(H) Anatomy and Physiology 1 Test Review
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Most abundant and variable tissue type
Connective tissue
Which type of tissue has cells not in direct contact?
Connective tissue
What is in between the cells in connective tissue?
Intercellular material called the matrix
What is the matrix composed of?
Fibers and ground substance (varies from liquid to solid depending on type of CT)
What are the types of cells in connective tissue?
Fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells
Fibroblasts characteristics
Do not move, produced during wound healing process, secretes proteins and produces fibers and ground substances
Macrophages characteristics
Move through connective tissues ingesting and eliminating large particles, bacteria and activating the immune system coming from white blood cells
Mast cells characteristics
Do not move, located near blood vessels, secrete heparin which prevents blood clots and histamine which dilate blood vessels in allergic response
What are the types of fibers in connective tissue?
Collagen or white fibers, elastic or yellow fibers, and reticular
Collagen/white fibers characteristics
Grouped in parallel bundles, appear as large pink fibers in slides, are tough, strong, resistant to stretch, flexible, and found in tendons, ligaments and deep layer of the skin
Elastic/yellow fibers characteristics
Thin branching fibers made of elastin, stretch and recoil like rubber, gives skin, lungs, arteries ability to stretch and recoil, have thinner and darker staining
Reticular characteristics
Thin and branched collagen fibers, form delicate framework for spleen and lymph nodes
What are the types of connective tissue?
Loose or areolar, adipose, dense regular, dense irregular, hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, fibrocartilage, bone, and blood
Loose or areolar connective tissue description
Contains loose arrangement of collagenous and elastic fibers, has scattered cell types and abundant ground substance
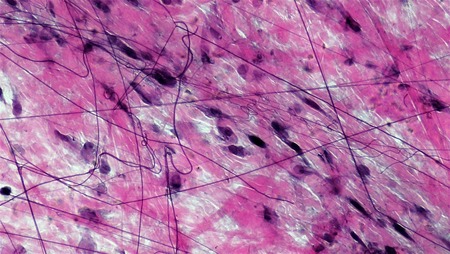
Loose or areolar connective tissue location
Underlies all epithelial, forms a passageway for nerves and blood vessels, located between nerves
Loose or areolar connective tissue function
Holds organs, anatomic structures, and tissues together
Adipose connective tissue description
Large, empty-looking cells with thins margins, nuclei pressed against cell membrane
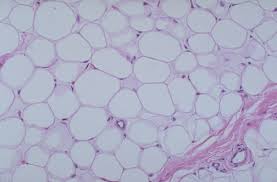
Adipose connective tissue location
Located in subcutaneous fat beneath the skin and surrounding organs
Adipose connective tissue function
Used for energy storage, insulation, and space filled as cushioning
Dense regular connective tissue description
Contains densely packed parallel collagen fibers, very few compressed fibroblast nuclei and little open space in between, has poor blood supply thus tissue repair is slow

Dense regular connective tissue location
Located in tendons and ligaments
Dense regular connective tissue function
Hold bones together and attach muscles to bones, very strong tissue
Dense irregular connective tissue description
Contains densely packed collagen fibers running in random directions with little open space in between
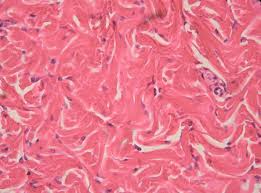
Dense irregular connective tissue location
Located in the deeper portion of skin and capsules around organs
Cartilage description
Special type of connective tissue: contains gel-like matrix, chondrocytes or cartilage cells are found within small chambers called lacunae and are fully within the matrix, no blood vessels thus diffusion must bring in nutrients and remove wastes, heals slowly
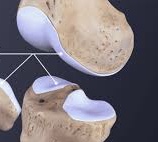
Cartilage function
Supports framework, attachments, protects underlying tissue and forms a model for crearing bones
Hyaline cartilage description
Has a clear, glassy, matrix; chondrocytes located in lacunae, and elastic fibers
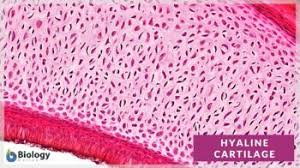
Hyaline cartilage location
Located in trachea, bronchi, larynx, and ends of bones
Hyaline cartilage function
Used for support
Elastic cartilage description
Chondrocytes located in lacunae and elastic fibers, most flexible cartilage
