Cross Sectional Anatomy Chapter 7 Abdomen
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
• List the structures of the abdominal cavity, and differentiate among those that are contained within the peritoneum and those that are contained within the retroperitoneum. • Describe the peritoneal and retroperitoneal spaces. • Describe the lobes, segments, and vasculature of the liver. • Define the structures of the biliary system. • State the functions and location of the pancreas and spleen. • Identify the structures of the urinary system. • List and identify the structures of the stomach and intestines. • Identify the branches of the abdominal aorta and the structures they supply. • Identify the tributaries of the inferior vena cava and the structures they drain. • List the muscles of the abdomen, and describe their functions. • List the vessels that form the portal vein, and describe the flow of blood through the portal hepatic system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
The peritoneum is divided into three layers: parietal, visceral, and retroperitoneal
True or False
False
The liver has a dual blood supply consisting of arterial blood from the common hepatic artery and nutrient-rich venous blood from the portal vein.
True or False
True
The portal vein is formed by the union of the superior mesenteric vein and splenic vein
True or False
True
The gallbladder's primary function is to produce bile
True or False
False
The pancreas has only an endocrine function, producing insulin
True or False
False
The spleen is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen
True or False
False
The left adrenal gland is positioned lower and more medial than the right adrenal gland
True or False
False
The kidneys are intraperitoneal organs
True or False
False
The stomach contains folds called rugae that allow for expansion
True or False
True
The large intestine consists of the cecum, colon, and rectum
True or False
True
Peritoneum
