Bacterial Infectious Diarrhea & Enteric Fever
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
diarrhea
-passage of 3 or more loose or liquid stools per day
OR
-bowel movements more frequently than is normal for the individual
WHO epidemiology of diarrhea
-most deaths are preventable
-2.2 million lack access to safe drinking water
-3 billion people lack access to handwashing facilities/soap
-673 million practice open defecation
-5th leading cause of death in children <5 yo
-lack of sanitation worsens gender disparities
-disproportionately affects children in world’s poorest regions
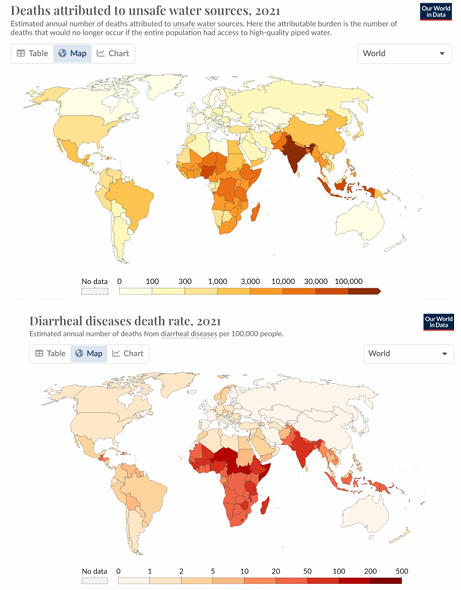
bacterial enteric infections
-watery (small intestine)
-blood (dysentery- colon)
-enteric fever (systemic)
clinical approach to bacterial infectious diarrhea/enteric fever
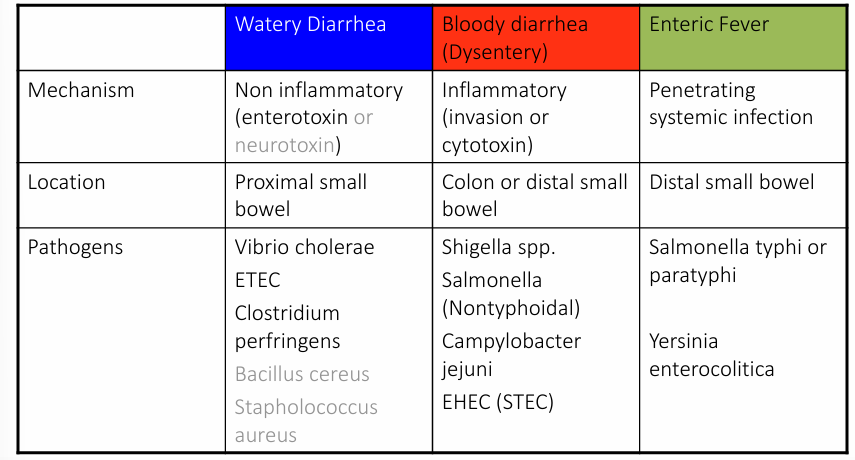
bacterial pathogens typical transmission
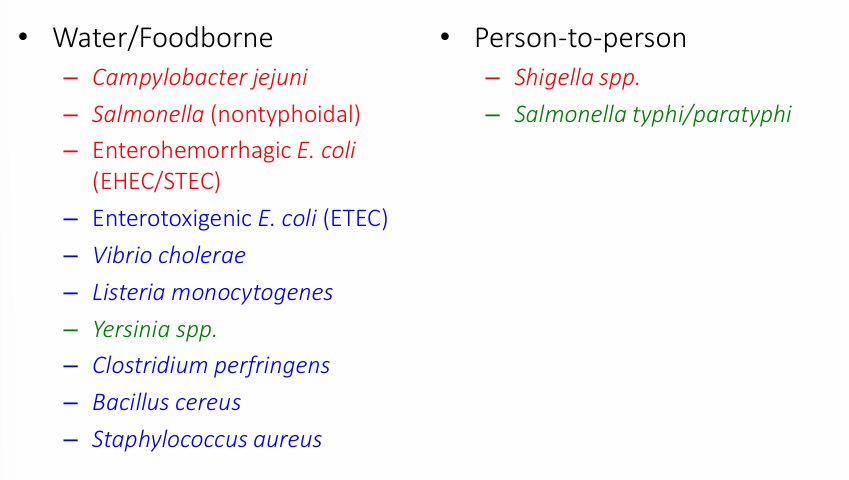
microbiology of infectious diarrheas

diarrhea pathogenesis
-inoculum size
-adherence
-toxin production: enterotoxin, cytotoxin (type of enterotoxin that injures cells), neurotoxin
-tissue invasiveness
diarrhea pathogenic mechanisms
-lower the inoculum, easier to spread person-person

diarrhea pathogenic mechanisms- toxin production & invasion

host defenses

pathogenic mechanisms- neurotoxins
-Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin: heat-stable toxin (incubation 2-4 hours), increase peristalsis by autonomic activation, resulting in intense vomiting/diarrhea
