HES 420 Weeks 1-4
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything up to (not including) QRS axis determination
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
The lower portion of the heart is (ironically) referred to as the ________.
apex
The upper portion of the heart is referred to as the _______.
Based
The majority of the heart lies to the _________ of the midline of the sternum.
Left
Heart size and weight can be influenced by….
age, body weight, exercise, heart disease, etc
Ejection fraction is defined as th
Ejection fraction (Ef) can be defined as…
a measurement expressed as a percentage that indicates how much blood the heart pumps out with each contraction
Normal Ef can range between…
55-70%
Ateries carry blood (away from/towards) the heart, veins carry blood (away from/towards) the heart.
away from; towards
The right atrium recieves ________ blood and sends it to the _______ ________.
deoxygenated; right ventricle
The right ventricle pumps _________ blood to the ________ __________ to be recieved by the lungs.
deoxygenated; pulmonary artery
Pulmonary veins bring _________ blood back to the heart from the lungs, specifically to the ________ _______.
oxygenated; left atrium
The left atrium sends ______ blood to the ______ ______.
oxygenated; left ventricle
The left ventricle sends __________ blood to the ________ .
oxygenated; aorta
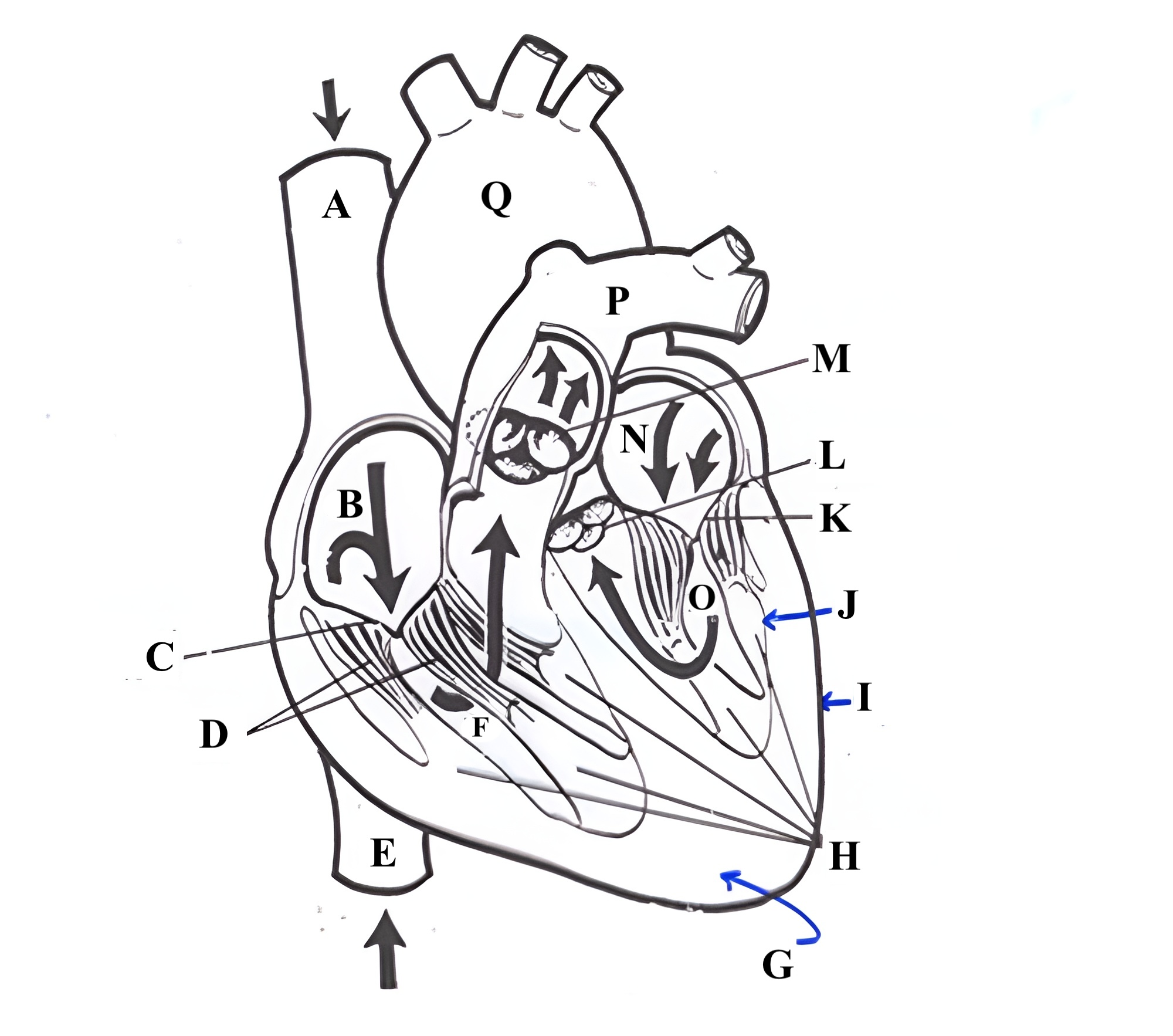
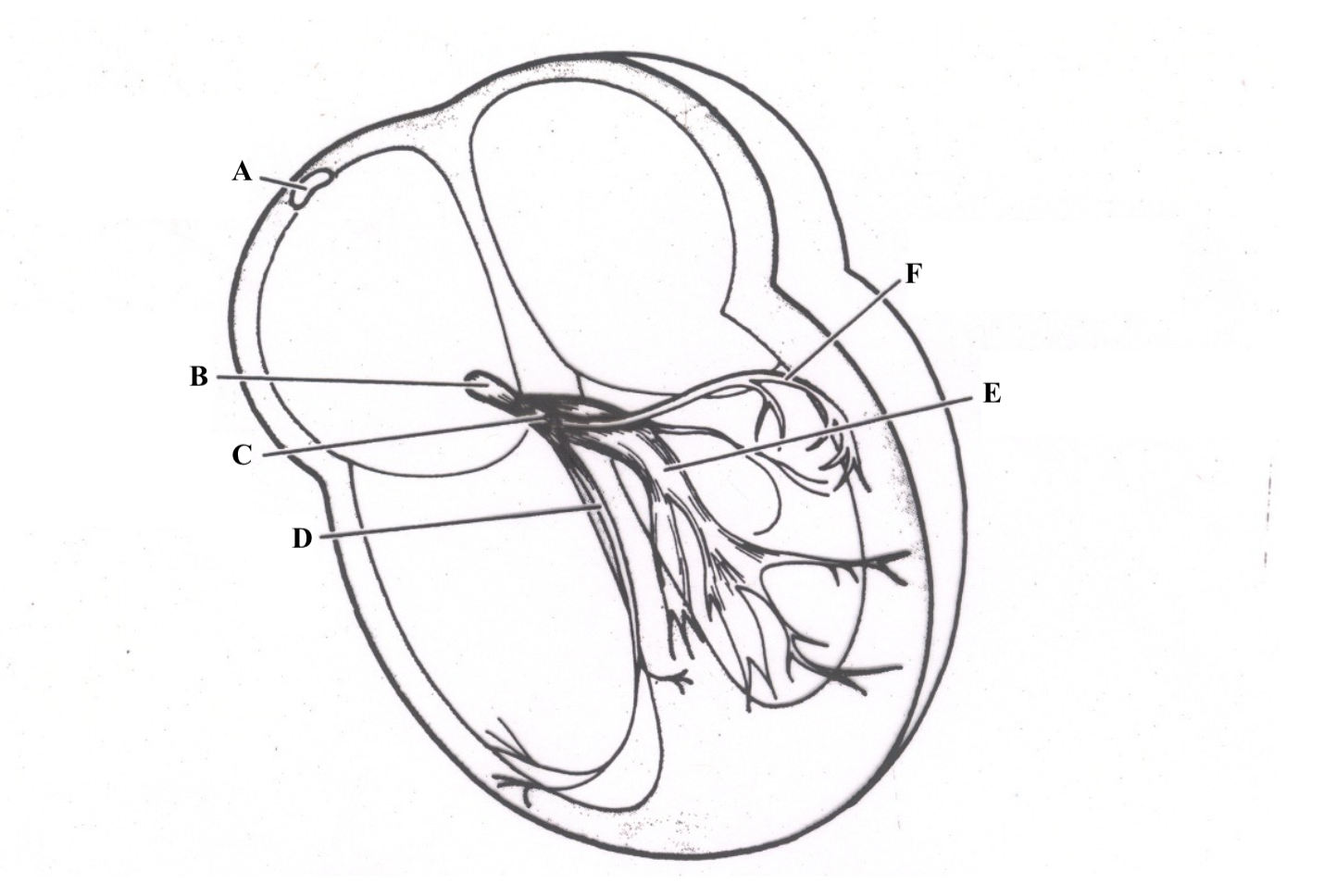
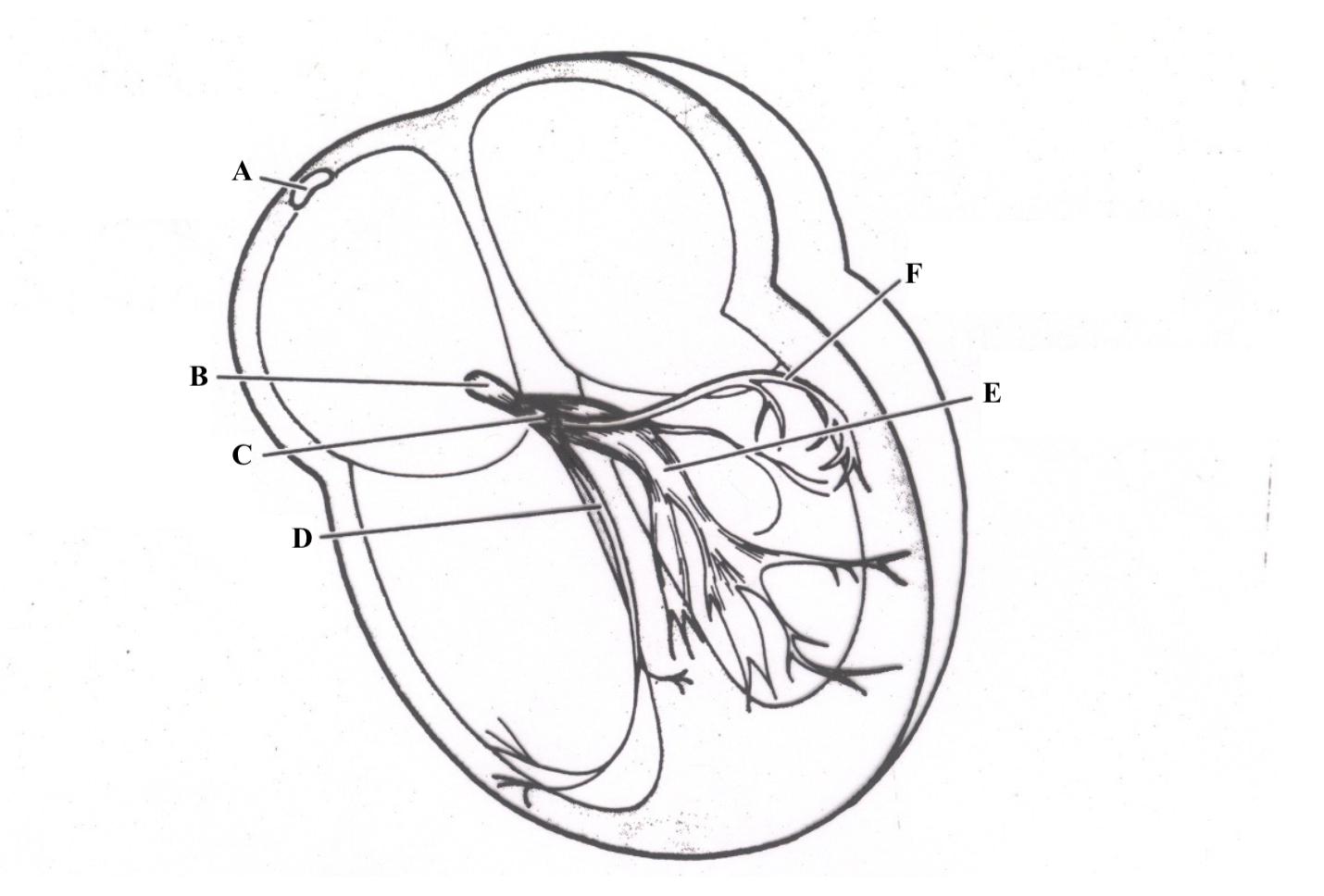
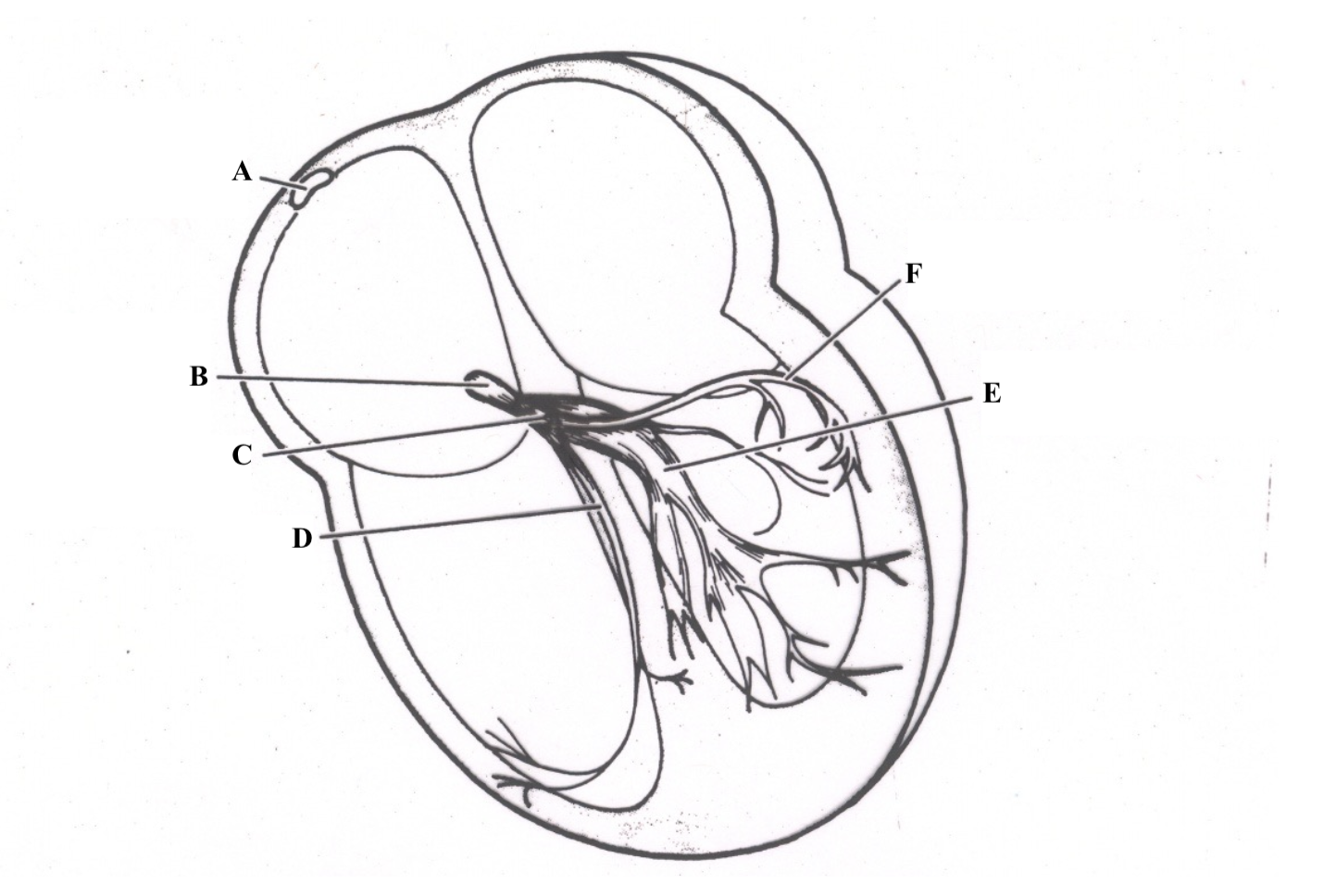
Structure A is the ________ _______ _______.
superior vena cava
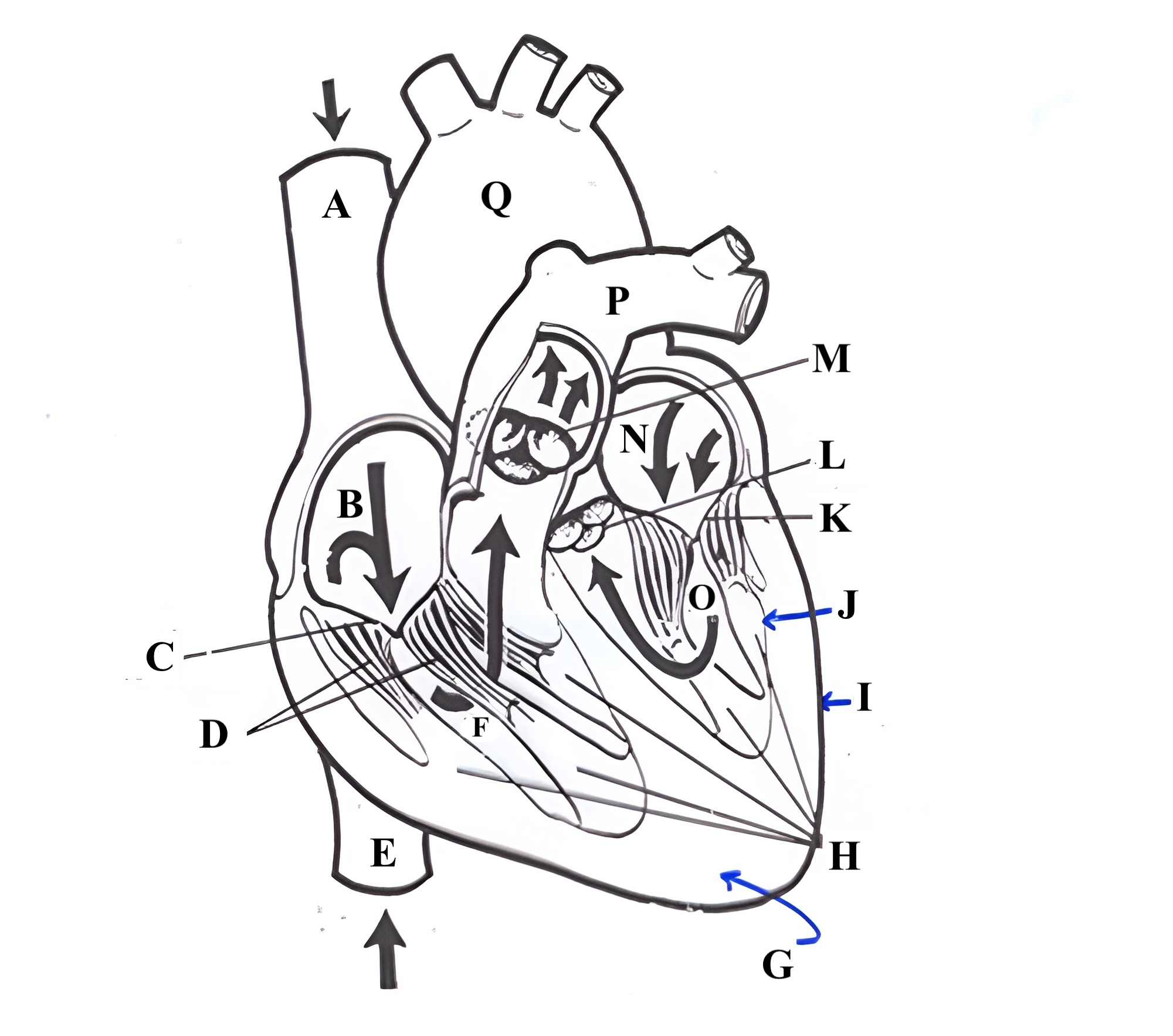
Structure B is the ________ ________.
