educate on likelihood of RD within 1 year
follow up as needed
What is the management for a PVD?
2-4 weeks
2-3 mos
6 mos
What is the follow-up schedule for a PVD if there is no retinal break or hemes?
1 week
2-4 weeks
3 mos
6 mos
What is the follow-up schedule for a PVD if there is no retinal break but there are mild VH or peripheral dot hemes?
next day by retina specialist bc of the high likelihood of retinal break
What is the follow-up schedule for a PVD if there is no retinal break but there are significant VH or pigmented vitreous cells present?
systemic CT disease resulting in skeletal abnormalities, aortic dissection, cardiac abnormalities
What is Marfan syndrome?
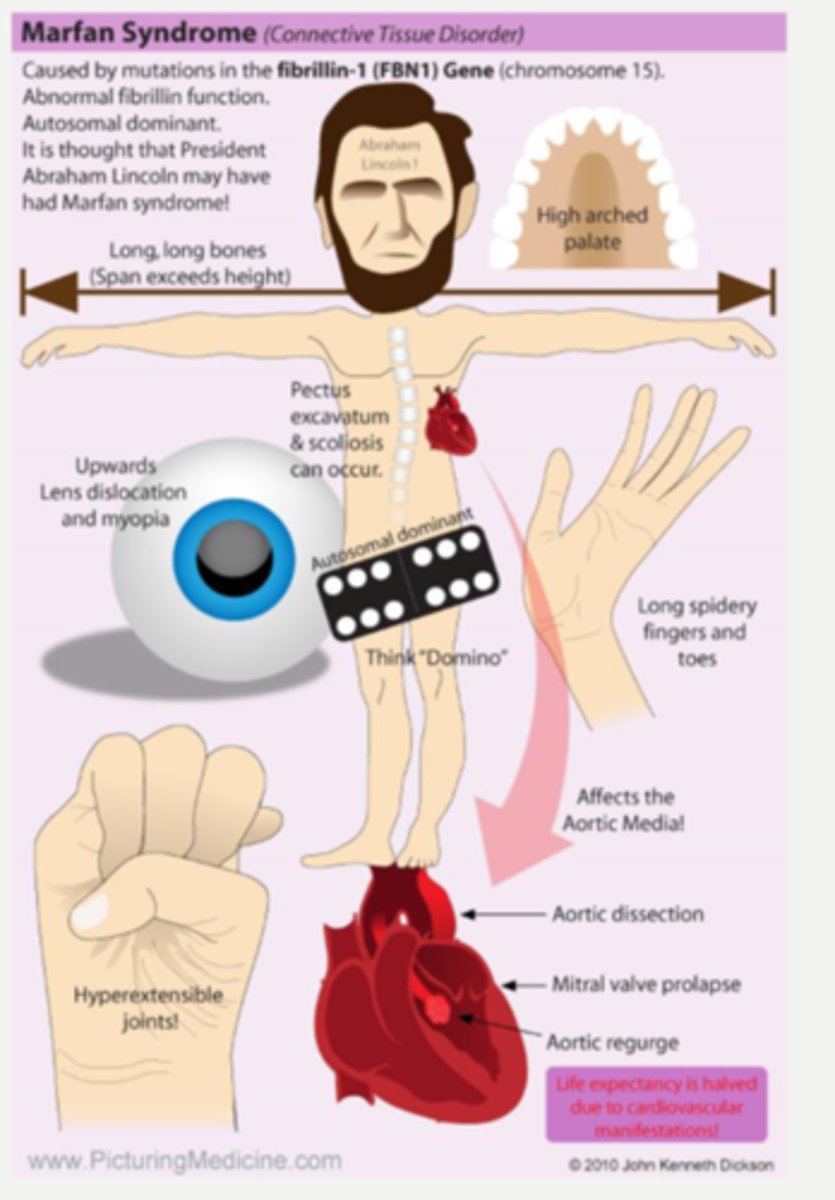
sup-temporal lens luxation = often good VA if visual axis not involved
axial myopia
vitreous degeneration
decreased corneal diameter
iris transillumination
RD
vitreous loss during CAT Sx
What are some ocular findings of Marfan syndrome?
systemic CT disease resulting in tissue fragility, increased skin elasticity, hypermobile joints, risk under general anesthesia
What is Ehlers Danlos?

high myopia
microcornea
glaucoma
angiod streaks
vitreoretinal degeneration w/ lattice common
RD
ptosis
strabismus
What are some ocular findings of Ehlers Danlos?
elevated plasma and urinary homocystine = skeletal and cardiovascular abnormalities, thrombotic vasc occlusions, high risk under anasthesia
What is homocystinuria?
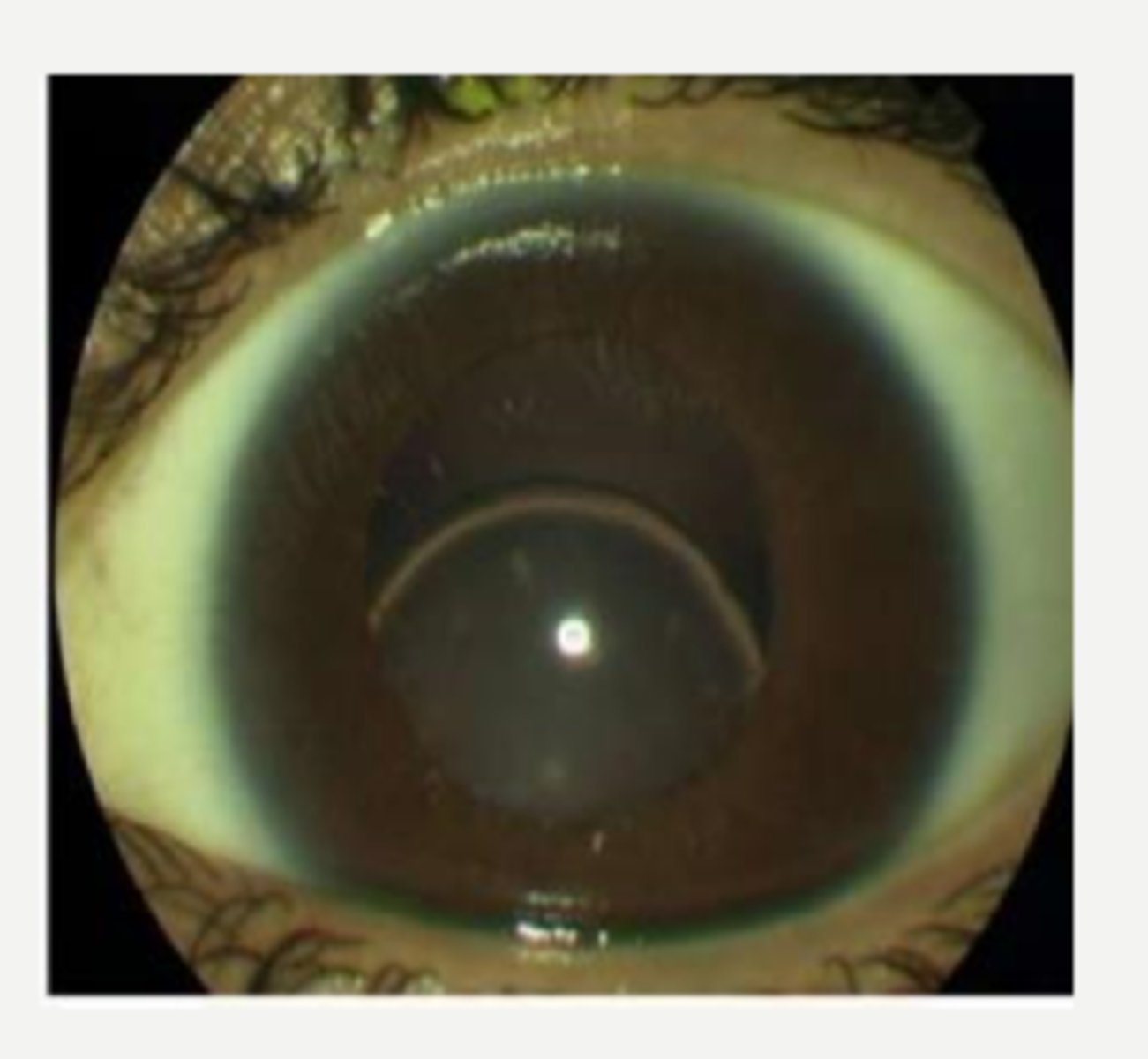
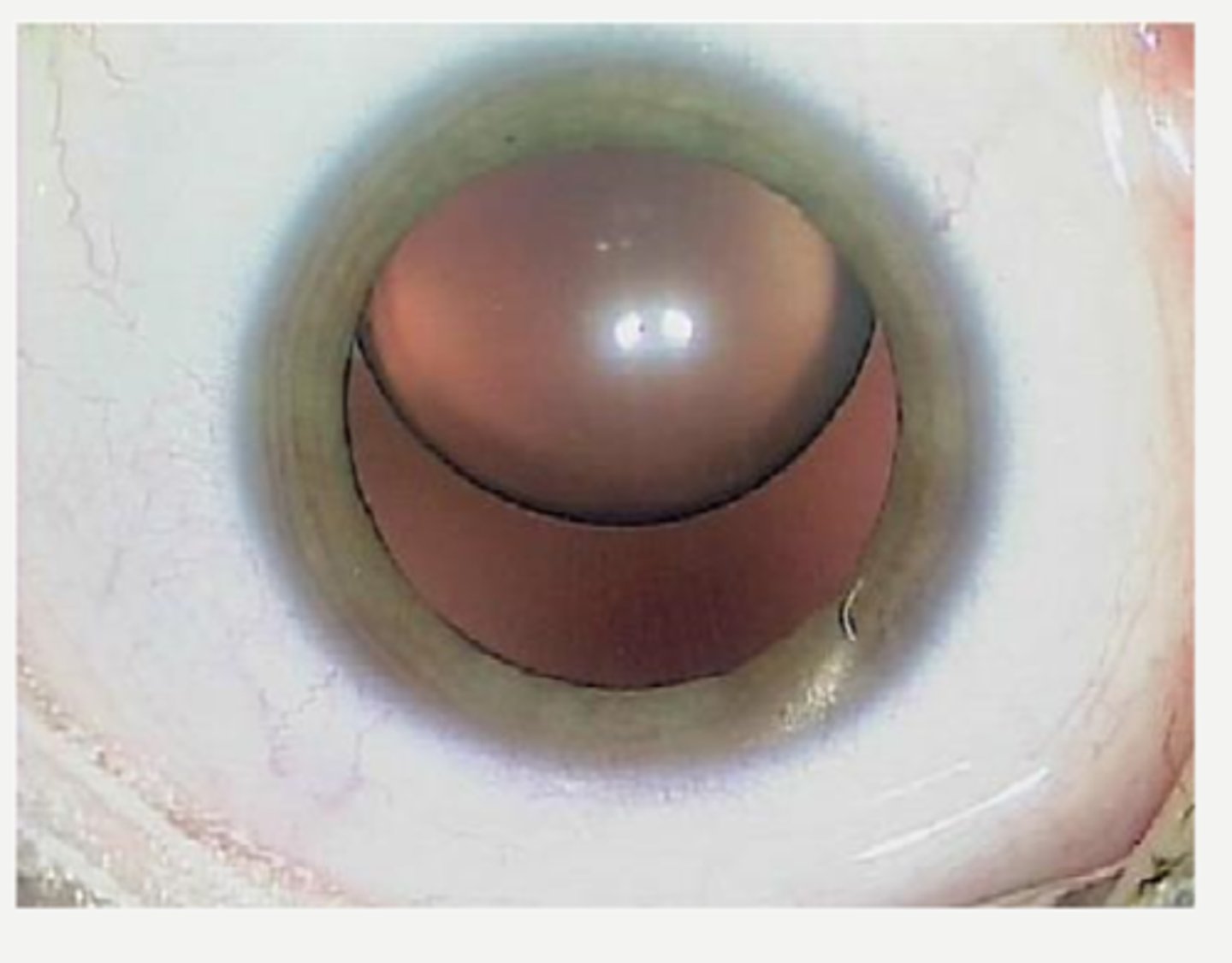
inferior lens luxation
vitreoretinal degeneration and detachment
What are some ocular manifestations of homocystinuria?
trauma or lens dislocation (rare) = anterior hyaloid membrane detaches and hangs in front of pupil
What causes anterior vitreous detachment?
retinal evaluation due to highly increased risk for retinal tears, dialysis, breaks
then 1 year f/u
What is the management for anterior vitreous detachment?