-Bacillus cereus enterotoxin: 2 enterotoxins (emetic- heat stable toxin, elaborated in starchy foods, incubation period 1-6 hours; diarrheal- incubation period 10-12 hours)
vomiting center (VC)
-located in the dorsolateral medulla adjacent to ascending reticular activating system & medullary centers controlling CV and respiratory reflexes
-afferent connections from cortex, limbic system, hypothalamus, vestibular centers, gut, and other viscera are known
-VC integrates input from central and peripheral afferents and modulates the autonomic and somatic motor response to noxious stimuli
-chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) located in floor of fourth ventricle provides specific receptors for circulating toxins in the blood, CSF relays info to the VC
cholera
-clinical: variable (genetic factors- 75% asymptomatic, 20% abrupt watery diarrhea, 5% severe watery diarrhea/vomiting/dehydration), dehydration, duration 1-3 days, no tenesmus/strain or abdominal pain/fever, shed 7-14 days
-treatment: rehydration (IV or oral rehydration solution (glucose and electrolytes)), antibiotics (tetracycline, quinolone, macrolide- local resistance patterns)
-protection: stomach acid, IgA and IgG against LPS, vaccine
Vibrio cholerae
-curved gram-negative facultative bacillus with single polar flagellum
-over 200 serogroups (based on O antigen in LPS), but only O1 (El Tor is a variant) and O139 are associated with epidemic and pandemic cholera (Non-O1 or non-O139 can be pathogenic and cause small outbreaks, cholera can be epidemic or endemic)
-susceptible to stomach acid so must ingest large quantities of bacteria