right atrium
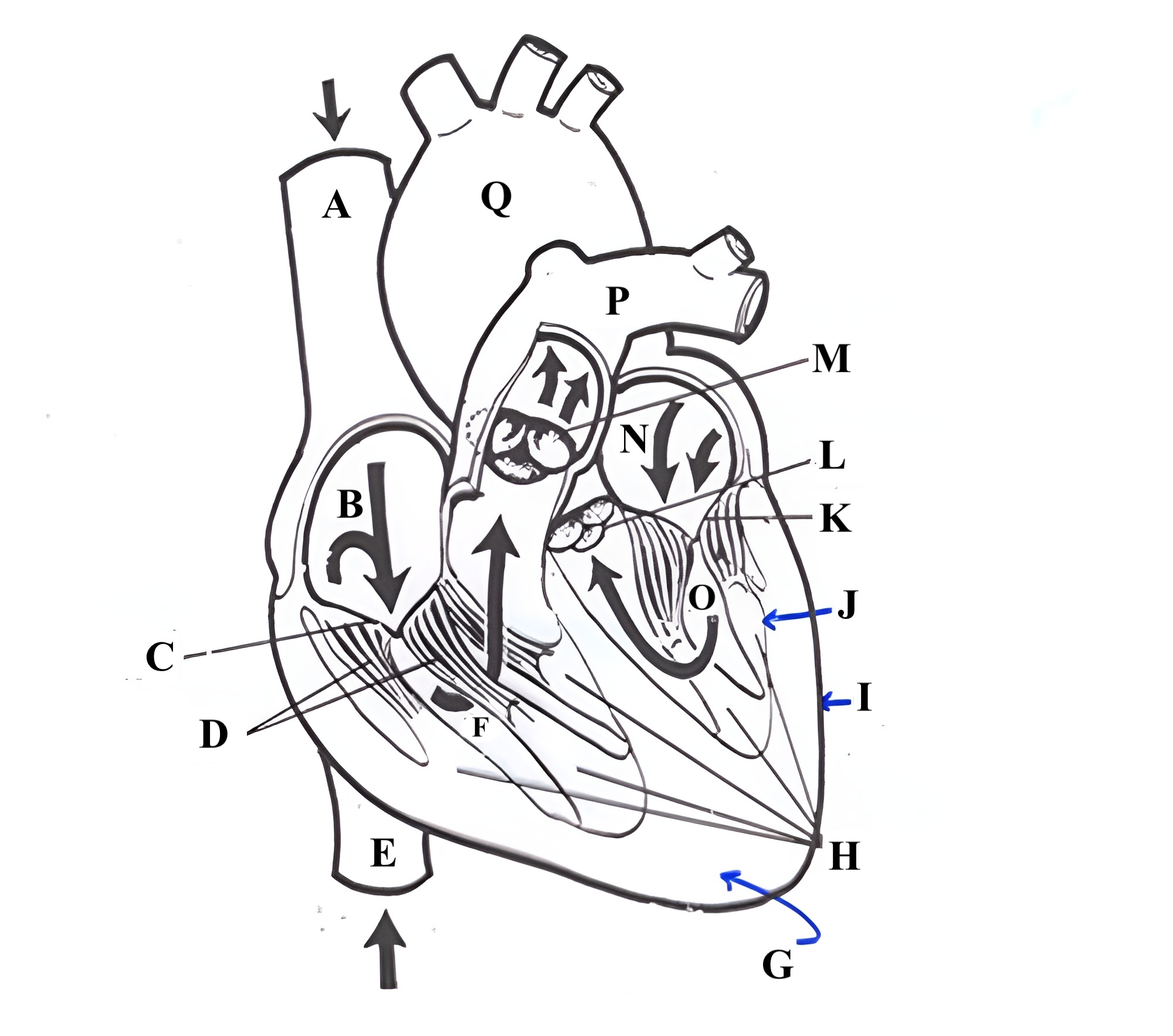
Structure C is the ________ ________.
tricuspid valve
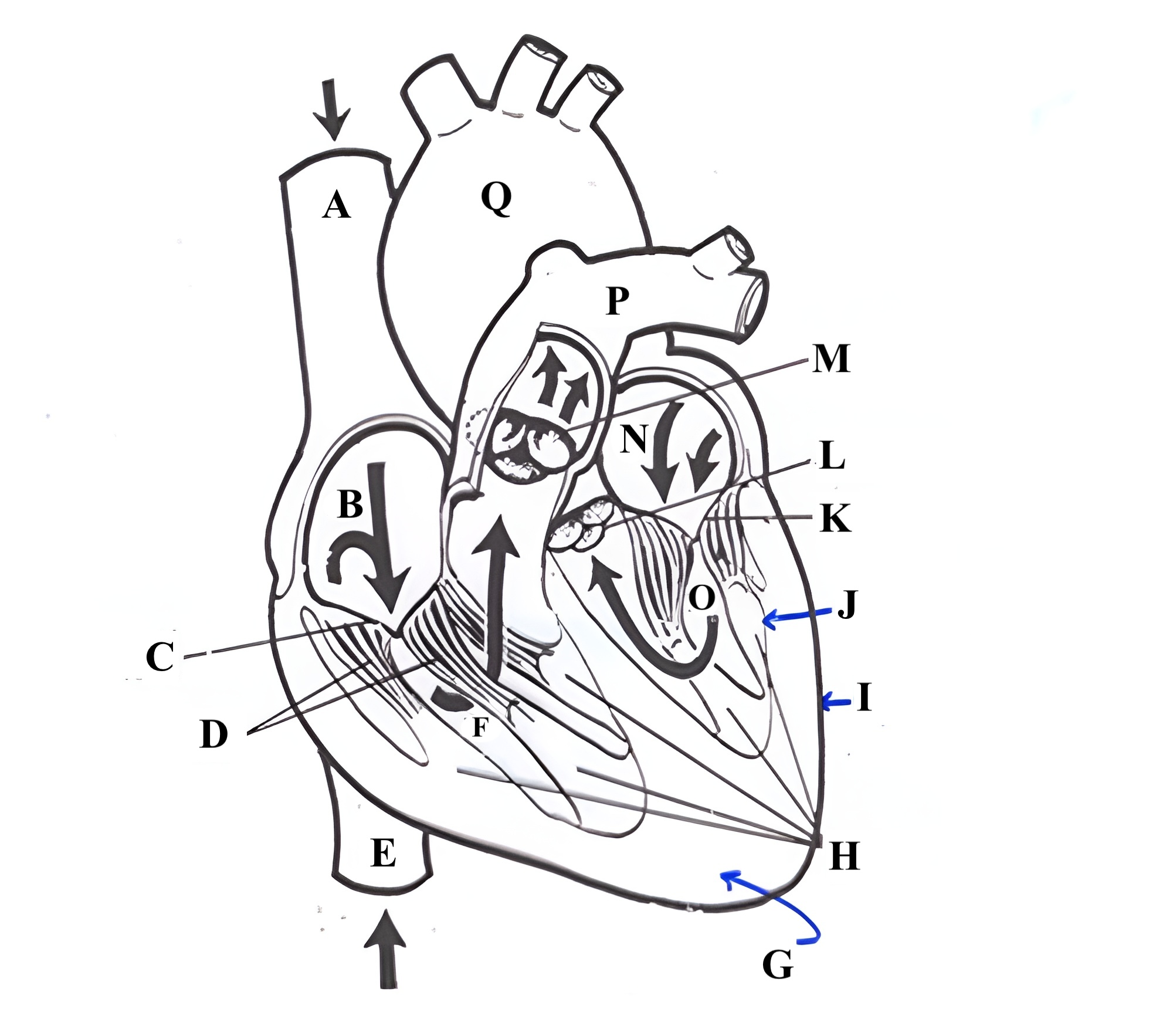
Structure D is the ________ _______.
chordae tendineae
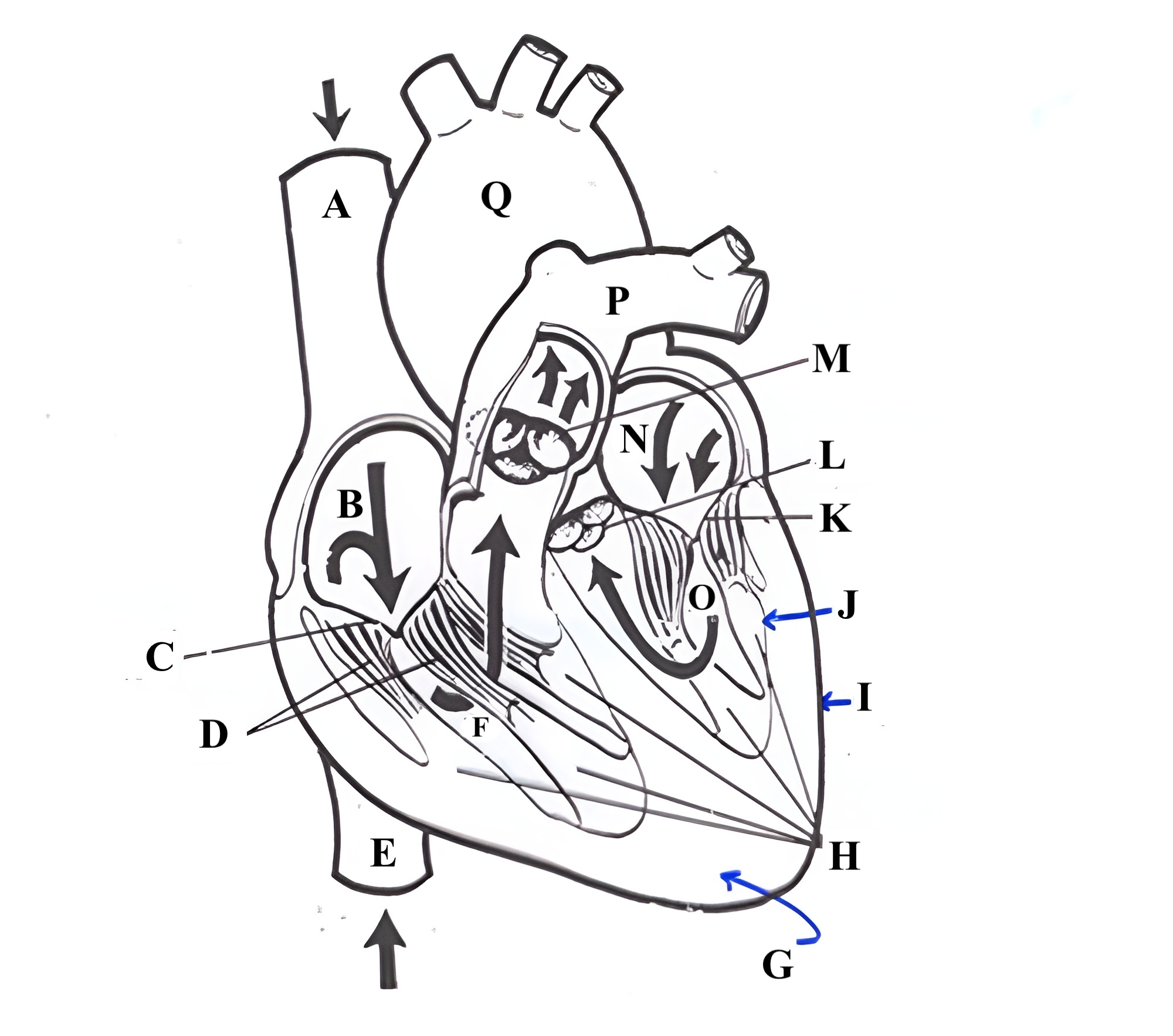
Structure E is the ________ ________ ________.
superior vena cava
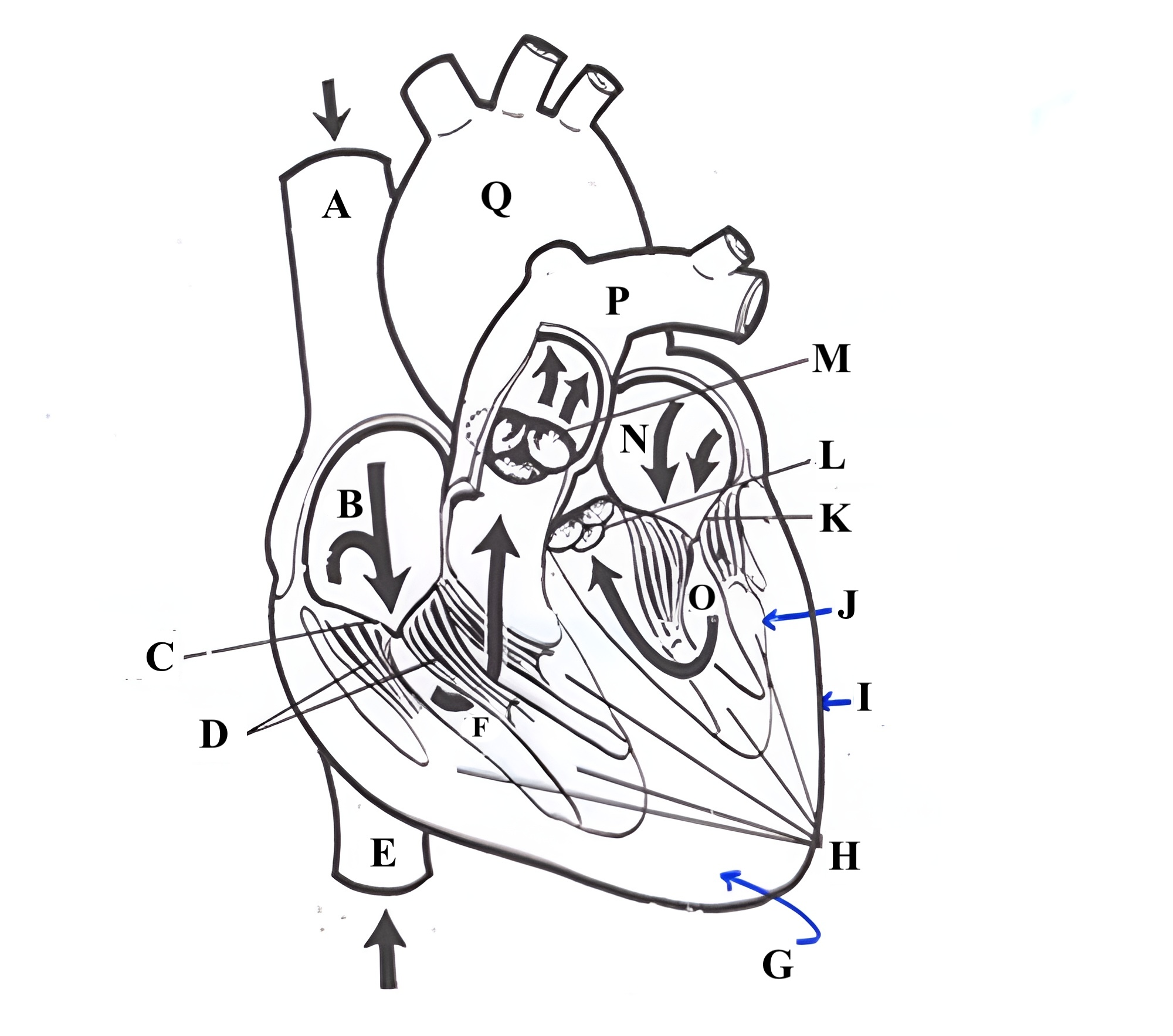
Structure F is the ________ ________.
right ventricle
Structure G is the _________ .
myocardium
Structure H is the _________ _______.
papillary muscles
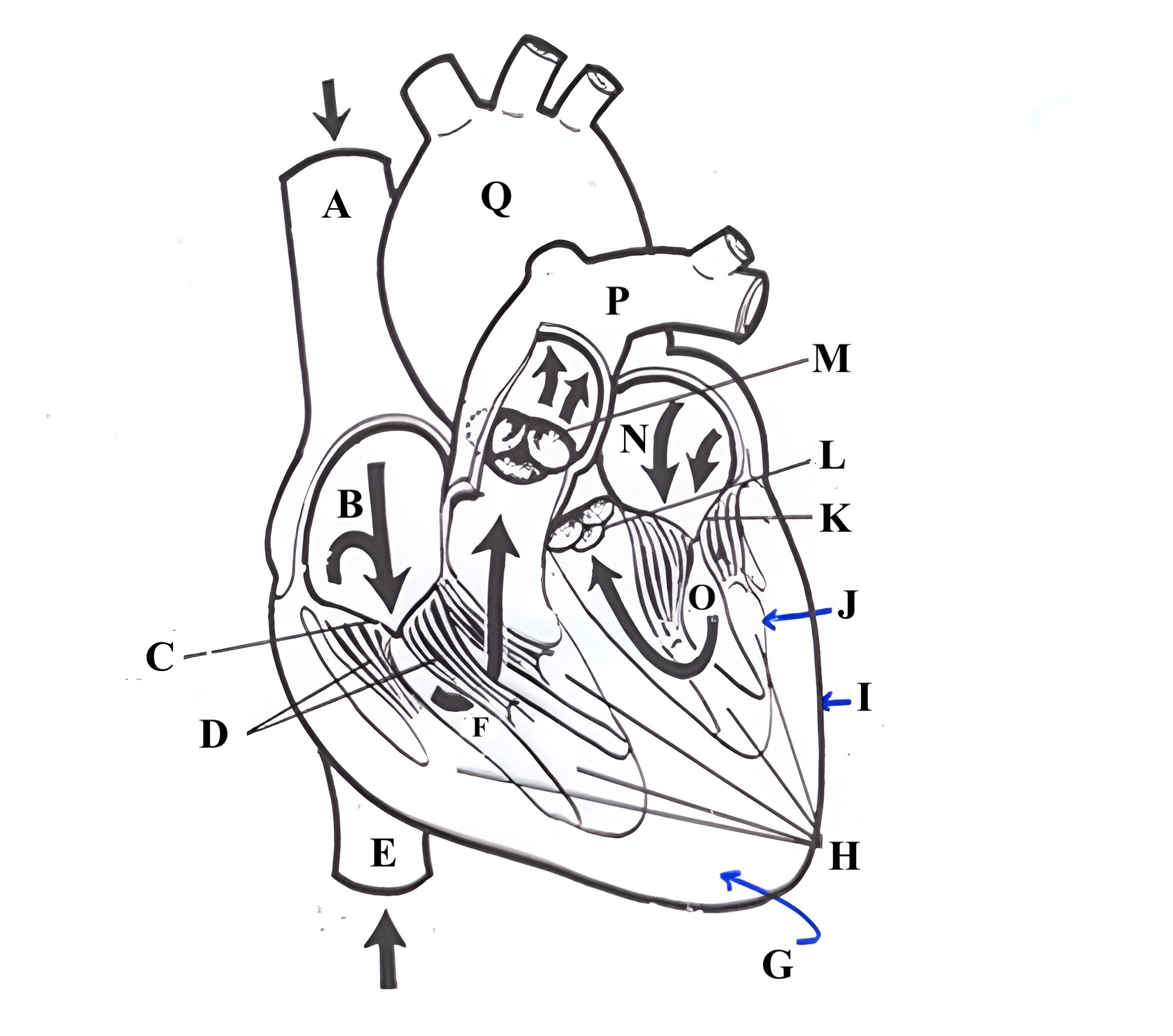
Structure I is the _________.
