the pancreas
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what are the two functions of the pancreas?
endocrine - hormonal
exocrine - digestive
what is the exocrine function of the pancreas?
produce and secrete:
- digestive enzymes
- bicarbonate
- water
where is the pancreas in relation to the duodenum?
the 'C' shaped duodenum curves around the head of the pancreas
where is the pancreas in relation to the stomach?
it lies inferiorly to the stomach, separated by the lesser sac
is the pancreas intraperitoneal?
no, it is retroperitoneal
where is the pancreas in relation to the spleen?
- it is anterior and medial to the spleen
- the tail of the pancreas is attached to the spleen by the lienorenal ligament (formed from the peritoneum)
what vessels surround the pancreas? (3)
- the aorta and inferior vena cava
- superior mesenteric artery
- the splenic and sup mes veins
where are the aorta and inf vena cava in relation to the pancreas?
posterior to head of pancreas
where is the sup mes art in relation to the pancreas?
posterior to the neck of the pancreas and anterior to the uncinate process
what are the 5 parts of the pancreas?
- head
- uncinate process
- neck
- body
- tail
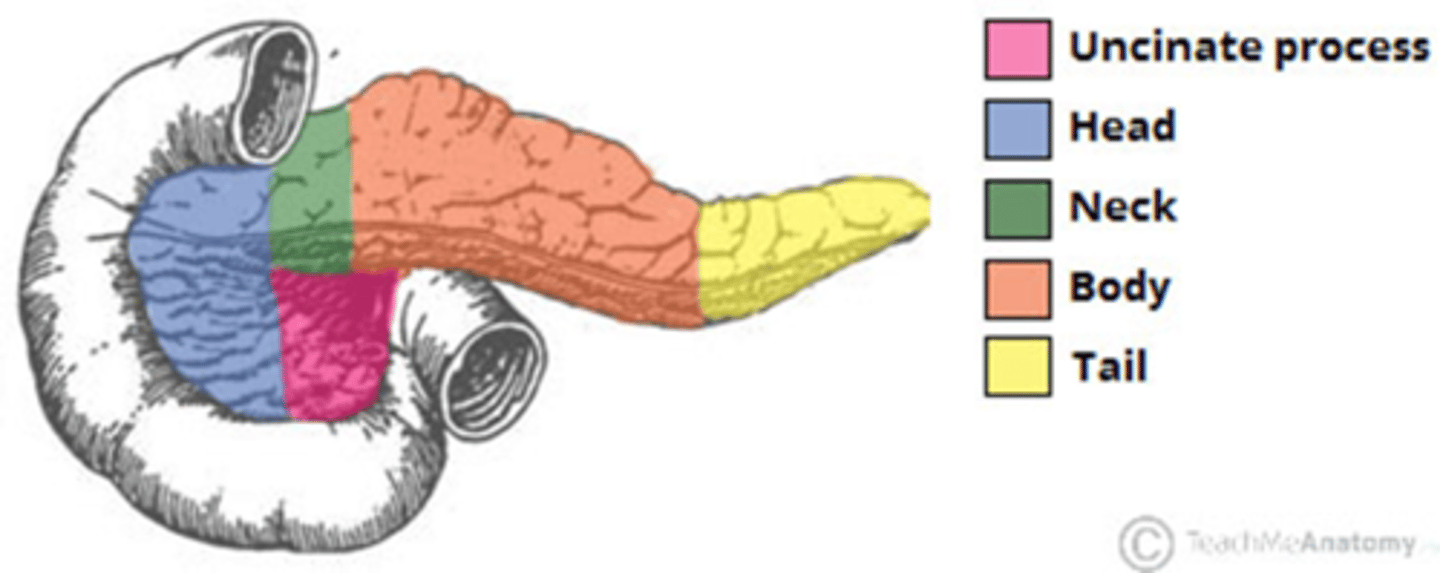
what is the head of the pancreas?
