csd3185 cumulative - exams 1-3
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
227 Terms
three main functions of outer ear
protection
amplification
localization
outer ear function
protection
anatomy of external ear and ear canal curvature
keeps things out
protects inside (middle/inner/brain)
what is the barrier between the outer and middle ear?
ear drum/tympanic membrane
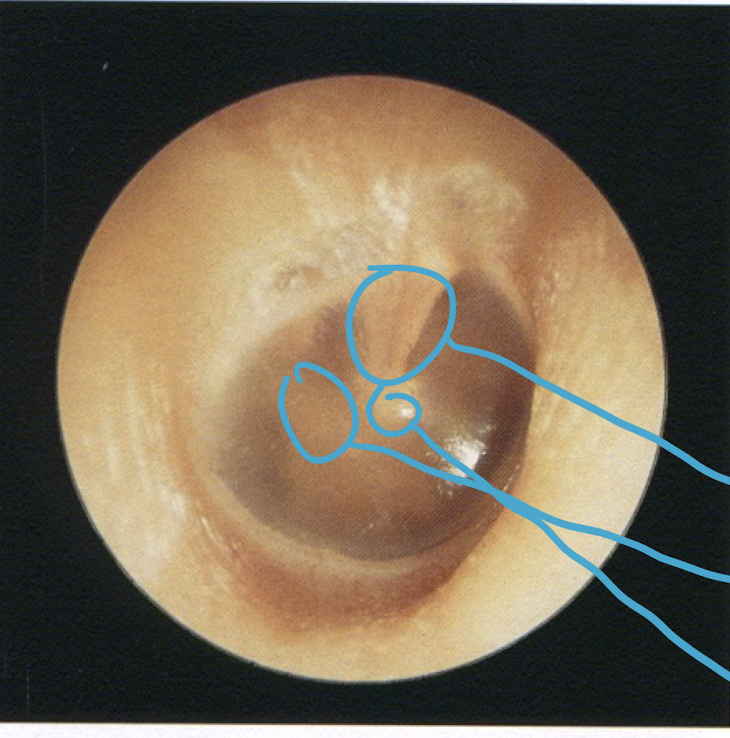
healthy ear drum
top circle
manubrium of the malleus

healthy ear drum
left circle
long process of the incus

healthy ear drum
bottom circle
umbo
cone of light
where is it located
light reflex on ear drum seen in a healthy, clear ear
anterior inferior quadrant (bottom right)
outer ear function
amplification
boosts frequencies in the 2-5 kHz range
due to curvature
outer ear function
localization
timing and intensity differences between 2 ears + pinna = help us identify where sound is coming from and we look in that direction first
the outer and middle ear are filled with ___
air
3 bones of middle ear
malleus
incus
stapes
the bones in the middle ear are fused together/free flowing
free flowing
when sound makes the ear drum move in and out, what does it do to the middle ear bones
makes the middle ear bones move together
middle ear function
impedance matching
ossicles pivot against each other to boost sounds ~30 dB to make up for the loss of intensity when moving from air → fluid (middle → inner)
middle ear function
how is impedance matching accomplished
difference in area of TM and stapes
boosts 24.6 dB
bones pivot → pressure force is directed to small area → goes to cochlea
middle ear function
too much sound = stapes pushes into cochlea and causes _______ which we don’t notice until it happens
hearing loss
middle ear
eustachian tube
