Topic 3 Bonus quizzes
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
D
Question 1:
What is the purpose of flow control in message timing?
A) To specify the destination of messages
B) To determine the priority of messages
C) To create backup copies of messages
D) To manage the rate of data transmission
B
Question 2:
When a data link frame is created for a communication between two devices on the same Ethernet network, which address does it use for the destination?
A) IP address of the destination
B) MAC address of the destination NIC
C) Hostname of the destination
D) Network address of the destination
C
Question 3:
What are Protocol Data Units (PDUs) called at the Network Layer of the OSI model?
A) Data
B) Segment
C) Packet
D) Frame
C
Question 4:
What is the function of the default gateway in a local area network?
A) To improve network security
B) To assign IP addresses to devices
C) To act as a doorway to other networks
D) To connect devices within the same LAN
B
Question 5:
If a message is too large to be transmitted in a single go, which protocol is responsible for dividing it into segments?
A) IP
B) TCP
C) Ethernet
D) WLAN
A
Question 6:
What type of addressing does the Data Link Layer use for communication between devices?
A) MAC Addressing
B) Logical Addressing
C) Port Addressing
D) Global Addressing
A
Question 7:
Which protocol is primarily responsible for sequencing individual segments in data transmission?
A) TCP
B) HTTP
C) UDP
D) FTP
B
Question 8:
Which addresses change from link to link or hop to hop?
A) IP Addresses
B) L2 Addresses
C) Network Addresses
D) L3 Addresses
ANSWER: B
D
Question 9:
What is the primary purpose of segmenting messages in data communication?
A) To encrypt the data for security
B) To convert data into binary format
