earthworm action potentials
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
why measure action potentials
To show how nerves operate
Action potentials are the way that nerves transmit information
Clinically Useful – To detect nerve malfunction in patients
with neurological disorders
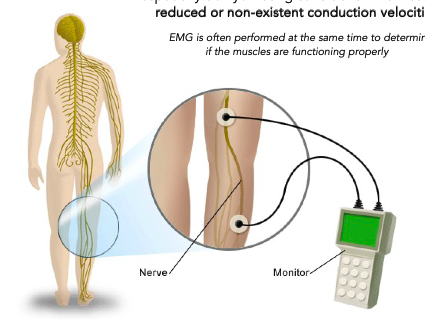
nerve conduction velocity tests
Used for diagnoses of various neuropathies, especially demyelinating conditions which result in reduced or non-existent conduction velocities
measures when an AP passes one part of the nerve and pick it up when it reaches the next part (if you know th distance too, you can measure the velocity)
EMG is often performed at the same time to determine if the muscles are functioning properly
why send signals with action potentials
its faster
Action Potentials aren’t the only way for cells to communicate
…diffusion of ions/hormones
• In single-celled animals, simple diffusion is sufficient
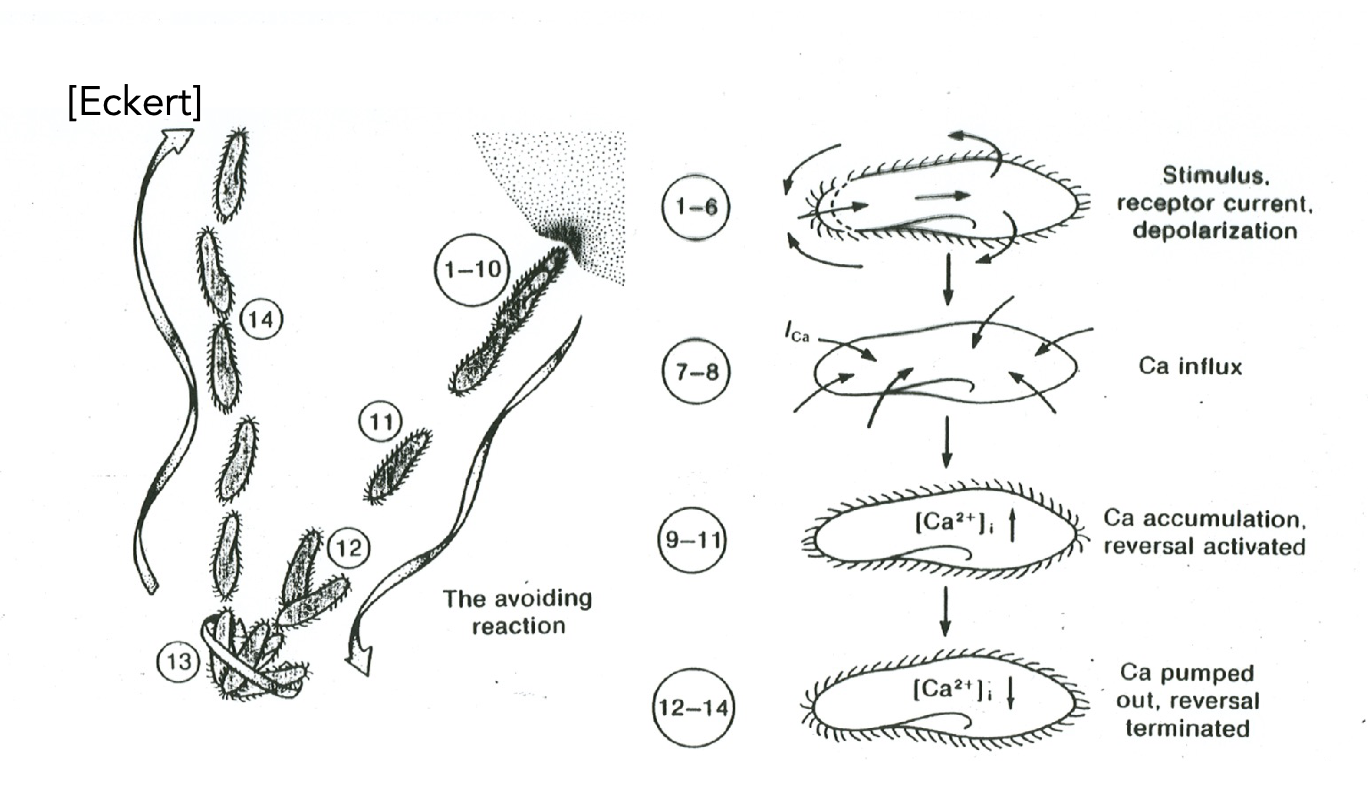
paramecium
single cell animal – behavior depends on internal Ca2+Diffusion is proportional to the square of the distance,
covered in cilia that’s moving, causing the paramecium to swim through the liquid environment
when the paracmecium runs into something, Ca+ channels open and Ca+ comes in, leading to reversal in the stroke of the cilia, so the paramecium swim in the opposite direction. until the Ca+ is pumped back out, to its original level, then the paramecium continue to swim in the forward direction