runs from middle ear to back of throat
purpose: keep middle ear at a normal atmospheric pressure
pressure of tube moves ear drum in and out = popping of ear drum
inner ear is filled with _____
fluid
inner ear
semicircular canals
fluid-filled canals related to balance, keeping fluid level even when leaning side-to-side
inner ear
cochlea
organ of hearing
within cochlea
internal hair cells
how many rows
function
1 row
fine tune frequencies
within cochlea
external hair cells
how many rows
function
3 rows
protective
within cochlea
what do hair cells do
hair cells move in a wave caused by stapes hitting basilar membrane; this wave travels along fluid/cells until it hits nerve associated with its pitch
within cochlea
tonotopic organization
different areas of the cochlea have different nerves tuned to different pitches
inner ear function
change:
mechanical vibration of inner ear fluid → neural impulses transmitted to the brain
otoscopy examines what 3 parts of the ear
outer
pinna
ear canal
tympanic membrane
to prevent patient pain and discomfort:
hold otoscope like a ____
brace patient with _____
pencil
pinkie
due to ear canal curvature:
pull pinna ___ and ___
curve otoscope ___
pull pinna back and up
curve otoscope up
otoscopy
examine the good/bad ear FIRST
good ear first
prevents infection spread
see normal anatomy
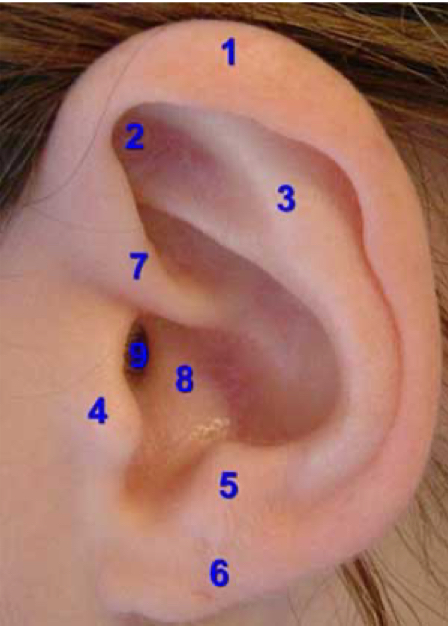
helix
1
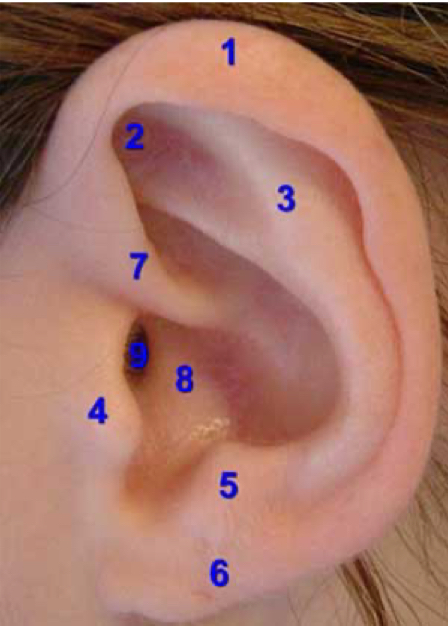
tragus
4
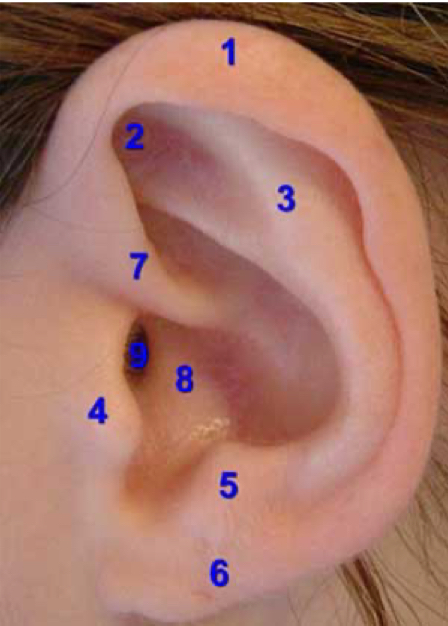
lobe
6
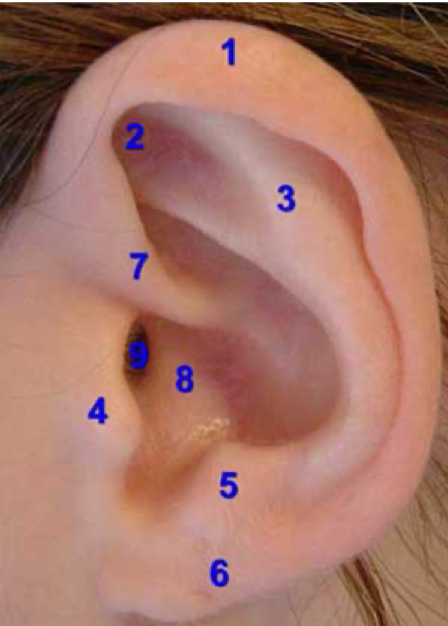
concha
8
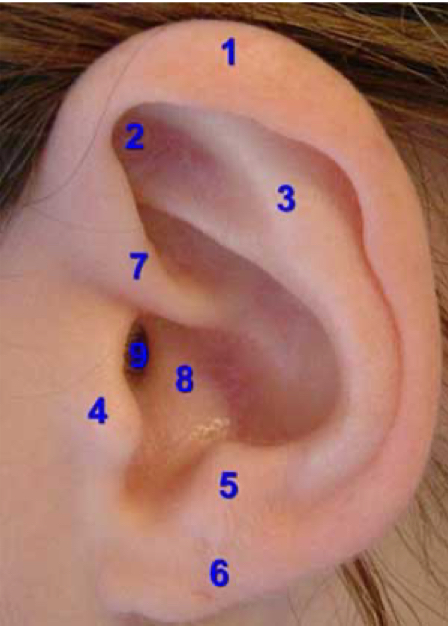
external auditory canal
9
normal otoscopy
darwin’s tubercle
bump of cartilage; common
no effect on hearing
normal otoscopy
prominent ears
“cup ears”; common; due to genes, malformed in utero
