Datasikkerhet modul 3: intro to Cryptography
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a Greek word meaning hidden text or writing:
Crypto = Hidden
Graphy = Writing or text
“The mathematical science that deals with transforming data to render it meaning unintellingble, prevent its undetected ateration or prevent its unathorized use.
What is Encryption?
The cryptographic transformation of data (called “plain text”) into a different form (called “cipher text” that conceals the data’s original meaning and prevents the original forrm from being used.
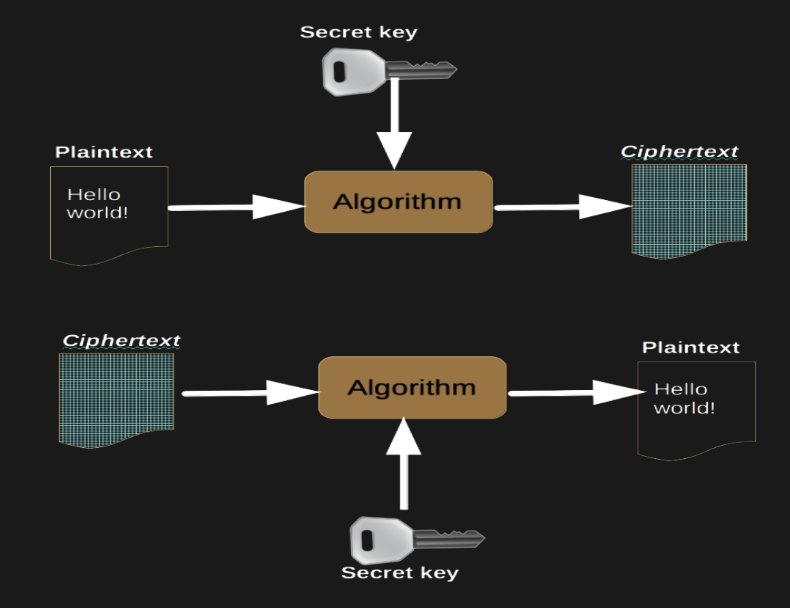
A common way to encrypt/decrypt a message is by using 2 inputs, why?
Do not rely on the algorithm by itself
One input is plaintext, and the other input is a secret known to those involved in the communication
Secret key is kept strictly secret
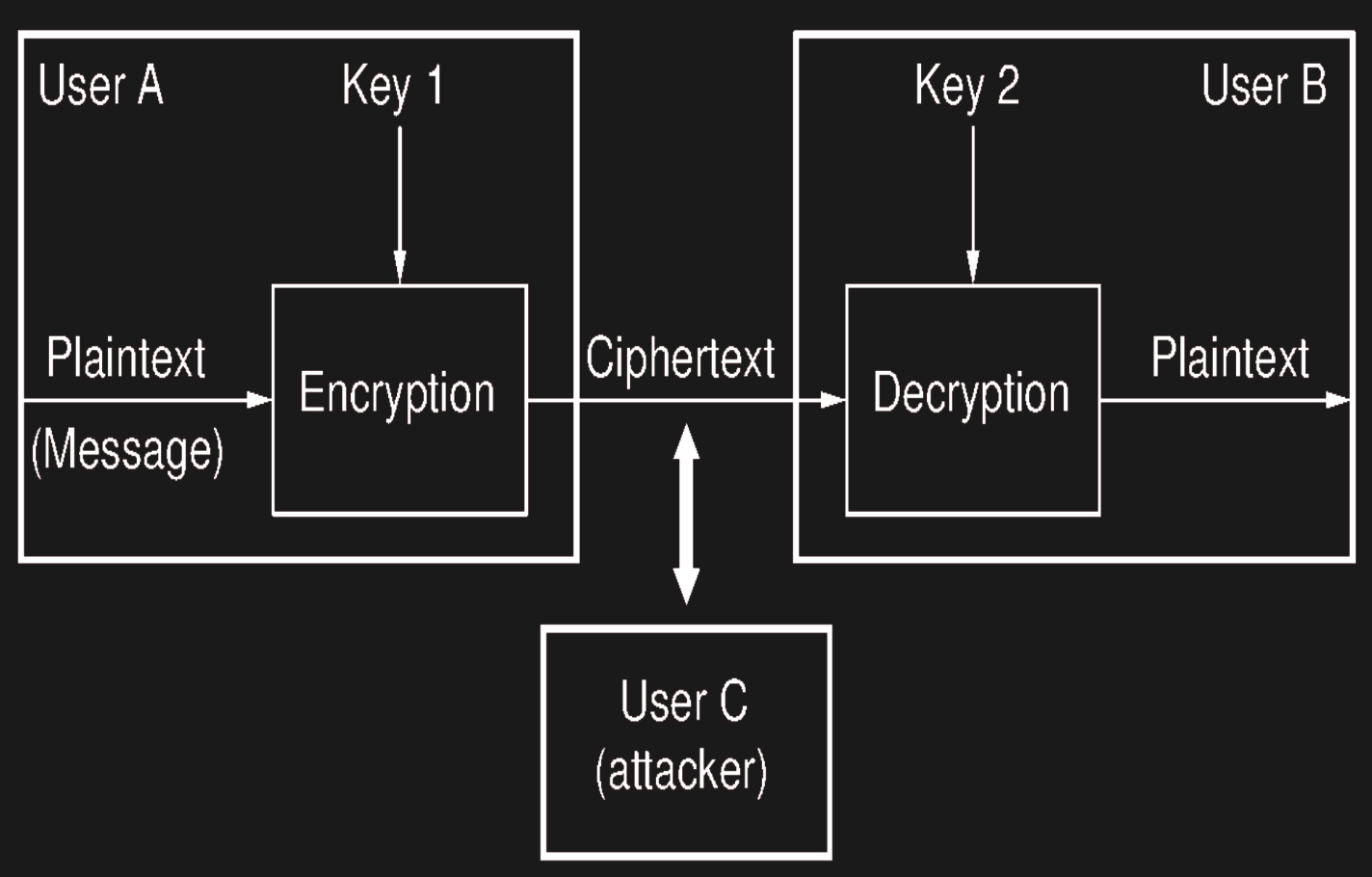
What is a cryptosystem?
A cryptosystem is like the “machinery” behind secure communication — it defines how encryption works, what algorithms are used, and how keys protect the data.
What are the different Encryption Techniques?
Encryption techniques:
The two basic building blocks of all encryption techniques are substitution and transposition.
Substitution: A method of encryption in which elements of the plain text retain their sequential position but are replaced by elements of cipher text. Example: Caesar Cipher (Mono-alphabetic) and Vigenère (polyalphabetic)
Transposition: A method of encryption in which elements of the plain text retain their original form but undergo some change in their sequential position.
Classical cryptography functions by manipulating the symbols of plaintext (like letters of the alphabet) using substitution or transposition rules — often with a secret key that determines how the message is changed.
What is a One-Time Pad?
An encryption algorith in which the key is a random sequence of symbols and each symbol is used for encryption only one time. A copy of the key is used similarly for decryption.
To ensure one-time use, the copy of the key used for encryption is destroyed after use, as is the copy used for decryption.
Implemented by Vernam Cipher.
Unbreakable when implemented correctly.
Each pad in the scheme must be:
Made up of truly random values
Used only one time
Securely distributed to its destination
Secured at sender’s and receiver’s sites
At least as long as the message
Why is it not used?
Complicated, not practical
In order for One-Time Pad to be secure, one must create a random secret key that is the same length as the plaintext and use it only once. For this reason, the concept of perfect secrecyu is abandoned for other more practical cryptographic algorithms.
What is a Random Number Generator and why do we need it?
A process that is invoked to generate a random sequence of values (usually sequence of bits) or an indiviudual random value.
