GI L2 - Liver and Pancreas
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
what are the two major functions of the pancreas
1. Secretion of gastric enzymes (exocrine- focus of current lecture)
2. Secretion of hormones (Insulin and Glucagon as discussed earlier)
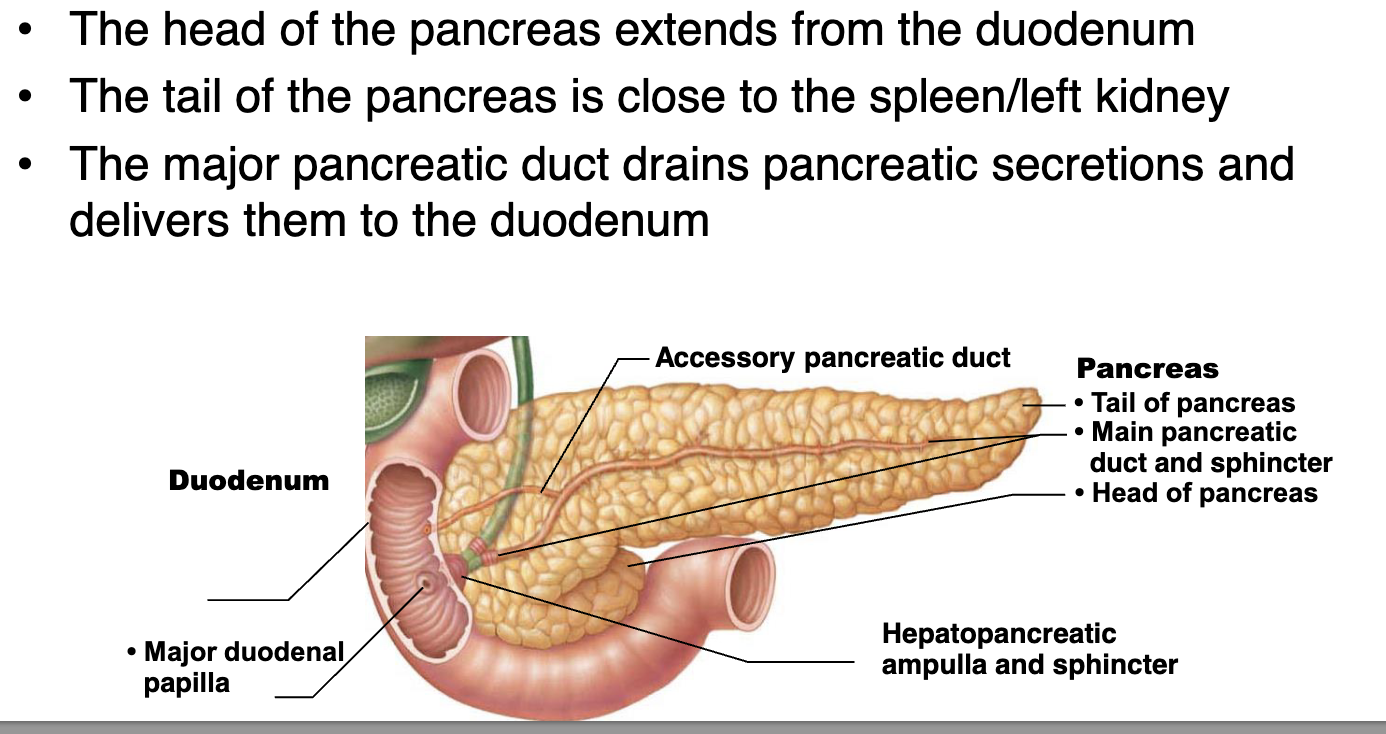