epicardium
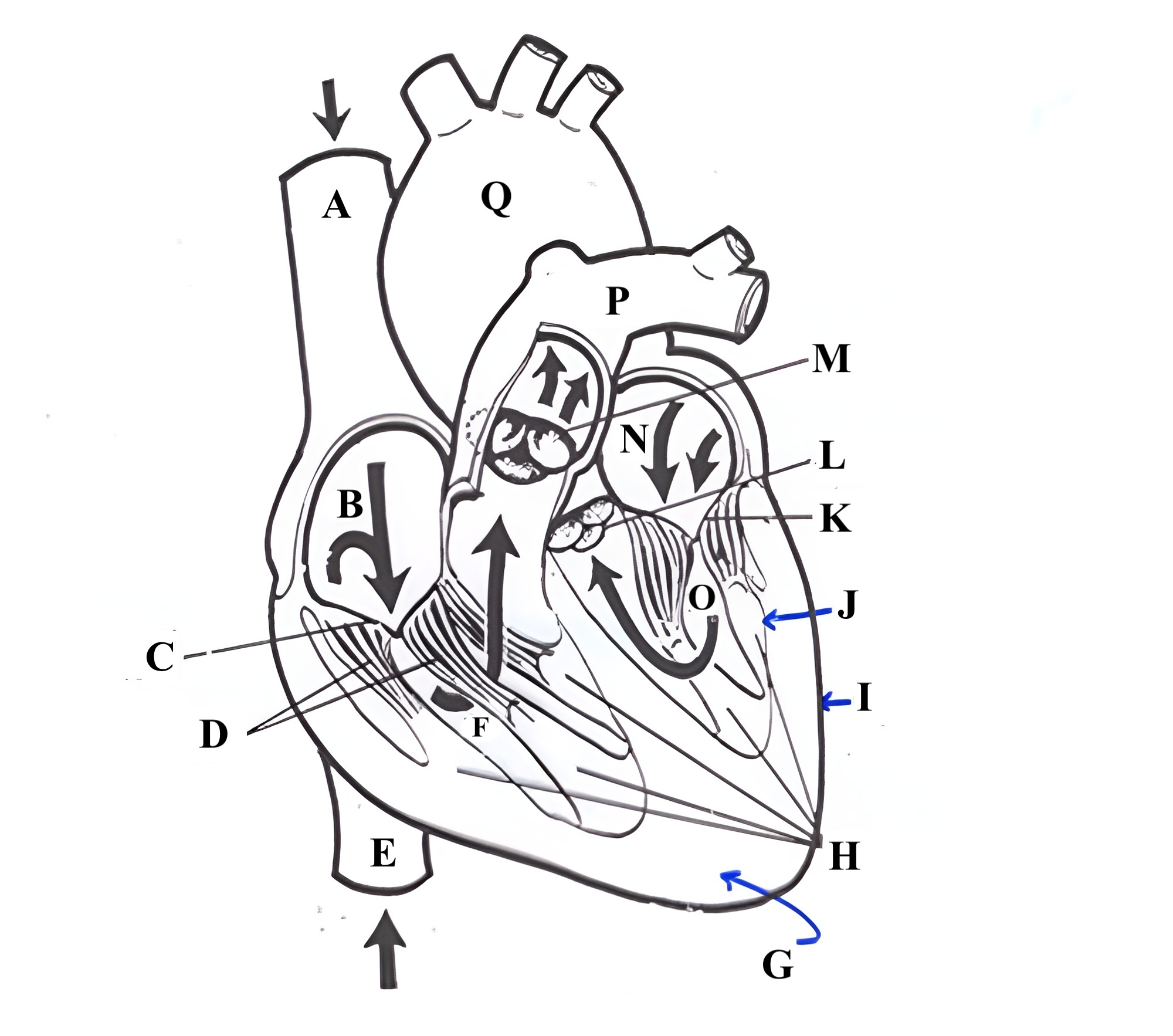
Structure J is the _________.
endocardium
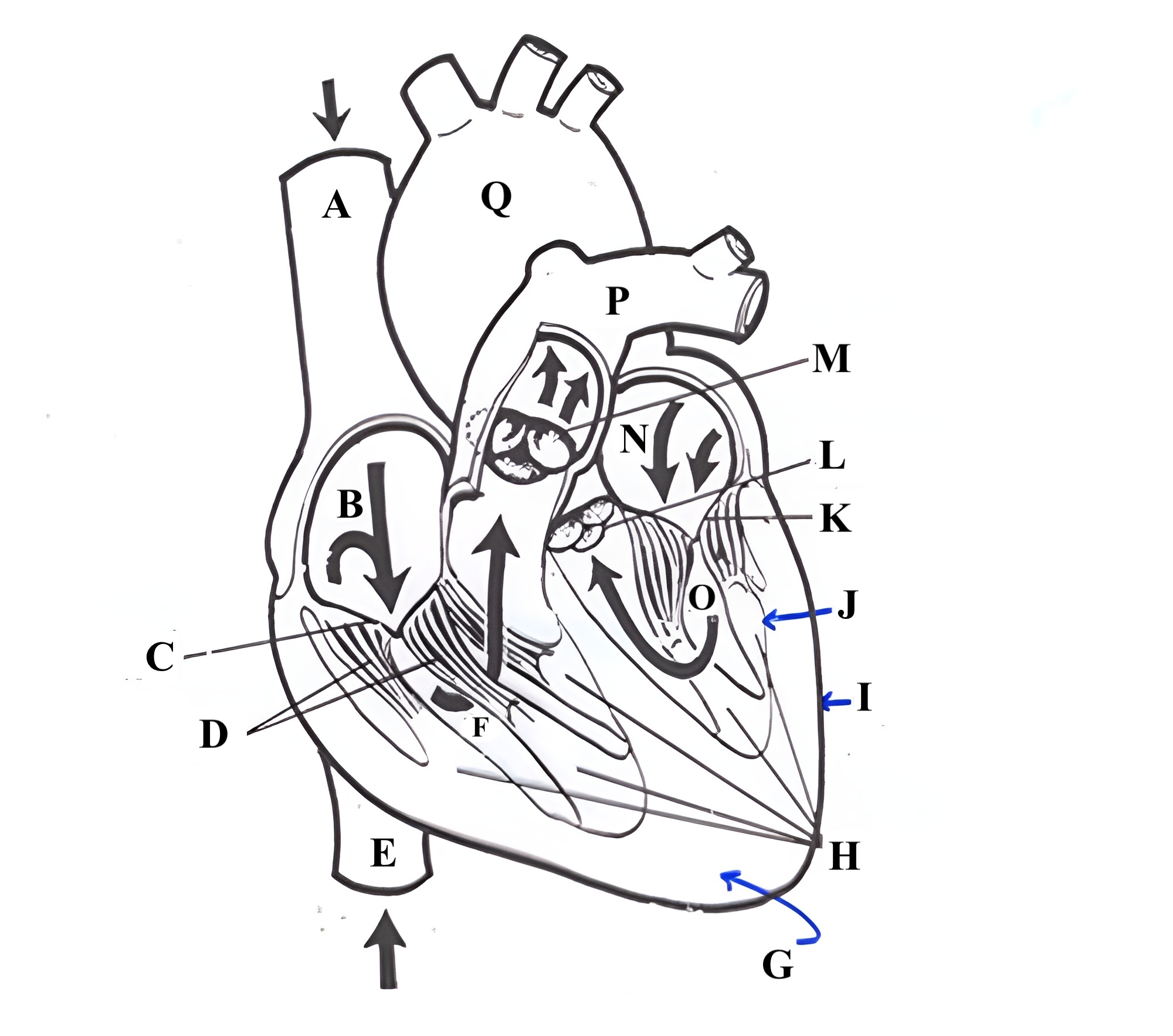
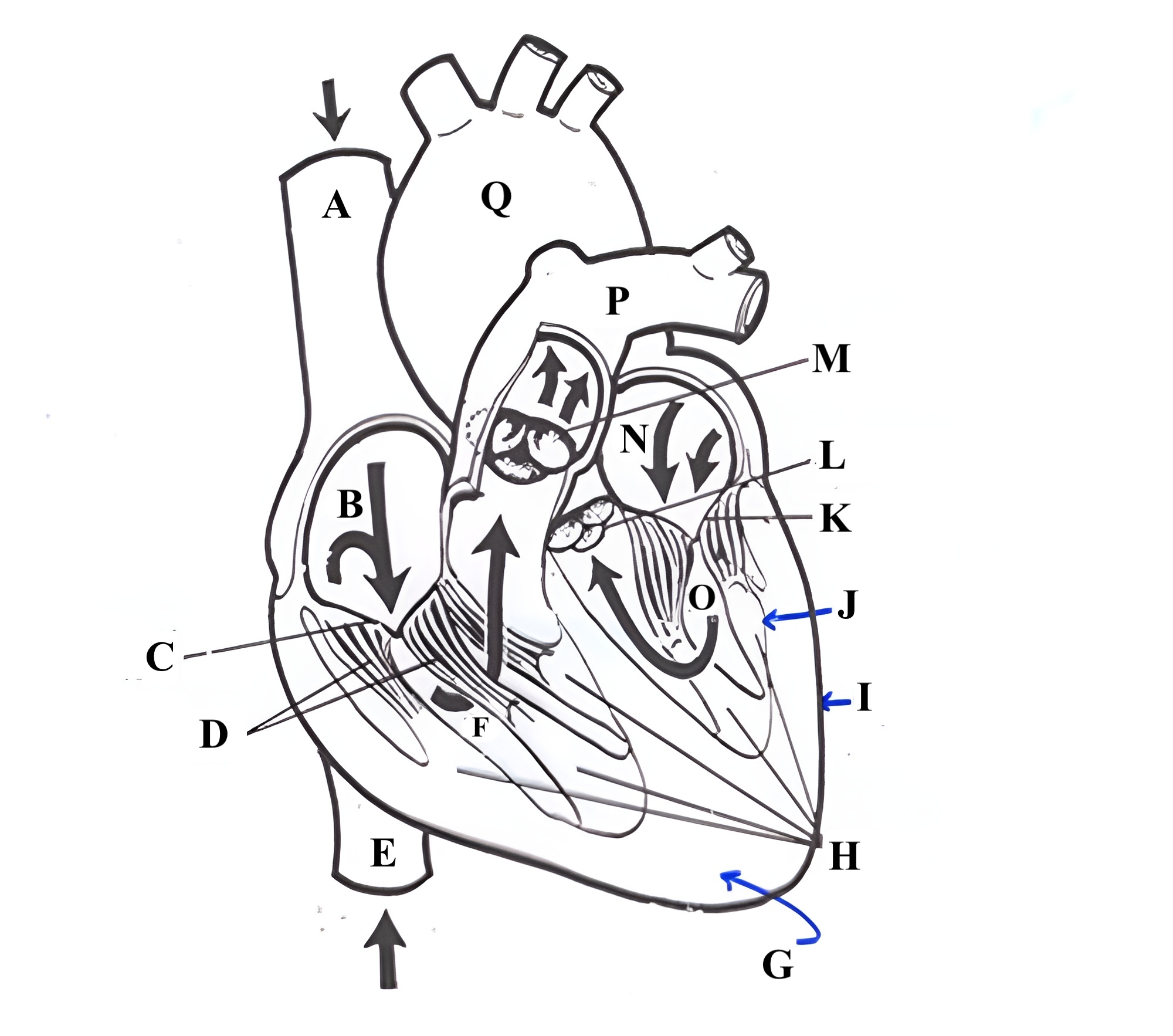
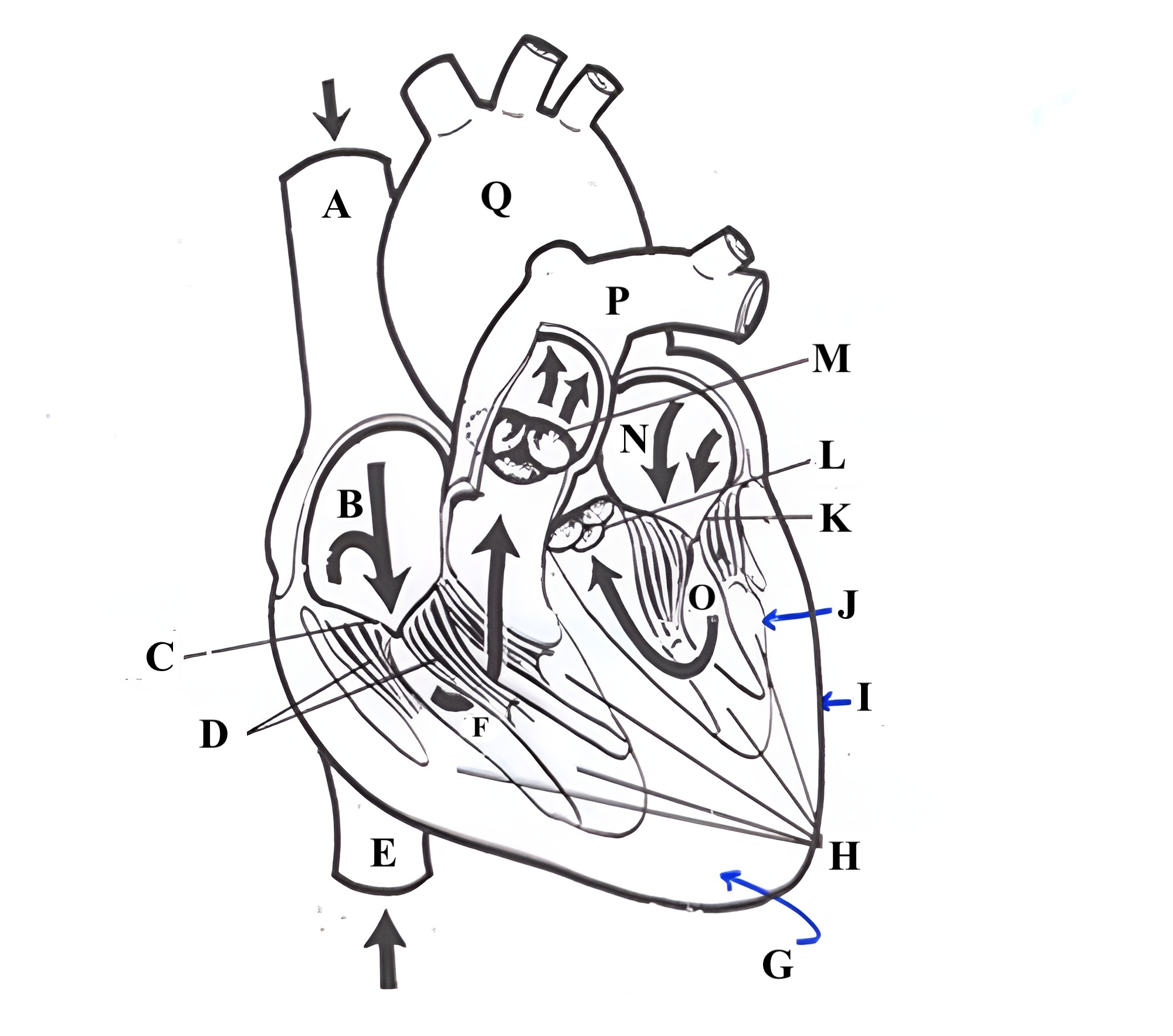
Structure K is the ________ _______.
mitral valve
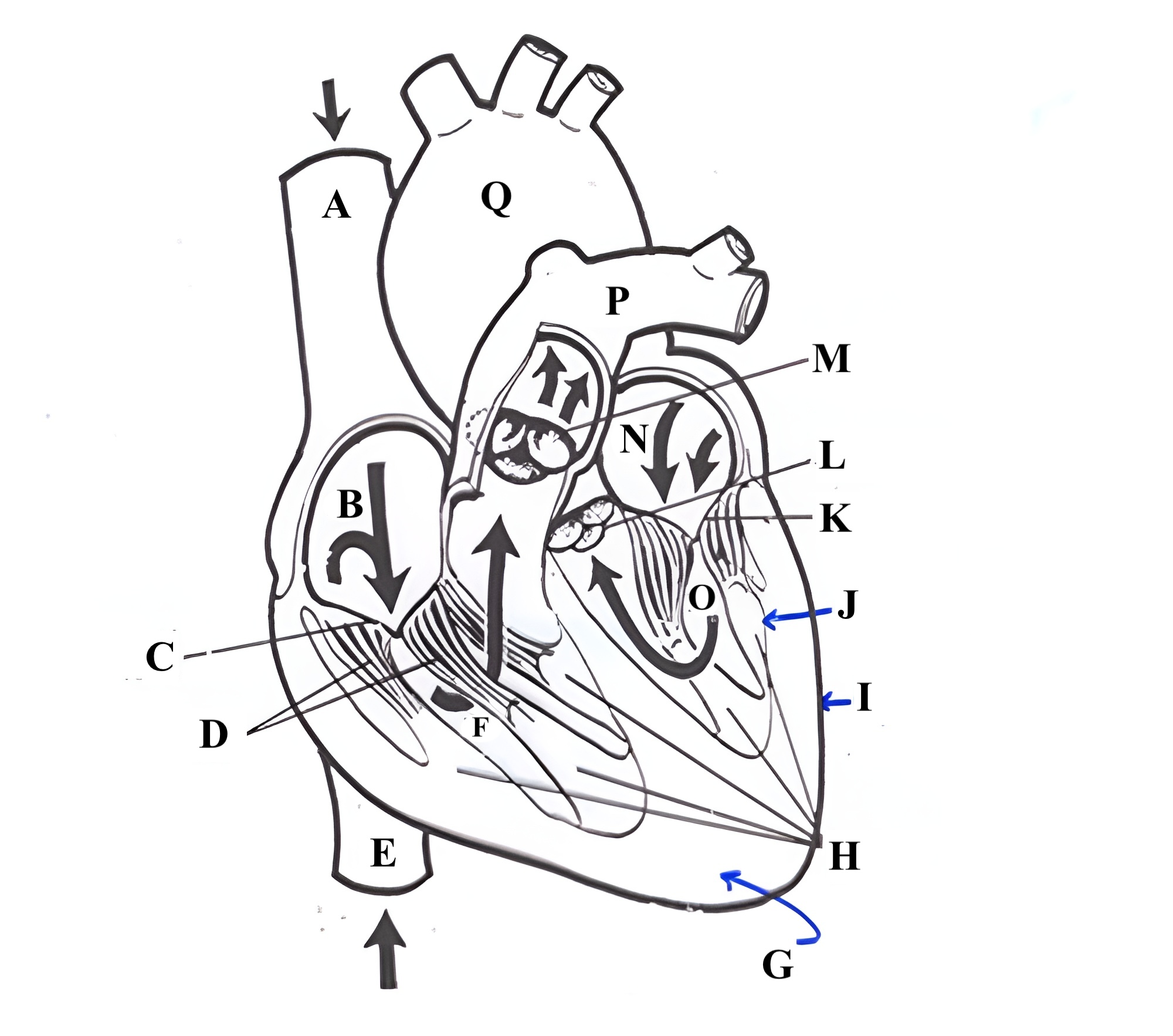
Structure L is the ______ ______.
aortic valve
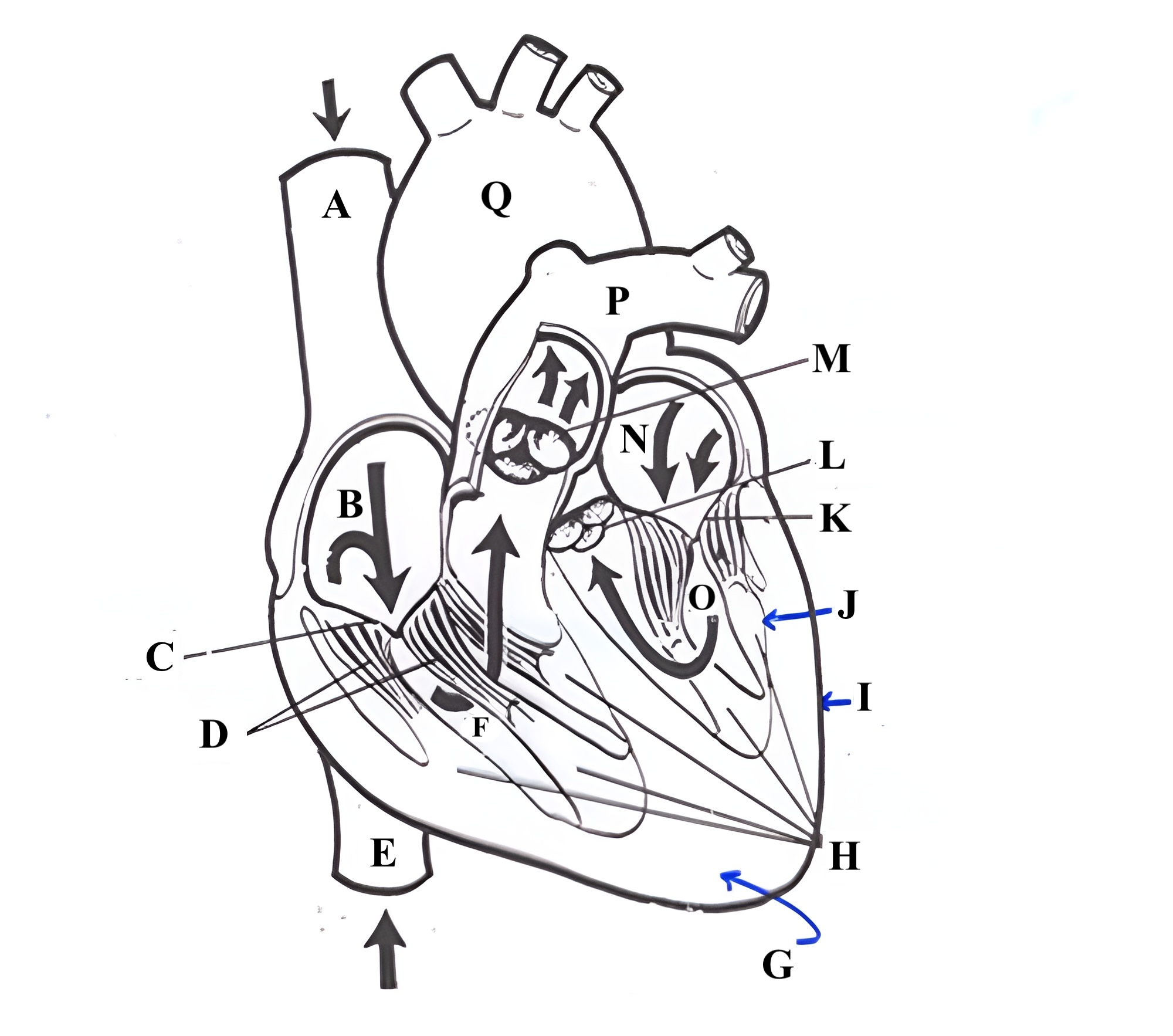
Structure M is the _______ ______.
