A2 Physics Magnetic Fields
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
draw a magnetic field line
they travel from a north pole to a south pole
What happens if there is an external magnetic field acting on a current-carrying conductor
current-carrying conductor produces its own magnetic field
when external magnetic field acting on it, it experiences a force
formula for force on a current-carrying conductor
F = BILsinθ; F is force on current-carrying conductor, B is magnetic flux density of applied magnetic field, I is current, L is length of conductor, θ is angle between the conductor and magnetic field
define magnetic flux density
force acting per unit current per unit length on a wire placed at right angles to the magnetic field
unit for magnetic flux density
tesla (T)
what does it mean if there is higher flux density
the magnetic field is stronger
what does each finger refer to in Fleming’s left hand rule
thumb is force, index is direction of applied magnetic field, middle is direction of current
what happens when a moving charge interacts with an applied magnetic field
it experiences a force since the moving charge produces its own field
formula for force on a particle with charge Q
F = BQvsinθ; F is magnetic force on particle, Q is charge of particle, v is speed of particle, θ is angle between charge’s velocity and magnetic field
define hall voltage
the potential difference produced across an electrical conductor when an external magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the current through the conductor
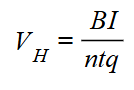
what do each letter mean in the hall voltage formula
B = magnetic flux density
q = charge on each charge carrier
I = current
n = number density of charge carrier
t = thickness of the conductor
derive hall voltage
define magnetic flux
product of magnetic flux density and the cross-sectional area perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field
formula for magnetic flux
Φ = BA
formula for magnetic flux linkage
NΦ = BAN
what is magnetic flux linkage
product of magnetic flux and number of turns
what is faraday’s law
induced e.m.f. is directly proportional to rate of change in magnetic flux linkage
what is lenz’s law
induced e.m.f. acts in the opposite direction of the force that caused the change in magnetic flux
difference between faraday’s and lenz’s law
faraday’s law is for magnitude of induced e.m.f. and lenz’s law is for the direction of induced e.m.f.
what is a magnetic field
a region where a force acts on a current-carrying conductor or moving charge