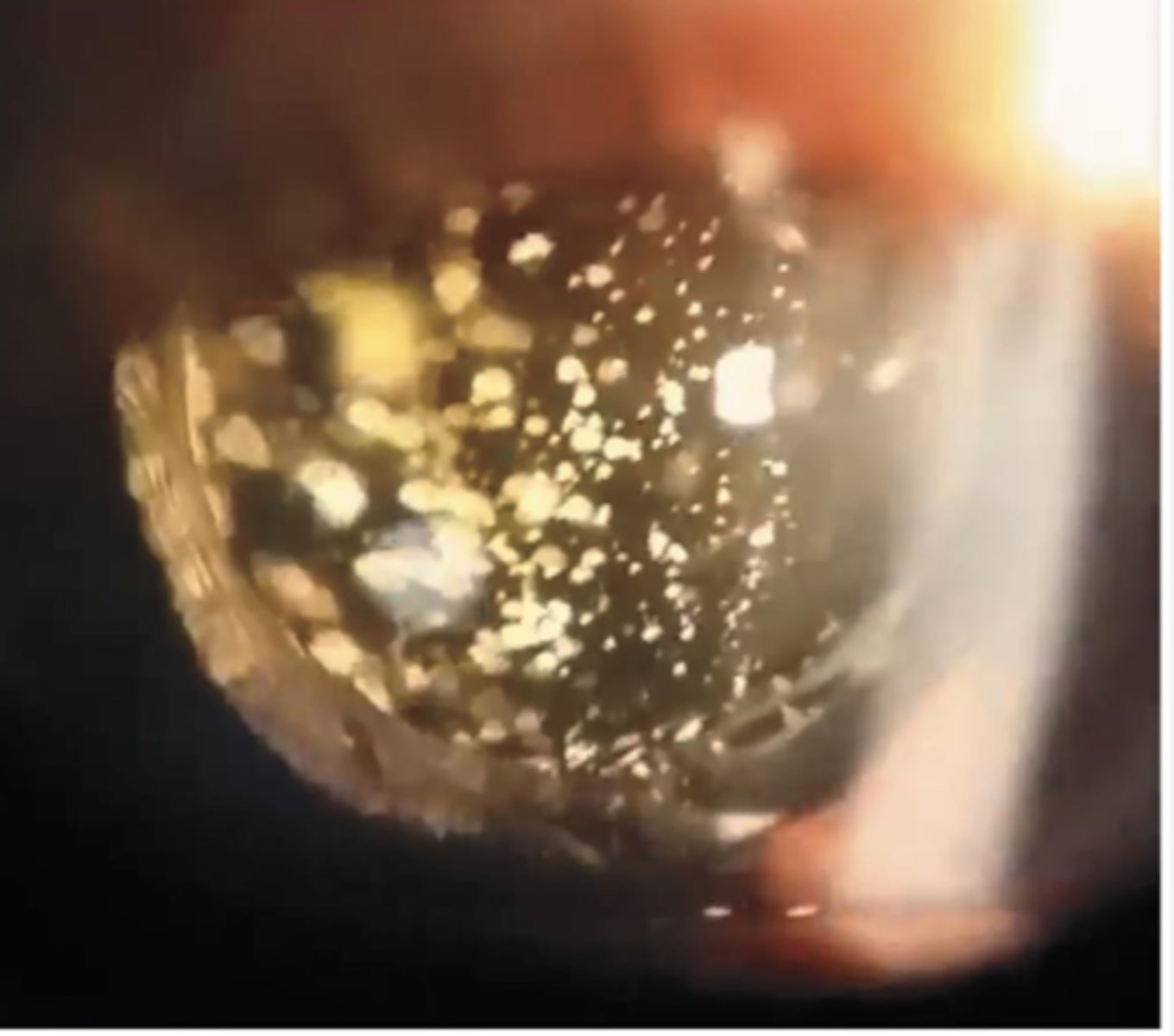
small yellow-white spheres of Ca, P, O, lipids that are suspended throughout collagen fibrils of vitreous
What is asteroid hyalosis?
unilateral
Is asteroid hyalosis usually unilateral or bilateral?
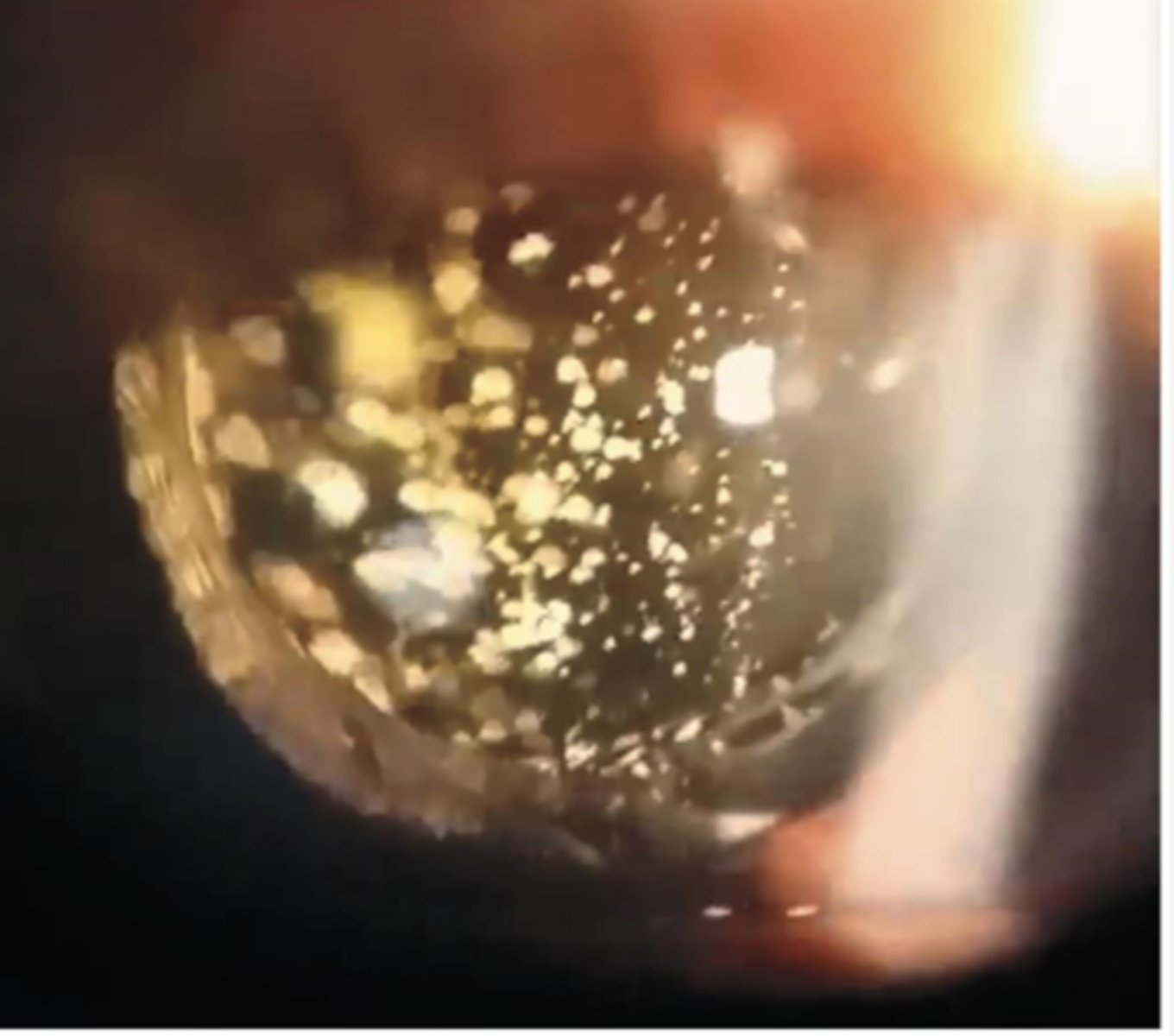
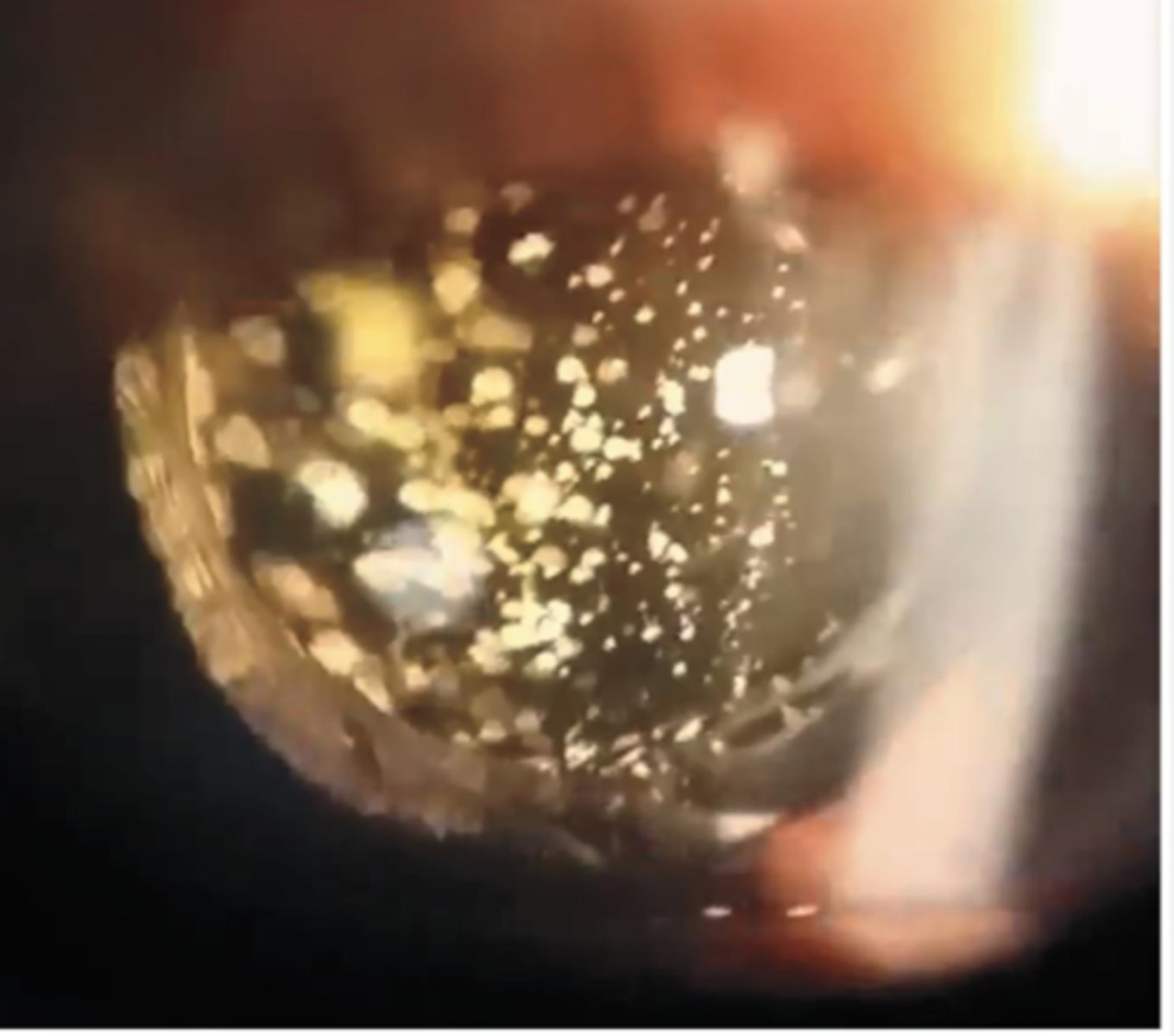
idiopathic most likely
What causes asteroid hyalosis?
no = typically asymptomatic, though pt MAY complain of floaters
Does asteroid hyalosis typically affect vision?
these are adherent to the vitreous framework, so they stay suspended with ocular movement
How can we differentiate asteroid hyalosis from synchisis scintillans, a similar DDx?
pt education
pars plana vitrectomy in extreme cases where VA is affected
What is the management for asteroid hyalosis?
