Anatomy: Heart and Fetal Circulation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Cardiovascular system
major components: heart, blood vessels, blood
major function: transportation of nutrients, oxygen, waste products, hormones
pulmonary circuit
right side of heart pumps blood to lungs, then returns to left side of heart, goes to lungs to pick up oxygen
systemic circuit
left side of heart pumps blood to body then it returns to the right side of heart, this blood travels everywhere in the body
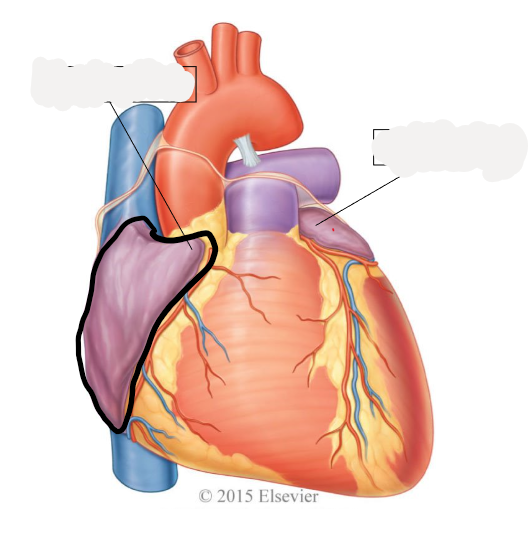
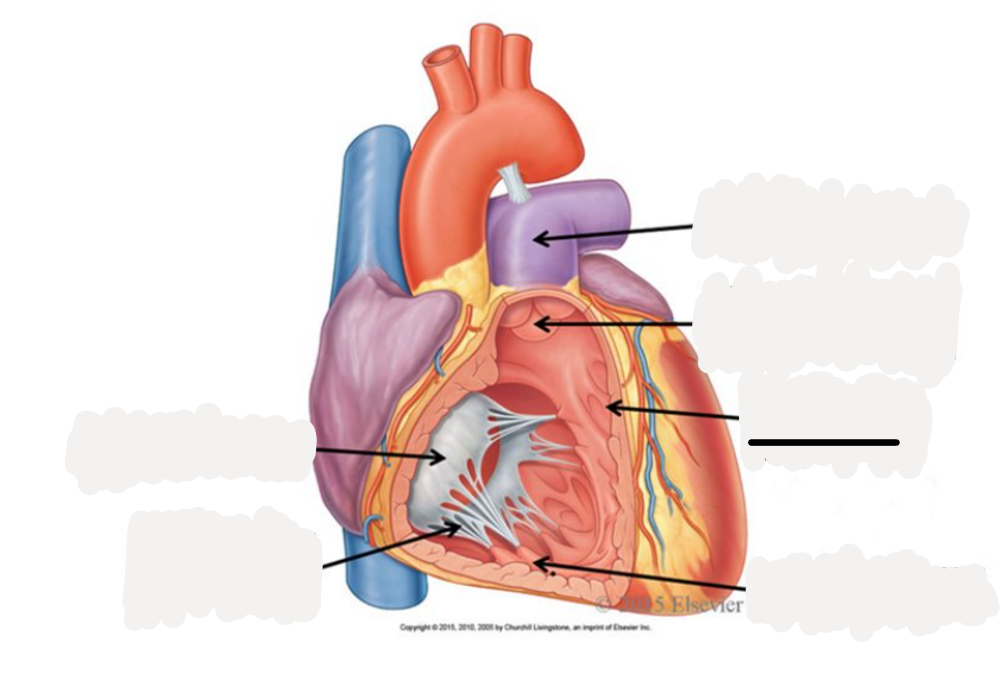
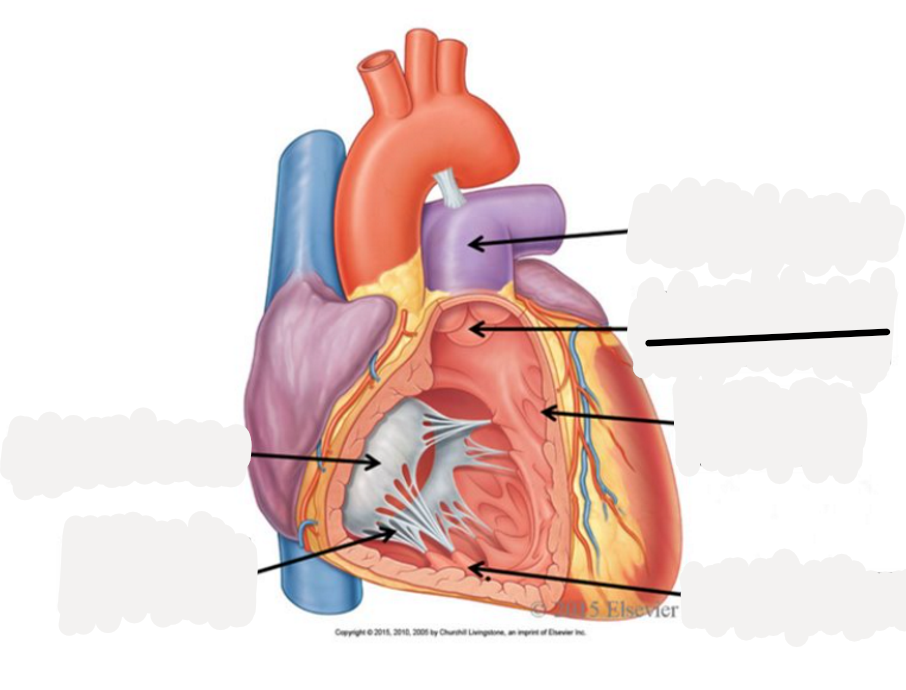
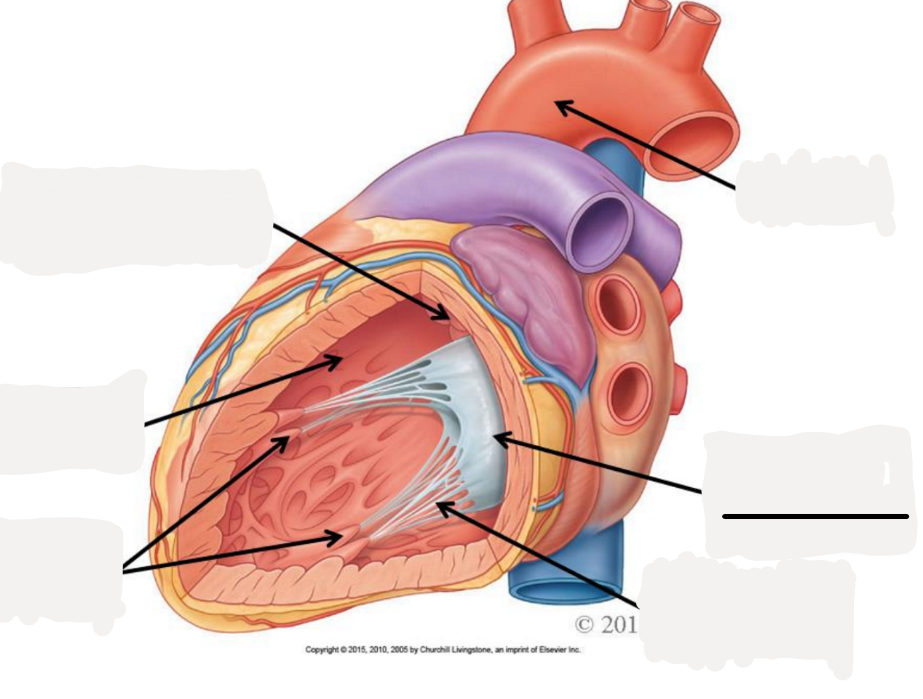
right auricle
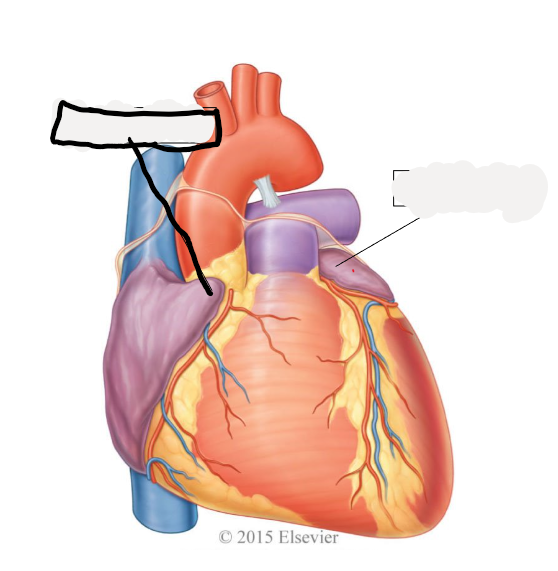
left auricle
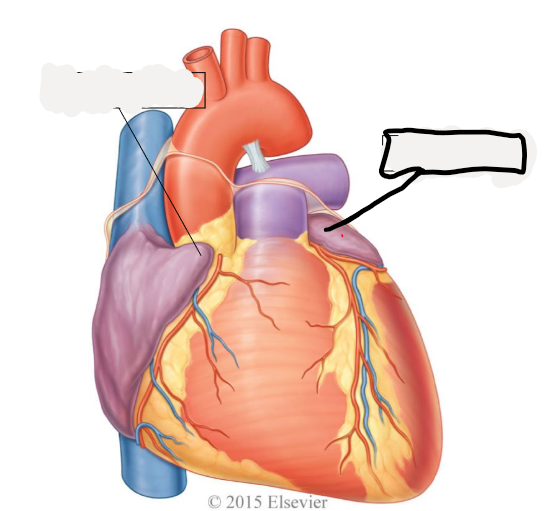
right atrium
receives oxygenated blood from SVC, IFC, coronary sinus
right ventricle