so, it is too slow for use in larger animals
action potentials
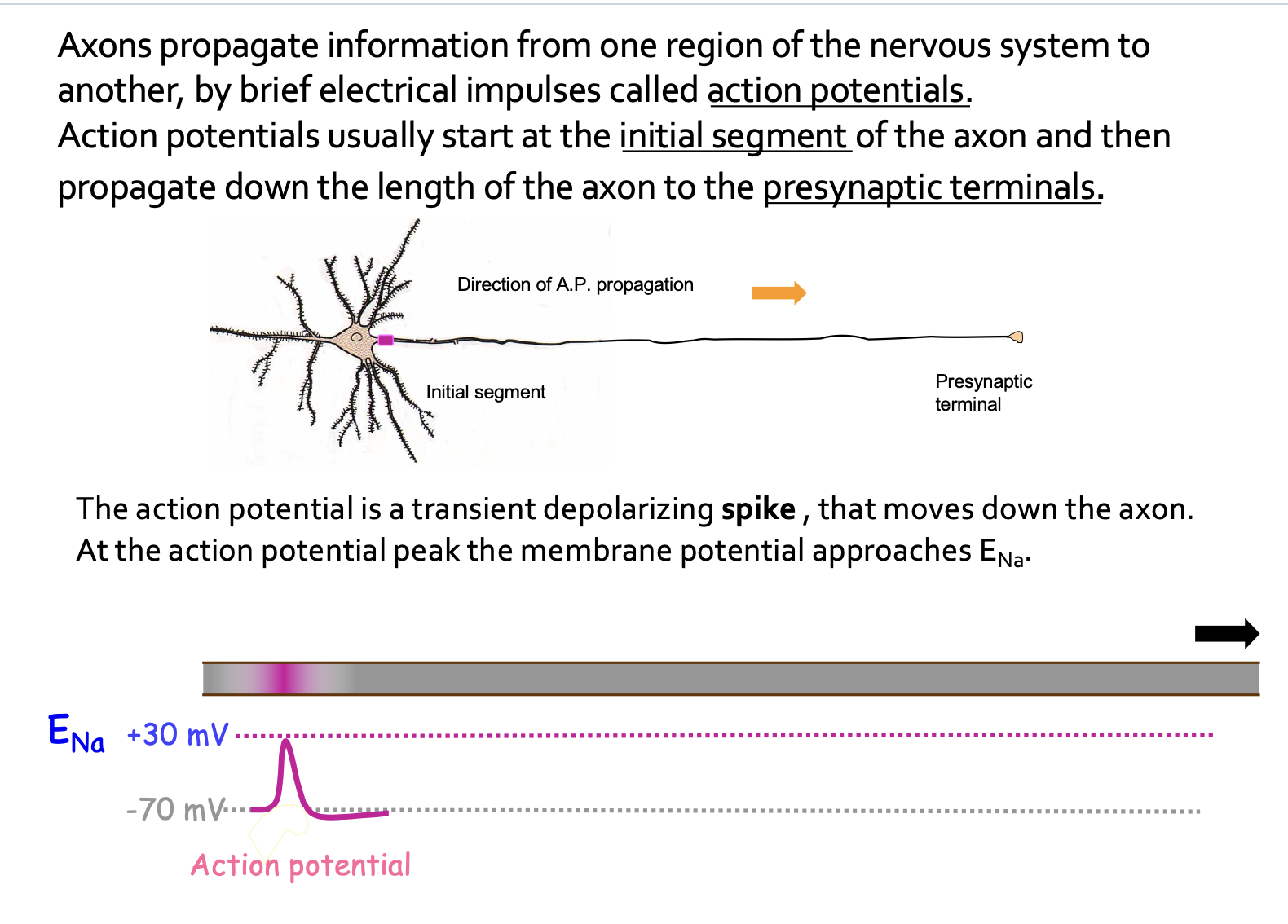
graph of action potential
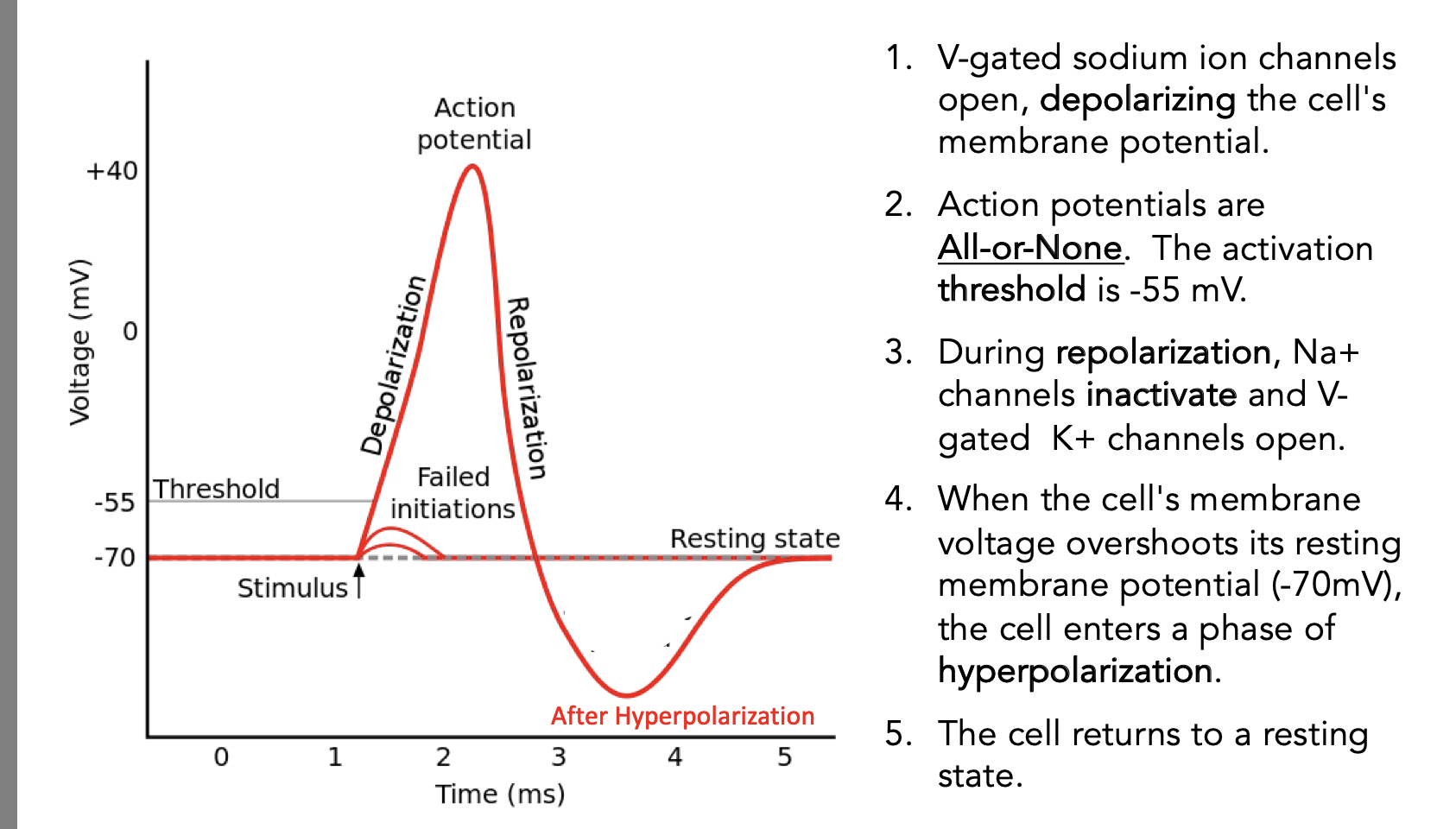
refractory periods
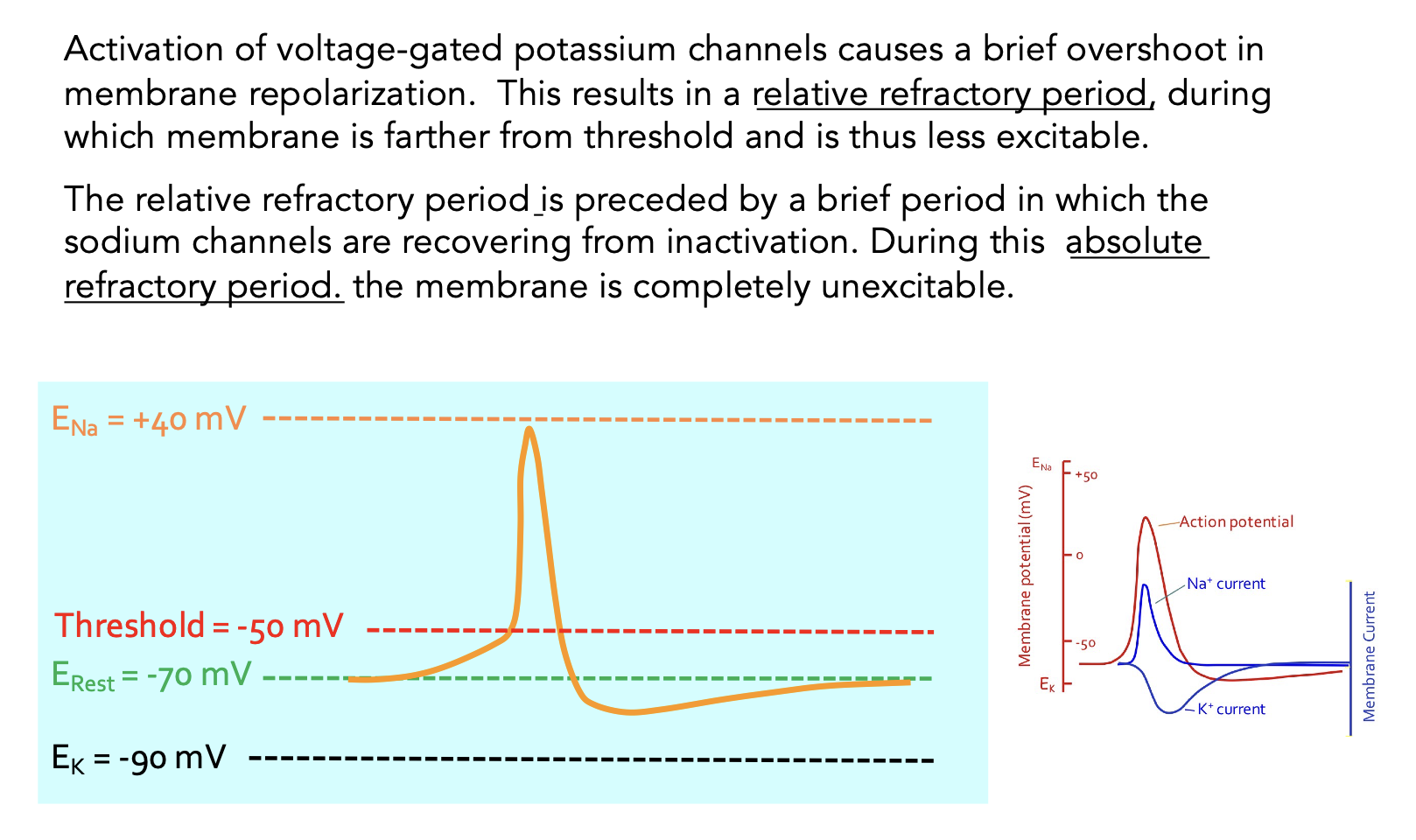
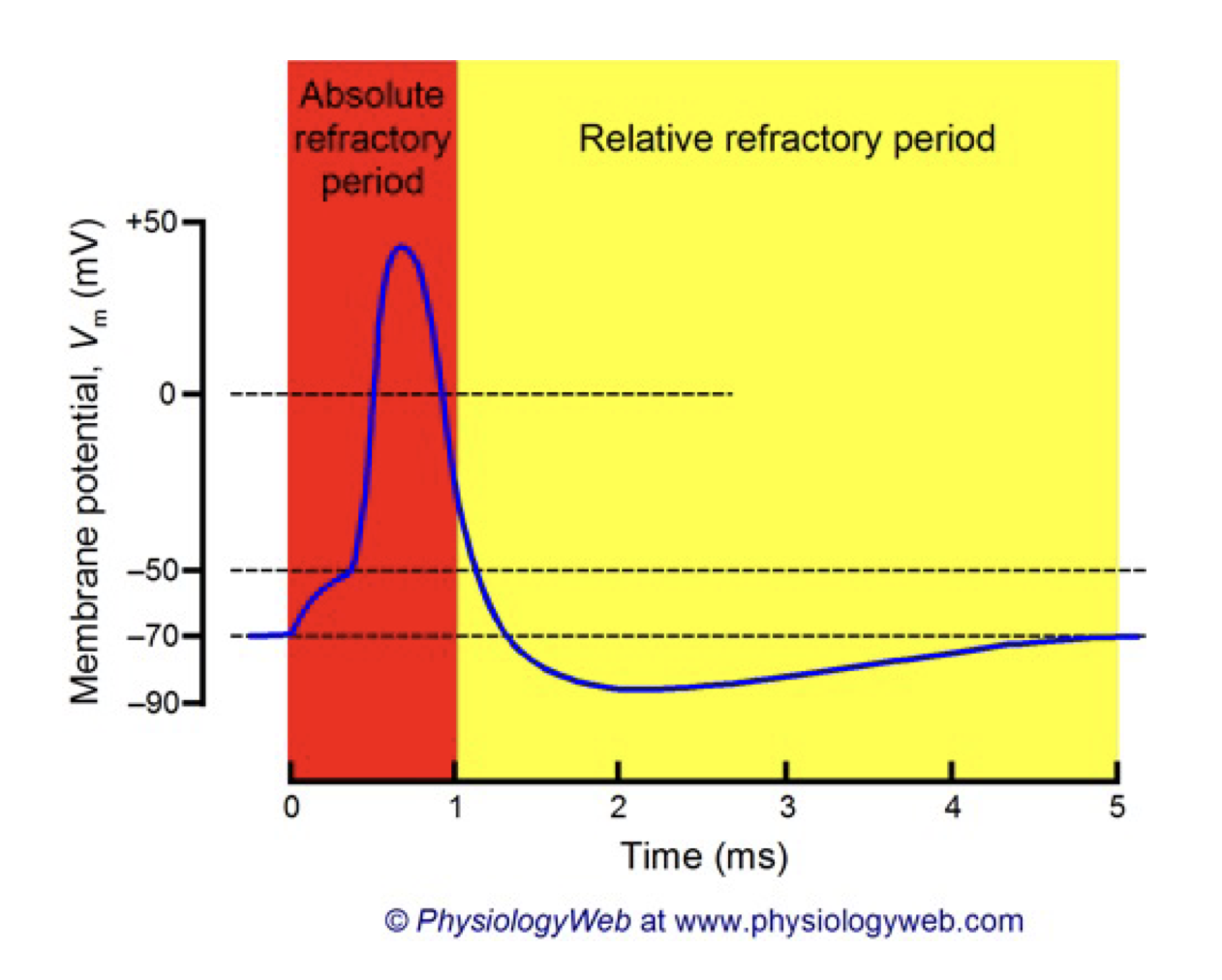
relative vs absolute refractory period
Refractory Periods are due to the inactivation properties of V-gated Na+ channels and the lag in K+ channel closing. While the Na+ channel is in an inactive state, it will not open in response to depolarization. This the absolute refractory period. After this period, there are enough Na+ channels in the closed (active) state to respond to depolarization. However, K+ channels that opened in response to repolarization are still open which keeps the membrane