pulmonic valve
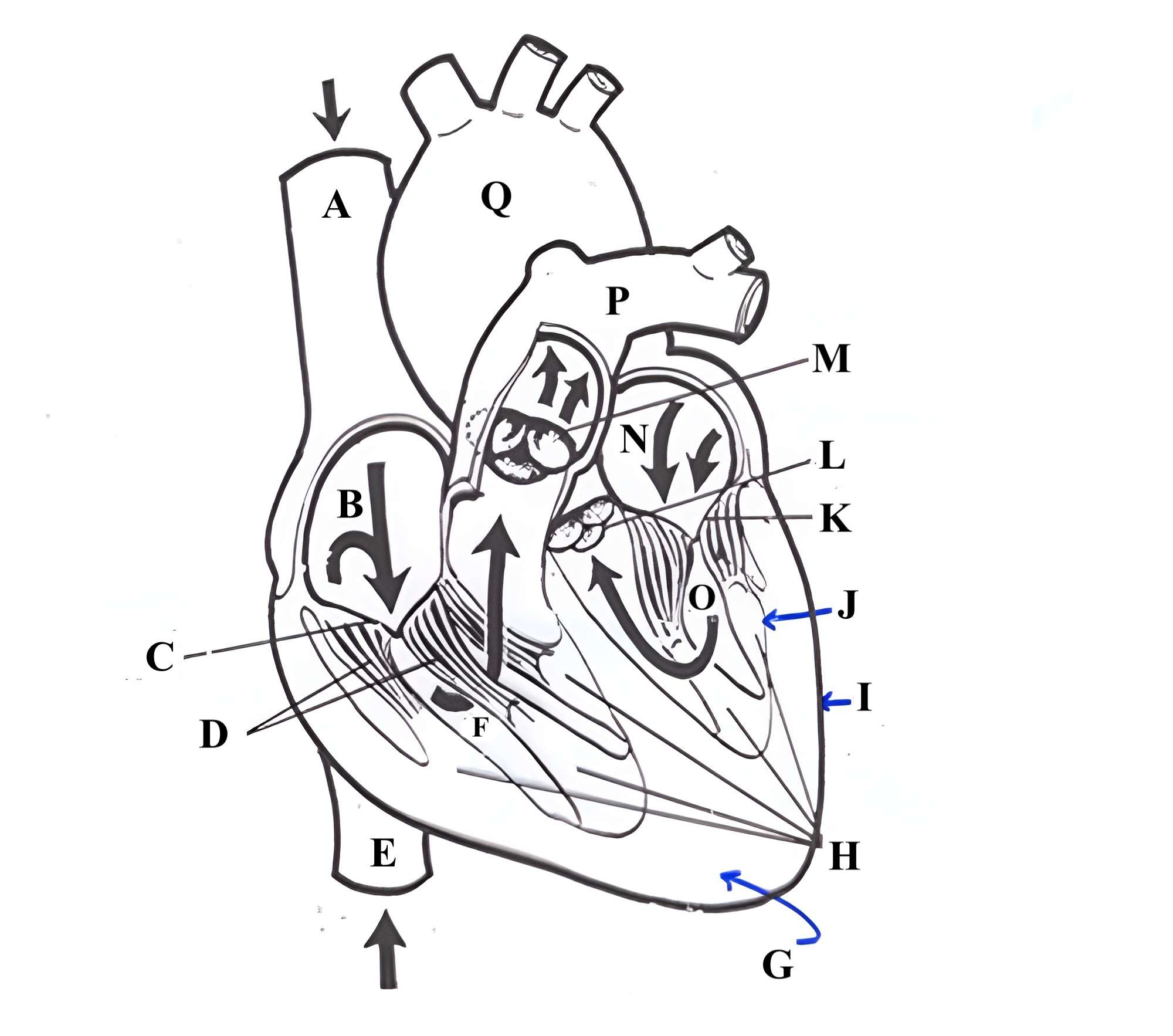
Structure N is the _____ _______.
left atrium
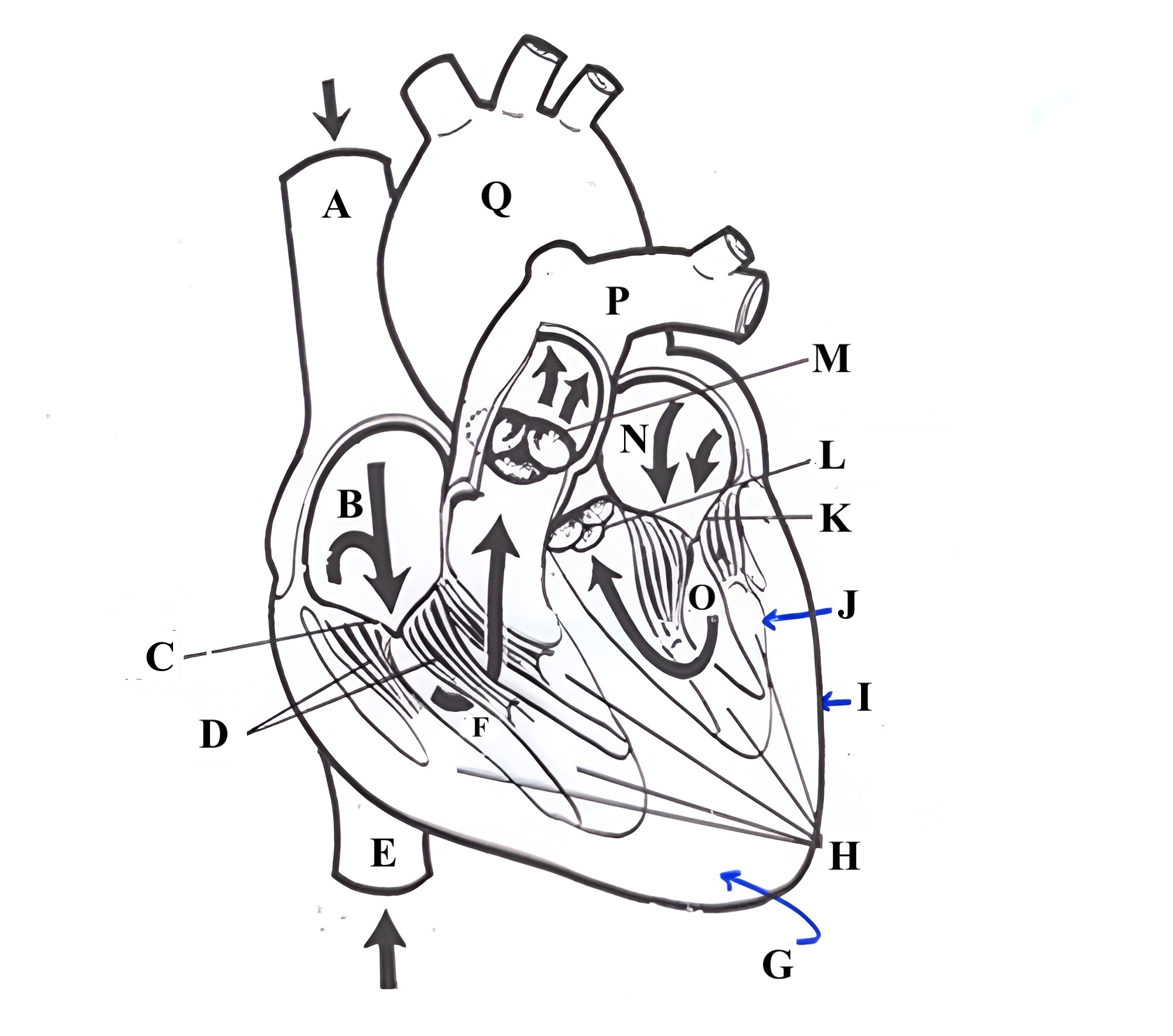
Structure O is the _______ _______.
left ventricle
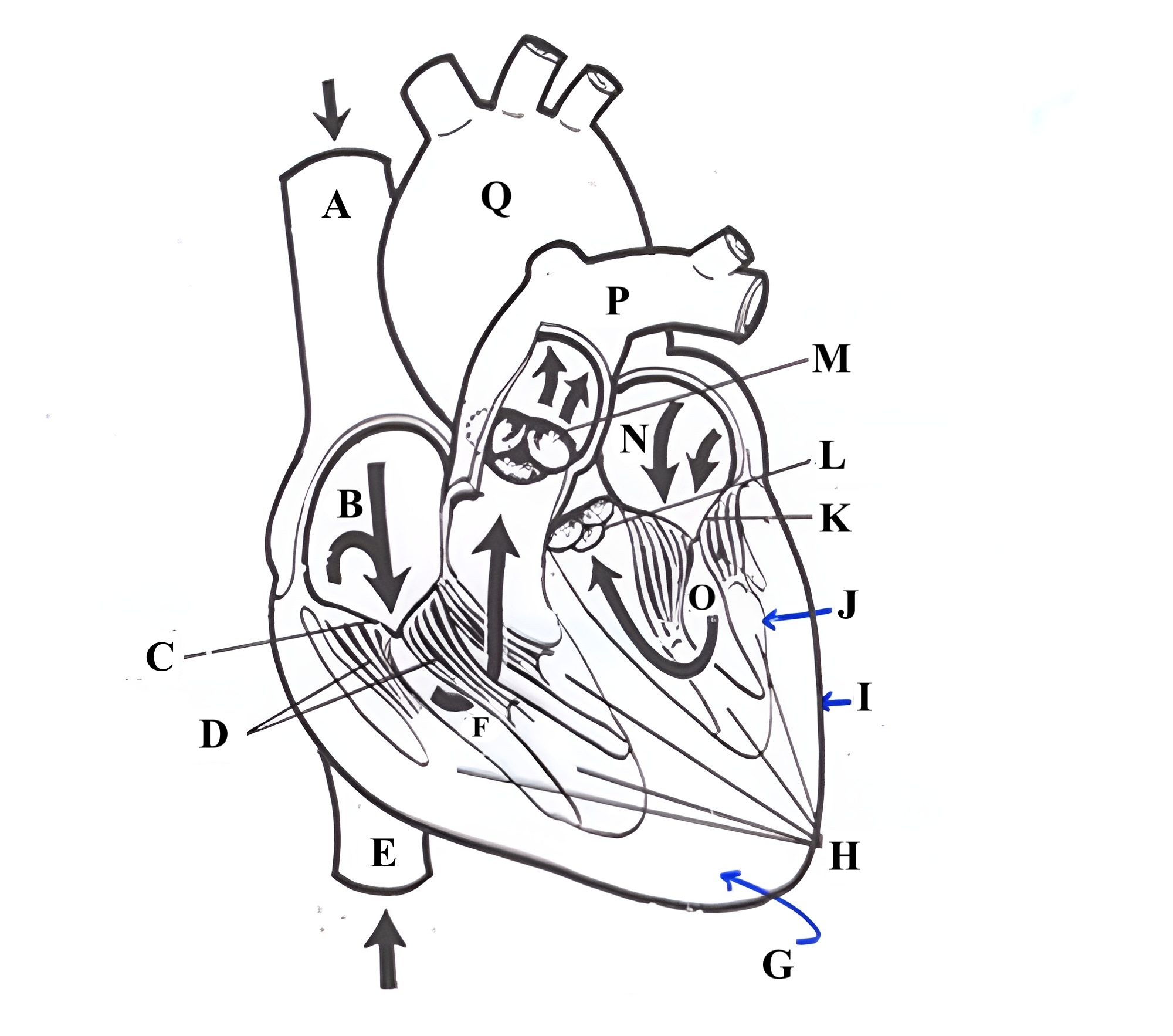
Structure P is the _______ _______.
pulmonary artery
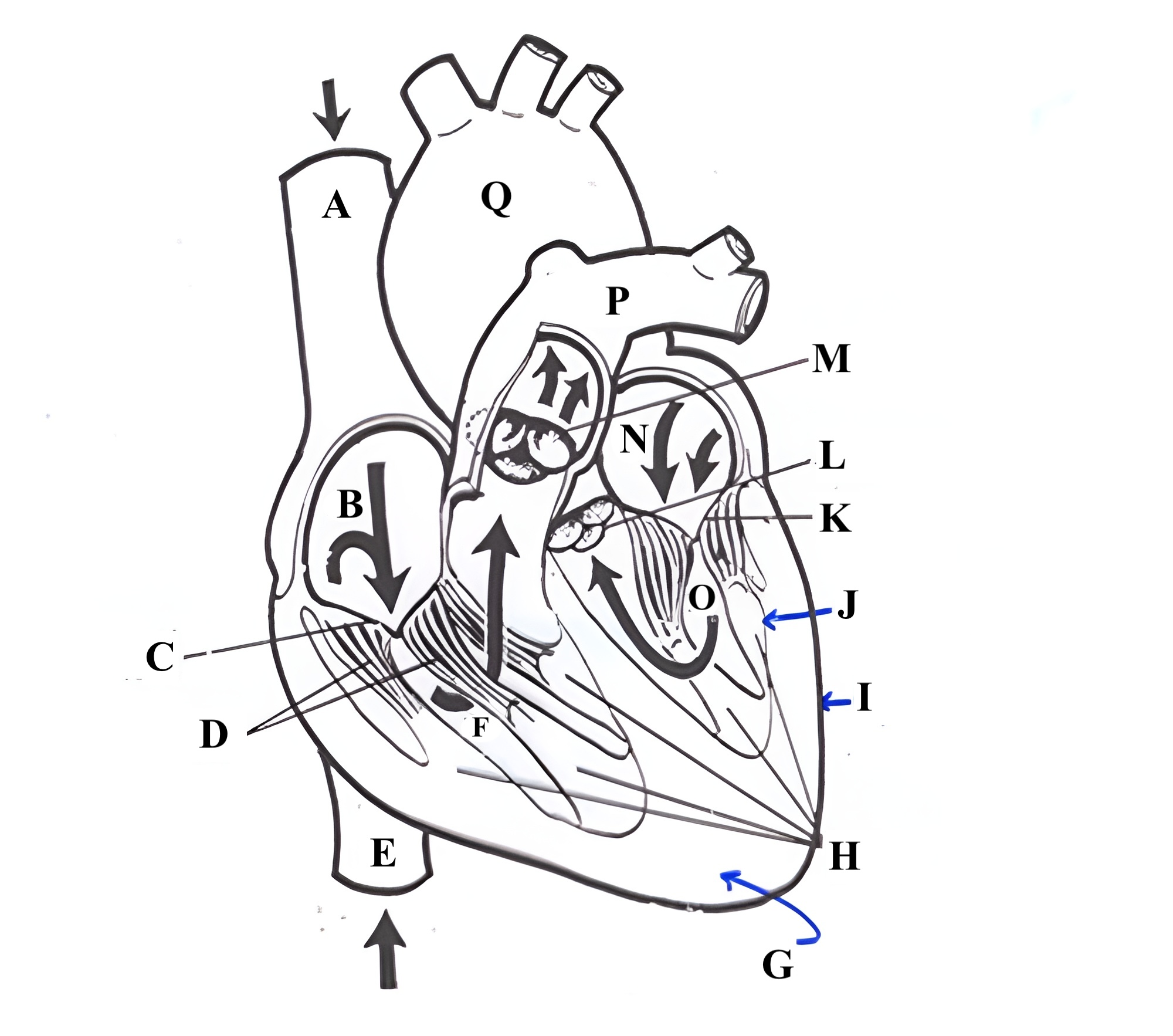
Structure Q is the ________ .
aorta
The 3 layers of the heart (deep to superficial in order) are the…
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium
This layer of the heart is the largest portion…
Myocardium
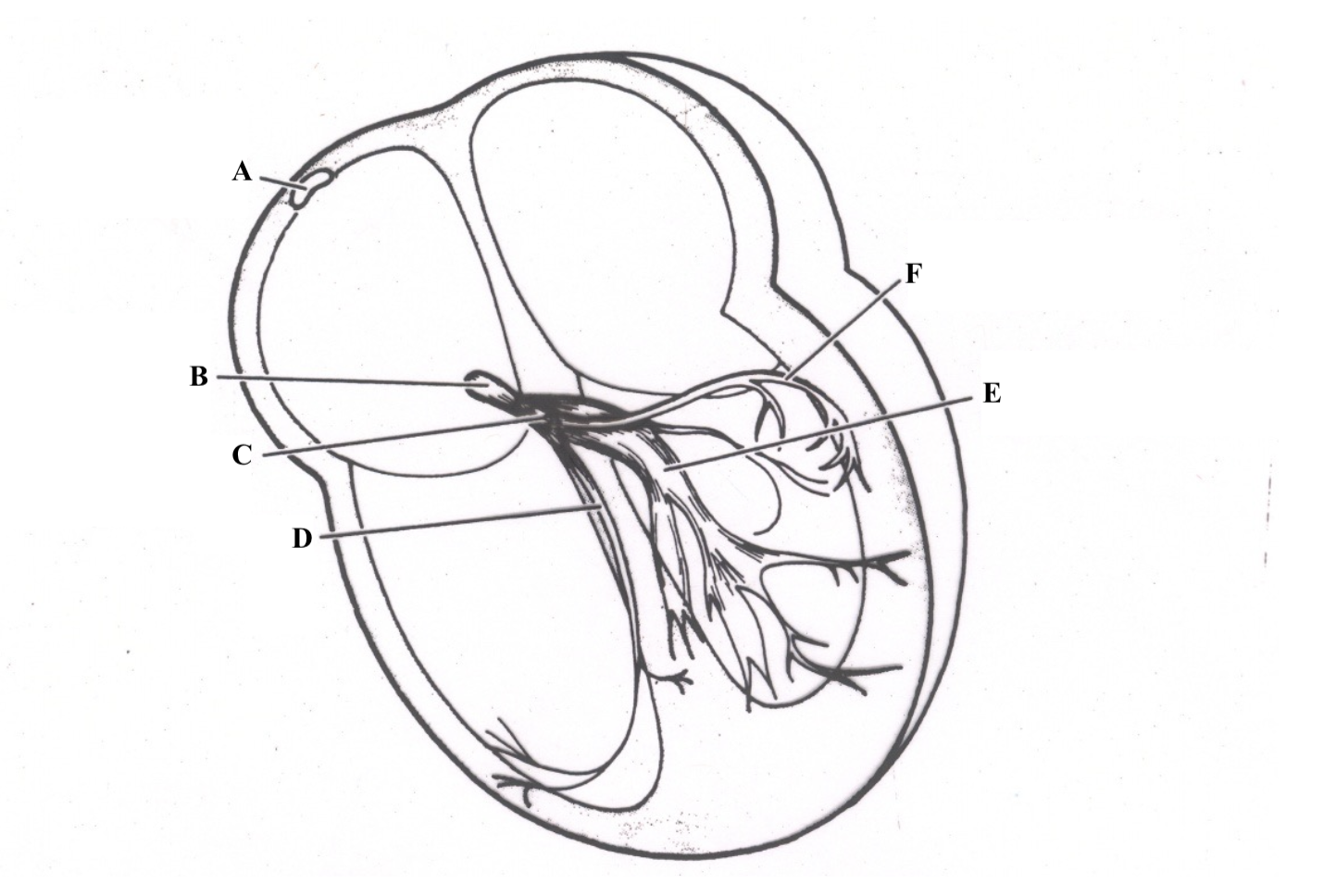
Structure A is the ______ ______.