discharges deoxygenated blood into pulmonary circuit via pulmonary trunk, which splits into pulmonary arteries
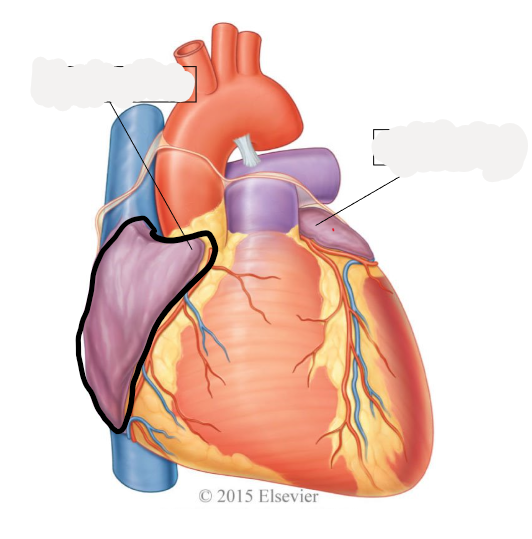
left atrium
receives oxygenated blood from 2 right and 2 left pulmonary veins
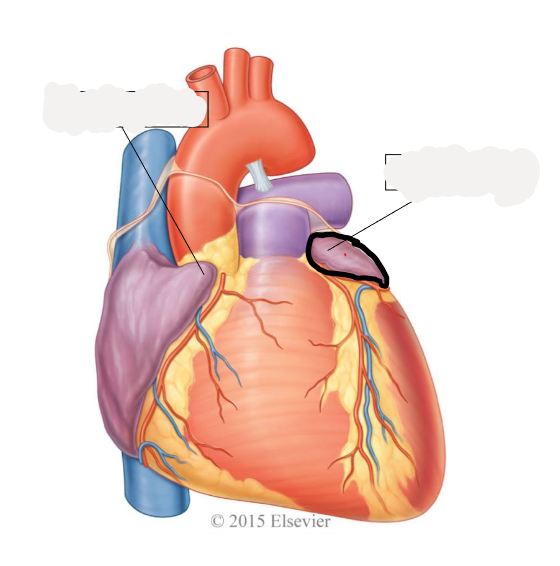
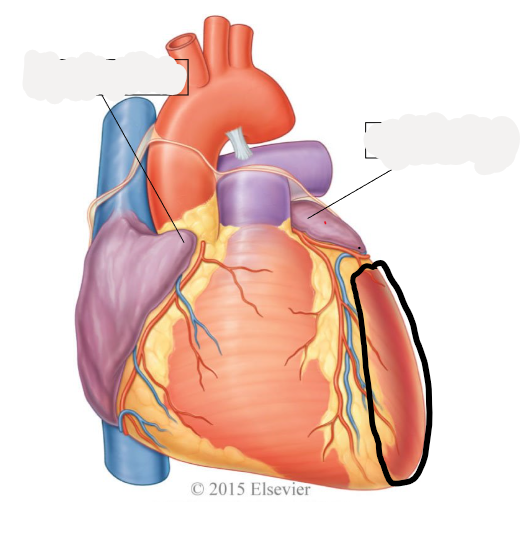
left ventricle
discharges oxygenated blood into systemic circuit via aorta, ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending aorta
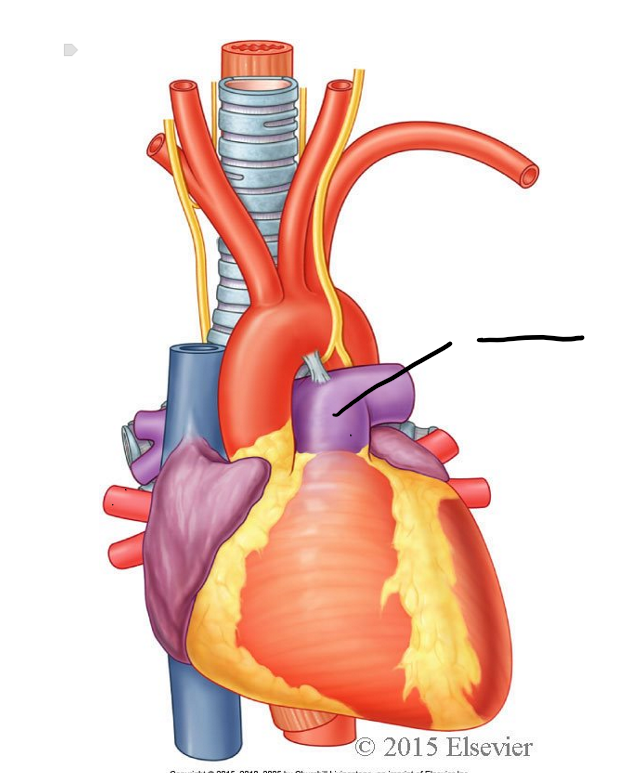
