Unit 6: Developmental Psychology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
1
New cards
Developmental psychology
A branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the lifespan
2
New cards
Nature vs. Nurture
-Nature: Innate biological factors that influence development and personality
-Nurture: External and environmental factors, including learning, that influence development and personality
-Nurture: External and environmental factors, including learning, that influence development and personality
3
New cards
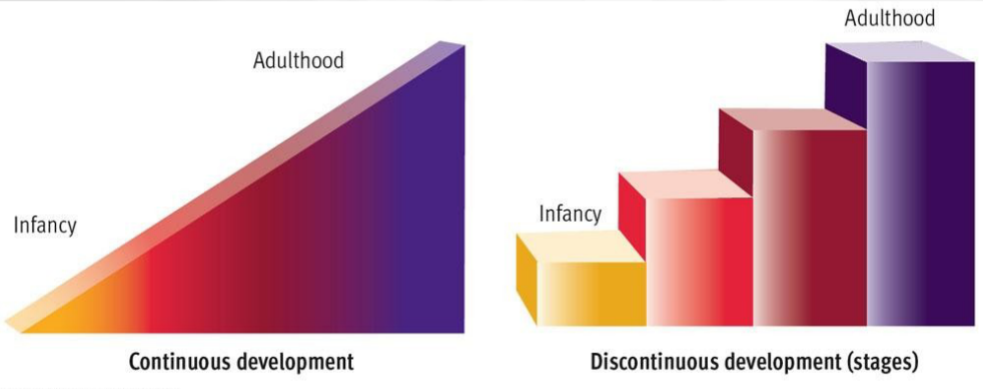
Continuity v. stages
Is development a gradual process or a sequence of stages?
4
New cards
Stability v. change
Stability implies personality traits present during infancy endure throughout the lifespan. In contrast, change theorists argue that personalities are modified by interactions with family, experiences at school, and acculturation
5
New cards
Germinal stage
first 2 weeks
Conception, implantation, formation of placenta
Fewer than half survive beyond this stage
Conception, implantation, formation of placenta
Fewer than half survive beyond this stage
6
New cards
Embryonic stage
2 weeks - 2 months
Formation of vital organs and systems
Most dangerous/harmful time for mother to use harmful substances because vital organs are being formed
Formation of vital organs and systems
Most dangerous/harmful time for mother to use harmful substances because vital organs are being formed
7
New cards
Fetal stage
2 months - birth
Bodily growth continues, movement capability begins, and brain cells multiply
Age of viability - after 25 weeks (can exist outside of womb)