no effect on hearing
normal otoscopy
preauricular tag
small skin tag; common in newborns
need to be referred to MD due to association with medical conditions
no effect on hearing
normal otoscopy
preauricular pit
pit on external ear; embryo develops weird
normal otoscopy
hairy tragus
often in men
interferes with normal migration of wax - leads to wax accumulation
normal otoscopy
hairy ear
occurs in males; genes
no effect on hearing
normal otoscopy
creased lobe
external = no hearing effect BUT
piercings might effect AuD pulling ear to see in
first 1/3 of a normal ear canal is
last 2/3 of a normal ear canal is
first 1/3: cartilaginous
last 2/3: bony
normal otoscopy
healthy ear drum (2) components
semi-transparent
light reflecting
normal otoscopy
wax is normal/abnormal
normal
normal otoscopy
dry cerumen
dried, flaky, excessive wax
looks like scabs
common in native american/indian
normal otoscopy
wet cerumen
moist, soft, brown
common in white and african
normal otoscopy
cerumen
if completely obstructing canal:
if large amount, but not completely obstructing:
if completely obstructing canal: can cause HL
if large amount, but not completely obstructing: AuD can’t see eardrum; doesn’t necessary imply HL
both
ENT/urgent care will flush or suction
in right ear, handle of malleus points:
in left ear, handle of malleus points:
right = right
left = left
normal otoscopy
tympanosclorosis
what does it look like in otoscopy
patches of calcification on ear drum
commonly associated with ventilation tubes, perforations, repeated infections
typically does not effect hearing
looks like
still see malleus
no cone of light/transparency

normal otoscopy
what type of tube is this
PE tube
usually fall out on their own, hopefully when no longer needed
functional life of 6-12 mo.