hyperpolarized. During this time, the membrane has a higher threshold for AP firing. This is the relative refractory period
intracellular recording
A single glass pipette is inserted into a cell and the potential is measure with respect to an extracellular reference electrode. Best used for large, invertebrate cells
extracellular recording
involves placing the stainless-steel recording electrode near the excitable cell and placing the reference electrode in the extracellular fluid. This records potential changes at the membrane surface. Advantage: Relatively easy to do, does not damage the cell.
drawbacks of EC recording
Potentials measured are smaller (microvolts vs. millivolts)
AP waveform depends on the geometry of the cell with respect to the electrode
Best suited to measuring:
1) that an AP has occurred or,
2) recording the activity of a population of cells
biphasic APs
Both intracellularly- and extracellularly-recorded APs are biphasic: they have both positive and negative portions
With intracellular recording, the negative phase of the action potential is due to
the opening of Kt channels - causing cell hyperpolarization
With extracellular recording, the negative phase of the AP is due to way in
which it is recorded:
Two wire recording electrodes (R1 and R2) are placed near the nerve, each connected to one input of the differential amplifier
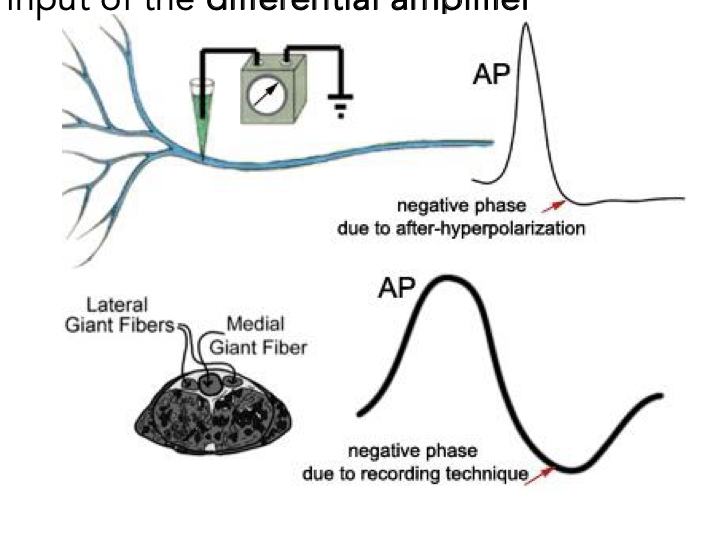
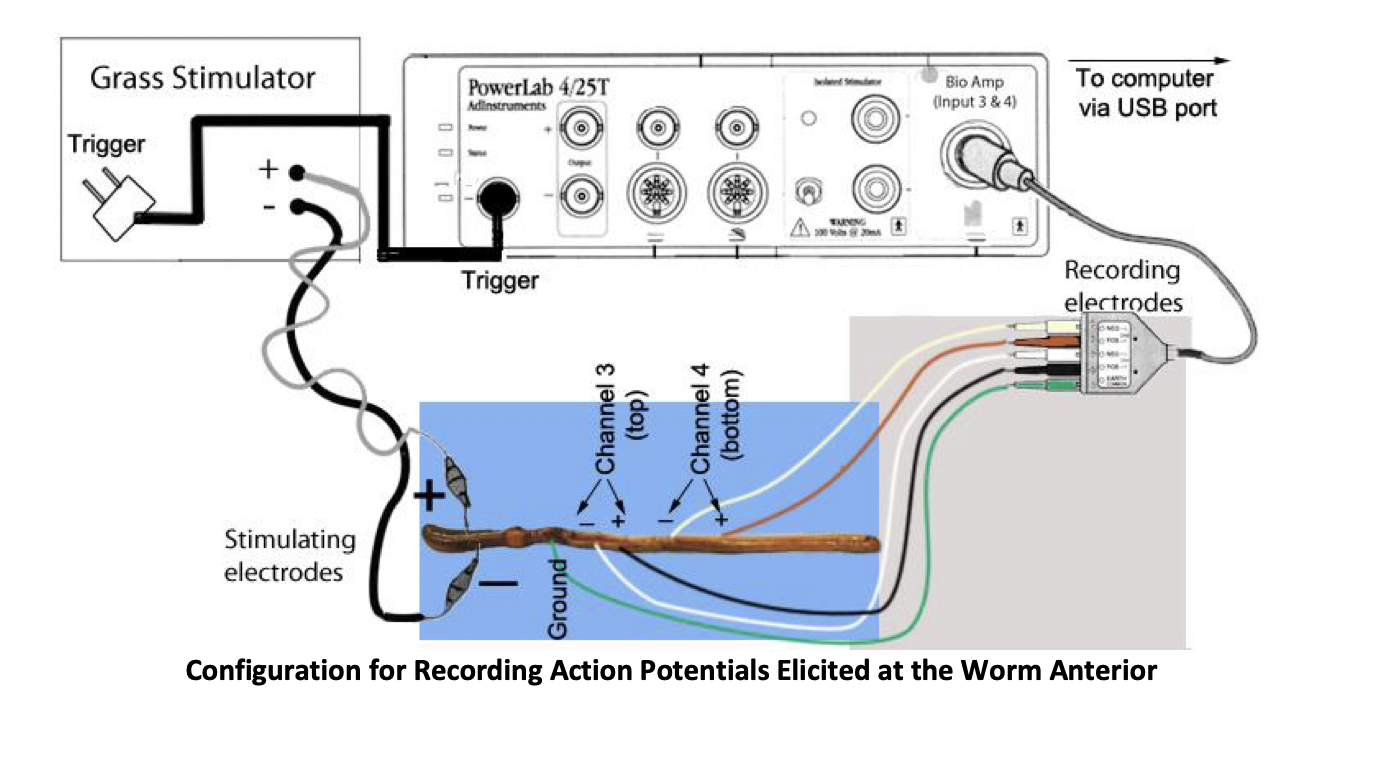
experimental setup
