Peds Exam 1 - NEED TO KNOWS
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Preterm
Born on or before the last day in the 36th week
(Before 37 weeks)
Early term
37 weeks to 38 weeks and 6 days
Full term
39 weeks to 40 weeks and 6 days
Late term
41 weeks to 41 weeks and 6 days
Post term
>42 weeks
small for gestational age (SGA) and causes
<10th percentile
Causes: genetic disorder, placental abnormalities, drug/etoh during pregnancy, infection
Large for gestational age (LGA)
>90th percentile
Causes: maternal gestational diabetes
low, very low, extremely low birth weight
Low: <2500 g
Very low: <1500 g
Extremely low: <1000g
When is BW doubled? Tripled?
Doubled at 6 months
Tripled at 1 year
When do babies gain back the weight they lost post birth?
Lose 10% in first few days
Regain in 10-14 days
Umbilical cord competent
2 arteries: carry deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta
1 veins carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
Complications associated with infants of diabetic mothers
-hypoglycemia
-hypocalcemia
-hyperbilurubinemia
-macrosomnia (overweight)
-RDS
-HOCM
What does APGAR stand for? What is it used for
Quick assessment of infants immediate adaption to life
Appearance
Pulse
Grimace
Activity
Respiration
How is APGAR graded?
>5 @ 1 min: smooth transition
<4 @ 1 min: severe depression, need resuscitation
<7 @ 5 min: high ris of CNS dysfunction/cardiac problems
Score again @ 10 min if infant cyanotic at 5 min
What does the new Ballard score assess?
Gestational age
Routine newborn protocol
-Eye prophylaxis: silver nitrate & erythro
-Vit K
-Hep B
-Labs
-hearing screenings
Newborn labs
-state newborn screening
-hematocrit
-glucose
-bili
-blood type
Cause of RDS
surfactant deficiency
Risk factors for RDS
-males
-preterm
-maternal DM
-monozygotic twins
-C section
-fam Hx
How to diagnose RDS
CXR: air bronchograms and ground glass appearance
PE: dec breath sounds, nasal flaring, tachypnea
Cause of transient tachypnea of the newborn
Fetal lung fluid not expelled in delivery, & retained in lung
Most common cause of respiratory distress in TERM infants
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
How to diagnose tachypnea of the newborn
CXR: inc lung volume w/ flat diaphragm, no air bronchogram/ground glass
PE: tachypnea (>60) nasal flaring
Presentation of necrotizing enterocolitis
Gastric residuals after feeding
Hematochezia
Abd wall tenderness