Bodily growth continues, movement capability begins, and brain cells multiply
Age of viability - after 25 weeks (can exist outside of womb)
8
New cards
Maternal nutrition
Malnutrition linked to increased risk of birth complications, neurological problems, and psychopathology
9
New cards
Maternal drug use
Tobacco, alcohol, prescription, and recreational drugs
Fetal alcohol syndrome causes face misproportions
Fetal alcohol syndrome causes face misproportions
10
New cards
Teratogens
Agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo and fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
11
New cards
Grasping reflex
Babies grab something in their palm like a finger
12
New cards
Rooting reflex
Baby will turn towards your hand when you brush their cheek or mouth
Helps babies find bottle or nipple for feeding
Helps babies find bottle or nipple for feeding
13
New cards
Cephalocaudal trend
head to foot development
babies can move their heads before their feet
babies can move their heads before their feet
14
New cards
Proximodistal trend
center to outward
babies can move their limbs before developing fine motor skills
babies can move their limbs before developing fine motor skills
15
New cards
habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
16
New cards
maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
17
New cards
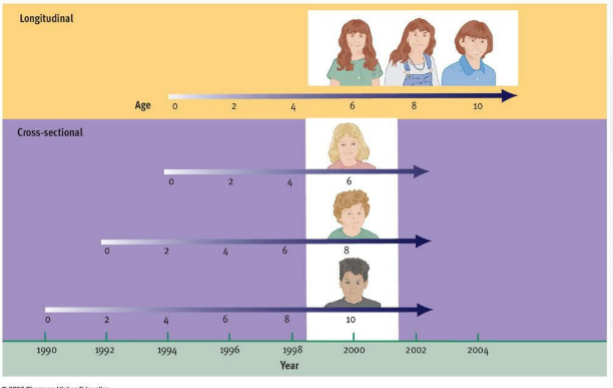
longnitudinal study
study the same subject/group over time
Pro: Allows you to avoid confounding factors
Con: people may drop out, takes longer
Pro: Allows you to avoid confounding factors
Con: people may drop out, takes longer