describe the location of the pancreas
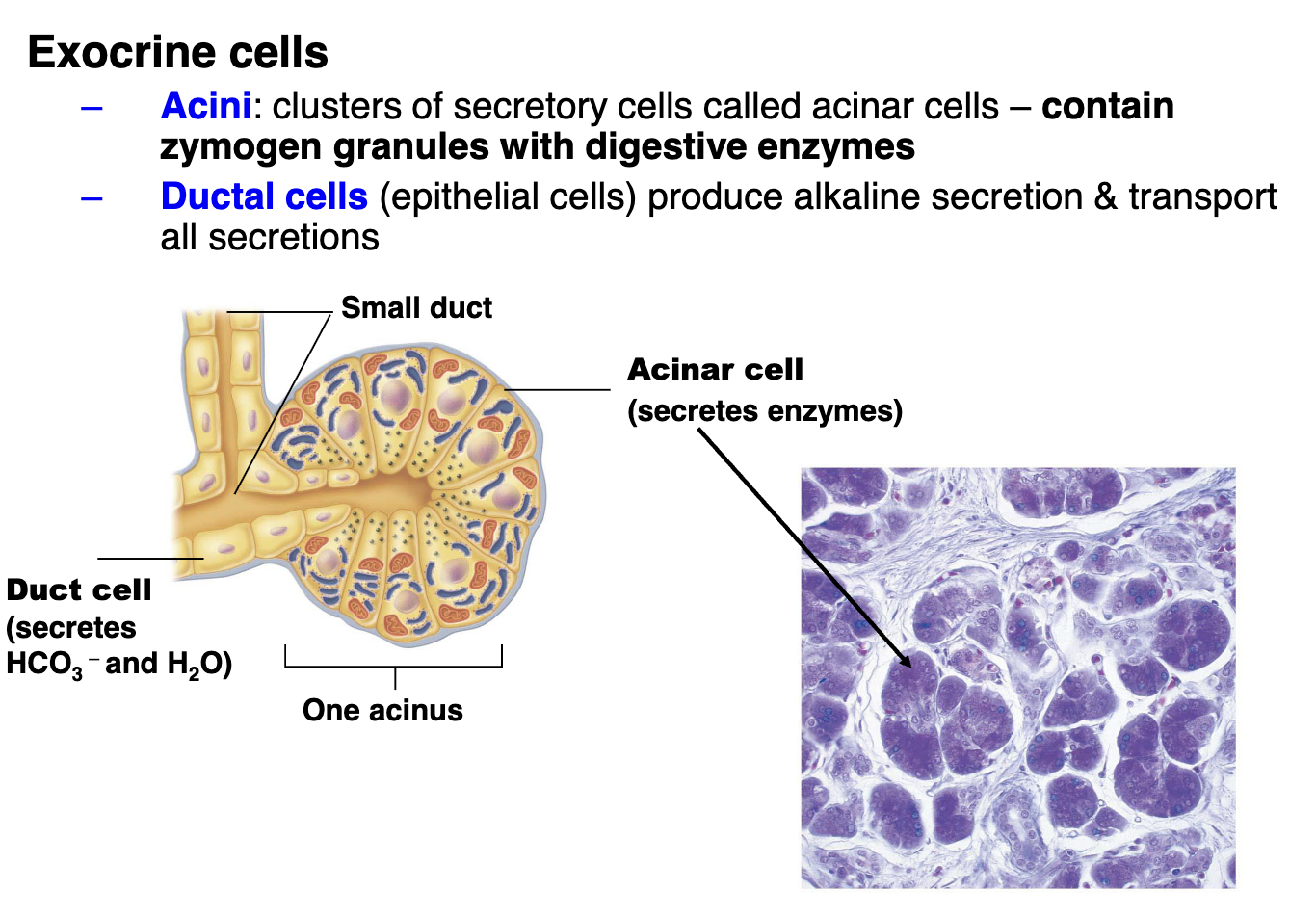
What are the exocrine cells in the pancreas
what are the Pancreatic enzymes
Proteolytic enzymes: break certain proteins apart
Trypsinogen: inactive but activated by enteropeptidase to form Trypsin.