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
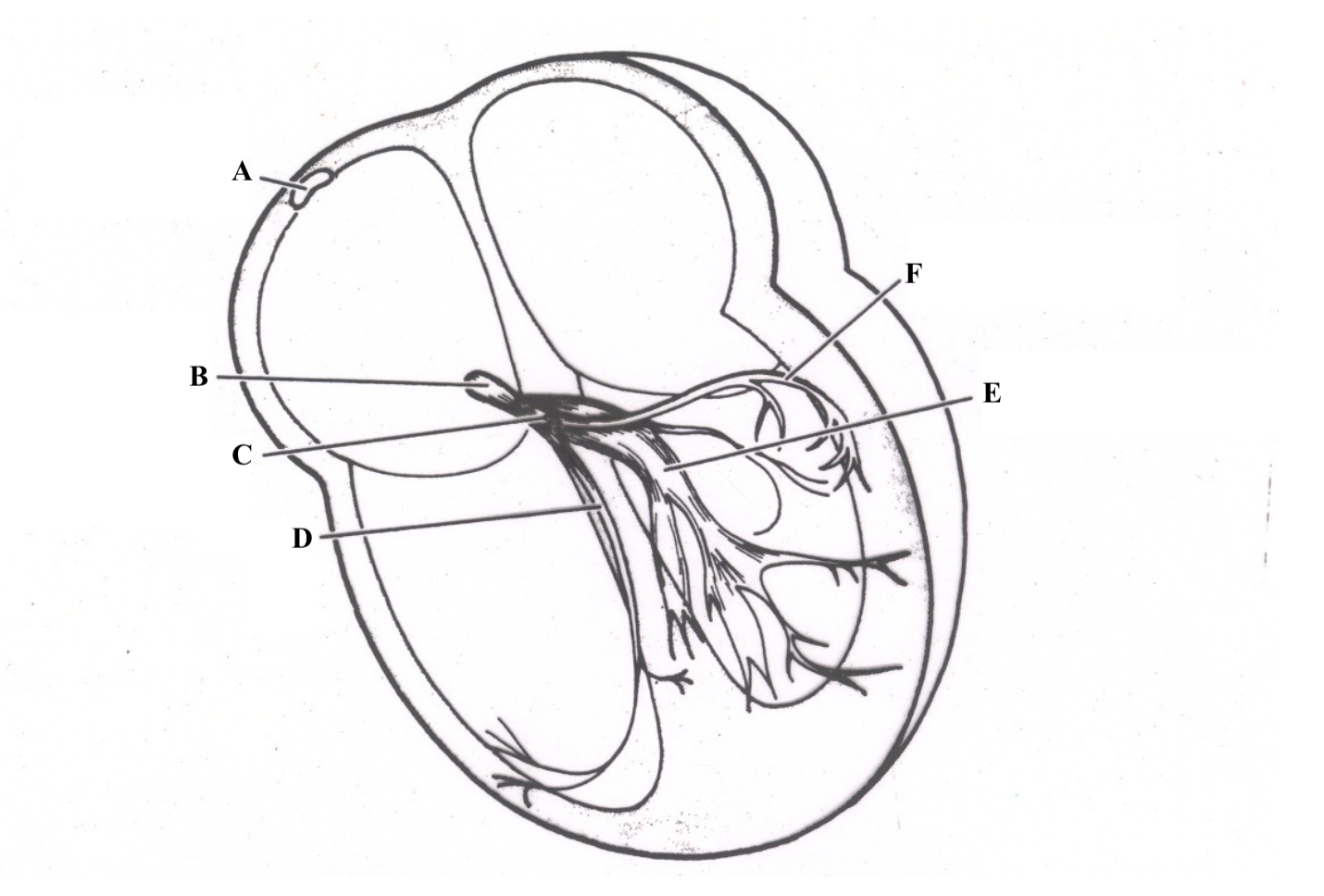
Structure B is the _______ _____.
atrioventricular (AV) node
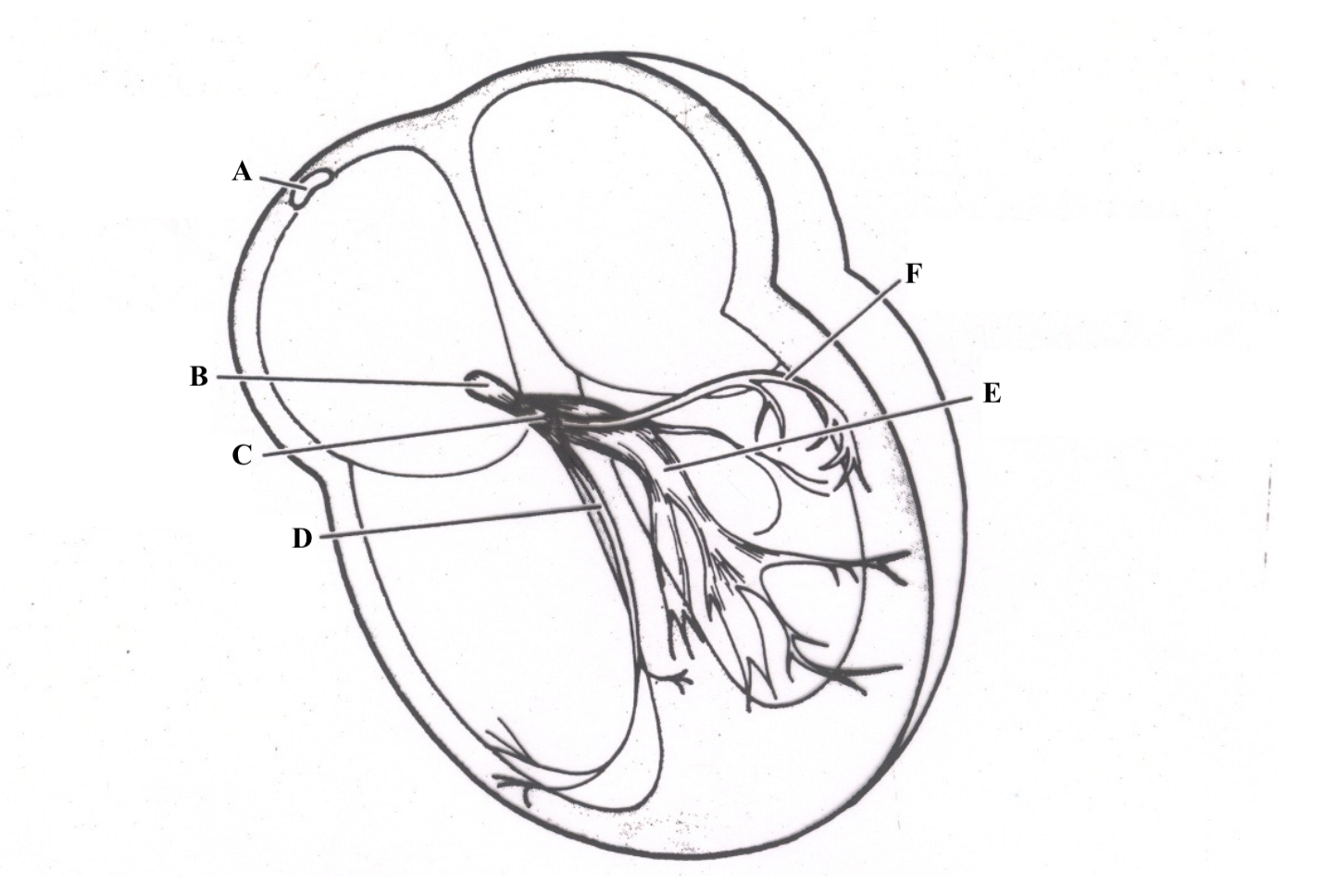
Structure C is the _____ __ ______.
Bundle of His
Structure D is the ________ ________ _______.
right bundle branch (RBB)
Structure E is the ________________.
left bundle branch (LBB) postieror fascicle
Structure F is the _______________.
Left Bundle Branch (LBB) anterior fascicle
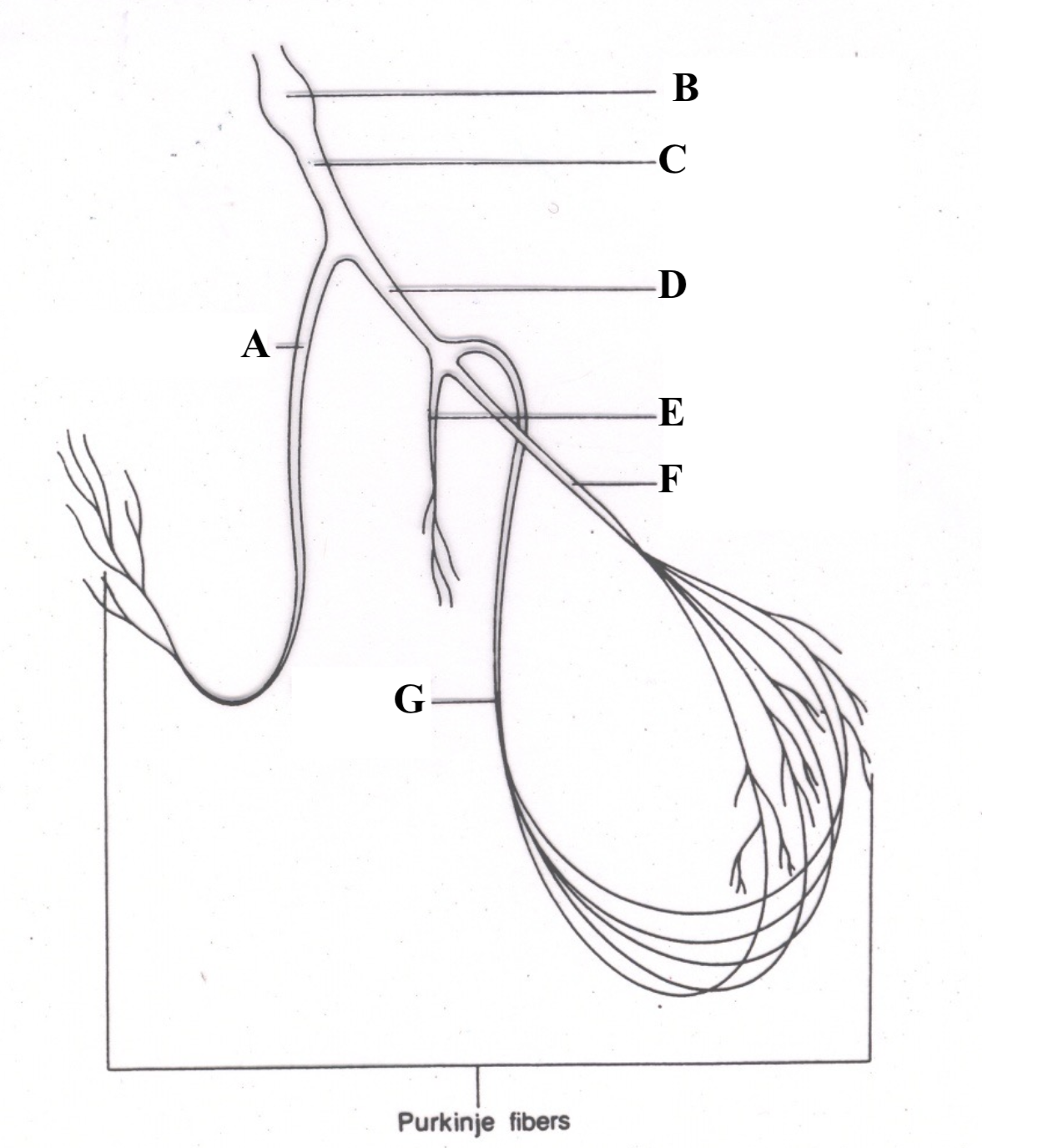
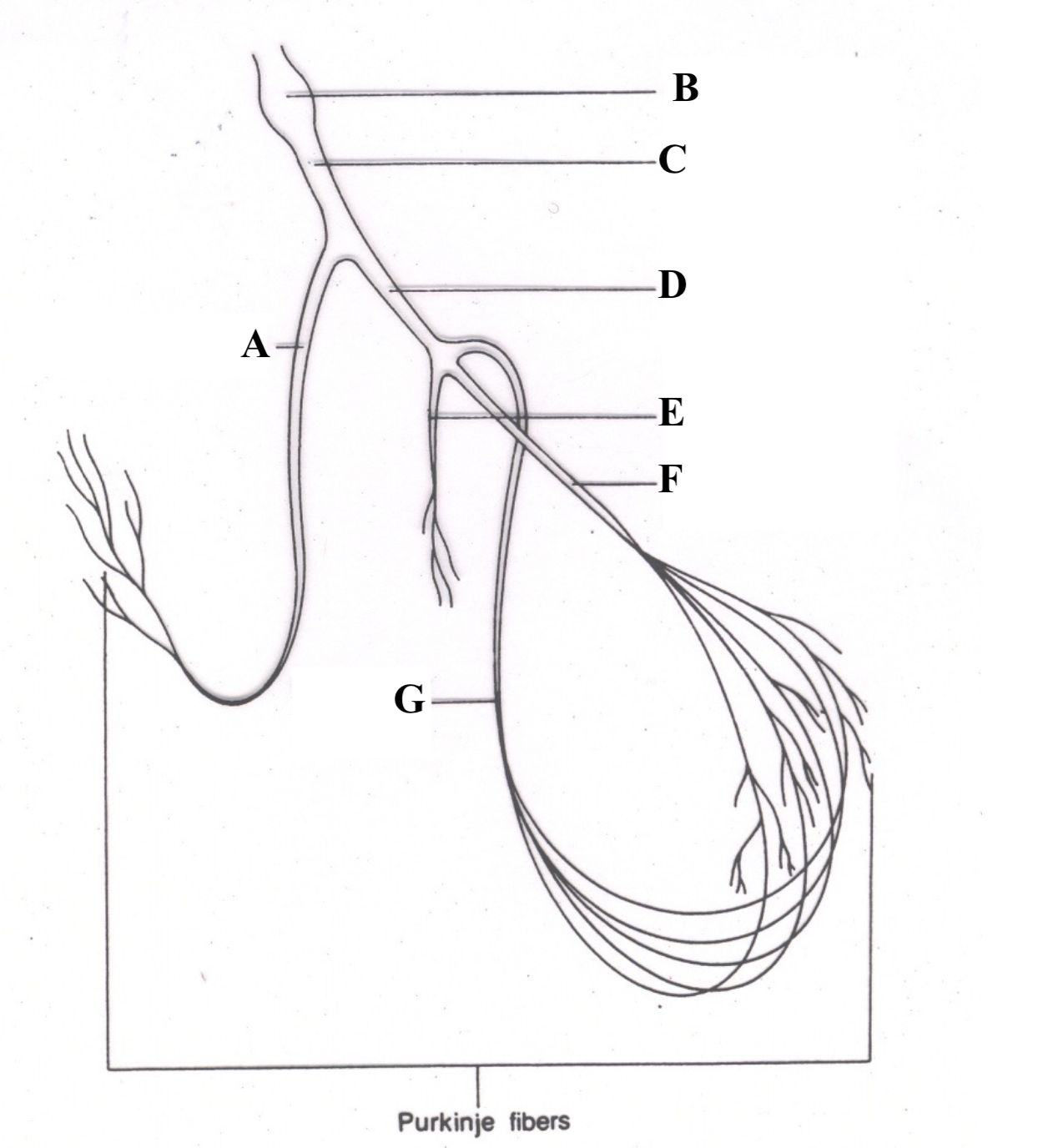
Structure A is the ______ ________ _______.
right bundle branch
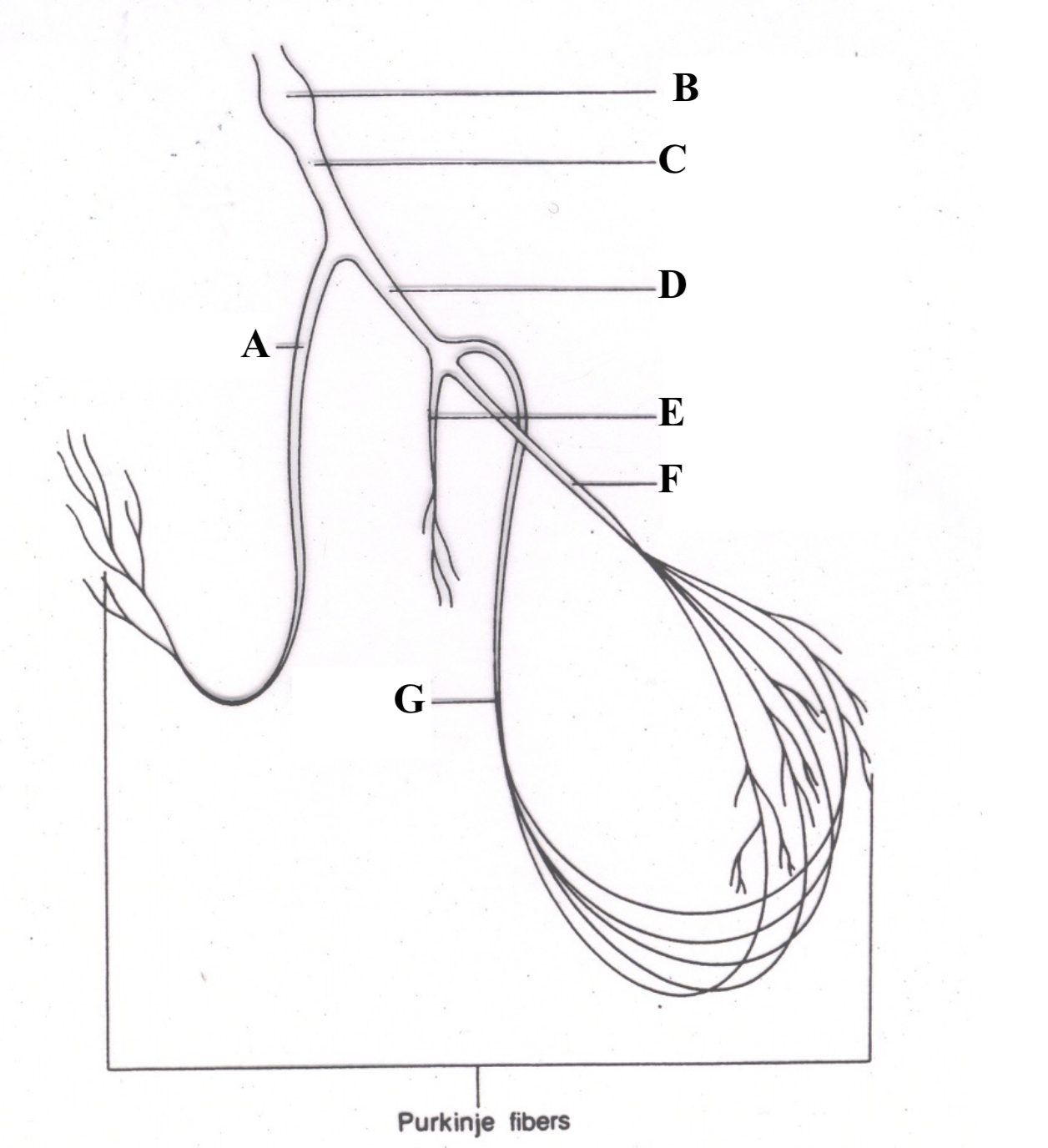
Structure B is the _______ ________.