C) To enhance the aesthetic of the data
D) To break messages into smaller units for efficient transmission
C
Question 10:
If a computer message is represented as a frame, what analogy can be used to describe this concept?
A) A picture in a frame
B) A document in a folder
C) A letter inside an envelope
D) A book inside a library
Flow Control
manages the rate of data transmission and defines how much information can be sent and the speed at which it can be delivered.
Multicast
one-to-many recipients
Broadcast
one-to-all recipients
Unicast
one-to-one recipient
Physical, Data link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application
Layers of the OSI model
Network Access, Internet, Transport, Application
Layers of the TCP/IP model
Data encapsulation
The process of placing one message format inside another message format.
data
upper layers
segment
transport
packet
network
frame
data link
bits
physical
Destination and source logical network addresses
What is the address type of the network layer
destination and source physical addresses
what is the address type of the data link layer
responsible for delivering the ip packet from original source to the final destination
what is the role/responsibility of the network layer address
responsible for delivering the data link frame from one network interface card to another NIC on the same network.
what is the role/responsibility of data link later address
Source IP address and Destination IP address
what addresses are contained in the IP packet header
Source MAC address and Destination MAC address
What addresses are contained in the Ethernet Frame Header
when the final destination is remote, the data link will use the MAC address of the default gateway
when is an ethernet frame sent to the default gateway