Chymo-trypsinogen (activated by trypsin)
Pro-carboxypeptidas (activated by trypsin)
Alpha-amylase: similar to salivary amylase, breaks down carbohydrates
Lipase: breaks down complex lipids (triglycerides)
Nucleases: break down nucleic acids
how does pancreatitis develop and what are common causes

name the 4 lobes of the liver
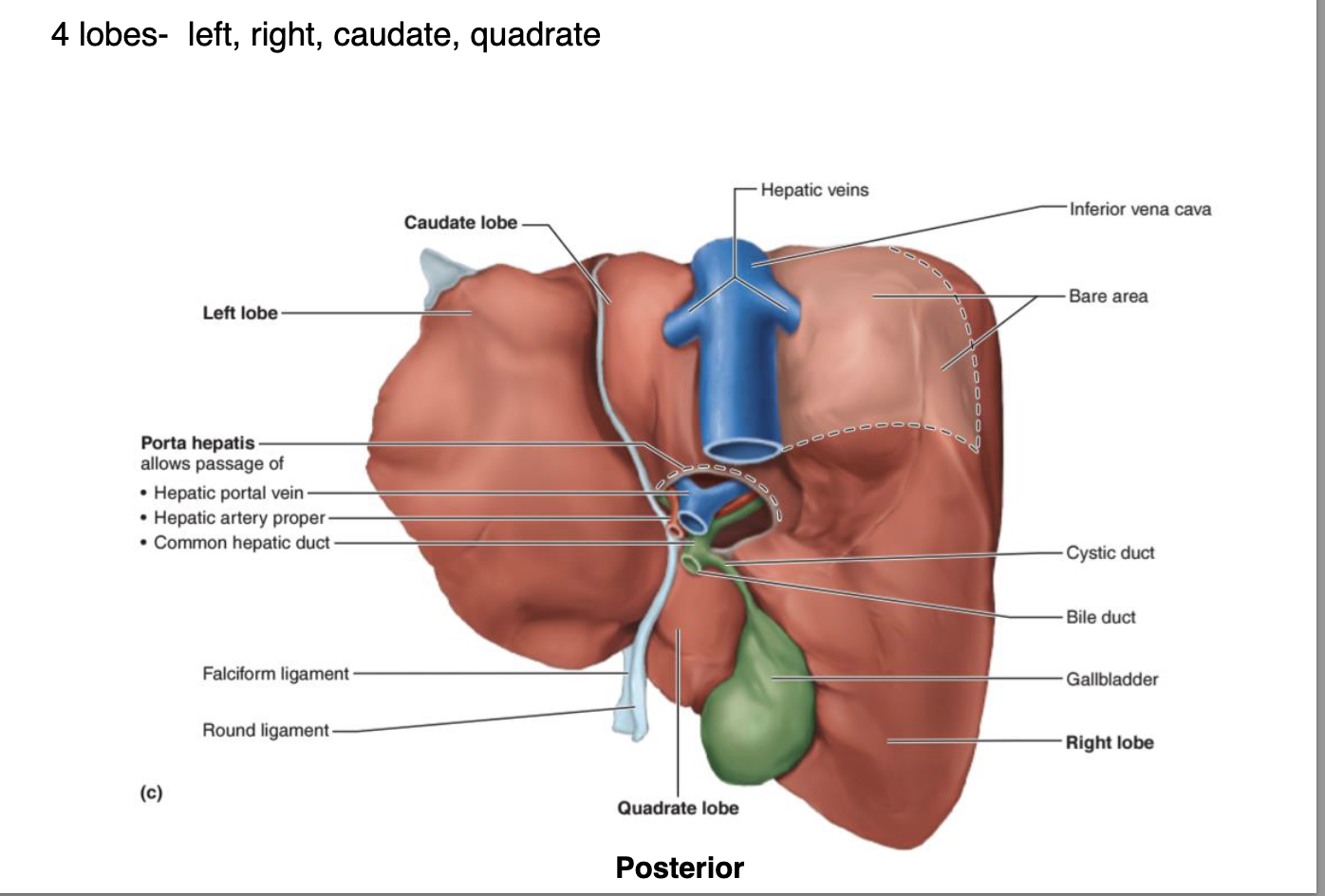
what system is the liver and gallbladder from
the biliary system, which is responsible for the production, storage, and transportation of bile. liver is the largest visceral organ.
