(2.3) cytoskeleton
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 2 - Bacteria
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what kinds of internal structures help to organize bacterial cells?
cytoskeleton
some cytoskeleton proteins involved in cell wall synthesis during cell division
FtsZ
MreB
other cytoskeletal proteins involved with moving internal items (e.g., plasmids, magnetosomes)
ParM
ff
cytoskeleton
series of internal proteins that assist in keeping everything in (or movinf it to) the right locations in cells
which cytoskeleton proteins involved in cell wall synthesis during cell division?
FtsZ
MreB
FtsZ
tubulin-related protein
polymerizes to form the Z-ring, a contractile structure at the inner membrane that marks the future division site and recruits cell wall-synthesis machinery
FtsZ labelling
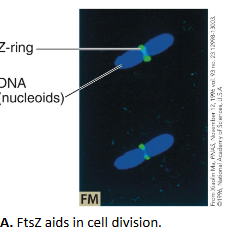
how do the z-ring and cell wall-synthesis machinery work together?
the z-ring pulls inward as FtsZ breaks down (GTP hydrolysis), helping the cell wall machinery pinch the cell in two; it disappears after division and grets rebuilt for the next round
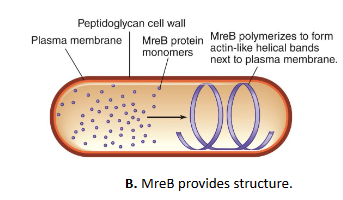
MreB
bacterial “actin-like” protein
behaves like actin in eukaryotes and forms long, helical filaments under the membrane
found in almost all non-spherical bacteria (ex, rod shaped, esp in multicellular form) → helps them stay rod-shaped by guiding where the cell wall gets built
MreB labelling
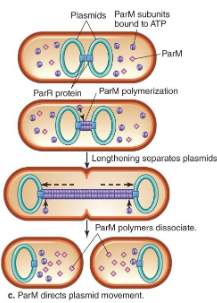
ParM
dorects plasmid movement to either side of the cell, ensuring plasmid segregation
mangetospirillium bacteria
white arrows →membrane that is surrounding the magnetism (that’s why these are considered ORGANELLES!)
high-res image of the plasmid membrane surrounding the magnetosomes
protein filaments found alongside the magnetosome chains: play a role in organizing them
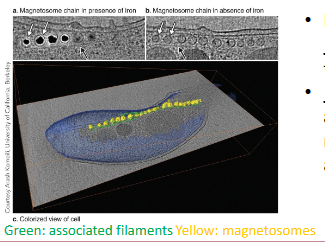
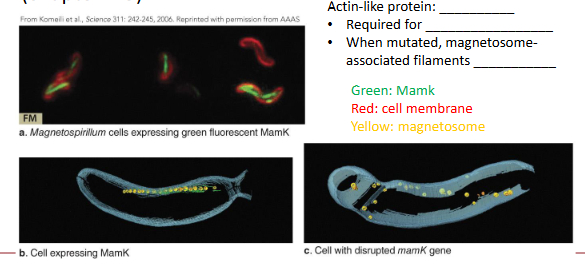
MamK
actin-like protein
required for magnetosome formation
when mutated, magnetosome-associated filaments disappeared
what happens when mamK gene is disrupted?
gene was fused to a fluorescent protein (GFP)
cell membrane is stained with red fluorescent dye
magnetosomes are no longer in the same line/ alignment like in image B
2.3 checkpoint