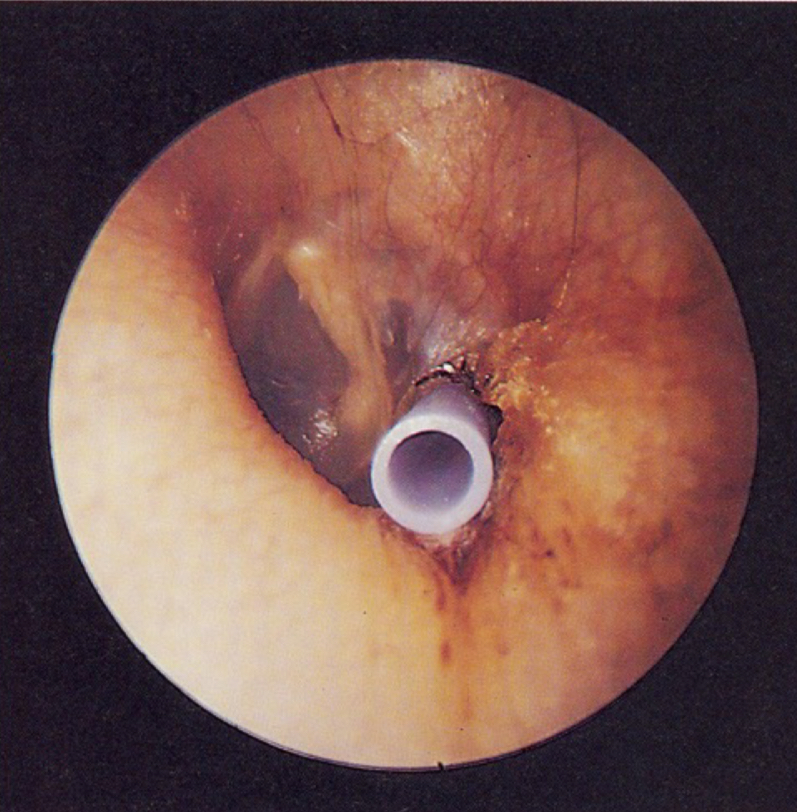
normal otoscopy
what type of tube is this
T tube
must be surgically removed
longer functional life, usually years
normal otoscopy
ventilation tubes
allow continuous aeration of the middle ear; bypasses dysfunctional eustachian tube
disordered otoscopy: pinna
anotia
absence of external ear
if internal structures intact but no opening = will have HL
conductive HL
disordered otoscopy: pinna
microtia
underdeveloped external ear; maybe underdeveloped/missing ear canal also
need to do bone conduction testing
conductive HL
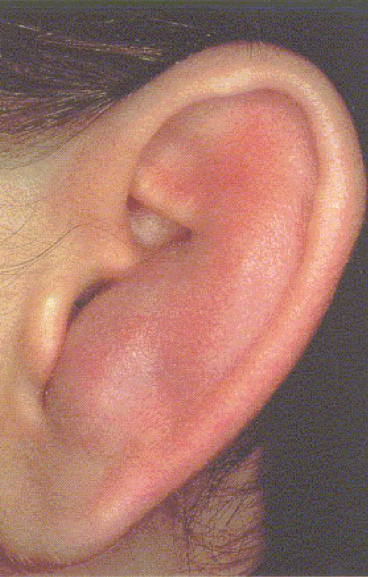
disordered otoscopy: pinna
auricular hematoma
“cauliflower ear”
repeated blunt trauma causes blood to collect and bruise
scarring or thickening of cartilage can occur
disordered otoscopy: pinna
keloids
overgrowth formed by connective tissue
response which occurs due to trauma/piercings
more common in those with more skin pigment
disordered otoscopy: pinna
carcinoma