- widest part of pancreas
- lies in the c-shaped curve of duodenum
- connected to duodenum by connective tissue
what is the head of the pancreas attached to?
duodenum by connective tissue
what is the uncinate process?
- a projection from the head, extending medially to lie beneath the body of the pancreas
- lies posteriorly to superior mesenteric vessels
what is the neck?
- located between the head and body
- overlies the sup mes vessels which form a groove on its posterior side
what is the body?
- located centrally, lies behind the stomach and to the left of sup mes vessels
what is the tail?
the left end which is attached to the spleen by the lienorenal ligament
which is the only part of the pancreas that is intraperitoneal?
the tail
what are the macroscopic features of the exocrine pancreas?
- lobulated, serous gland
- composed of approx one million 'berry-like' clusters of cells called acini
how are the acini connected?
by short intercalated ducts
how does the duct system of the pancreas work?
- the short intercalated ducts (from acini) unite and drain into a network of intralobular collecting ducts - intralobular collecting ducts drain into interlocular ducts and into the main pancreatic duct
- the pancreatic duct runs the length of the pancreas and unites with the common bile duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla of Vater
- this structure opens into the duodenum via the major duodenal papilla
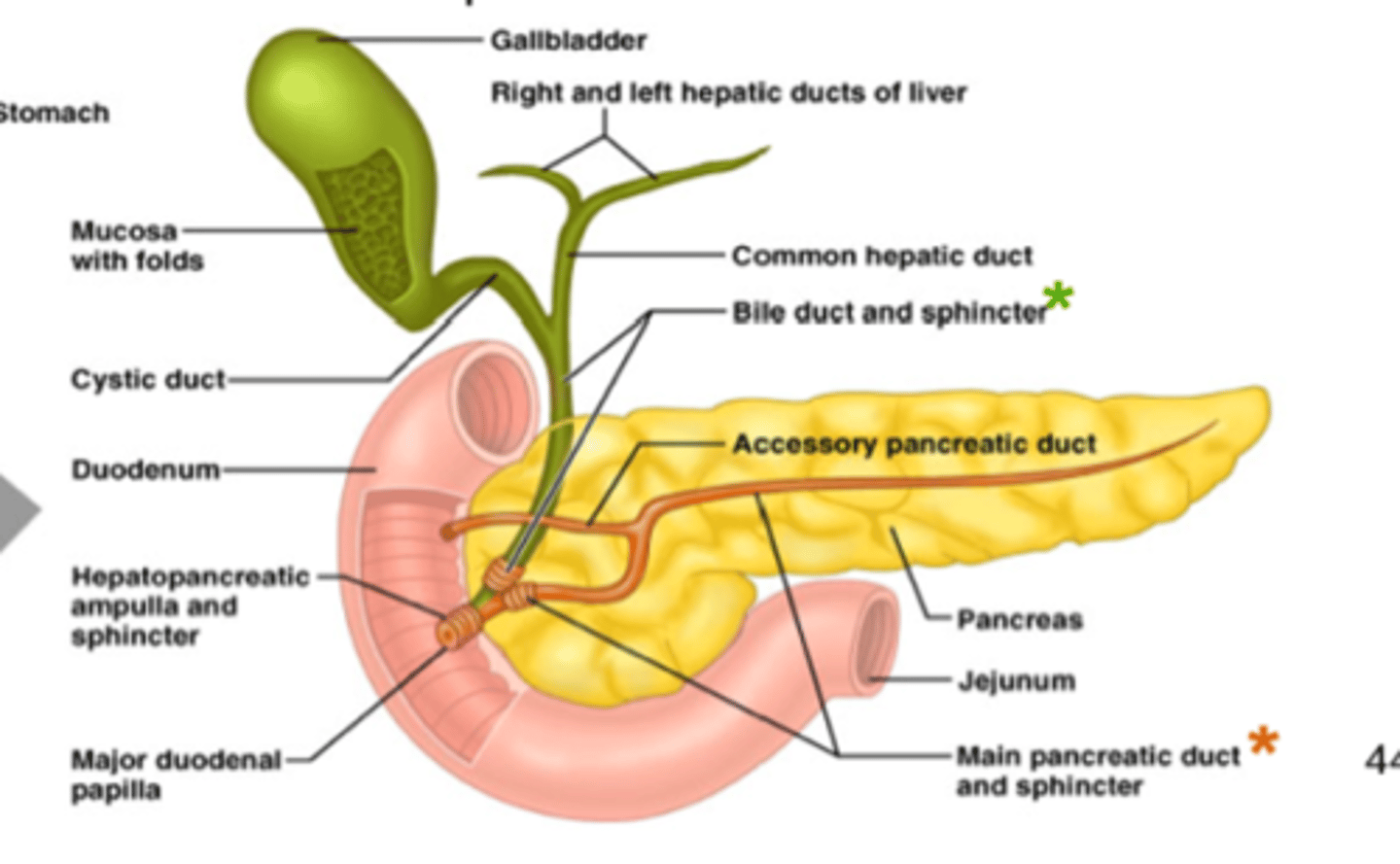
what is another name for the accessory pancreatic duct?
duct of Santorini
where does the duct of Santorini empty into?
minor duodenal papilla
how are secretions into the duodenum controlled?
by the sphincter of Oddi, which surrounds the hepatopancreatic ampulla
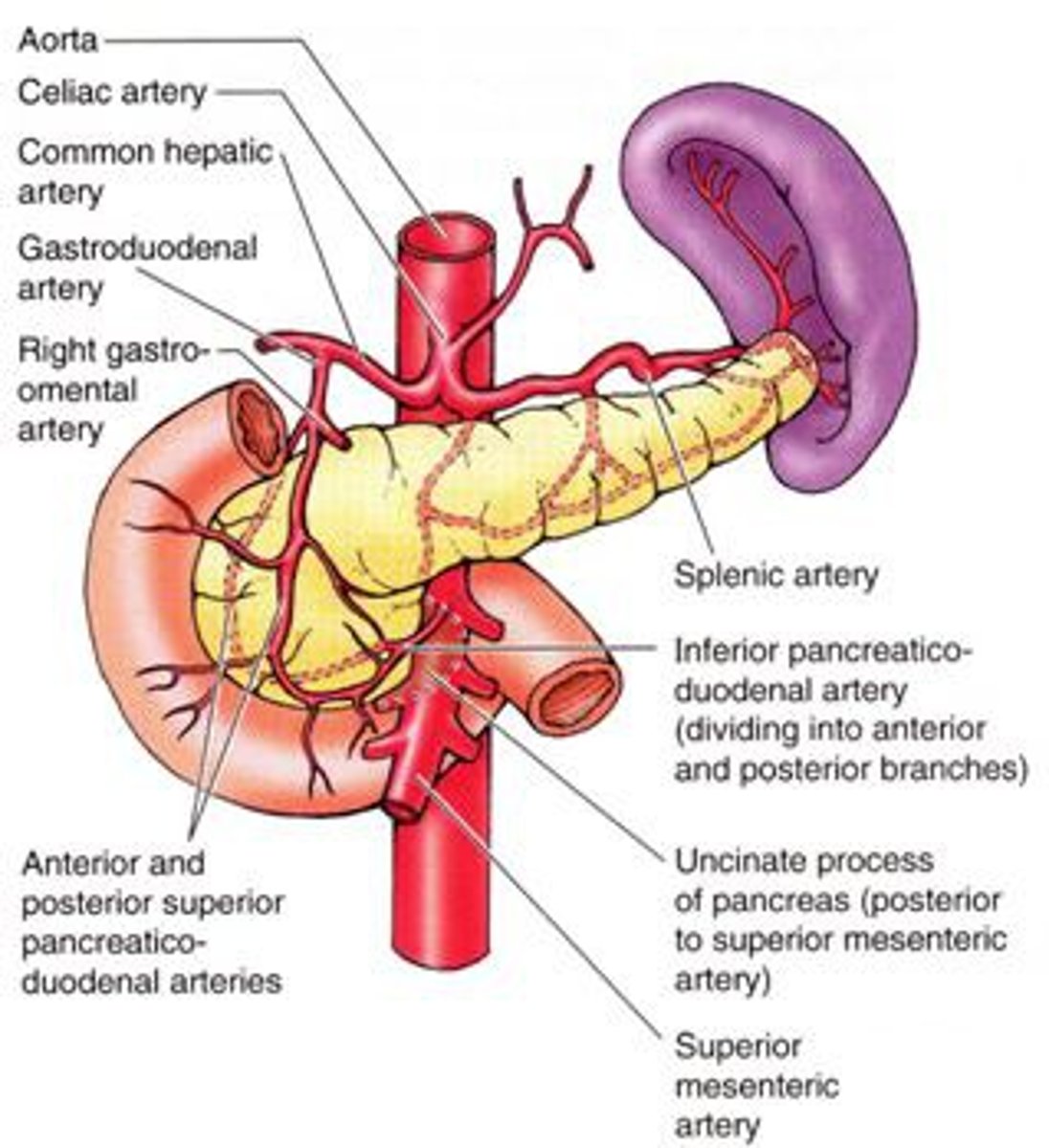
what arteries supply blood to the pancreas? (2)
- supplied by pancreatic branches of the splenic artery
- head of pancreas is also supplied by the superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries, which are branches from the gastroduodenal (coeliac trunk) and superior mesenteric arties, respectively