Double-layered serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity
Liver
Organ with four lobes that performs metabolic regulation and bile production
Gallbladder
Organ that acts as a reservoir for bile
Pancreas
Organ that produces digestive enzymes and insulin
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ, responsible for filtering blood and immune response
Adrenal Glands
Produces steroid hormones and is located superior to the kidneys
Kidneys
Bean-shaped retroperitoneal organs responsible for filtering blood and producing urine
Small intestine
Contains three main divisions: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Large intestine
Contains taeniae coli, haustra, and epiploic appendages
Inferior vena cava
Major vein that carries blood from the lower body to the heart
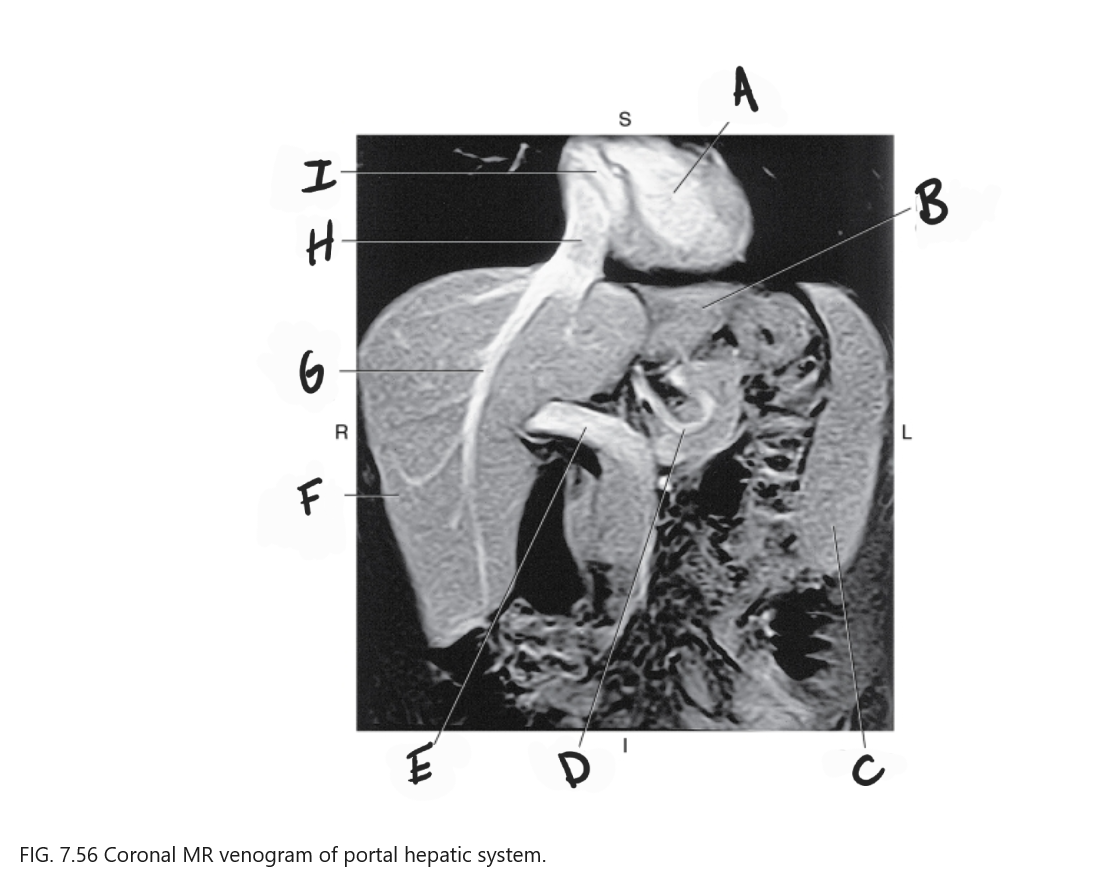
What is A
Left ventricle
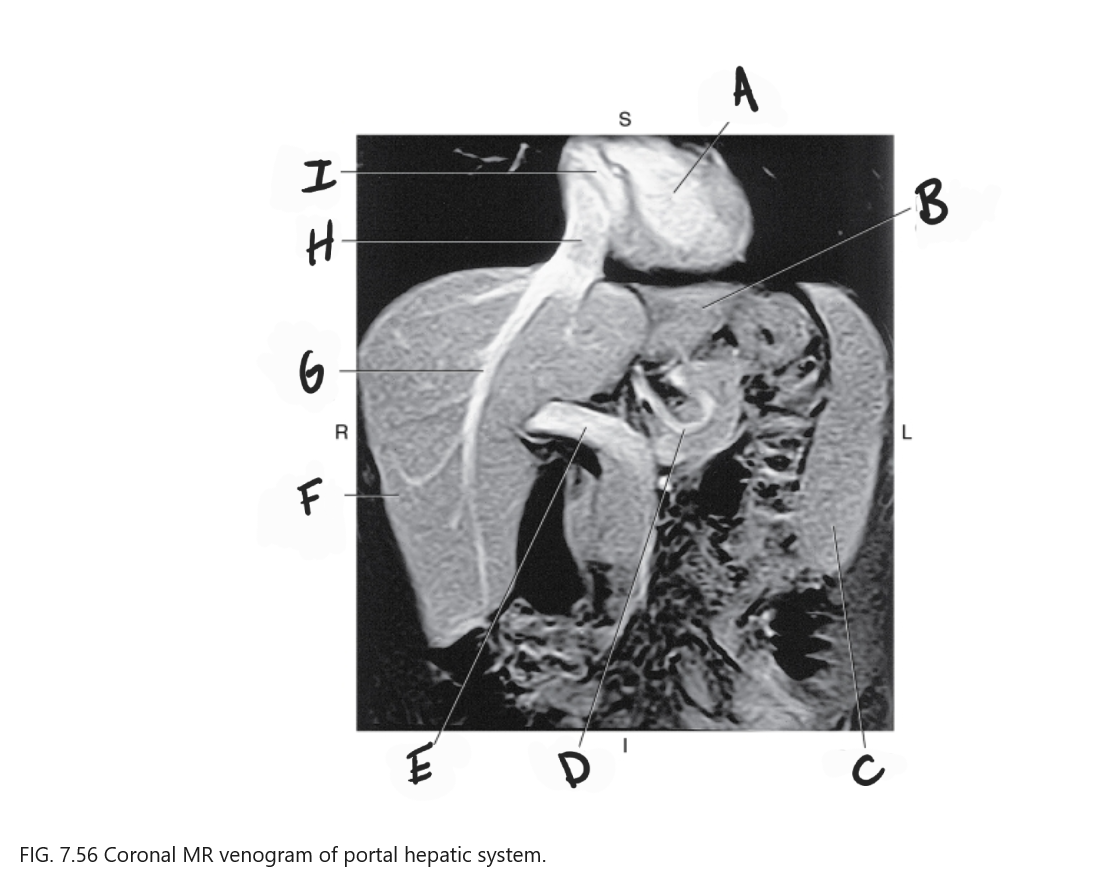
What is B
Left lobe of liver
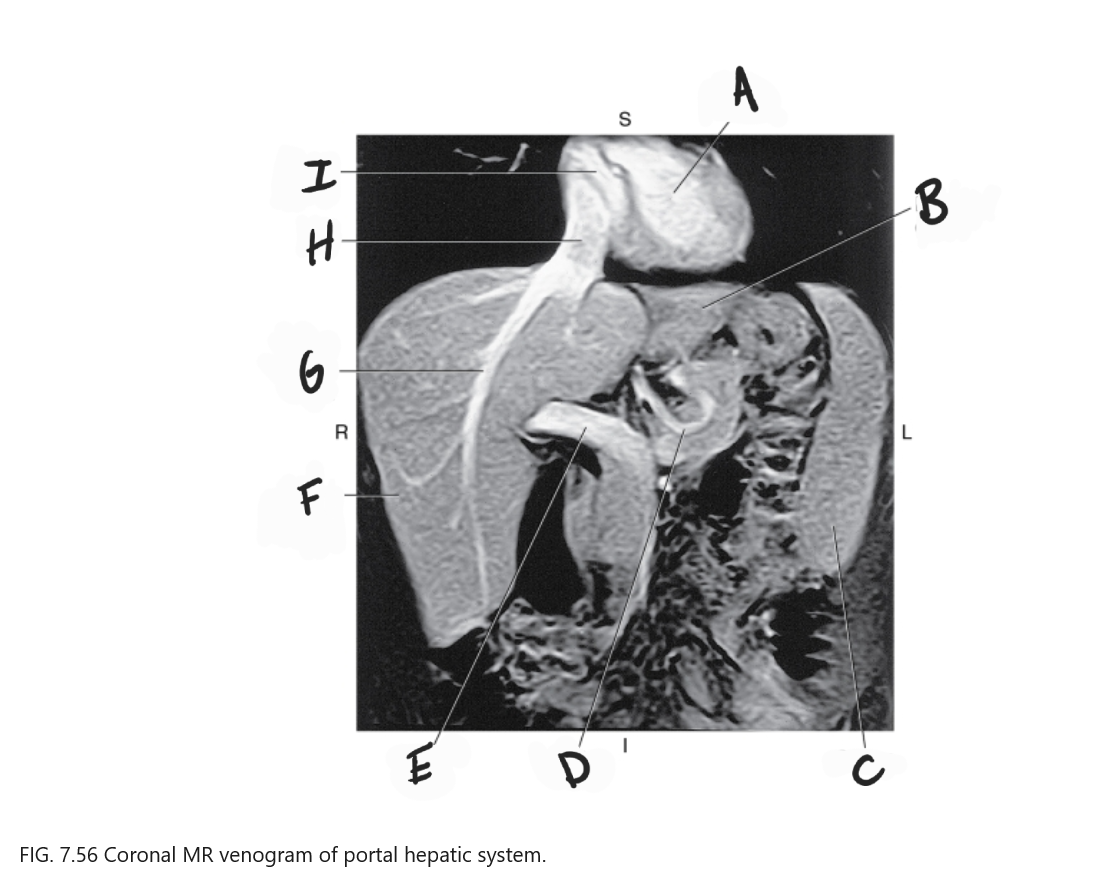
What is C
Spleen
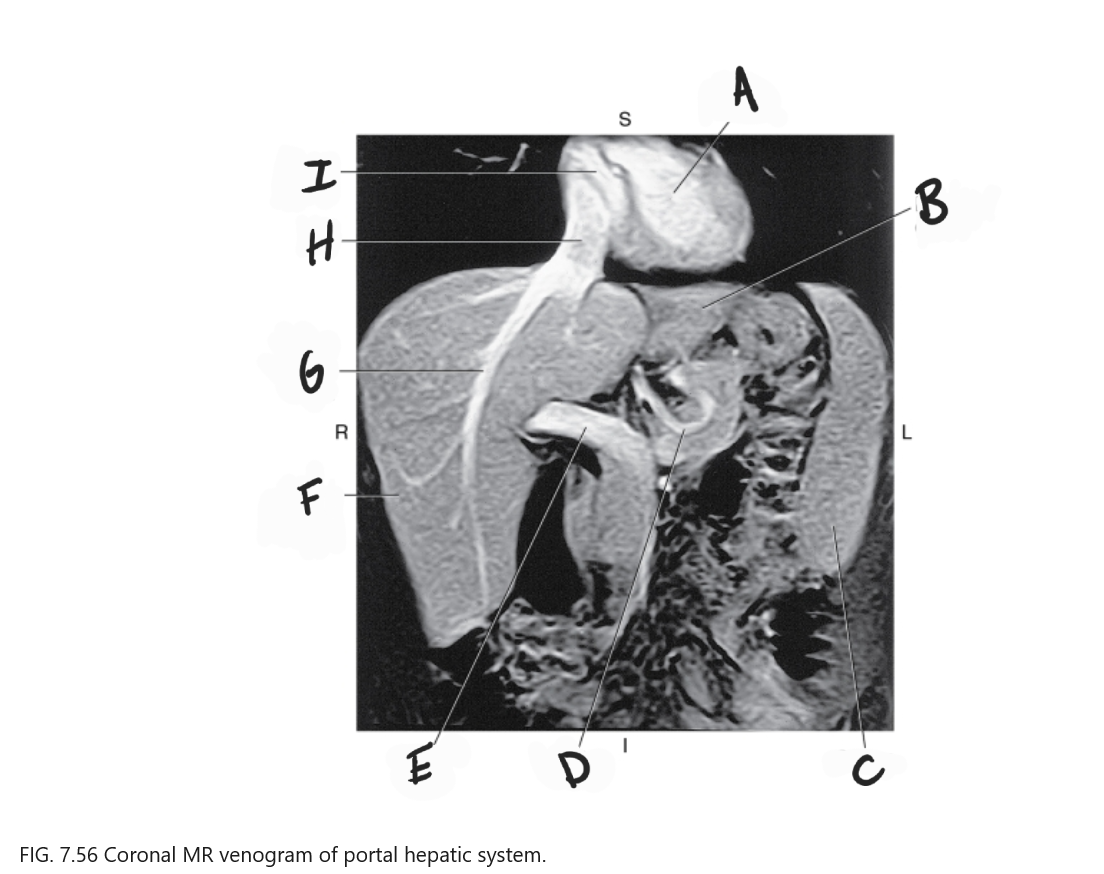
