GACE SCIENCE
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
qualitative observation
An observation that describes using your 5 senses. It also uses NO numbers.
quantitative observation
An observation that deals with a number or amount
Inference
A conclusion reached on the basis of evidence and reasoning
Hypothesis
An educated guess
dependent variable
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested.
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Steps in a scientific investigation
Make observations, ask a question, form a hypothesis, test the hypothesis, draw conclusions, communicate results
System
A group of parts that work together as a whole
discuss the importance of models in teaching science to children
models such as styrofoam ball model of the solar system is important for conceptual understanding in young children
climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time
three changes in the environment
forest destruction, pollution, and global warming
three different types of rocks
igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface
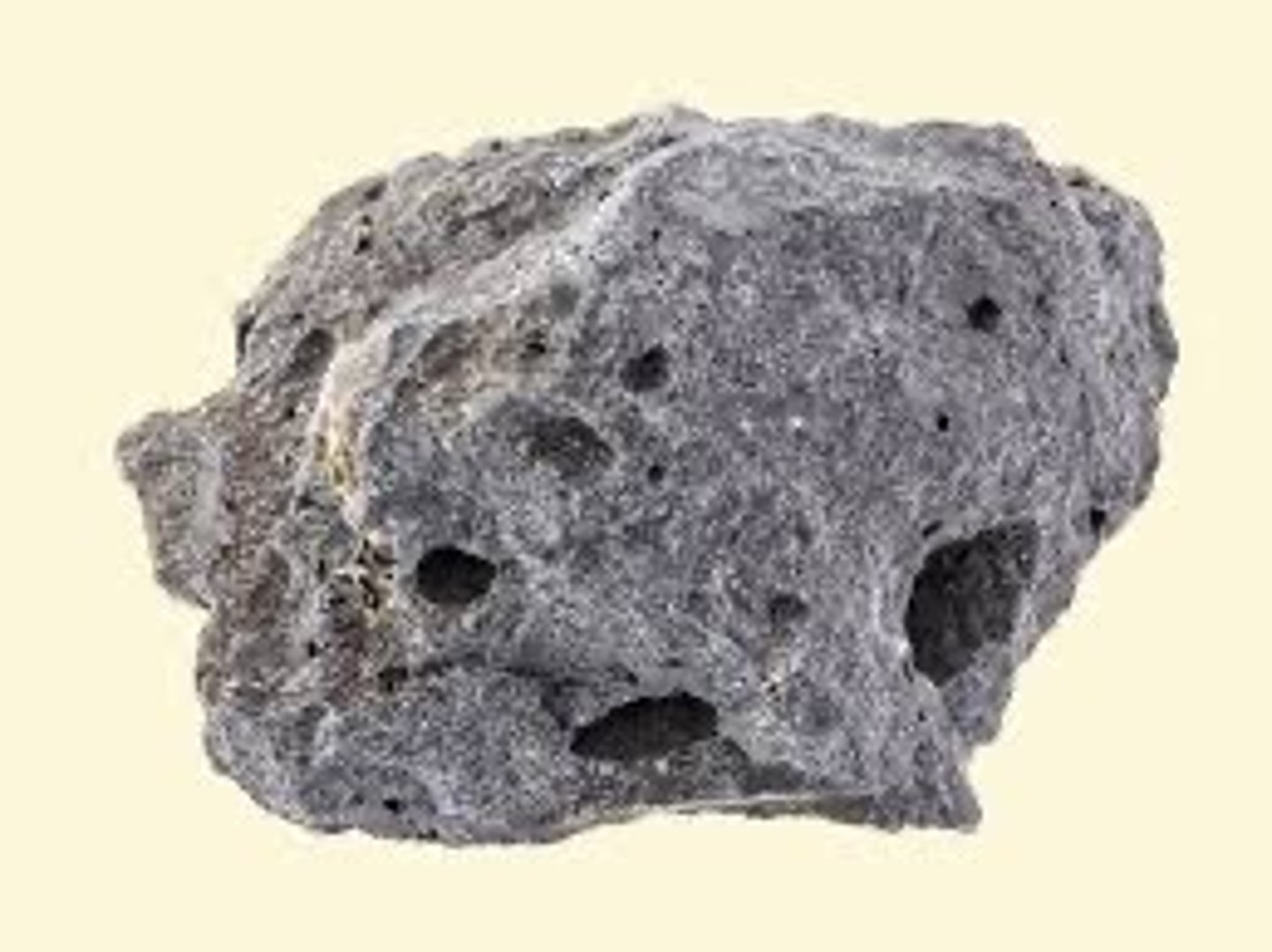

sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together

metamorphic rock
rock that has been changed by heat and pressure
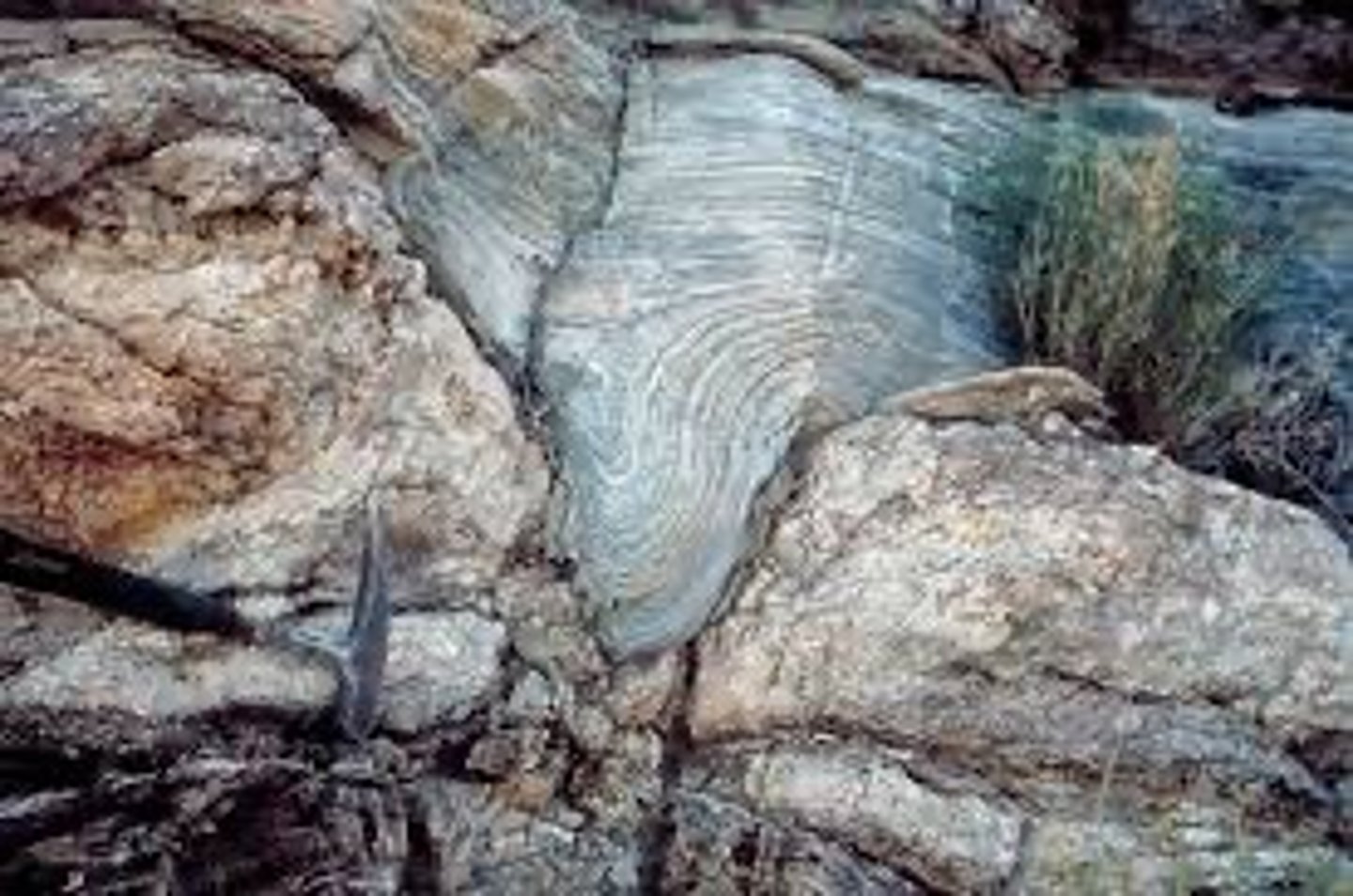

Erosion
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil are broken down and carried away (i.e. weathering, glaciation)
formation of sedimentary rocks
weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation
Palentology
the study of fossils
Fossils
Preserved remains of once-living organisms (footprints)
Topography
A description of surface features of land.
2 changes to earth's topography
plate movement and the water cycle
How are mountains formed?