pulmonary trunk
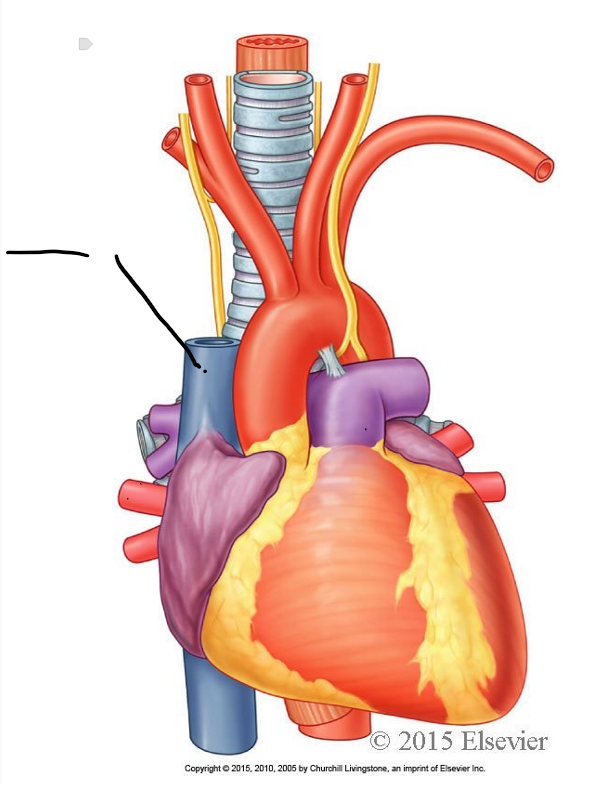
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava

pulmonary veins
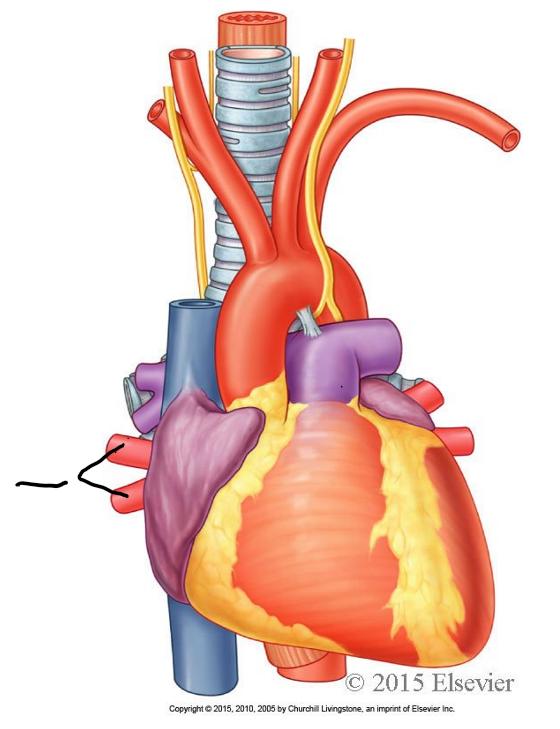
pulmonary arteries
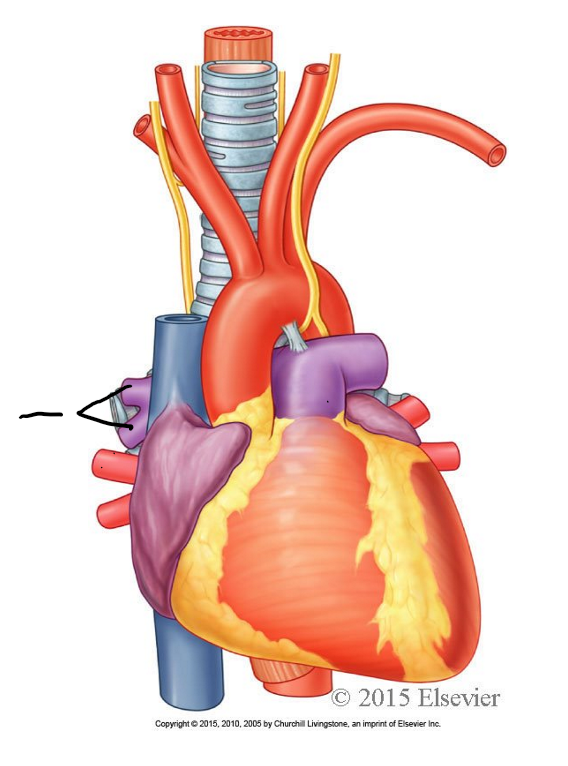
aorta
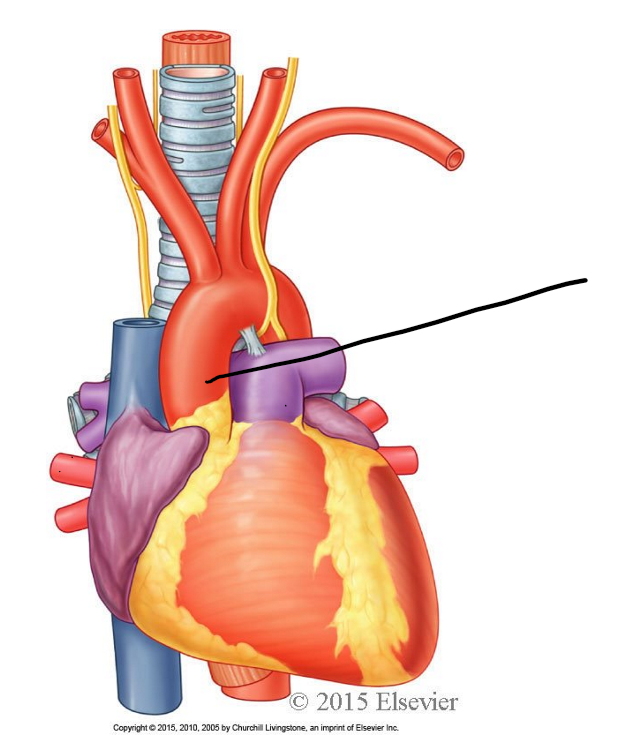
atrioventricular valves
prevent backflow into atria
tricuspid valve: between right atrium and right ventricle
bicuspid or mitrial valve: between left atrium and left ventricle