What is D
Gastric Vein
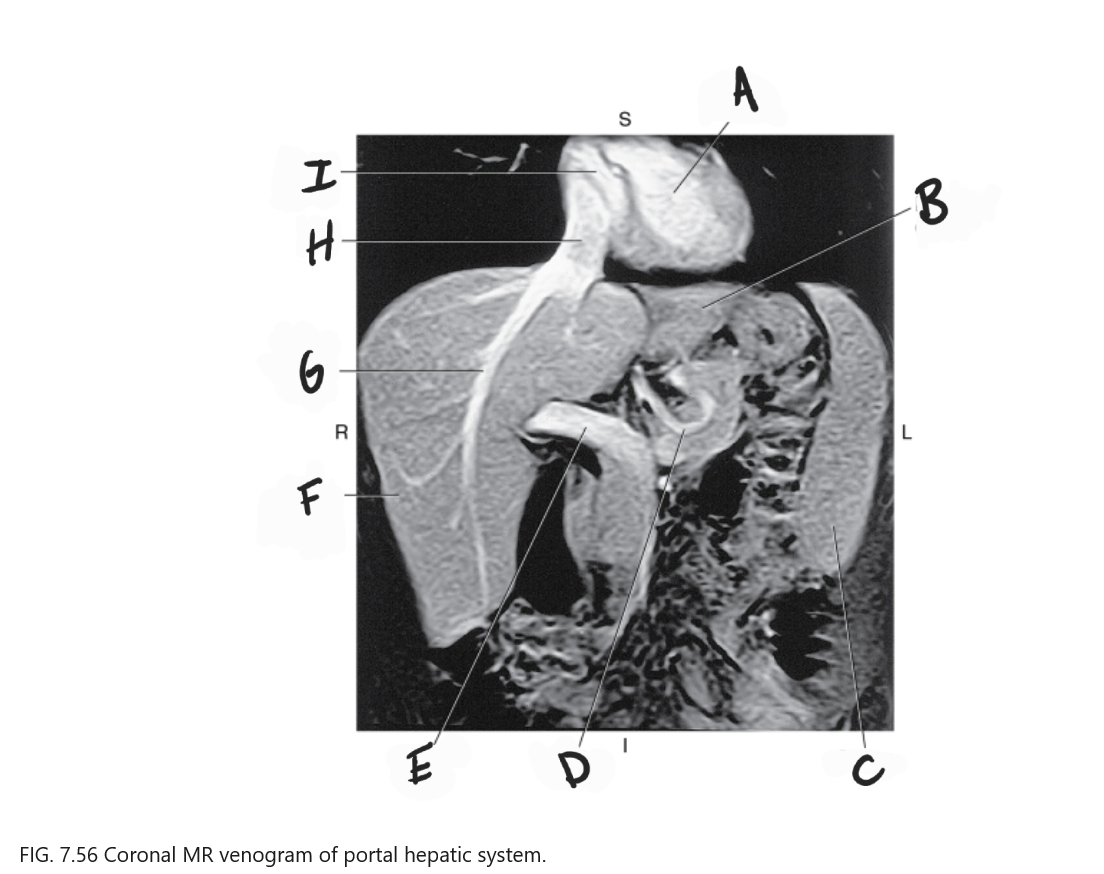
What is E
Portal vein
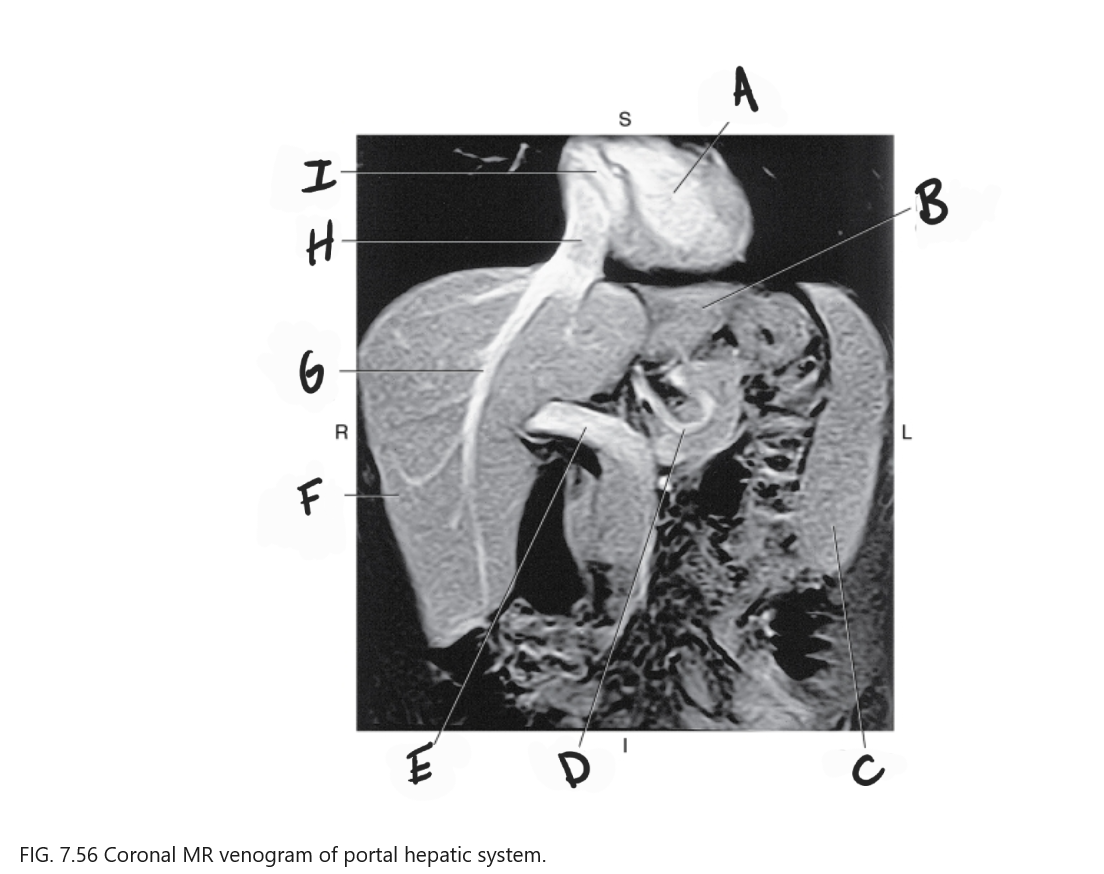
What is F
Right lobe of liver
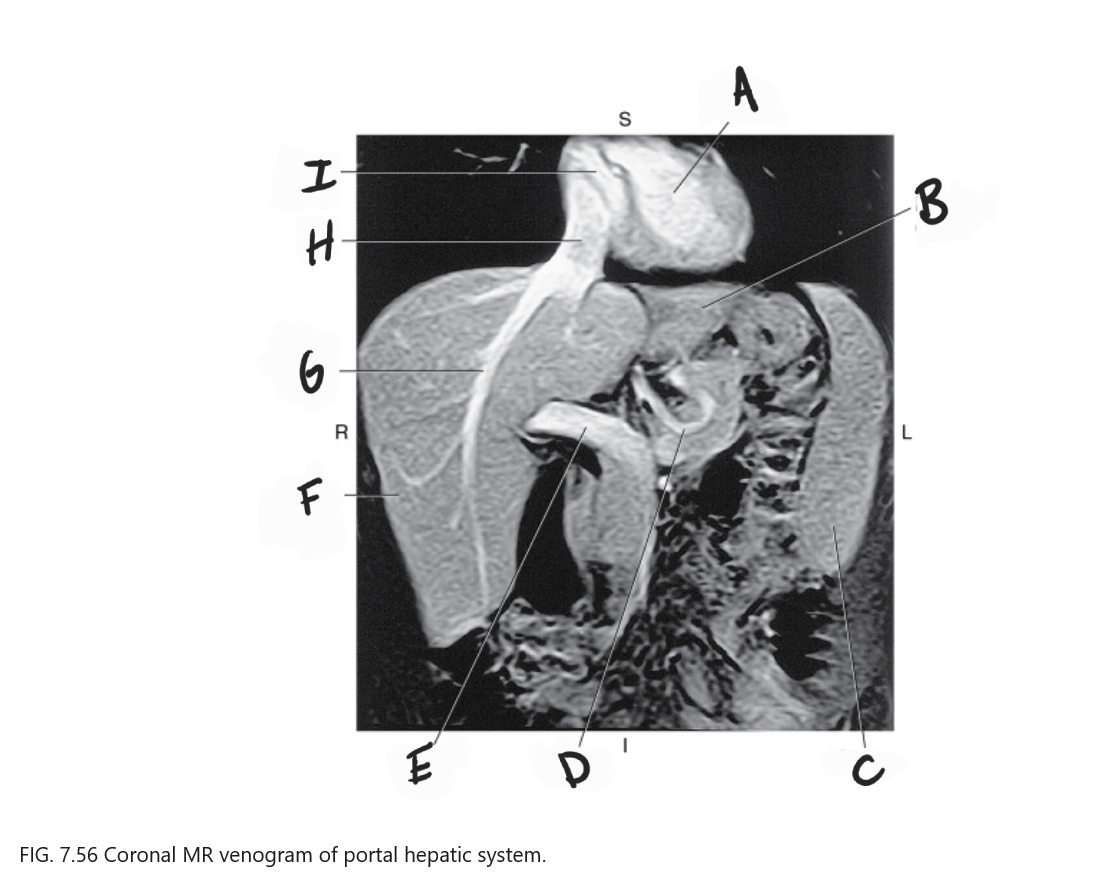
What is G
Right hepatic vein
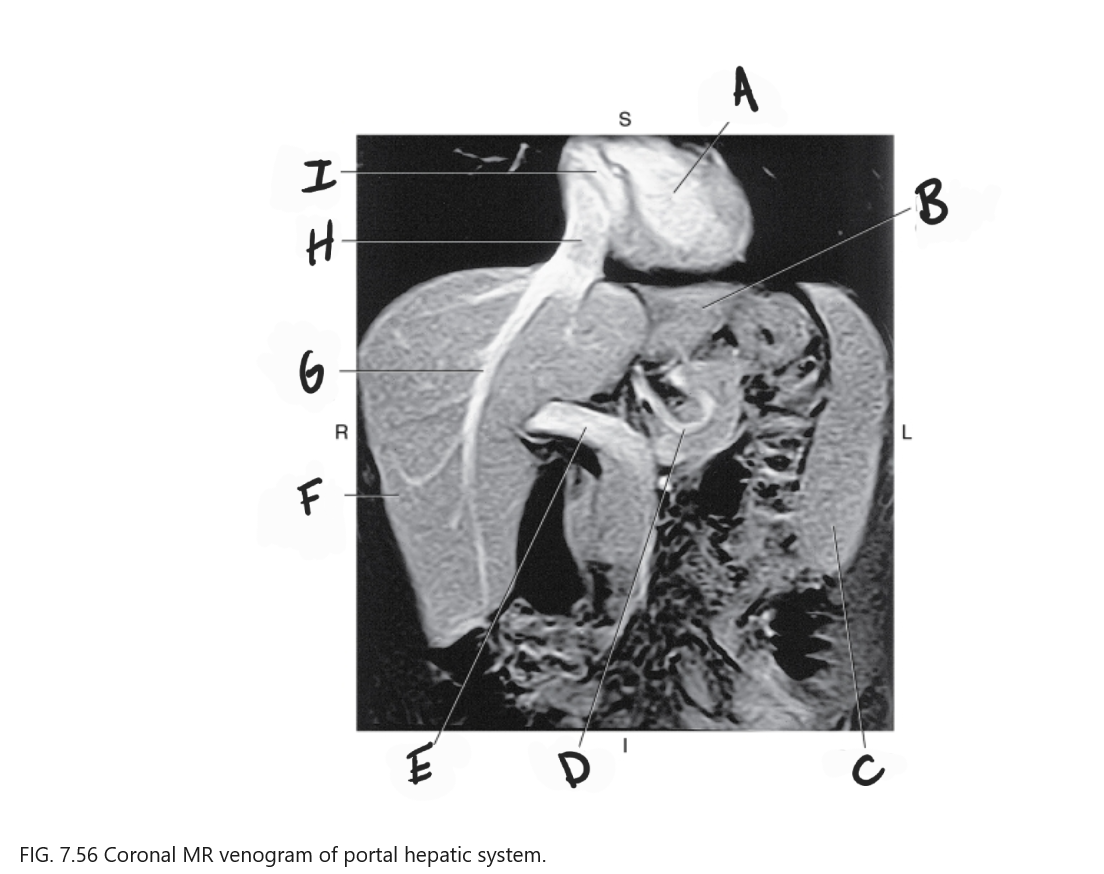
What is H
IVC
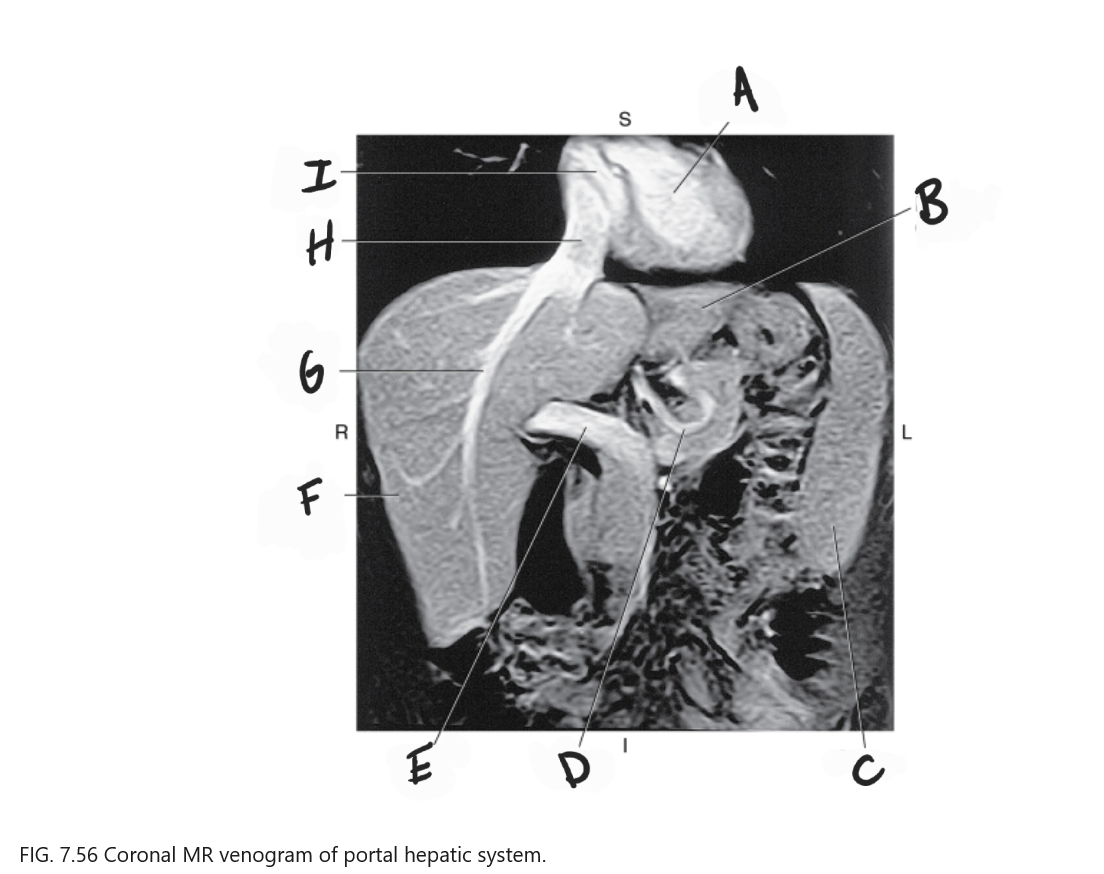
What is I
Right atrium
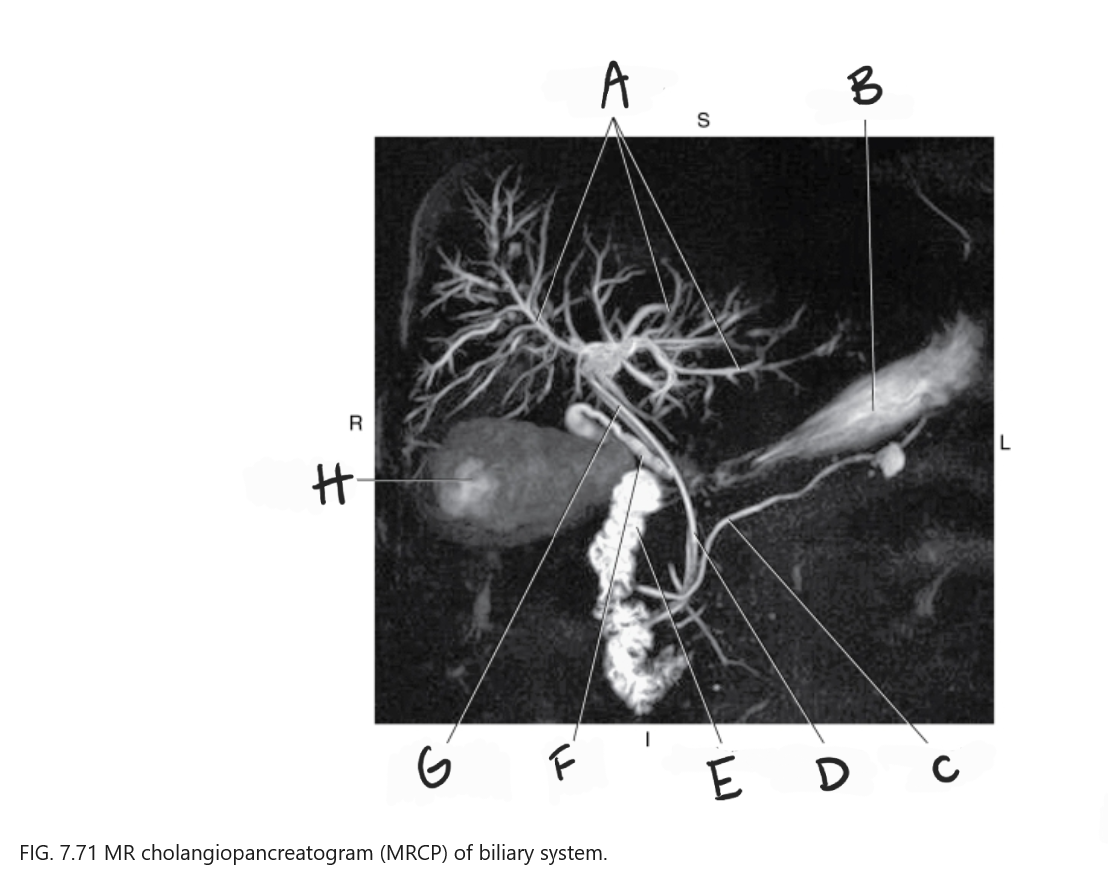
What is A
Intrahepatic ducts
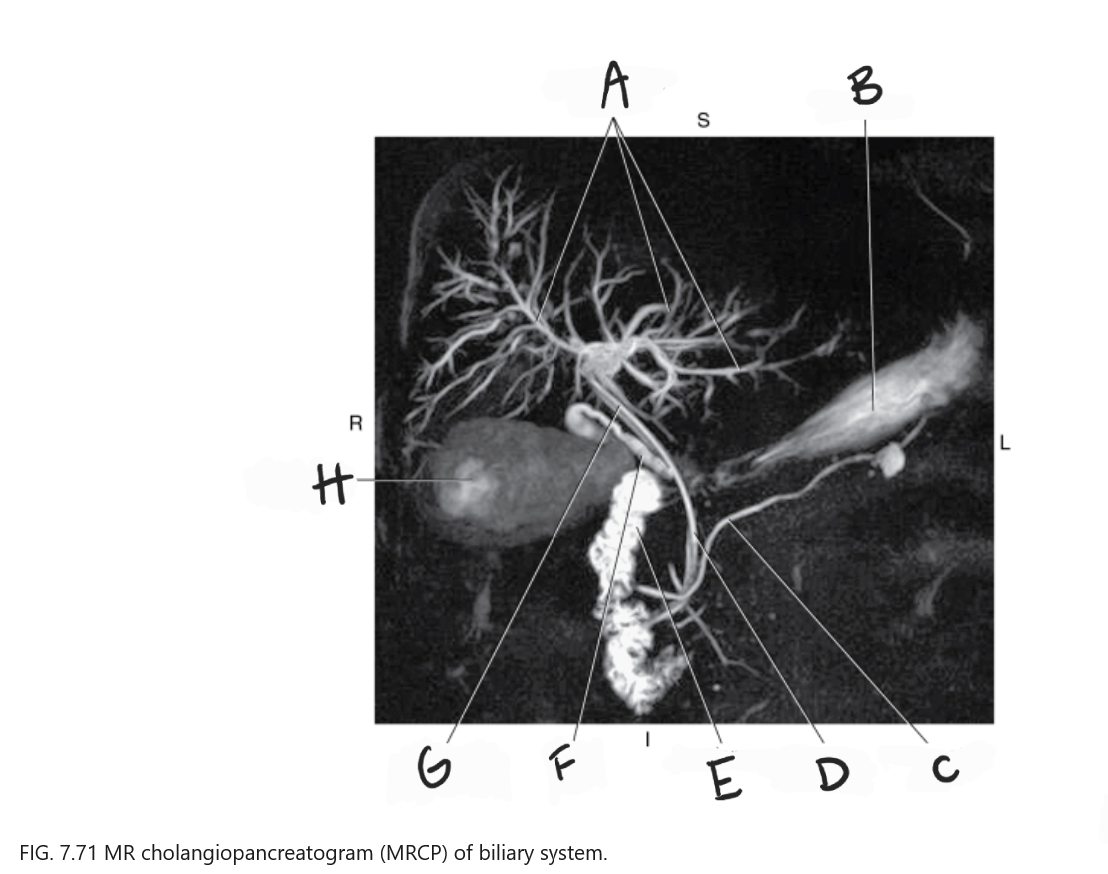
What is B
Stomach
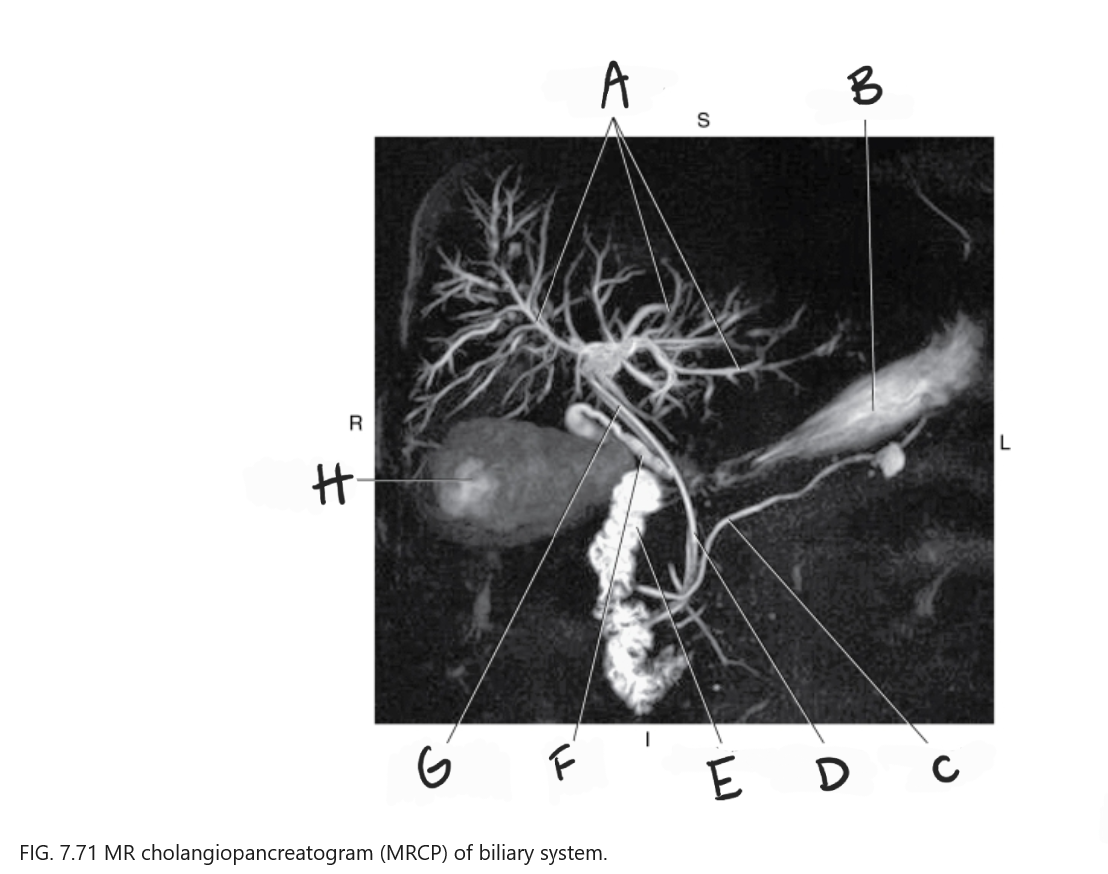
What is C
Pancreatic duct
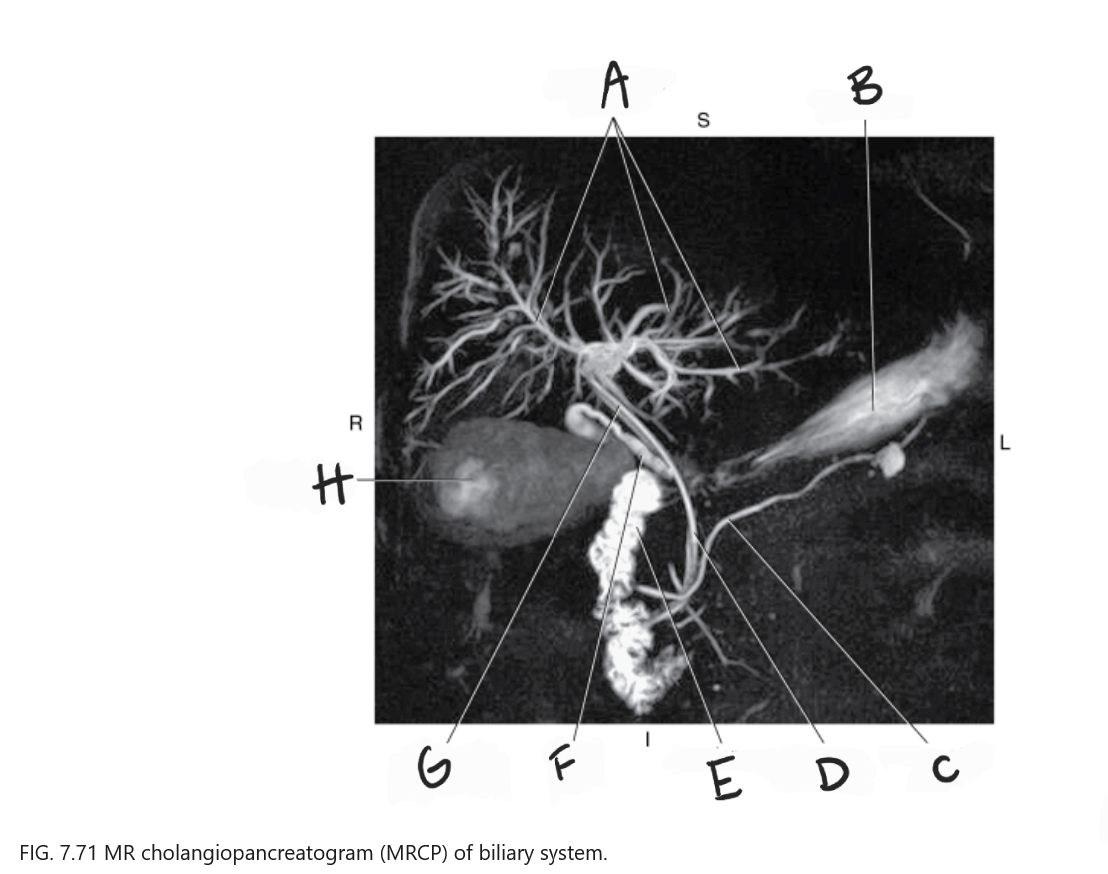
What is D
Common bile duct
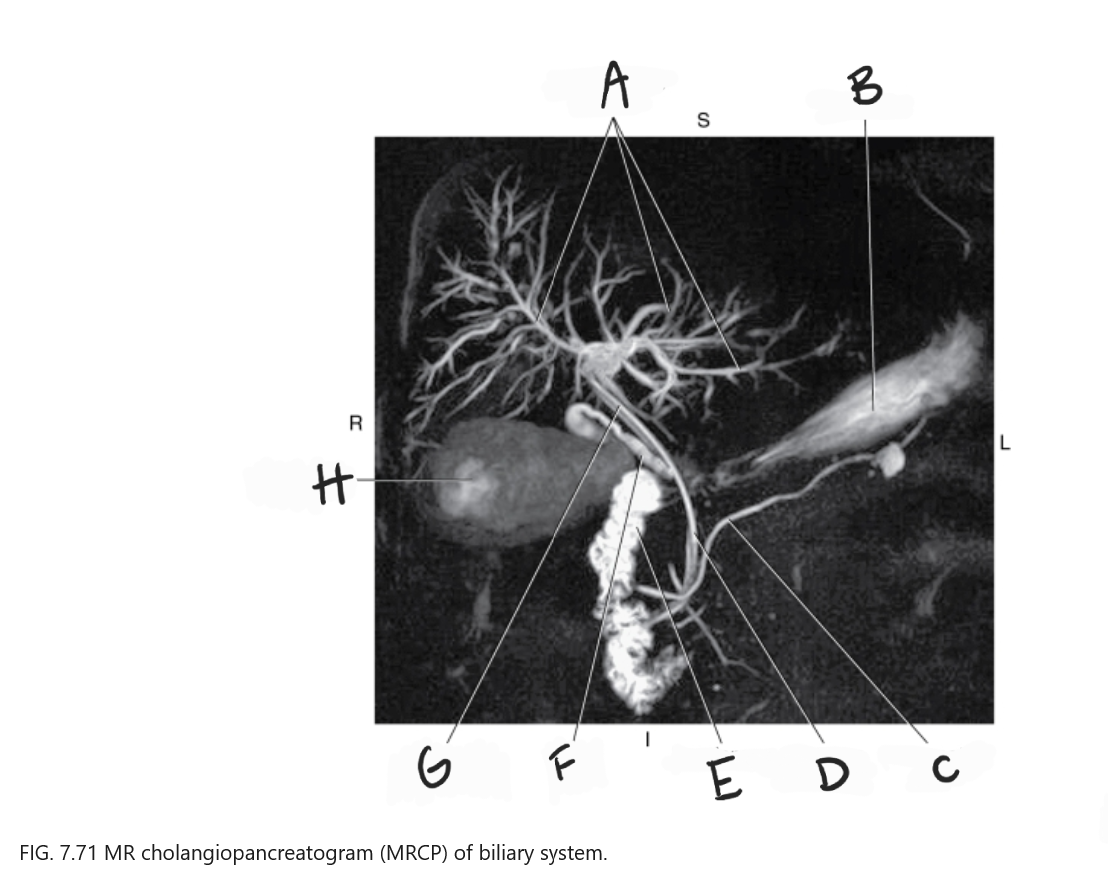
What is E
Duodenum
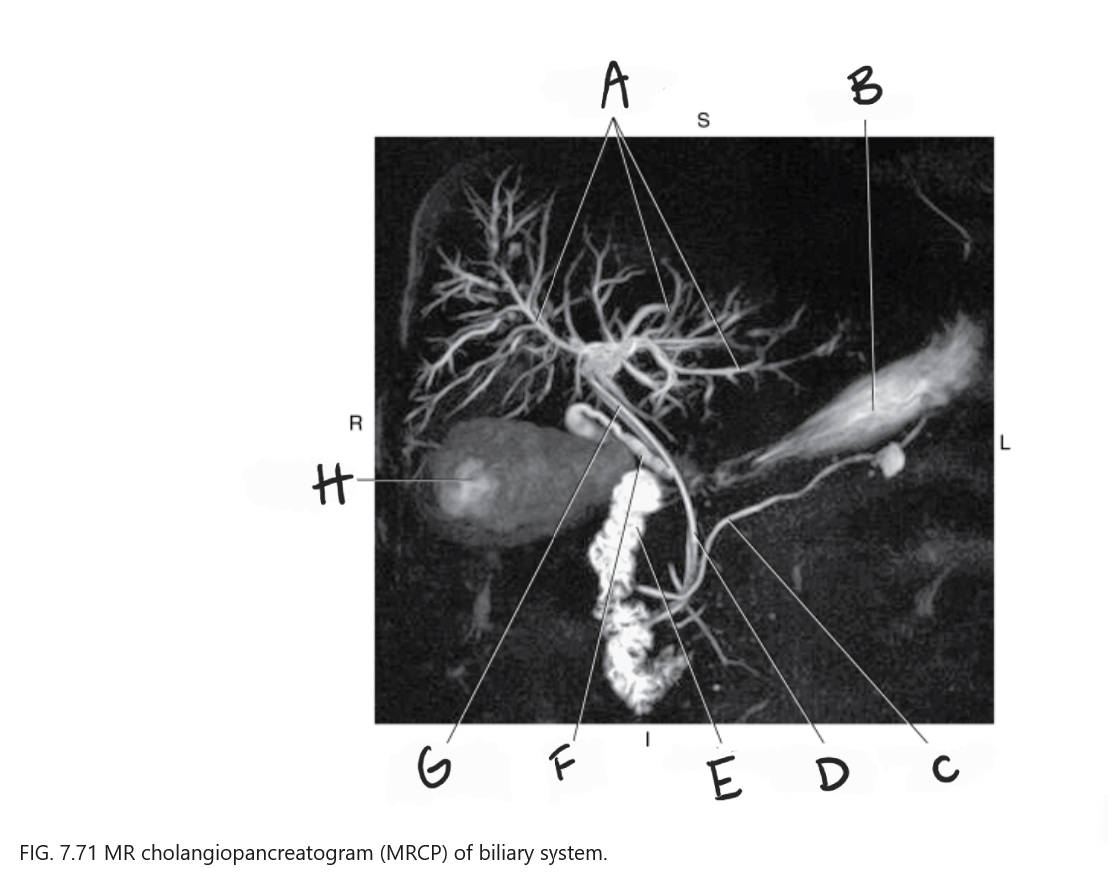
What is F
Cystic duct
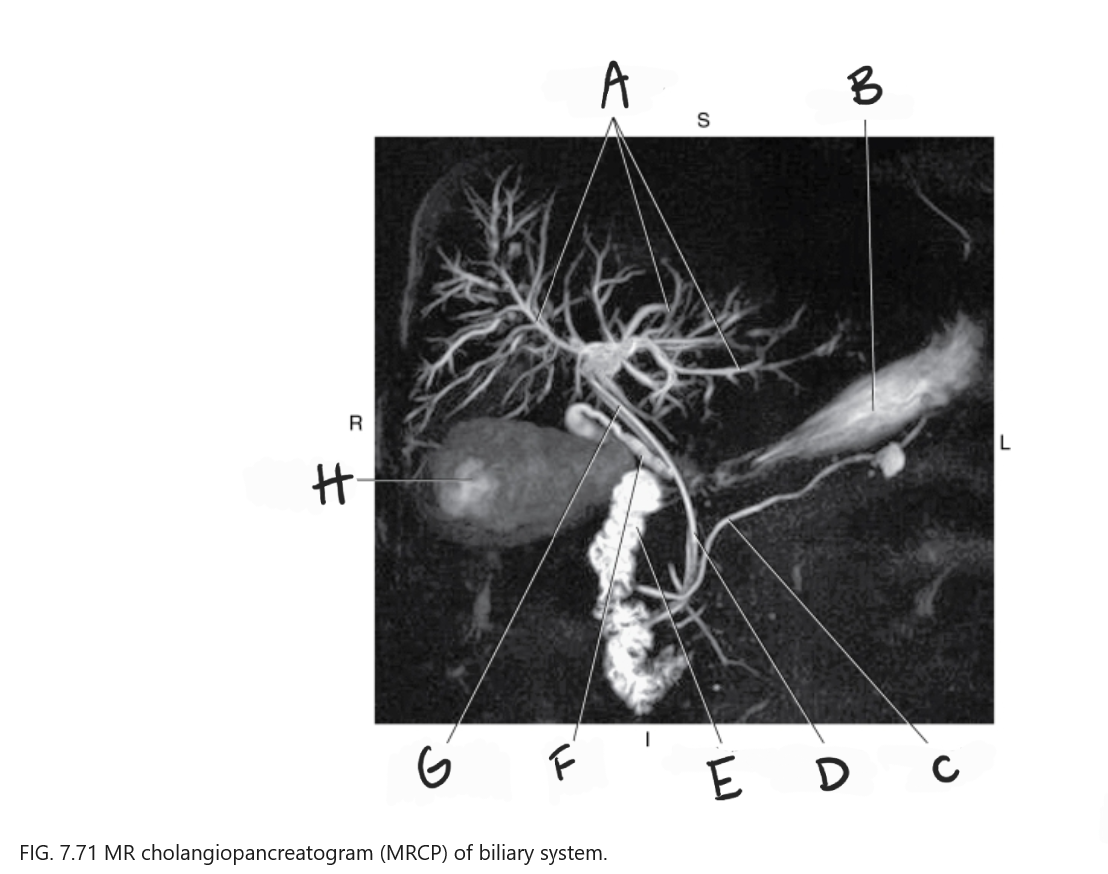
What is G
Common hepatic duct
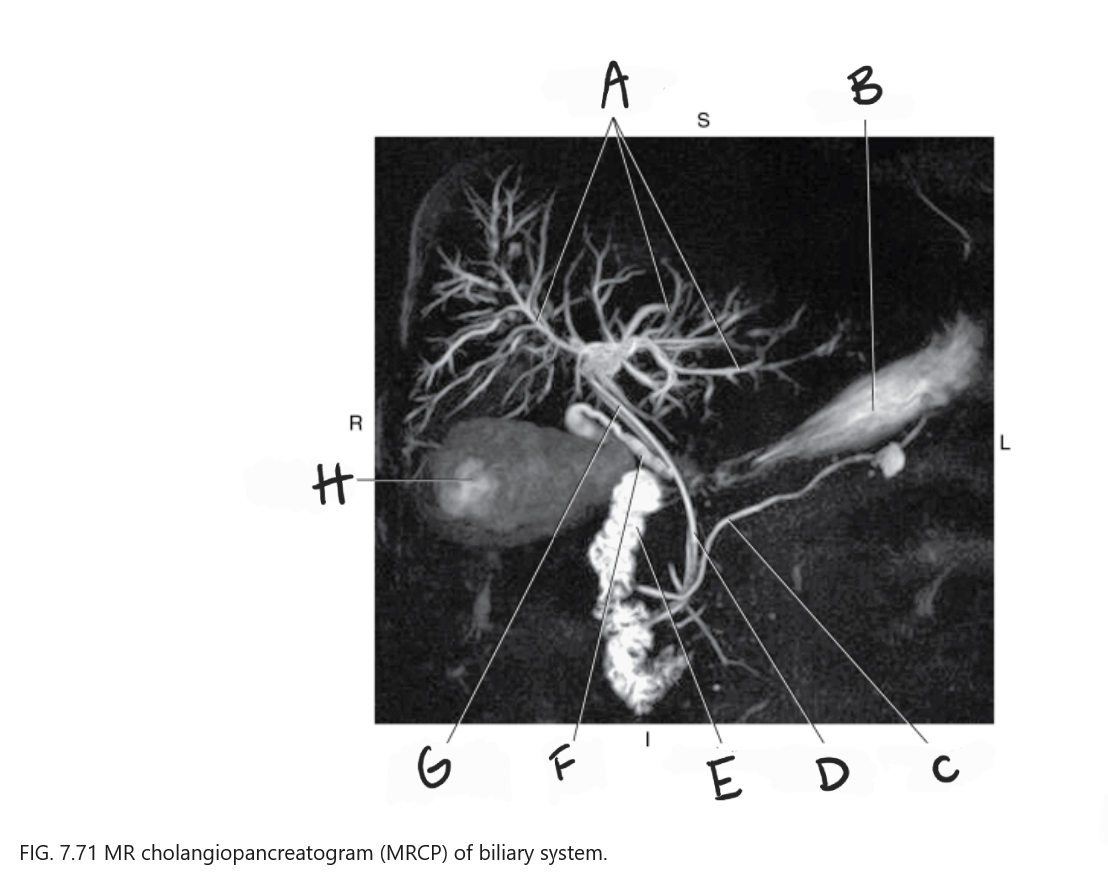
What is H
Gallbladder
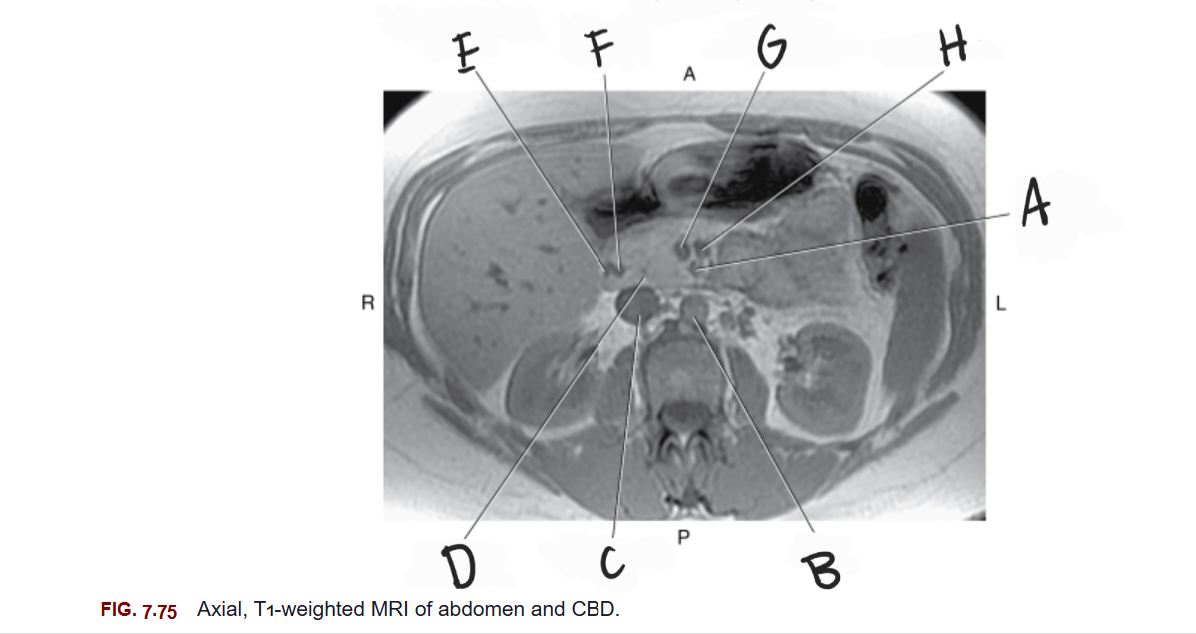
What is A
Superior mesenteric artery
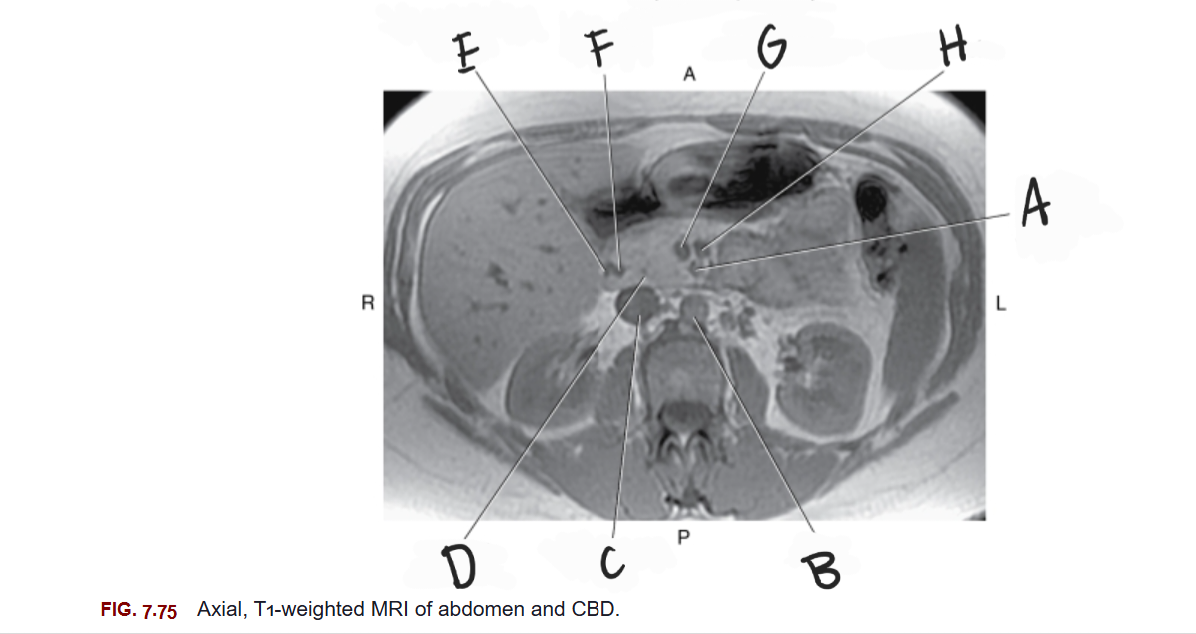