skin cancer; occurs on pinna exposed to repeated sun exposure
refer to MD
disordered otoscopy: pinna
split lobule
results from pulled earring/heavy earring wear
disordered otoscopy: pinna
contact dermatitis
reaction to nickel found in jewelry
disordered otoscopy: canal
aural atresia
malformed/none/very small ear canal
associated with microtia
conductive HL
disordered otoscopy: canal
hyper cerumenosis
buildup of excessive earwax; didn’t produce or clear correctly
treat by frequent removal
disordered otoscopy: canal
impacted cerumen
dark colored, tightly packed wax
does not cause HL
disordered otoscopy: canal
occluded cerumen
completely blocks the canal
needs to be removed
causes HL
disordered otoscopy: canal
does impacted or occluded cerumen cause hearing loss
occluded cerumen
disordered otoscopy: canal
foreign bodies
must refer to MD to have bodies removed
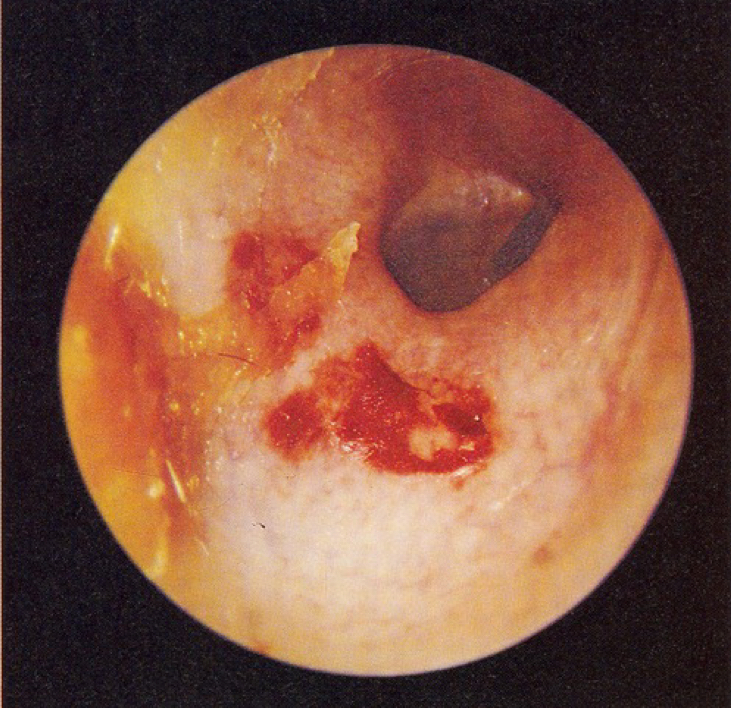
disordered otoscopy: canal
abrasion of canal
caused by sticking things in ears to scratch them