Random nubers are required in cryptography for:
Key generation
Salting
Nonces (random bits of string often used in time-stamping)
True randomness is very difficult to achieve, therefore many application and operating systems use pseudorandom number generator instead. Pseudorandom number generators generate a sequence of values that appears to be random (unpredictable) but is actually generated by a deterministic algorithm.
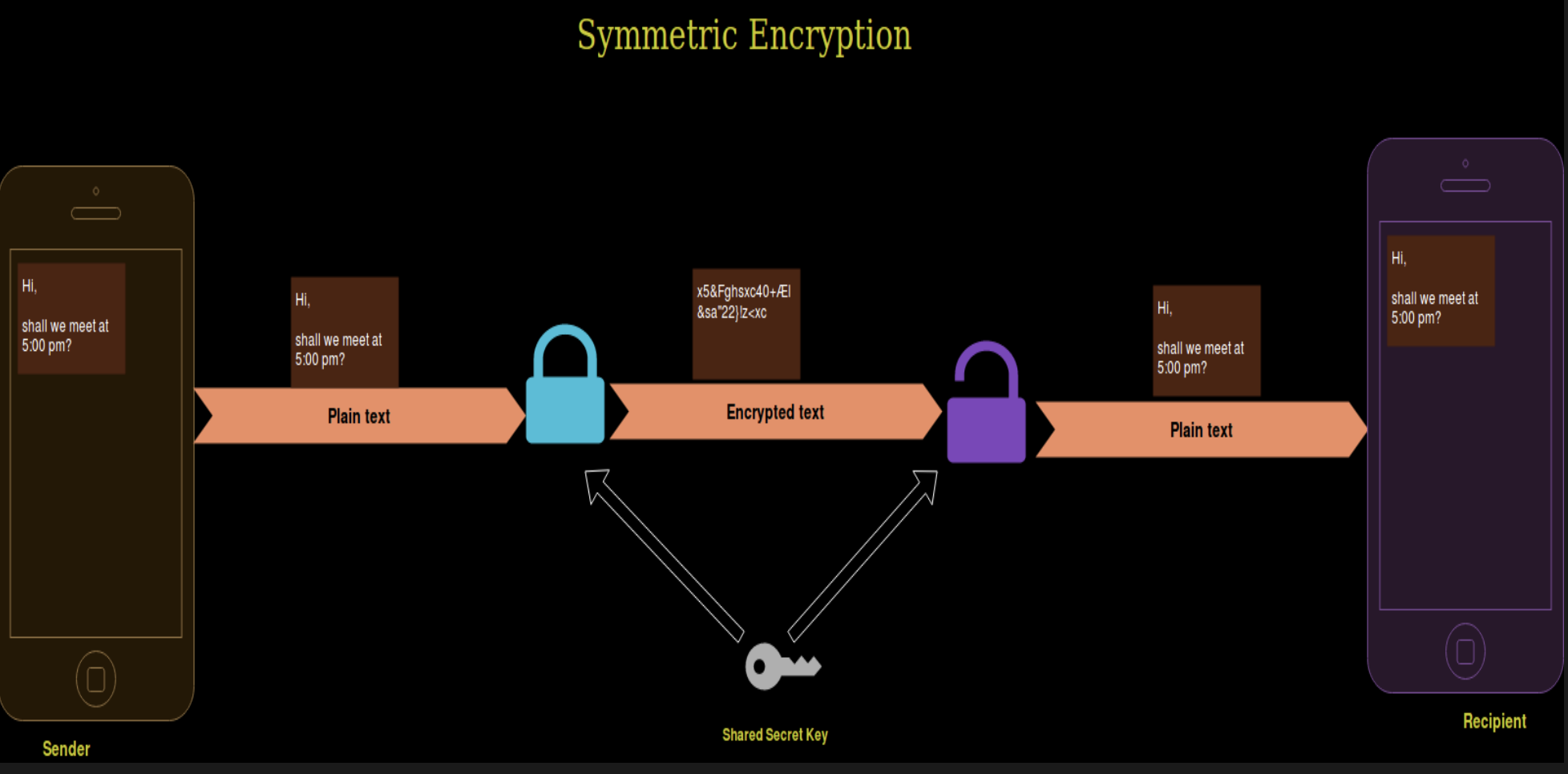
What is Symmetric Cryptography?