What is B
Aorta
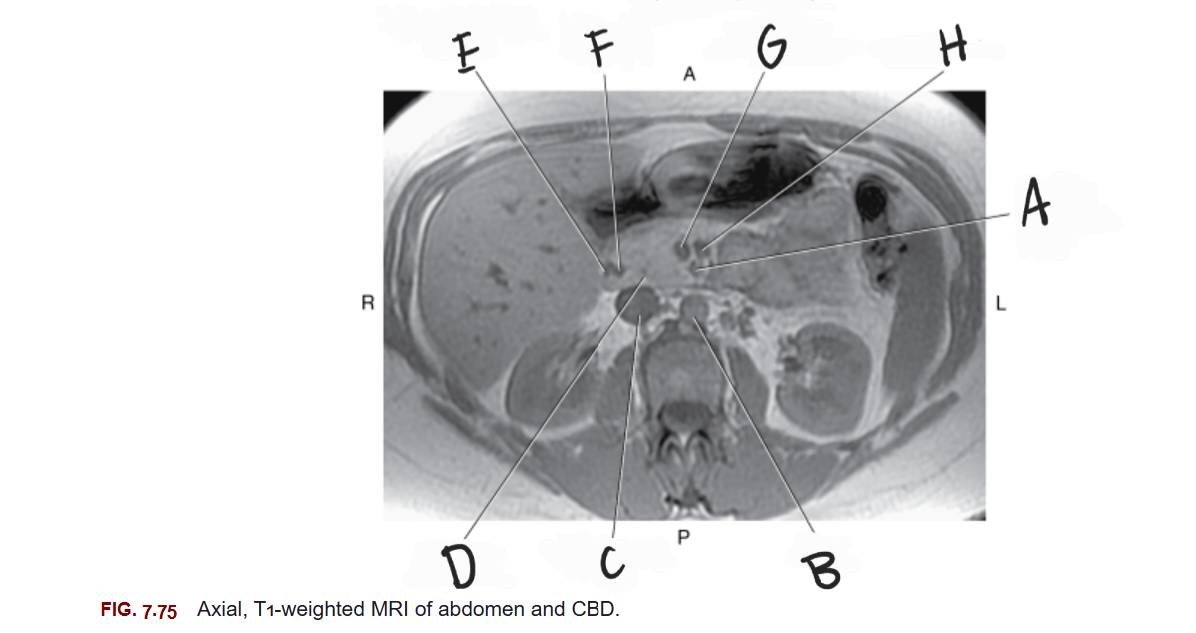
What is C
Inferior vena cava
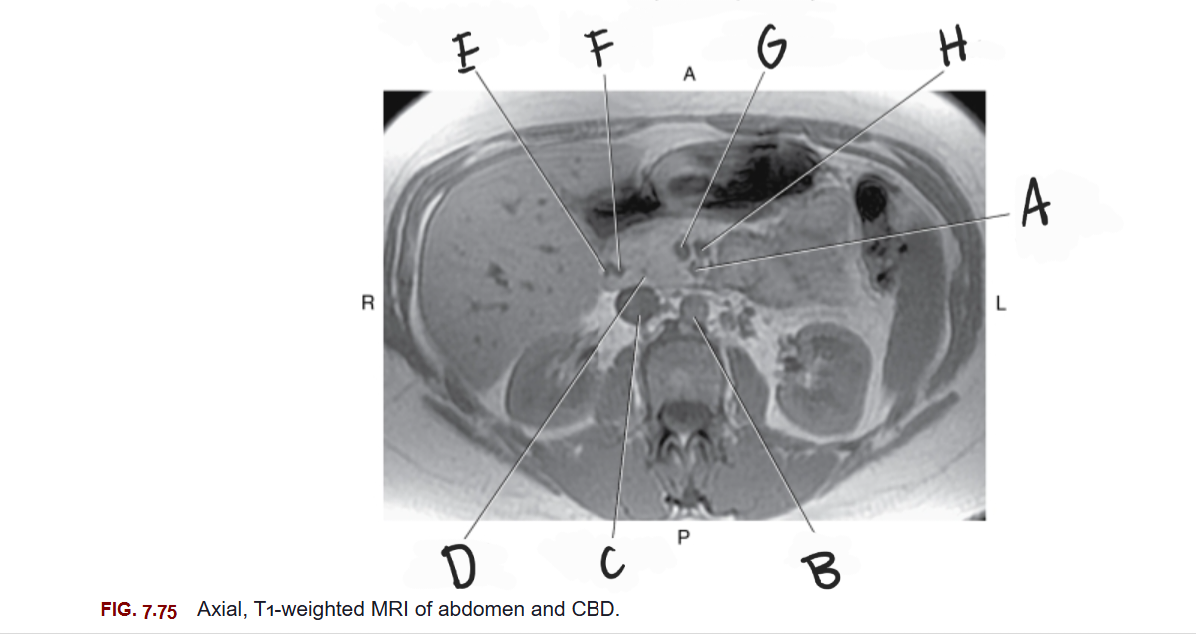
What is D
Head of pancreas
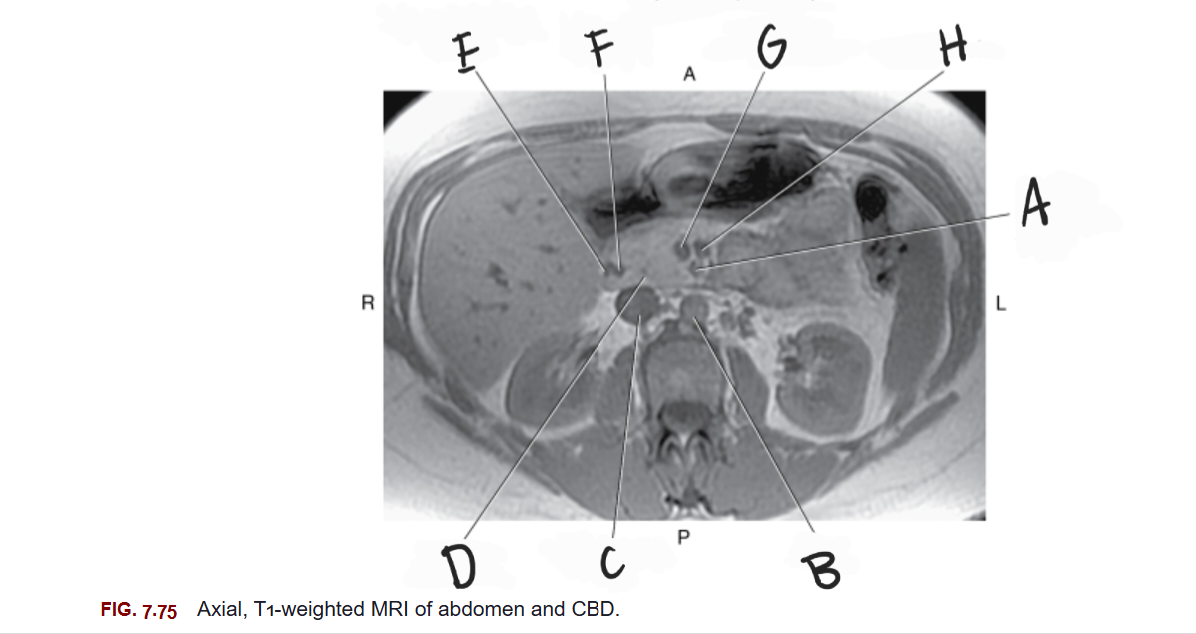
What is E
Gastroduodenal artery
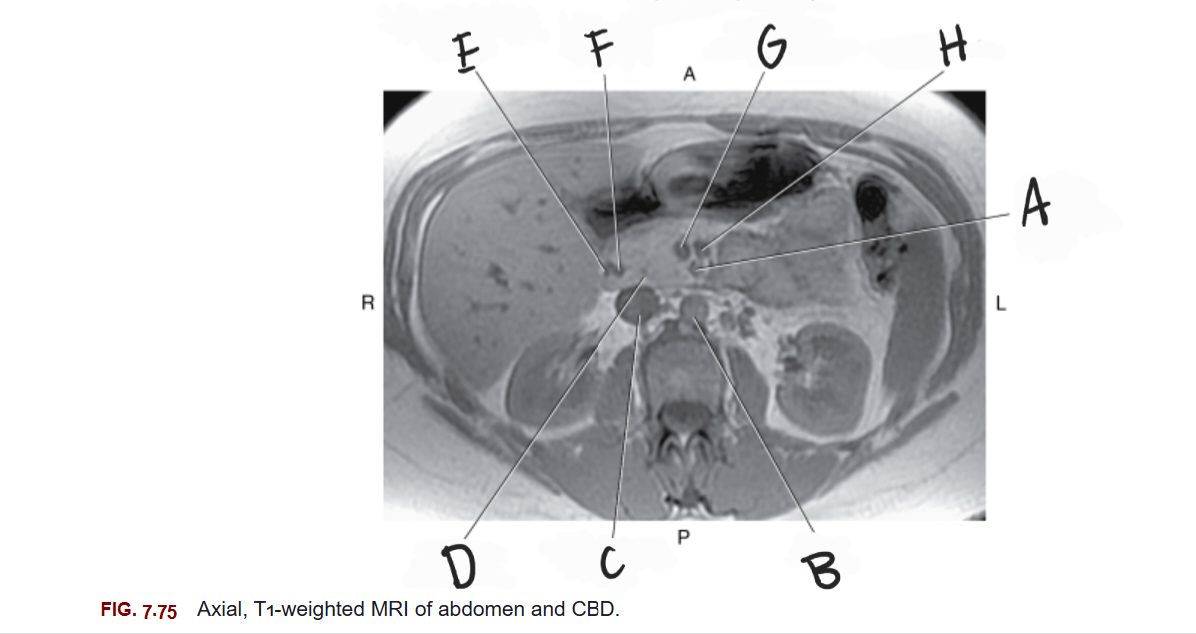
What is F
Common bile duct
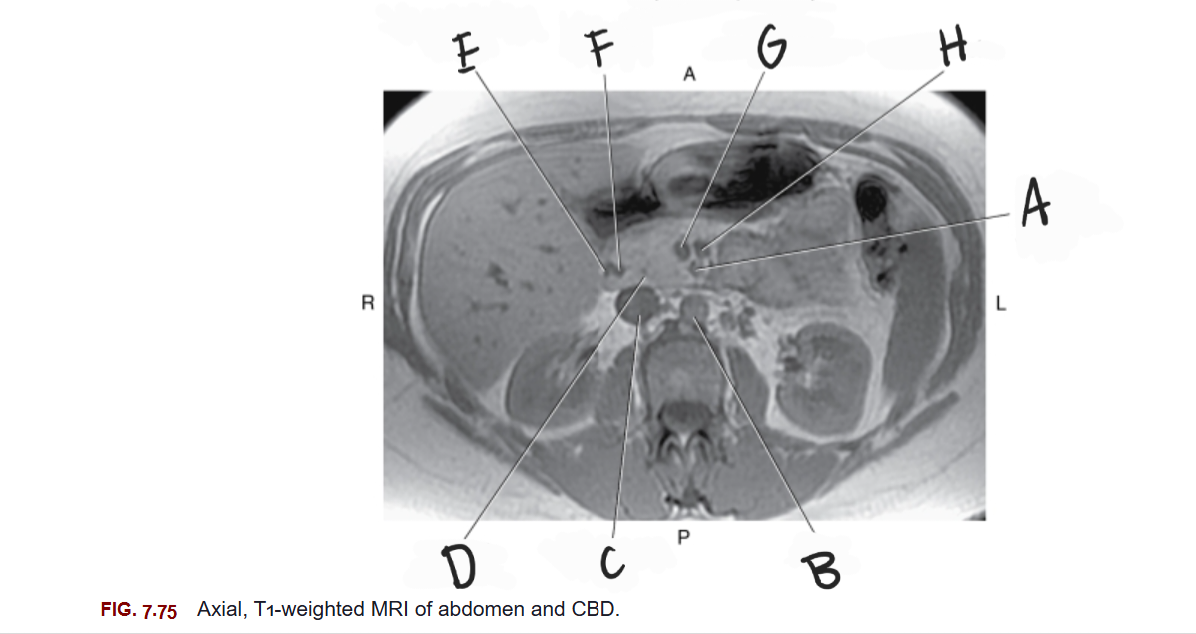
What is G
Superior mesenteric vein
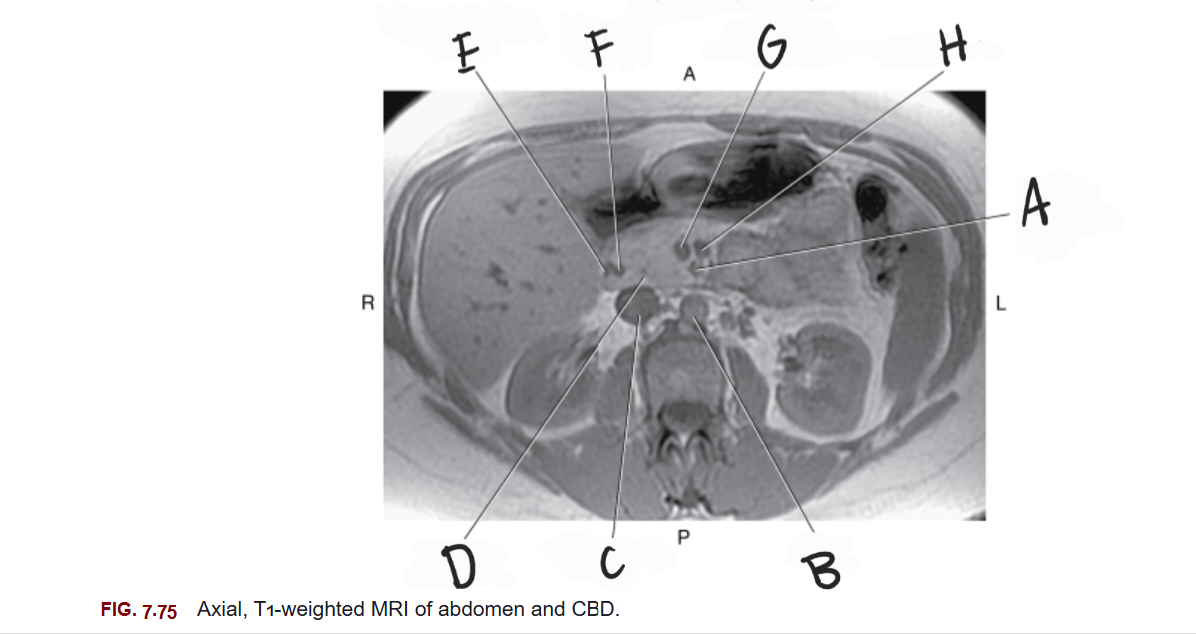
What is H
Splenic vein
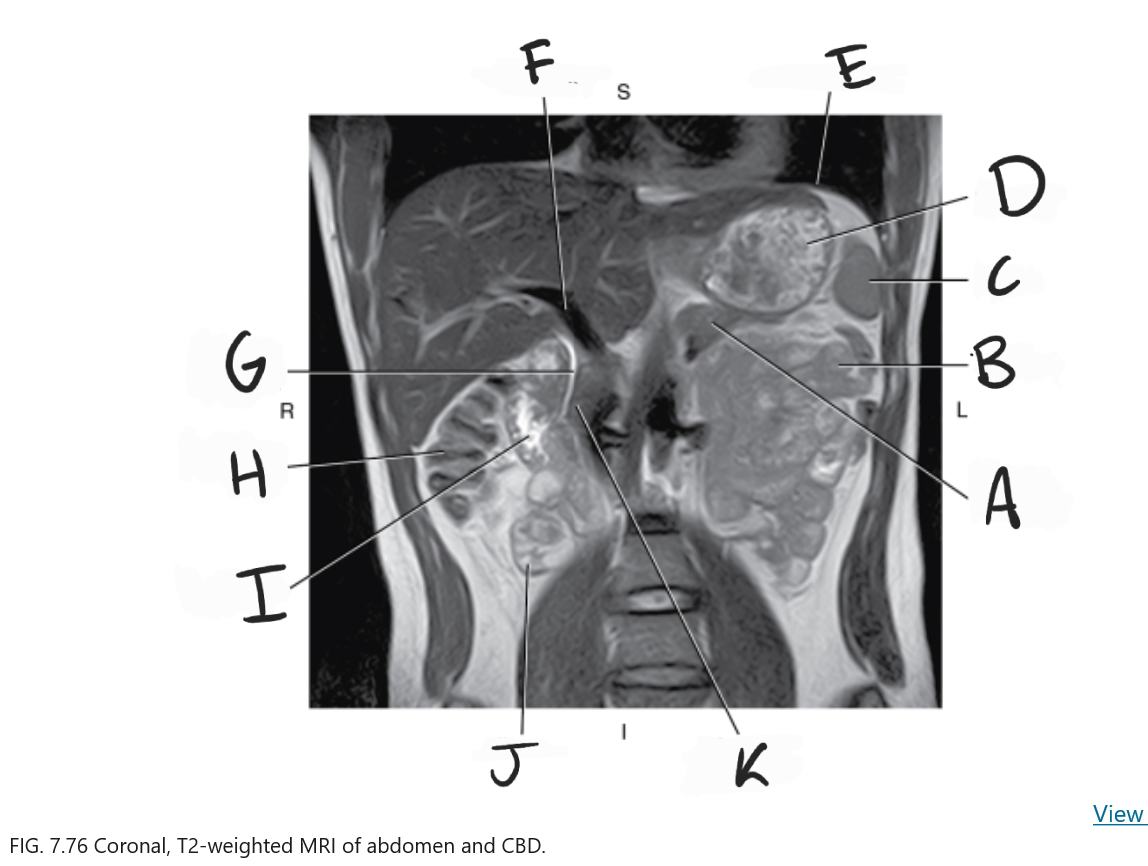
What is A
Body of pancreas
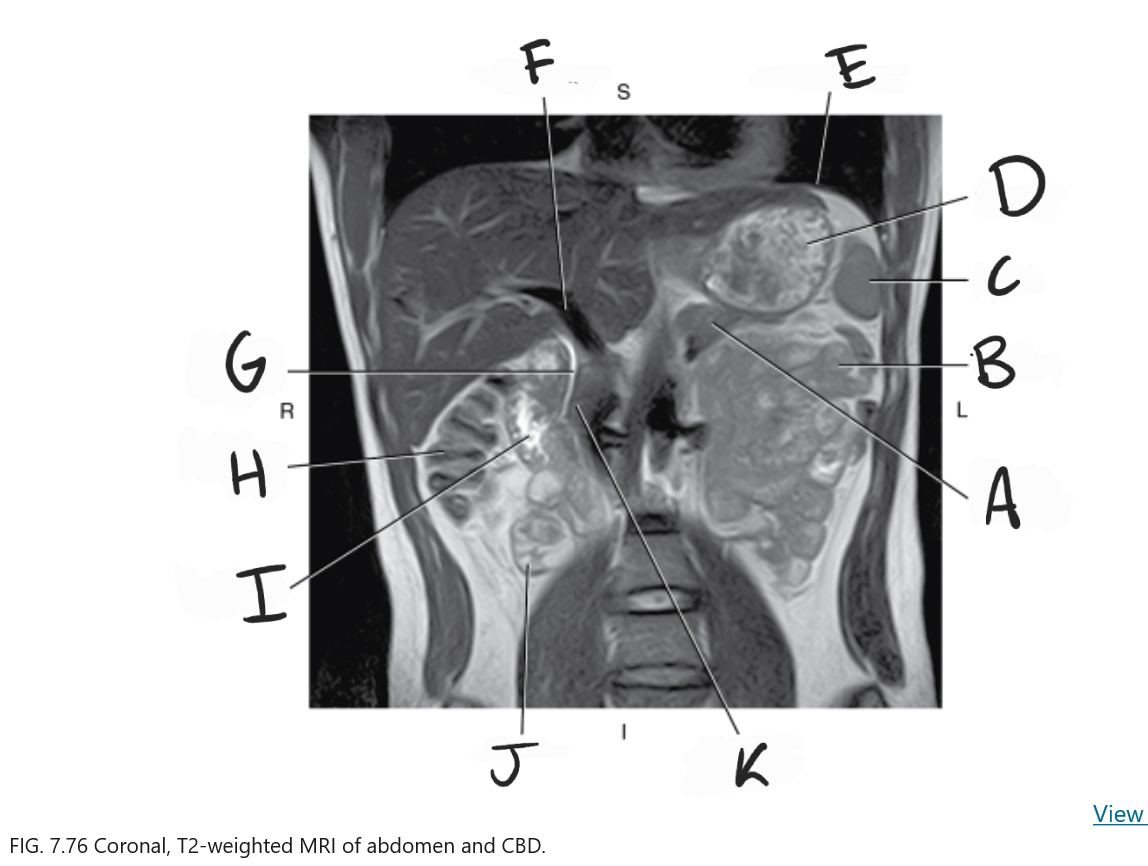
What is B
Jejunum
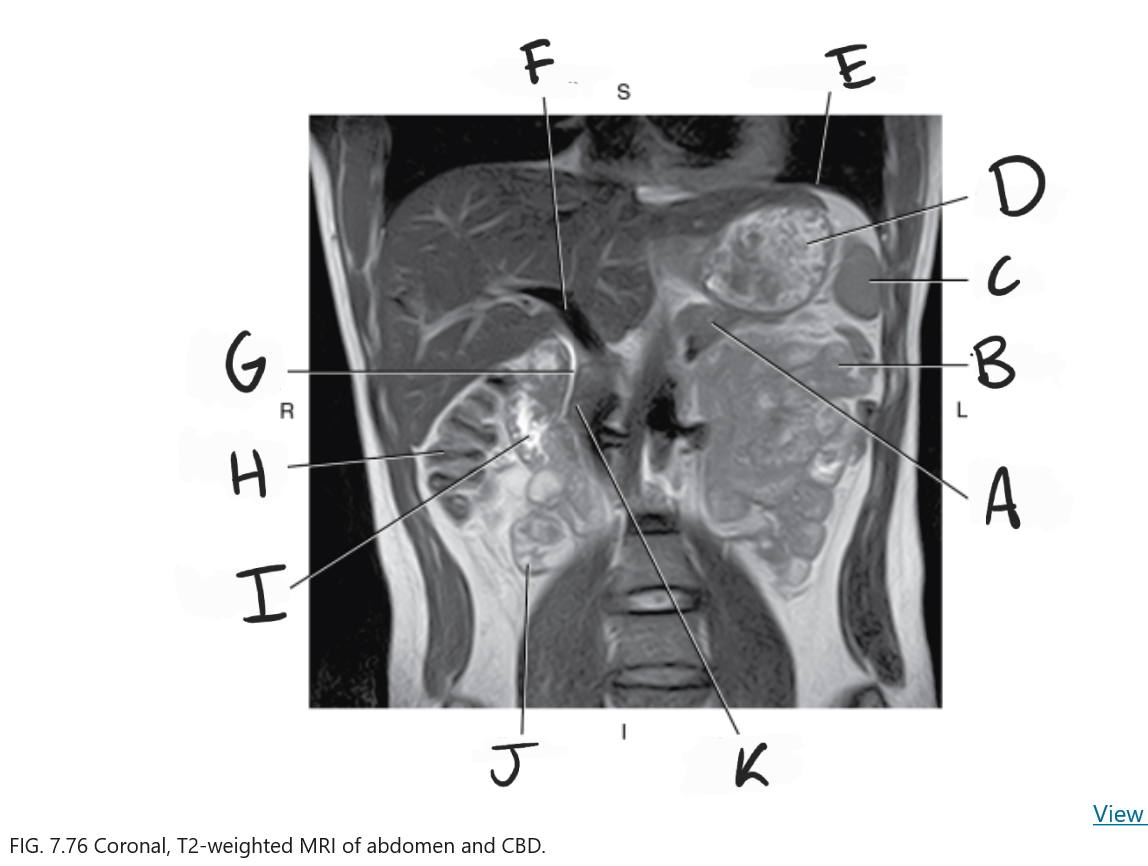
What is C
Spleen
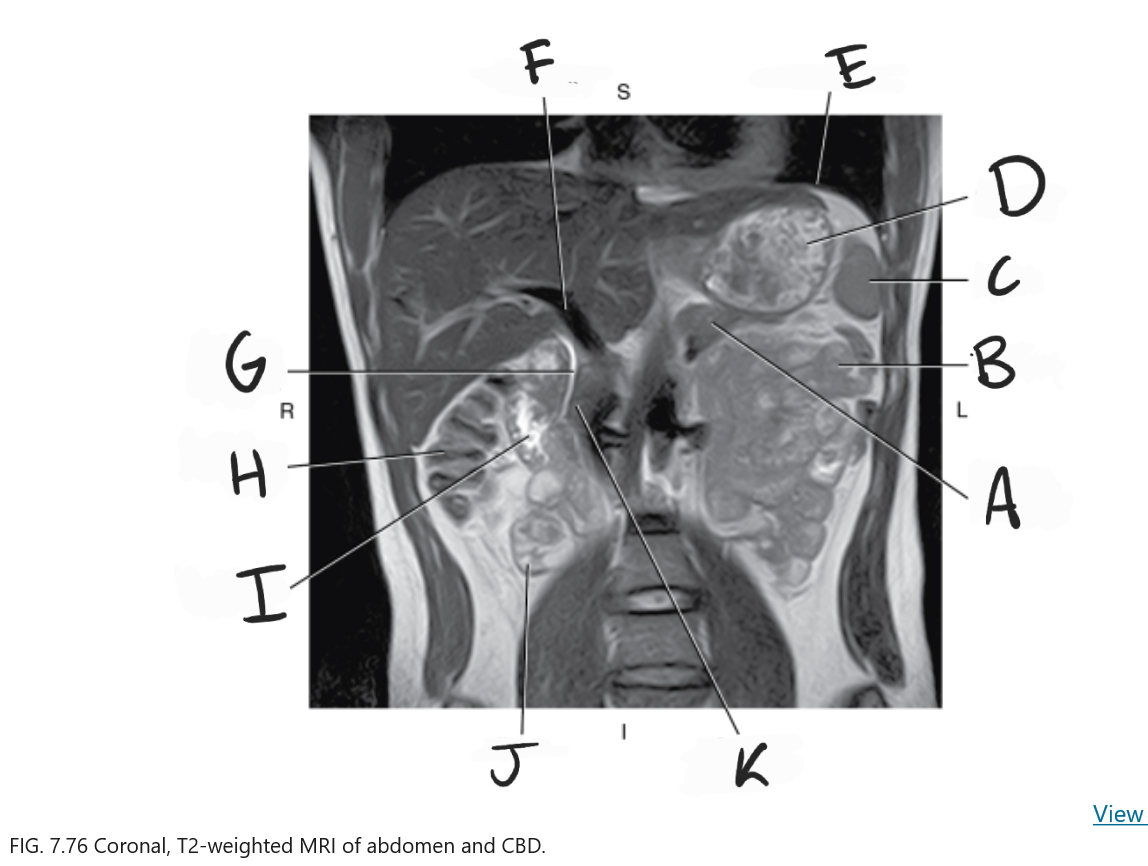
What is D
Stomach
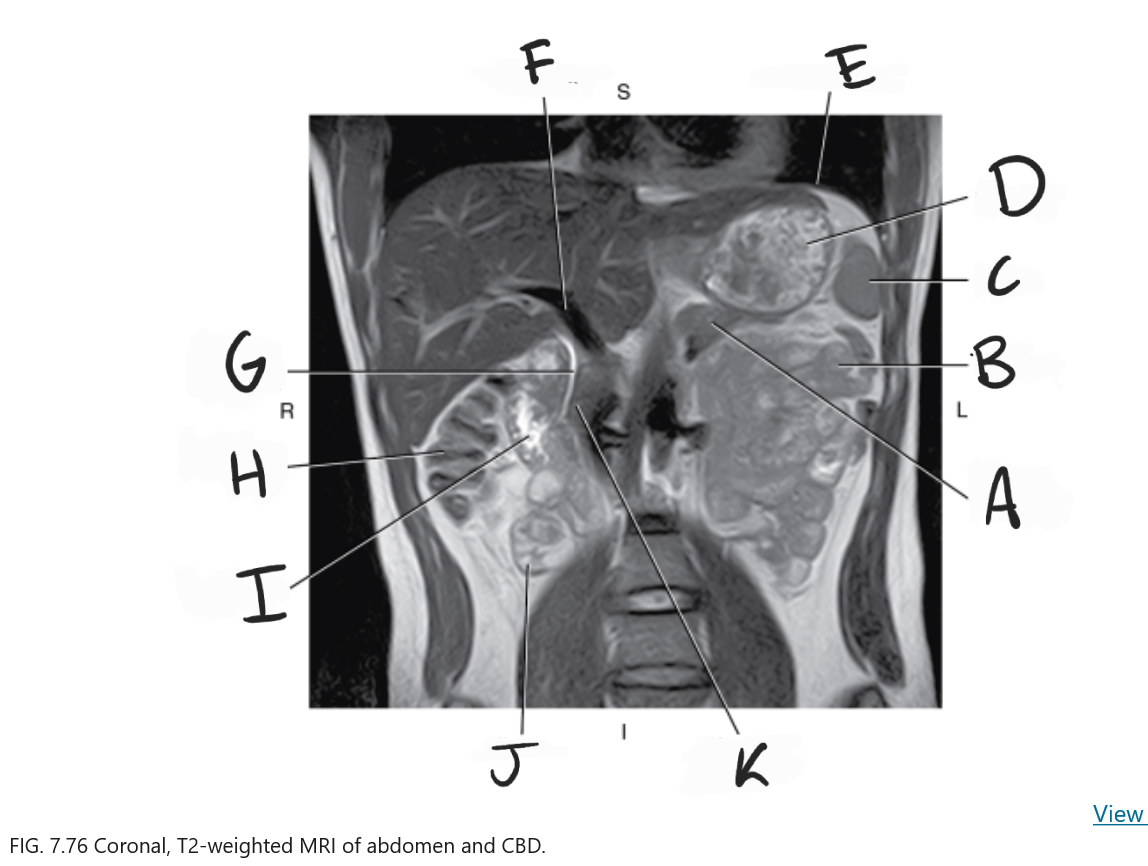
What is E
Diaphragm
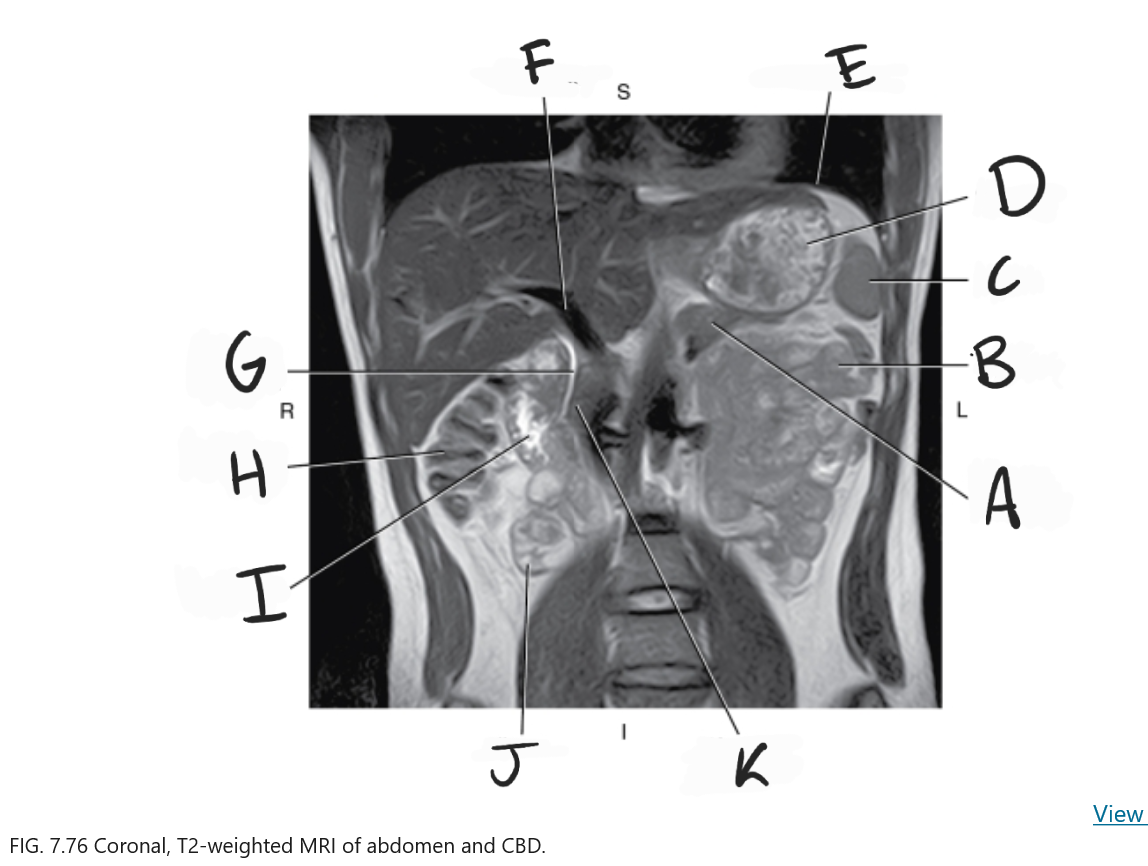
What is F
Portal vein
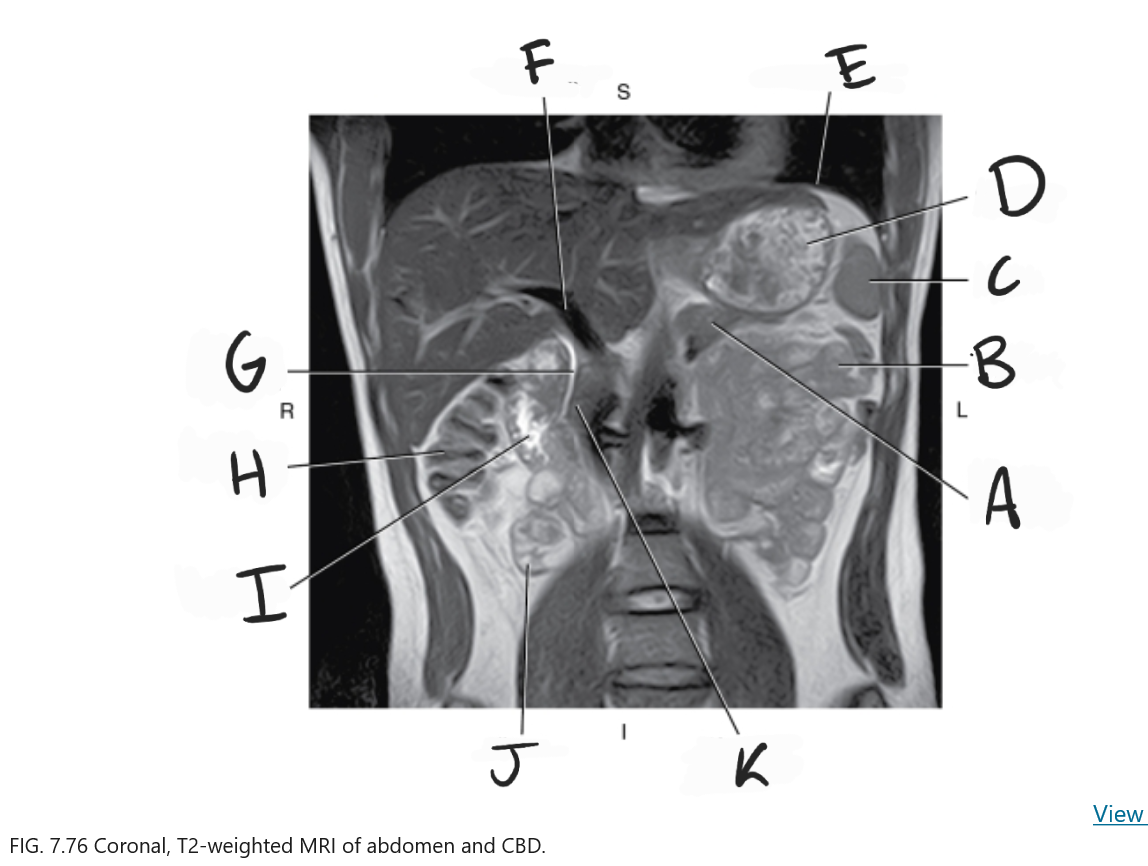
What is G
Common bile duct
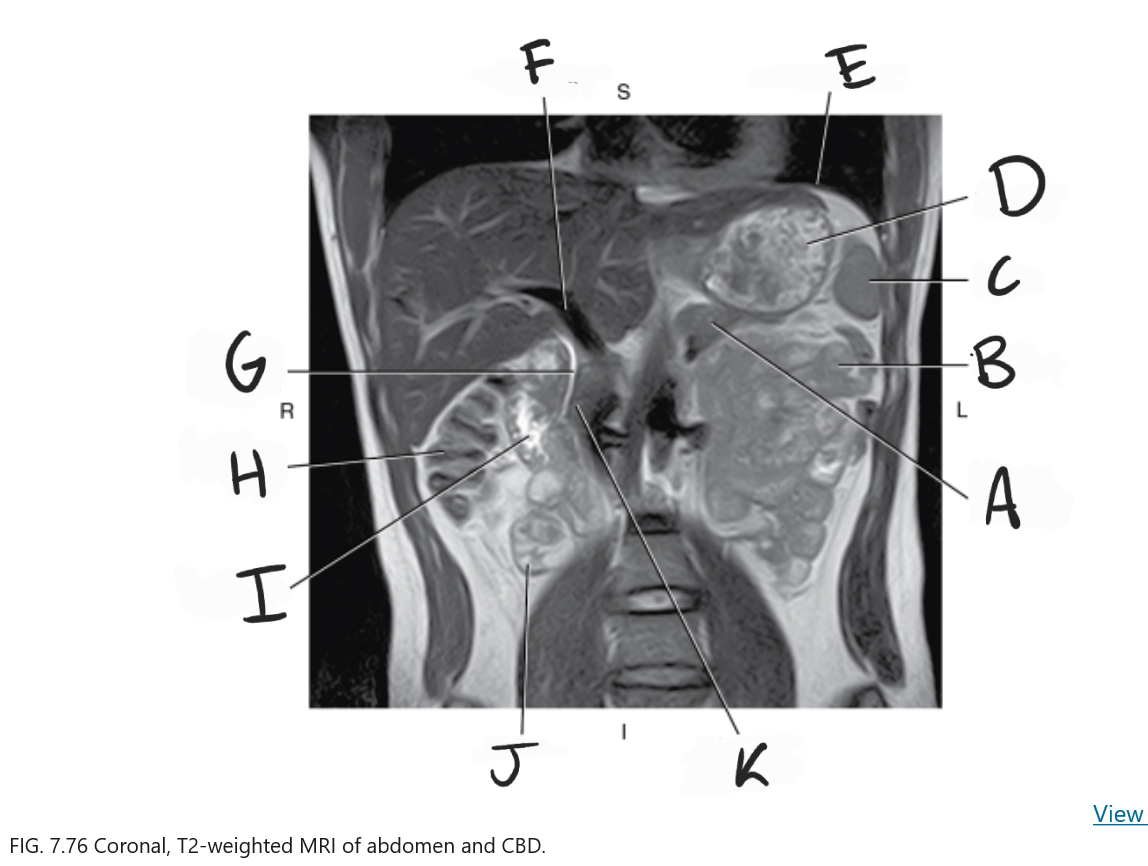
What is H
Ascending colon
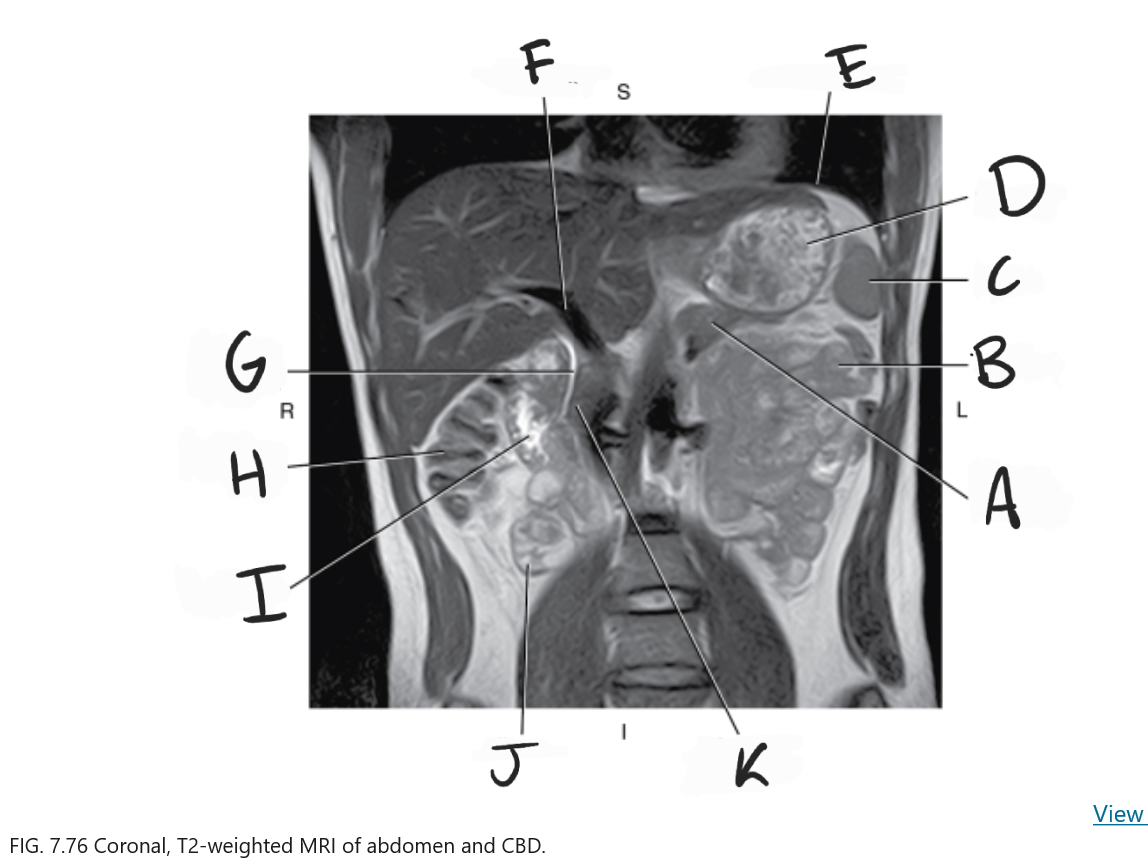
What is I