Plates or parts of plates are forced up as plates crash together
constructive
mountains, volcanoes, and sediment deposits
destructive
ravines, trenches, and weathering following erosion
physical properties
A characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance
What are physical properties?
color, density, hardness, and conductivity
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
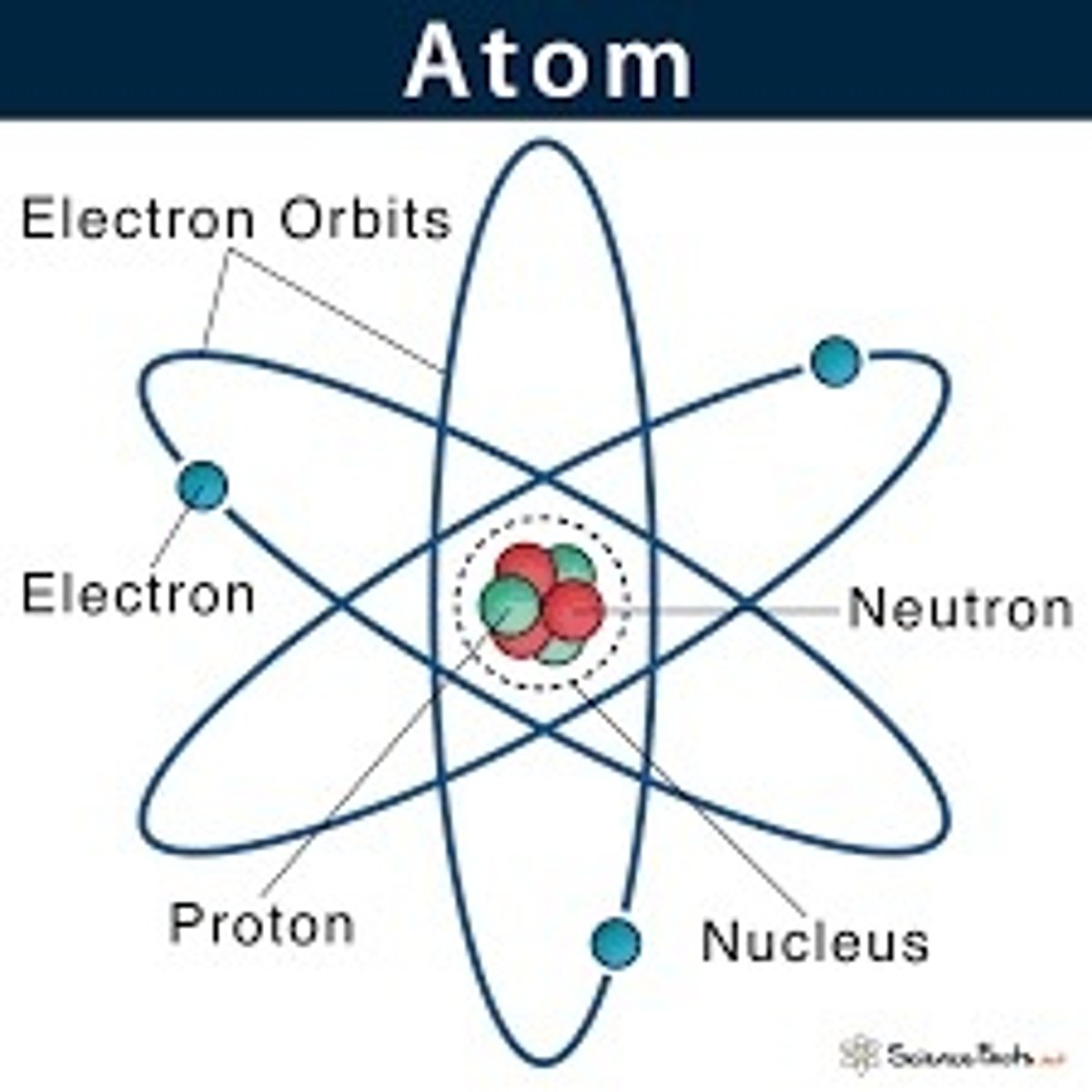
Structure of an atom
Nucleus holds protons and neutrons, and electrons orbit the nucleus
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
eukaryotes
Cells that contain nuclei
Function of DNA
stores genetic information
metamorphosis
change of form (butterfly)
Larva of butterfly
caterpillar
pupa of butterfly
chrysalis
incomplete metamorphosis
egg, nymph, adult
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
abiotic factors
Nonliving components of environment.