describe the microscopic anatomy of the liver
– Liver lobules
Hexagonal structural and functional units
Composed of plates of hepatocytes (liver cells) that filter and process nutrient-rich blood
Central vein located in longitudinal axis
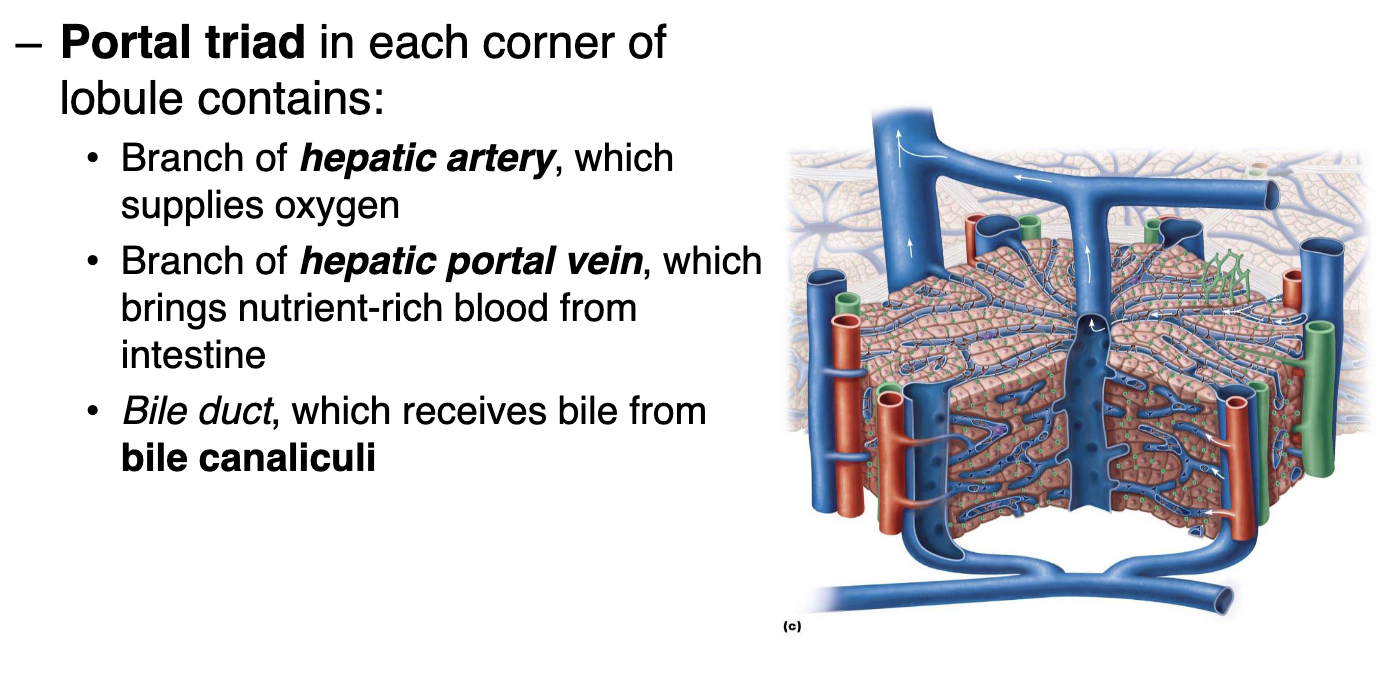
what does the portal triad contain in each corner of lobule.