18
New cards
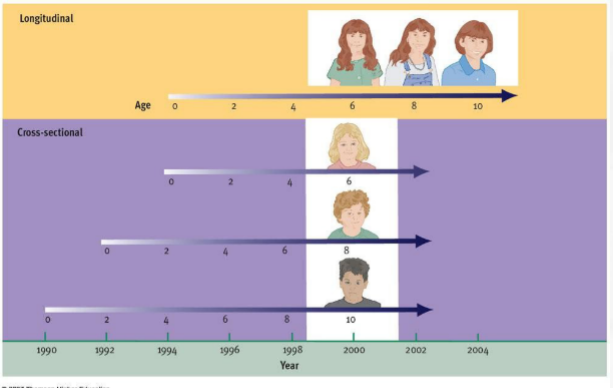
Cross-sectional study
studying different groups of different ages/characteristics at the same time
Pro: Immediate and easier
Con: Possible confounding variables
Generational differences
Events that happen in people’s lives
Nature vs nurture
Pro: Immediate and easier
Con: Possible confounding variables
Generational differences
Events that happen in people’s lives
Nature vs nurture
19
New cards
Differences in Temperments of Babies (Kagan & Snidman, 1991)
-Inhibited: 15 - 20%
-uninhibited: 25 - 30%; become stable over time, genetically based
-uninhibited: 25 - 30%; become stable over time, genetically based
20
New cards
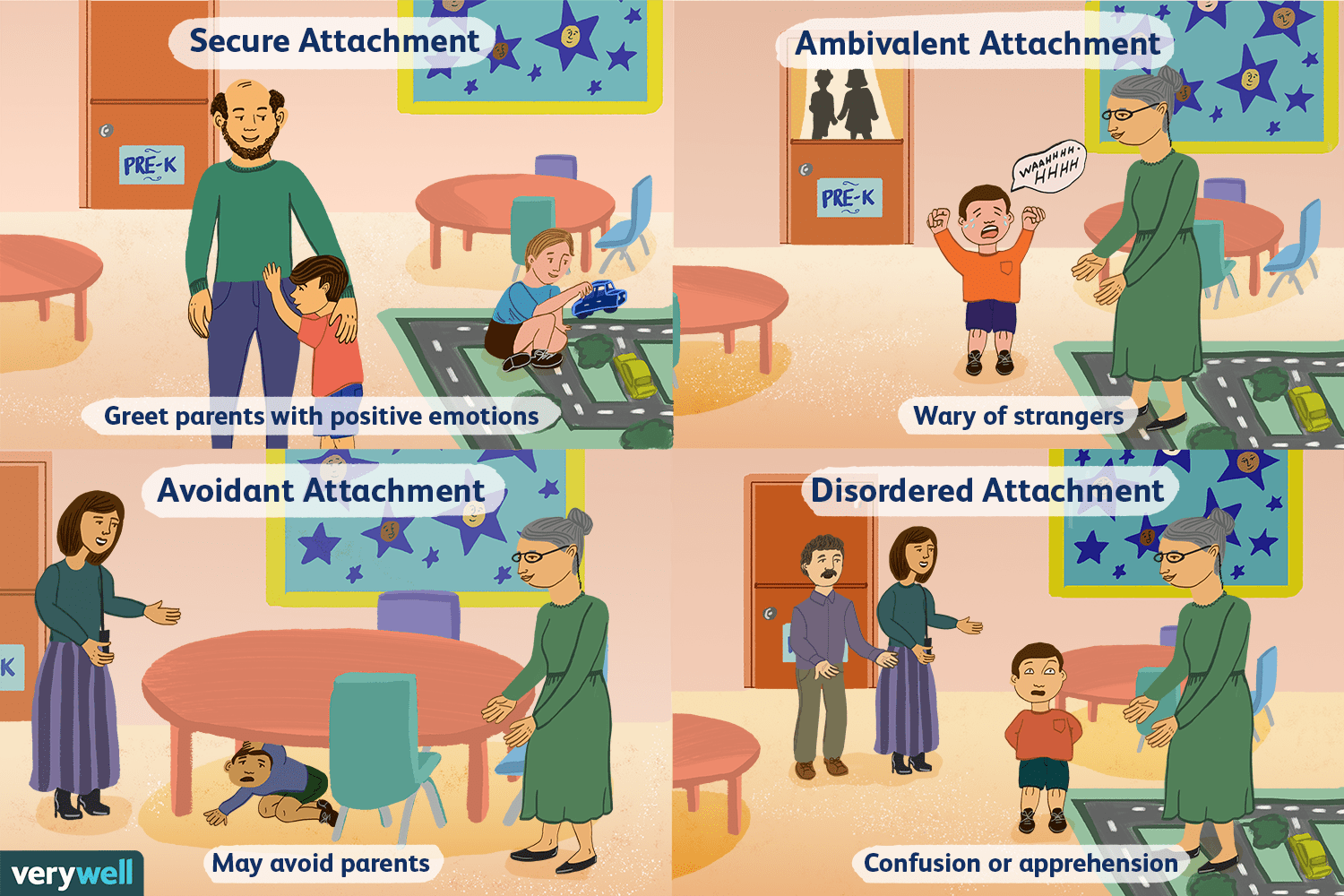
Mary Ainsworth
-created the strange situation (1979) and studied patterns of attachment
-secure, anxious-ambivalent, and avoidant attachment
-secure, anxious-ambivalent, and avoidant attachment
21
New cards
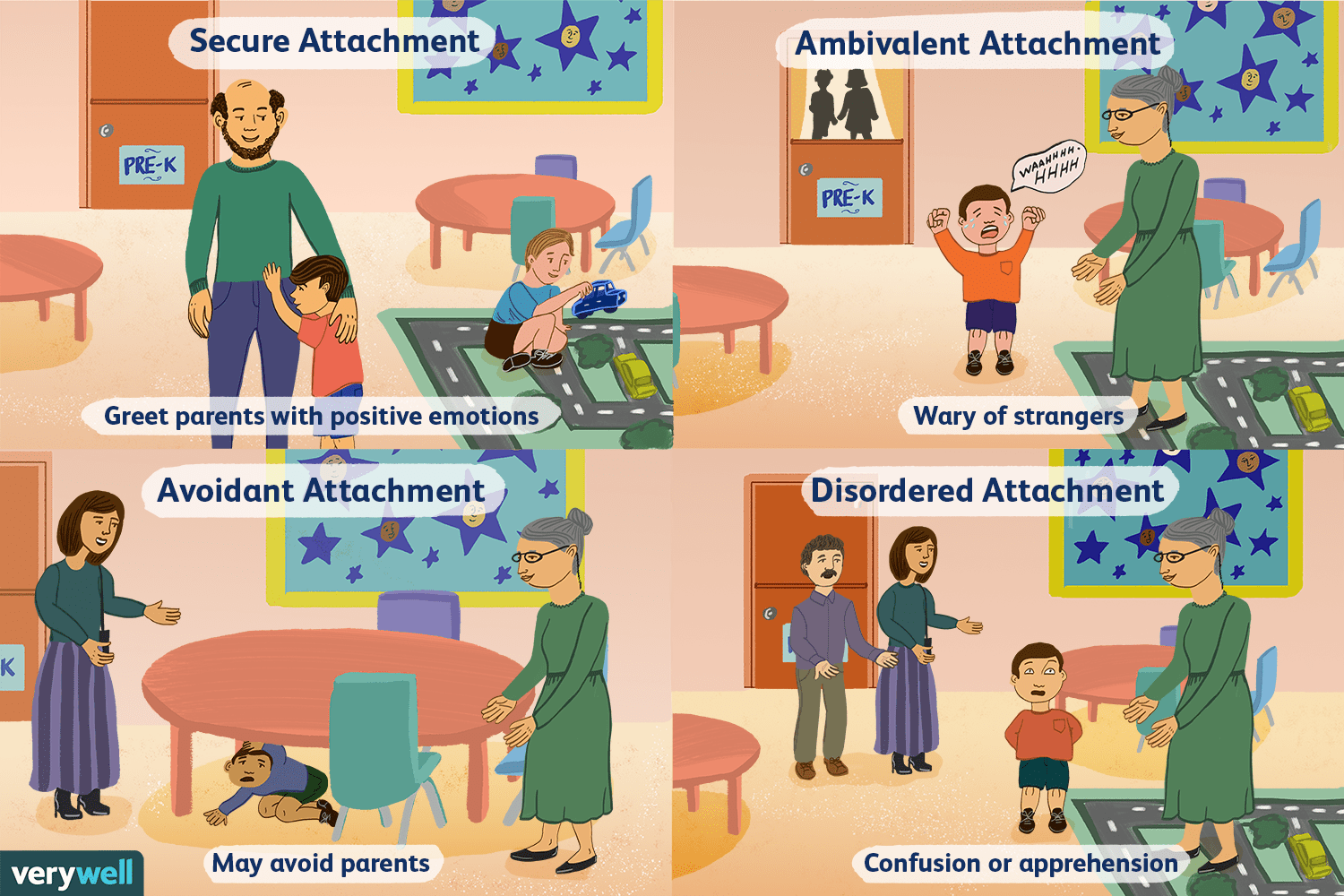
Secure attachment
-from strange situation experiment by Ainsworth
-Indicative of authoritative parenting style, 70% of infants, distressed when mom leaves, happy when she comes back
-Indicative of authoritative parenting style, 70% of infants, distressed when mom leaves, happy when she comes back
22
New cards
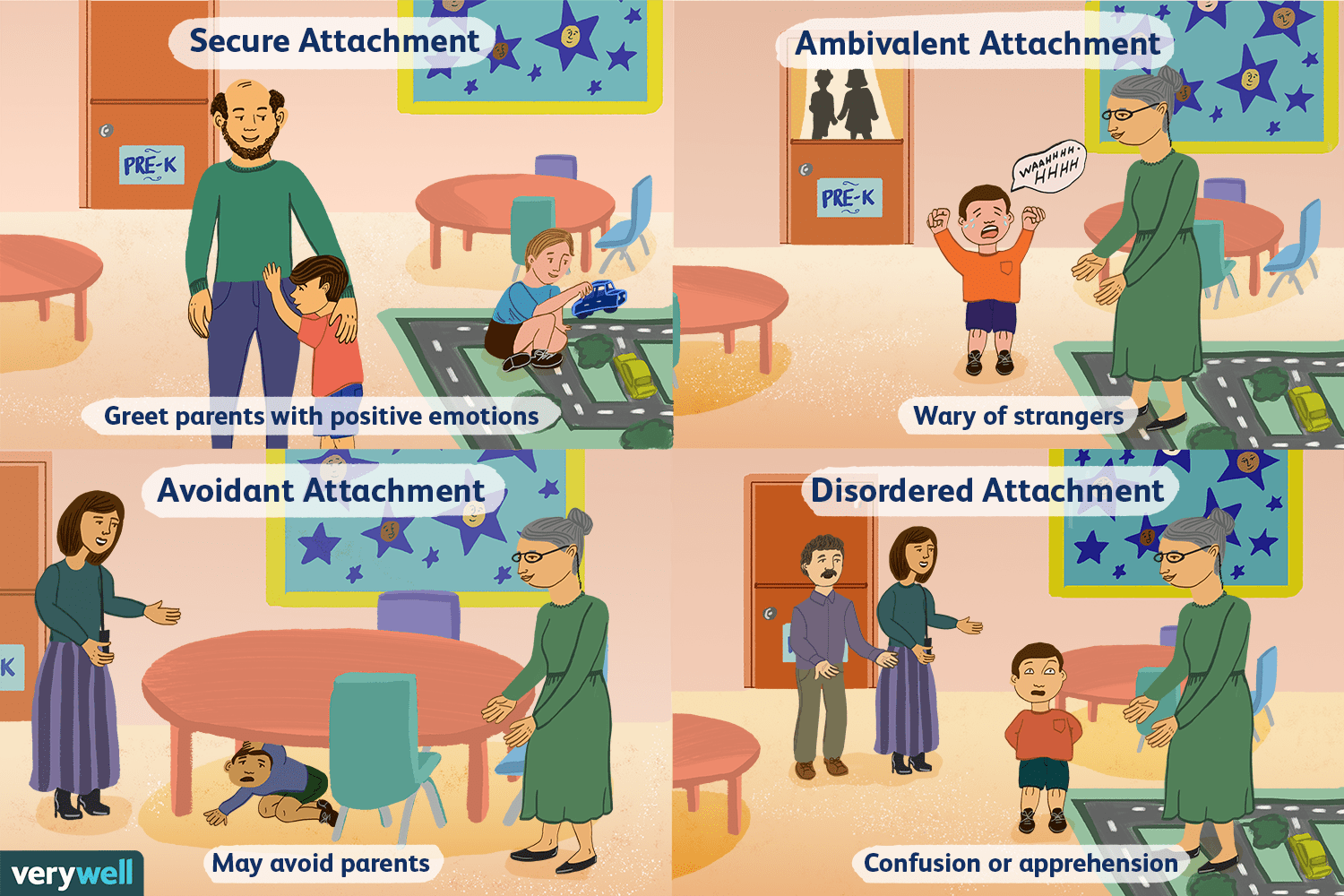
Anxious-ambivalent attachment
-from strange situation experiment by Ainsworth
-Indicative of authoritarian parenting style, distressed when separated from the caregiver but does not feel reassured when the caregiver returns, 15%
-Indicative of authoritarian parenting style, distressed when separated from the caregiver but does not feel reassured when the caregiver returns, 15%