Vibrio cholerae pattern and transmission
-both an endemic and epidemic pattern
-transmission through contaminated food and water, person-to-person transmission unusual
-lives in aquatic environments attached to algae or crustacean shells via surface protein
-multiplies when temperature, salinity, and nutrients are suitable
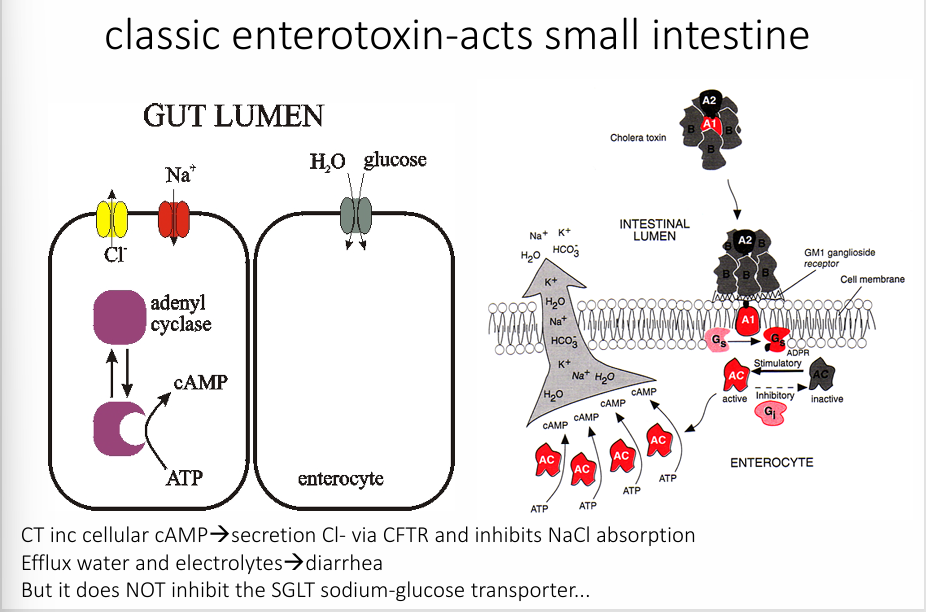
cholera pathogenesis
-consume water or fecally-contaminated food
-incubation usually 1-2 days (2 hr to 3-5 days incubation period)
-survive the acidity of the stomach
-get to the small intestine where they bind to the epithelium via pili including toxin-coregulated pillus (TCP) and aggregate to protect them from bile
-secretion of cholera toxin
cholera toxin
Yemen
-largest cholera outbreak in modern times
->1 million suspected cases
->3000 deaths reported since 2017
-due to civil war
Escherichia coli
-enterobacteriaceae
-lactose-fermenting GN rods
-pili
-flagella
-many toxins (may include shiga like toxins STX-1 and STX-2 toxins)
-found in human and GI tracts of many animals including cattle, the main reservoir for EHEC
E. coli types

ETEC (enterotoxigenic E. coli)
-840 million cases/year worldwide
-traveller’s diarrhea (30%) cases
-heat-stable (STa) or heat-labile toxin that causes hypersecretion of fluids in the small intestine
-STa: small monomeric peptide, binds to transmembrane guanylate cyclase C receptor on the intestinal epithelium, leading to an increase in cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), inc fluids out, prevents fluids in