What are the functions of the liver
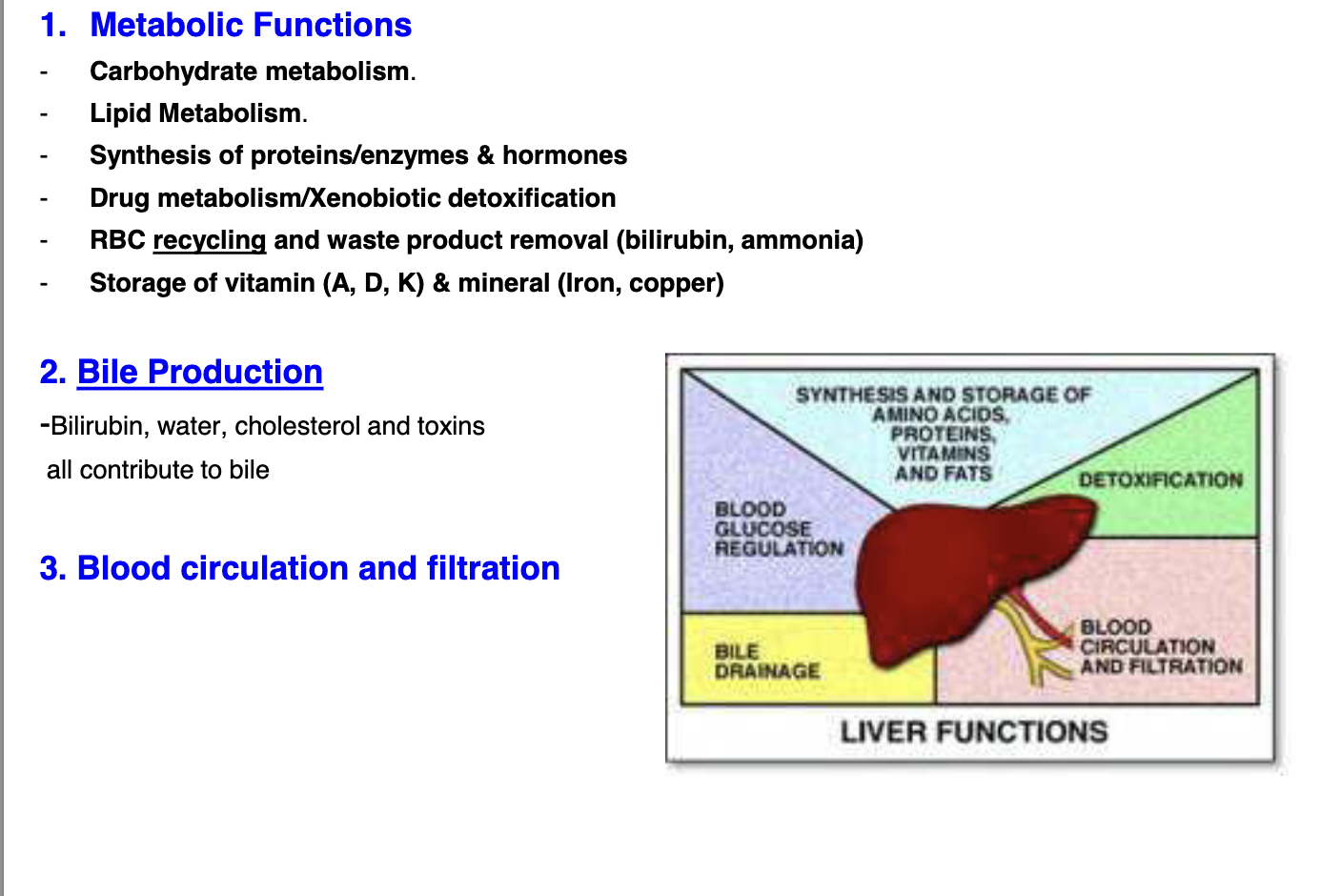
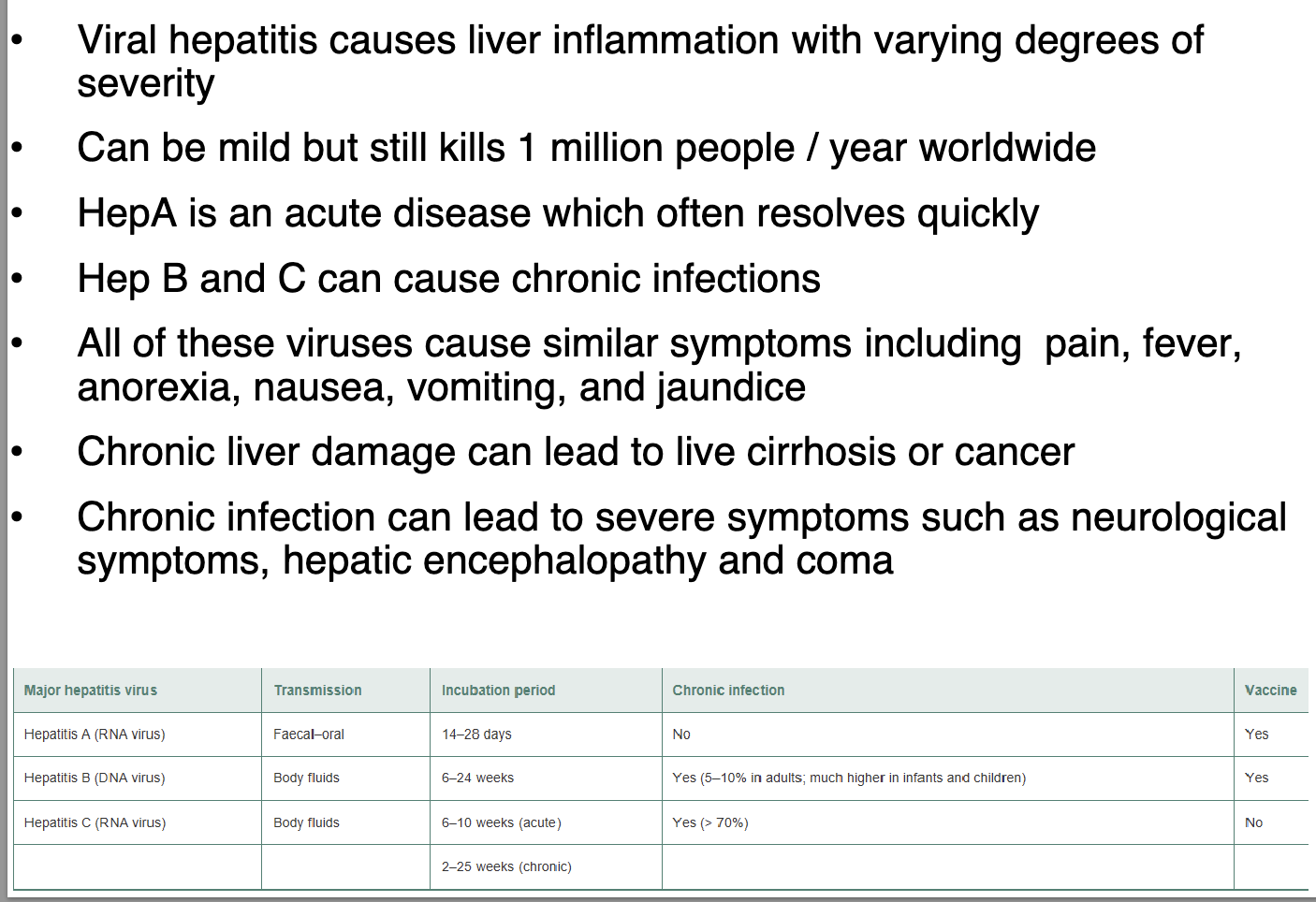
what are the symptoms and complications of Viral Hepatitis
what is fatty liver disease associated with? What are the symptoms
chronic alcohol use : alcoholic liver disease
Excessive intake of fats and sugars : non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Both are reversible if the cause is removed as while the inflammation can
cause liver damage, the liver can regenerate
• Symptoms similar to viral hepatitis
• Increased rates of regeneration can lead to cancer
• Extensive damage → liver fibrosis→ cirrhosis→ liver failure
what are 3 characteristics of the Gallbladder?