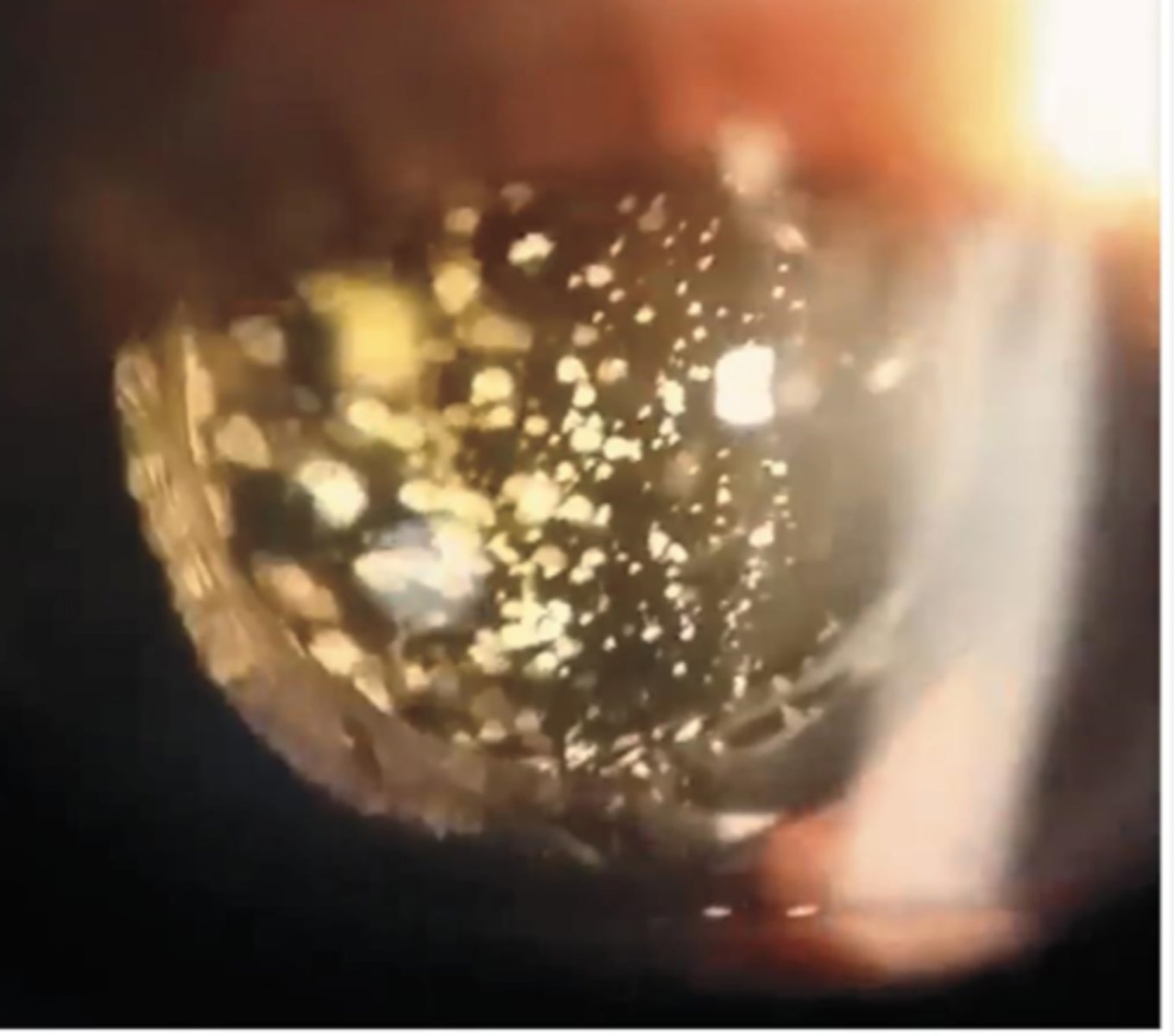
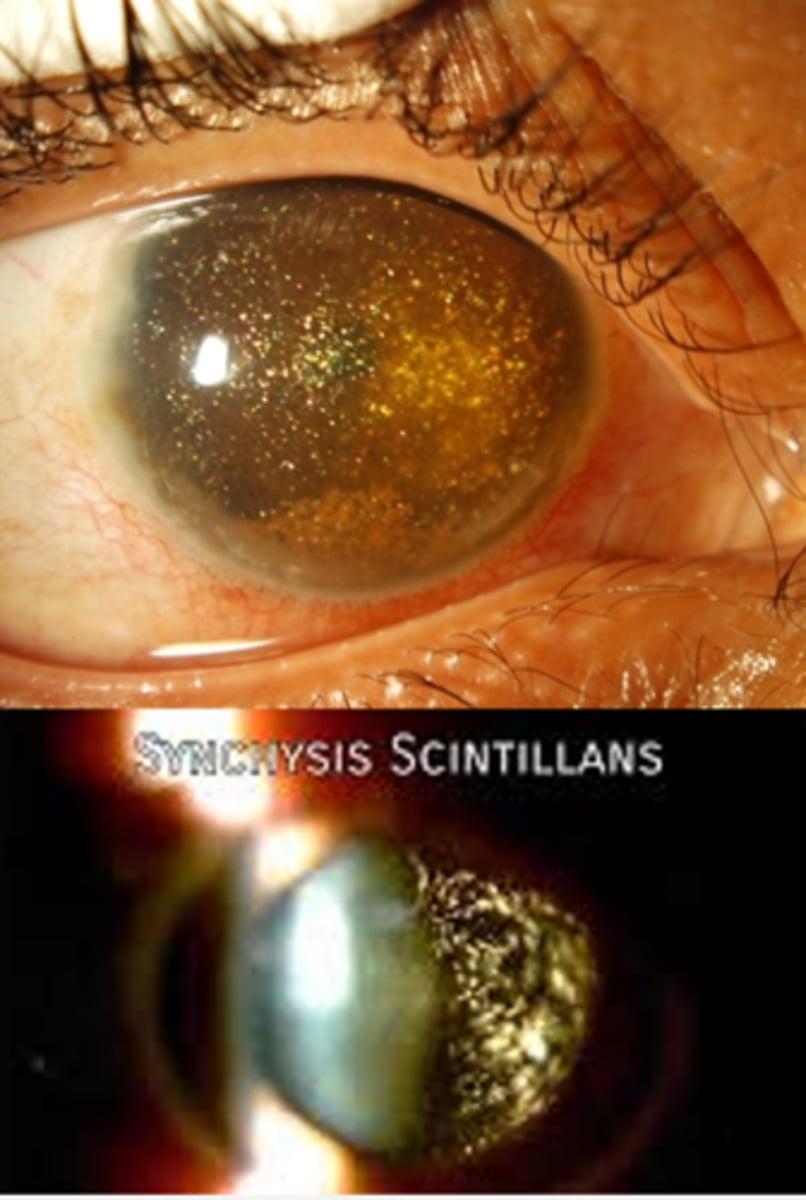
rare degenerative ocular condition characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol crystals in the vitreous
What is synchysis scintillans?
severely diseased or blind eyes
What causes synchysis scintillans?
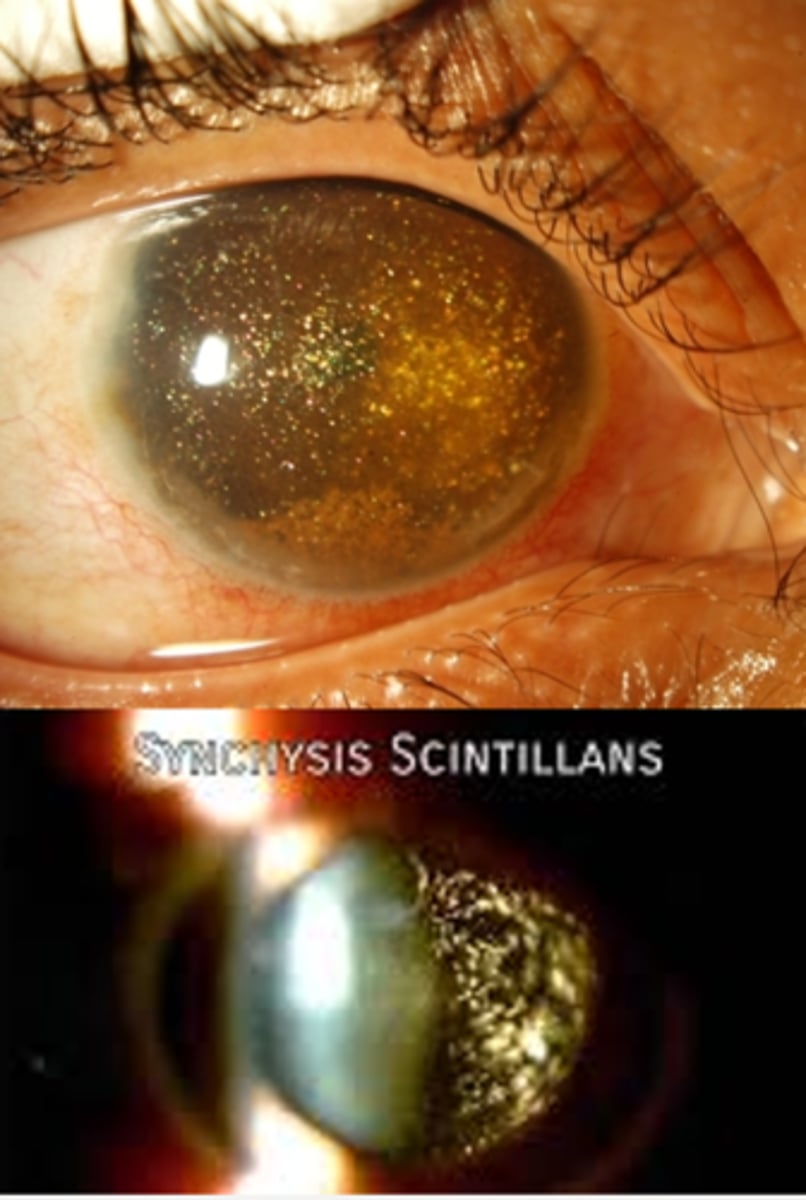
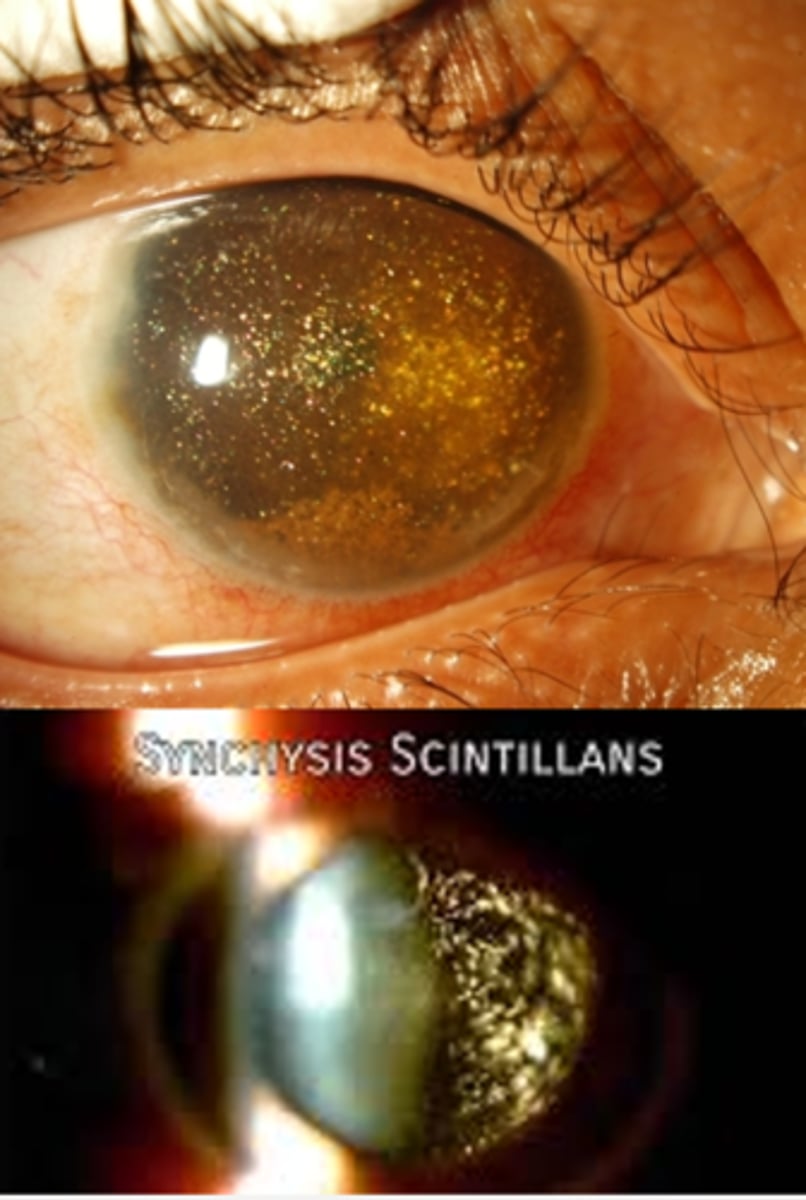
these are NOT attached to the vitreous framework, so they settle after ocular movement like a snow globe effect
How can we differentiate synchysis scintillans from asteroid hyalosis, a similar DDx?