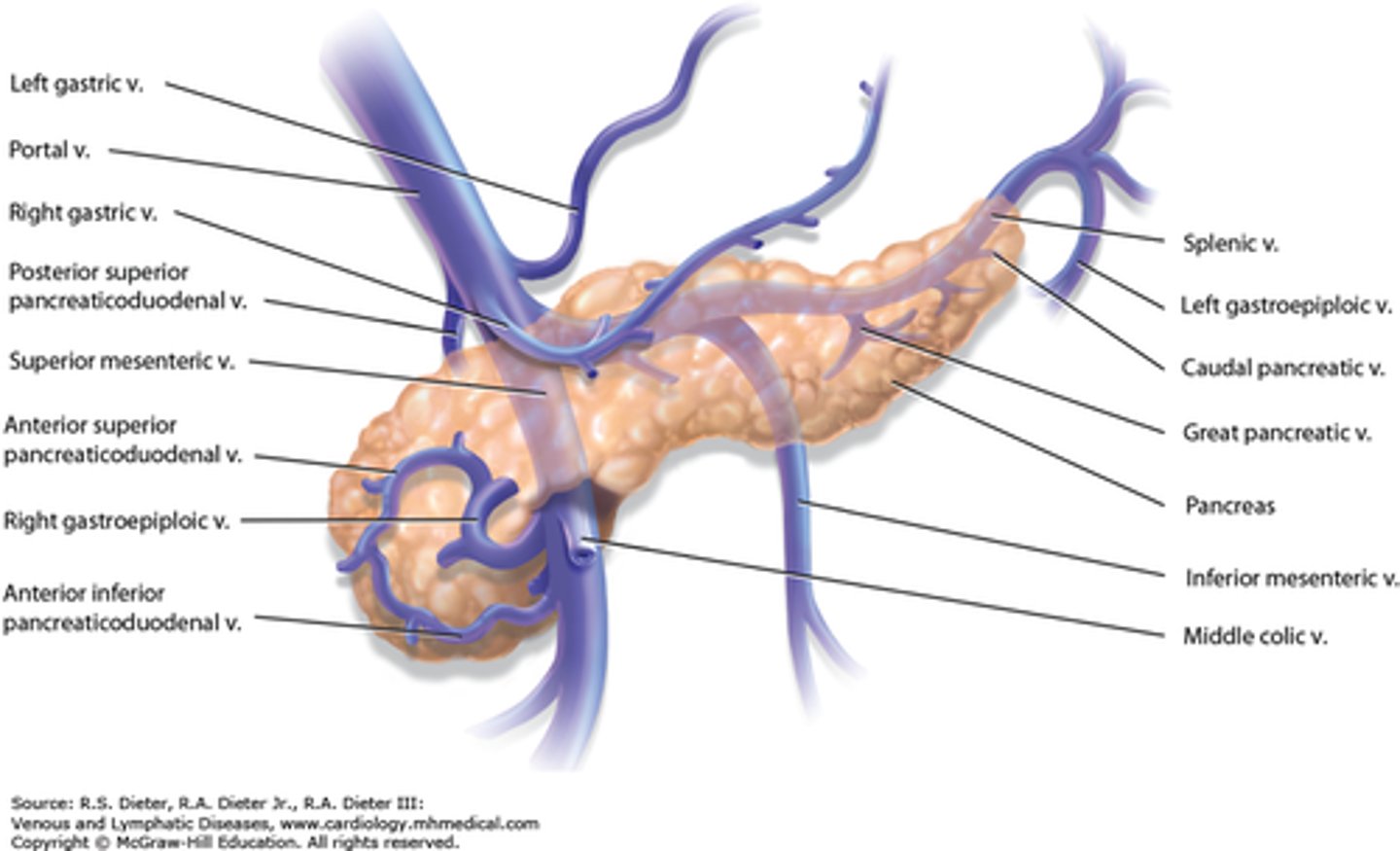
what veins drain blood from the pancreas? (2)
- pancreatic veins drain via the splenic vein
- head of pancreas is drained by superior mesenteric branches of hepatic portal vein
what nerves supply the pancreas?
parasympathetic - vagus nerve (CN X)
sympathetic - greater and lesser splanchnic nerves (T5-12)
both from superior mesenteric plexus
what is the ratio of endocrine to exocrine pancreas?
98% exocrine
2% endocrine
what does the exocrine pancreas consist of?
the acinus and its duct system
what is the acinus?
acinar cells that are specialised in enzyme synthesis, storage and secretion
what is the duct system for?
it modifies the aqueous secretions
what does the endocrine pancreas consist of?
the Islets of Langerhans
what make up the Islets of Langerhans?
alpha cells - make up 15-20% and produce glucagon
beta cells - make up 65-80% and produce insulin and amylin
delta cells - make up 3-10% and produce somatostatin
gamma cells - make up 3-5% and produce pancreatic polypeptide
epsilon cells - make up less than 1% and produce ghrelin
what does glucagon do generally?
increases blood glucose levels
what stimulates alpha cells to release glucagon?
hypoglycaemia
what does insulin do generally?
decreases blood glucose levels
what stimulates beta cells to release insulin?
- hyperglycaemia
- glucagon-like peptide 1
- acetylcholine
- sulphonylureas (antidiabetic)
what stimulates beta cells to release amylin?
fatty acids
what does amylin do?
- slows gastric emptying
- decreases glucagon release
what does somatostatin do?
inhibits insulin, glucagon, pancreatic enzyme secretion, and gastric emptying
what stimulates delta cells to release somatostatin?
glucose
what does pancreatic polypeptide do?
inhibits:
- pancreatic bicarbonate and enzyme secretion
- gallbladder contraction
- cck
stimulates gastric acid secretion
what stimulates gamma cells to release pancreatic polypeptide?
protein
what does ghrelin do?
stimulates appetite
what stimulates ghrelin release?
glucagon
what is another name for the main pancreatic duct?
the duct of Wirsung