semilunar valves
prevents backflow into ventricles
pulmonary semilunar valve: between right ventricle and right pulmonary trunk
aortic semilunar valve: between left ventricle and aorta
systole
ventricles contract to pump blood out of heart
tricuspid + bicuspid valves close (S1, “lub”)
diastole
ventricles relax to allow blood to fill them
tricuspid and bicuspid valves open, aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves close
(S2, “dub”)
layers of the heart
epicardium (most superficial), myocardium, endocardium (most deep)
pectinate muscle
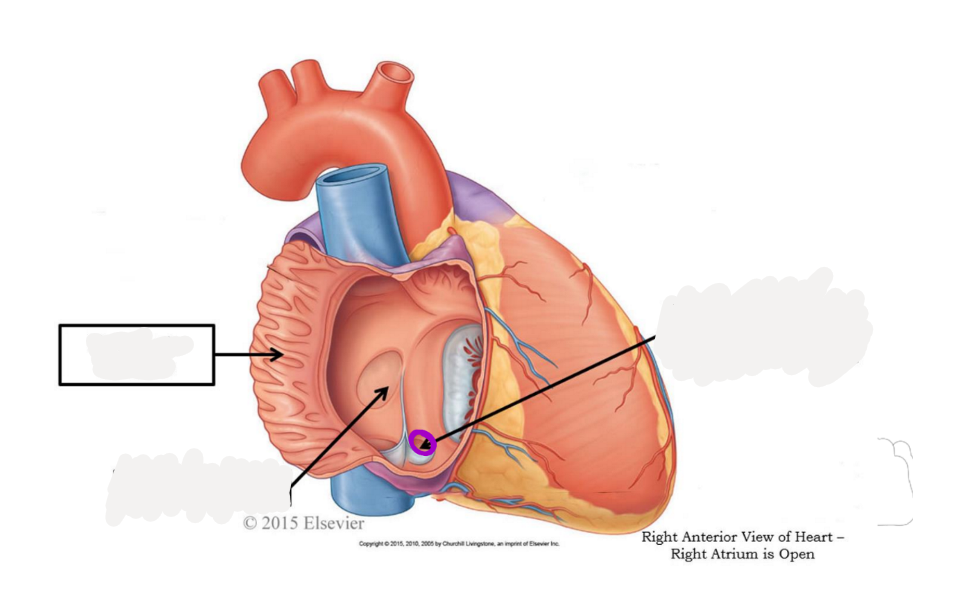
fossa ovalis
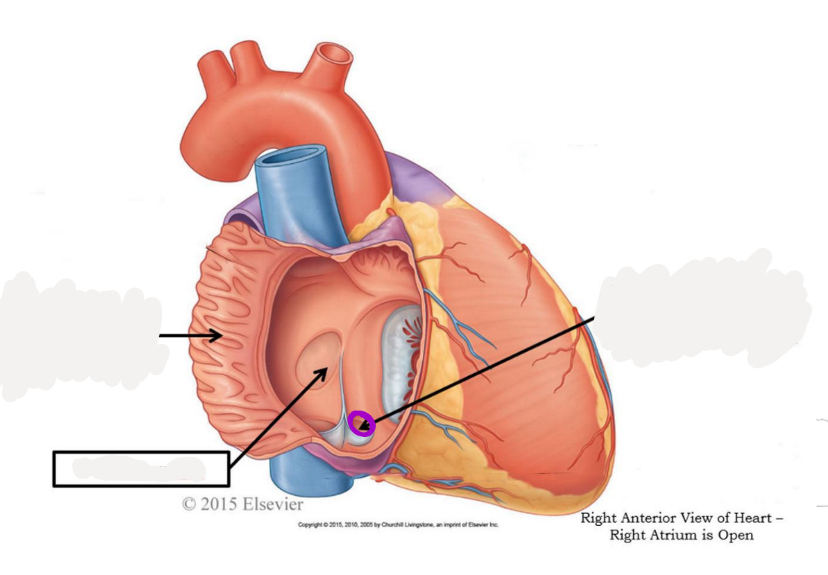
opening of coronary sinus
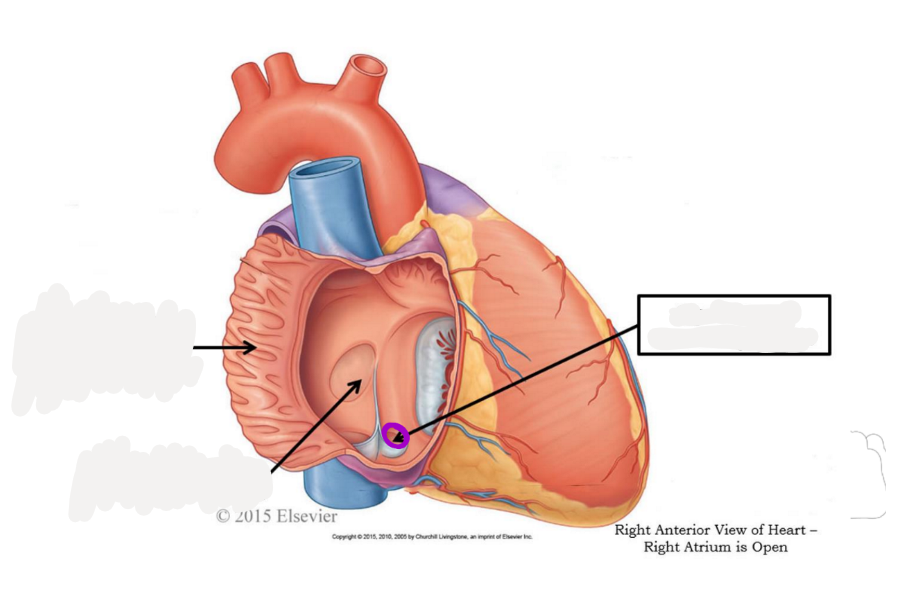
tricuspid valve
chordae tendoneae
papillary muscle
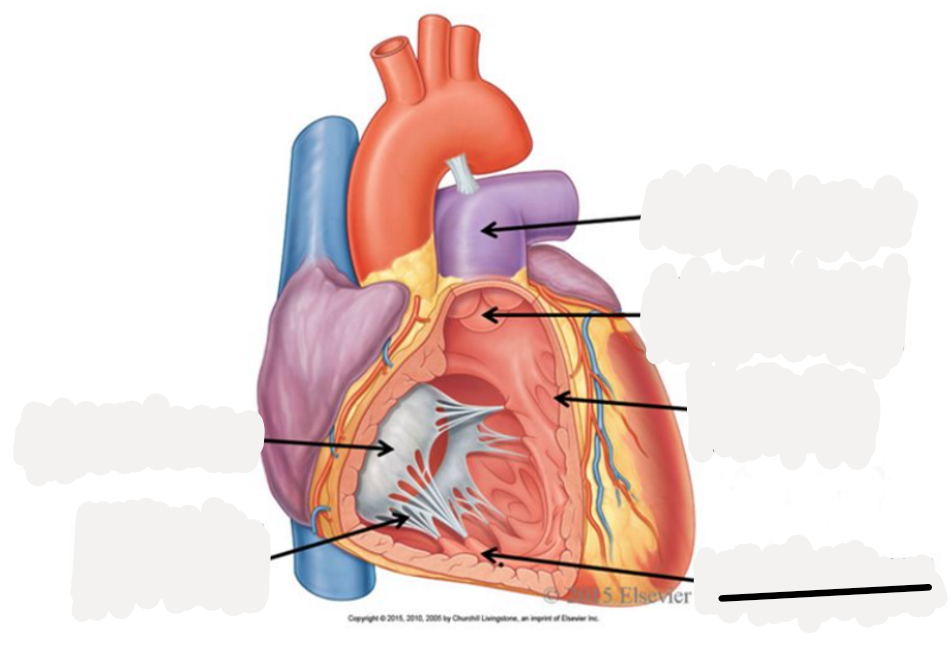
trabeculae carneae
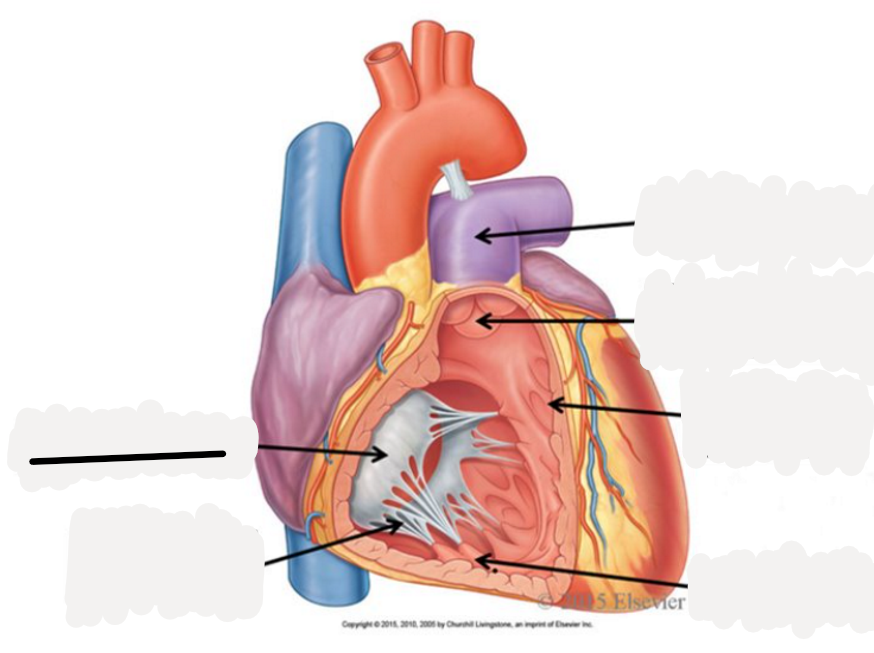