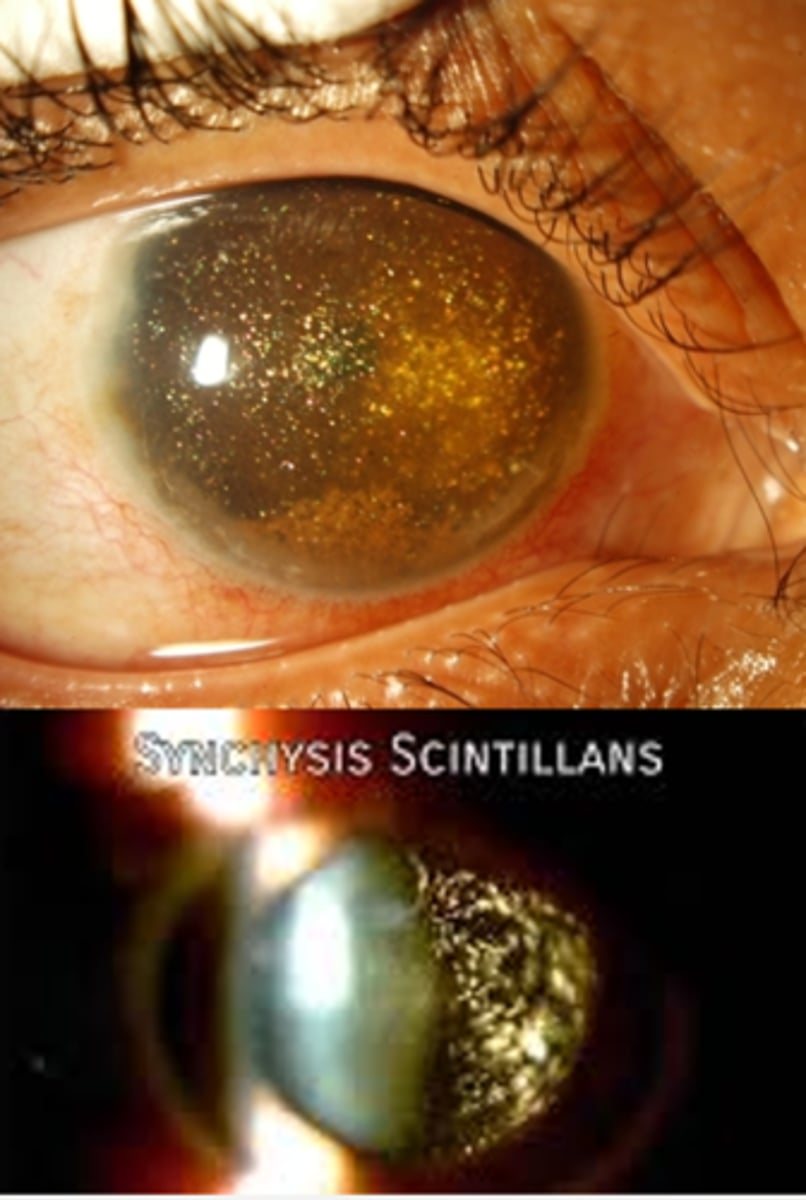
crystals can into AC = pseudohypopyon
What is a possible complication of synchysis scintillans?
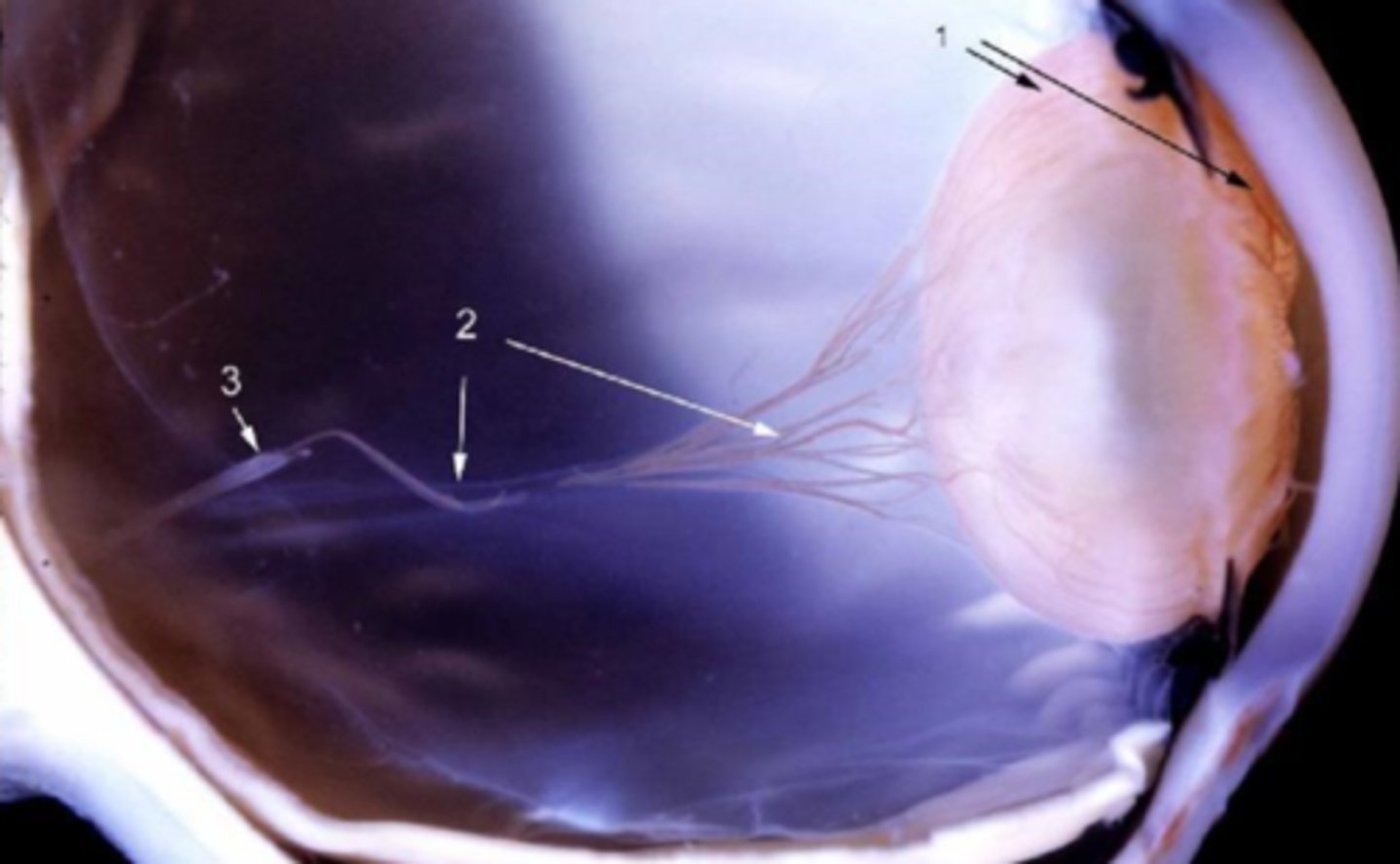
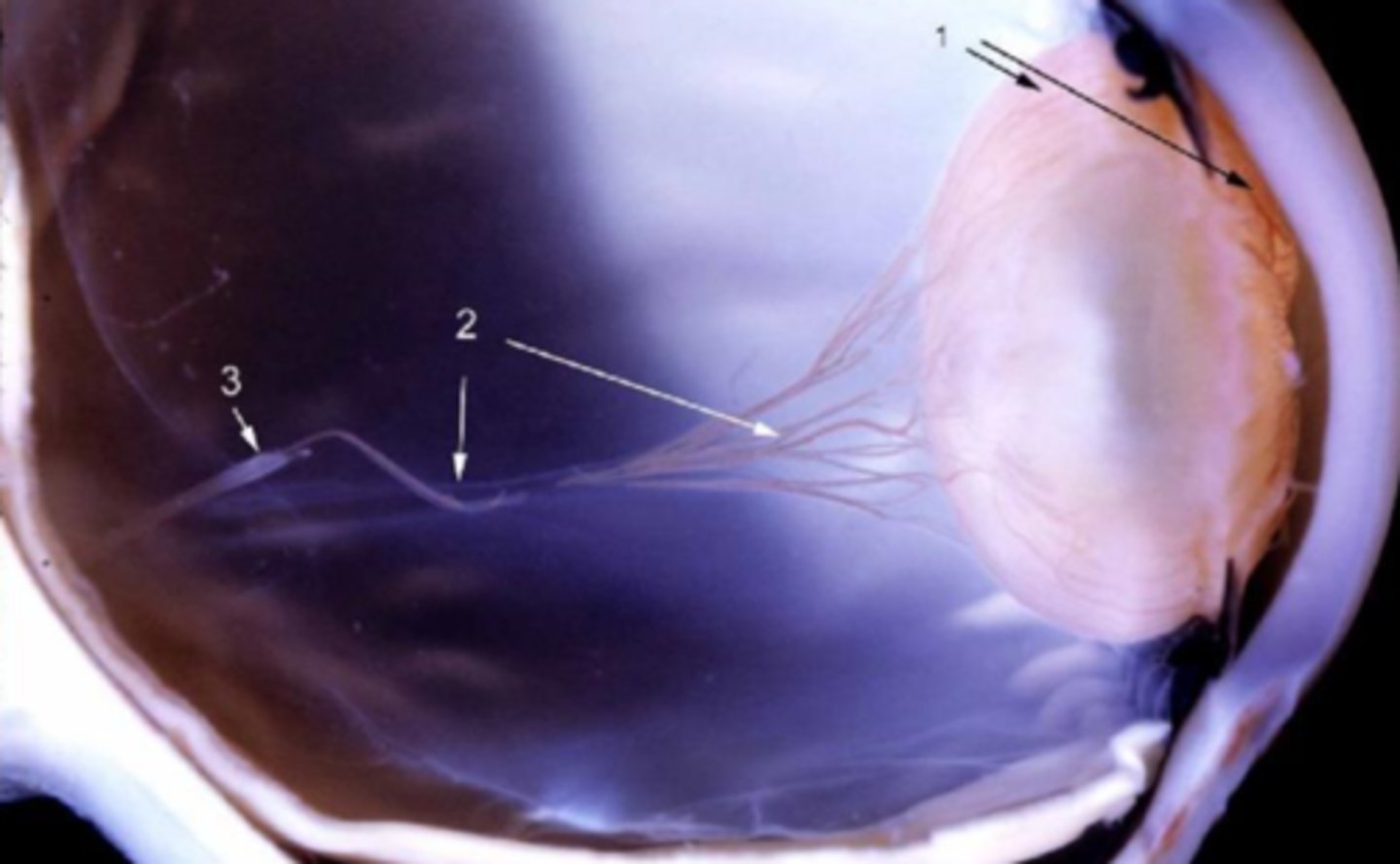
hyaloid artery (2 and 3 in diagrim) in primary vitreous does NOT undergo normal involution by macrophage-mediated apoptosis
What is persistent fetal vasculature (PFV)?
anterior form >>> posterior form or combo
Which forms of PFV tend to have better outcomes?
unilateral
Is PFV usually unilateral or bilateral?
non-heritable
can be associated with AD (NDP gene) or AR (ATOH7 gene) inheritance
Is PFV usually heritable or non-heritable?
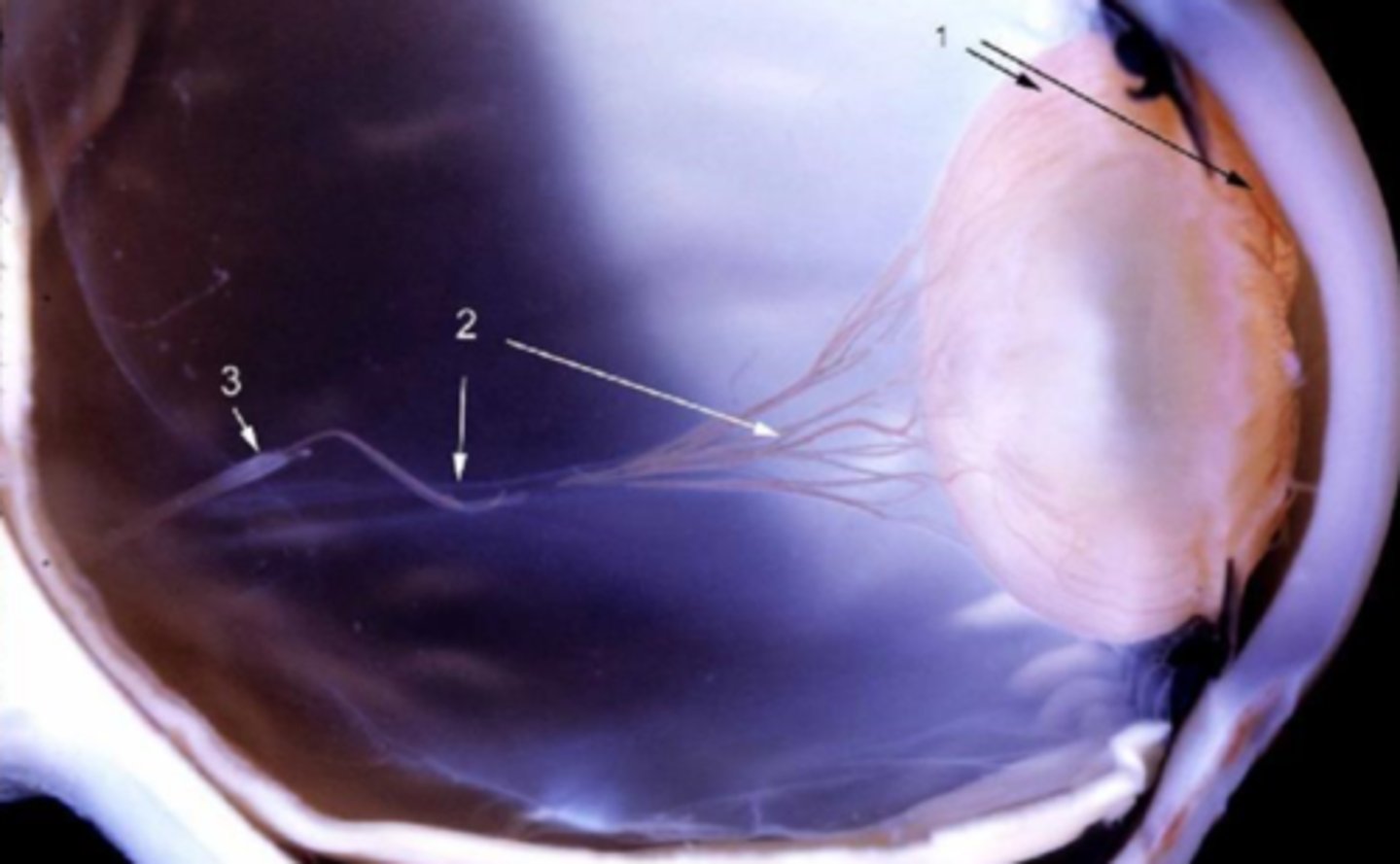
anterior PFV, severe form
What form of PFV is seen here?