not problem UNLESS it causes/you get an ear infection
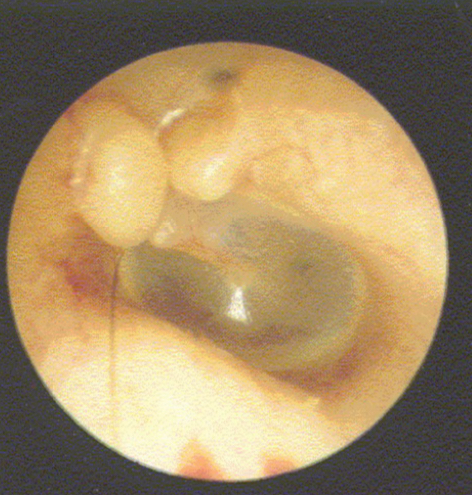
disordered otoscopy: canal
exostoses
growth: excess bony growths
due to cold water/pressure (sky divers/deep sea)
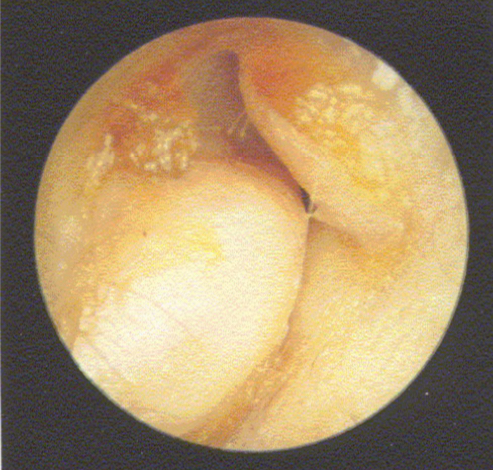
disordered otoscopy: canal
osteoma
growth: bony tumors grown into ear
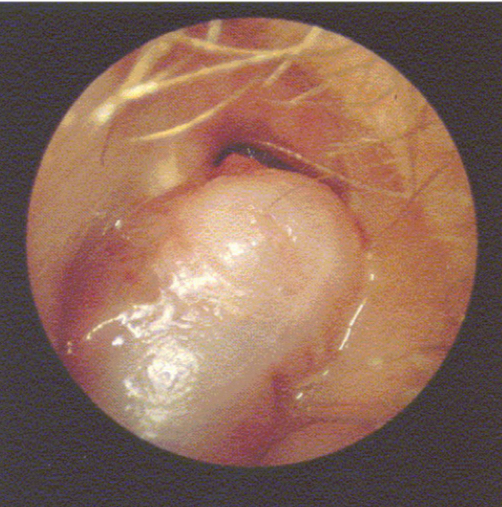
disordered otoscopy: canal
polyps
growth: projecting masses of swollen or tumorous membrane
if starts to affect hearing = needs to be treated
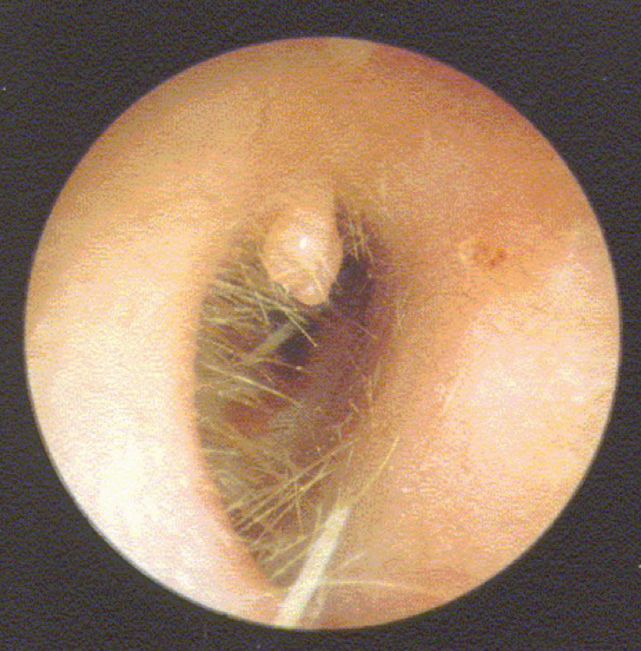
disordered otoscopy: canal
papilloma
growth: benign tumor resulting from overgrowth of epithelial tissue
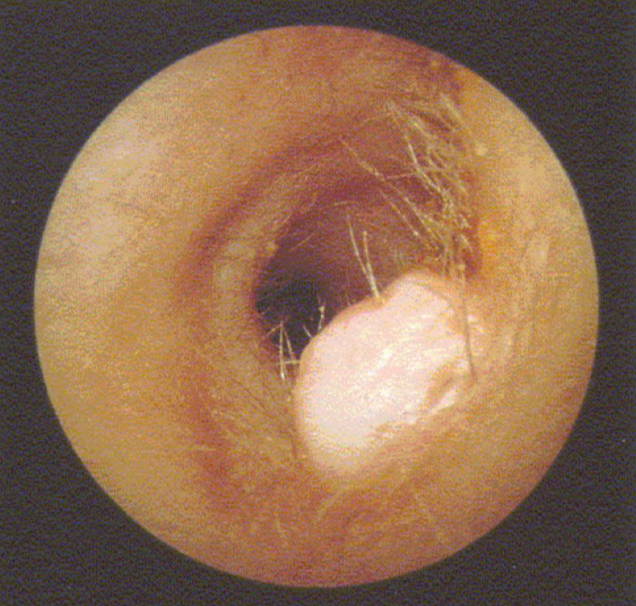
disordered otoscopy: canal
fibroma
growth: benign tumor consisting of fibrous tissue
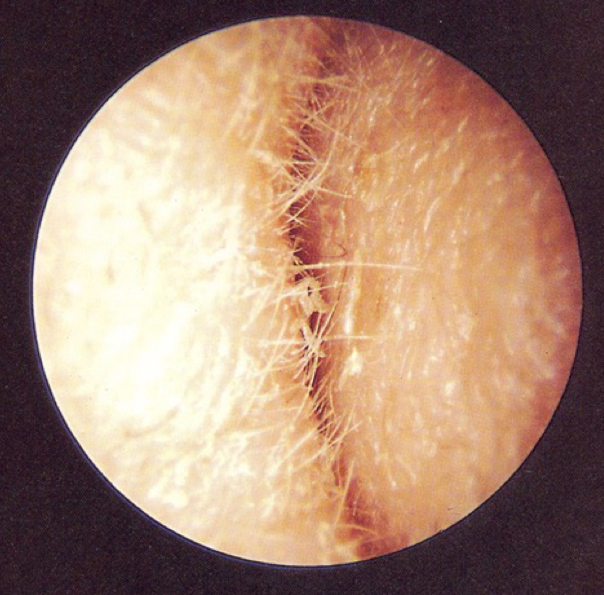
disordered otoscopy: canal
collapsing ear canal
caused by deficiency in supporting cartilage; elderly
caused by headphones that push on your ear