23
New cards
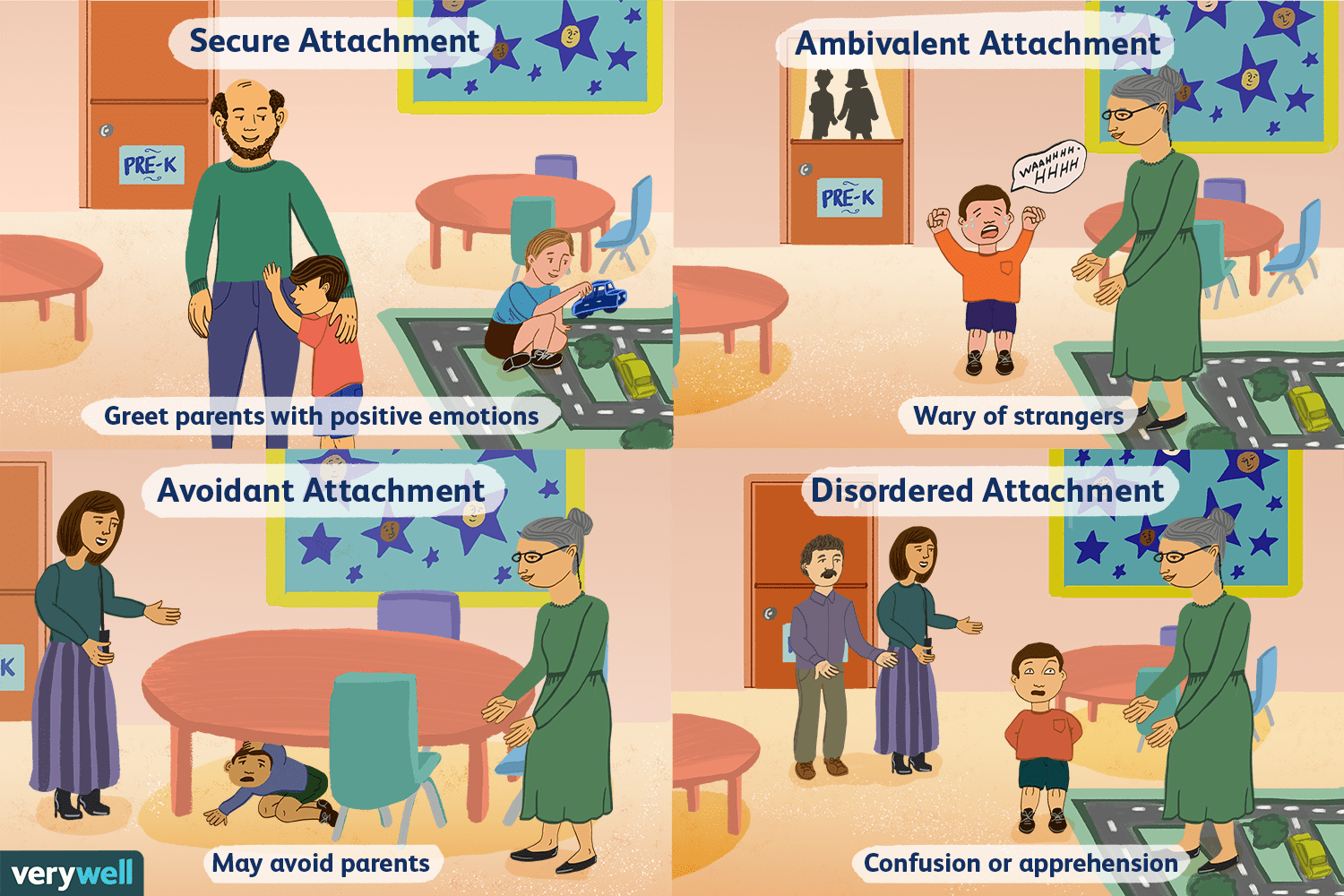
Avoidant attachment
-from strange situation experiment by Ainsworth
-Indicative of hands off parenting style, doesn't care about mom and is equally comfortable with a stranger, 15%
-Indicative of hands off parenting style, doesn't care about mom and is equally comfortable with a stranger, 15%
24
New cards
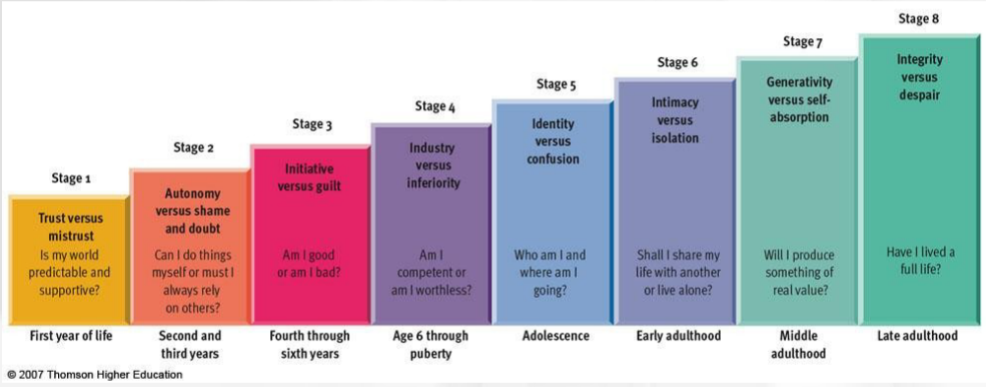
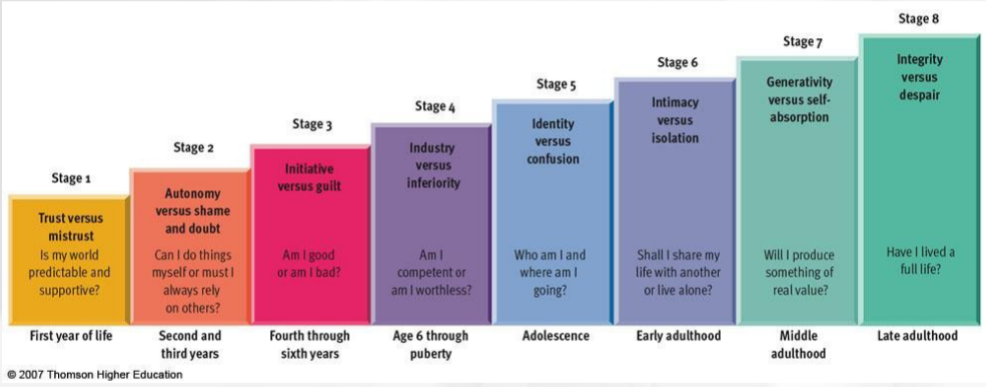
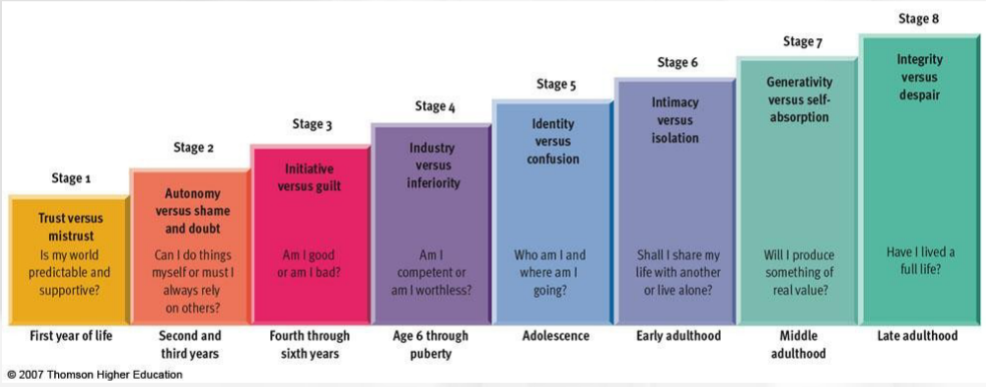
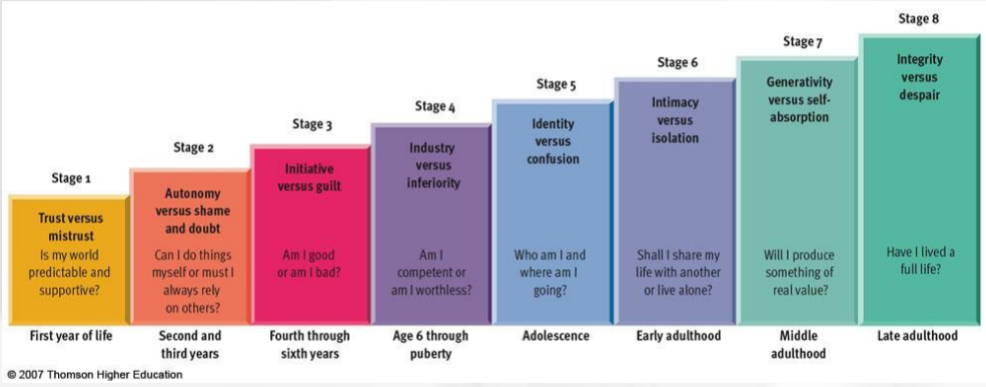
Erik Erickson
-Eight stages spanning the lifespan
-Psychosocial crises determine balance between opposing polarities in personality
-Key challenge is forming a sense of identity
-Psychosocial crises determine balance between opposing polarities in personality
-Key challenge is forming a sense of identity
25
New cards
Visual Cliff Experiment
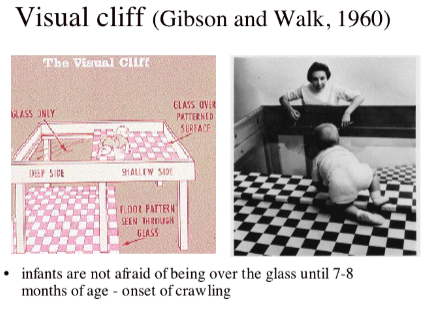
26
New cards
Jean Piaget
studied children to understand how children acquired knowledge and skills; cognitive development
27
New cards
schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
28
New cards
assimilation
interpreting one's new experience in terms of one's existing schemas
29
New cards
accomodation
adapting one's current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
30
New cards
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived, Piaget thought iy developed at 2 years of age
31
New cards
Representational thought
whenever one thinks about his or her surroundings using images or language
32
New cards
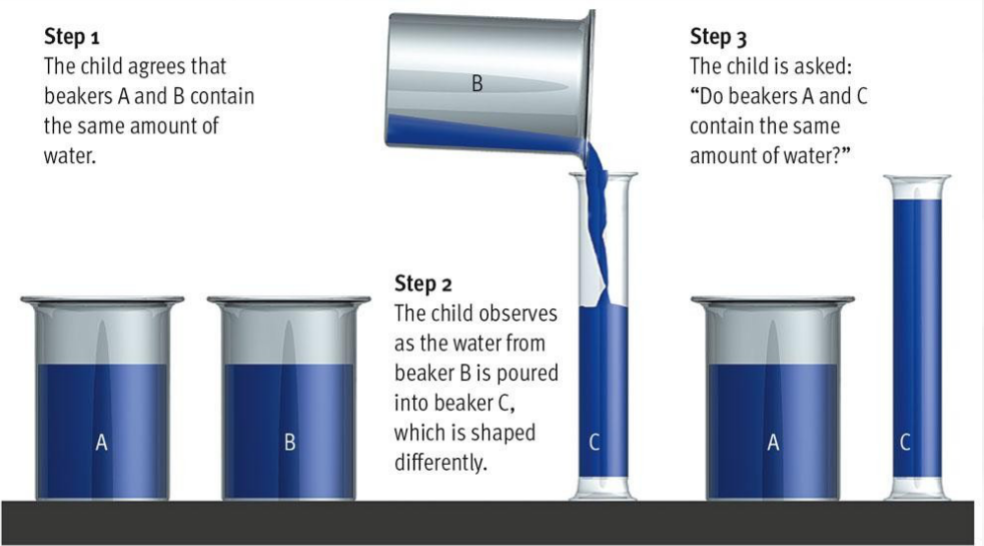