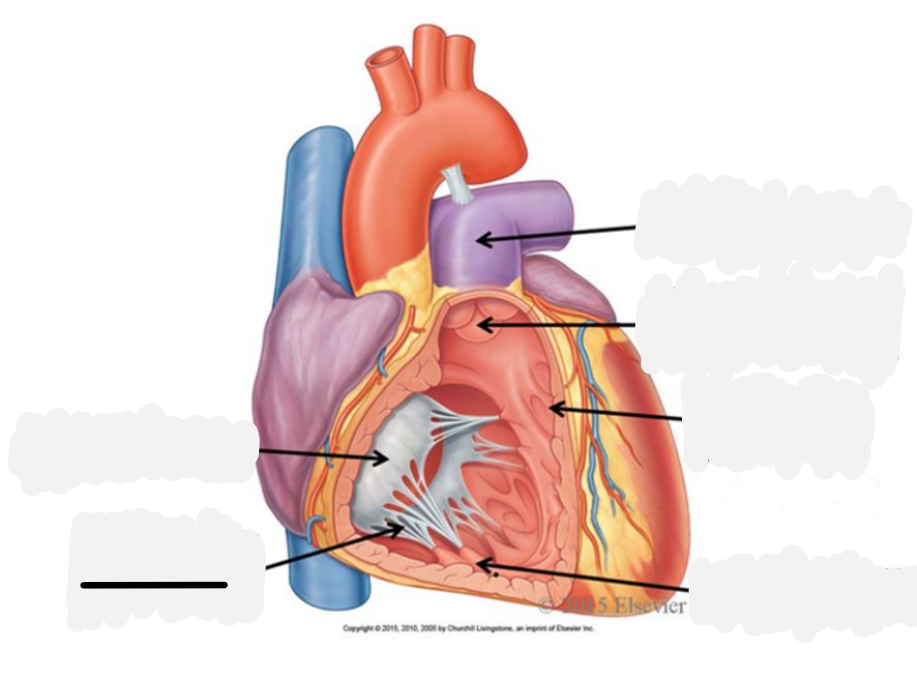
pulmonary semilunar valve
aortic semilunar valve
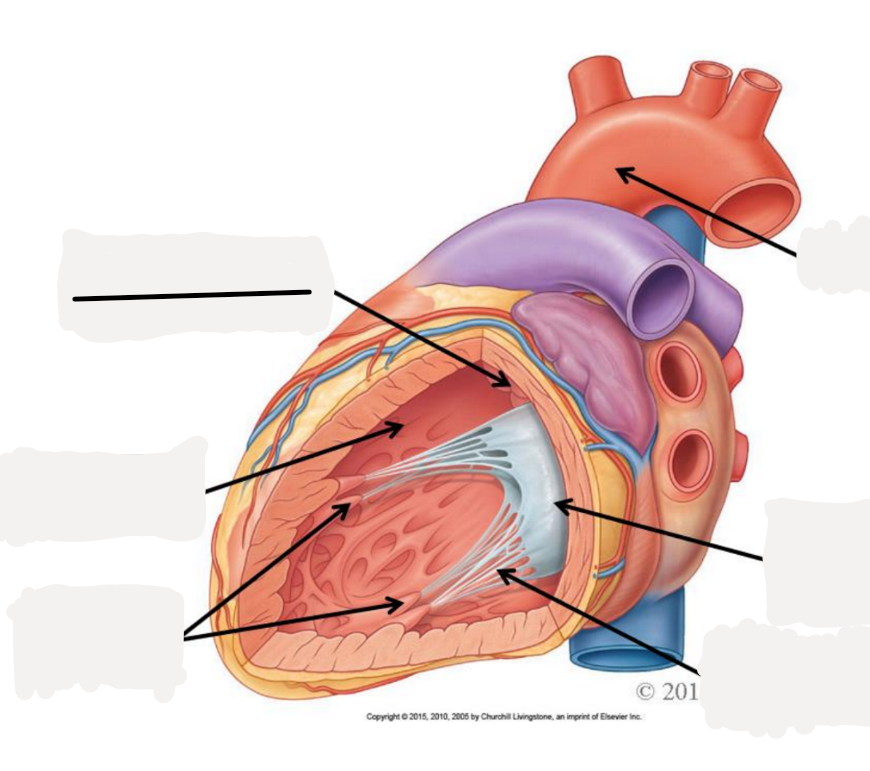
bicuspid (mitrial) valve
right marginal artery, small cardiac vein
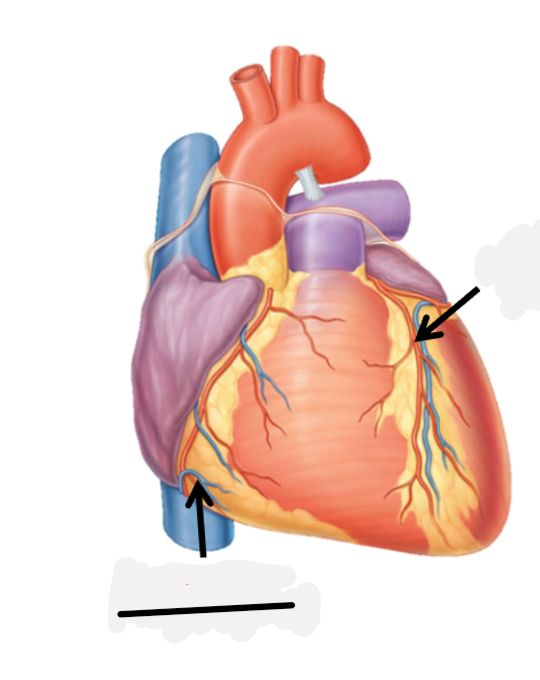
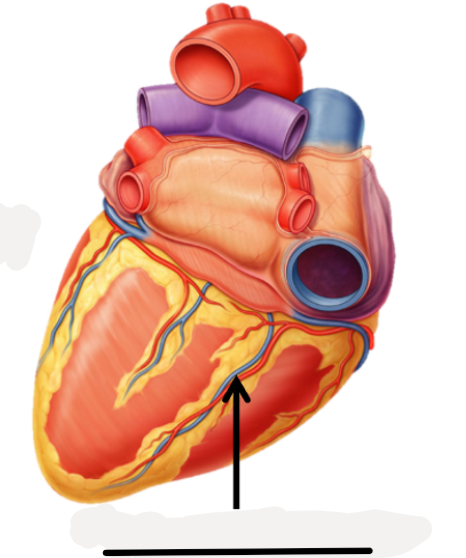
anterior interventricular artery, great cardiac vein
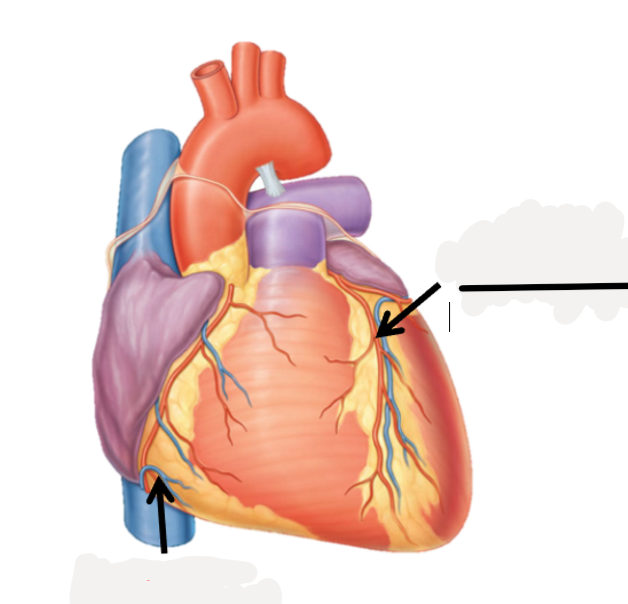
posterior interventricular vein, middle cardiac vein
umbilical vein
passes through primitive liver and carries oxygenated blood to IVC, regresses to form ligamentum teres (found within edge of the falciform ligament)
foramen ovale
hole that shunts blood from right atrium to left atrium to bypass lungs. small amount of blood flows to tissue for nourishment. closure after birth forms fossa ovalis
ductus arteriosus
shunts blood that made it to left pulmonary artery to aorta, closure after birth forms ligamentum arteriosum