Symmetric cryptography is a branch of cryptography in which the algorithms use the same key for borth of two counterpart cryptographic operations (encryption and decryption).
Classical cryptography was based solely on symmetric cryptography.
Challenge: key exhange
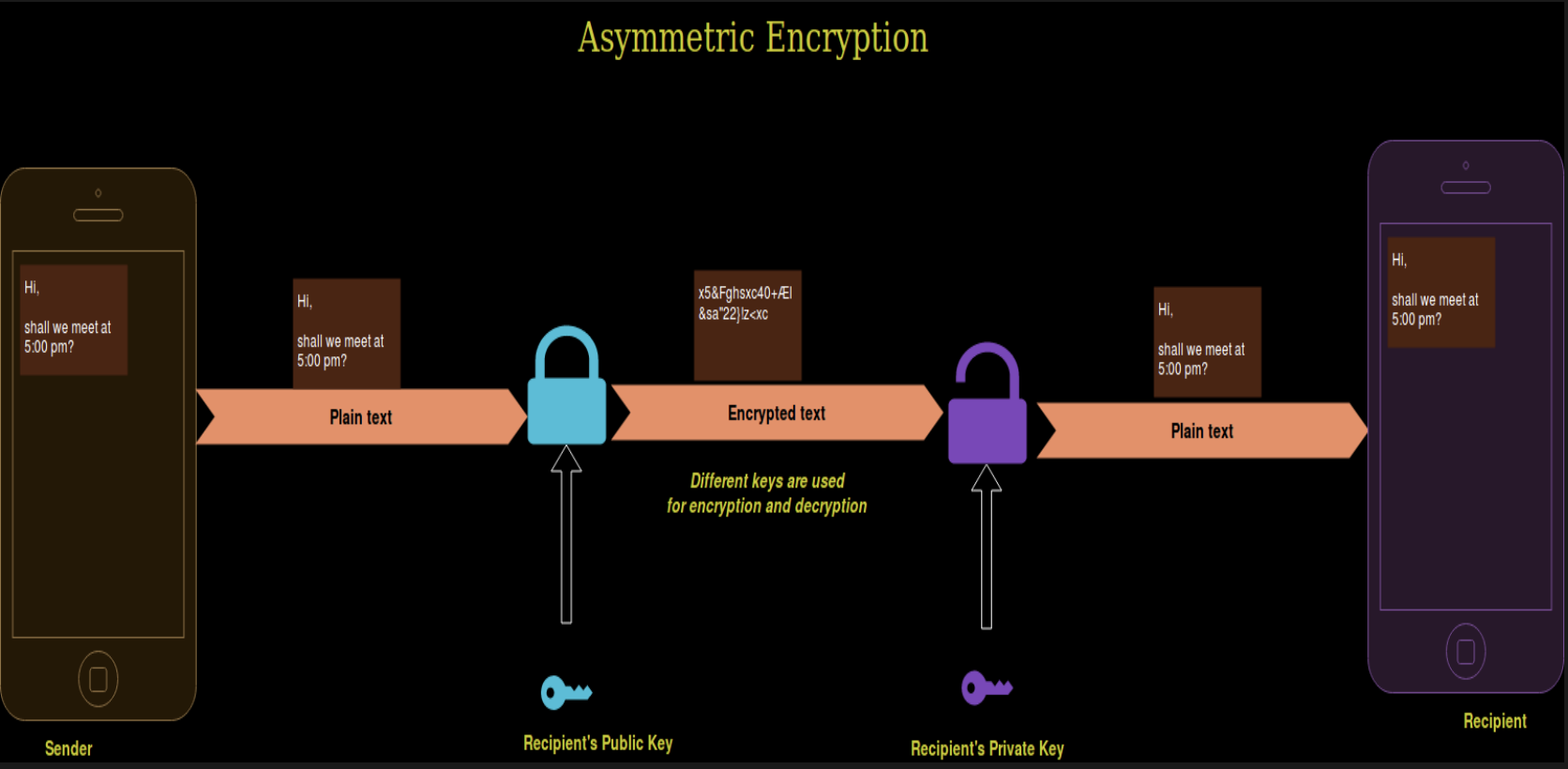
What is Asymmetric Cryptography?