Apnea, bradycardia
How to diagnose necrotizing enterocolitis
KUB: pneumatosis intestinalis
Most common hernia on the left side
Bochdalek
When are pregnant women tested for strep?
35-37 weeks
If postive: treat w PCN or amoxicillin
Cause of jaundice @ day 1, 2-3 days, 1 week, and 3 weeks
Day 1: always pathological
Day 2-3: physiologic/sepsis
1st week: breast fed
3rd week: biliary atresia
What is a Bhutani nomogram used for?
Assess risk of developing severe hyperbilirubinemia based on age and total bili
Normal bili levels in term vs preterm
Term: <12
Preterm: <15
Complications of jaundice in the newborn
kernicterus
-lethargy
-vomiting
-irritability
-poor feeding
-crying
Prevention of SIDS
-regular prenatal care
-avoiding tobacco
-supine sleep position
-avoid blankets, bumpers, pillows
-avoid co sleeping
caput succedaneum
Superficial edema that crosses suture line
Reconfigure in 1 week
Absent red reflex is indicative of
Retinoblastoma
cause of retinopathy of prematurity
-hypoxia, hypotension that disrupts normal angiogenesis
-incomplete retinal vascularization
Turner's syndrome presentation
-wide set nipples
-excessive nuchal skin
-lymphedema
Weak pulses could mean
-possible coarctation
-left ventricular flow obstruction
When should you be worried about a sacral tuft/sinus tract
If sinus tract or tuft of hair present
(If not: benign)
Sacral tuft/sinus tract can be indicative of
-spina bifida
-meningocele
-myelomeningocele
Abnormal develop of acetabulum and femur w/ mechanical instability of the hip
Hip dysplasia
Barlow vs Ortolani Maneuver
Barlow: dislocates by adducting and pulling down
Ortalani: reduces the joint but ABducting w/ anterior pressure
Galaezzi sign
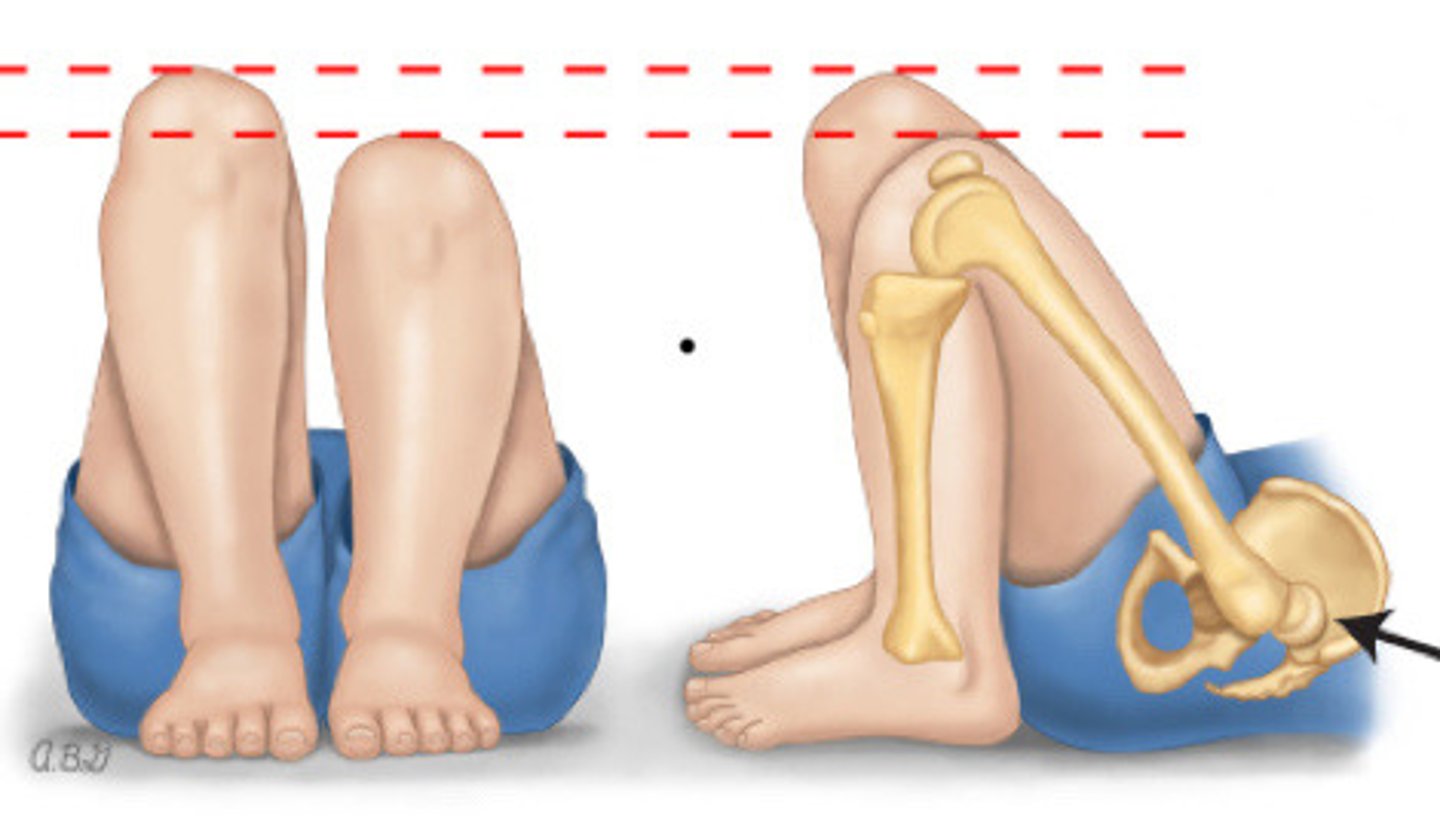
What do you evaluate during a neuro exam
Movement and reflexes
Open vs closed spina bifida
Open: myelomeningocele
Closed: spina bifida occulta
Waiters tip sign
Erb's palsy
Erb duchenne palsy
-Adduction and internal rotation of the shoulde
-elbow extension and pronation of forearm
-intact grasp reflex
PHACE syndrome
Posterior fossa malformation
Hemangioma
Arterial abnormalities
Cardiac abnormalities
Eye abnormality's
Sternal cleft
Most common vascular tumor of infancy
Hemangioma
When are screening tests done?
At physicals:
-9 mo
-18 mo
-24 mo
-30 mo
Screenings for autism
M-CHAT
CARS
CHAT
@ 18 mo and 24 mo physicals
Involuntary muscle reaction to a stimulus
Reflex
Absense of Moro reflex suggests?