is the door or gateway to all other remote locations a has an IP address that is part of the local LAN
What is the purpose of the default gateway
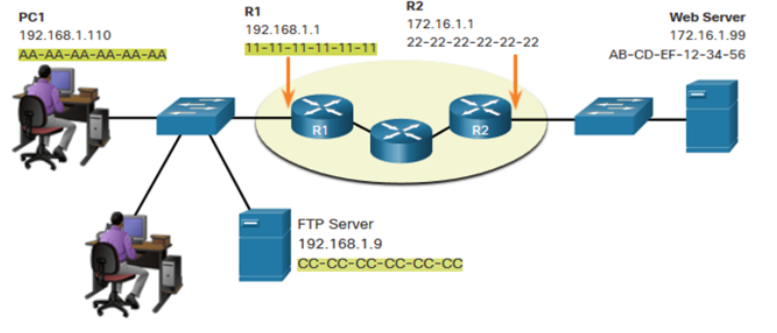
192.168.1.110
When sending data from PC1 to the Web Server, what are:
What is the source ip address in this picture
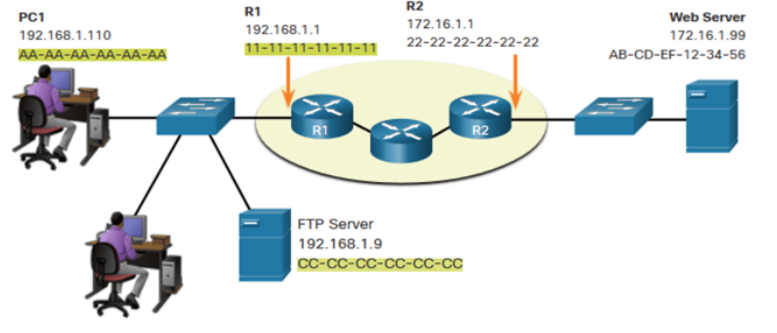
172.16.1.99
When sending data from PC1 to the Web Server, what are:
What is the destination IP address in this picture
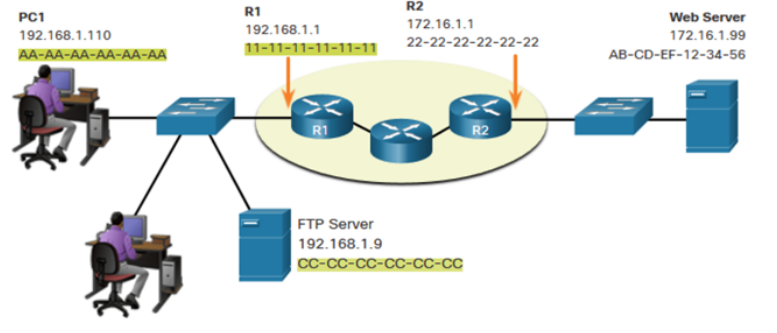
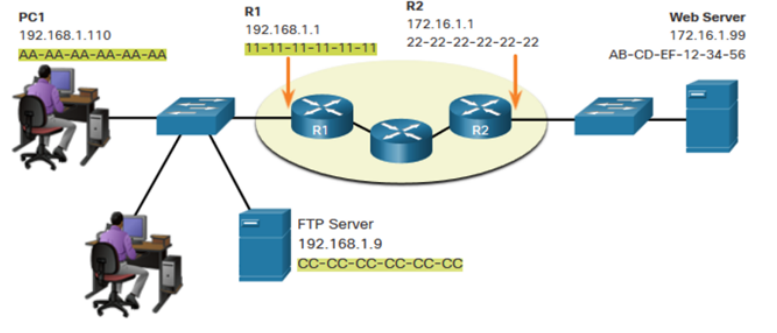
AA-AA-AA-AA-AA-AA
When sending data from PC1 to the Web Server, what are:
What is the source MAC address in this picture
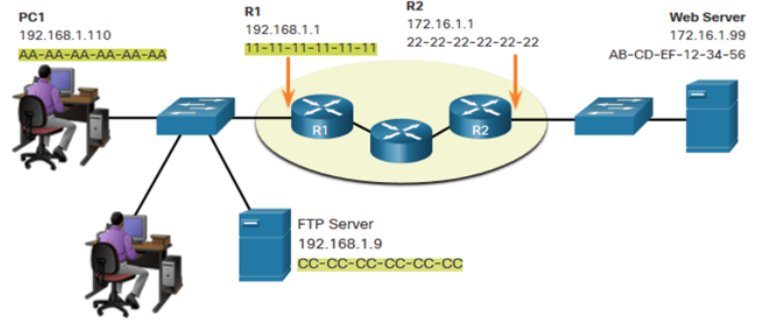
11-11-11-11-11-11
When sending data from PC1 to the Web Server, what are:
What is the destination MAC address in this picture
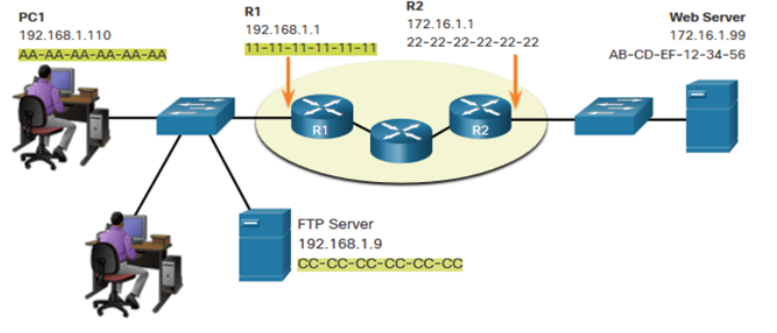
192.168.1.9
When sending data from PC1 to the FTP Server, what are:
What is the destination Ip address in this picture
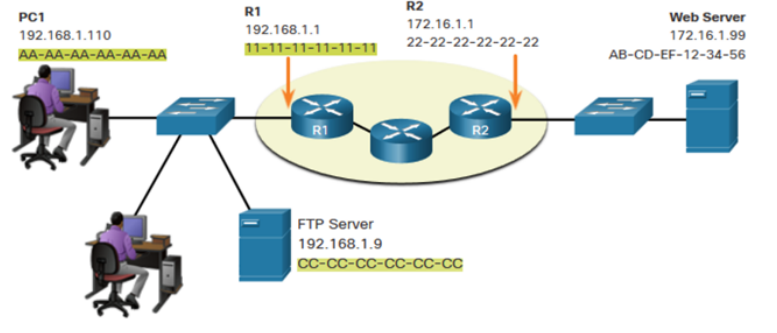
AA-AA-AA-AA-AA-AA
When sending data from PC1 to the FTP Server, what are:
what is the source MAC address in this picture
CC-CC-CC-CC-CC-CC
When sending data from PC1 to the FTP Server, what are:
What is the destination MAC address in this picture
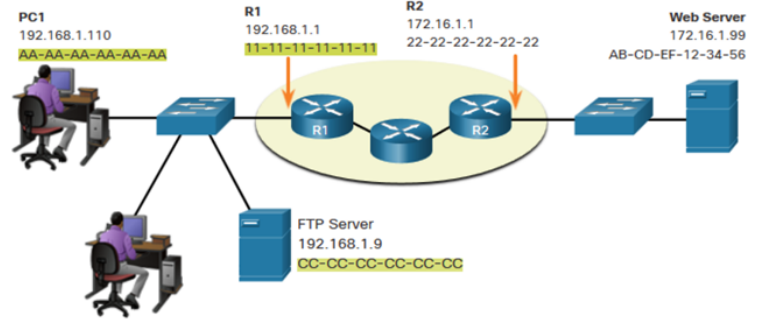
No default gateway address was used because they are in the same network
What is the Default Gateway address for PC1 and FTP Server?
192.168.1.1
What is the Default Gateway address for the Web server?
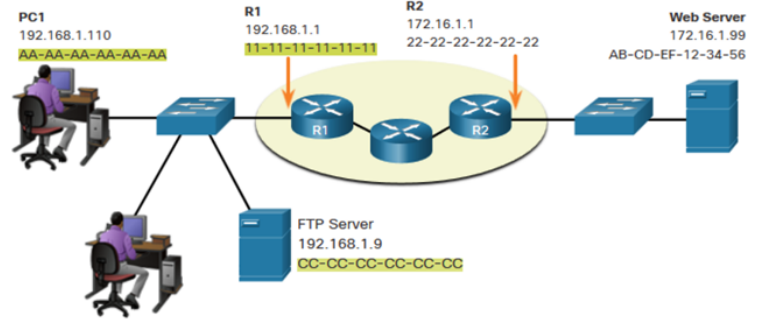
is the IP address of the router interface connected to the local LAN
What is the address of the default gateway (DGW)?
its traffic will be confined to the LAN only
What happens if a device does not have the default gateway address configured?