Electrical stimulation of the earthworm ventral nerve cord using two pairs of stainless-steel pin electrodes placed near the nerve, recording the potential difference between the two points on the nerve
first use grass stimulator, when we reach the threshold, we produce an action potential

vertebrate nerves
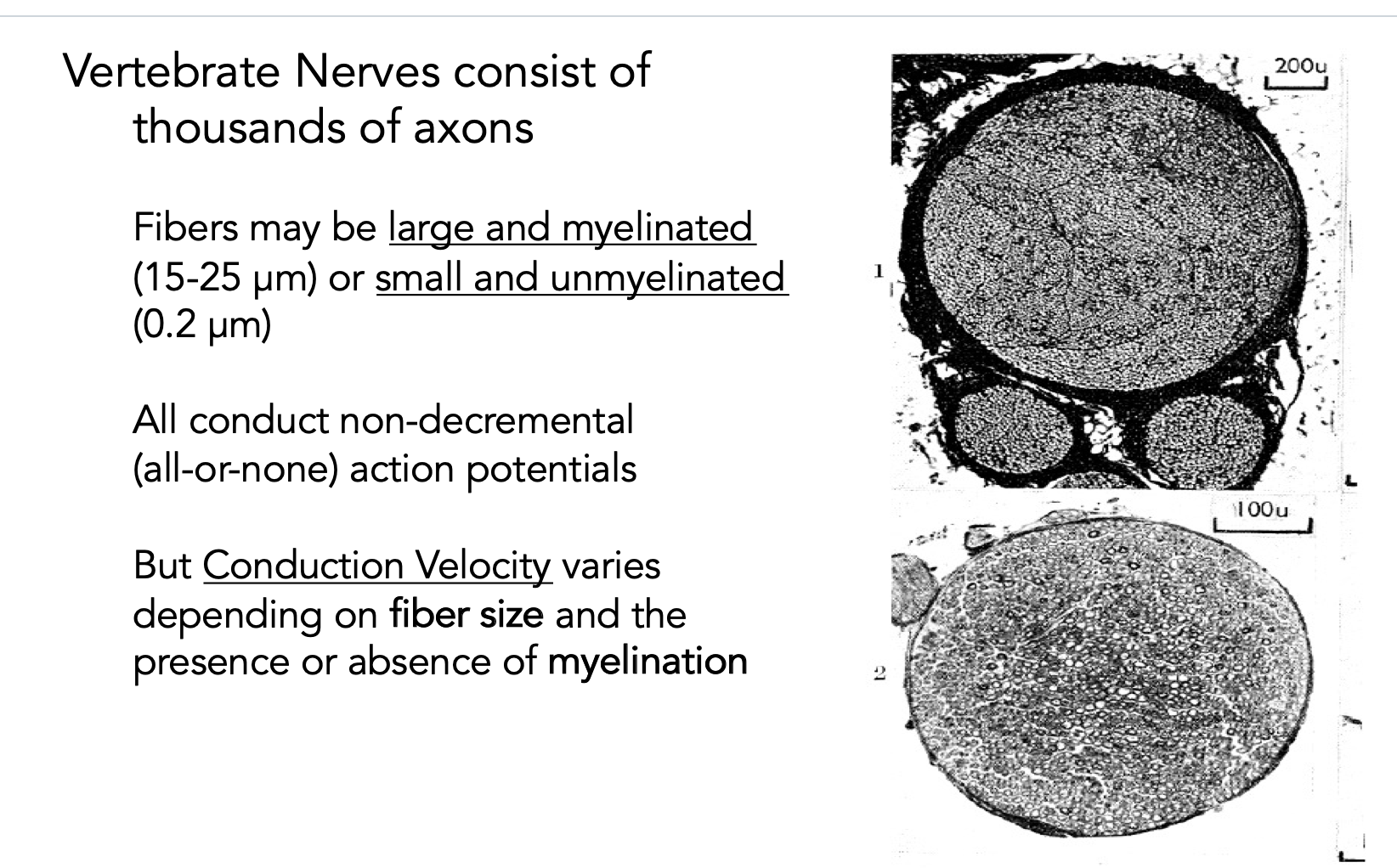
if myelinated, AP faster, if bigger fibre, AP faster
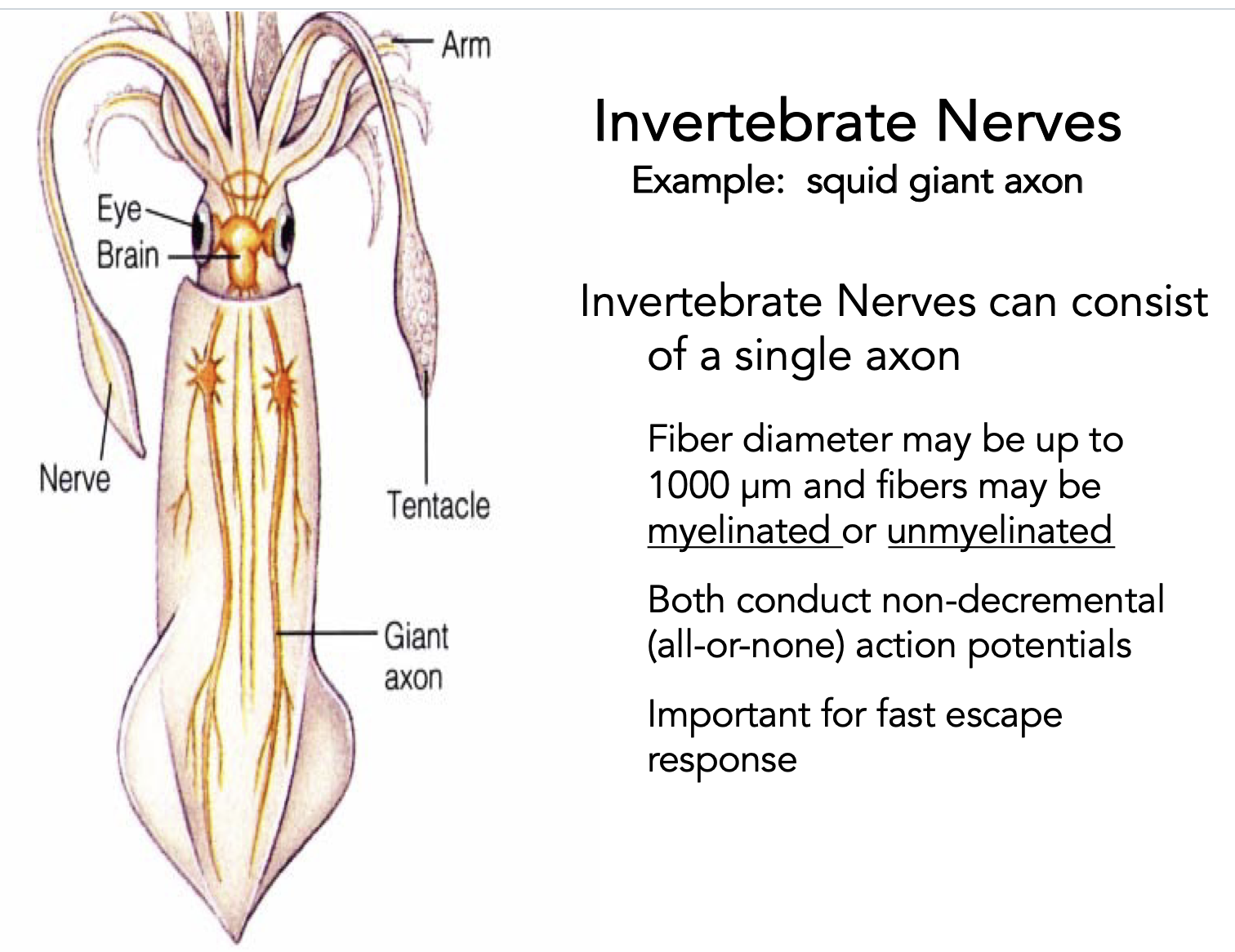
invertebrate nerves
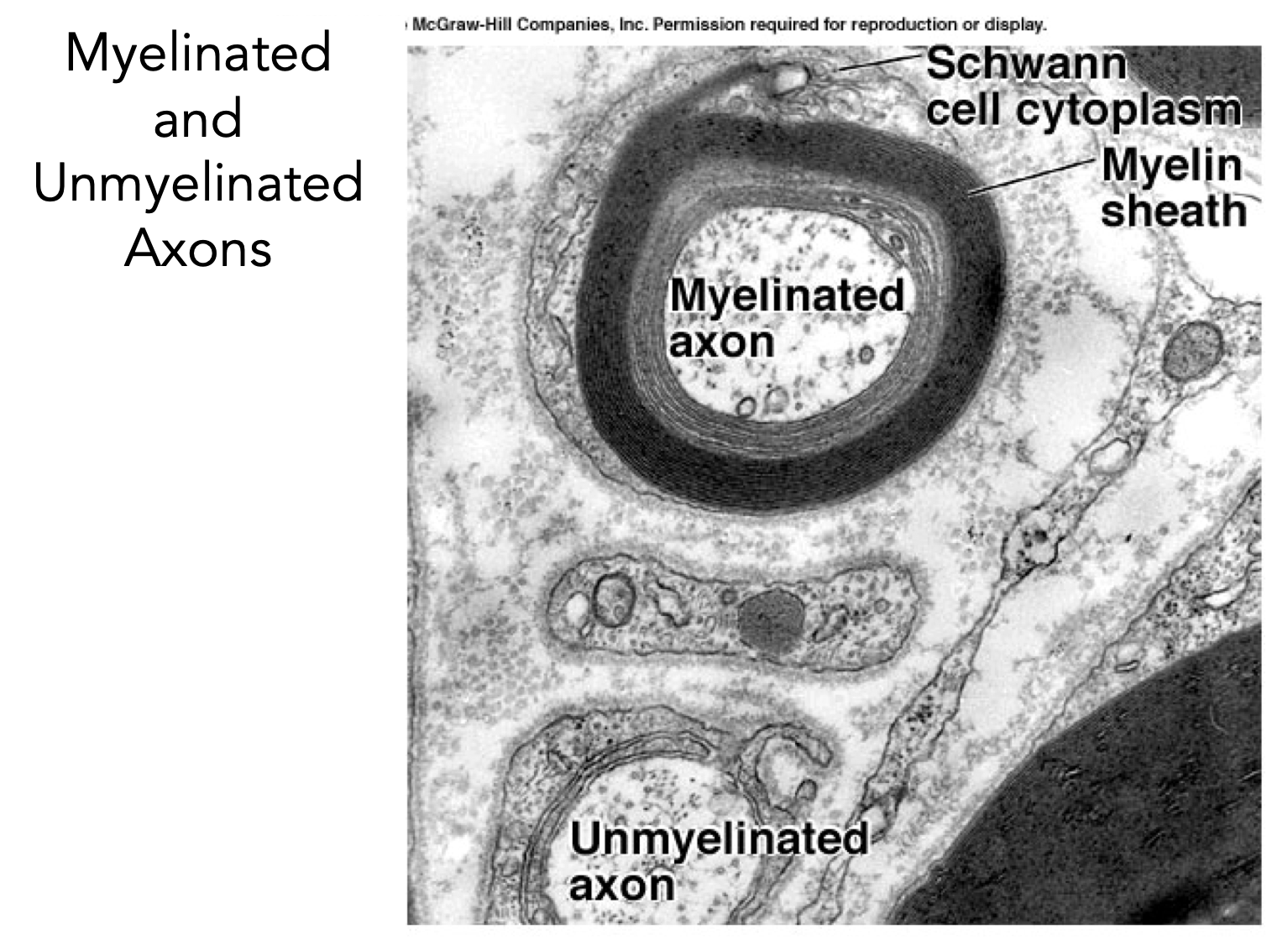
myelinated vs unmyelinated axons
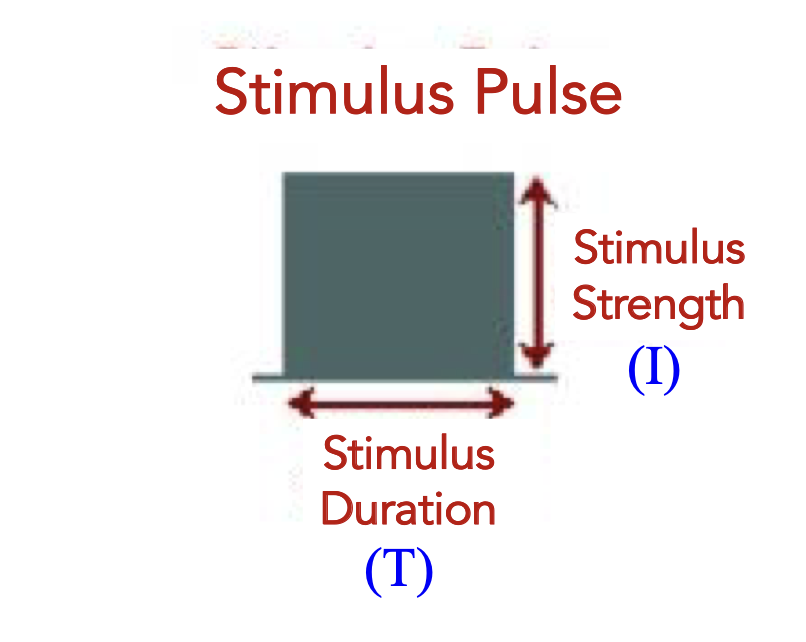
strength duration curve
charge transferred = Q
Q=IxT
amount of charge required to activate the fibre is Qt, and stimulus duration is D, the current It required to achieve activation is It = Qt/D
