Speech Pathology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Licensure
granted by state to allow practice of a position
Certification
Product offered by an outside organization
Accreditation
Assurance a program meets specific quality standards

What is 1
frontal lobe

What is 2
parietal lobe
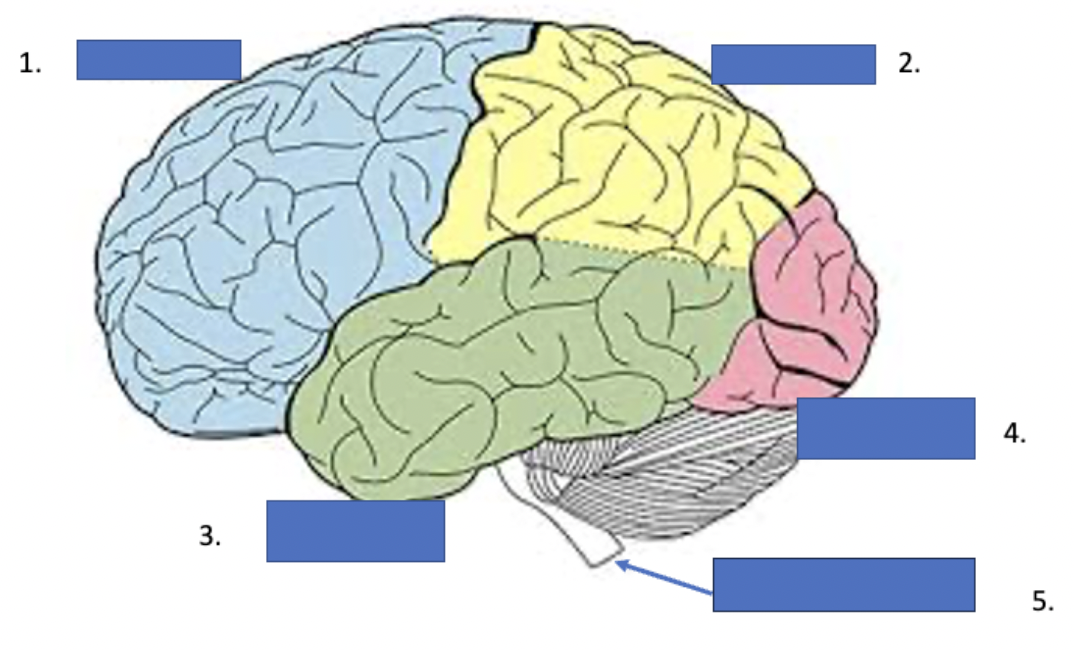
What is 3
temporal lobe
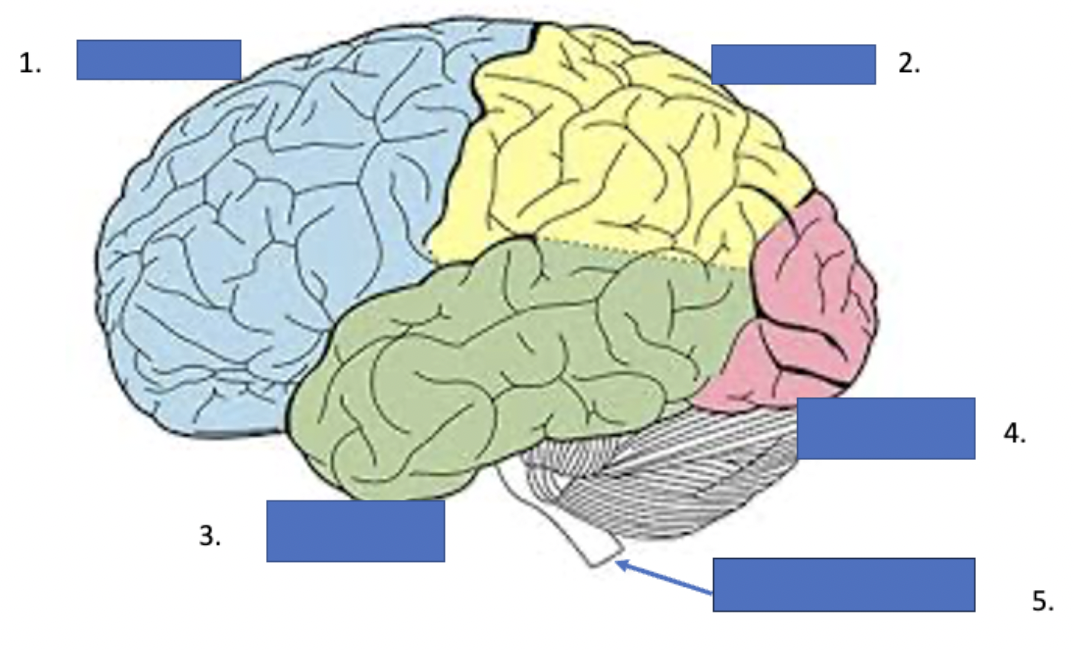
What is 4
occipital lobe
At what age does canonical babbling typically begin, and why is its onset clinically significant?
6–8 months; predicts first words and later vocabulary size
What is the difference between “speech” and “language,” and why does that distinction matter?
Speech is about sounds; language is about meaning and structure
Which of the following best shows how gesture supports preverbal language learning?
A parent points to an object while labeling it
Which of the following describes “protowords”?
Transitional forms, consistently used for objects but not real words
What happens to infants’ ability to perceive phonemes between 3–12 months?
They lose sensitivity to non-native contrasts while tuning to native ones
12-14 months
1st words
18-20 months
50 words
24-27 months
2 word combinations
36 months
3 word sentences
What are the three anatomy components required for speech?
Respiratory system, larynx, and upper and nasal airways.
This is the term used as a general cover term for phonation
voice
T or F: The articulators (lips, tongue, velum/soft palate) do not impact the speech sounds.
false
Sounds produced with an open vowel tract are known as
vowels
Sounds produced by restricting airflow in some way are known as
consonants
What is its Role in Speech Production: Respiratory
power supply
What is its Role in Speech Production: Phonatory/Laryngeal
vibrations
What is its Role in Speech Production: Articulation
shaping sounds
What is its Role in Speech Production: Resonance
changes quality
Target word = dog. Child's production = "daw"
final consonant deletion
Target word = stop. Child's production = "top"
cluster reduction
Target word = sun. Child's production = "tun"
stopping of fricatives
Target word = banana. Child's production = "nana"
weak syllable deletion
Target word = ring. Child's production = "wing"
gliding of liquids
Acoustic energy to mechanical energy
tympanic membrane
Mechanical energy to hydraulic energy
oval window
Hydraulic energy to electrochemcial energy
basilar membrane
Where do you find high frequency sounds on along the basliar membrane?
at the base, near the oval window
What are two important functions of the bones of the middle ear (the ossicular chain)?
intensify the sound, transmit sound from tympanic membrane to oval window