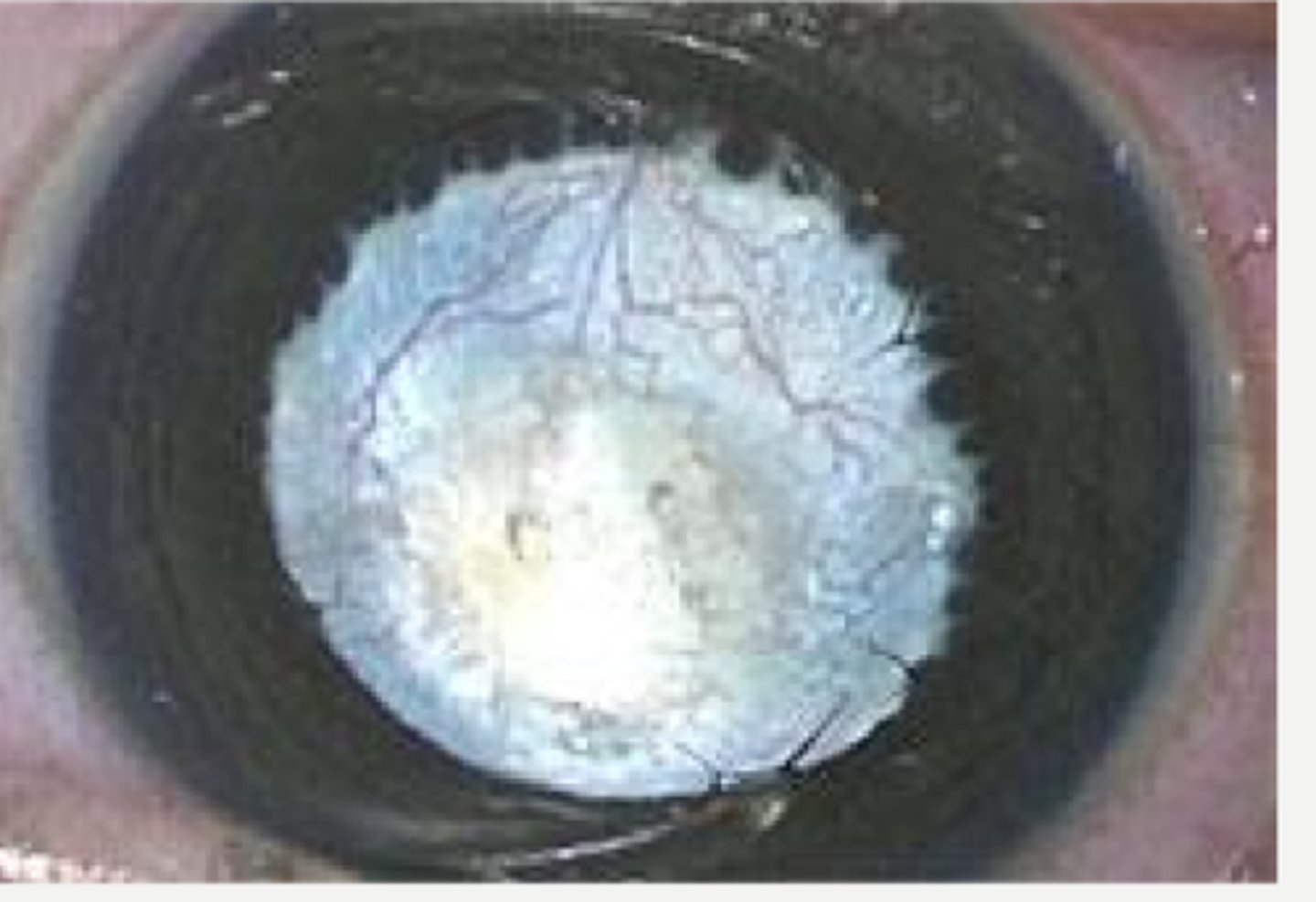
leukocoria
microphalmia
CATs
elongated or drawn in CB processes
shallow AC when eye is small = glaucoma
retrolental fibrovasc membranes = cause traction on peripheral retina
intralenticular hemorrhages bc BV still acive
dilated iris BV
strabismus bc of reduced VA
ectropian uvea
iris coloboma
What are some signs and complications of anterior PFV?
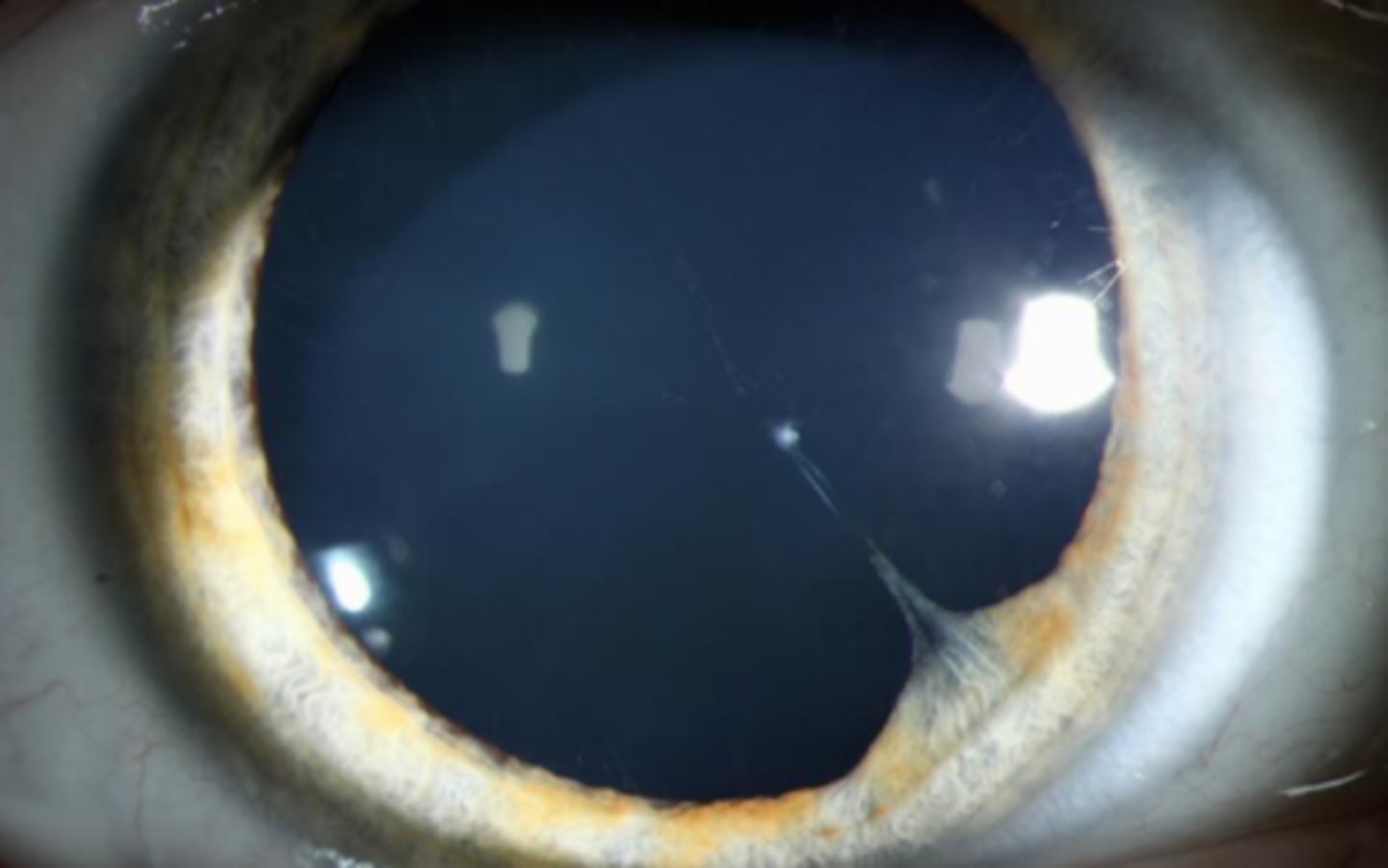
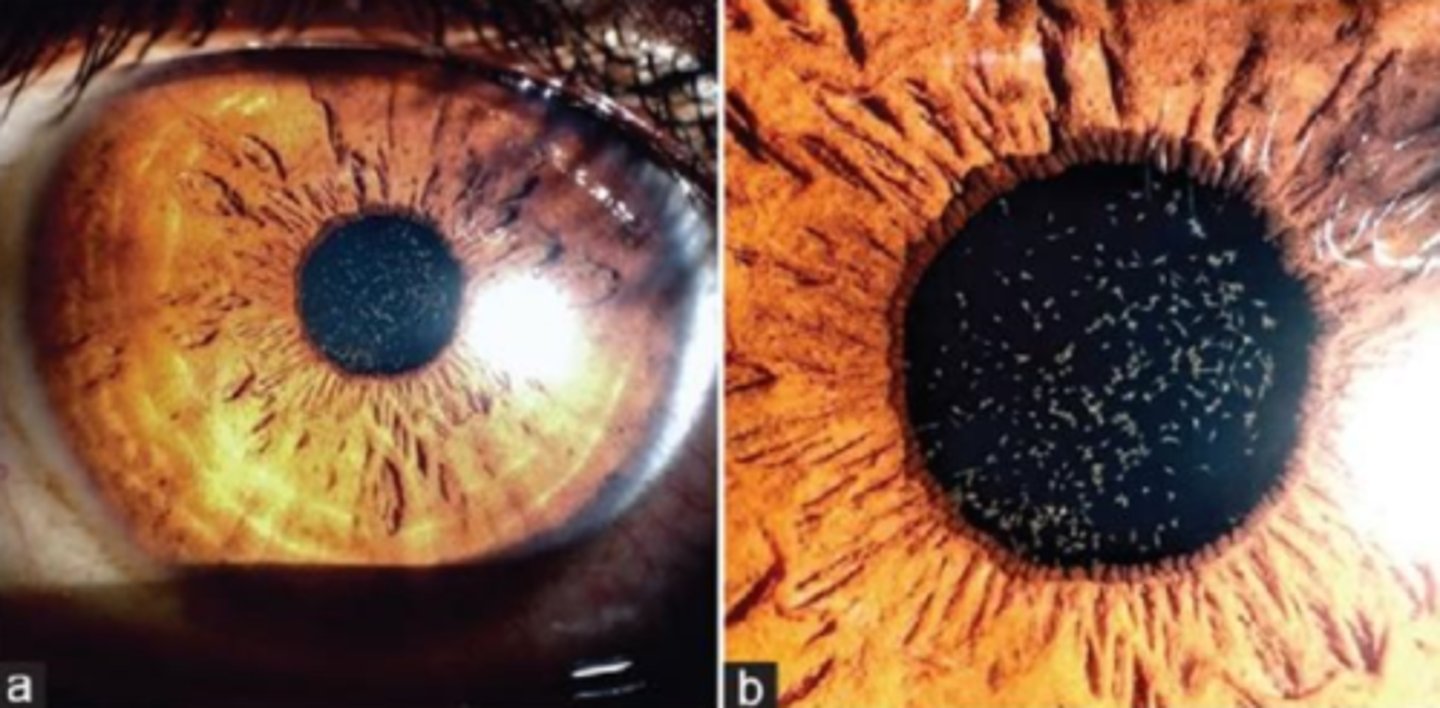
persistent pupillary membrane (PPM) = remnant of anterior tunica vasculosa lentis on iris/lens = usually benign, no effect on VA
What form of anterior PFV is seen here?

epicapsular stars = remnant of anterior tunica vasculosa lentis on anterior lens
What form of anterior PFV is seen here?