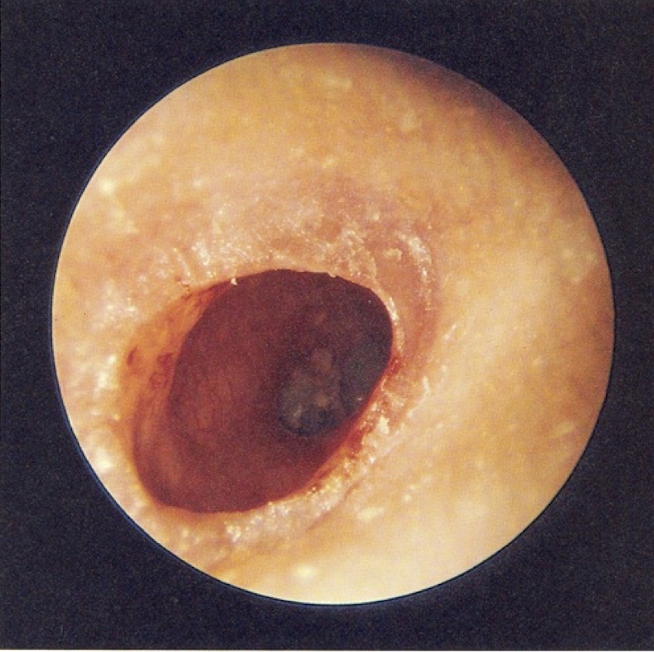
disordered otoscopy: canal
stenosis of external auditory meatus
abnormal narrowing; caused by repeated infections or trauma
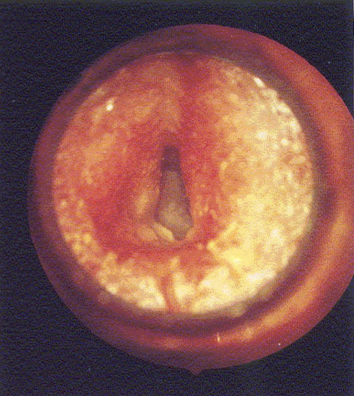
disordered otoscopy: canal
otitis externa/external otitis
“swimmers ear”; caused by fungal or bacterial infection
constantly getting ears wet leads to damage to ear immune defenses; leads to infection
inflammation/pus
refer to MD
conductive HL
disordered otoscopy: canal
necrotizing malignant external otitis complications
necrotizing: causing the localized death of living tissue
malignant: tending to infiltrate and spread from one part of body to another
external otitis can eat through ear and into brain; fatal
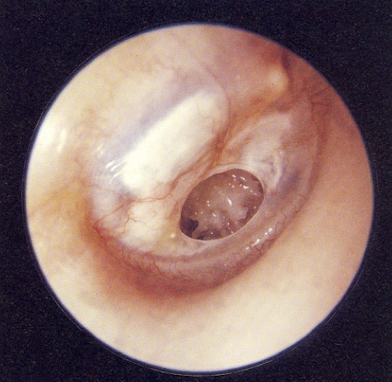
disordered otoscopy: eardrum/TM
TM perforation
hole in ear drum
susceptible to infection
spontaneously heals or can be patched
conductive HL - determined by position on TM
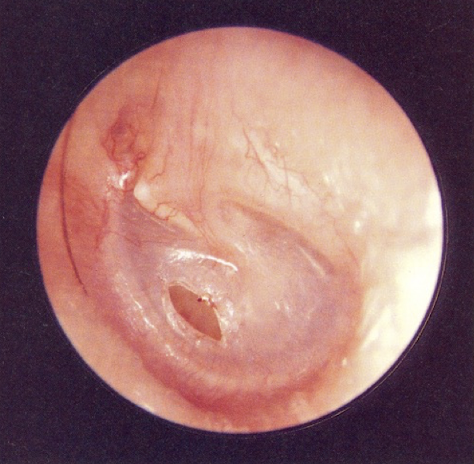