Atrioventricular (AV) node
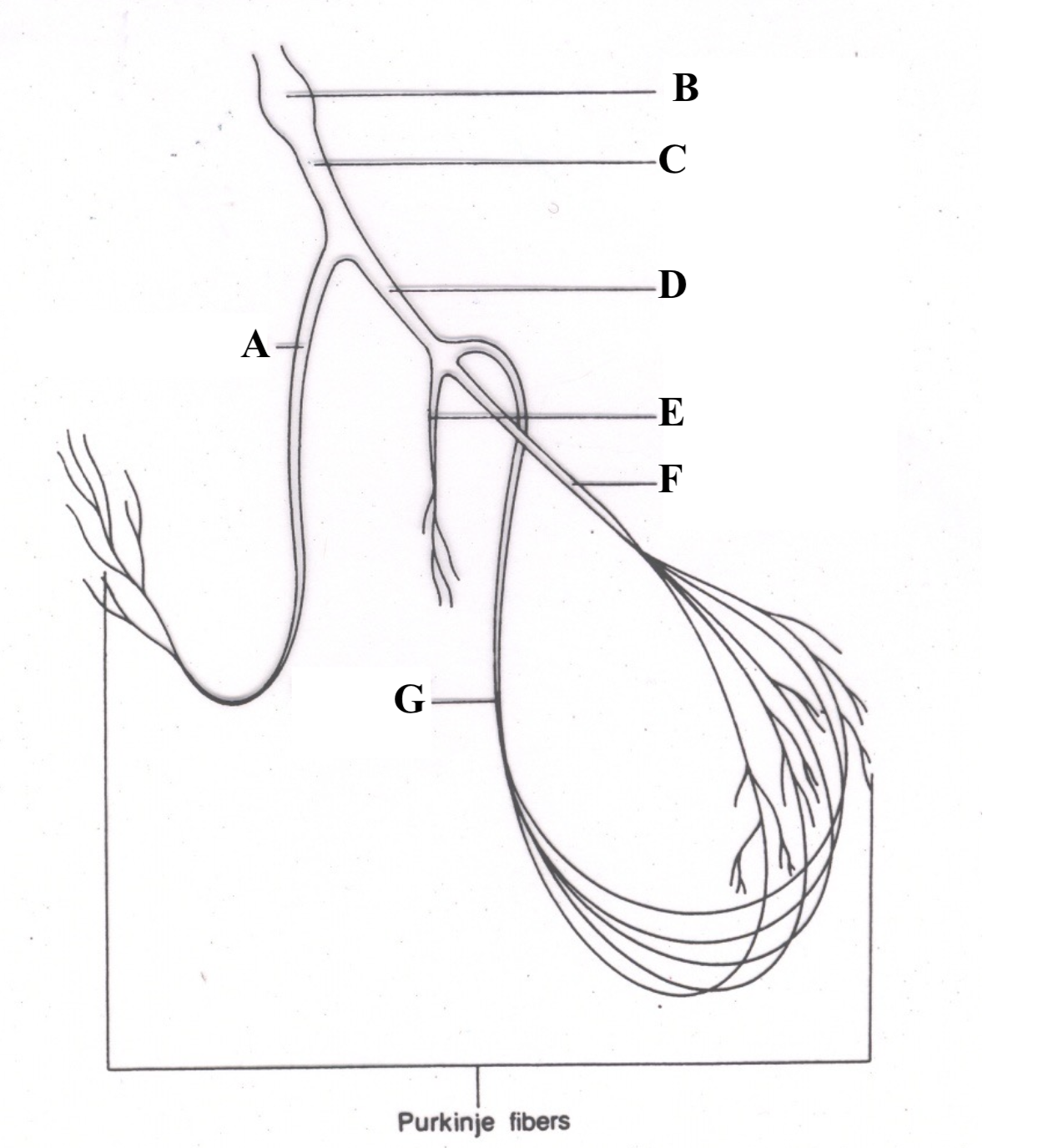
Structure C is the ________ __ ________.
Bundle of His
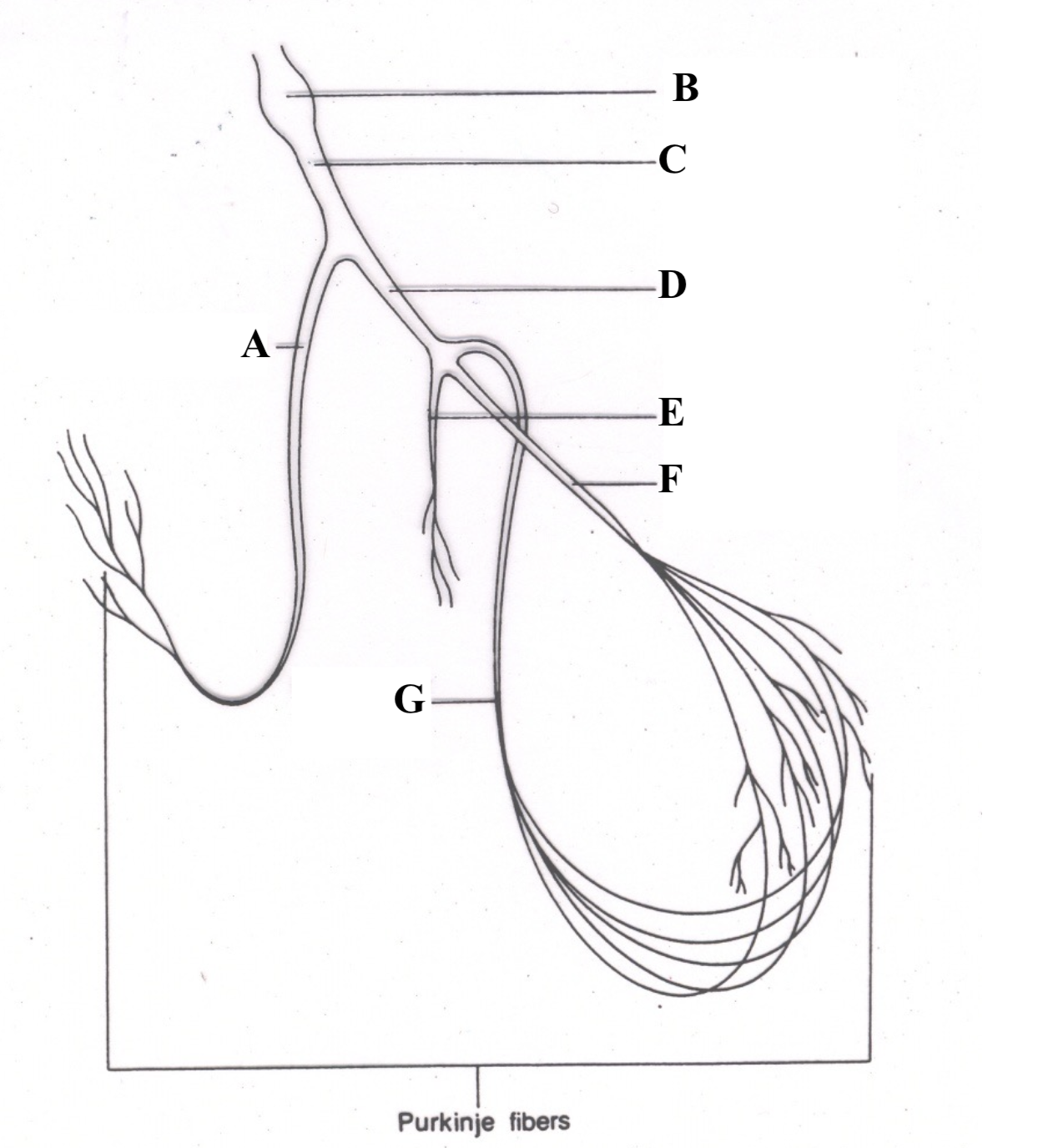
Structure D is the _______ ______ ______.
left bundle branch
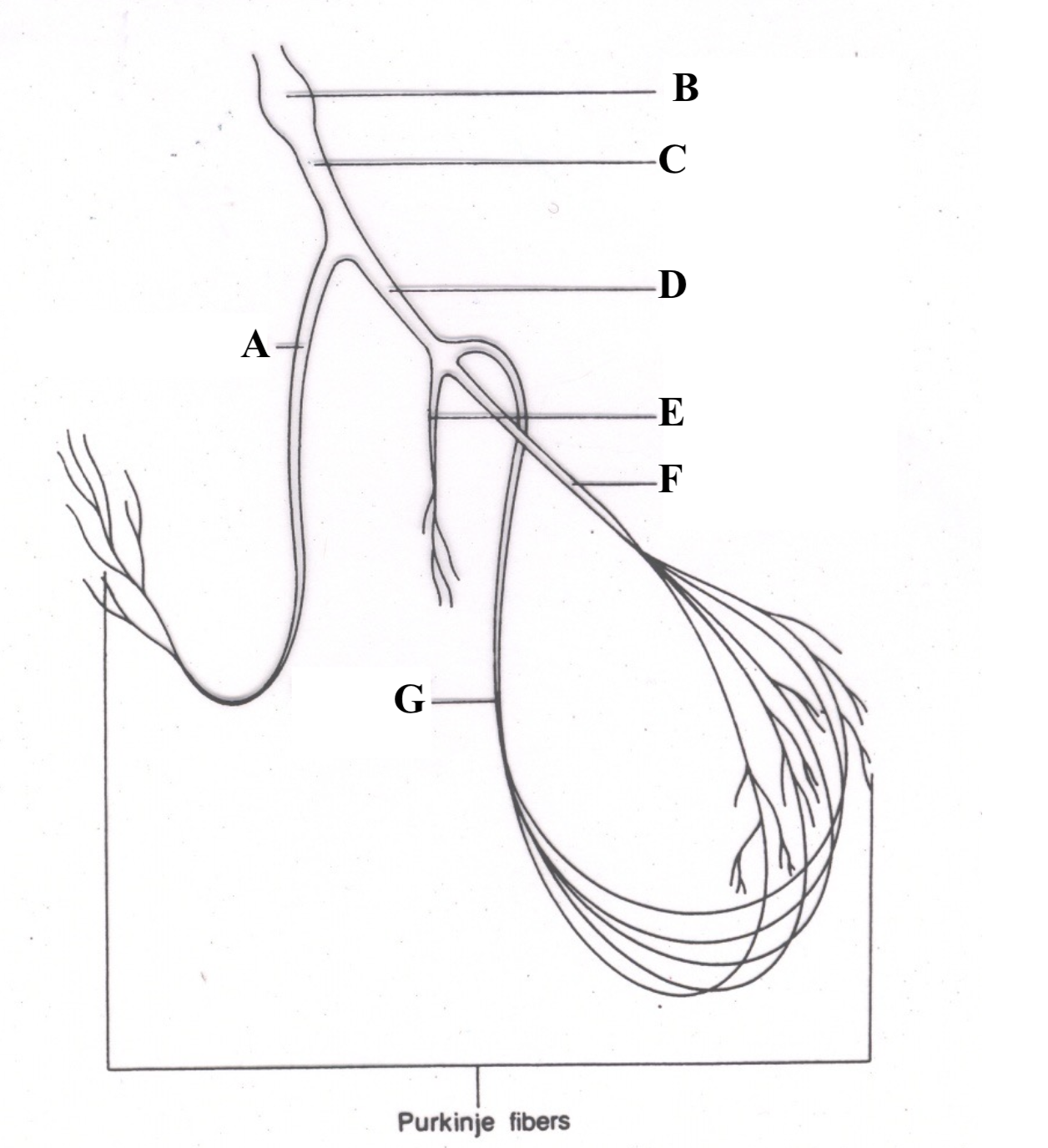
Structure E is the _________ ________.
septal fascicle
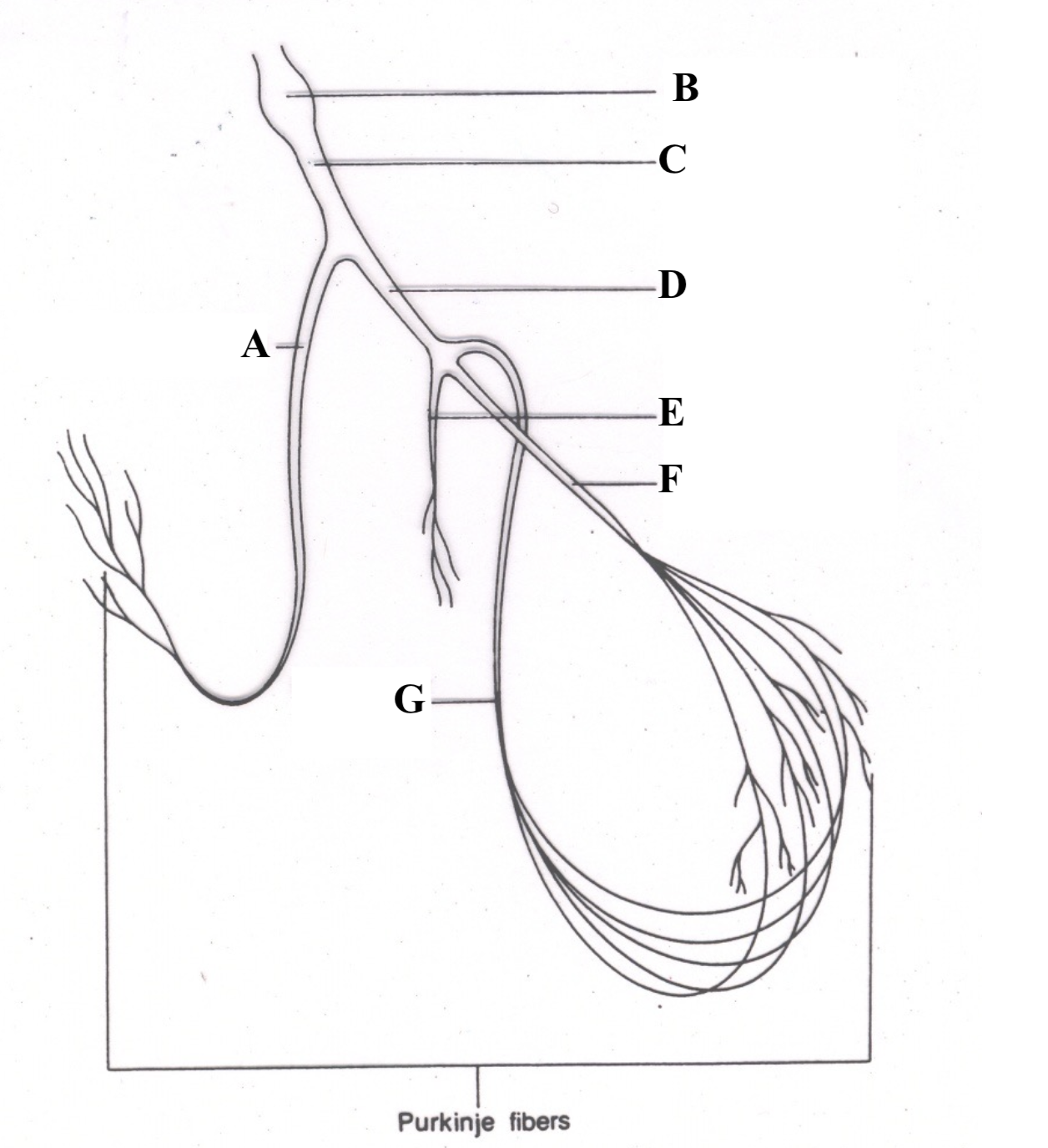
Structure F is the ______ ________ _______.
left anterior fascicle
Structure G is the ______ _______ _____.
left posterior fascicle
Coronary arteries are responsible for supplying the __________ with ________.
Heart; oxygenated blood (nutrients)
Coronary arteries branch directly off of the _________ .
Aorta
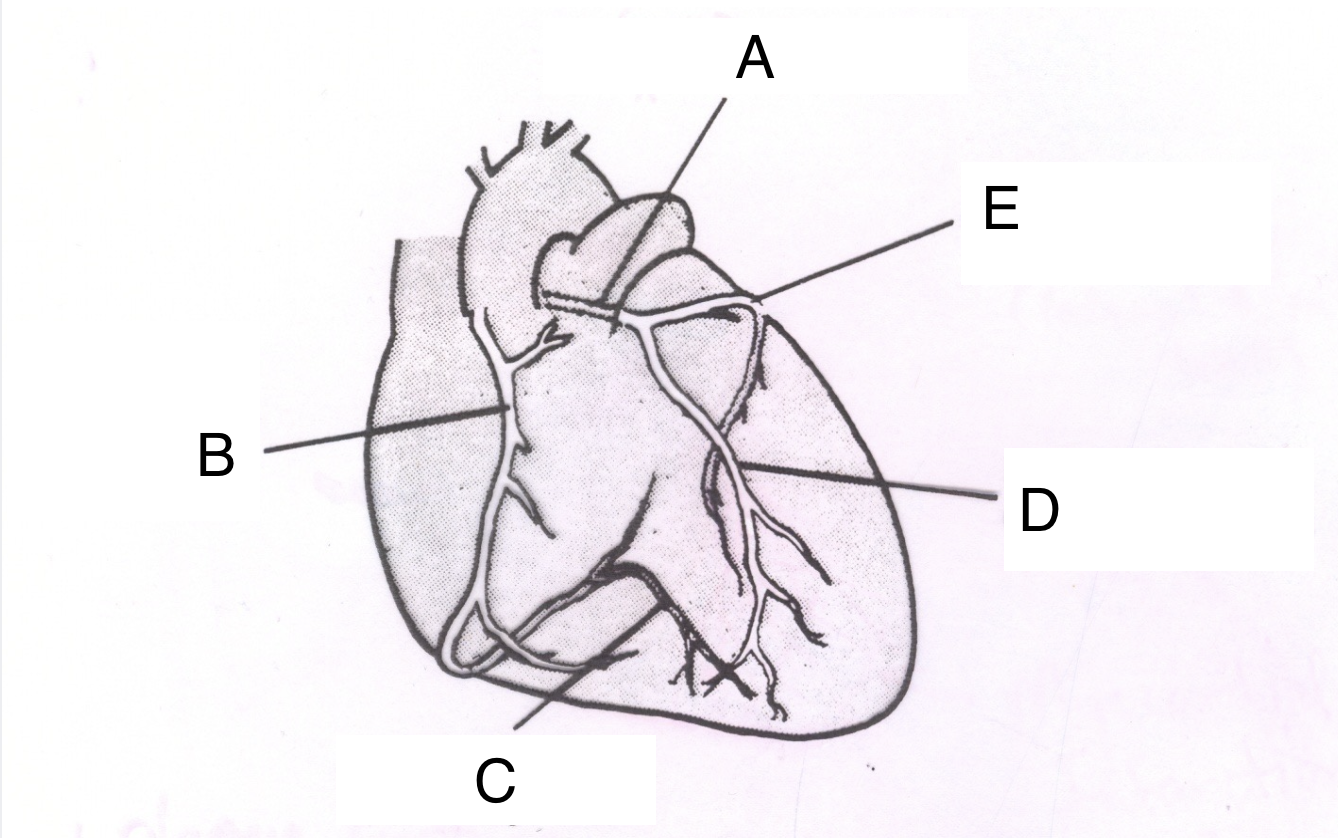
Structure A is the ________ _________ ________.
left coronary artery
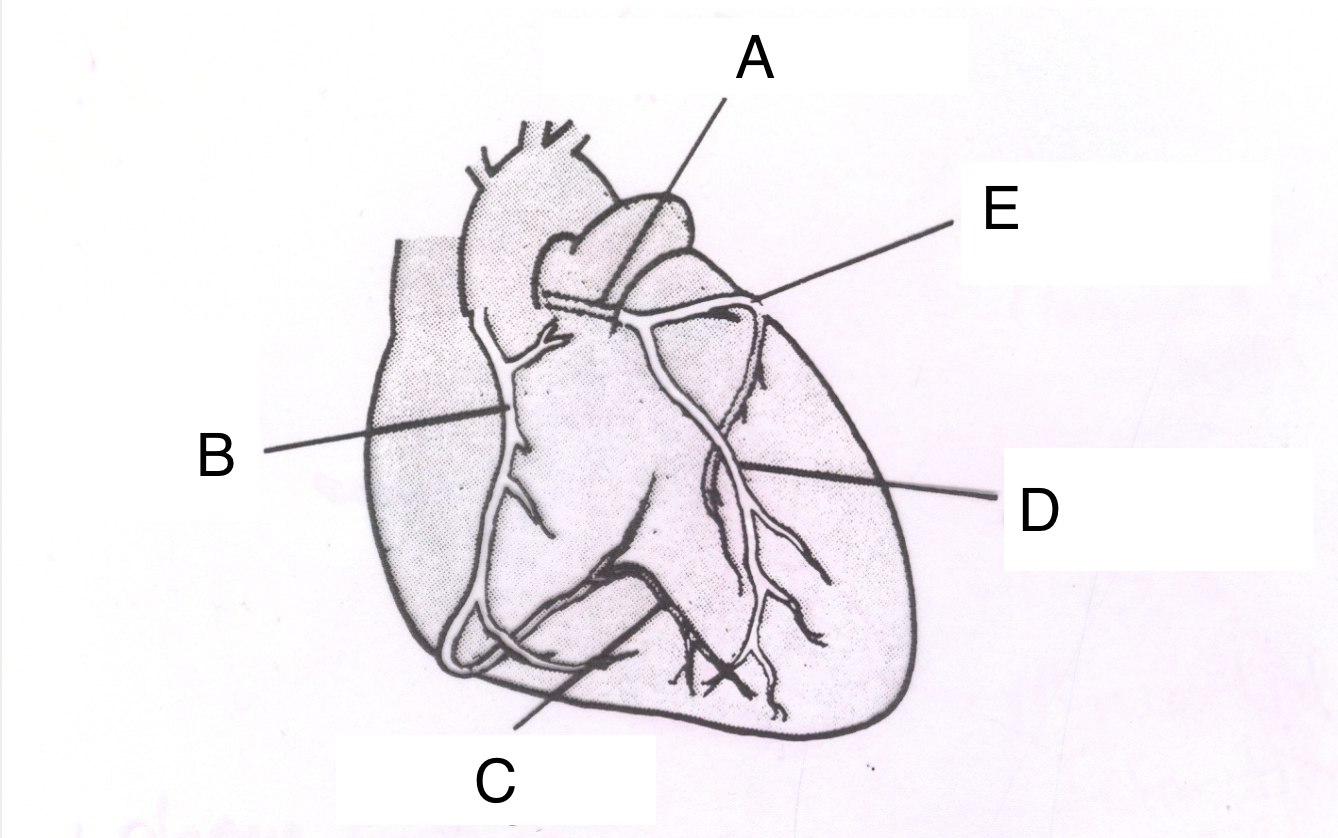
Structure B is the ________ ________ _______.