different vertebrate nerve conduction velocities
different nerves have different speeds, like pressure is faster than pain
grass simulator
only change the duration and amplitude
figure out what the threshold is for your action potential at a given duration and given am[litude
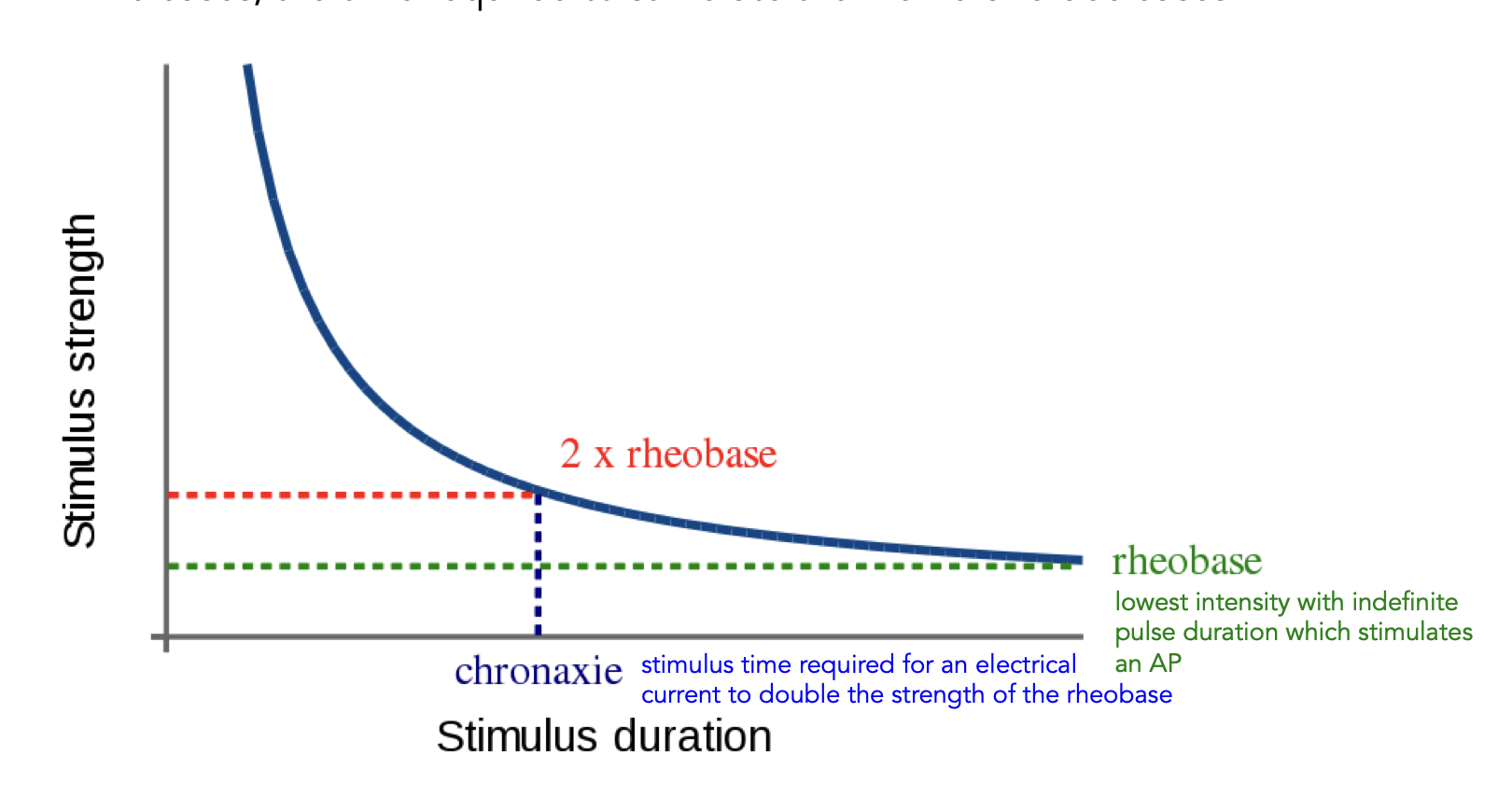
rheobase
lowest intensity with indefinite pulse duration which stimulates an AP
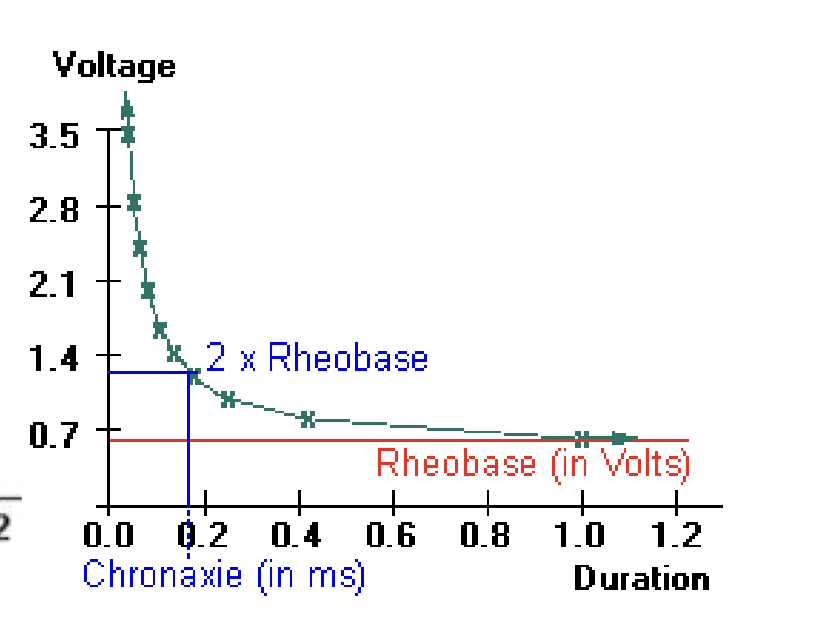
chronaxie
stimulus time required for an electrical current to double the strength of the rheobase

steps of the experiiment
behavioural test to touch head/tail to see what response is
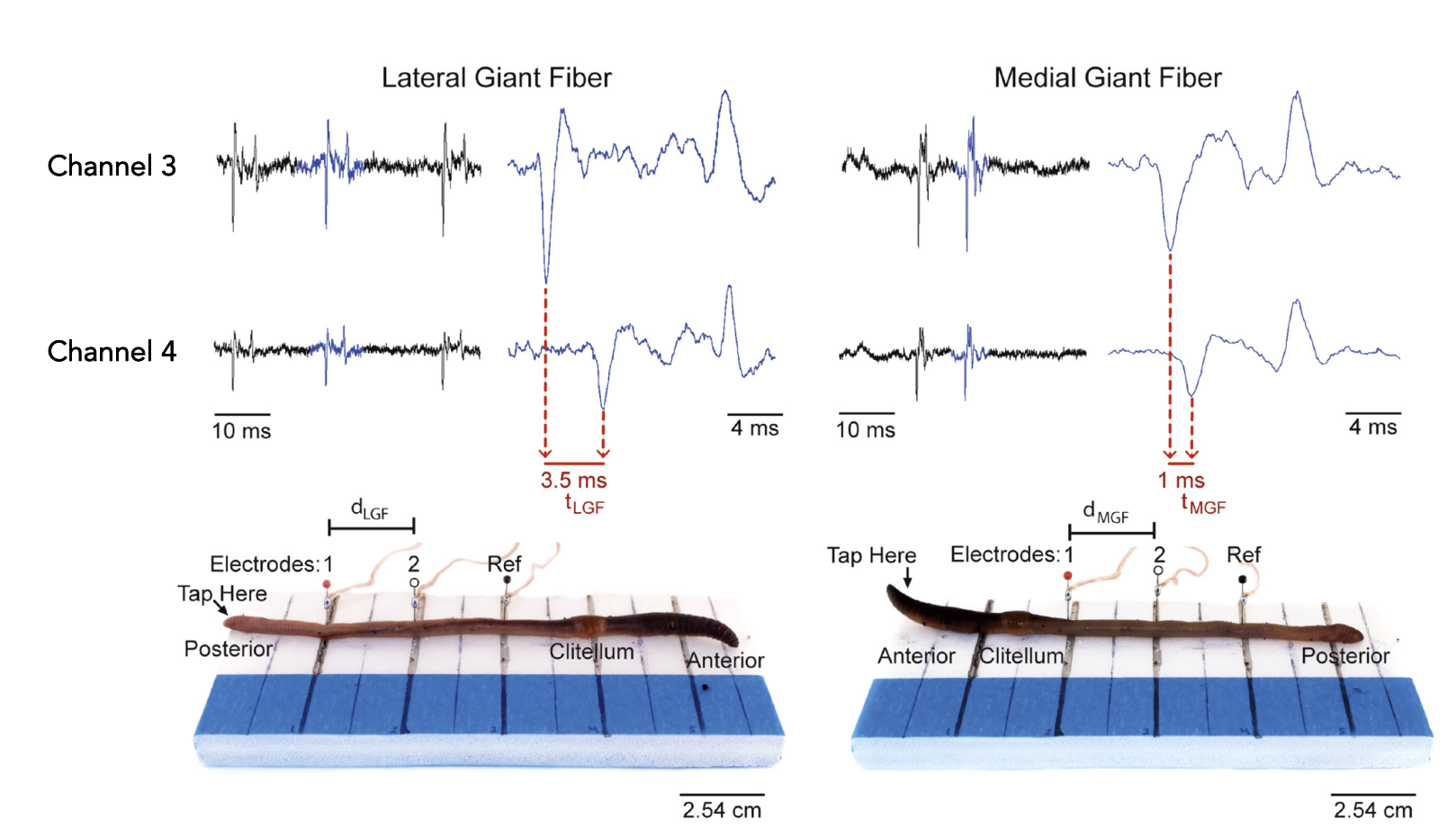
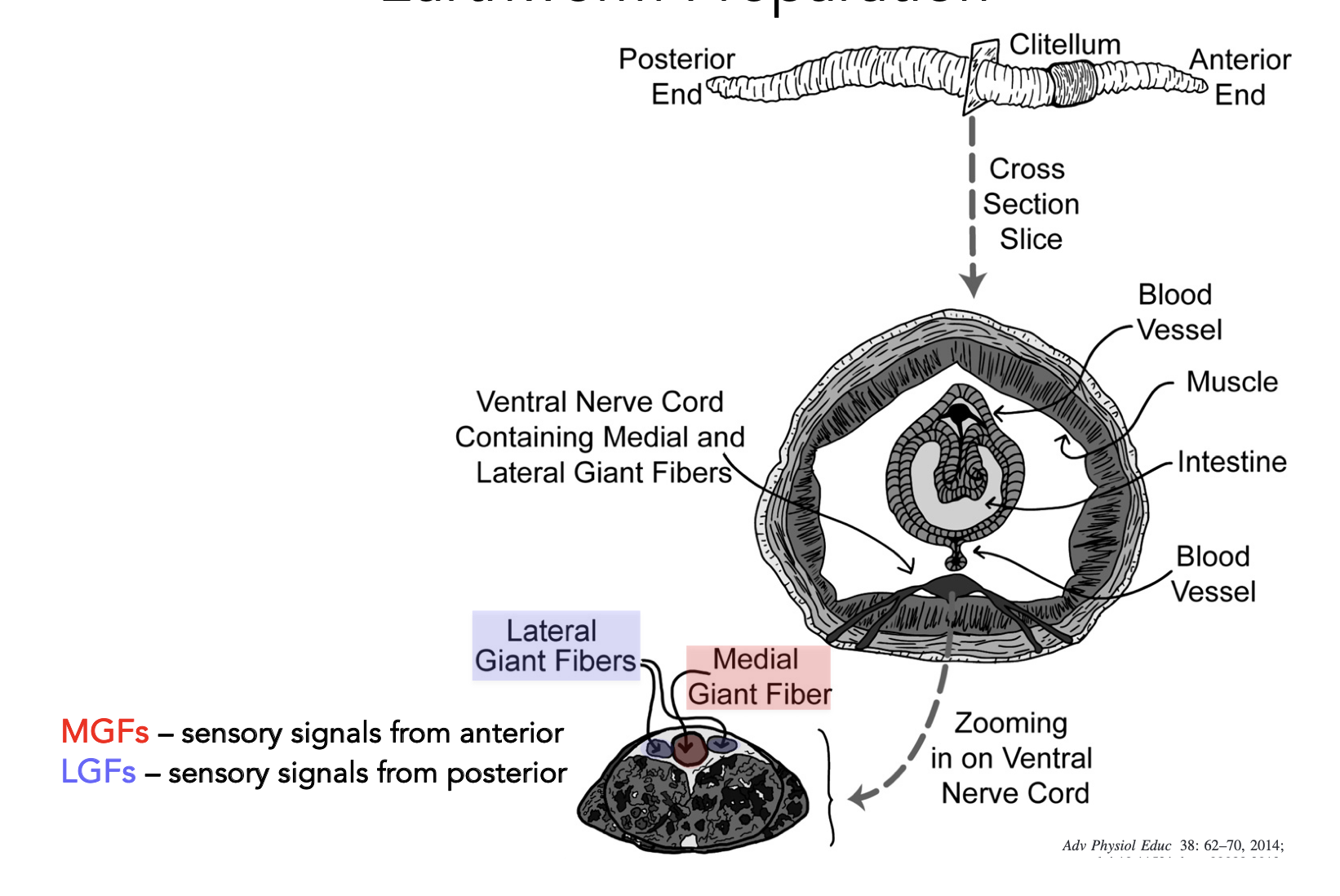
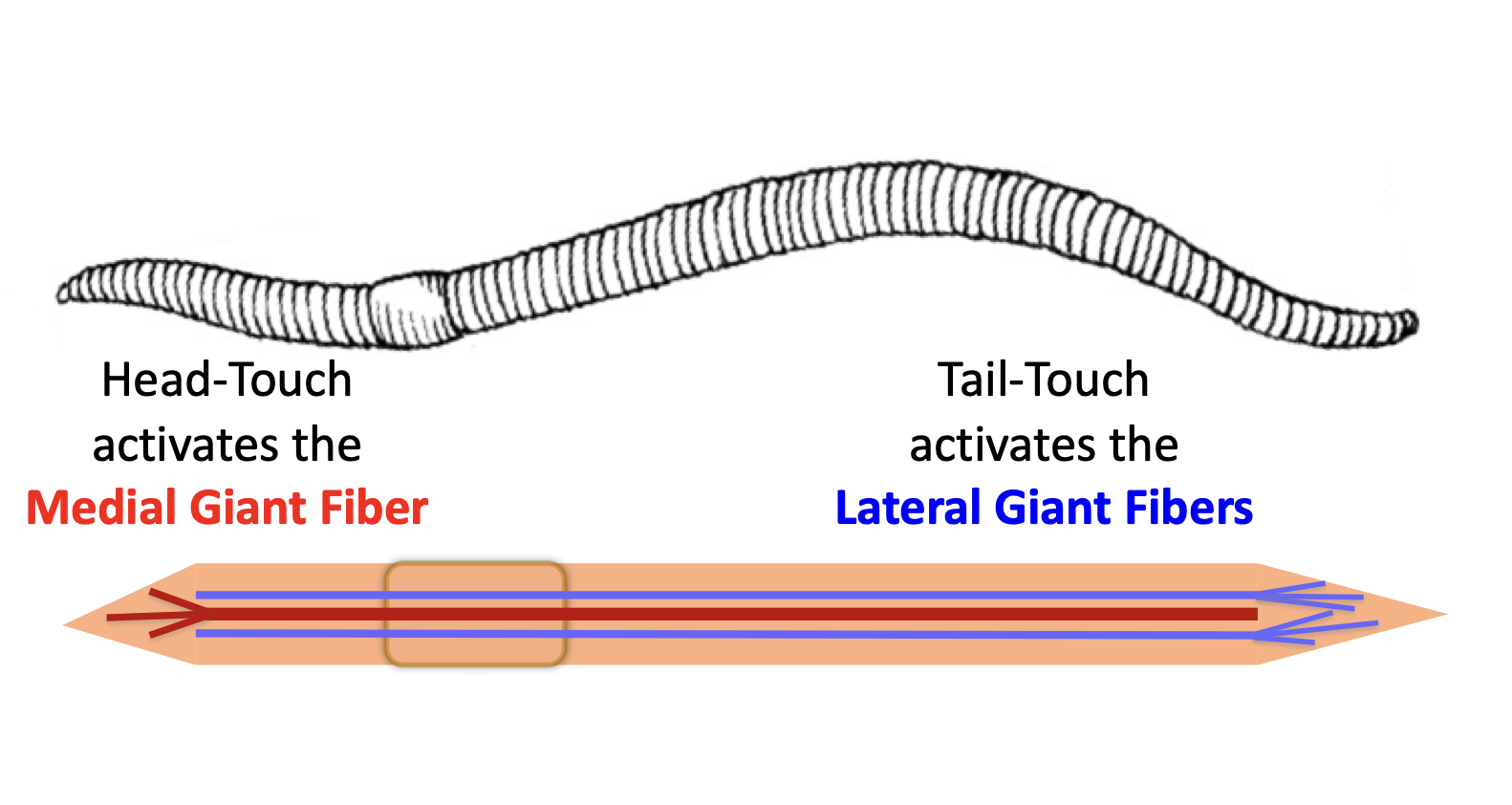
