2.1.2- designing, creating and refining algorithms
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Write a program to calculate the volume of a fish tank based on its dimensions and report the results back to the user
identify the
-input
-process
-output
input- length:real/float
height:rela/float
width:real/float
lengthxheightxwidth
output: volume:real/float
write a program that will ask the user for the number of students in their class and then prompt to enter each their test scores in a range 0-100. It should then output the highest, lowest and average score to user
identify
-input
-process
-output
-NumofStudents:integer
CurrentScore:integer
-process-TotalScore=TotalScore+CurrentScore
AverageScore=TotalScore/NumOfStudents
store list of scores in an array and loop through array and return min score and max score
-output; MinScore:integer
MaxScore:Integer
AveScore:real/float
Input
-anything which needs to be supplied to the program so that it can meet its goals
-often input from the users
-consider an appropiate variable name and data type for the input
processes
-consider what calculations need to be performed while the program is running
-does data need to chnage formats or data types
output
-consider what your program needs to output
-consider what form this output needs to take -consider an appropiate variable name and data type for any output
what are structure diagrams
-illustrate problem decomposition
-can be used for developers to understand a problem to code and and to share with users during systems analysis
-produced using a method called step-wise refinement
-lowest level of nodes should achieve a single task
what are pseudocodes
text-based way of representing the sequences of steps in an algorithm without worrying about the syntax or rules of a particular language
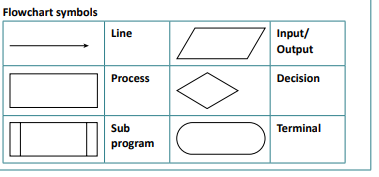
state the flowchart symbols
what is a global variable
identifies a variable that can be used in a subroutine or function instead of it being declared inside the function or subroutine which would only make it available to a particular function
constants
these are values that don’t change throughout the life of the program
-do not say that they are variables
difference between while loop and do loop
a while loop will not necessarily have its code executed but the condition is checked at the beginning of the statement, whereas with the do loop the code inside the loop will execute at least once because the condition is checked at the end of the statement
memorise ocr exam reference language
okay
what are the two main types of error
-syntax
-logic
what are syntax errors
are errors which break the grammatical rules of the programming language
-they stop it from being run/translated
what are logic errors
errors which produce unexpected output
-on their own they won’t stop the program running
const voting_age=18
your_age=(input(“how old are you?”))
if (your_age>=voting_age) then
print(“you are old enough to vote”)
else
print(“you are not old enough to vote”)
endif
-spot what the error is
-is it syntax or logic
-missing a type conversion from string to integer
-syntax error
what are trace tables
typically involves examining a printed extract of program code and running through the program