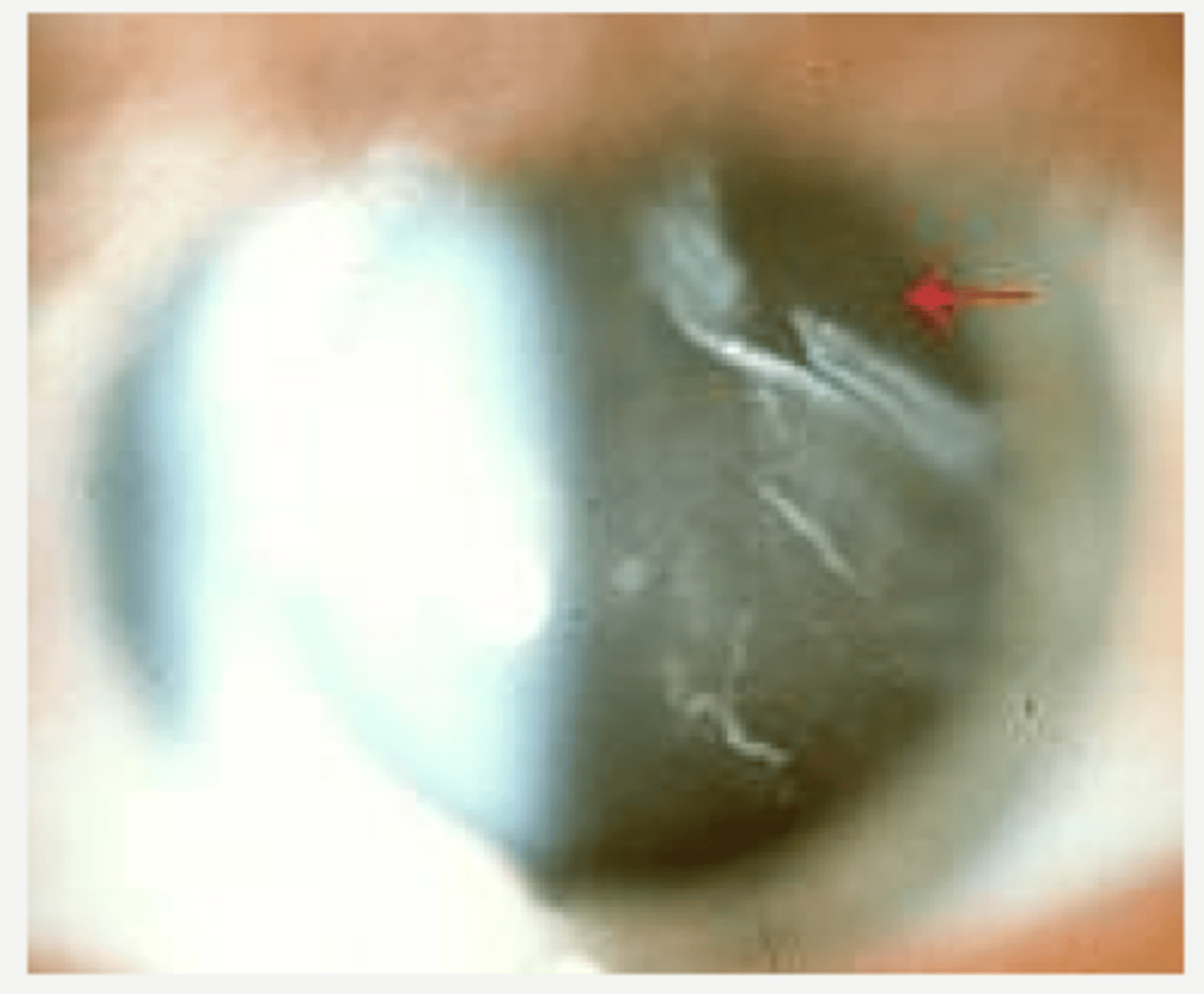
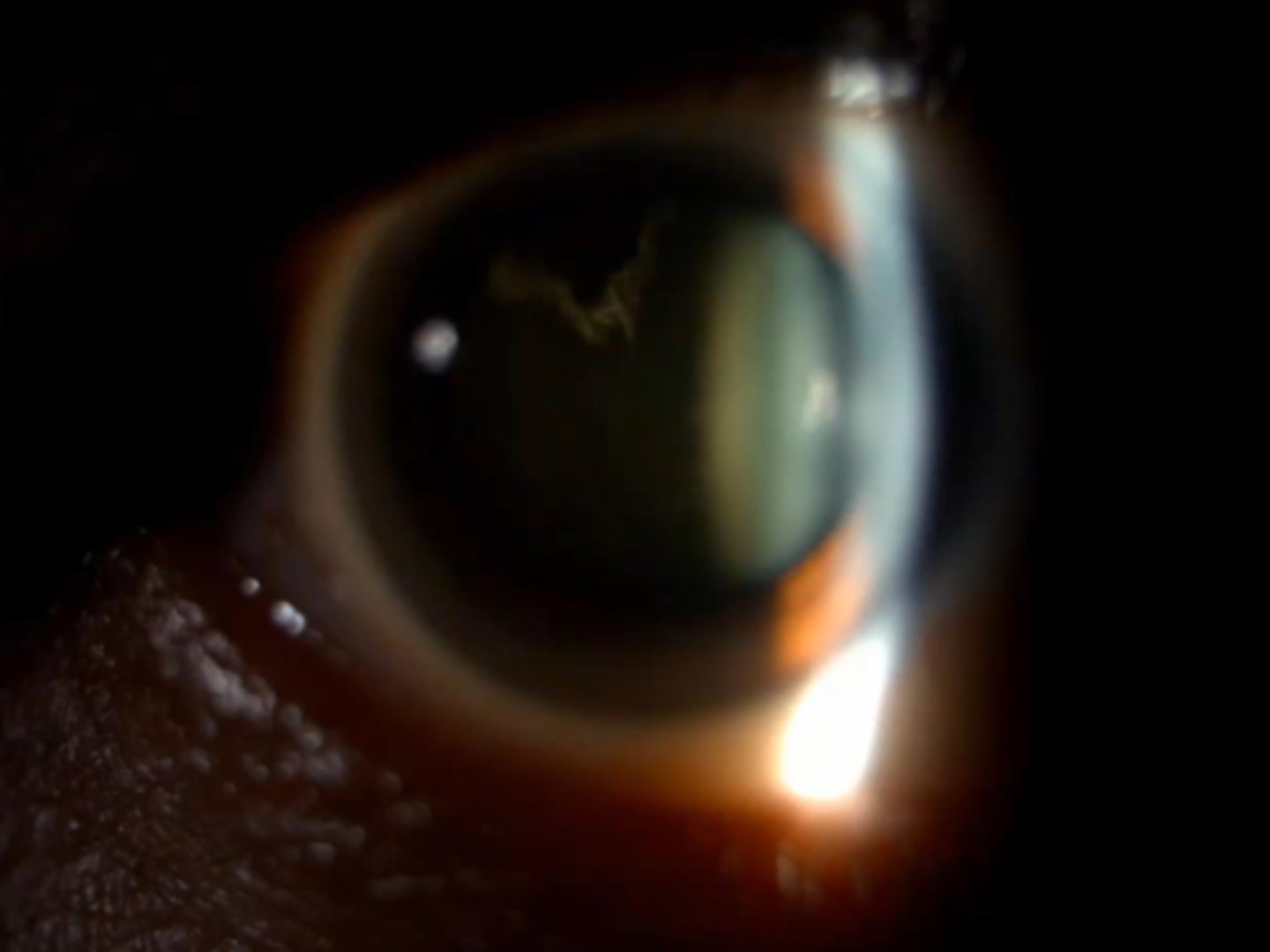
Mittendorf dot = attachment of anterior hyaloid artery on posterior lens
What form of anterior PFV is seen here?
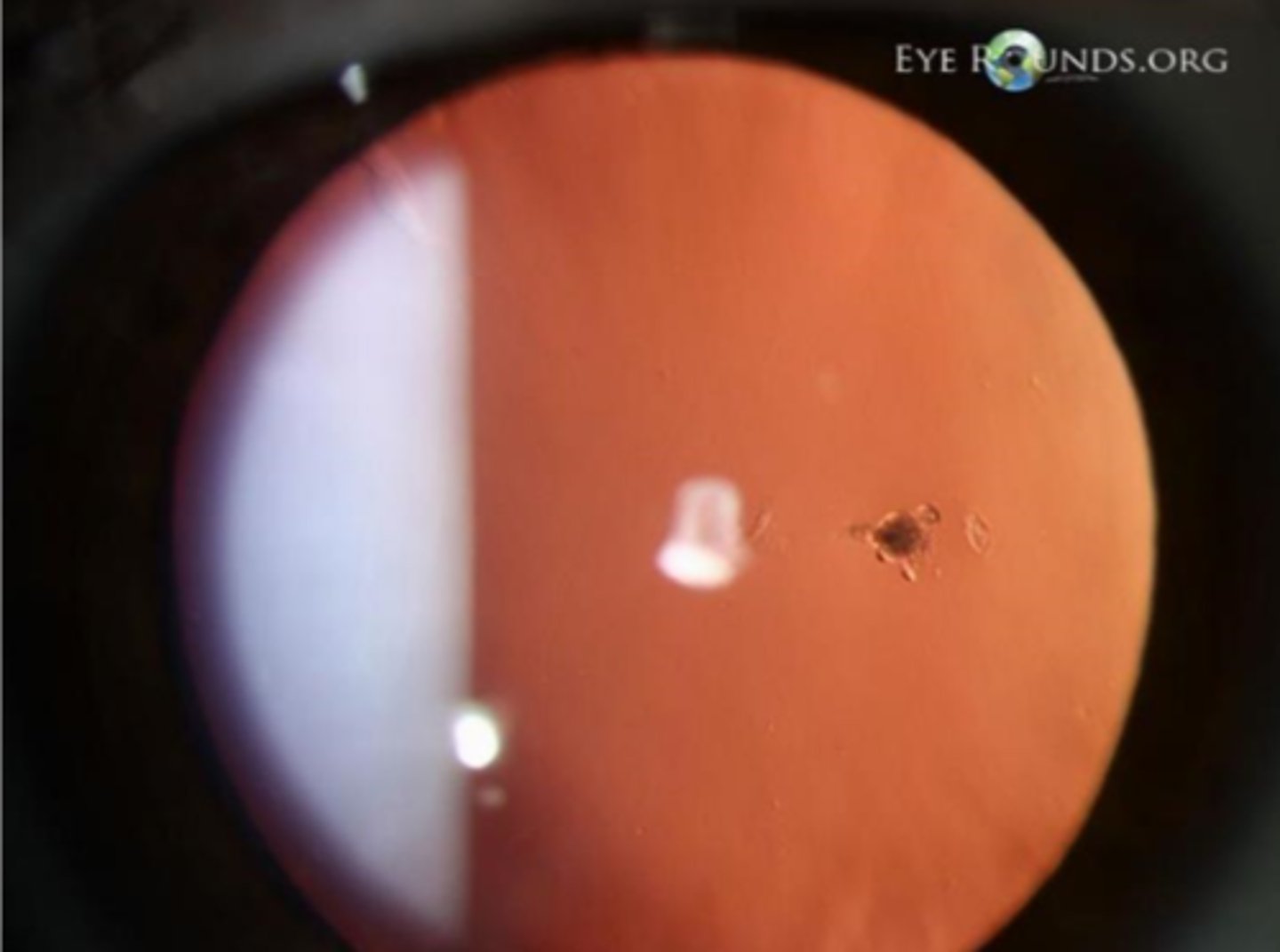
leukocoria
microphalmia
retinal folds = tractional RD of the posterior pole
hypoplastic/dyplastic ONH
vitreous memb/stalk = hazy fibrotic stalk with peripapillary macular traction and fluid
strabismus bc of reduced VA
macular pigment disruption or hypoplastic macula
clear lens!
What are some signs and complications of posterior PFV?
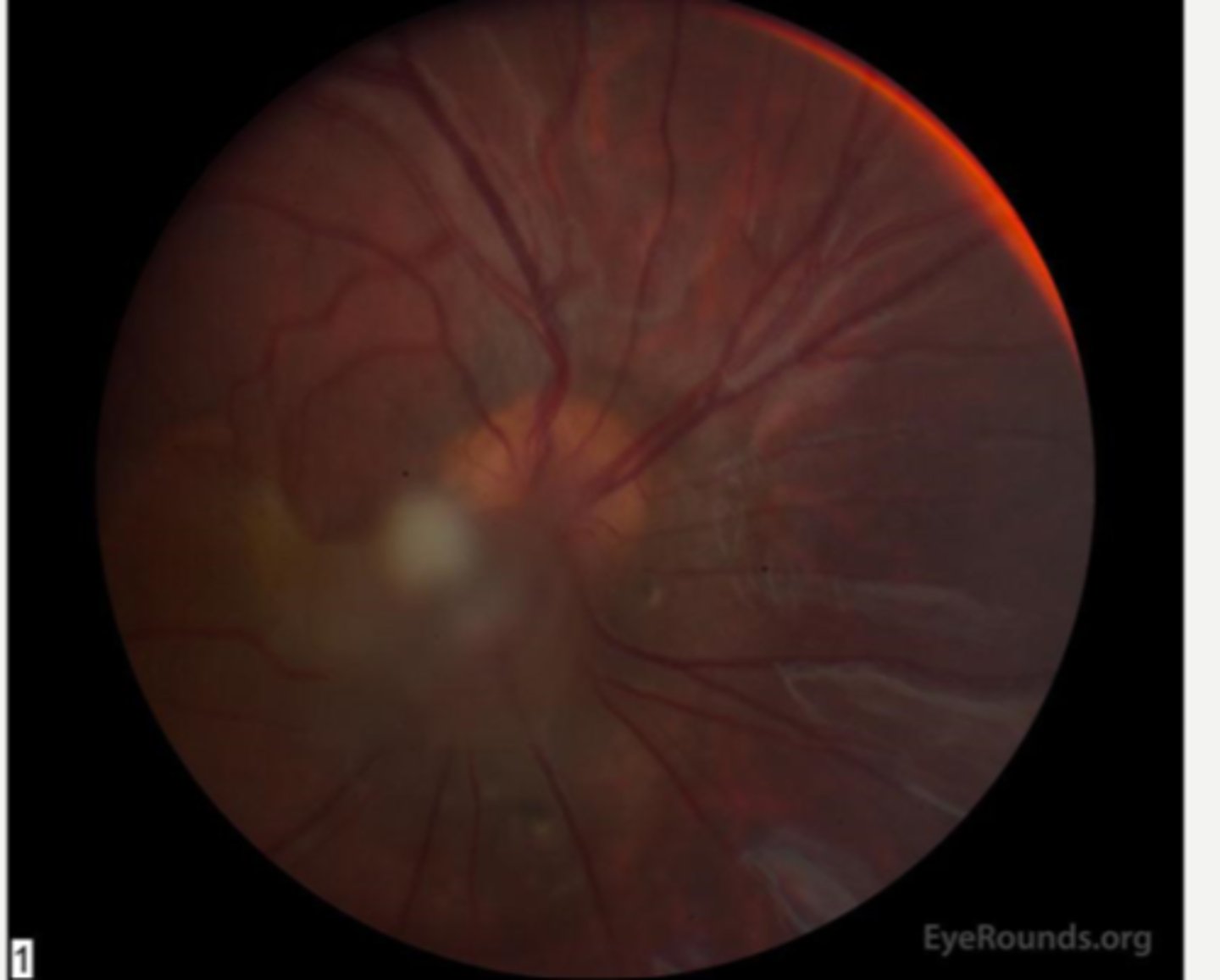
vitreous stalk may have active vasc and traction = RD
How can posterior PFV be vision threatening?