Absent: UMN lesion
Incomplete: brachial plexus injury
Asymmetric Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR)
Childs head is turned to the side and assumes the fencer position
parachute reflex
extension of extremities when thrust downward in the prone position
I would personally know all of the reflexes cuz he could switch em up
:)
What age does an infant grasp objects and brings to mouth
4 months
What age does an infant have mature pincer grasp
12 mo
What age does an infant have early pincer grasp
9 mo
What age does an infant transfer objects from hand to hand
6 mo
Language development rule of 4s
2 years: 50% intelligible to strangers
3 years: 75% intelligible
4 years: 100% intelligible
normal dysfluency stuttering occurs when
2.5 - 5 yrs and is not distressing to child
How to manage stuttering
-reassurance
-if >5 yr : speech therapy
-SSRIs
Trisomy 21
Down syndrome
Features of Down syndrome
-intellectual disability
-dementia
-atlantoaxial instability
-inc cardiovascular risk (VSD, CHD)
-hypotonia
Most common sex chromosome abnormality in females
Turner syndrome
Cause of turner syndrome
Absence of an X chromosome
Turner syndrome presentation
-short stature
-sexual infantilism
-primary hypogonadism
-ovarian dysgenesis
-nipple hypertelorism
Cause of Klinefelter syndrome
Extra X chromosome in males
Klinefelter syndrome presentation
-micropenis
-hypospadias
-small testes
-cryptorchidism
-infertility
-gynecomastia
-incomplete virilization
-hypergonadotropic
Treatment of Klinefelter syndrome
-testosterone therapy
-ref to endocrine/genetics
Cause of fragile X syndrome
Religion of a single trinucleotide gene sequence (CGG) on the X chromosome
Developmental features of fragile X syndrome
-delayed milestones
-speech delay
-impaired short term memory
Prader-Willi Syndrome cause
Paternal deletion of chromosome 15q11
Features of Prader-Willi Syndrome
Infant: neonatal hypotonia, poor weight gain
Early childhood: weight gain, speech delay
Adolescence: behavioral issues, CV probs d/t obesity, OSA
(Short, obese, fish mouth, hypogonadism)
Genetic condition that increases connective tissue growth
Marfans
MC cardiopulmonary disorders with marfans
1. Aortic root dissection
2. MVP
Cause of marfans syndrome
Mutation in fibrillin 1 gene
Autosomal recessive disorder of cholesterol biosynthesis
Smith-lemli-opitz syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome features
-Thin vermillion border of upper lip
-smooth philitrum
-short palpebral fissure
Catch 22
Deletion of 22q
Cardiac defect
T cell defect
Cleft palate
Hypocalcemia
Treacher Collin's syndrome definition and cause
Def: autosomal dominant disorder of craniofacial development
Cause: mutation on chromosome 5
Features of Treacher Collin's
-malar hypoplasia
-hearing loss
-G tube feedings d/t swallowing prob
-Coloboma lower lid
-beak like nose
-micrognathia
-cleft palate
PKU
Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
Autosomal recessive
PKU features
-seizures
-hyperactivity
-aggressive behavior
-intellectual disability
Most common breath holding spell
Cyanotic: related to tantrums
Crying: breath holding: cyanotic: LOC
ADHD diagnostic criteria
Inattentive: 6+ sx
Hyperactivity: 6+ sx
Associations with ADHD
-learning disabilities
-mood disorders (depression)
Pattern of hostile and defiant behavior that is excessive
Oppositional defiant disorder
Persistent pattern of behavior that violates rules/norms and the basic rights of others
Conduct disorder
Night terrors vs nightmares
Terrors: occur in stage 3 of sleep, no recollection of event, 18 months-6 yrs
Nightmares: occurs during REM, may remember
Night terrors are are precipitated by
Stress, illness, sleep deprivation
Night terror presentation
Child awakened from deep sleep seemingly confused, dilated pupils, and sweating
Most common congenital heart defect
VSD
What CHD is common in Down's syndrome
ASD
Features of CoA
-murmur loudest @ ULSB, left interscapular
-bounding radial pulses
-diminished femoral pulses
tetrad of tetralogy of fallot
PROV
Pulmonary stenosis
RVH
Overriding aorta
VSD
Ebstein Anomaly
Tricuspid vale is displaces towards the apex of the right ventricle
Ebstein anomaly is commonly associated with
Maternal lithium ingestion
Marfan syndrome genetics
75% inherited
25% new mutation
50% chance of passing it only offspring
Venous hum is caused by
Turbulence in SVC