-LT1: 80% homology to cholera toxin AB5
-1-2 days incubation, 3-5 days symptoms
-watery, non-bloody diarrhea, cramping
-host cell is NOT invaded by whole bacterium
EHEC/STEC (enterohemorrhagic E. coli)
-low inoculum (<100)
-attaches to epithelial cells
-injects several proteins via type III secretion apparatus including: Tir which then appears at the epithelial cell surface and serves as a receptor for the bacteria (intimin on the bacterium binds to Tir), proteins involved in disrupting and reorganizing host cell actin
-all have lysogenic phase encoding STX-1 and/or STX-2 (binds to 28S ribosome, disrupts protein synthesis, causes cell death of both epithelial cells and capillaries → hemorrhagic colitis; may cause HUS (5-10% children <10 years): shiga-toxin enters the circulation and damages endothelial cells, binds to PMNs, and induces proinflammatory state)
hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
-due to circulating STX (usually STX-2, binds to glomerular epithelial cells): hemolytic anemia with fragmented erythrocytes, acute renal injury, thrombocytopenia, CNS symptoms, HTN
-can cause capillary thrombosis and inflammation/damage colonic mucosa → hemorrhagic diarrhea
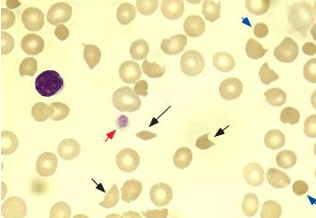
course of EHEC in children
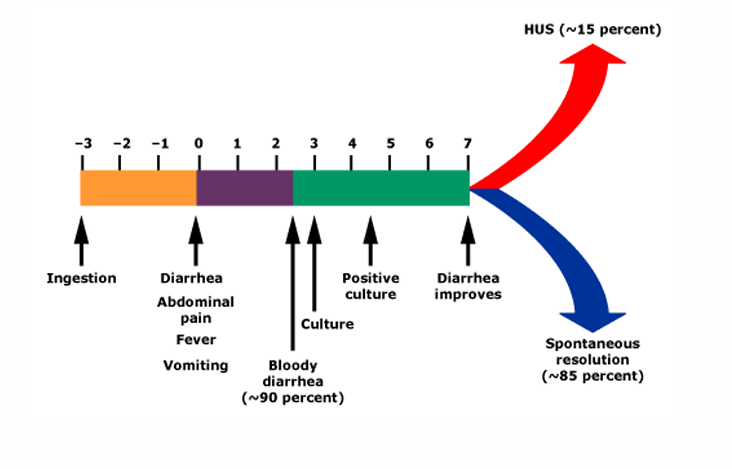
E. coli O157 outbreaks

Shigella clinical manifestations
-12 hours after ingestion, bacterial multiplication begins in the small intestines resulting in abdominal pain, cramping, watery diarrhea, and fever