A thin-walled muscular sac on ventral surface of liver
• Stores and concentrates bile by absorbing water and ions
• Muscular contractions release bile via cystic duct, which
flows into bile duct
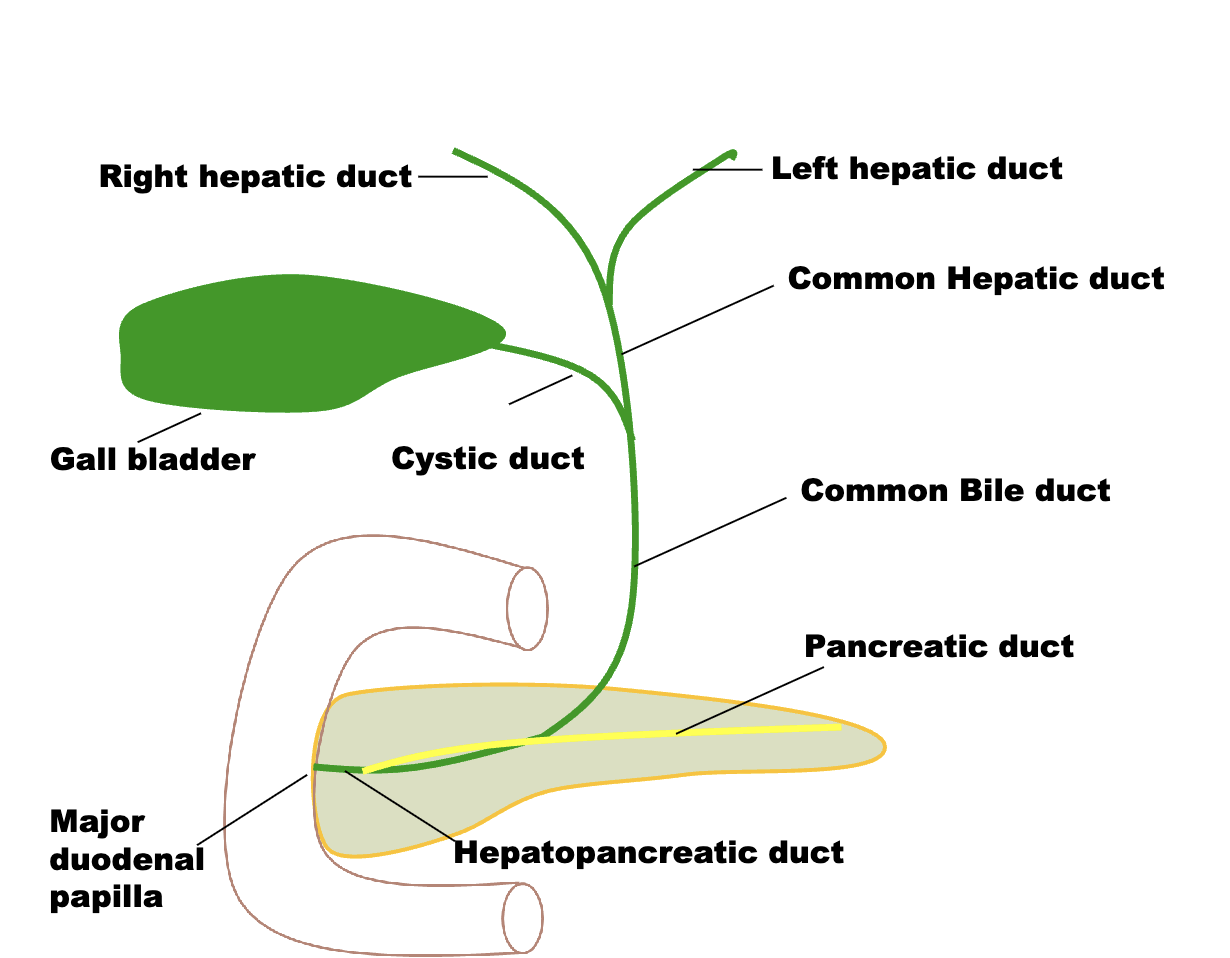
Name the 9 ducts of the biliary System?
What are the functions of bile
One function of the liver is to produce & secrete bile (600-1200ml/day)
An alkaline solution containing bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, neutral fats, phospholipids, and electrolytes
Stored in gallbladder and discharged into duodenum.
• Bile functions:
Lipid digestion & absorption; absorption of cholesterol and fat soluble vit; A, D, E, & K.
