Glycolysis pt 2
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
fermentation
general term for processes that extract energy (as ATP) but do not consume oxygen or change the concentrations of NAD+ or NADH
lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate accepts electrons from NADH and is reduced to lactate while regenerating the NAD+ necessary for glycolysis
lactate is carried in blood to the liver, where it is converted to glucose during recovery
ethanol (alcohol) fermentation
pyruvate is further catabolized to ethanol
regenerates NAD+
lactate dehydrogenase
catalyzes the reduction of pyruvate to lactate
Hexokinase is inhibited by
the product, Glucose 6-Phosphate
Phosphofructokinase-1 regulation
ATP inhibits PFK-1
ADP and AMP allosterically relieve this inhibition by ATP
fructose 2,6-bisphosphate regulationes
mediates the rapid hormonal regulation of glycolysis
binds to PFK-1 and increases its affinity for fructose 6-phosphate
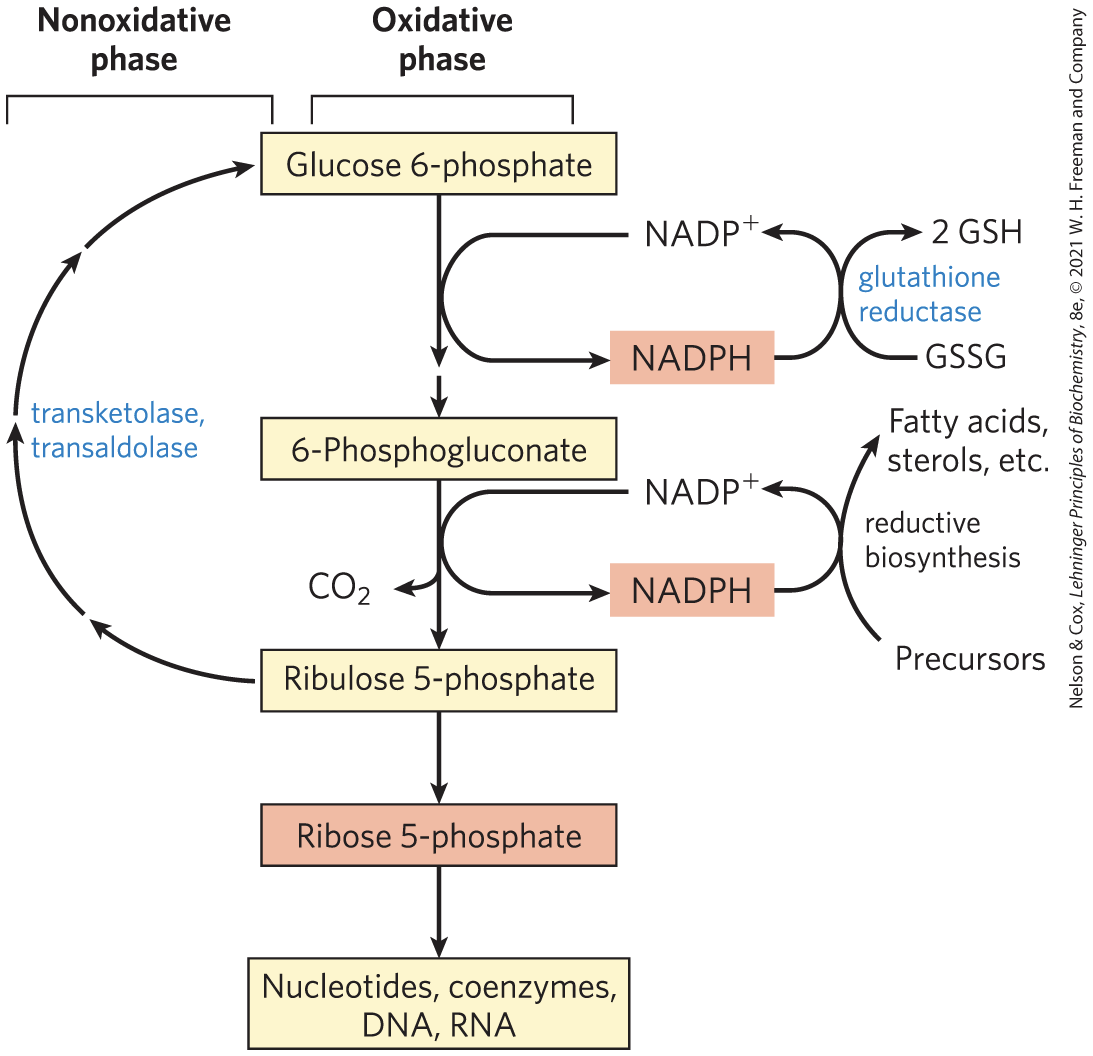
Purpose of pentose phosphate
Nucleotides, coenzymes, DNA, RNA
Overall Equation for the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
glucose 6-phosphate + 2NADP+ + H2O →
ribulose 5-phosphate + CO2 + 2NADPH + 2H+
Cells and Tissues That Use the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
rapidly dividing cells
tissues that carry out extensive fatty acid synthesis require the NADPH
tissues that actively synthesize cholesterol and steroid hormones require the NADPH
Pentose phosphate steps