conservation
the principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects, develops between ages 7-11
33
New cards
egocentrism
iin Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
“Why does the sun shine?” “So I can play outside!”
“Why does the sun shine?” “So I can play outside!”
34
New cards
theory of mind
people's ideas about their own and others' mental states- about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts and the behavior these might predict
35
New cards
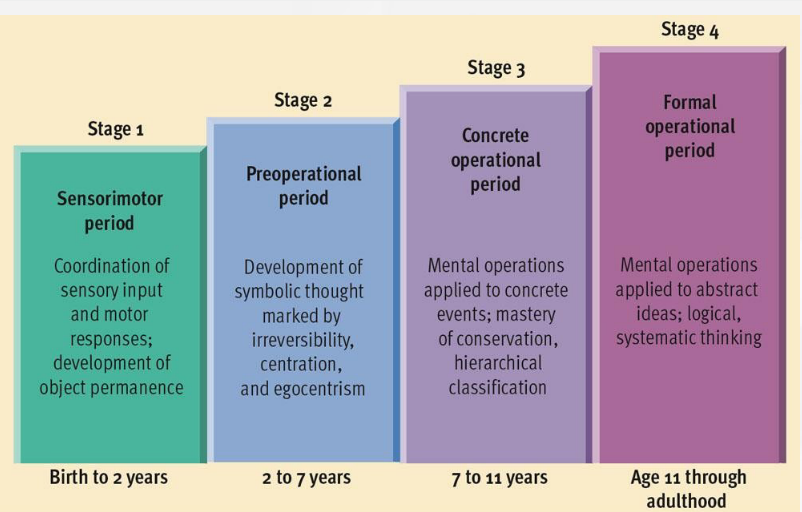
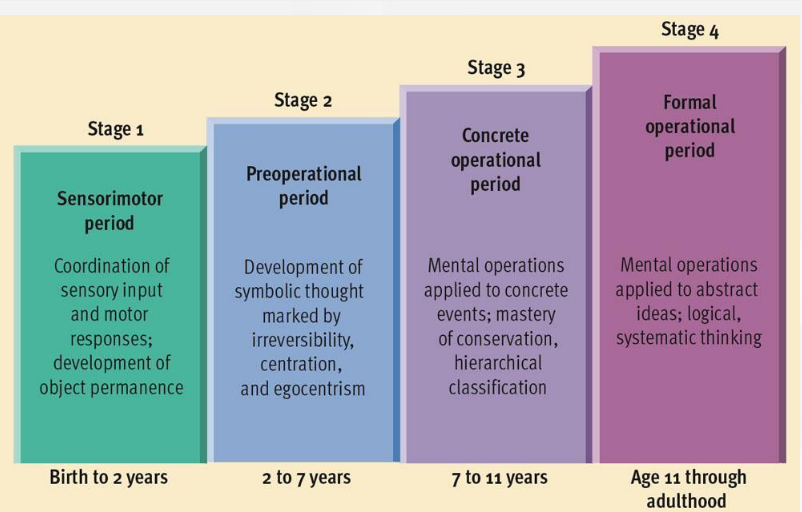
sensorimotor stage
coordination of sensory input and motor responses; development of object permanence
Birth-2 years
Birth-2 years
36
New cards
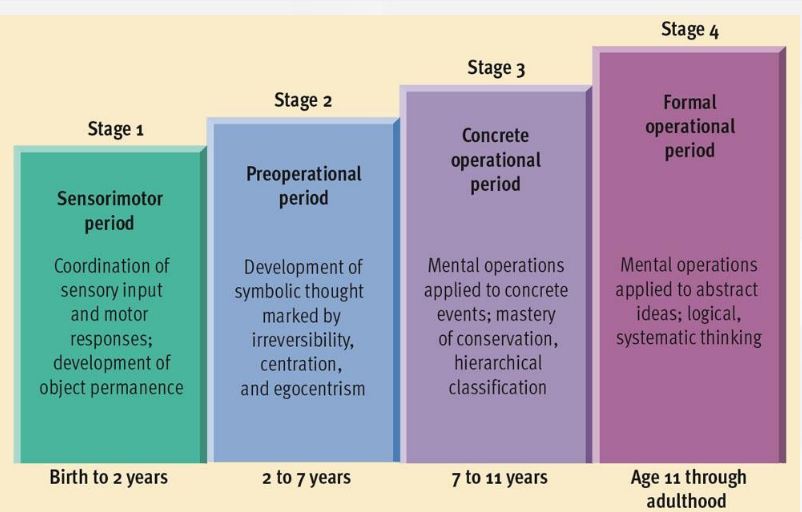
preoperational stage
development of symbolic thought marked by irreversibility, centration, and egocentrism
2-7 years
2-7 years
37
New cards
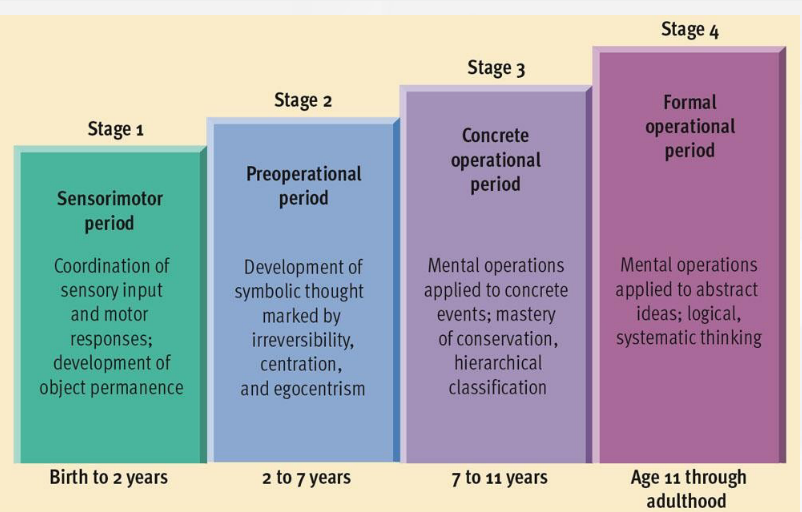
concrete operational stage
children gain mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events, mastery of conservation
7-11 years
7-11 years
38
New cards
formal operational stage
people begin to think logically about abstract concepts; logical systematic thinking
11-adulthood
11-adulthood
39
New cards
stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
40
New cards
Imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
41
New cards
attachment
an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation
42
New cards
Surrogate monkey experiment
Harry Harlow (1971)
found that the baby monkeys preferred to cling to the terry cloth surrogate even when food was provided by the wire surrogate, comfort and stability over food
