4. Effect Size and Power
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is an effect size?
An effect size measures how big or important a result is — not just whether it’s statistically significant.
Where a p-value tells you if an effect exists, the effect size tells you how much of an effect there is.
Gives the practical importance of a result
What is an effect size in terms of explaining variance?
effect size expresses the proportion of variance in one variable that is accounted for by another variable (or set of variables).
So, if an effect size = 0.25, that means 25% of the variability in the outcome is explained by the predictor(s).
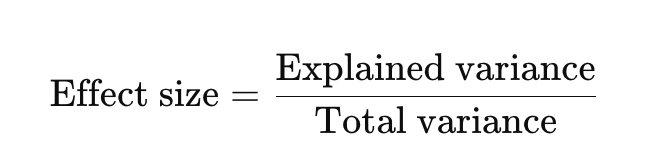
What is the measure of effect size used for correlations and regression?
r or R squared
What is the measure of effect size used for t-tests?
Cohen’s d
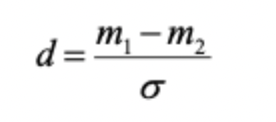
What is involved in Cohen’s d?
d is the difference in means - scaled by the standard deviation
a standardised score (similar to z-score but conducted on means rather than individual scores)
because we scale by standard deviation, d does not depend on sample size
What is involved in Cohen’s d for ANOVA?
Cohen’s d for ANOVA is the difference between the largest and smallest group means scaled by standard deviation
note that the standard deviation is assumed to be constant across groups
What are the 3 various conventions to decide on SD for Cohen’s d for ANOVA?
averaging the group SDs
taking the smaller SD
pooling the variances
What is Eta squared used for and what does it provide us with?
used for a one way ANOVA
the proportion of variance explained by your experiment
What is Partial Eta Squared used for and what does it tell us?
Used with factorial ANOVAs
SPSS will give this in ANOVA table
tells you the proportion of variance that is uniquely explained by each IV
What are the Eta values scaled between?
scaled between 0 and 1
What is power analysis?
Power analysis is a statistical method used to determine how much data (sample size) you need to reliably detect an effect if one truly exists.
It’s about making sure your study isn’t too small to find a real effect or so large that you waste resources.
What is the core concept of statistical power?
Power of a statistical test
ability to detect an effect when it is actually there
ability of a test to correctly reject the null hypothesis
What are the 3 factors that power depends on?
sample size (n)
effect size (d)
criteria for significance (alpha level)
What occurs if studies are underpowered with too few participants?
lack of power to detect effect - type 2 error (false negative)
increased chance of type 1 error (false positive)
What happens if we estimate power across many published studies?
It is often worryingly low
e.g. in neuroscience, Button et al estimated the median power of studies is around 0.08-0.31
Low power and replication crisis
Low power explains failure to replicate.
when only significant low-powered results get published, the literature becomes filled with inflated and unreliable effects — explaining why replications (which use larger samples) often find smaller or null effects
How does power analysis relate to ethics?
Demonstrating your study has sufficient power is often a requirement for ethical approval
there is no justification for running a study if it doesn’t stand a reasonable chance of being informative
What happens to power when sample size increases?
when sample size increases so does power
more participants = increased chance of finding a significant effect (if there is one)
we can also ask how many subjects we need to detect an effect of this size at a given power
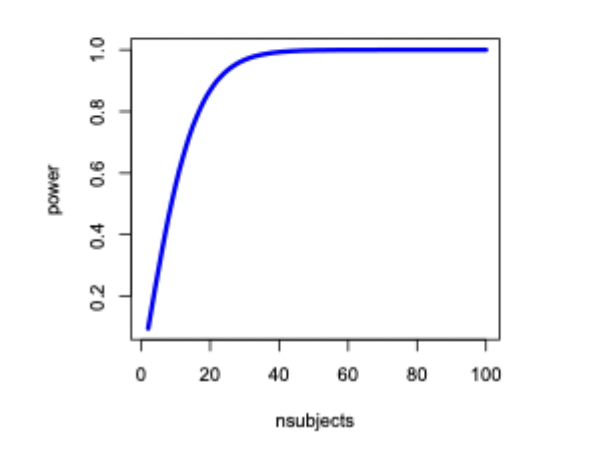
What level of power is typically considered good?
0.8
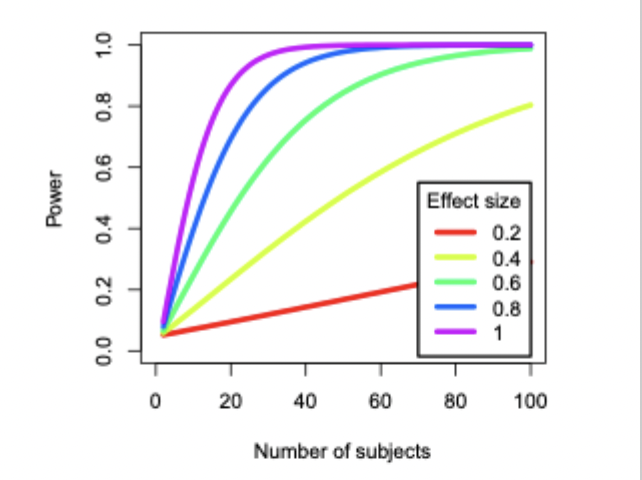
How does effect size relate to participants and power?
smaller effect sizes need more participants to achieve higher power
if we know two of these things we can estimate the other
How can we approximate effect size when there is not much literature on your phenomenon?
Guess/approximate
could use cohen’s heuristics
not very satisfying or likely to be informative
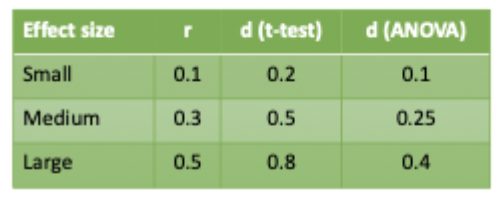
How can we use a pilot study to estimate effect size?
run a pilot with fewer participant to estimate the effect size
doesn’t matter if this study comes out significant, you cant still get an estimate or r
you can use this estimate to project how many participants you should test
but estimates of effect sizes are largely unreliable with small samples
How can we use previous studies to estimate effect size?
do a literature search
look for studies investigating similar phenomenon
use their results to work out an expected effect size for your experiment
a-priori power estimates are not exact but better than guessing
How can finding or conducting a meta-analysis allow us to estimate effect size?
Do a literature search
if there are many previous studies you can calculate an average effect size across all of their results
if meta-analyses have already been published, effect sizes can be taken from these
What might happen to estimates of effect size for complex designs (factorial)
unlikely you will have sufficient precision in your estimates of effect size
main effect and interactions/ power analysis may not be meaningful
What’s involved in calculating how many participants are required for a study?
given effect size, power, alpha
What is involved in calculating the minimum required effect size detectable?
given power, sample size, and alpha
What is involved in calculating observed power?
Given effect size, alpha and sample size
Which software do we conduct power analysis in?
G*Power