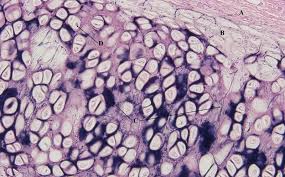
Elastic cartilage location
Located in external ear and epiglottis
Elastic cartilage function
Maintains shape and flexibility
Fibrocartilage description
Contains extensive collagen fibers, very tough
Fibrocartilage location
Located in intervertebral discs and meniscus in knees
Fibrocartilage function
Used for tensile strength and as a shock absorber
Spongy bone general description
looks spongy, is delicate, fills heads of long bones, and is always covered by compact bone
Compact bone general description
Looks more solid, has more complex arrangement, the cells and matrix surrounding vertically oriented blood vessels in long bones
Bone description
Calcified matrix is located in concentric lamellae or rings around the haversian canal containing blood vessels, osteocytes or bone cells are found in the lacunae between the lamellae and connected by the canaliculi or tubes in the matrix
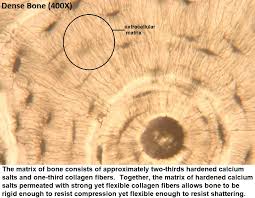
Bone location
Found in the skeleton
Bone function
Used for physical support, a leverage for muscles, and mineral storage
Blood description
A formed element of red and white blood cells and platelets
Blood location
Located in blood plasma or fluid matrix
Blood function
Used to transport substances and helps maintain homeostasis
Oval-shaped cell with a large, dark nucleus located off the center
Plasma cell
Irregular shaped cells with small pale nuclei and cytoplasm crowded with dark staining secretory granules
Mast cells
Large, round shaped cells with the nucleus and cytoplasm pushed to the margin of the cell
Adipose cells
Oval to irregular shaped cells with small nuclei
Macrophages
Large, long, flat, branching cells with large, light colored nuclei
Fibroblasts
Most abundant cells in connective tissue
Fibroblasts
Responsible for production and maintenance of fibers and ground substance
Fibroblasts
Active phagocytes (eliminators of large particles and bacteria)
Macrophages
Big eaters
Macrophages
Engulf and destroy damaged cells and pathogens
Macrophages
Synthesizes and stores fat
Adipose
Contains heparin and histamine
Mast cells
Stores and releases a compound that prevents blood from clotting as it flows throughout the body
Mast cells
Stores and releases a compound that initiates the inflammatory response and allergic reactions
Mast cells
Main producers of antibodies
Plasma cells
Produces a compound that helps fight infection, pathogens, and cancer
Macrophages
Located beneath the dermis of the skin, digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts, in between muscles, around blood vessels, nerves, and joints
Cushions organs, provides support, allows for independent movement, and the phagocytic cells provide dense against pathogens
Loose connective tissue
Located beneath the skin, primarily at sides, buttocks, breasts, behind the eyeballs, and around the kidneys
Adipose tissue
Provides padding and cushions shocks, insulates, and stores energy reserves
Adipose tissue
Located between the skeletal muscles and skeleton, between bones, forms the covering of skeletal muscles and the capsules of visceral organs
Dense tissue
Provides a firm attachment, conducts pull of muscle, reduces friction between muscles, stabilizes relative positions of bones, helps prevent over expansion of organs such as the urinary bladder
Dense tissue
Resists compression, prevents bone-to-bone contact, and limits relative movement
Fibrocartilage
Provides support while tolerating distortion without damage and returns to original shape
Elastic cartilage
Provides stiff but relatively flexible support, and reduces friction between bony surfaces
Hyaline cartilage
Located between tips of ribs and bones of sternum, covers bone surfaces at synovial joints, and supports larynx, trachea, and bronchi whilst forming parts of nasal septum
Hyaline cartilage
Located in intervertebral discs separating vertebrae along the spinal column, pads within knee joints, and between pubic bones in pelvis
Fibrocartilage
Located in pinna external ear, auditory canal, and epiglottis
Elastic cartilage
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, smooth, cardiac
How are all 3 muscle tissue types different?