found that the baby monkeys preferred to cling to the terry cloth surrogate even when food was provided by the wire surrogate, comfort and stability over food
43
New cards
critical period
an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces proper development
44
New cards
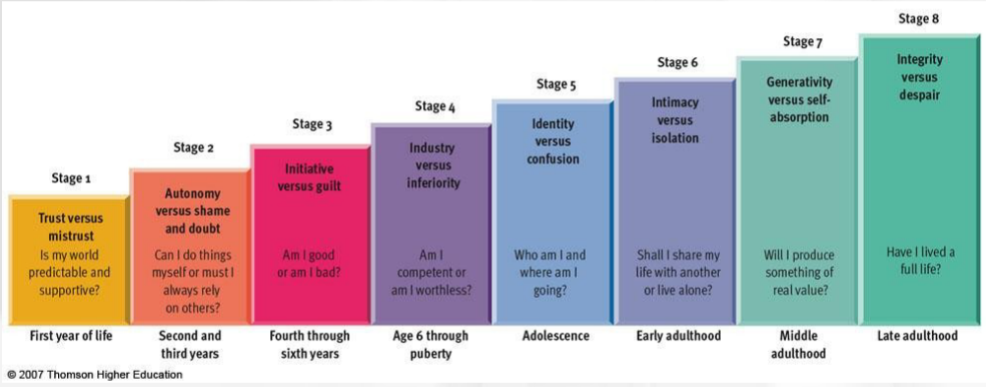
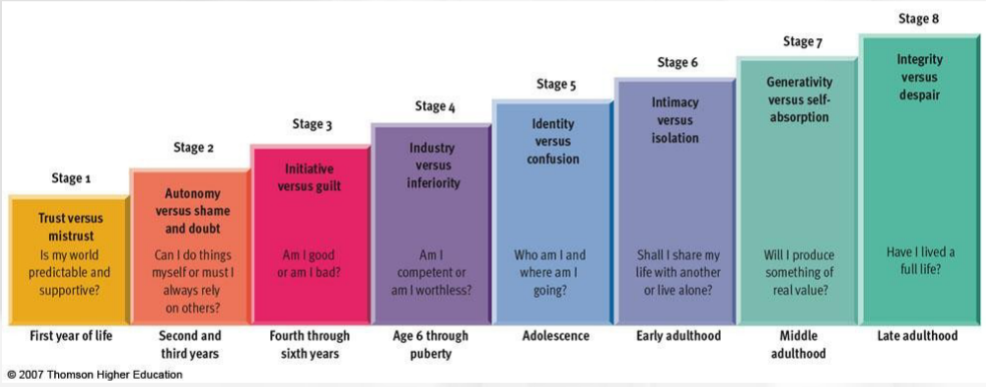
Erikson Stage 1
Trust vs mistrust
Is my world predictable and supportive?
First year of life
Is my world predictable and supportive?
First year of life
45
New cards
Erikson Stage 2
Autonomy vs shame and doubt
Can I do things myself or do I rely on others?
Second and third years of life
Can I do things myself or do I rely on others?
Second and third years of life
46
New cards
Erikson stage 3
Initiative vs guilt
Am I good or bad?
Fourth through sixth years
Am I good or bad?
Fourth through sixth years
47
New cards
Erikson stage 4
Industry vs inferiority
Am I competent or worthless?
6-puberty
Am I competent or worthless?
6-puberty
48
New cards
Erikson stage 5
Identity vs confusion
Who am I and where am I going?
adolescence
Who am I and where am I going?
adolescence
49
New cards
Erikson stage 6
Intimacy vs isolation
Do I share my life or live alone?
early adulthood
Do I share my life or live alone?
early adulthood
50
New cards
Erikson stage 7
generativity vs self-absorption
Will I produce something of value?
middle adulthood
Will I produce something of value?
middle adulthood
51
New cards
Erikson stage 8
Integrity vs despair
Have I lived a full life?
Late adulthood
Have I lived a full life?