we’re measuring action potentials from the Medial Giant fibre, and two smaller lateral giant fibres
Behavioral Responses – Touch Stimulation
Action Potential Characteristics – Electrical Stimulation
Conduction Velocity – Electrical Stimulation
Strength-Duration Curves – Electrical Stimulation
Action Potential Characteristics – Touch Stimulation
Conduction Velocity – Touch Stimulation
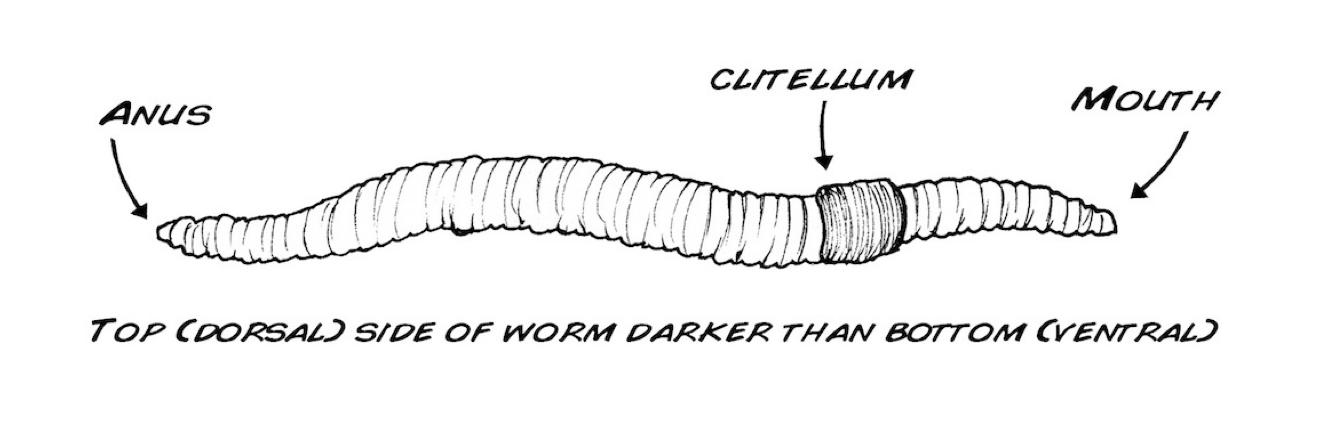
anatomy of a worm
differences in touching vs electrical stimulus
but electrical stimulus would stimulus either MGF or LGF. more likely to activate the larger one so prob MGF
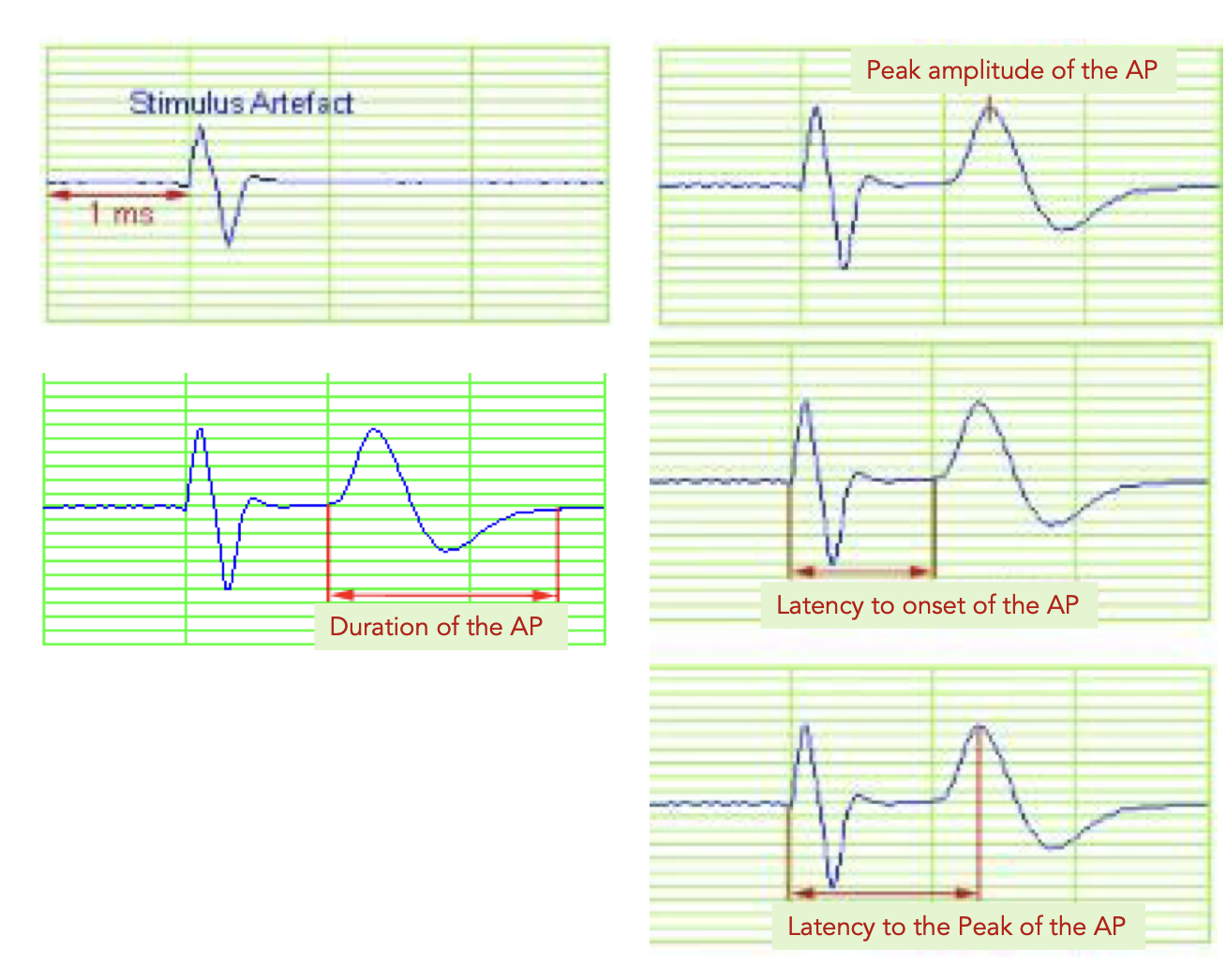
how to read the graphs
measure latency, and duration and distance (speed)
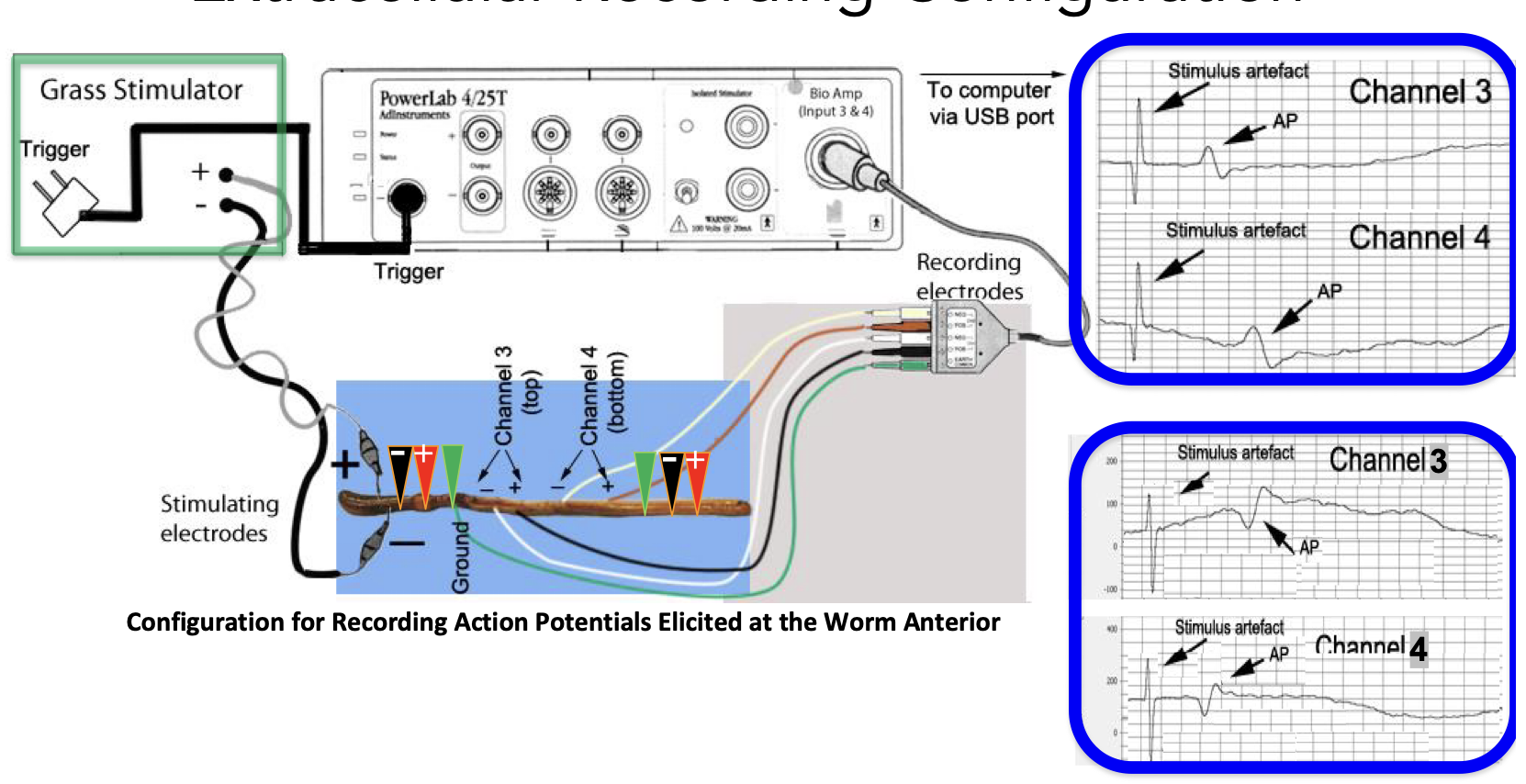
touch stimulation on LGF vs MGF