A modern branch of cryptography (popularly known as public-key cryptography) in which the algorithms use a pair of keys (public and private) and use a different component of the pair for each of two counterpart cryptographic operations (encryption and decryption, or signature creation and signature verification).
Public key encrypts or verifies
Private key decrypts or signs
What is a Hash Function and how can it help us with Data Integrity?
A hash function is a one-way mathematical algorithm that converts data of any size into a fixed-length value (hash or digest).
To be secure and useful, a cryptographic hash function must meet these requirements:
Quick Computation:
It should be easy and fast to compute the hash valuehfrom a messagem.Deterministic:
The same input messagemmust always produce the same hashh.Pre-image Resistance:
Given only a hash valueh, it should be computationally infeasible to find the original messagemsuch thatH(m) = h.
→ Example: Knowing only the hash of a password shouldn’t let you recover the password.Collision Resistance:
It should be infeasible to find two different inputsxandythat produce the same hash (H(x) = H(y)).
→ Prevents attackers from creating two different documents with the same hash.
It ensures data integrity because even the smallest change in the message produces a completely different hash — so if two hashes match, the data is intact.
Examples: SHA-2, SHA-3, BLAKE, BLAKE2, RIPEMD-160, RIPEMD-256, RIPEMD-320, Whirlpool
Uses: File verification, password storage, digital signatures, blockchain.
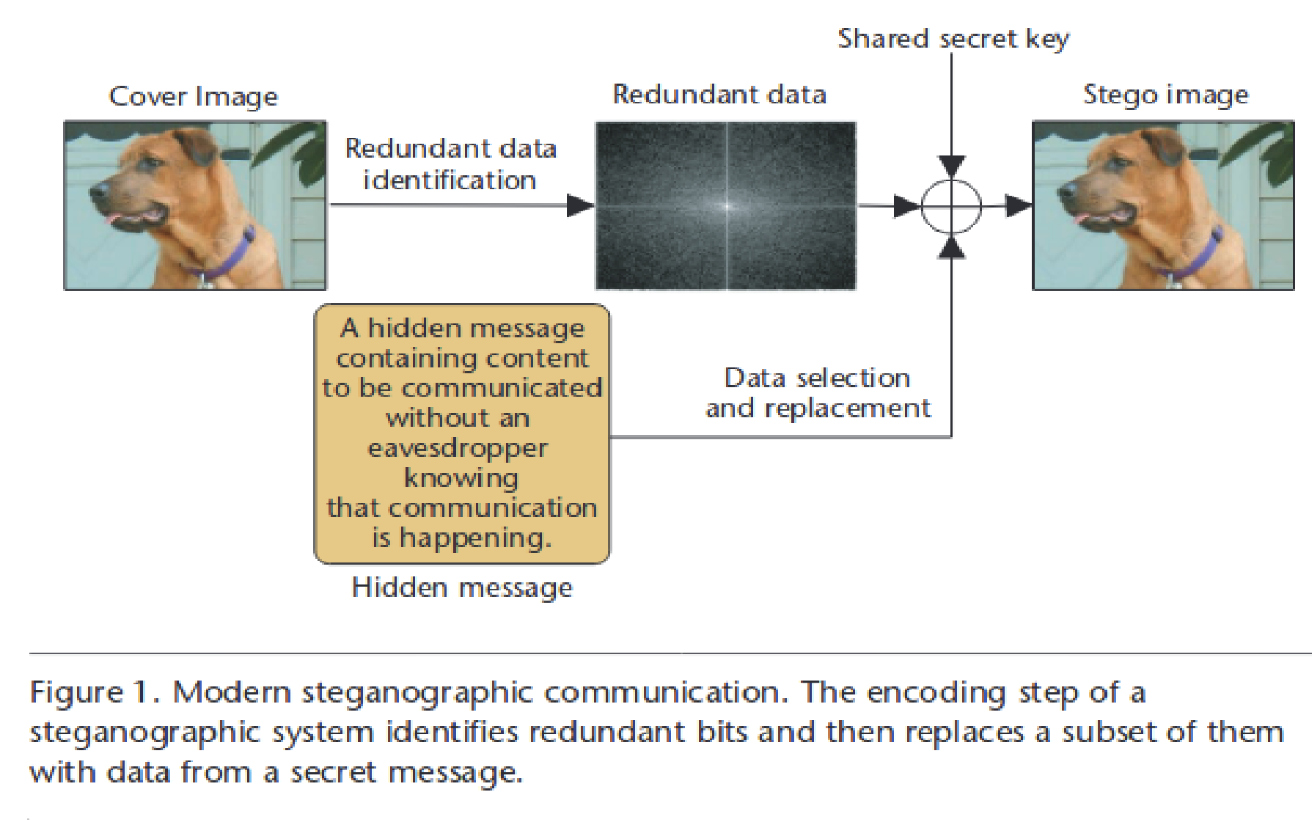
What is Steganography and how does it work?
Steganography is a Greek word meaning to hide or cover text or writing.
“Methods of hiding the existence of a message or other data. This is different than cryptography, which hides the meaning of a message but does not hide the message itself.”
What command can we use in Linux to calculate a hash value using OpenSSL?
openssl dgst -shaXXX