Duodenum
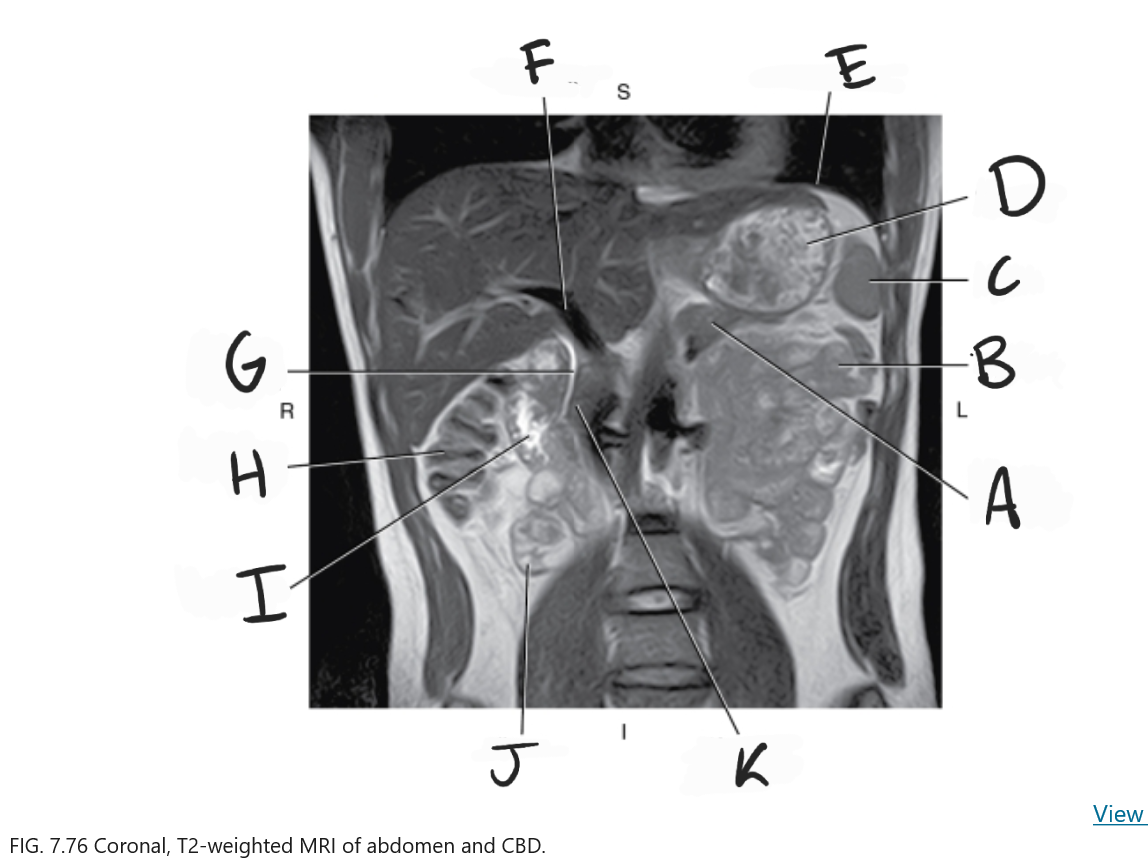
What is J
Ileum
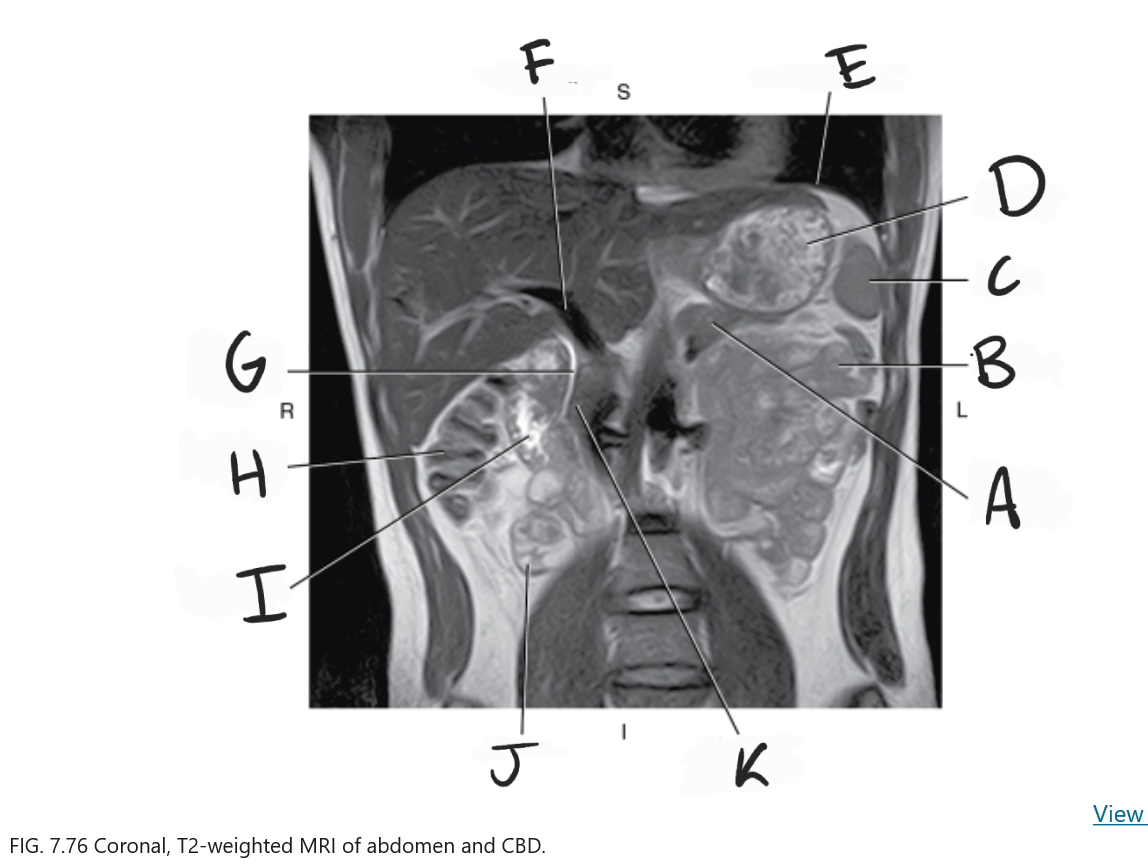
What is K
Head of pancreas
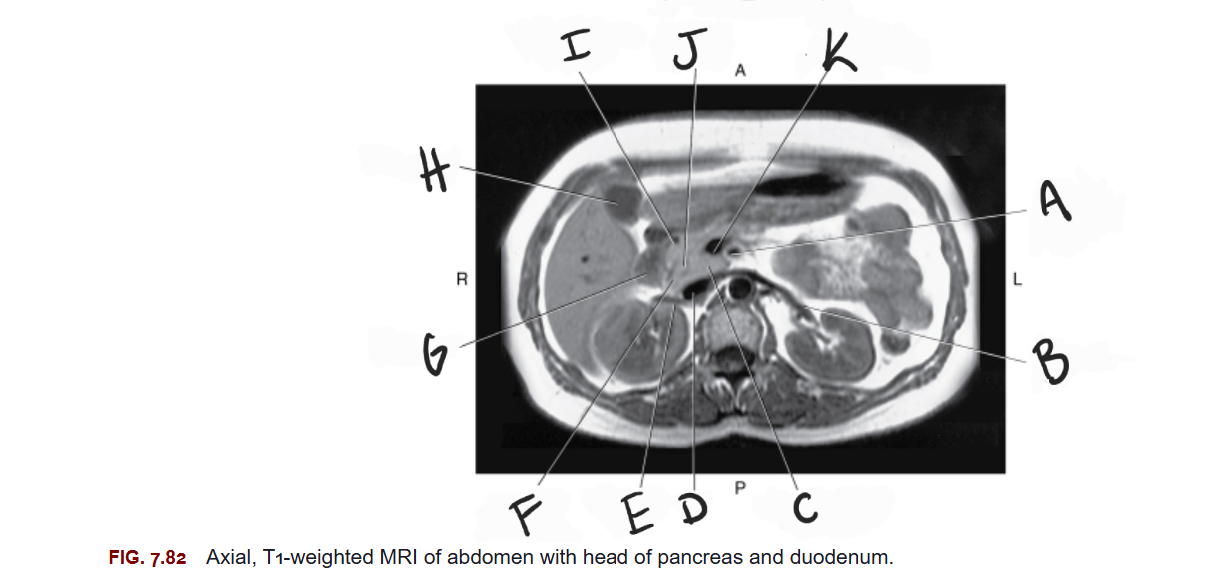
What is A
Superior mesenteric artery
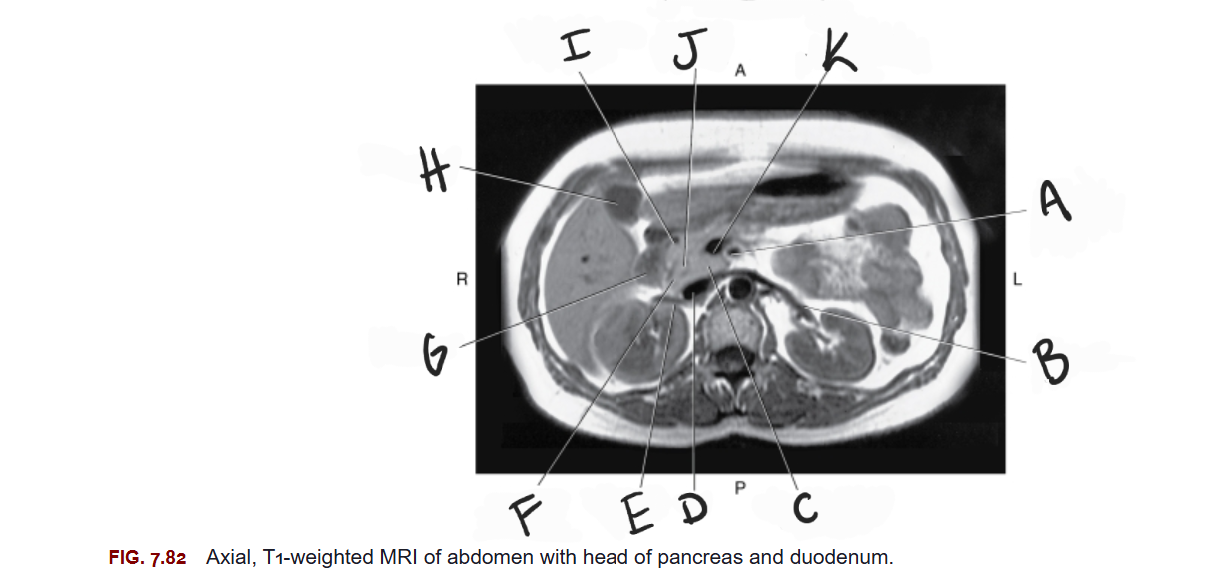
What is B
Left renal vein
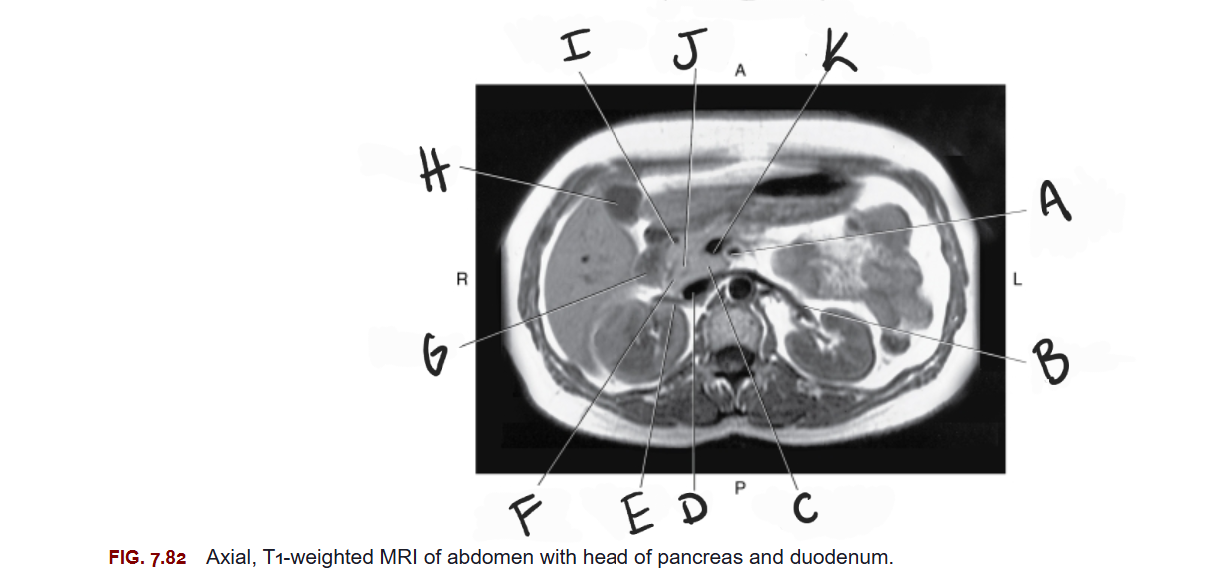
What is C
Uncinate process of pancreas
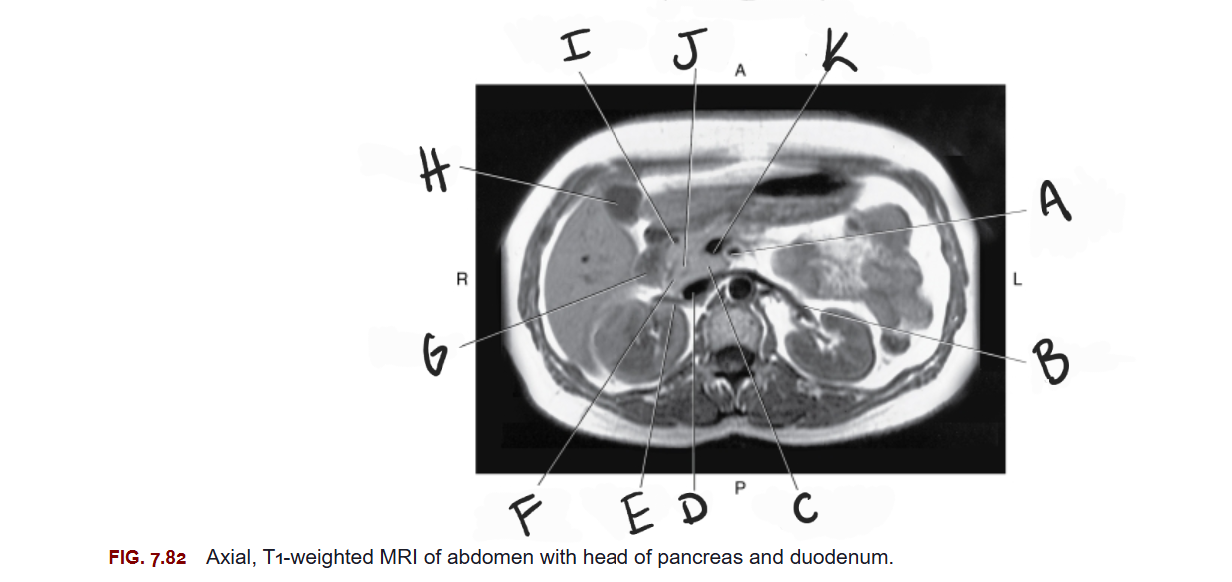
What is D
IVC
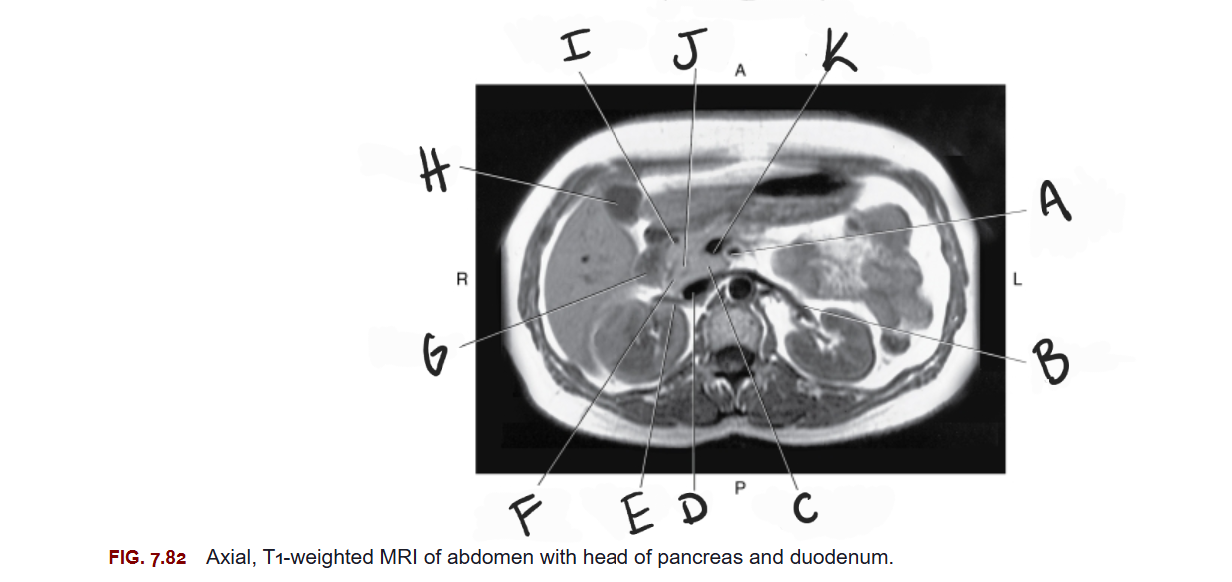
What is E
Right renal vein
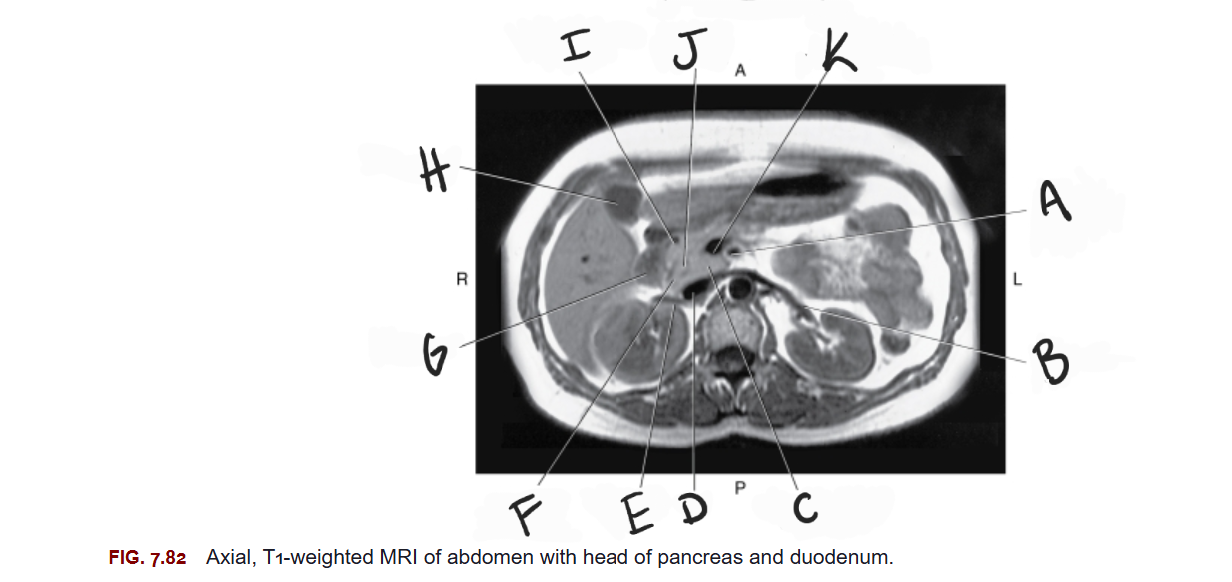
What is F
Head of pancreas
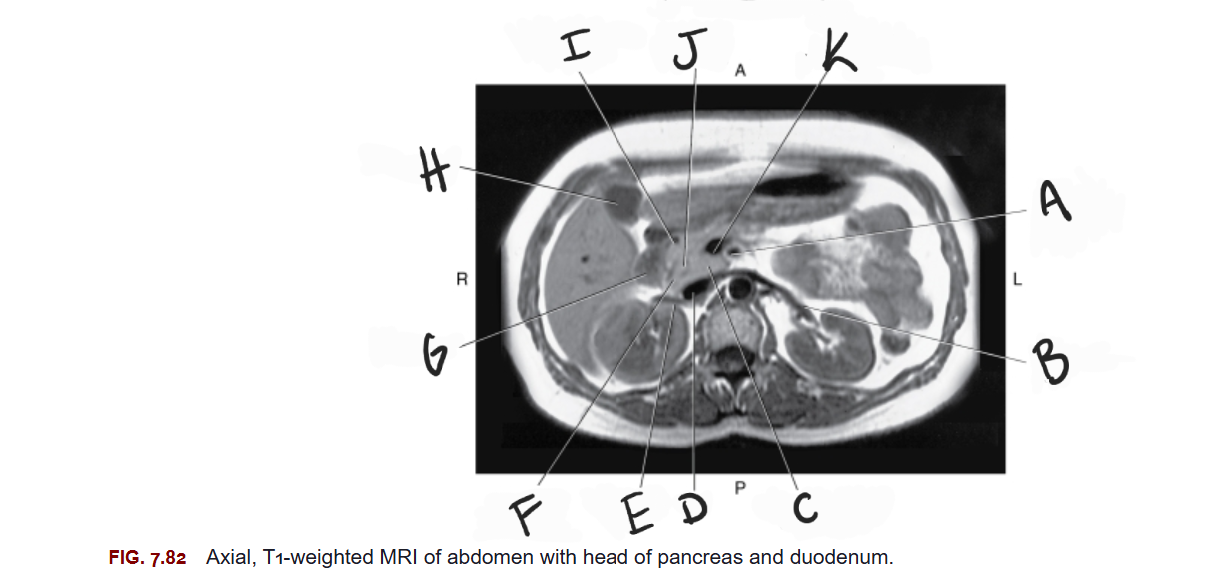
What is G
Duodenum
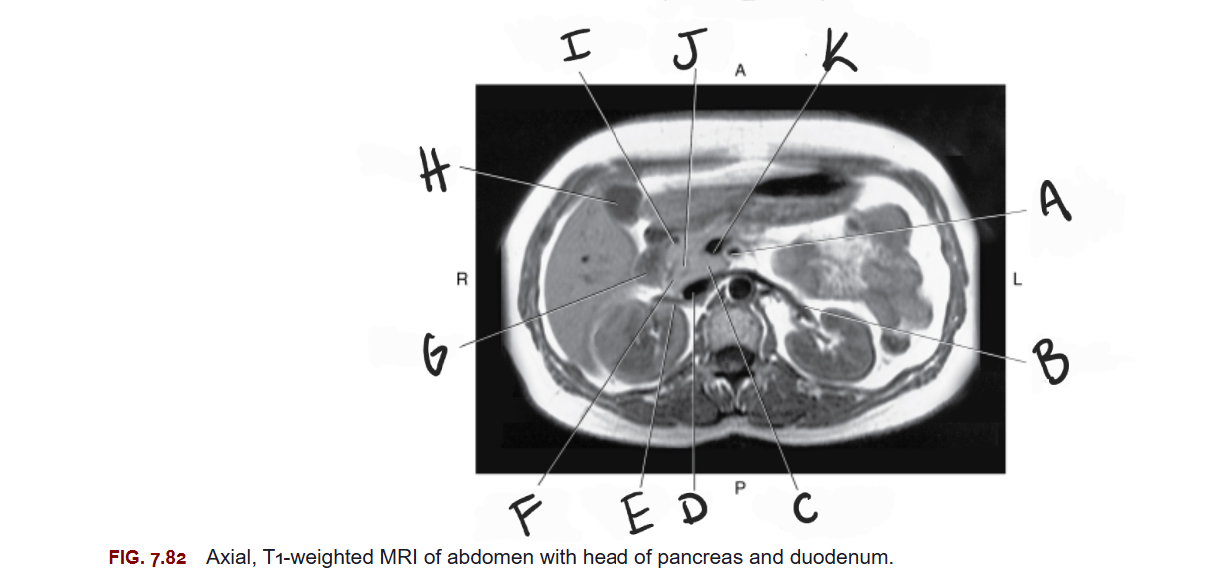
What is H
Gallbladder
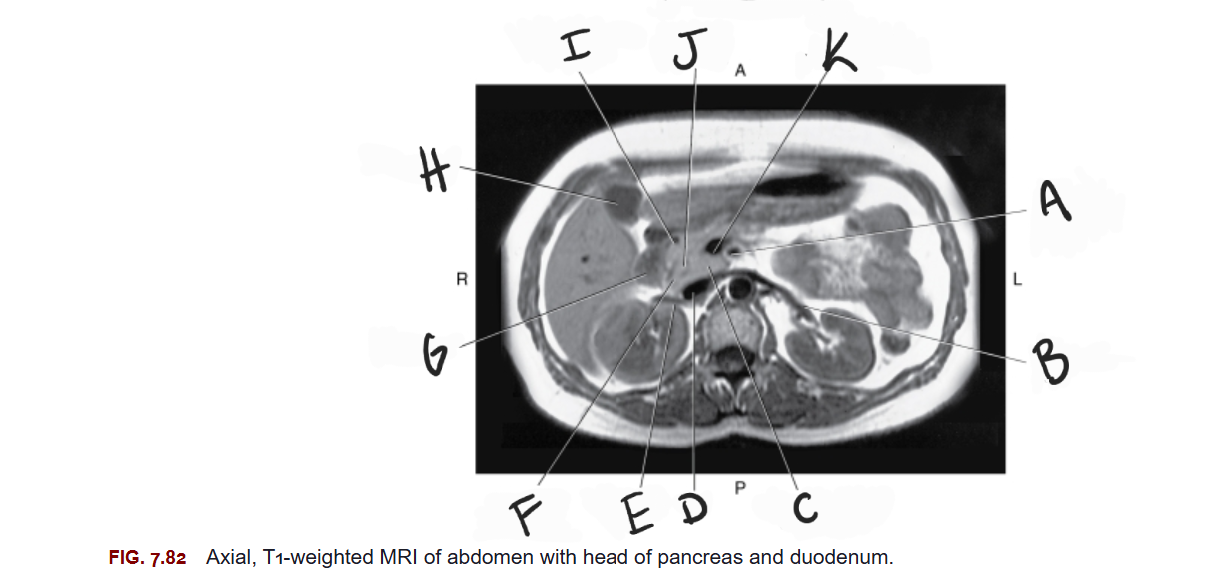
What is I
Gastroduodenal artery
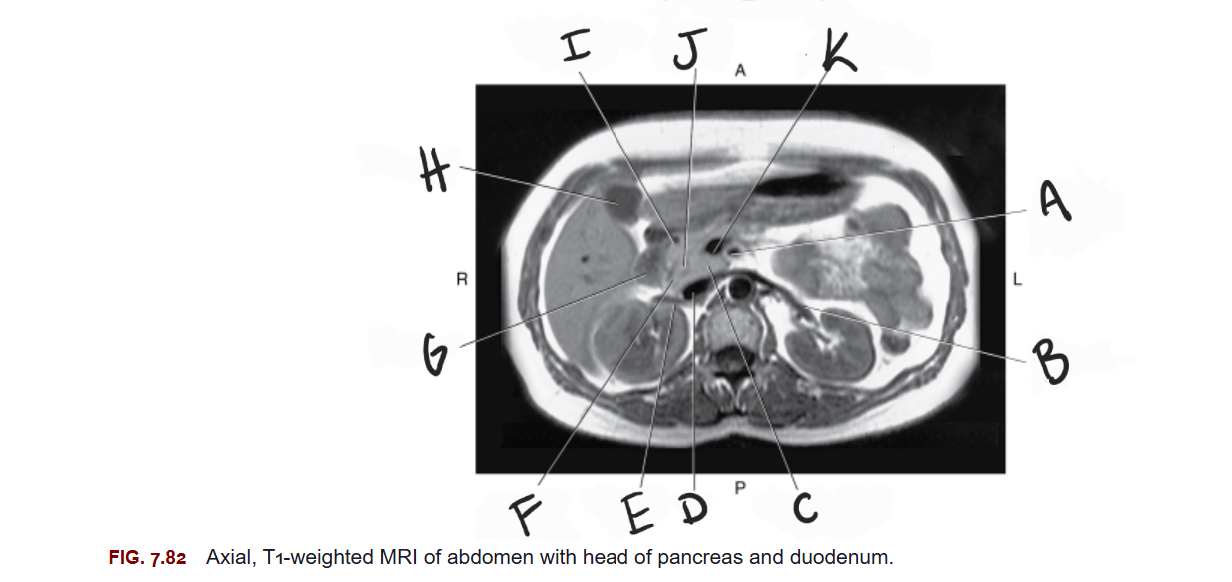
What is J
Common bile duct
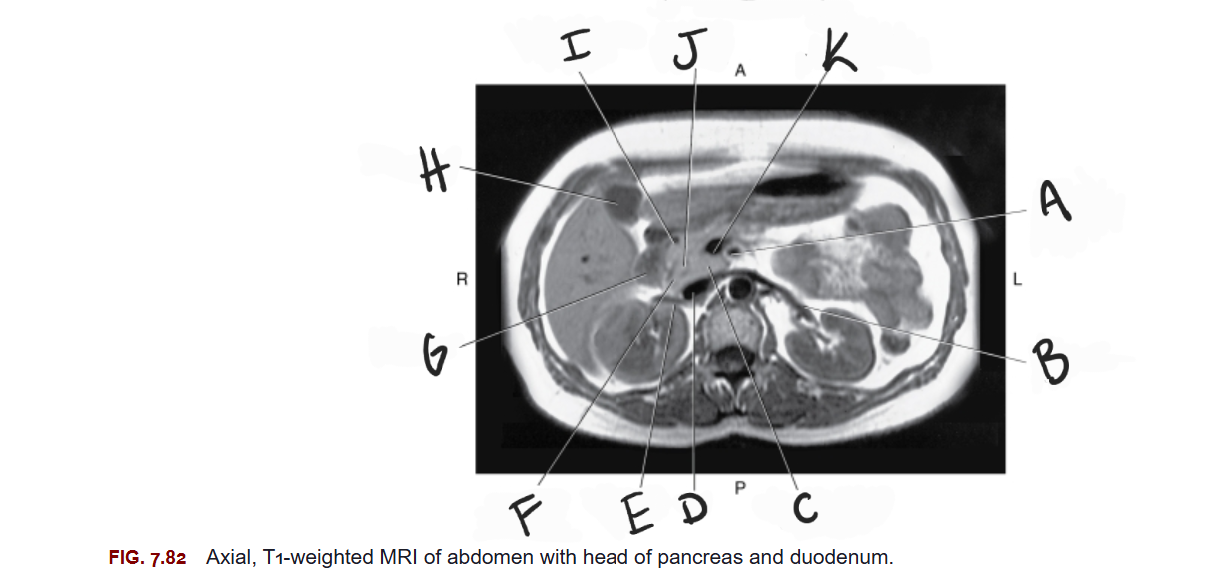
What is K
Superior mesenteric vein
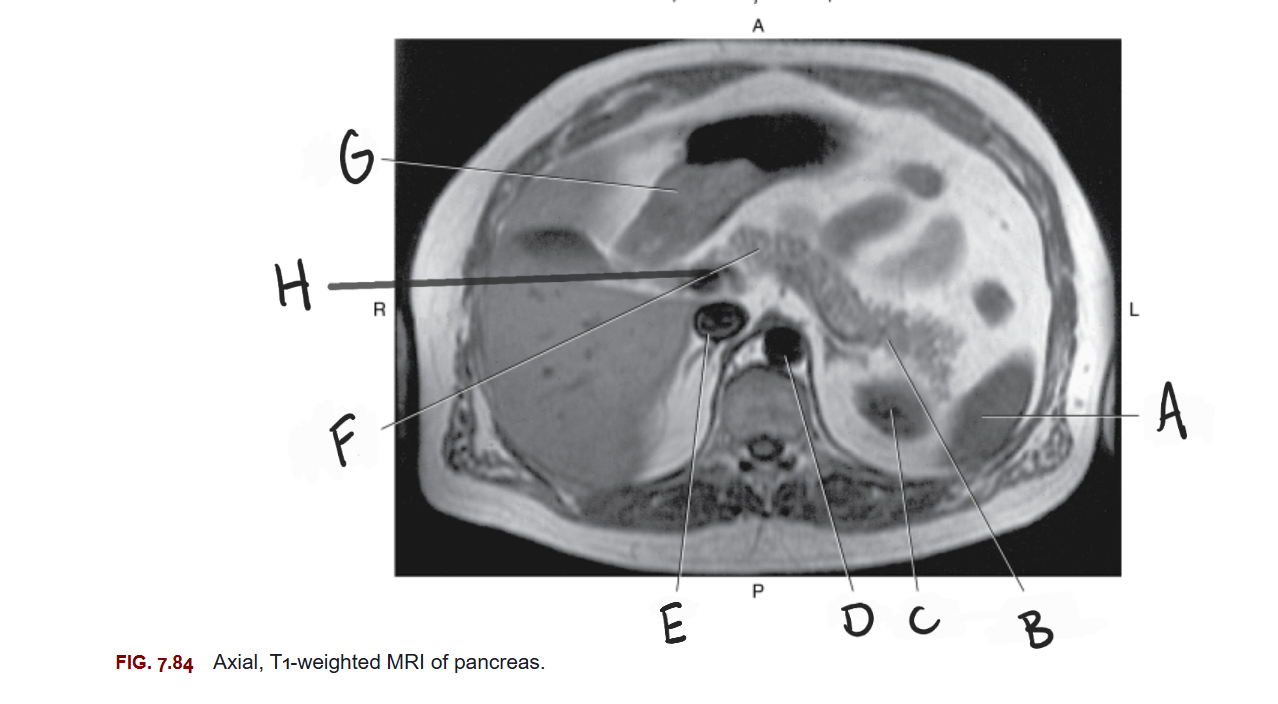
What is A
Spleen
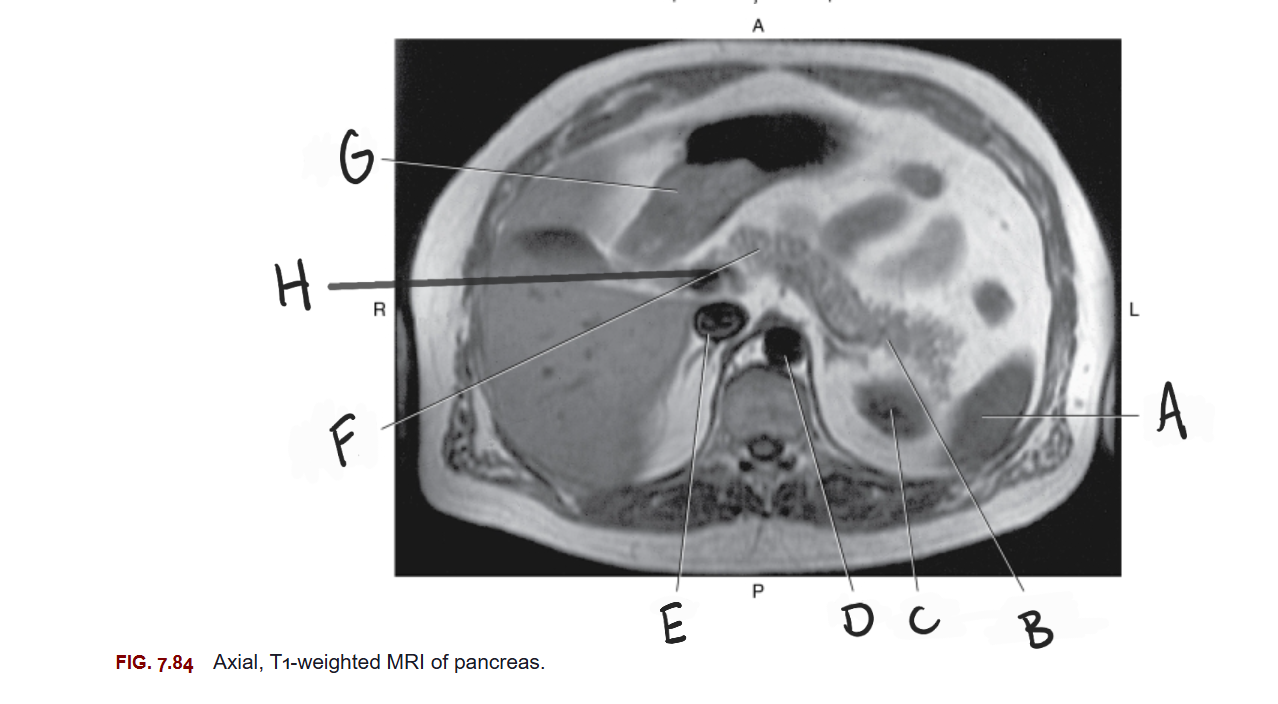
What is B