B
1. What is the process of converting information into the proper form for transmission?
A. Formatting
B. Encoding
C. Encapsulation
A
2. Which one is a component of message timing?
A. Flow control
B. Sequence numbers
C. Retransmit time
B
3. Which one is a component of message timing?
A. Sequence numbers
B. Access methods
C. Retransmit time
F
4. Which one is a component of message timing?
D. Sequence numbers
E. Retransmit time
F. Response timeout
B
5. Which delivery method is used to transmit information to one or more end devices, but not all
devices on the network?
A. Unicast
B. Multicast
C. Broadcast
A
6. What is the purpose of the sequencing function in network communication?
A. To uniquely label transmitted segments of data for proper reassembly by the receiver
B. To determine if data is corrupted during transmission
C. To ensure data flows at an efficient rate between sender and receiver
D. To guarantee delivery of data
B
7. UDP and TCP belong to which layer of the TCP/IP protocol?
A. Internet
B. Transport
C. Application
D. Network access
D
8. Which protocol operates at the network access layer of the TCP/IP model?
A. IP
B. DNS
C. HTTP
D. Ethernet
A
9. A device receives a data link frame with data and processes and removes the Ethernet
information. What information would be the next to be processed by the receiving device it?
A. IP at the internet layer
B. UDP at the internet layer
C. TCP at the transport layer
D. HTTP at the application layer
D
10. What is the process of dividing a large data stream into smaller pieces prior to transmission?
A. Duplexing
B. Sequencing
C. Multiplexing
D. Segmentation
D
11. What is the general term that is used to describe a piece of data at any layer of a networking
model?
A. Frame
B. Packet
C. Segment
D. Protocol data unit
A
12. What is the PDU associated with the transport layer?
A. Segment
B. Packet
C. Frame
D. Bits
B
13. What is the PDU associated with the Network layer?
A. Segment
B. Packet
C. Frame
D. Bits
B
14. What is the PDU associated with the Data Link layer?
A. Bits
B. Frame
C. Packet
D. Segment
C
15. What are the PDUs associated with the following order of the OSI layers: 1 - Transport layer; 2
- Network layer; 3 - Data Link layer; 4 - Physical layer?
A. 1 - Data; 2 – Frame; 3 - Packet; 4 – Bits
B. 1 - Segment; 2 - Data; 3 - Frame; 4 – Bits
C. 1 - Segment; 2 - Packet; 3 - Frame; 4 - Bits
D. 1 - Packet; 2 - Segment; 3 - Frame; 4 - Data
C
16. Which protocol stack layer encapsulates data into frames?
A. Network
B. Transport
C. Data link
D. Application
B
17. What is the name of the process of adding protocol information to data as it moves down the
protocol stack?
A. Sequencing
B. Encapsulation
C. Segmentation
D. De-encapsulation
A
18. True or false? Frames exchanged between devices in different IP networks must be forwarded
to a default gateway.
A. True
B. False
B
19. True or false? The right-most part of an IP address is used to identify the network that a device
belongs to.
A. True
B. False
B
20. True or False? Data Link addresses are physical so they never change in the data link frame
from source to destination.
A. True
B. False
A
21. What is used to determine the network portion of an IPv4 address?
A. Subnet mask
B. MAC address
C. Right-most part of the IP address
D. Left-most part of the MAC address
D
22. Which statement is true regarding network layer addresses?
A. Network layer addresses are physical and 48 bits in length.
B. Network layer addresses are expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits.
C. Network layer addresses are responsible for delivering the data link frames the same
network.
D. Network layer addresses are logical and are responsible for delivering of the IP packet
from the original source to the final destination.
A
23. Which statement is true regarding data link layer addresses?
A. Data link layer addresses are physical and are responsible for delivering the data link
frame from one network interface card (NIC) to another NIC on the same network.
B. Data link addresses are responsible for delivering of the IP packet from the original
source to the final destination.