Example:
echo -n "HELLO" | openssl dgst -sha224
→ Calculates the SHA-224 hash of the text “HELLO”.
Why do both commands produce the same hash value?
echo -n "HELLO" | openssl dgst -sha224
cat testhashfunction.txt | openssl dgst -sha224Because both commands hash exactly the same input text (“HELLO”) —
hash functions are deterministic, meaning the same input always produces the same output.
How do you extract a hidden message from an image file using steghide in Linux?
Download the image (with potential hidden data):
wget http://www.cs.hioa.no/~ismail/ITPE3100/star-trek-enterprise.jpgExtract the hidden message:
steghide extract -v -sf star-trek-enterprise.jpgEnter the passphrase
Steghide creates the output fsymmeile, like msg.txt
Read the extracted message:
cat msg.txt
Which of the following is considered a cryptographic hash function?
DSA
BLAKE2512
BLAKEs256
MD4
MD5
RSA
WHIRLPOOL
DES
BASE64
SHAKE128
You can run:
openssl list -digest-algorithmsBLAKEs256
SHAKE128
SHA224
MD5
MD4
BLAKE2512
WHIRLPOOL
What do we mean when we say that a hash has the preimage resistance strength property?
Given a randomly chosen hash value, hash_value, it is computationally infeasible to find an x so that hash(x) = hash_value. This property is also called the one-way property.
What do we mean when we say that a hash has the second preimage resistance strength property?
That it is computationally infeasible to find a second input that has the same hash value as any other specified input. That is, given an input x, it is computationally infeasible to find a second input x’ that is different from x, such that hash(x) = hash(x’).
What do we mean when we say that a hash has the collision resistance strength property?
That it is computationally infeasible to find two different inputs to the hash function that have the same hash value. That is, if hash is a hash function, it is computationally infeasible to find two different inputs x and x’ for which hash(x) = hash(x’).