Tail of pancreas
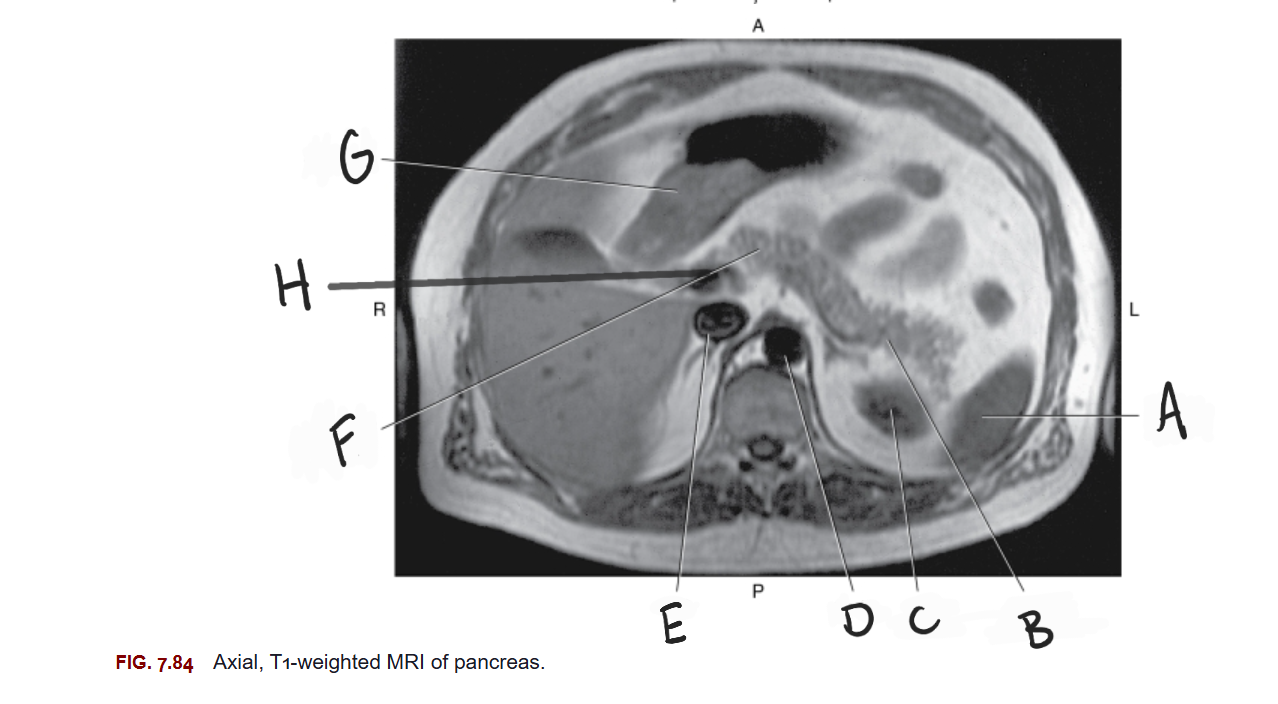
What is C
Left kidney
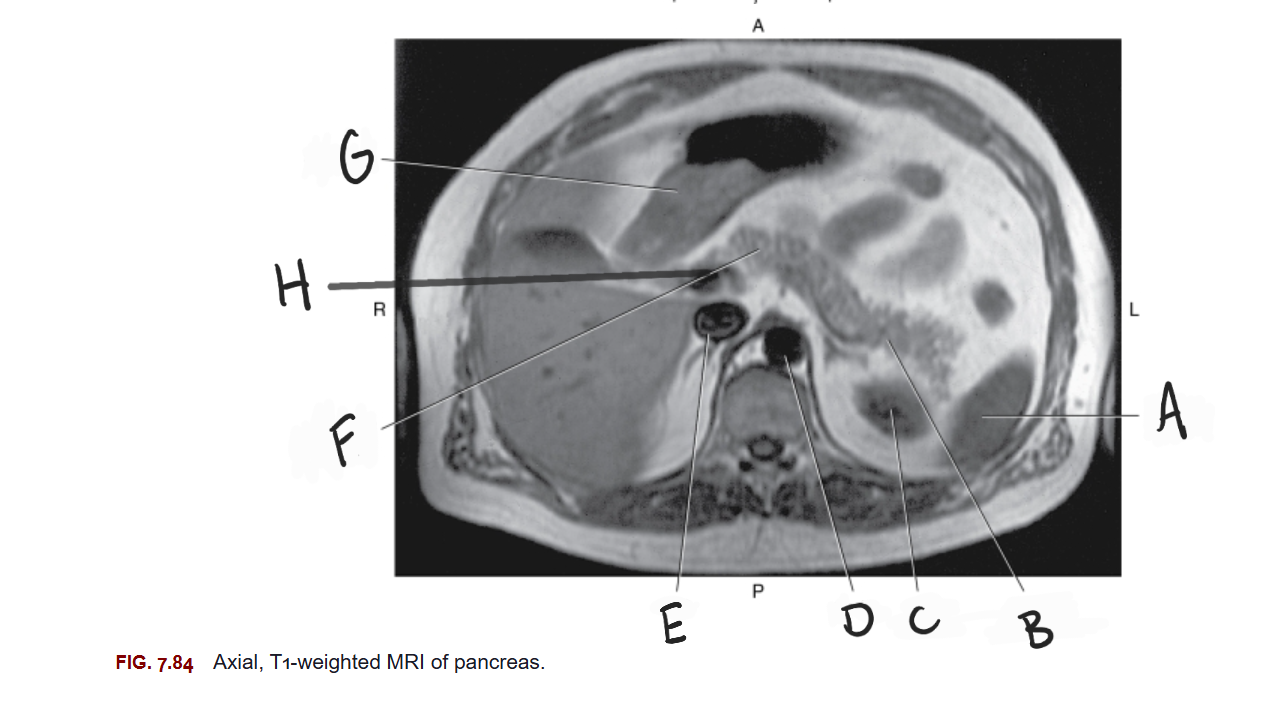
What is D
Aorta
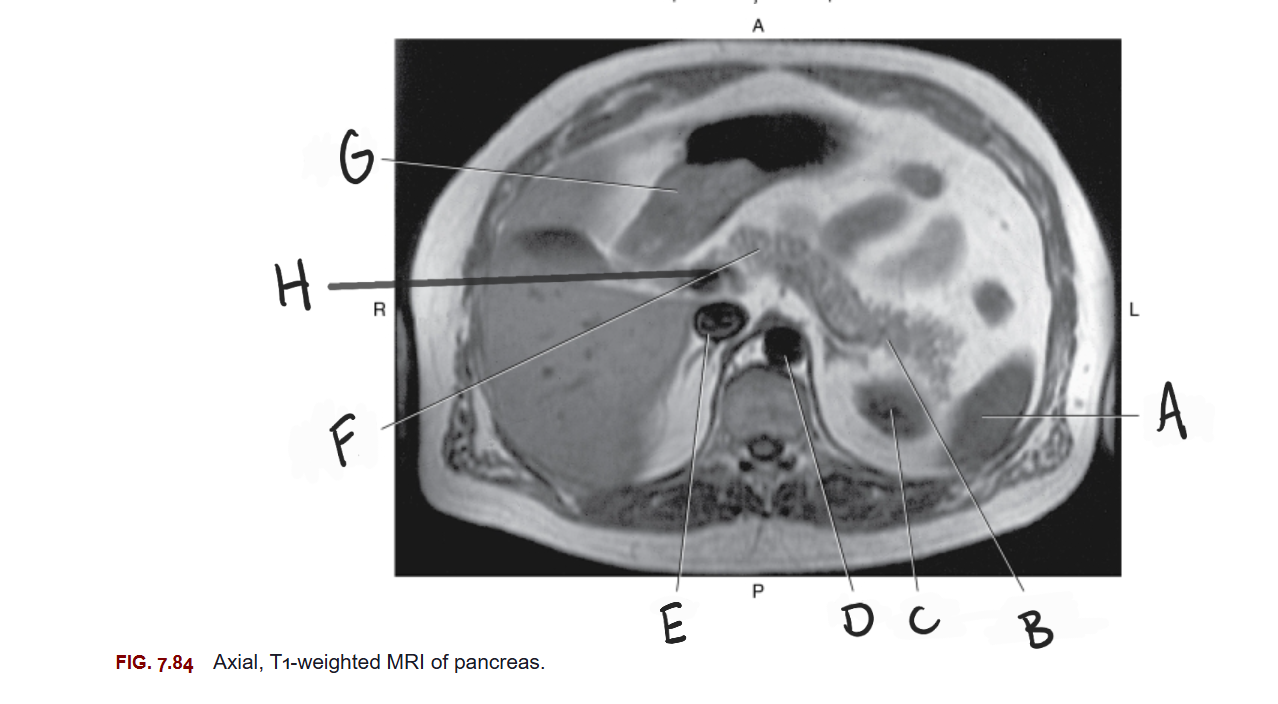
What is E
IVC
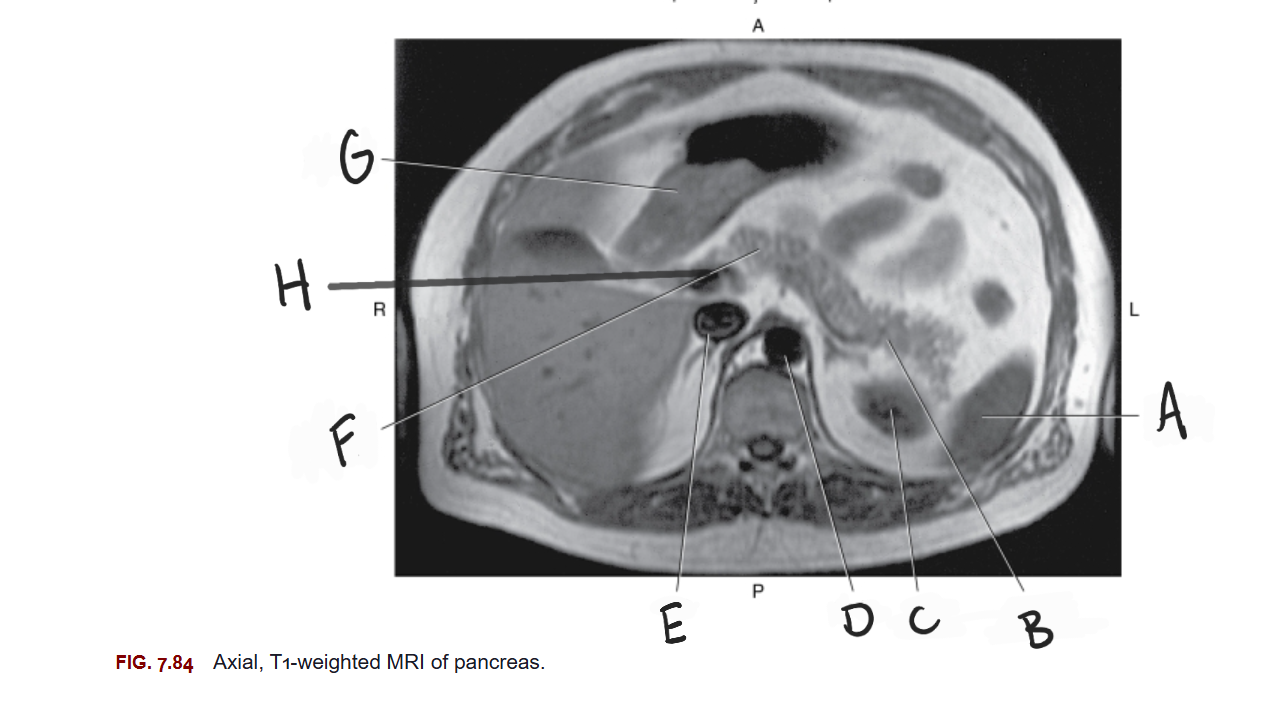
What is F
Body of pancreas
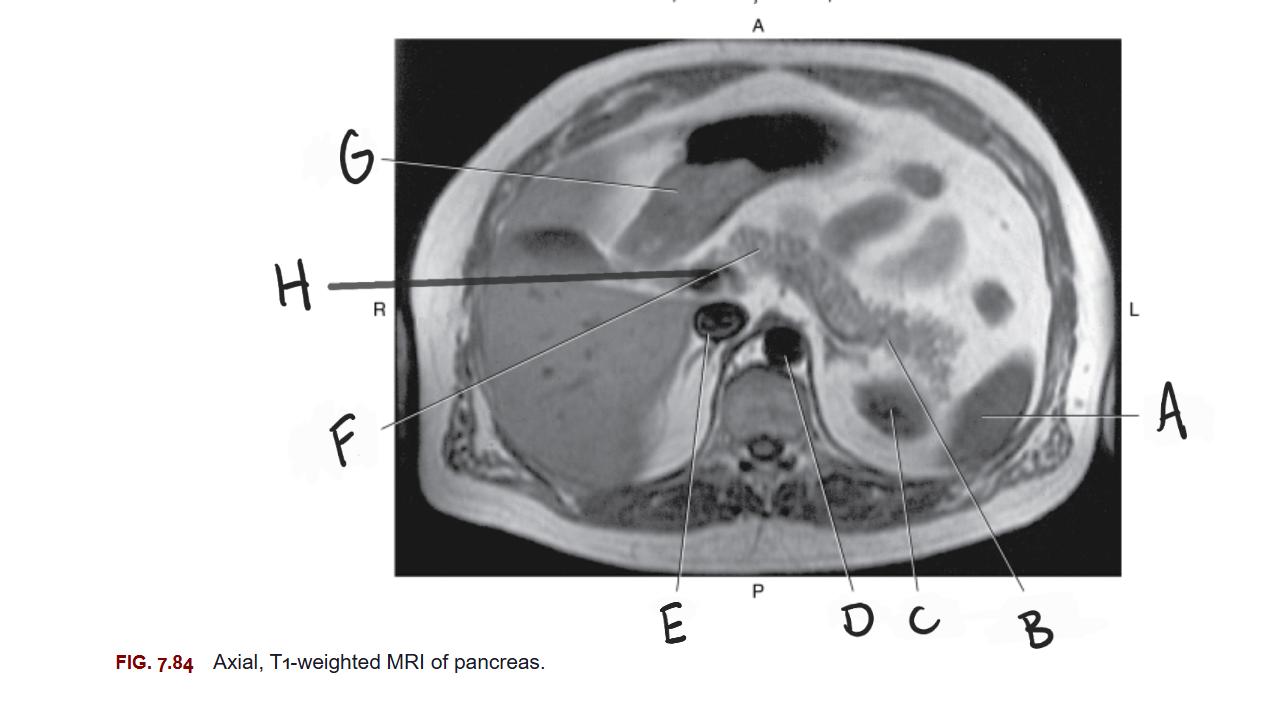
What is G
Stomach
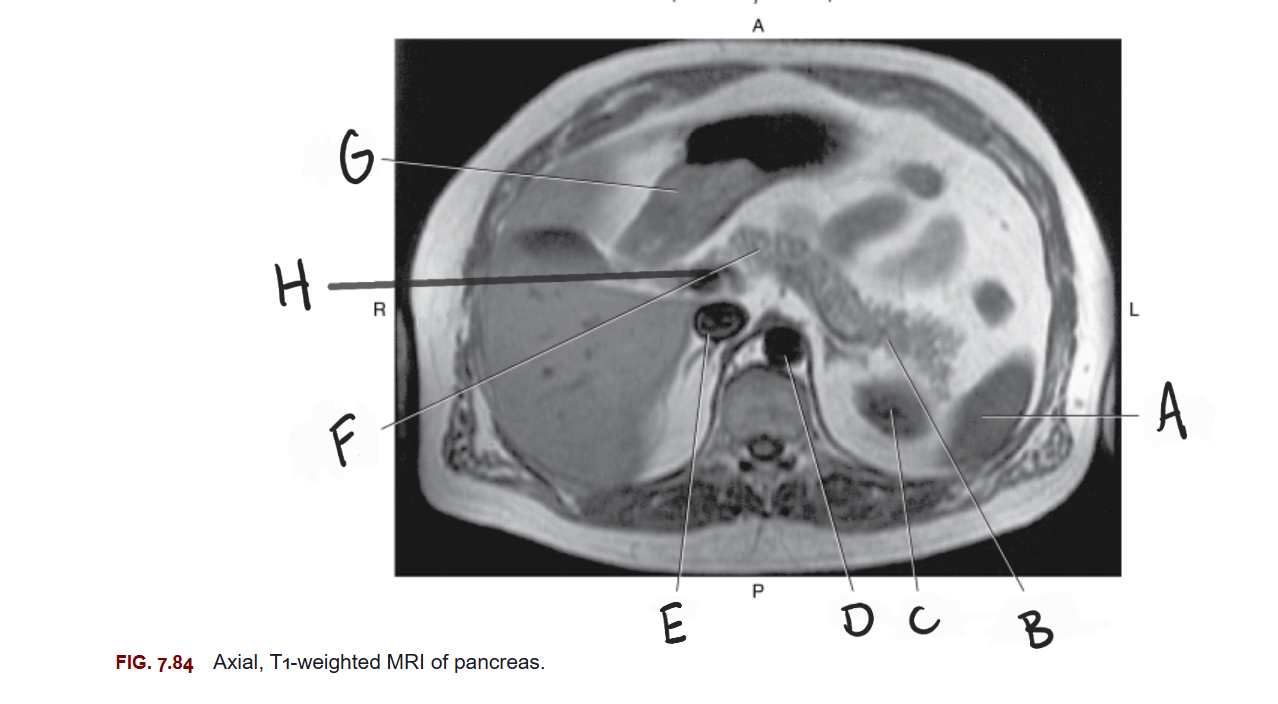
What is H
Portal vein
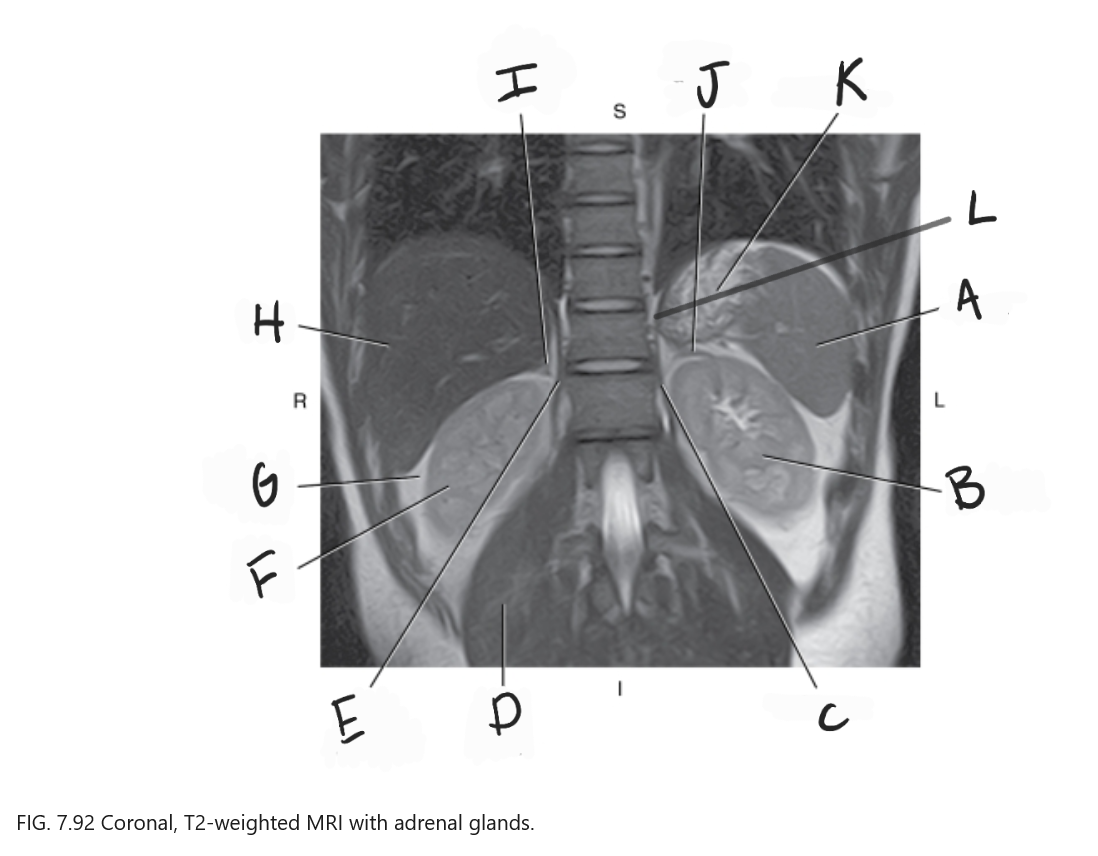
What is A
Spleen
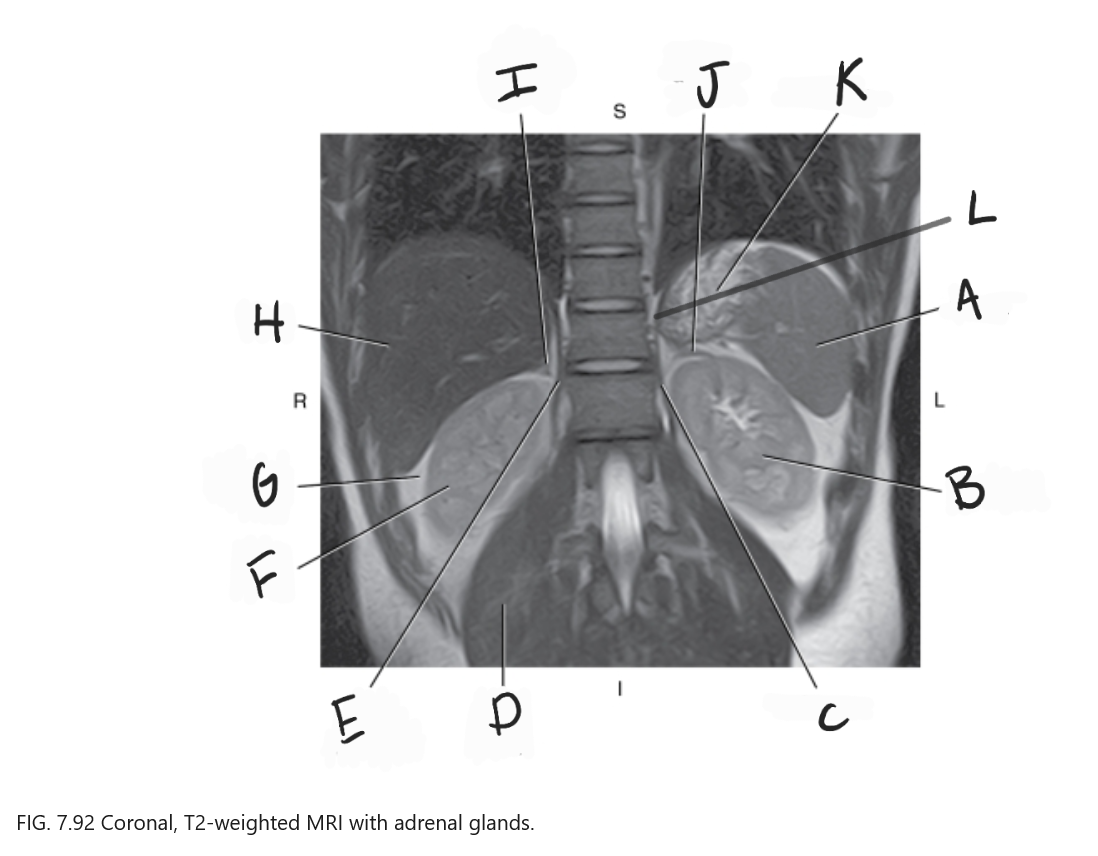
What is B
Left kidney
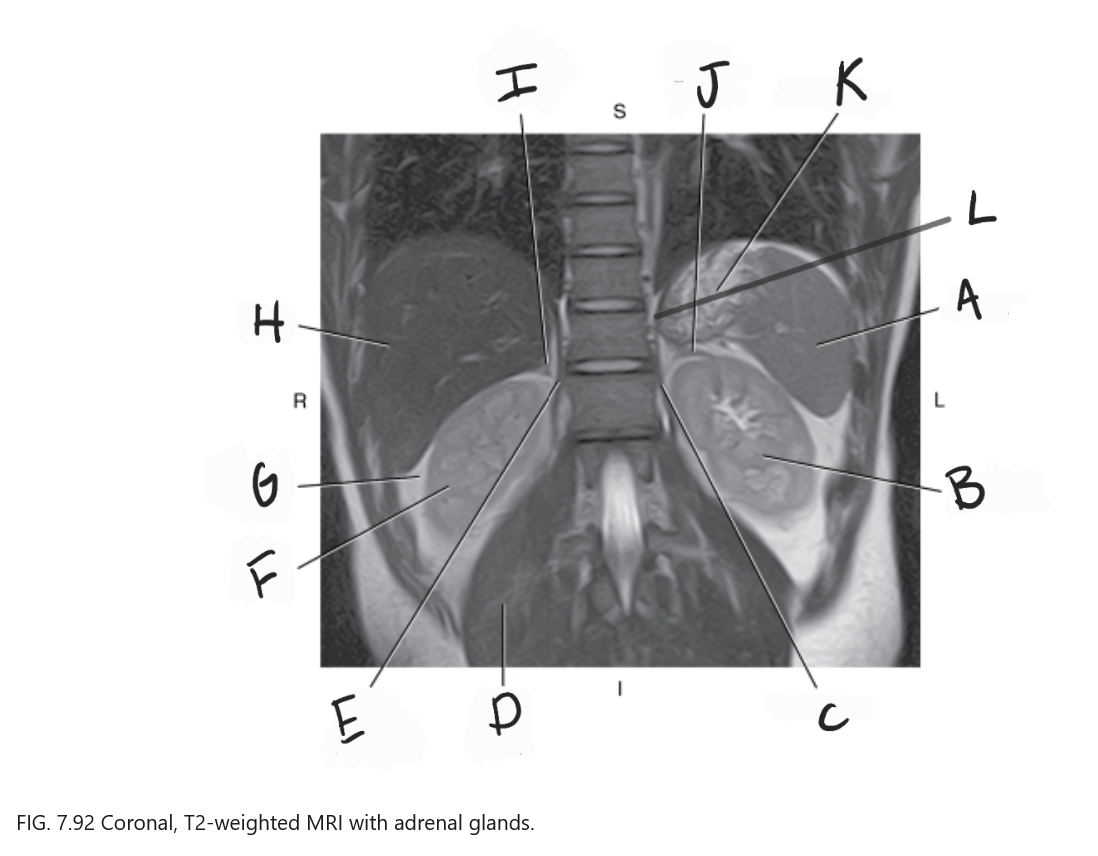
What is C
Left crus
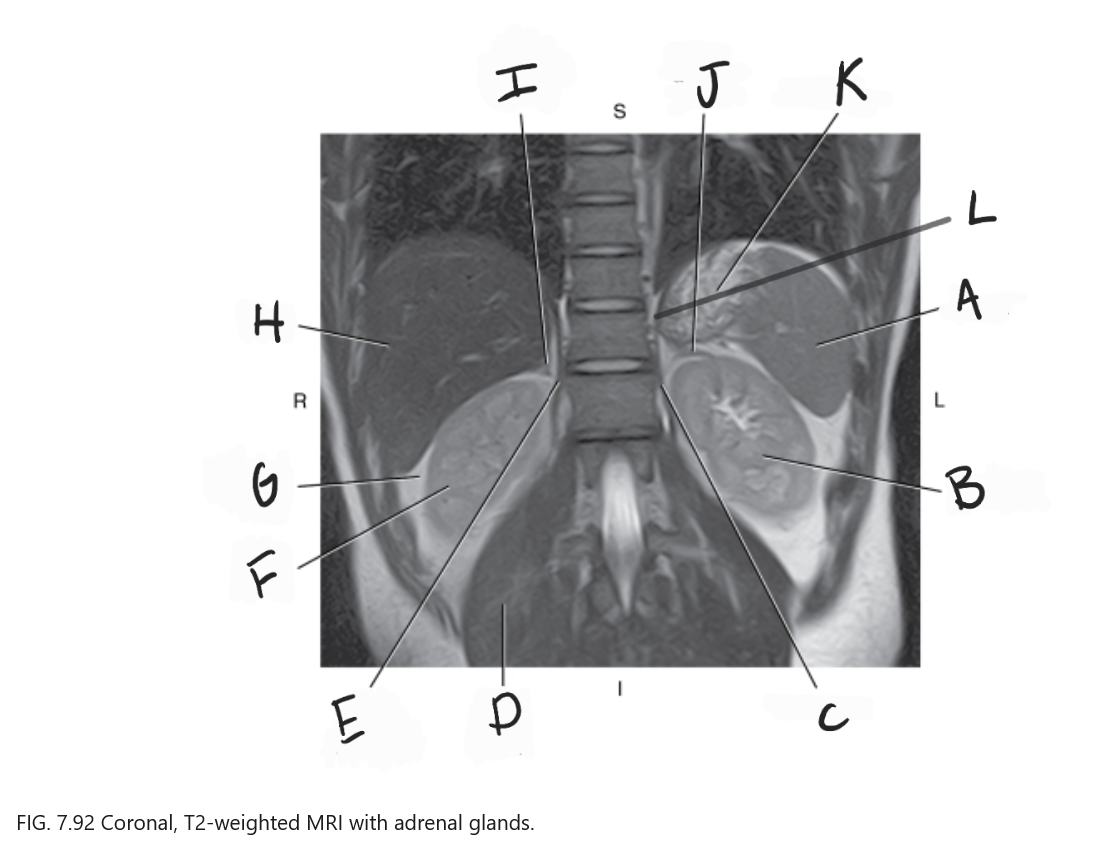
What is D
Right psoas muscle
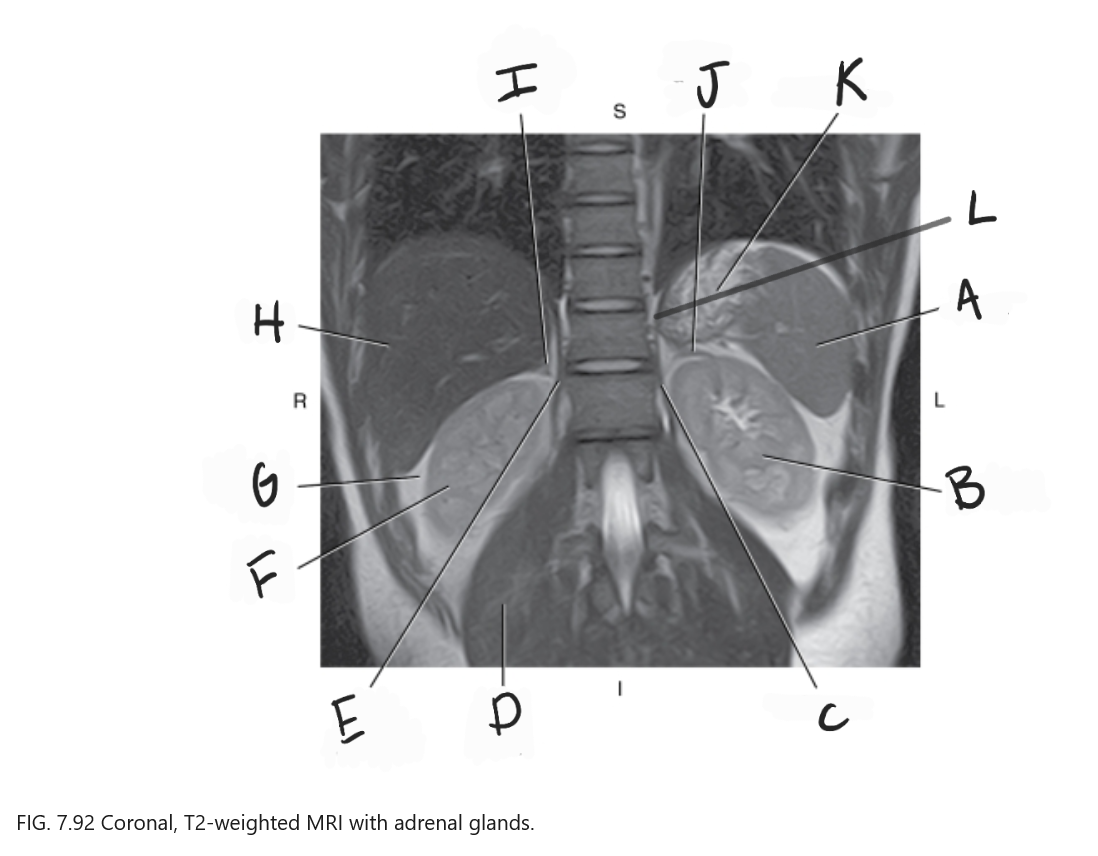
What is E
Right crus of diaphragm
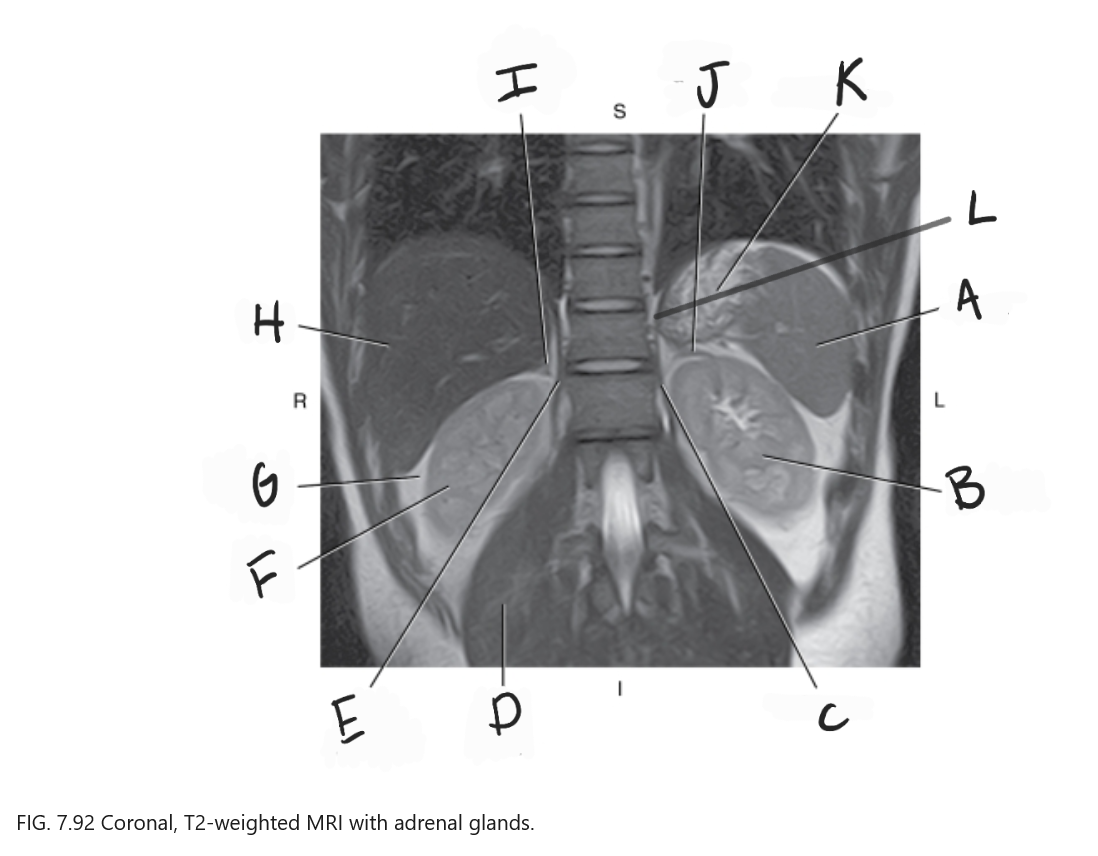
What is F
Right kidney
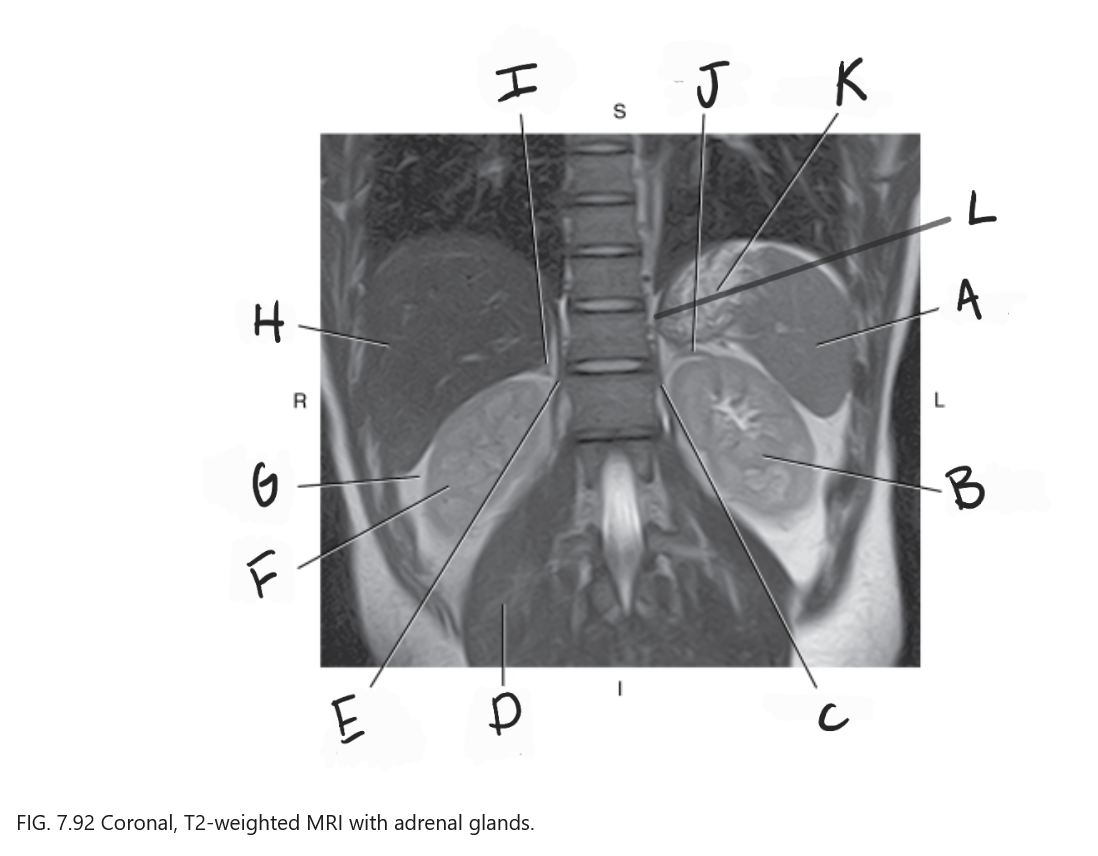
What is G
Perirenal fat
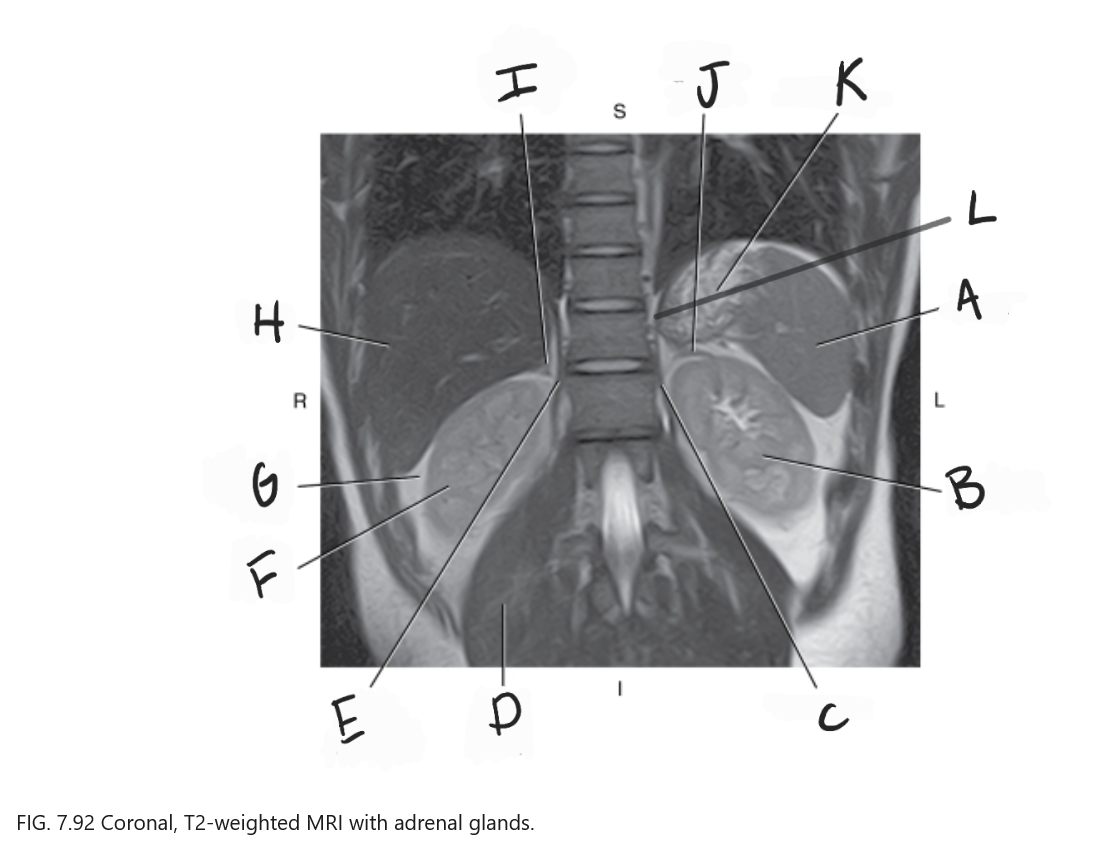
What is H
Liver
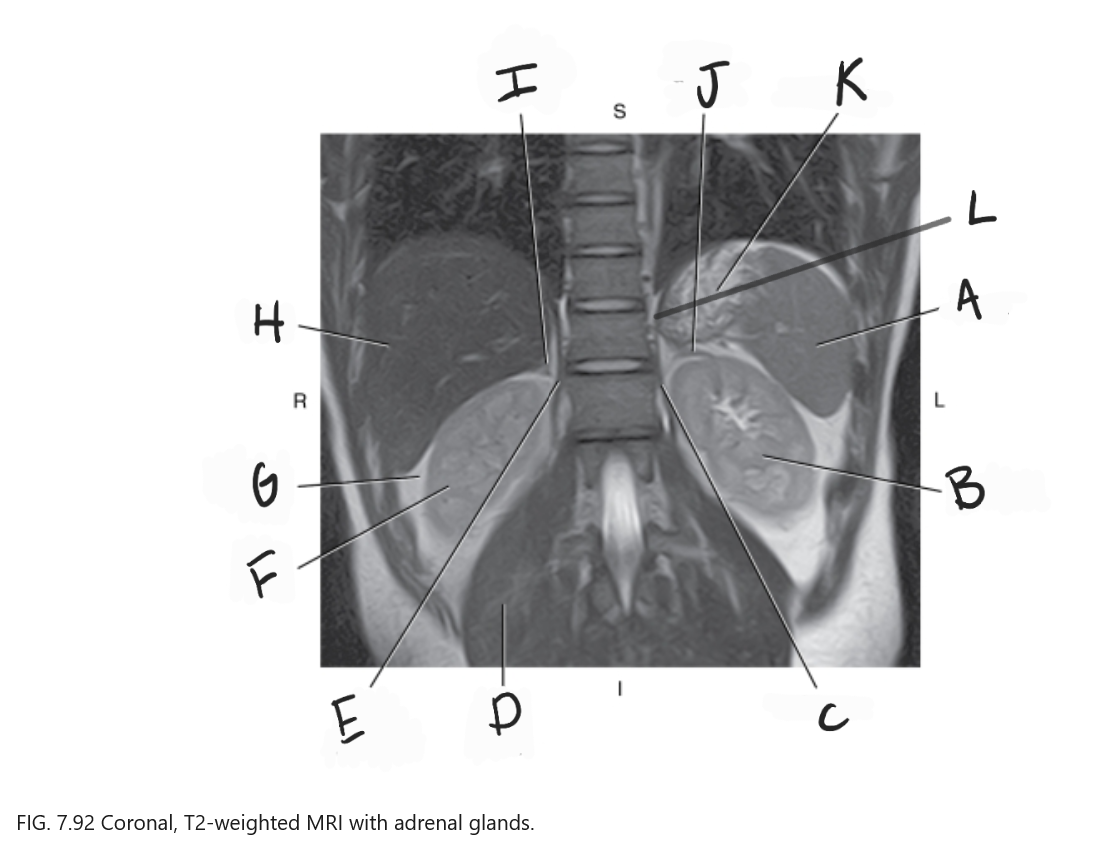
What is I
Right adrenal gland
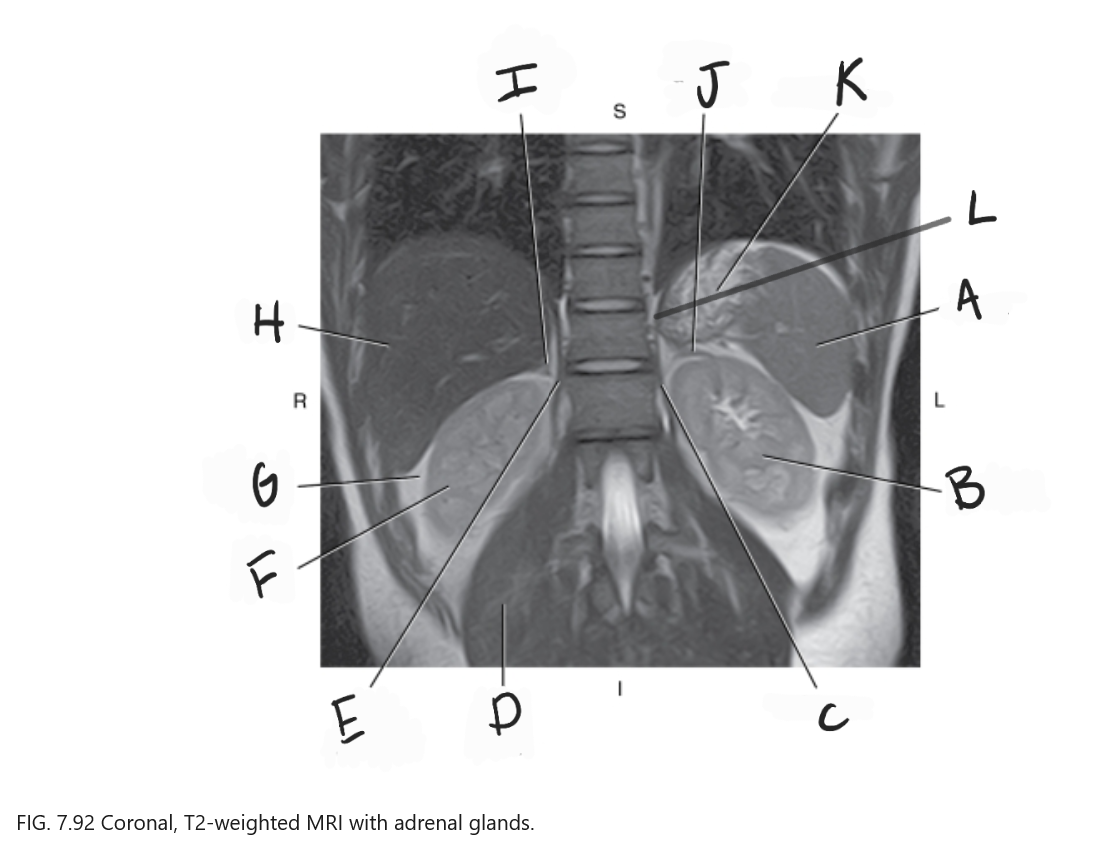