C. Data link layer addresses are 32 bits in length.
D. Data link layer addresses are logical
D
24. What is done to an IP packet before it is transmitted over the physical medium?
A. It is tagged with information guaranteeing reliable delivery.
B. It is segmented into smaller individual pieces.
C. It is encapsulated into a TCP segment.
D. It is encapsulated in a Layer 2 frame
B
25. What process is used to place one message inside another message for transfer from the
source to the destination?
A. Access control
B. Encapsulation
C. Flow control
D. Decoding
B
26. A web client is sending a request for a webpage to a web server. From the perspective of the
client, what is the correct order of the protocol stack that is used to prepare the request for
transmission?
A. HTTP, IP, TCP, Ethernet
B. HTTP, TCP, IP, Ethernet
C. Ethernet, TCP, IP, HTTP
D. Ethernet, IP, TCP, HTTP
B
27. Which logical address is used for delivery of data to a remote network?
A. Destination MAC address
B. Destination IP address
C. Source MAC address
D. Source IP address
C
28. Which layer of the OSI model defines services to segment and reassemble data for individual
communications between end devices?
A. Session
B. Network
C. Transport
D. Presentation
C
29. Which type of communication will send a message to a group of host destinations
simultaneously?
A. Unicast
B. Anycast
C. Multicast
D. Broadcast
D
30. What type of communication will send a message to all devices on a local area network?
A. Unicast
B. Allcast
C. Multicast
D. Broadcast
D
31. In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
A. To interpret information
B. To break large messages into smaller frames
C. Negotiate correct timing for successful communication
D. To convert information to the appropriate form for transmission
A
32. What type of delivery uses data link layer addresses?
A. Local delivery
B. Remote delivery
C. Local and remote delivery
D. Remote delivery using routers
A
33. What layer of the TCP/IP protocol model determines the best path through the network?
A. Internet
B. Transport
C. Application
D. Network access
D
34. What method can be used by two computers to ensure that packets are not dropped because
too much data is being sent too quickly?
A. Response timeout
B. Access method
C. Encapsulation
D. Flow control
B
35. Which statement accurately describes a TCP/IP encapsulation process when a PC is sending
data to the network?
A. Data is sent from the internet layer to the network access layer.
B. Segments are sent from the transport layer to the internet layer.
C. Frames are sent from the network access layer to the internet layer.
D. Packets are sent from the network access layer to the transport layer.
A
36. When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4
configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
A. Subnet mask
B. Default gateway
C. DNS server address
D. DHCP server address
B
37. What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
A. Session
B. Internet
C. Transport
D. Network access
D
38. Refer to the exhibit. ServerB is attempting to contact HostA. Which statement correctly identify
the addressing that Server B will generate in the process?
A. Server B will generate a packet with the destination IP address of Router B.
B. Server B will generate a packet with the destination IP address of Router A.
C. Server B will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of Router A.
D. Server B will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of Router B.
B
39. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as a single layer of the TCP/IP
model?
A. Network, data link
B. Data link, physical
C. Session, transport
D. Transport, network
B
40. At which layer of the OSI model would a logical address be added during encapsulation?
A. Transport layer
B. Network layer
C. Data link layer
D. Physical layer
A
41. At which OSI layer is a source IP address added to a PDU during the encapsulation process?
A. Network layer
B. Data link layer
C. Transport layer
D. Application layer
A
42. At which OSI layer is a source MAC address added to a PDU during the encapsulation
process?
A. Data link layer
B. Application layer
C. Transport layer
D. Presentation layer
D
43. When sending data on the path from the source device to the final destination device, which
layer addresses are changing, and which layer addresses stay the same?
A. Both Layer 2 addresses and Layer 3 addresses change
B. Layer 3 addresses change, Layer 2 addresses stay the same
C. Both Layer 2 addresses and Layer 3 addresses stay the same
D. Layer 2 addresses change, Layer 3 addresses stay the same