Major route for cholesterol synthesis & degradation
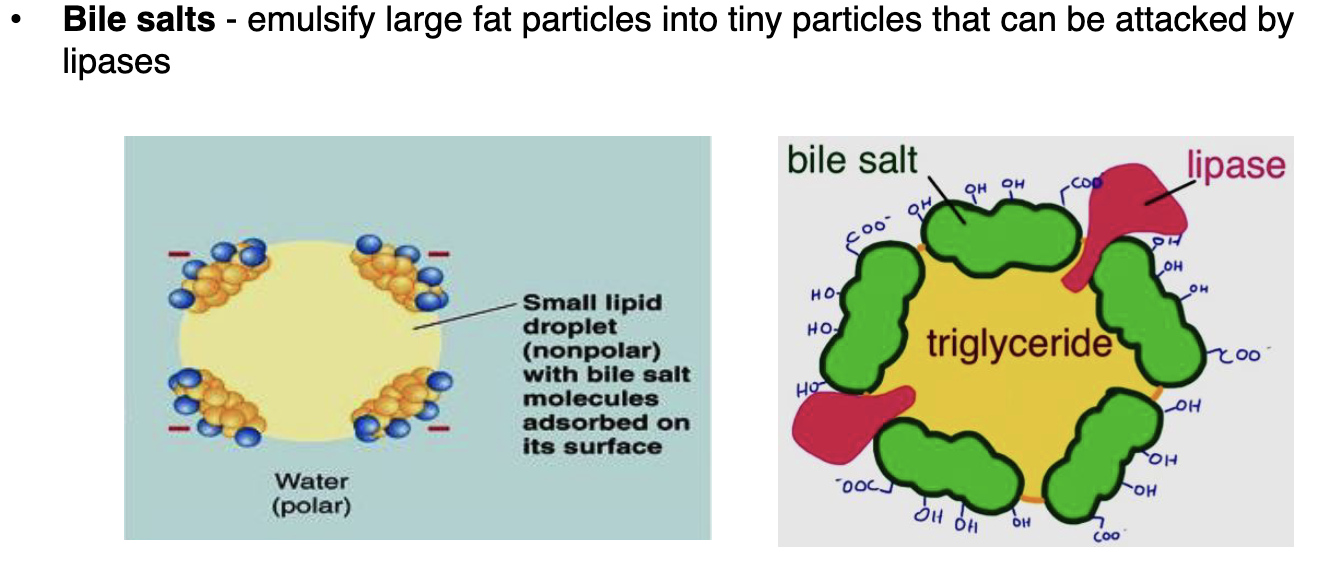
What are bile salts
where do the bile duct and pancreatic duct unite,
in the wall of the duodenum
how does bile and Pancreatic secretion go into the small intestine?

what organ secretes hormones that control bile release
Duodenum
Cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulated by proteins and fats to trigger release of pancreatic enzymes and bile
Secretin stimulated by acid to trigger bicarbonate release
What is the most common type of gallstone and its cause?
Cholesterol stones caused by too much cholesterol in bile (cholelithiasis).
What complications can arise from a gallstone blocking the common bile duct or hepatopancreatic duct?
It can lead to inflammation of the gallbladder or pancreatitis.
Why might someone need to reduce fat in their diet after gallbladder removal?
Without the gallbladder, bile isn’t stored and released efficiently, making fat digestion harder.
What are some common risk factors for developing gallstones?
Being female, pregnant, over 50, or obese.
What are pigment stones and what causes them?
A type of gallstone caused by excess bilirubin in bile.
What enzymes are involved in carbohydrate digestion and where do they act?
Salivary amylase in the mouth starts breaking down starch.
Pancreatic amylase continues in the small intestine, forming disaccharides.
Brush border enzymes (e.g., lactase, maltase, sucrase) in the small intestine break disaccharides into monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, and galactose
How are proteins digested from the stomach to the small intestine?
Pepsin in the stomach (activated by HCl) breaks proteins into large polypeptides.
In the small intestine, pancreatic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase) break them into smaller peptides.
Brush border enzymes (aminopeptidase, carboxypeptidase, dipeptidase) complete digestion into amino acids.
What enzymes and processes are involved in fat digestion and where do they occur?
Lingual lipase (mouth) and gastric lipase (stomach) have minor roles.
In the small intestine, bile salts emulsify fats, and pancreatic lipase digests them into monoglycerides and fatty acids.
How are nucleic acids digested and what are the final products?
In the small intestine, pancreatic ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease break RNA/DNA into nucleotides.
Brush border enzymes (nucleosidases and phosphatases) then break these into pentose sugars, nitrogenous bases, and phosphate ions.