Through appearance, number of nuclei, function, and location
What are the individual cells in muscle tissues called?
Muscle fibers, because they are fibers
Skeletal muscle description
Consists of long, cylindrical, unbranched cells with striations and multiple nuclei just beneath the cell membrane
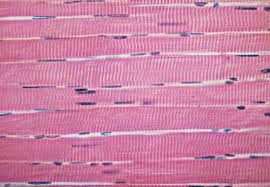
Skeletal muscle location
Connected to bones
Skeletal muscle function
Give muscle cells the ability to contract, are used for movement, facial expression, posture, breathing, speech, swallowing, body heat, and excretion, all function under voluntary control
Smooth muscle description
Consists of non-striated, short spindle shaped cells, with only one central nucleus
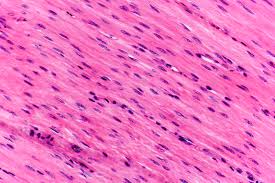
Smooth muscle location
Found in walls of hollow organs such as the GI tract, stomach, and bladder
Smooth muscle function
Used for swallowing, GI tract function, labor contractions, control of airflow, erection of hairs, and controls of pupils, all under involuntary control
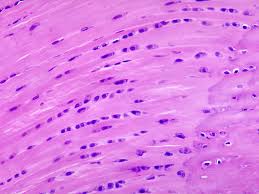
Cardiac muscle description
Consists of short branched cells with striations, intercalated discs (dark line where one cell touches another), and one central nucleus per cell
Cardiac muscle location
Found only in the heart
Cardiac muscle function
Pumps blood to and from the heart
What is hypertrophy?
The enlargement of cells
What is atrophy?
The shrinkage of cells
How does hypertrophy occur?
Through exercise, all an increase in the size of cells
How does atrophy occur?
Through aging (senile) or lack of use of the tissue (disuse)
Nervous tissue description
Contains large neurons (primary cell type) with long dendrites and axons, surrounded by much smaller neuroglial cells which lack dendrites and axons
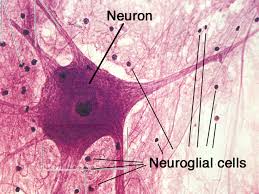
Nervous tissue location
Located in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Neuroglia description
Varies
Neurons function
Used for internal communication between cells, coordination, regulation, can sense changes, and transmit nerve impulses throughout the body
Neuroglia function
Used for support, carrying on phagocytosis, and helps supply nutrients to neurons
What are the distinguishing characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Cells are tightly packed with little space between them, the bottom surface is attached to the basement membrane, cells rapidly reproduce, and tissue lacks blood vessels and supply
What are the main functions of epithelial tissue?
Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, and sensory reception
Simple squamous epithelial description
Single row of flat cells with flat nuclei
Simple squamous epithelial function
Allows for rapid diffusion of substances, secretion of serous fluid, reduces friction, controls vessel permeability, and absorbs
Simple squamous epithelial location
Found in alveoli (lungs), walls of capillaries, lines inside of blood vessels, ventral body cavities, heart, blood vessels, parts of kidney tubules, and inner cornea
Simple cuboidal epithelial description
Single row of cube-shaped cells with centrally located round nuclei
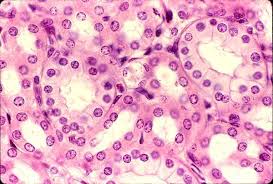
Simple cuboidal epithelial function
Absorption, secretion and production of mucus
Simple cuboidal epithelial location
Found in ovaries, ducts of the liver, thyroid, mammary, salivary and other glands, most kidney tubules