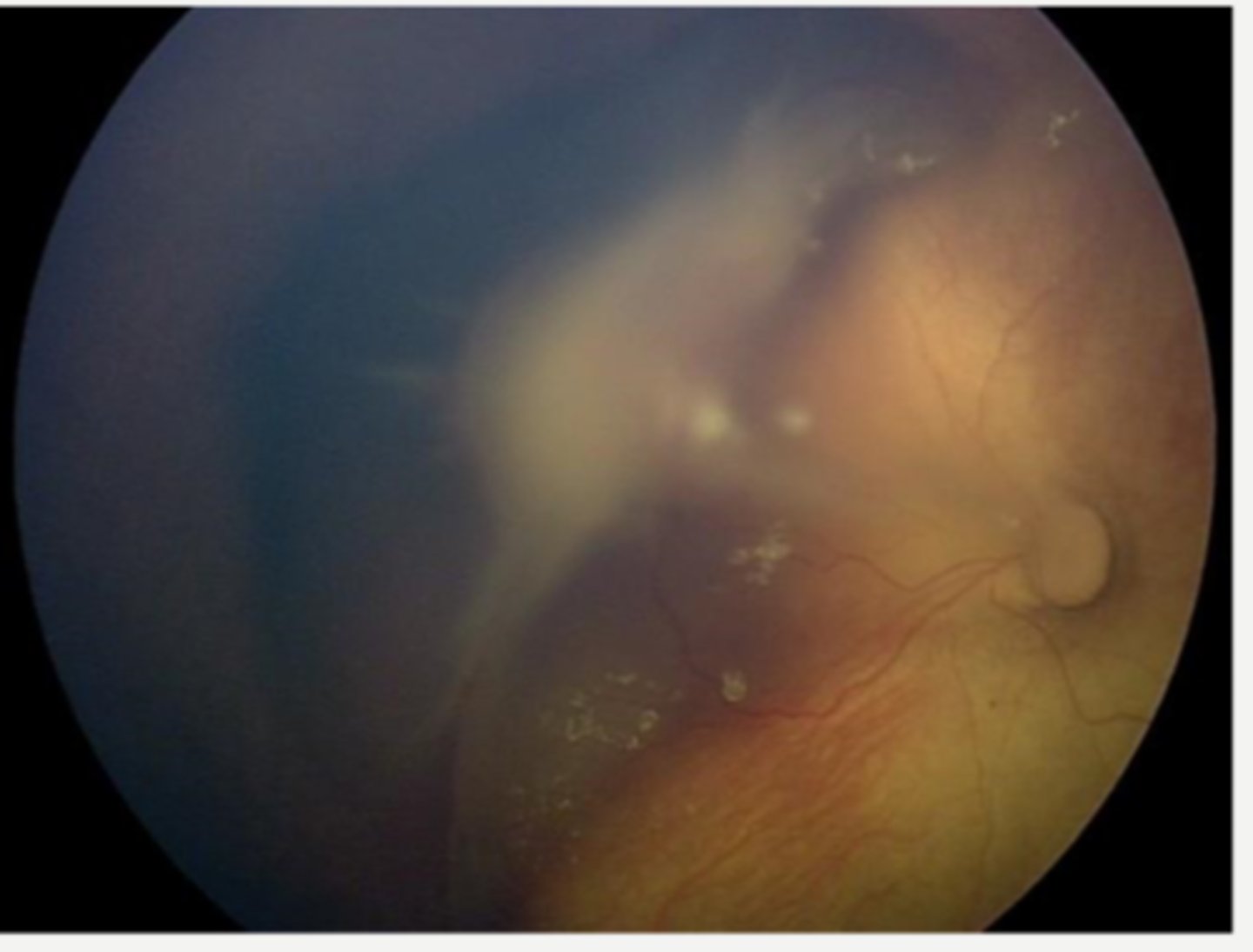
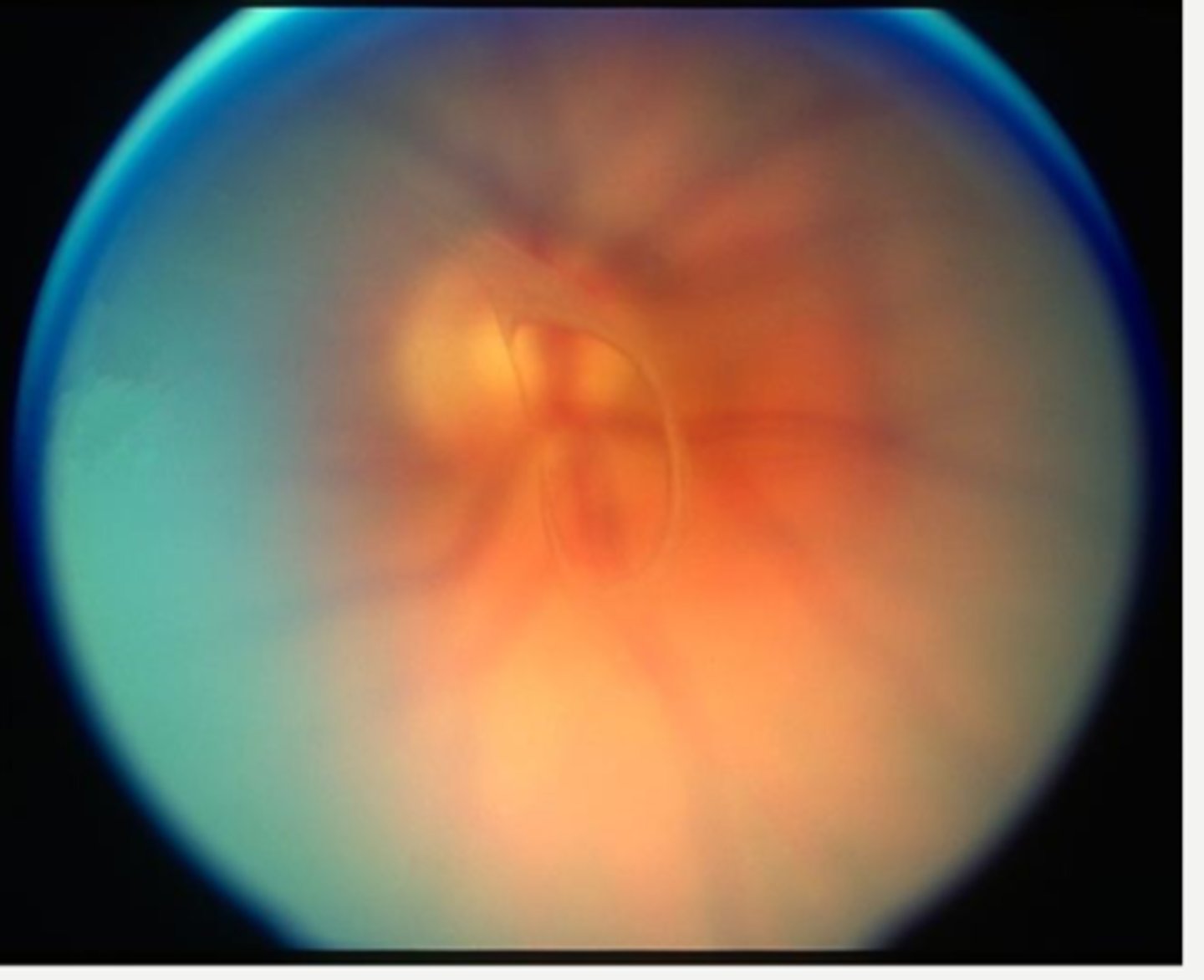
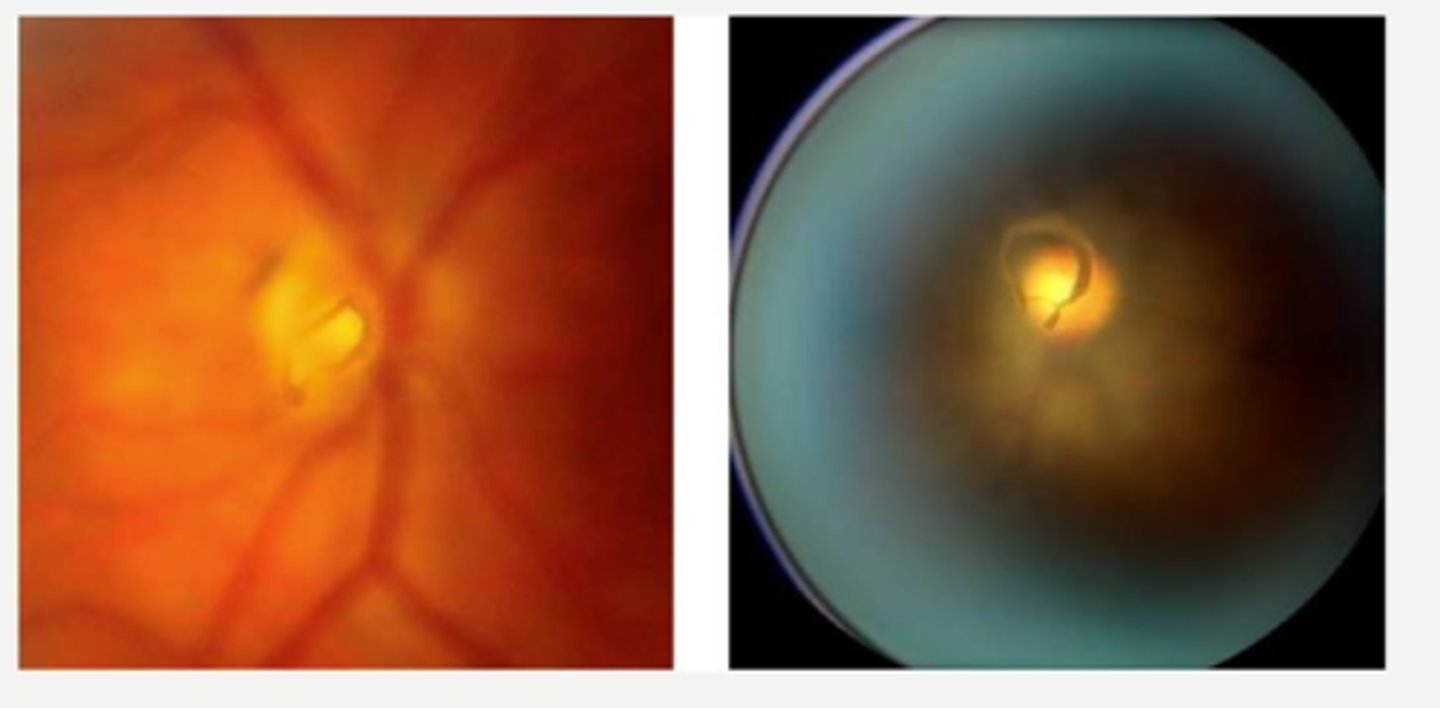
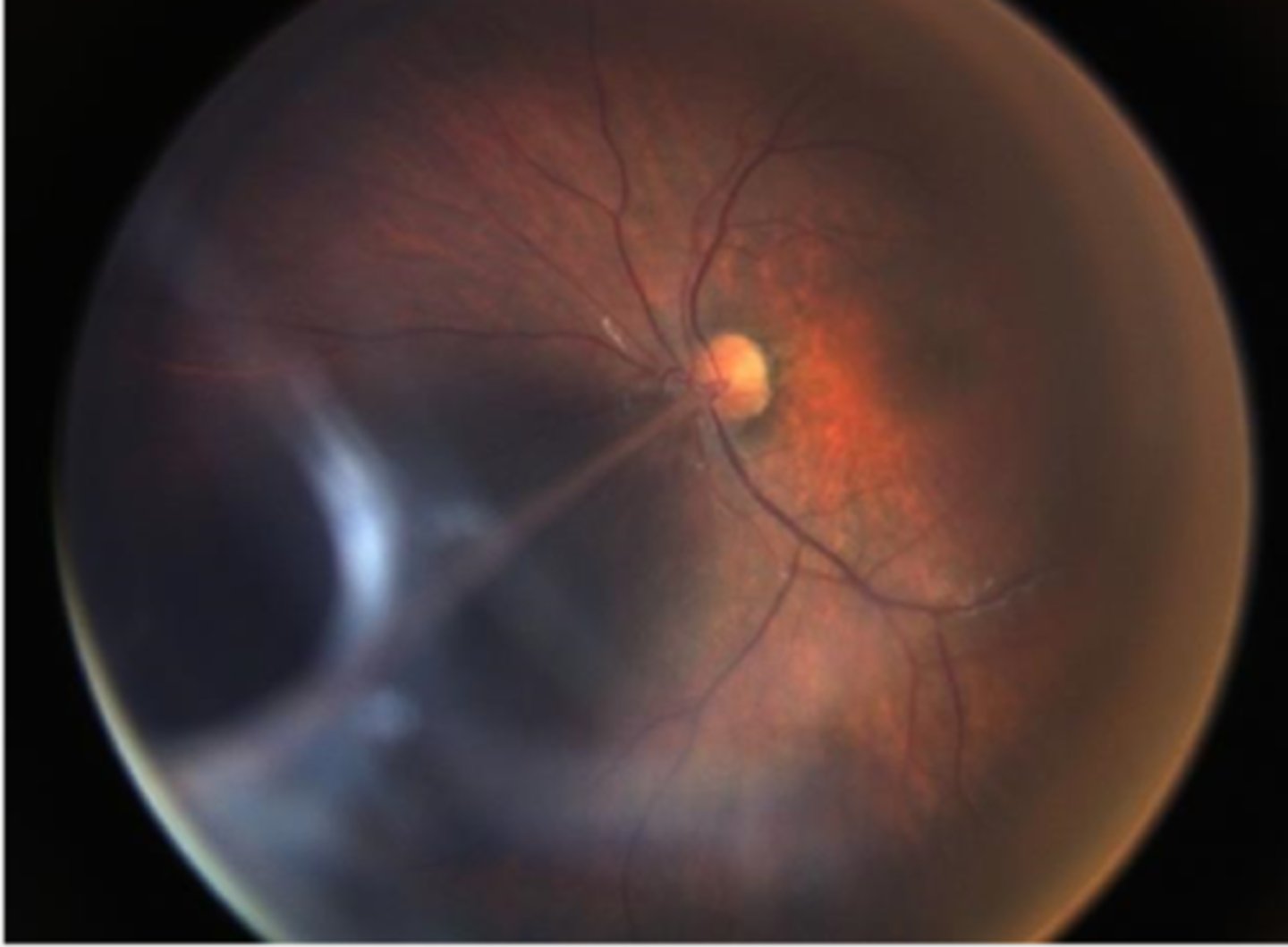
Bergmeister's papillae = benign remant of sheath around hyaloid artery at ONH
What form of posterior PFV is seen here?