right coronary artery
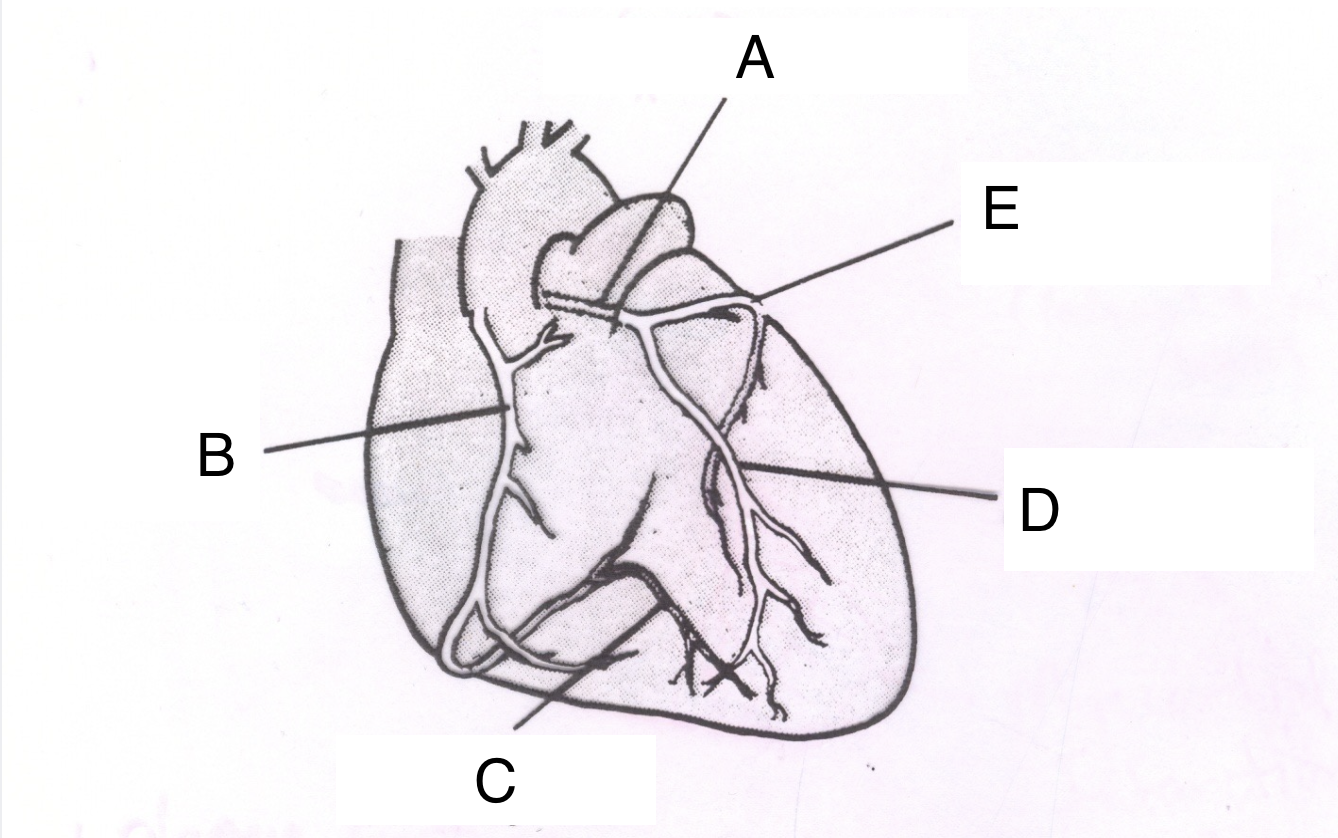
Structure C is the __________ ________ ________.
posterior descending branch
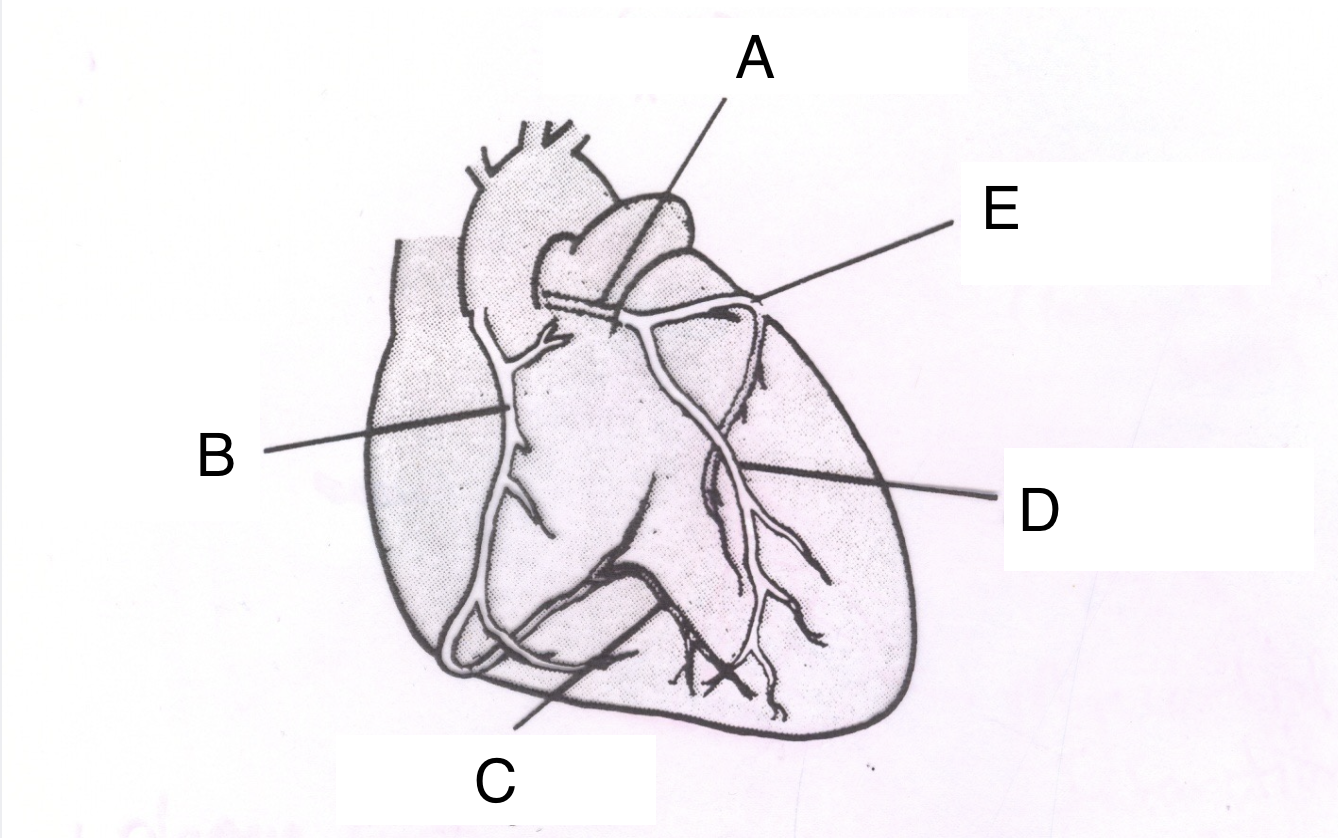
Structure D is the _________ __________ _________ ________.
Left anterior descending branch
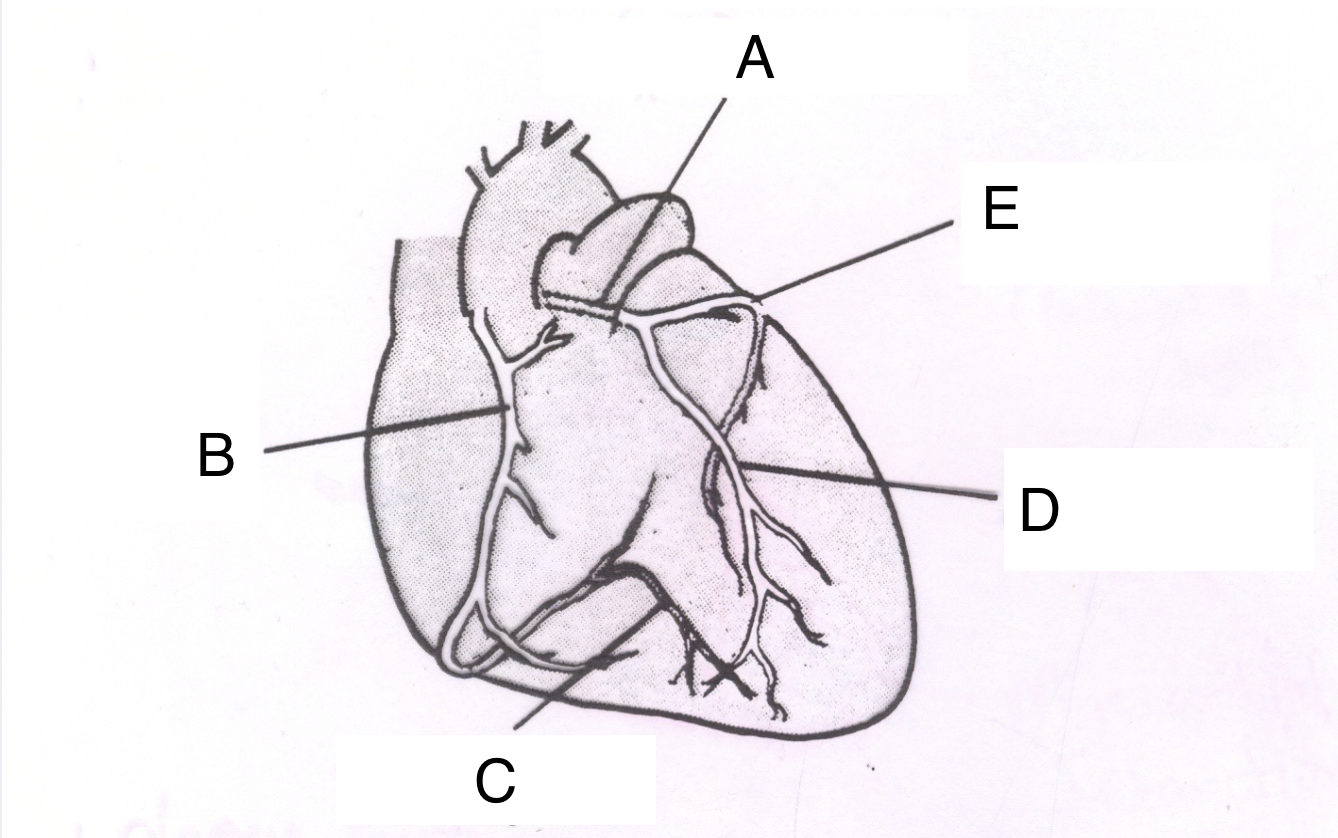
Structure E is the _____________ ___________.
circumflex branch
Disease ihibited blood flow through normal vasculature can result in increased reliance on ___________ ________.
collateral vasculature
Ateriosclerosis
Chronic disease of arterial system characterized by thickening and hardening of vessel walls
Artherosclerosis
A form of arteriosclerosis, caused by fatty-like deposits (plaques)
Heart disease (coronary artery disease) is defined as…
the presence of plaques or lesions in the coronary arteries
Ischemia is defined as…
inadequate blood flow and oxygen supply to the myocardium (heart muscle tissue)
Classic angina is…
chest pain with exertion
Variant angina is…
chest pain during rest
Silent ischemia is…
ischemia without any symptoms
At rest our cells are (negatively/positively) charged, and refered to as (polarized/depolarized).
negatively; polarized
Depolarization involves the influx of (negative/positive ions) into the cell.
Positive
Myocardial cells have 3 distinct properties. These are…
Automaticity
Excitability
Conductivity
Automaticity is defined as…
the ability to depolarize spontaneously
Excitability is defined as…
the ability to depolarize and repolarize when excited by an electrical stimulus
Conductivity is defined as…
the ability to transfer electrical impulses to neighboring cells
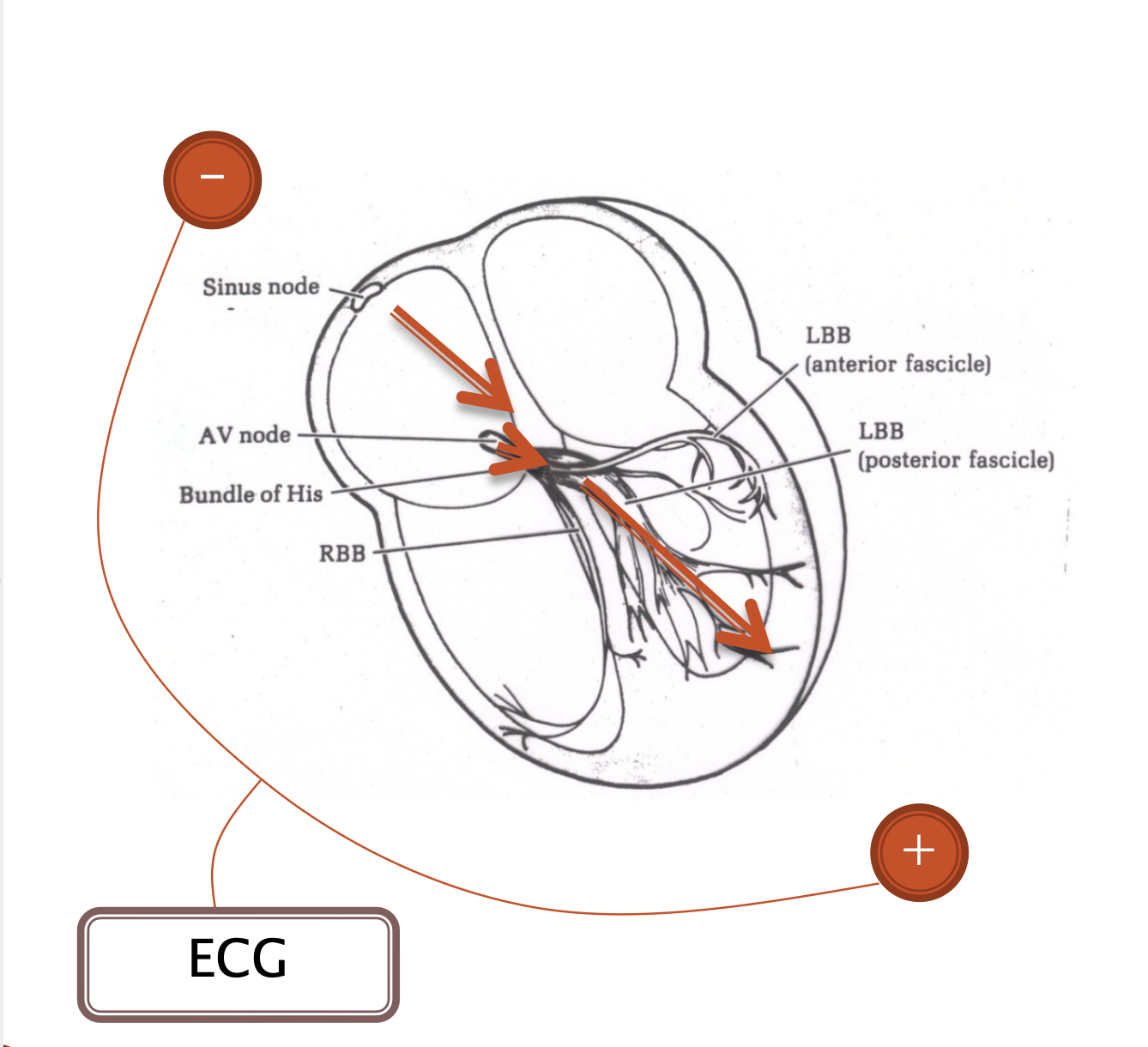
The mean vector flow of the depolarization wave can be thought of as traveling from the (left/right) atrium to the (left/right) ventricle
Right ; left
P waves can be…
positive, negative, or biphasic
Q waves are always (positive/negative) and come (before/after) the __ wave. (in lead II)
Negative; before; R
R waves are always… (in lead II)
Positive
S waves are always (positive/negative) and come (before/after) the __ wave. (in lead II)
Negative; after; R
T waves can be…
positive, negative, biphasic
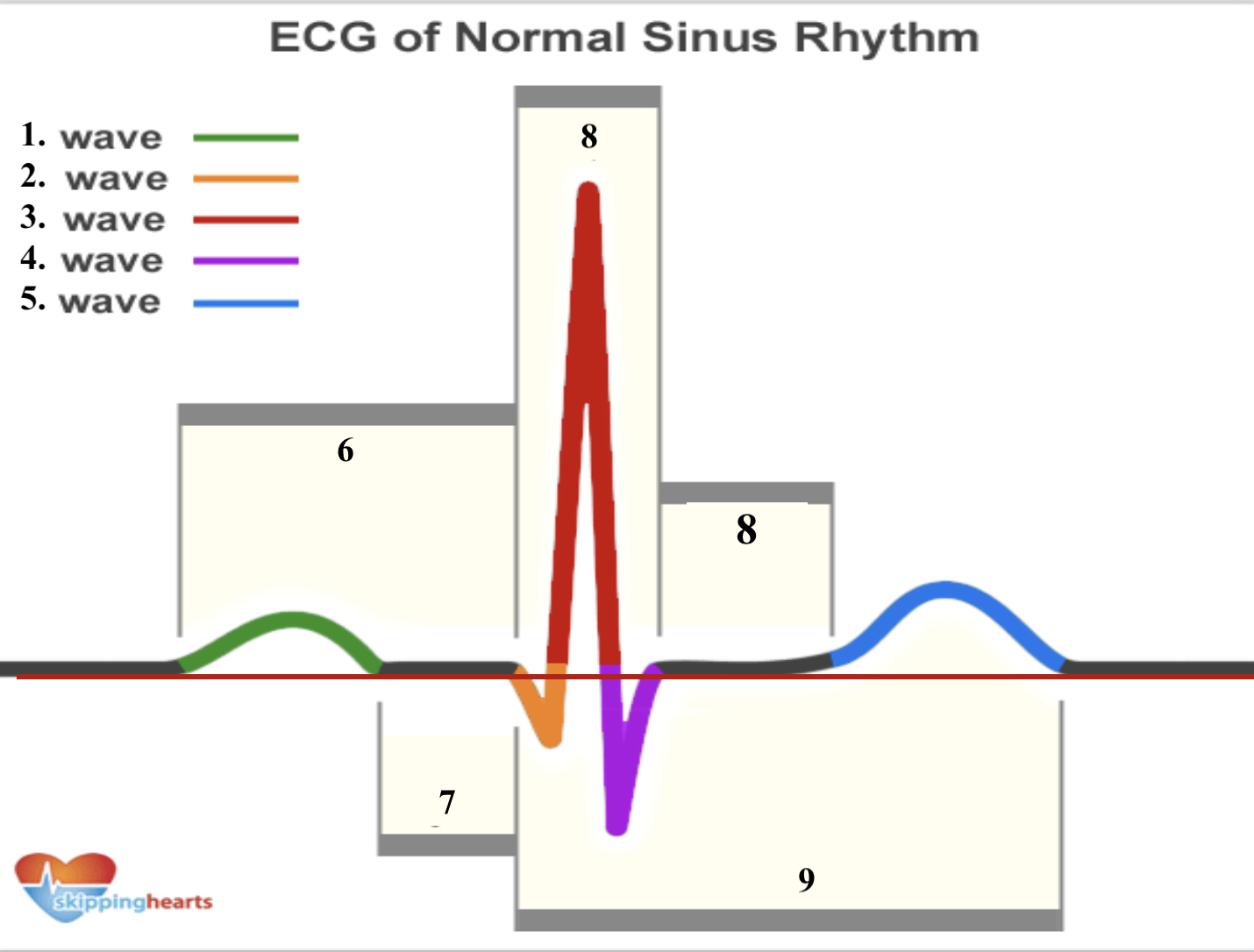
Structure 1 (green line) is a __ _________.