What is J
Left adrenal gland
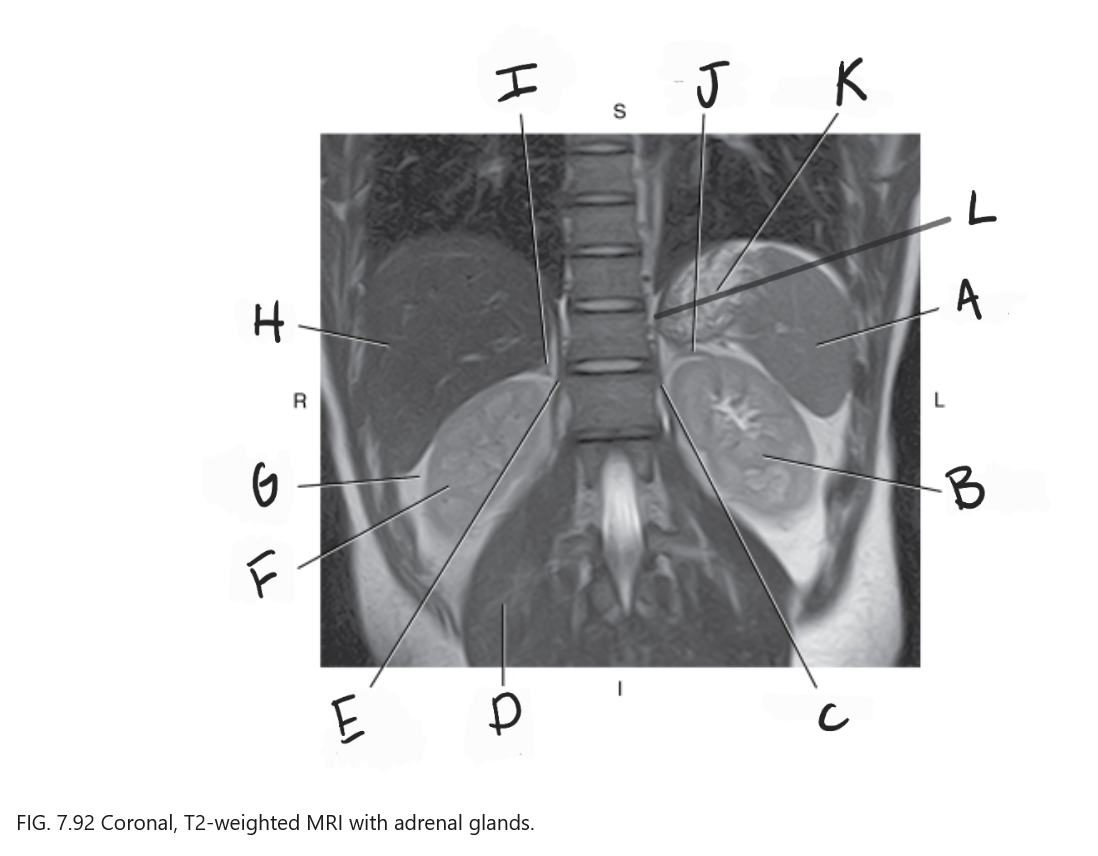
What is K
Stomach
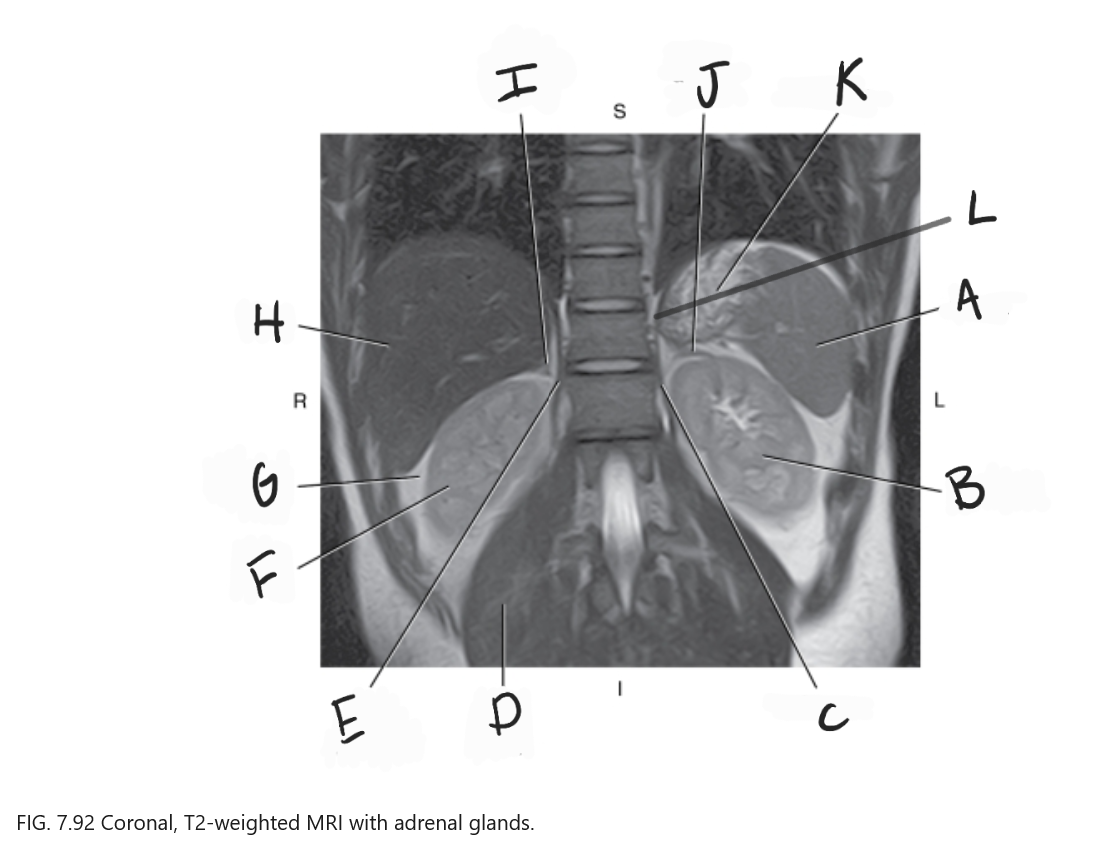
What is L
Crus of diaphragm
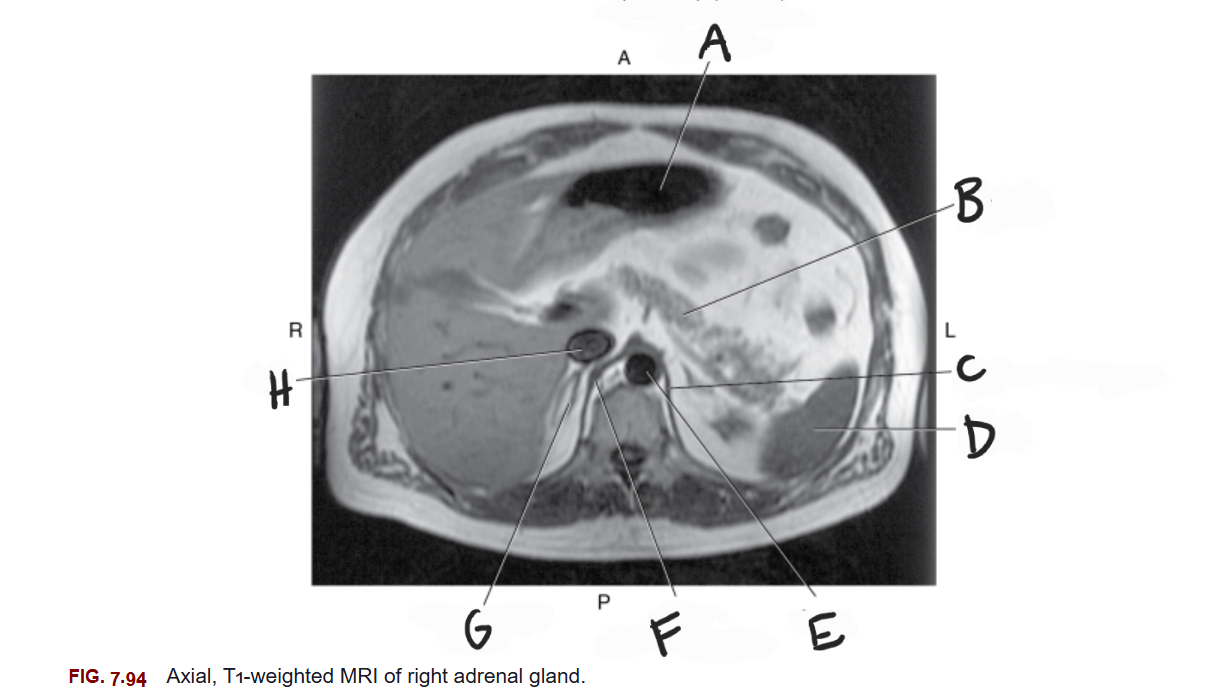
What is A
Stomach
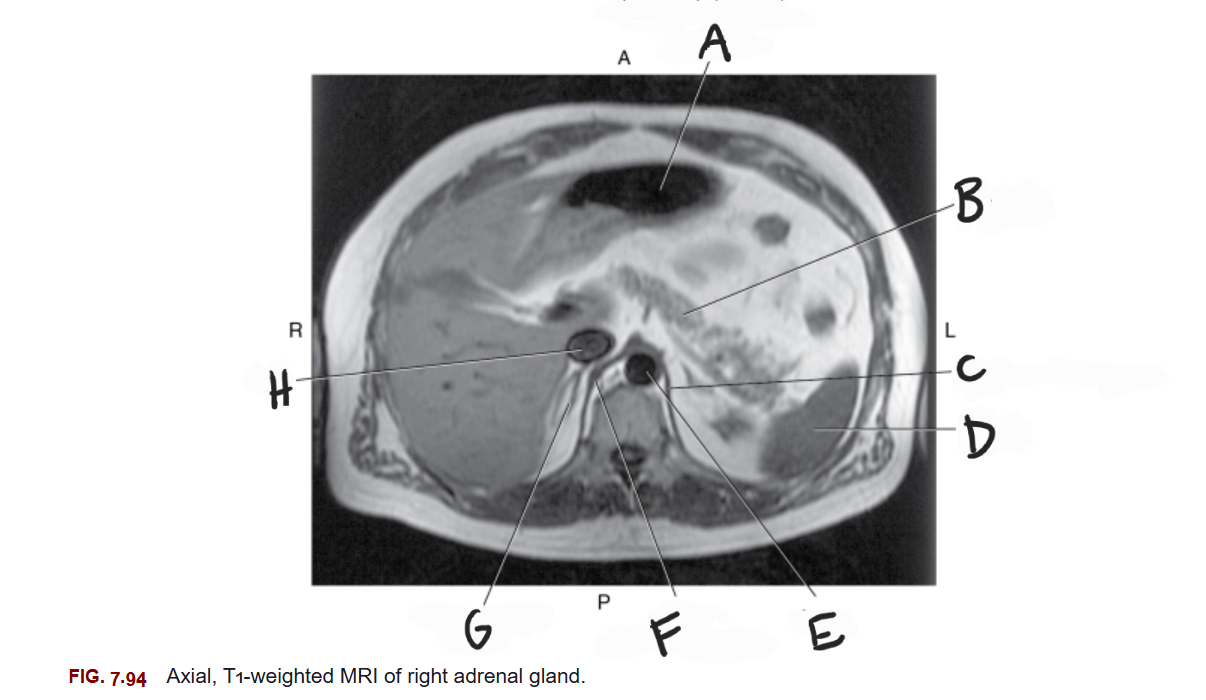
What is B
Pancreas
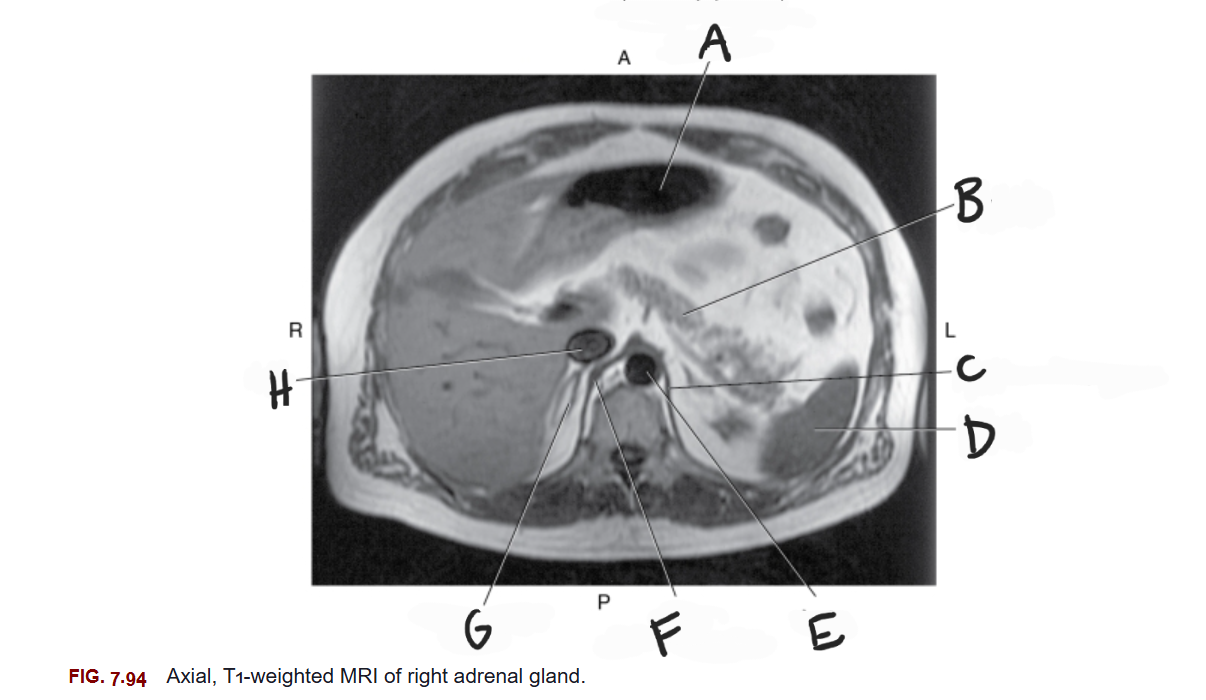
What is C
Left crus of diaphragm
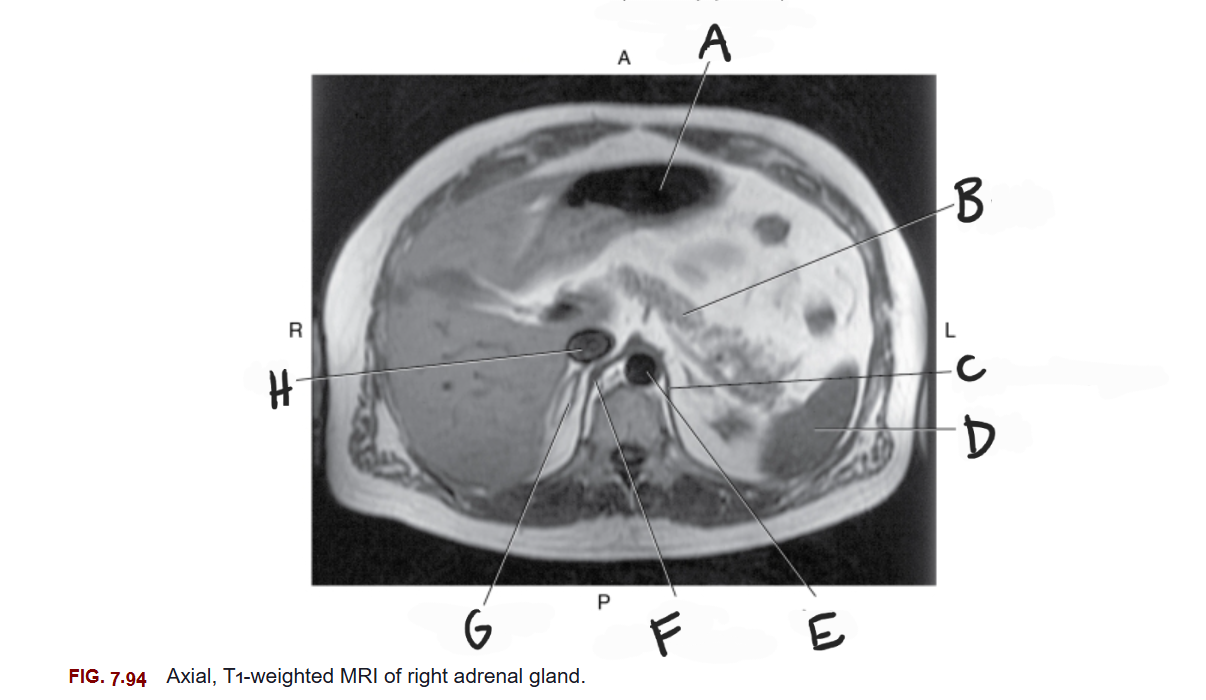
What is D
Spleen
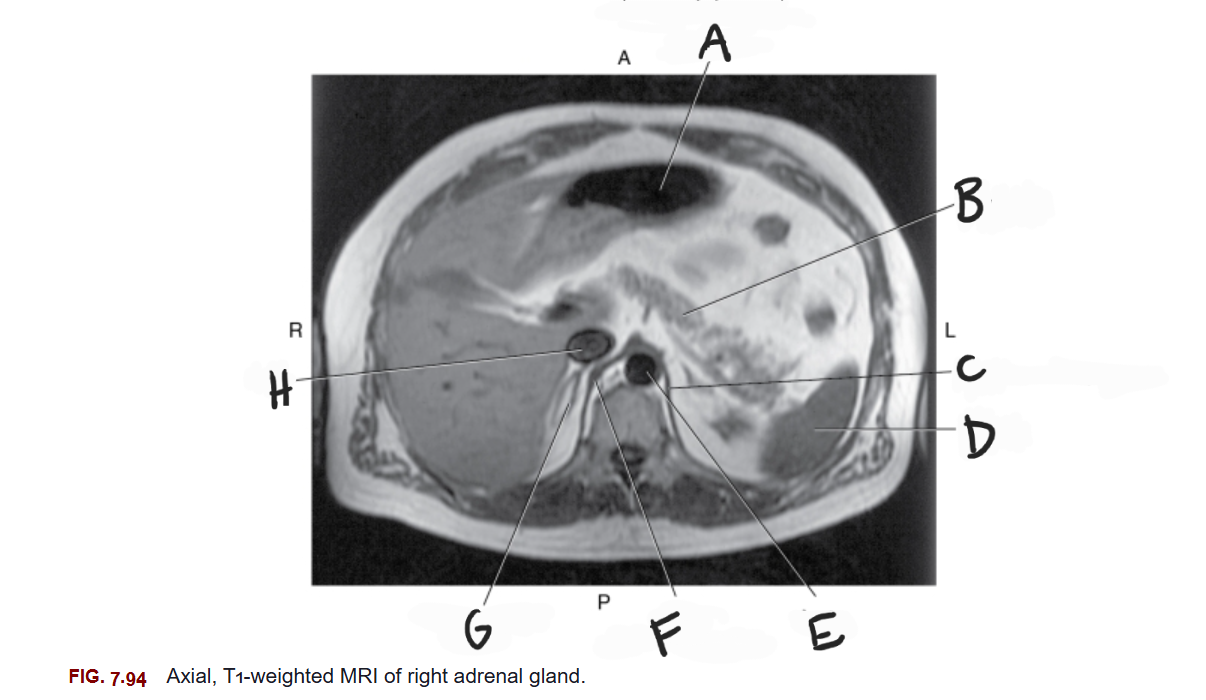
What is E
Aorta
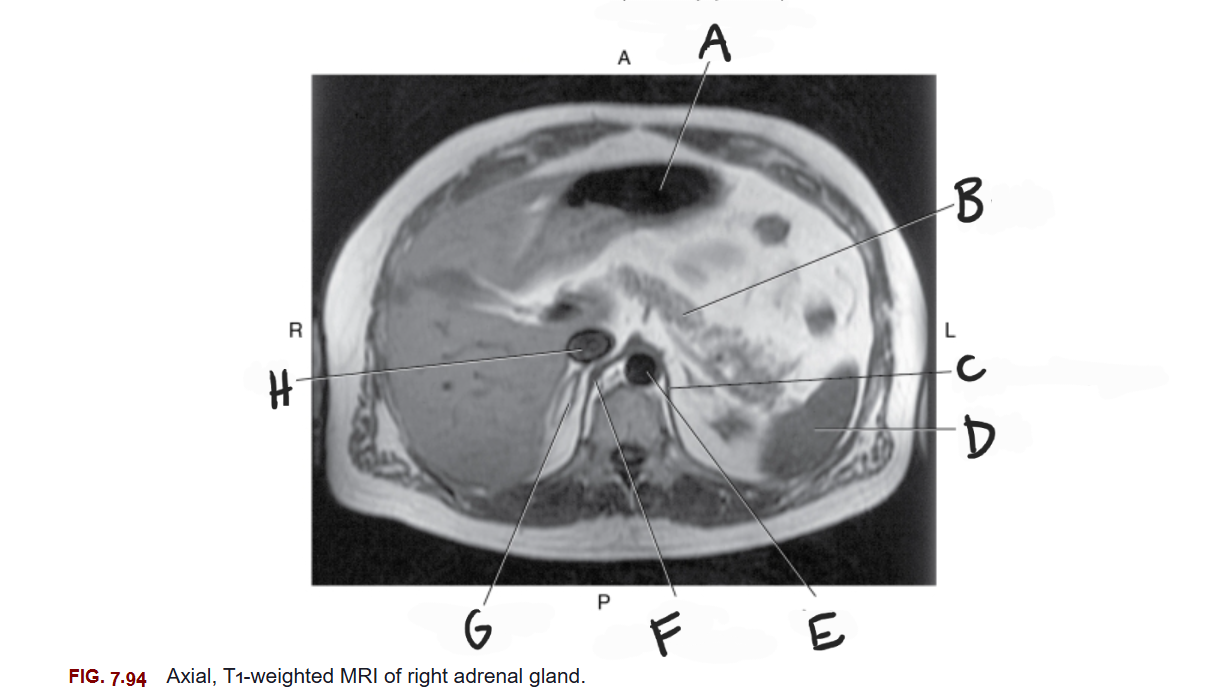
What is F
Right crus of diaphragm
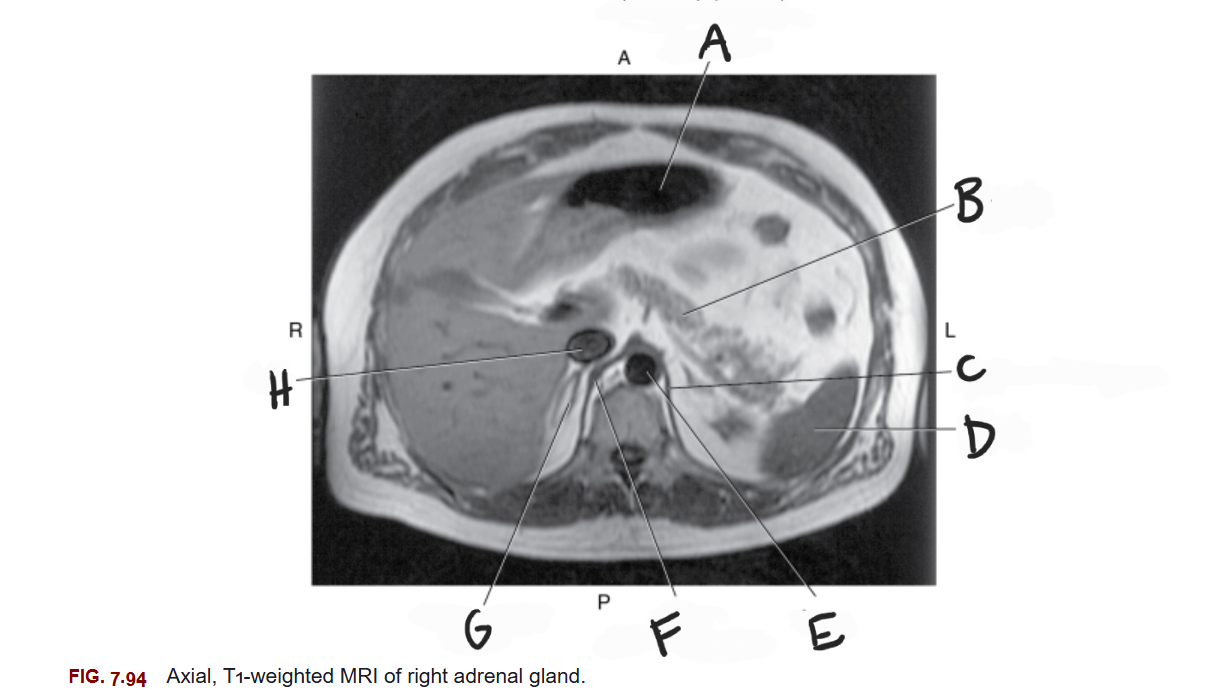
What is G
Right adrenal gland
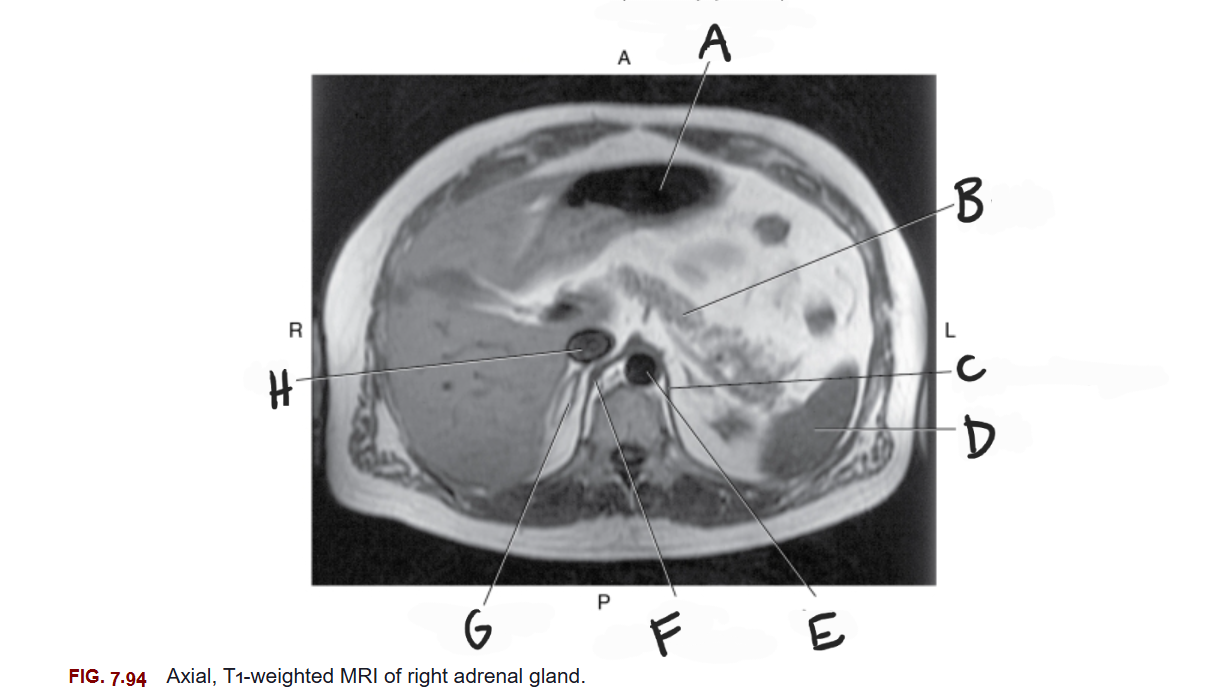
What is H
IVC
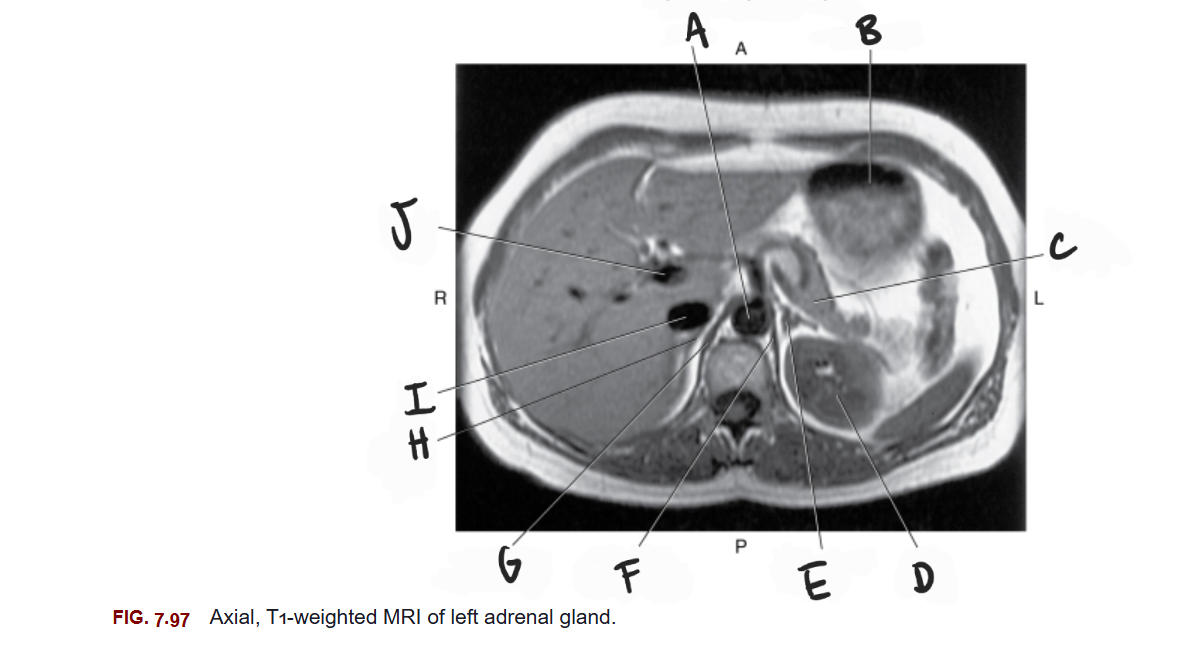
What is A
Aorta
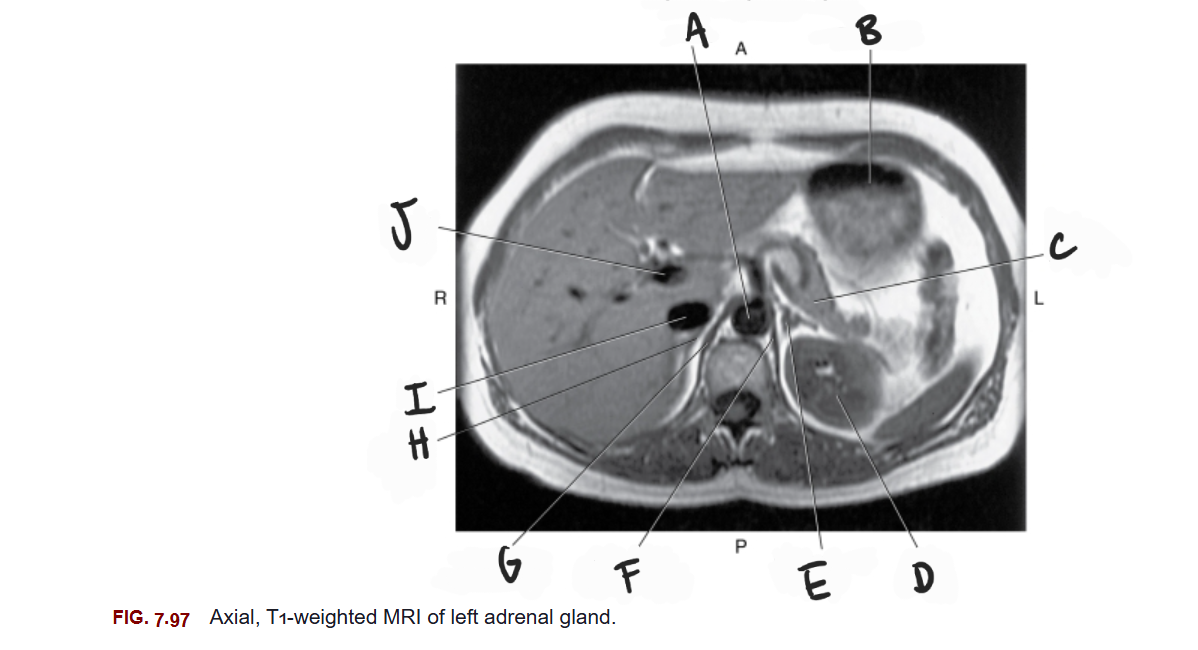
What is B
Stomach
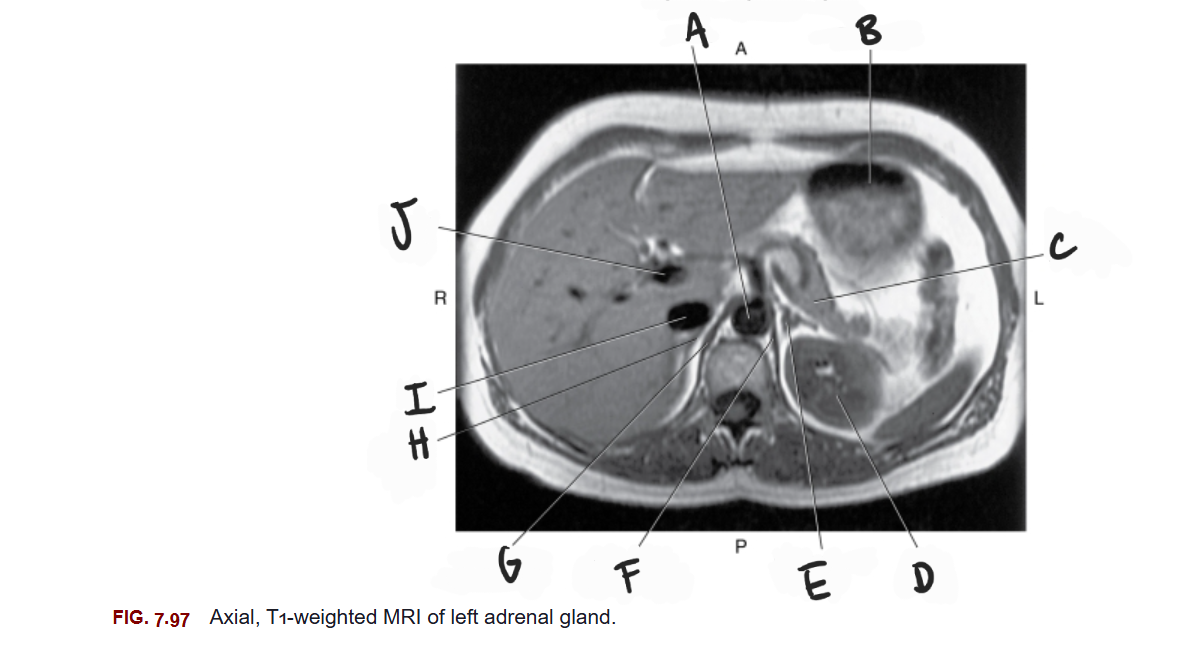
What is C
Tail of pancreas
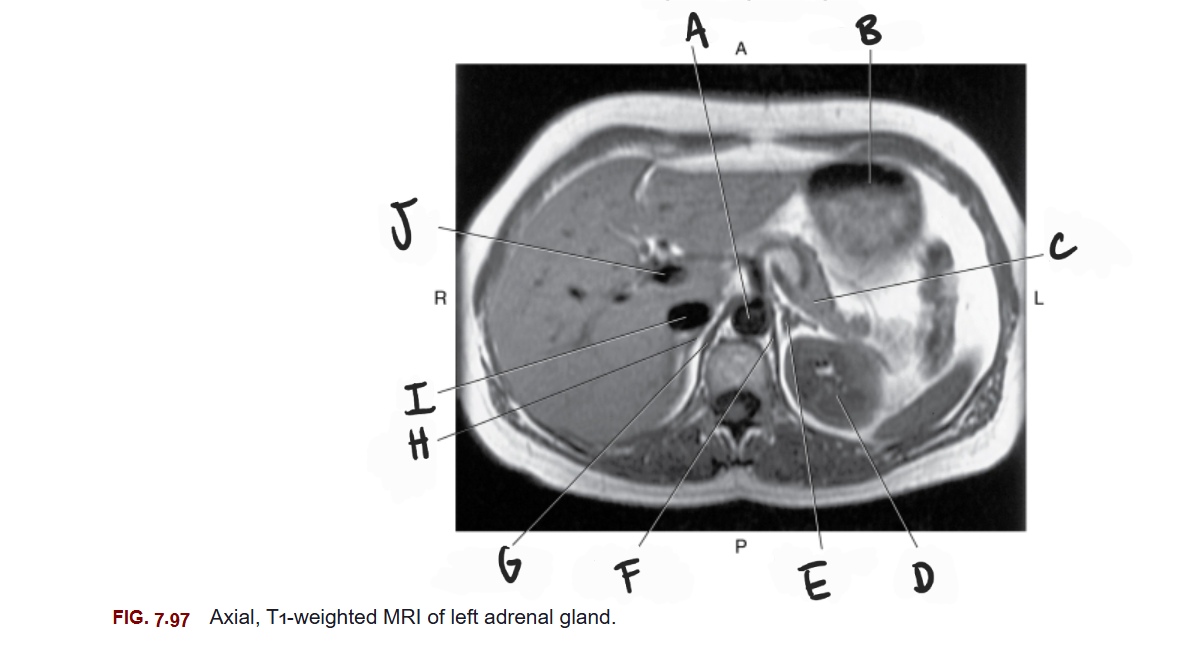
What is D
Left kidney
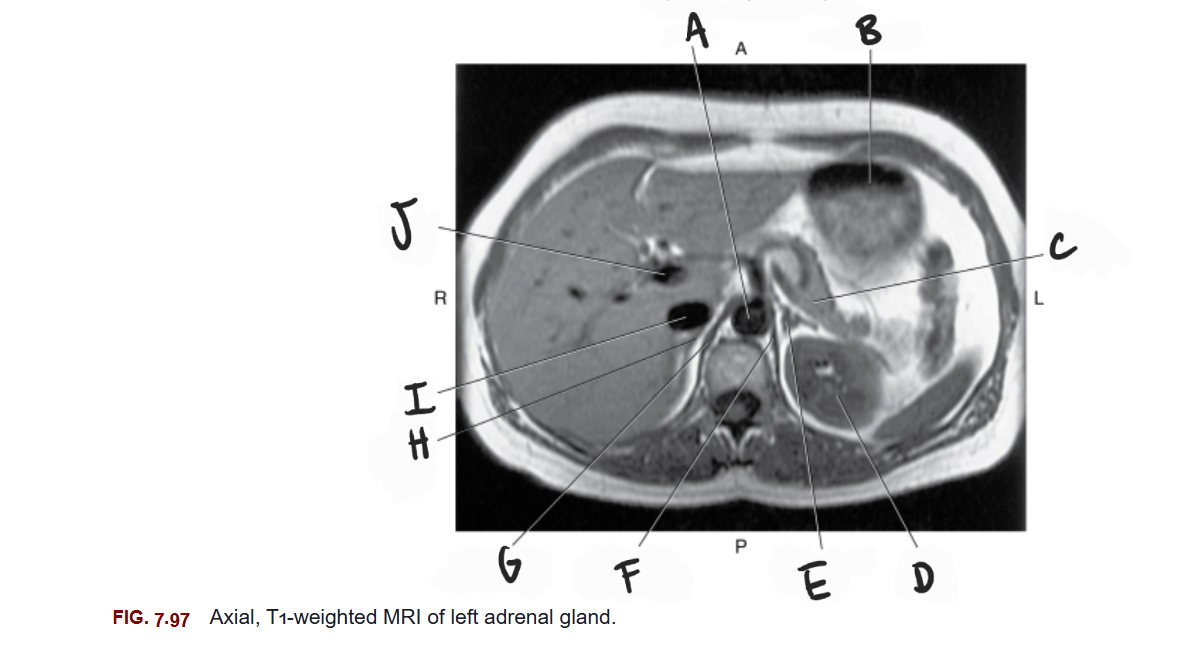
What is E
Left adrenal gland