NSE 212
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
w1: what is research + its significance
research = systematic, rigorous, logical investigation aiming to answer questions about nursing phenomena (occurrences, situations)
significance:
expands discipline’s unique body of knowledge
forms the foundation for evidence-informed nursing practice
allow practice to change according to work environments and most common health issues
maintains the profession’s societal relevance (important, useful, respected in society)
w1: evidence-based practice vs evidence-informed practice
evidence-based practice = research + clinical expertise + patient preference (research is top priority)
evidence-informed practice = research + clinical expertise + patient preference + context/resources (more flexible)
research utilization + EIP
apply research findings to improve pt care
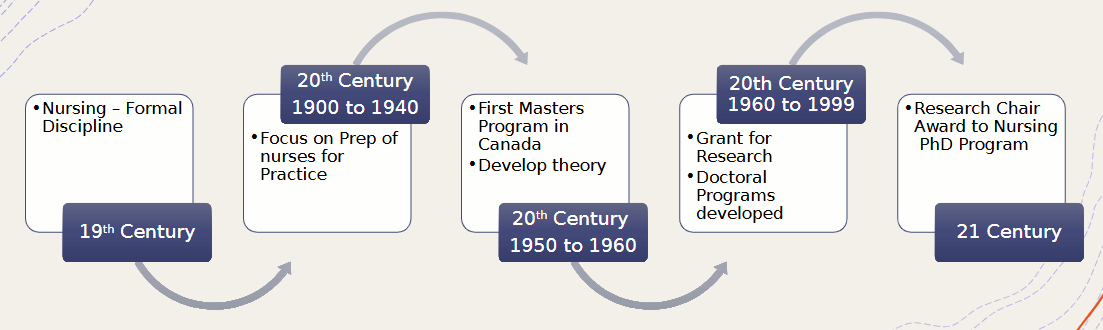
w1: historical perspectives of nursing research
w1: future direction + trends in research
community-based care
health promotion, risk reduction
reducing disparities in healthcare
research on older adults
interdisciplinary collaborative practice
use of technology
needs of indigenous peoples
w1: nurses’ role in research
consumer
understand charts
generator of clinical questions
ask questions
investigator/participant in research
nurse researcher
protector of research participants
when pt are taken adv during research, duty as nurse to step in
w1: professional standards of practice - CNA position statement
all nurses must collaborate with other healthcare stakeholders to faciitate evidence-informed decision-making and practice
sources of evidence need to be critically appraised before their findings are incorporated into decision making
w1: professional standards of practice - individual nurses
individual nurses support evidence-informed nursing practice by:
using their education to provide optimal care
reading and critiquing research in nursing and health sciences
generating research questions and sharing them with leaders/researchers
participating in or conducting research
evaluating and promoting evidence-informed practice
w1: entry-to-practice competencies
DO READING
w1: CNO code of conduct - REVIEW
nurses respect client’s dignity
nurses provide inclusive and culturally safe care by practicing cultural humility
nurses provide safe and competent care
nurses work respectfully with the health care team
nurses act with integrity in clients’ best interest
nurses maintain public confidence in the nursing profession
w1: 4 philosophical foundations and characteristics of research
nature of knowledge
philosophical foundations
paradigms
characteristics of quantitative research
w1: the nature of knowledge + theoretical/empirical knowledge
nurses use curiosity to question phenomena in clinical practice
they ask questions to improve care delivery, innovate methods and create best practice guidelines
these questions lead to a knowledge-development process, involving:
knowledge gap - notice missing info
knowledge generation - creating research to answer question
knowledge distribution - sharing findings (publications, reports, networks)
knowledge adoption - applying new knowledge in practice and policies
knowledge review/revision - ongoing updates as new issues arise
Theoretical/empirical knowledge (aka scientific knowledge)
theoretical knowing = developing/testing theories/ideas
empirical knowing = involves observations (ex: delivering interventions, conducting surveys/questionnaires)
theoretical knowing is informed by empirical knowing
w1: philosophical terms - ontology, epistemology, methodology, context, aim of inquiry, researcher values
ontology = science/study of “being”
Q: what can be said to exist?
epistemology = the issue of “truth”
Q: how do we know what we know
methodology = discipline-specific principles, rules, and procedures that guide the research process
context = personal, social, political environment factors that may influence research findings
aim of inquiry = goals of research
explanation, prediction and control
researcher values = personal beliefs of the researcher
w1: paradigm + nursing paradigm
paradigm (greek word paradeigma meaning “pattern”) = different ways of viewing the world
have a set of assumptions about what is reality, how knowledge is created and what is valuable to learn
nursing paradigms = how philosophical questions are answered depends on the nursing paradigm used to guide the research process
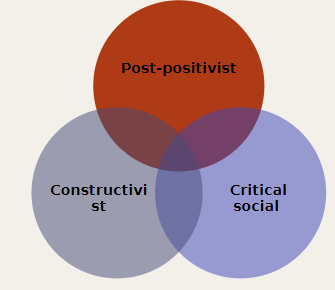
w1: paradigms and research methods
research methods = principles, rules, procedures that guide the process of knowledge acquired
different paradigms will determine the research methods
post positivist paradigm = quantitative research method