Late adulthood
52
New cards
Kholberg
Studied moral development
53
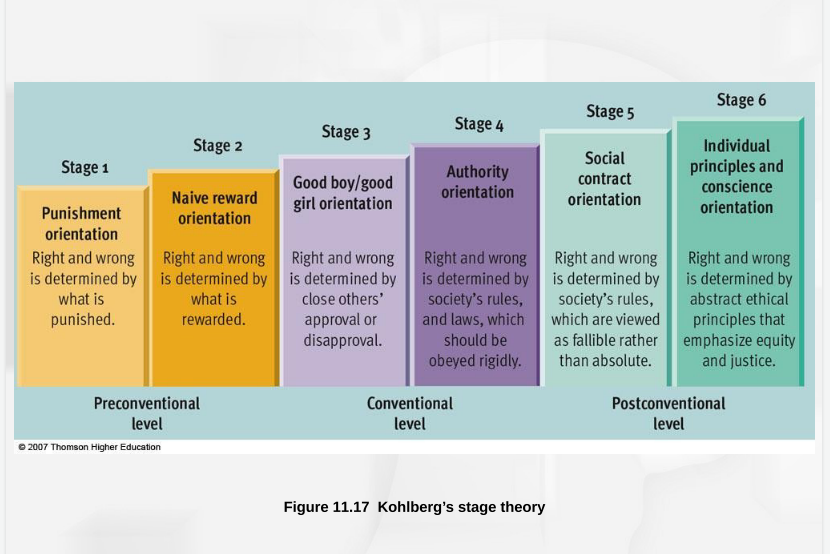
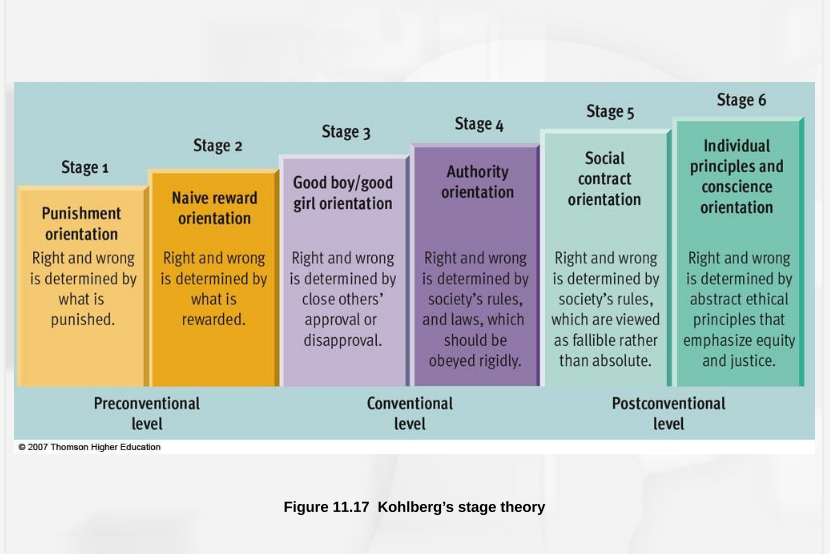
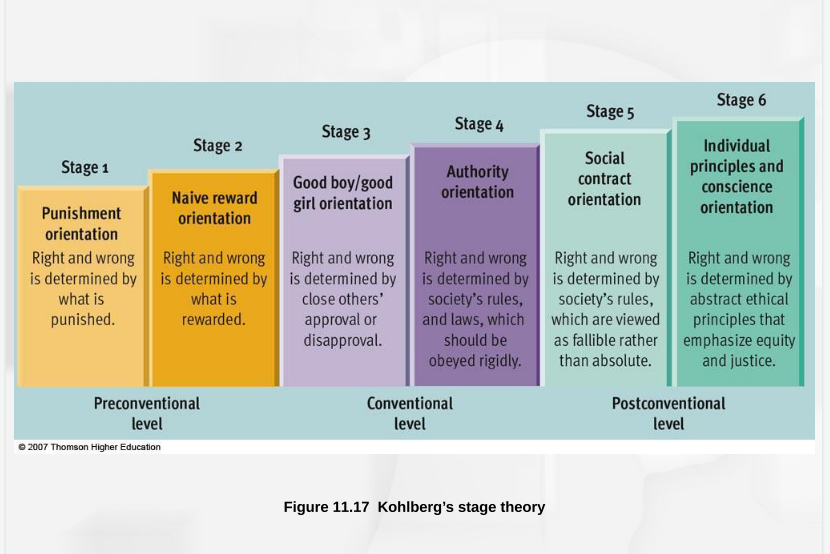
New cards
Preconventional level
Before age 9, children act out of self-interest (not wanting to get in trouble)
Stage 1: Obedience and punishment
Right vs wrong determined by what you get away with
Stage 2: Instrumental relativists
Right vs wrong determined by reward
Stage 1: Obedience and punishment
Right vs wrong determined by what you get away with
Stage 2: Instrumental relativists
Right vs wrong determined by reward
54
New cards
Conventional level
Begins in early adolescence (older children, adolescents, and most adults)
cares for others and upholds laws and social rules simply because they are the laws and rules (social approval)
Stage 3: Good boy/nice girl
Right vs wrong determined by approval of others
Stage 4: Authority
Right vs wrong determined by infallible laws
cares for others and upholds laws and social rules simply because they are the laws and rules (social approval)
Stage 3: Good boy/nice girl
Right vs wrong determined by approval of others
Stage 4: Authority
Right vs wrong determined by infallible laws
55
New cards
Postconventional level
Follows own set of ethical principles, only select few reach this level of morality (MLK, Ghandi, Hitler); Rare with adolescents and few adults
Stage 5: Social contract
Right vs wrong determined by fallible laws, flexible
Stage 6: Universal ethics principle
Right vs wrong determined by personal abstract principles using many perspectives
Stage 5: Social contract
Right vs wrong determined by fallible laws, flexible
Stage 6: Universal ethics principle
Right vs wrong determined by personal abstract principles using many perspectives
56
New cards
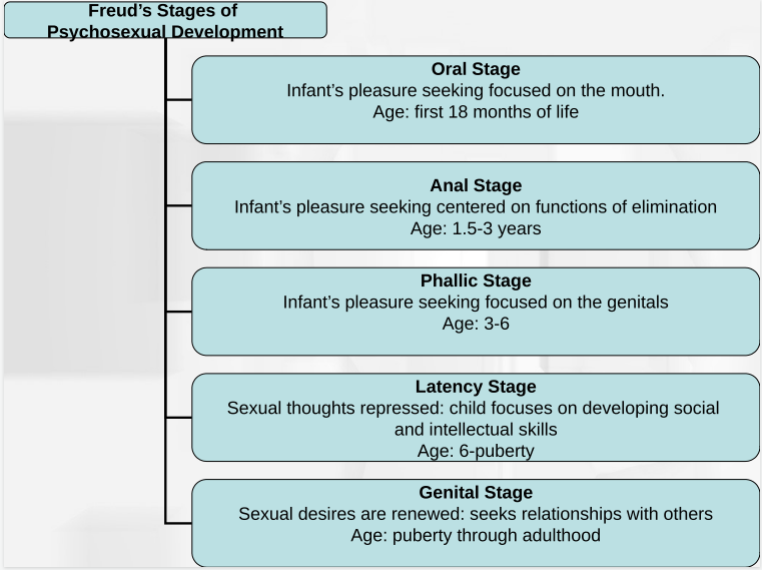
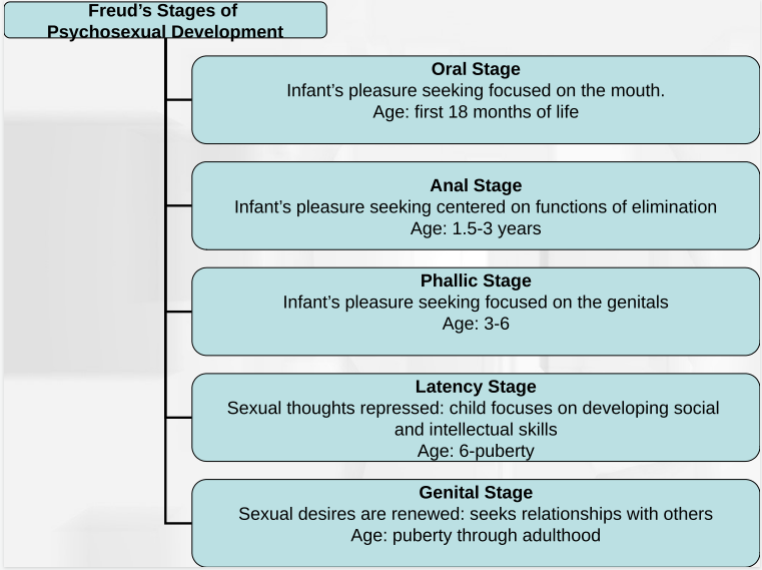
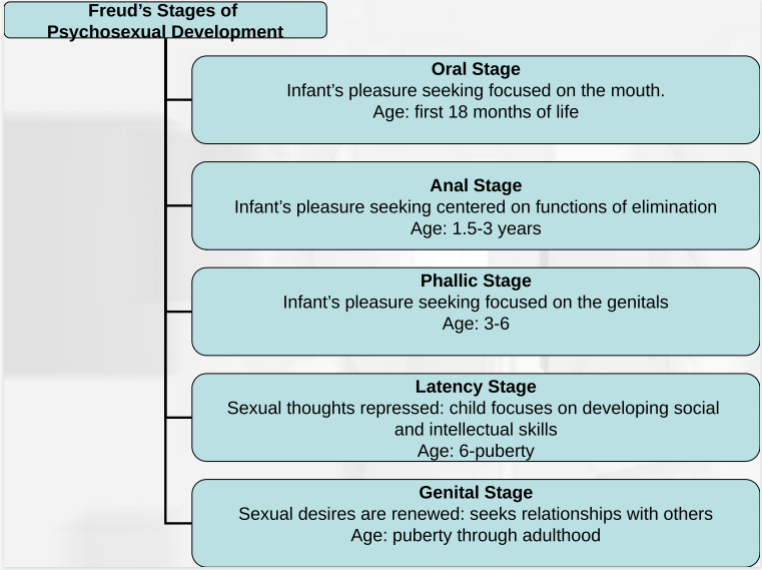
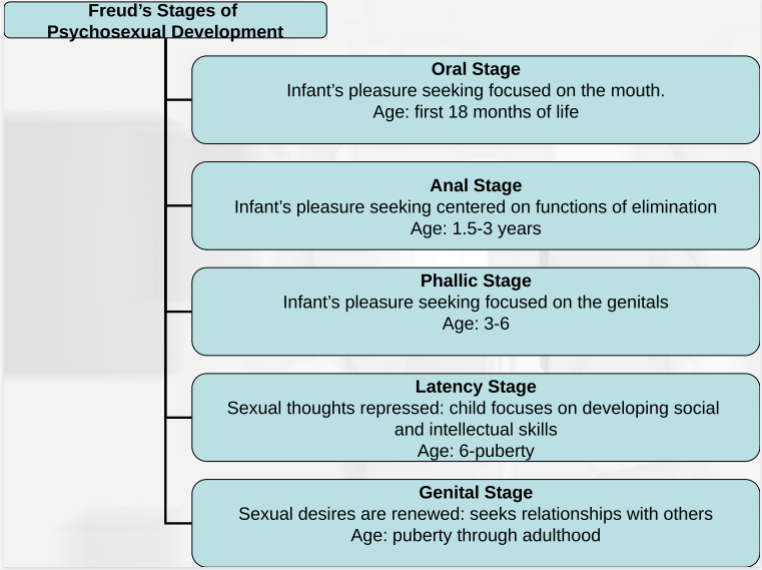
Sigmund Freud
studied psychosexual development
57
New cards
Oral stage
Pleasure focused on mouth
First 18 months
Oral Receptive: oral fixation leads to biting and smoking, passive, needy, sensitive
Oral aggressive: oral fixation leads to verbal aggression
First 18 months
Oral Receptive: oral fixation leads to biting and smoking, passive, needy, sensitive
Oral aggressive: oral fixation leads to verbal aggression
58
New cards
Anal stage
Pleasure focused on functions of elimination
1.5-3 years
Anal retentive: strict toilet training, obsessively clean, controlling, possessive
Anal expulsive: lax toilet training, leads to poor organization and possibly aggression
1.5-3 years
Anal retentive: strict toilet training, obsessively clean, controlling, possessive
Anal expulsive: lax toilet training, leads to poor organization and possibly aggression
59
New cards
Phallic stage
Pleasure focused on genitals
3-6 years
Issues can lead to vanity and impulsiveness
3-6 years
Issues can lead to vanity and impulsiveness
60
New cards
Latency stage
Sexual thoughts repressed, child focuses on social and intellectual skills
6-puberty
Issues can lead to immaturity and relationship issues
6-puberty
Issues can lead to immaturity and relationship issues
61
New cards