-as the colon is invaded → onset of severe lower abdomen pain, accompanied by urgency, tenesmus, and blood mucoid stools (dysentery)
-resolution of fever in a few days
-illness lasts for average of 7 days
-colonic shedding for 1-4 weeks
-antibiotics can reduce shedding
Shigellosis transmission
-contaminated: hands, food, water (sewage)
-oral-anal contact
Shigella characteristics
-small non-motile GN rod, member of Enterobacteriaceae, tribe Escherichieae (human host or non-human primates)
-very similar to E. coli, except no flagella and they are non-lactose fermenteres
-40 serotypes, 4 species: Shigella sonnei (most U.S. cases), S. flexneri (developing countries), S. dysenteriae, S. boydii (less common)
-S. dysenteriae type A1 is most virulent and potent producer of STX (shiga toxin): usually found in tropical, developing areas
Shigella pathogenesis
-low inoculum (<200 organisms, few as 10): person-to-person spread, direct fecal contamination of food, secondary cases common
-acid resistant
-invasion of intestinal epithelial cells, moving from small to large intestines, with multiplication and mucosal destruction including ulceration and abscess formation
-enterotoxin AND cytotoxin elaboration (STX)
-penetration beyond mucosa is rare
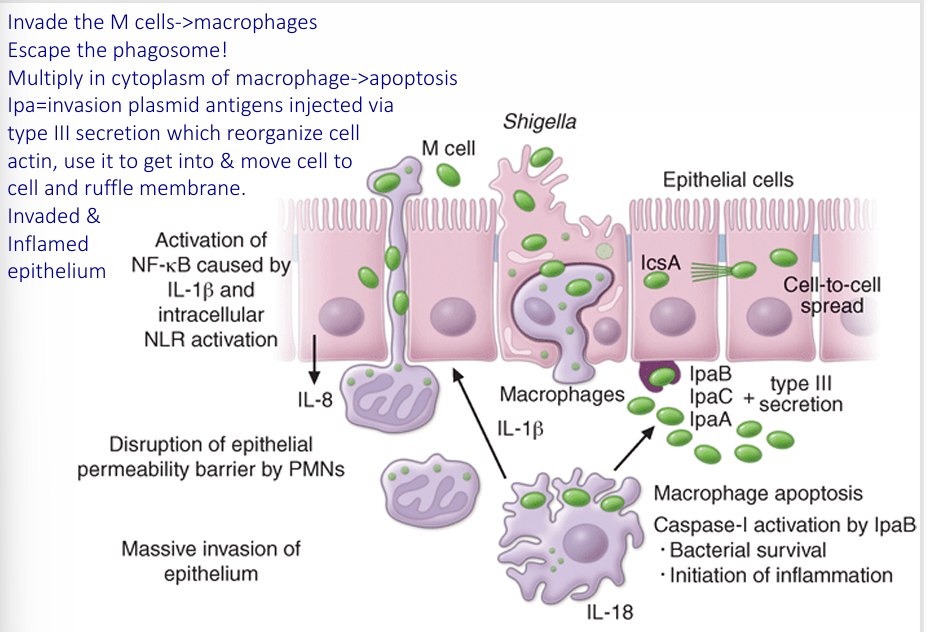
pathogenic mechanisms
-2 enterotoxins, but also a cytotoxin: shiga toxin (STX)
Shiga toxin (AB5 toxin)
-produced by S. dysenteriae 1
-not necessary for virulence
-B subunit binds to host cell glycolipid (Gb3) and facilitates transfer of A subunit
