Pelvis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are some key differences between the male and female pelvis?
Female pelvis is larger and wider
Female has a wider pelvic inlet
Female pubic angle is obtuse whereas male is acute
Male pelvis is more elongated
What is Paget’s disease?
Thickening of the bone most commonly in the pelvis
What is myeloma?
A type of blood cancer that arises from bone marrow
What’re the most common reasons for imaging the pelvis?
Fractures
Dislocation/subluxation
Osteoarthritis
Osteomyelitis
Myeloma
Paget’s
Post surgery
What is osteomyelitis?
Bone infection caused by bacteria
What is the standard series of views for a pelvis?
AP Pelvis
Lateral hips
Inlet and outlet views
Why do you suspend respiration for pelvic imaging?
Prevents bowel gas movement
What can happen if you over-rotate your legs?
Block the lesser trochanter from being visible
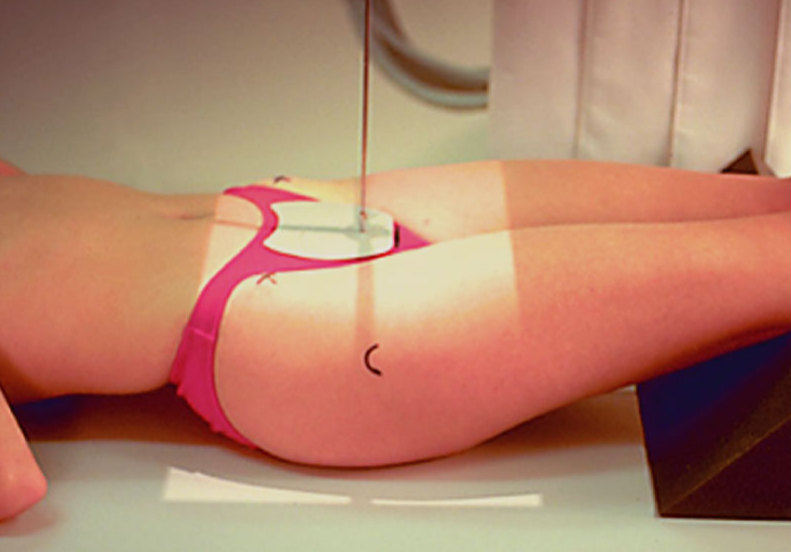
Patient Positioning for a AP Pelvis:
Patient orientation
Leg rotation
Key notes
Patient orientation: supine
Leg rotation: 15 degrees internally
Key notes:
Arms across stomach
Suspended breathing
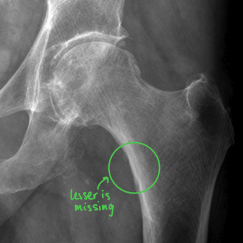
Which way is the leg rotated in this image?
Externally rotated
Greater trochanter and femoral neck are superimposed
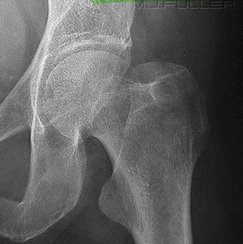
Which way is the leg rotated in this image?
Adequate internal rotation
Maximum visualisation of femoral neck, greater and lesser trochanter
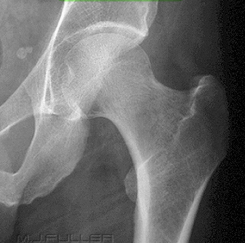
Name this view
AP Pelvis
AP Pelvis
Collimation:
Centering point:
Leg rotation
Collimation:
Laterally: skin margins
Superiorly: Iliac crests
Inferiorly: 10cm below greater trochanters
Centering point: midpoint between ASIS and pubic symphysis
Leg rotation: internally rotated 15 degrees
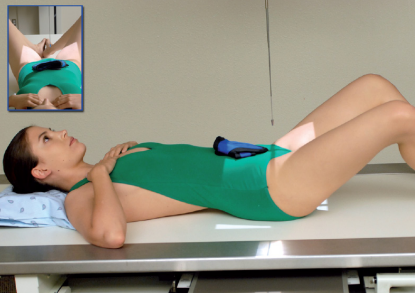
Name this view
Lateral pelvis (frog lateral)
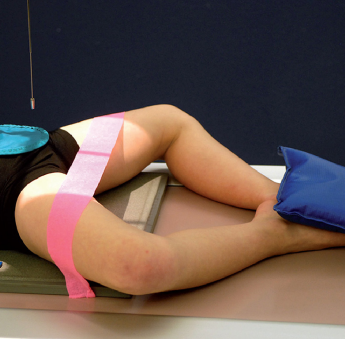
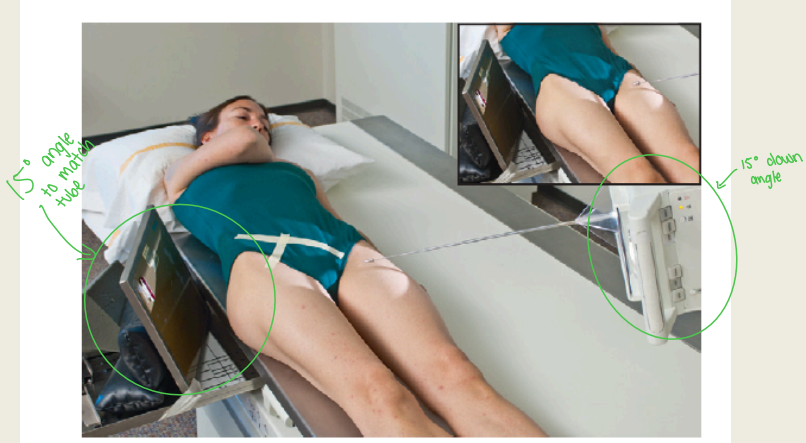
Name this view
Modified axio-lateral