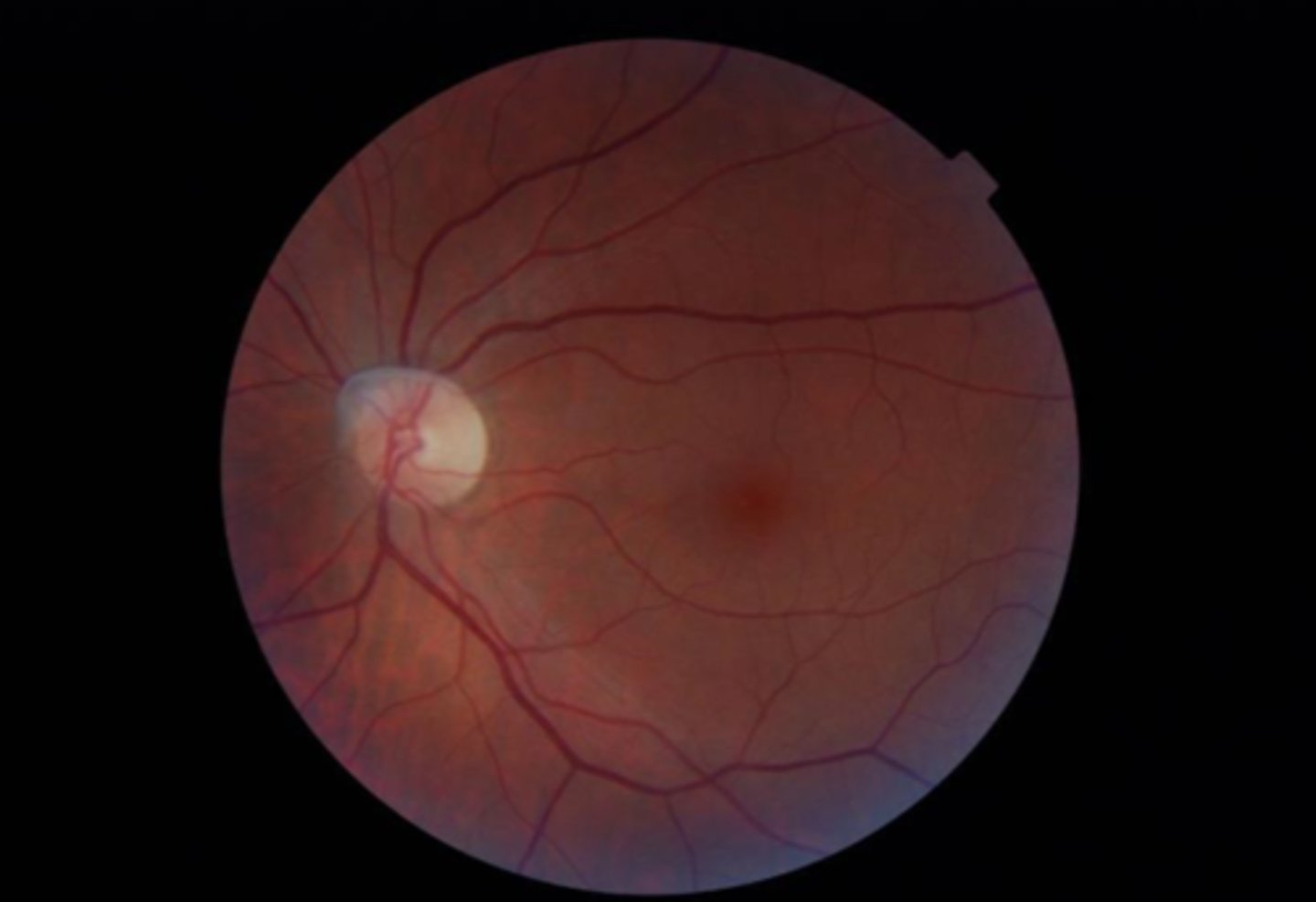
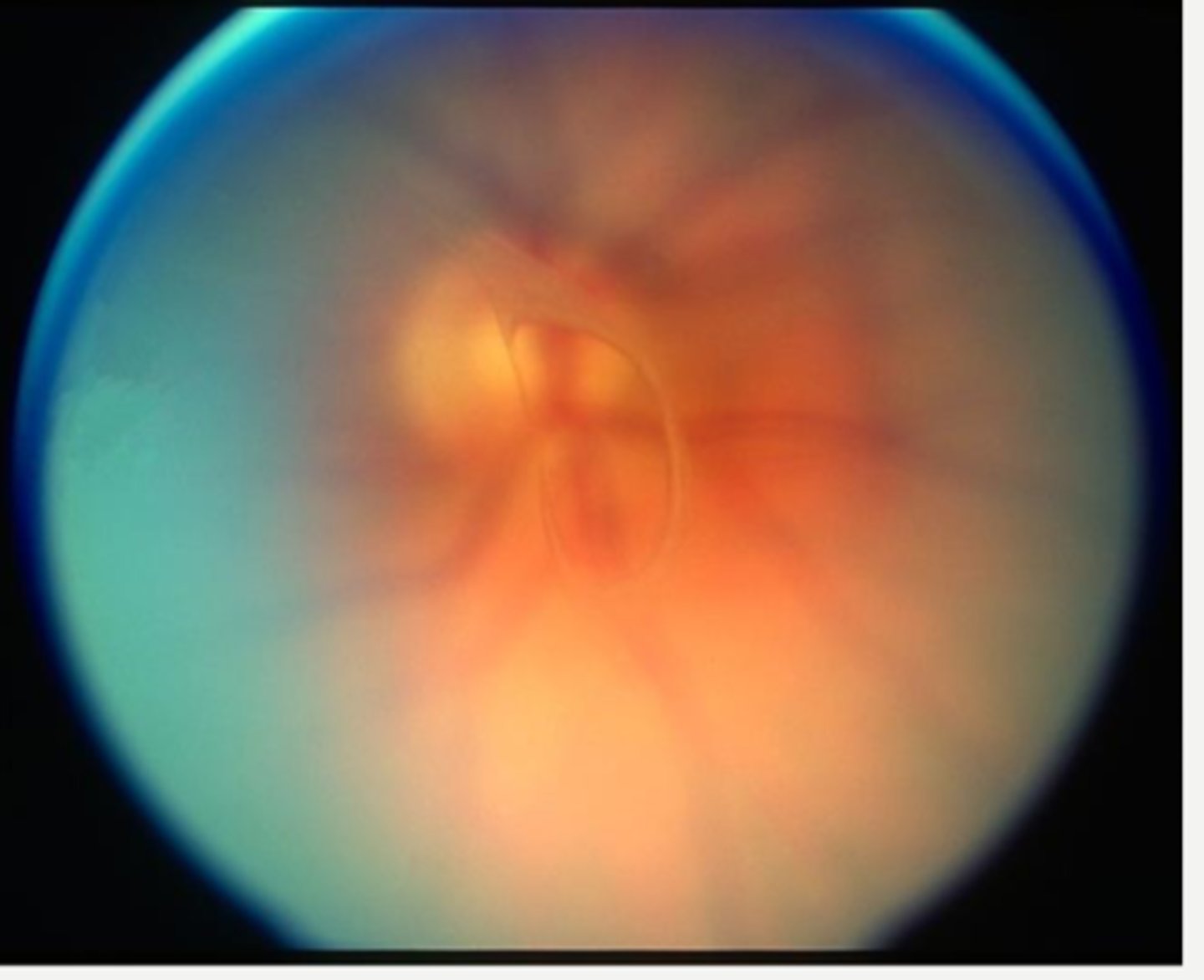
remnant of hyaloid artery
What form of posterior PFV is seen here?
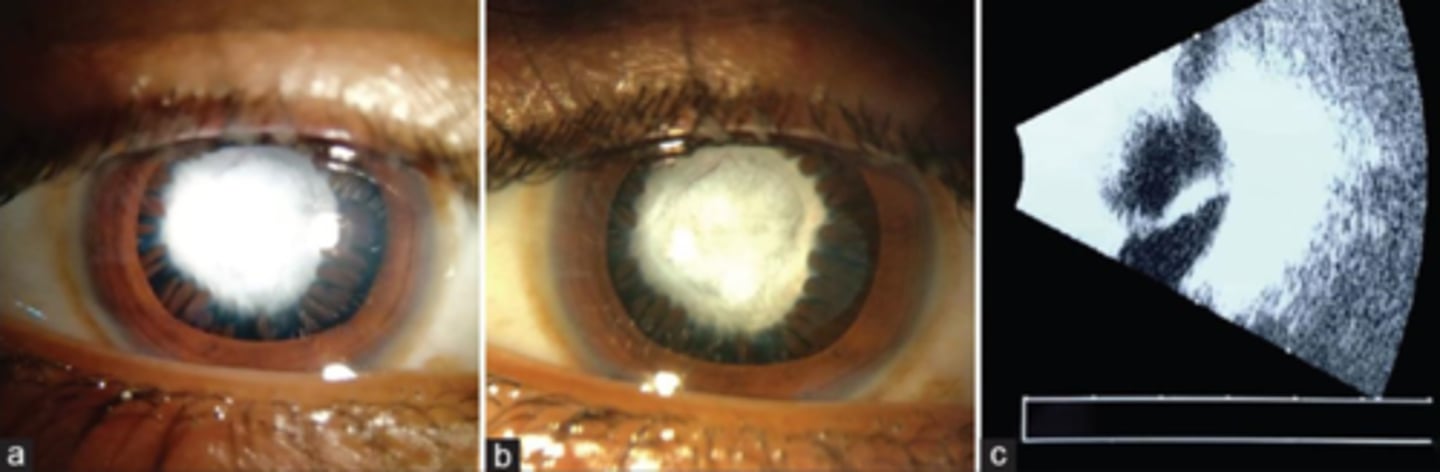
combination ant + post form with stalk
What form of PFV is seen here?
observe if benign
R/O ddx like retinoblastoma, ROP
surgical intervention like lensectomy or vitrectomy if...
visual axis occluded = amblyopia
retinal traction = RD or break
shallow AC = angle closure glaucoma
How do we manage PFV?