-A subunit disrupts the protein synthesis by preventing binding of aminoacyl-transfer RNA to the 60S ribosomal subunit
-results in destruction of intestinal cells and villi, decreasing intestinal absorption
-similar to STX-1 and can be associated with HUS
salmonella
-microbiology-member Enterobacteriaceae
-GN, facultative anaerobic rod
-S. enterica has numerous serovars

clinical manifestations of Nontyphoidal Salmonella

typhoid fever- clinical manifestations of S. typhi and S. paratyphi
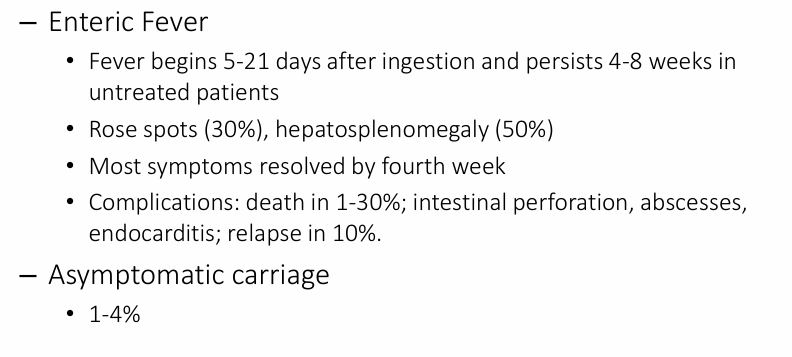
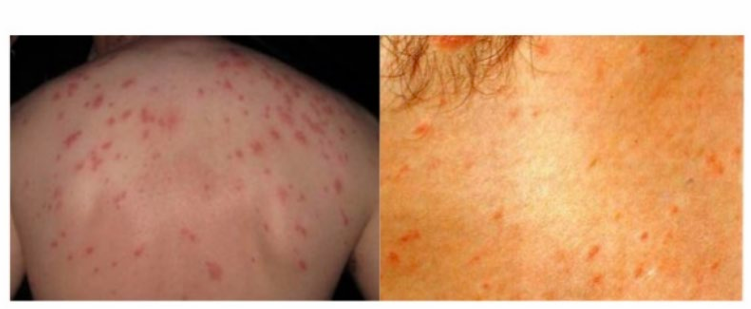
-Rose spots- bacterial emboli to the skin
-rash of Typhoid fever
salmonella pathogenesis- tissue invasion
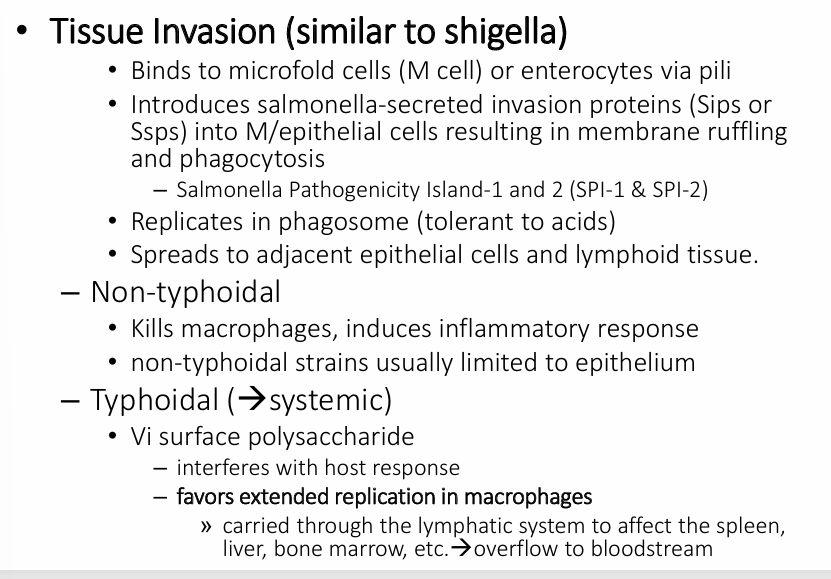
salmonella pathogenesis
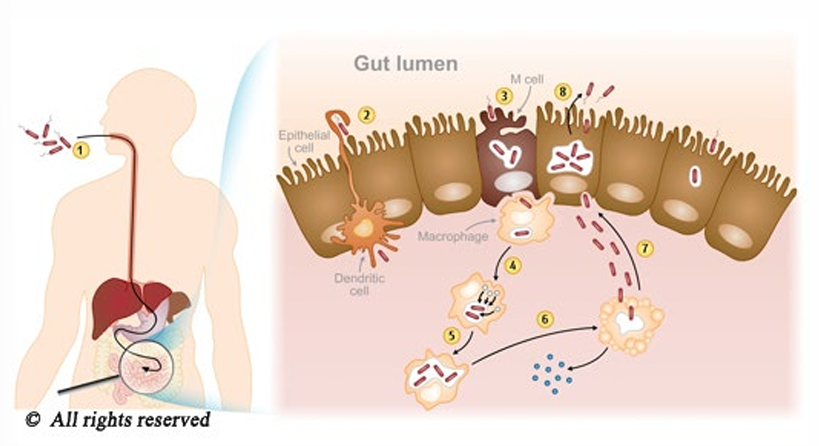
approach to patient with acute diarrhea
-don’t usually present, but if they do…
-history:
-clinical features: onset (abrupt, gradual) and duration, stool characteristics and frequency, associated symptoms, systemic symptoms (thirst, tachycardia, orthostasis, decreased urination), lethargy, altered sensorium)
-epidemiological features: travel to developing areas, consumption of unsafe foods or water, illness in others with common food source, sick contacts, oral-anal sexual contact, recent antibiotics or hospitalization, underlying medical conditions, on laxatives?
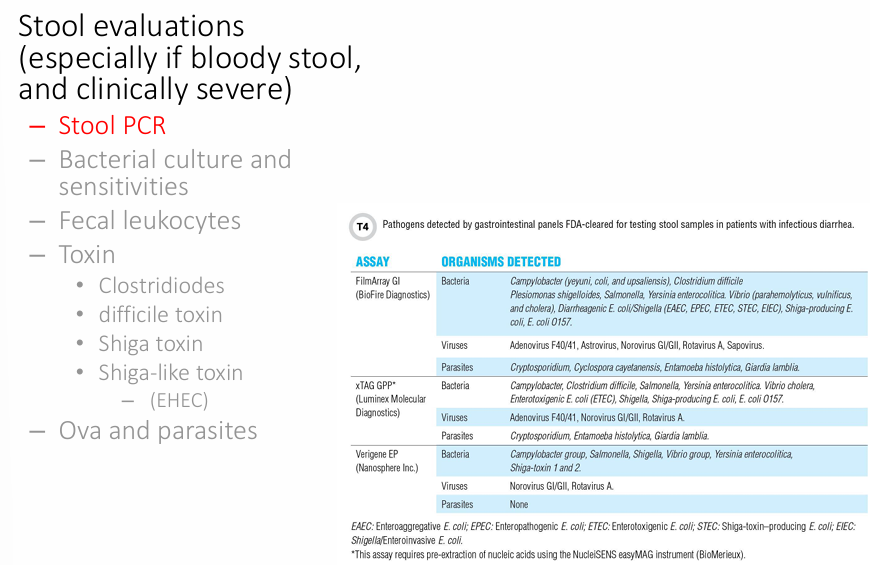
-stool evaluations
diarrhea treatment
-rehydration most important
-antibiotics: moderately-severe invasive disease (shigella, campylobacter, salmonella), avoid antibiotics for EHEC
take home points