p wave
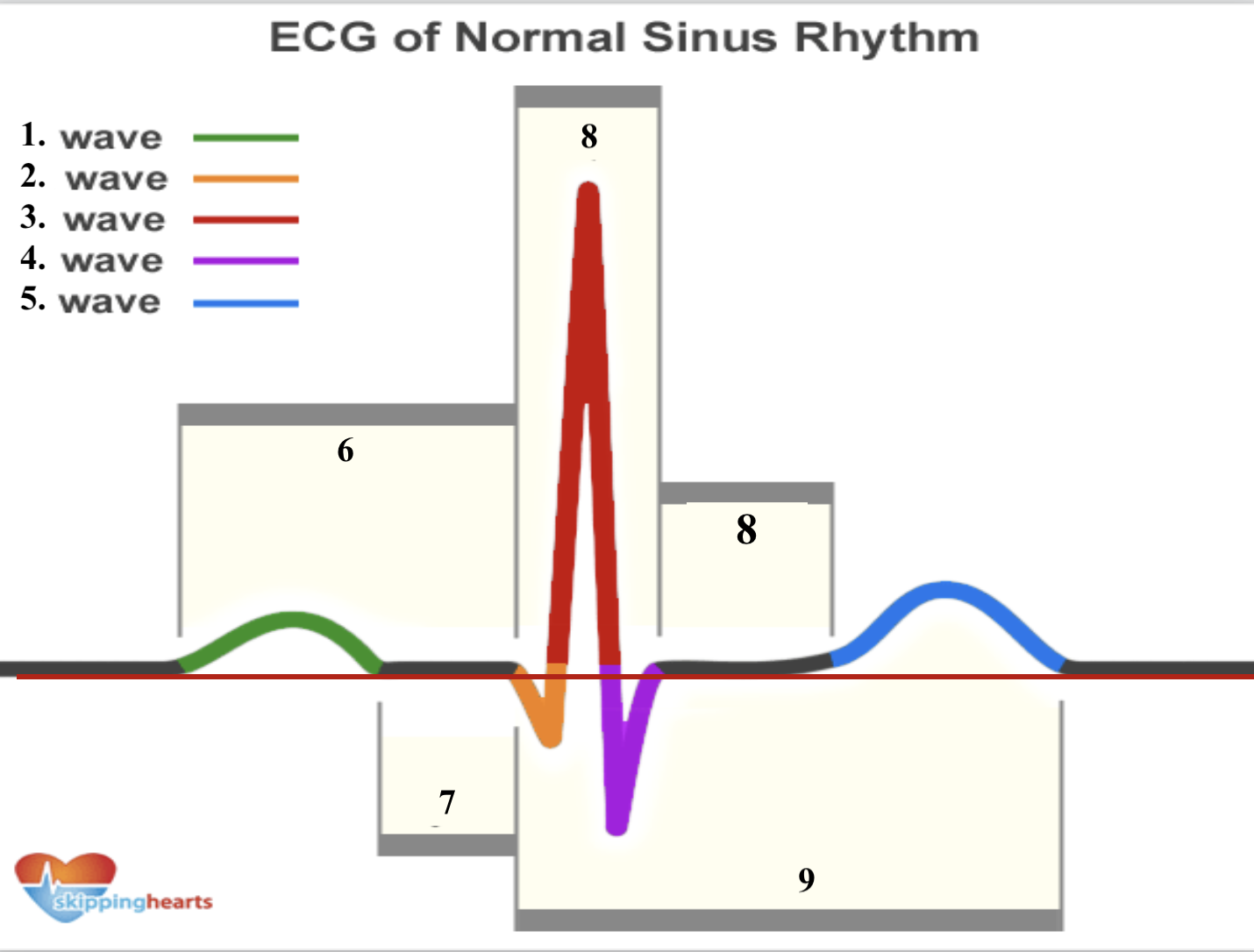
Structure 2 (orange line) is a __ _________.
q wave
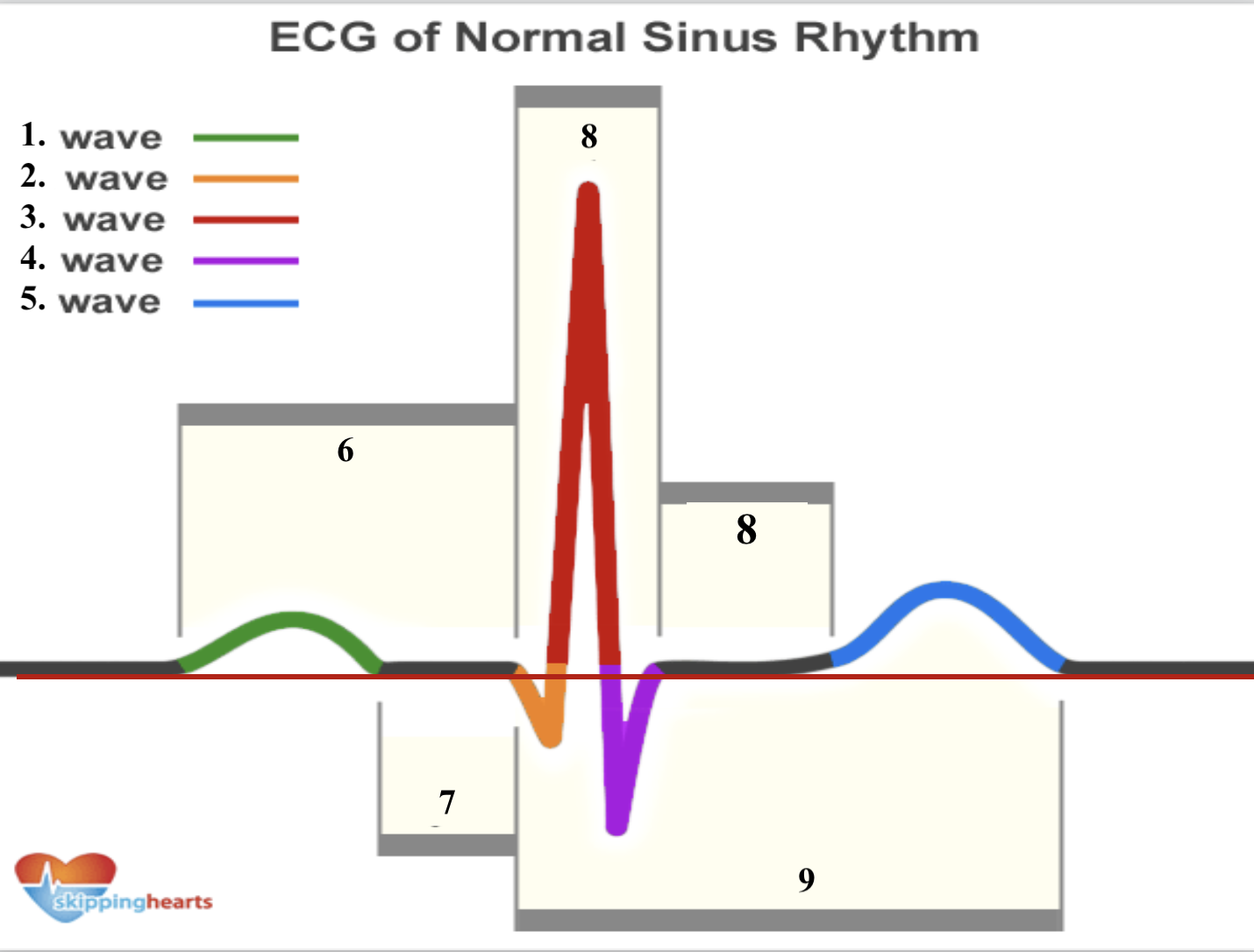
Structure 3 (red line line) is a __ _________.
r wave
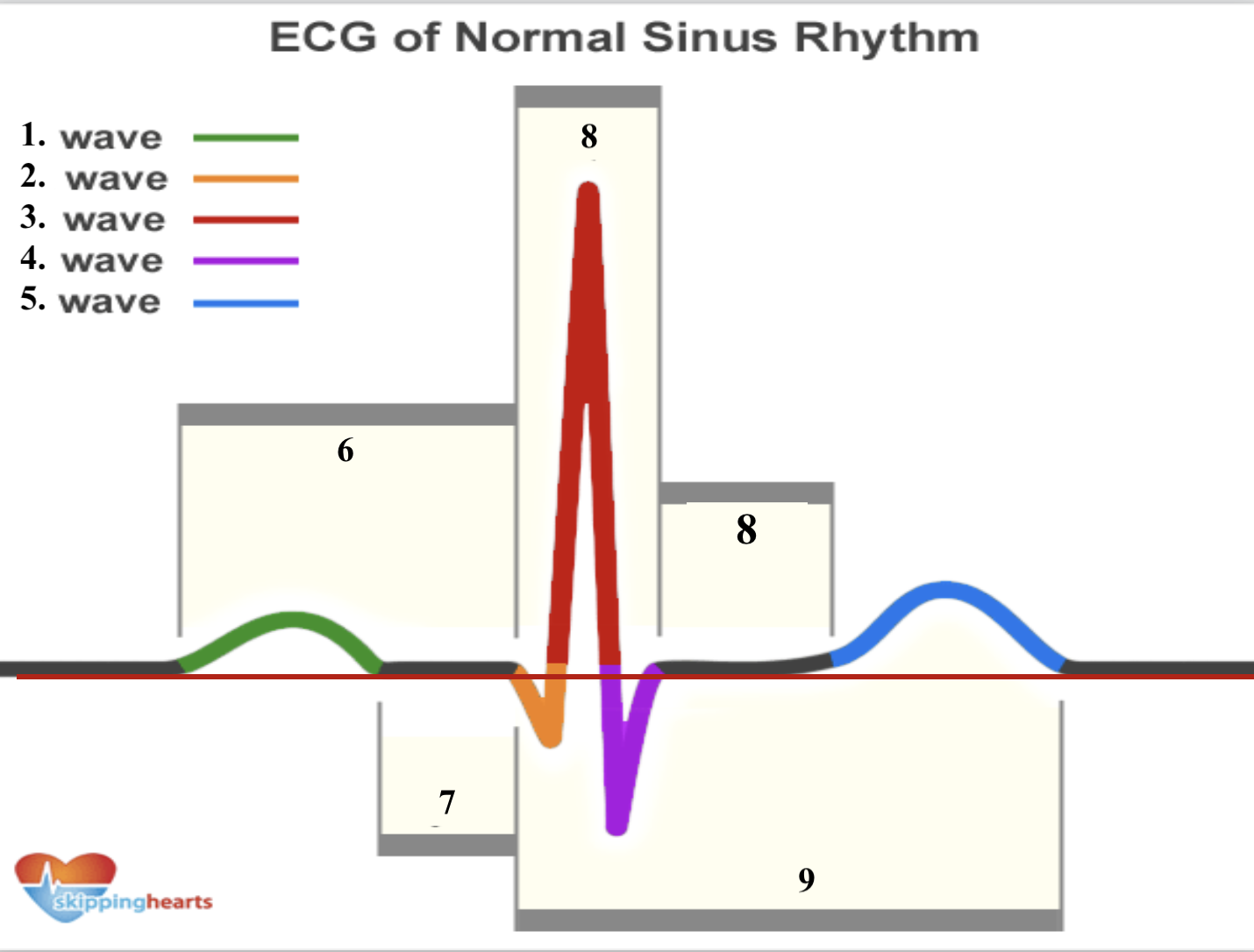
Structure 4 (purple line) is a __ _________.
s wave
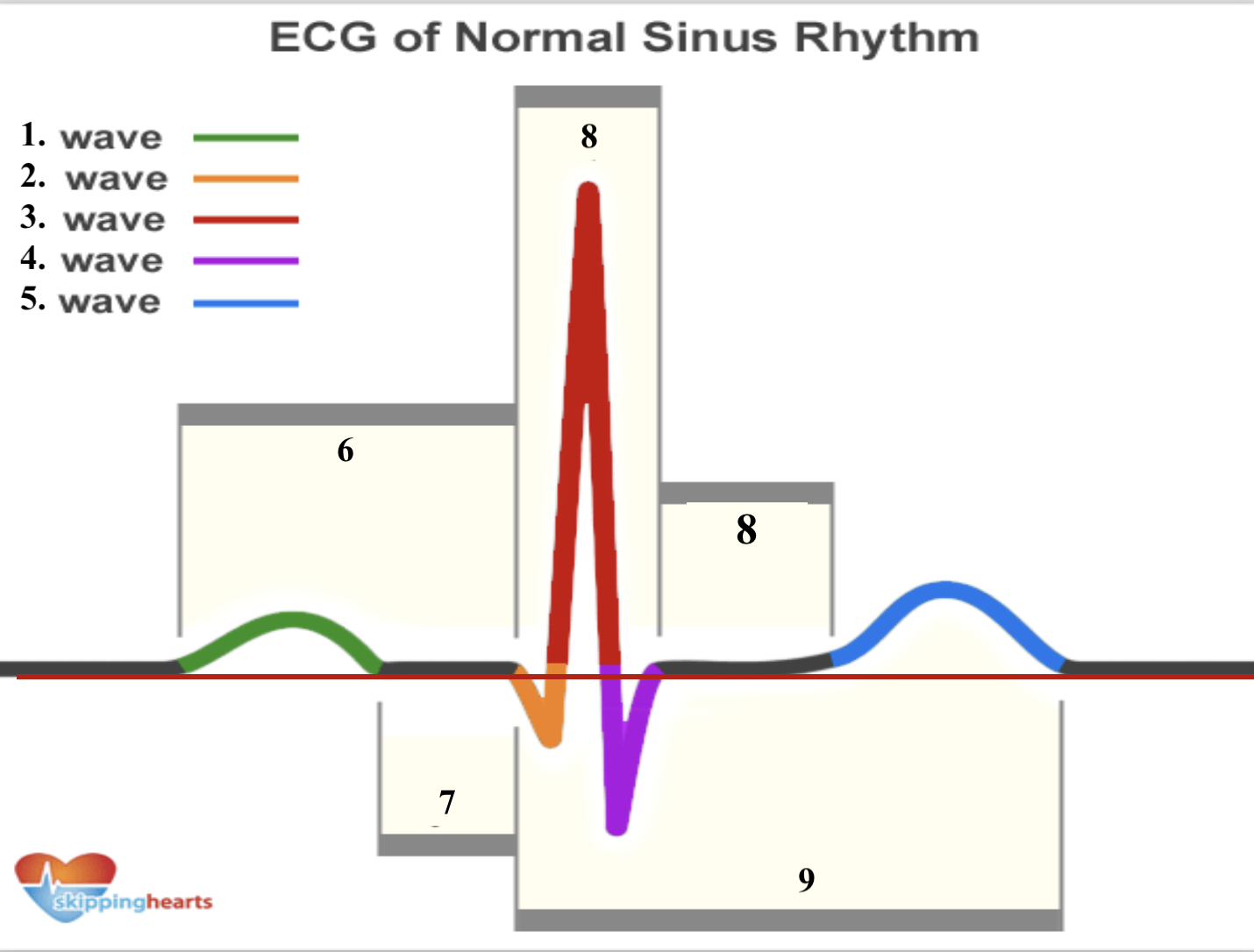
Structure 5 (blue line) is a __ _________.
t wave
What event in the heart is the p wave associated with?
Atrial depolarization
What event in the heart is the qrs complex associated with?
ventricular depolarization
What event in the heart is the t wave associated with?
ventricular repolarization
On ECG paper, the x axis displays __________ measured in __________, and the y axis displays ____________ measured in ____________.
time, seconds; amplitude, millivolts
With ECG paper, standard calibration involves one small square equal to __________ on the x axis, and ___________ on the y axis
.04 sec; .1 mV
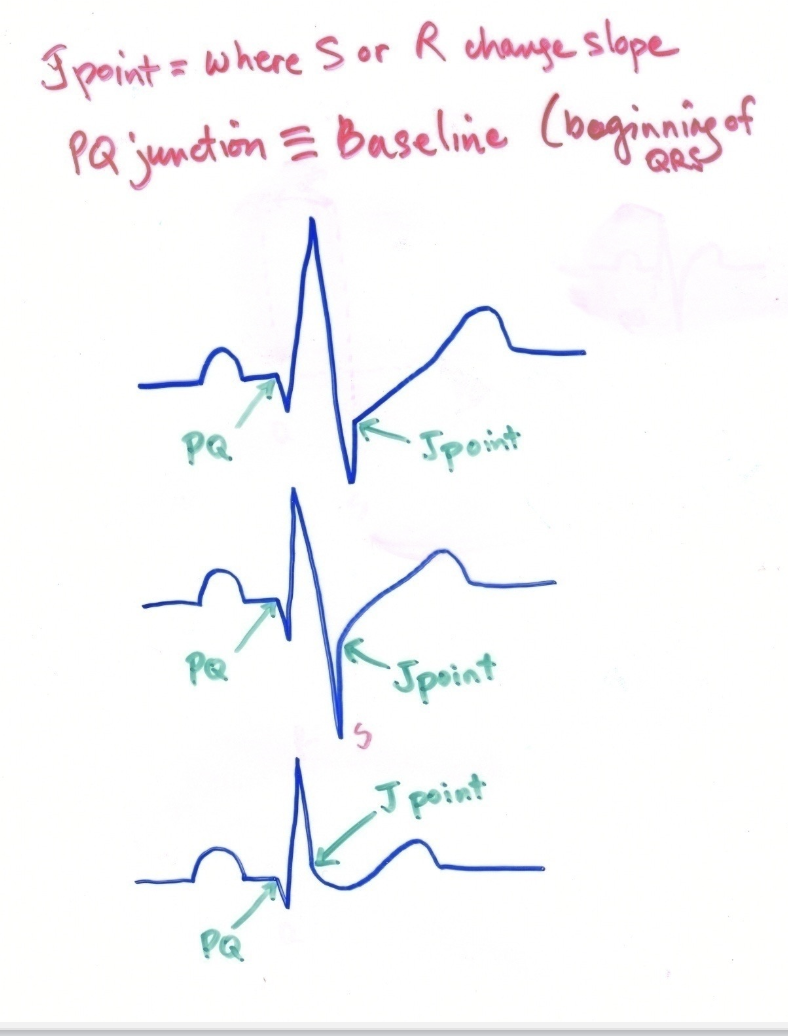
The pq junction can be defined as ____________________ and serves as our _______________.
the beginning of the qrs complex; baseline
A normal duration for the QRS interval is ___________.
< .10 seconds
A normal duration for the QT interval is ___________.
< .50 seconds
A normal duration for the PR interval is __________ .
< .21 seconds
Refractory period can be defined as the time that ______________.
the cell membrane is unresponsive to new stimuli
The absolute refractory period differs from relative refractory period in that…
absolute refractory period occurs before the relative refractory period
membranes are unresponsive to new stimuli, regardless of strength (for the absolute refractory period)
We can determine heart rate on an ECG strip (w/o reading the # the Q stress gives us) in 3 ways. What are they?
# of R waves in 6 seconds x 10
1500 / mm between two R waves
HR guide sheet/ruler
The SA node node fires at a regular rate of ____ - _____ bpm.
60 - 100
In normal sinus rhythm, p waves, PR intervals, and R to R should all be _________.
consistent
One common sign of sinus arrthymia involves R to R intervals varying by at least __________.
3 mm
Sinus bradycardia involves consistent waves/intervals but a HR of _________.
<60 bpm
Sinus tachycardia involves consistent waves/intervals but a HR of _________.
>100 bpm