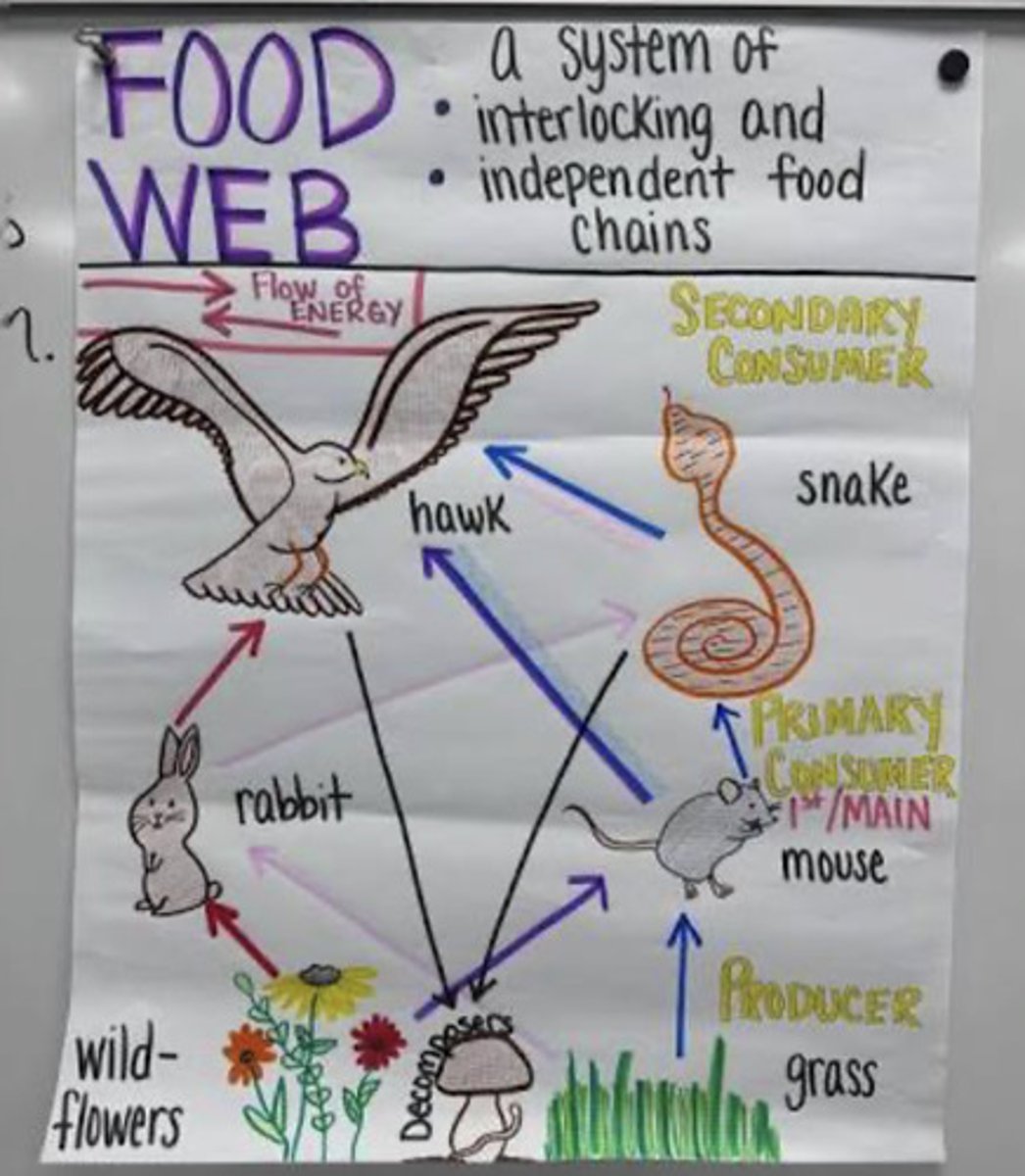
food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
Herbivore
A consumer that eats only plants.
Carnivore
A consumer that eats only animals.
Omnivores
eat both plants and animals
Food webs are models that show
how energy is transferred in an entire ecosystem
Symbiosis
A close relationship between two species that benefits at least one of the species.
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
Inherited traits
characteristics that are passed from parent to offspring
learned behavior
a behavior that has been learned from experience or observation
Adaptations
inherited characteristics of organisms that enhance their survival and reproduction in specific environments
Producer
An organism that can make its own food.