Genital stage
Sexual desires are renewed, seeks relationships with others
puberty-adulthood
Issues can lead to self-obsessiveness
puberty-adulthood
Issues can lead to self-obsessiveness
62
New cards
Authortatian parenting
High control with little warmth, no discussions
Aim to cultivate hard work, respect, and obedience
Produces overachievers
Aim to cultivate hard work, respect, and obedience
Produces overachievers
63
New cards
Authoritative/democratic parenting
High control and high warmth
Set rules but allow discussions
Best style in theory
Set rules but allow discussions
Best style in theory
64
New cards
Permissive parenting
Warmth but little control
Less rules and punishments
Children struggle with independence
Less rules and punishments
Children struggle with independence
65
New cards
Neglectful parenting
No warmth or control
May meet physical needs but nothing else
Children struggle with basically everything
May meet physical needs but nothing else
Children struggle with basically everything
66
New cards
Pubescence/Puberty
the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction
67
New cards
Primary sex characteristics
Reproductive organs + genitalia
68
New cards
Secondary sex characteristics
Traits that develop at puberty
Examples: breasts, menarche, voice changes, body shape
Examples: breasts, menarche, voice changes, body shape
69
New cards
Menarche
First occurrence of menstruation
Early menarche leads to more distress and emotional difficulty with transition to adolescence
Early menarche leads to more distress and emotional difficulty with transition to adolescence
70
New cards
Spermarche
First occurrence of sperm production
Late spermarche leads to distress and emotional difficulty with transition to adolescence
Late spermarche leads to distress and emotional difficulty with transition to adolescence
71
New cards
Adolescence neural changes
Increasing myelinization (faster connections)
Synaptic pruning (reshaping neurons)
Changes in prefrontal cortex (decision making)
Synaptic pruning (reshaping neurons)
Changes in prefrontal cortex (decision making)
72
New cards
Maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
Maturation differs between sexes
Girls who mature early, boys who mature late experience emotional distress with transition to adolescence
Maturation differs between sexes
Girls who mature early, boys who mature late experience emotional distress with transition to adolescence
73
New cards
James Marcia
studied Identity statuses and development
74
New cards
Identity diffusion
Absence of struggle for identity with no obvious concern about it
75
New cards
Identity Foreclosure
Unquestioning adoption of parental or societal value
76
New cards
Identity Moratorium
Actively struggling for a sense of identity
77
New cards
Identity acheivement
Successful achievement of a sense of identity
78
New cards
Fluid intelligence
Ability to reason, learn, think abstracly and solve problems
Decreases with age
Decreases with age
79
New cards
Crystallized intelligence
Prior learning and past experiences, based on facts
Increases with age
Increases with age
80
New cards
Menopause
the time of natural cessation of menstruation
Estrogen decreases
Estrogen decreases