disordered otoscopy: eardrum/TM
myringotomy
incision made as part of insertion of PE tube
eventually skin will close around
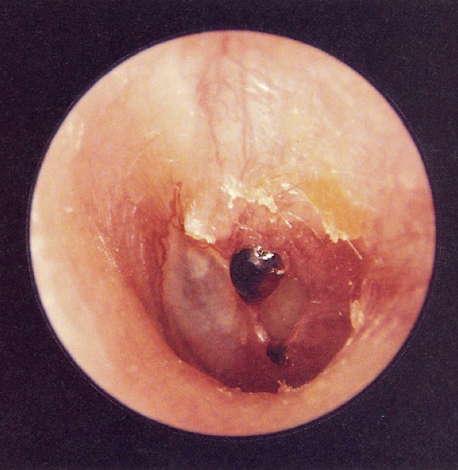
disordered otoscopy: eardrum/TM
traumatic perforation
result of blow to head or trauma from something inserted into TM
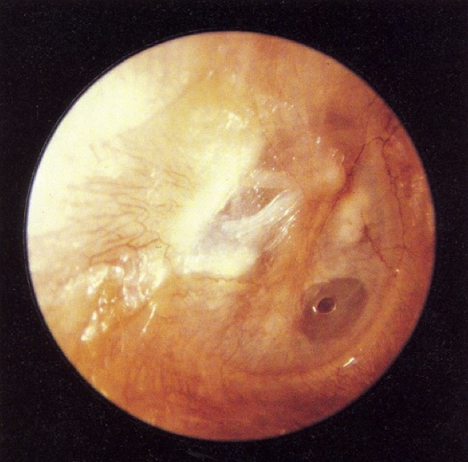
disordered otoscopy: eardrum/TM
perforation
could be from blow to head, vibrations from explosion; repeated ear infections

disordered otoscopy: eardrum/TM
monomere
healed perforation with incomplete fibrous layer
looks like hole but is not
might be HL
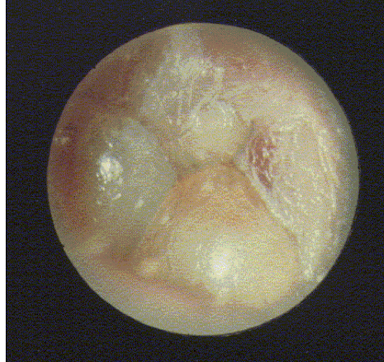
disordered otoscopy: eardrum/TM
myringitis
infection of the eardrum; rapid onset
usually self resolves
conductive HL
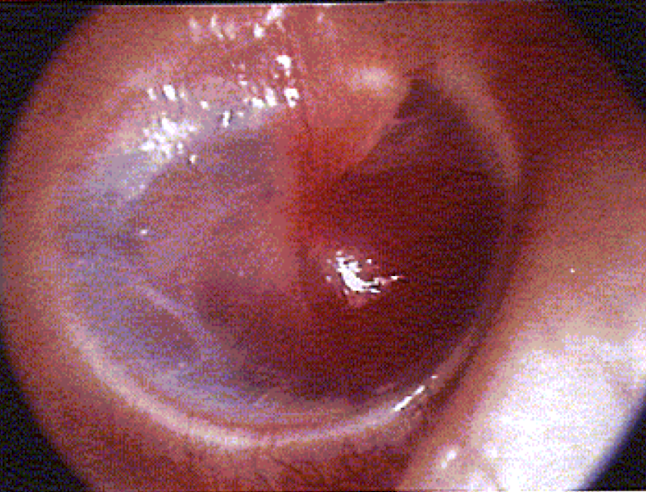
disordered otoscopy: middle ear
glomus tumor
middle ear growth: blood-fed tumor originating from cells found in middle ear
reddish-blue mass behind intact TM; pulsing
refer to ENT for diagnosis
conductive HL for most
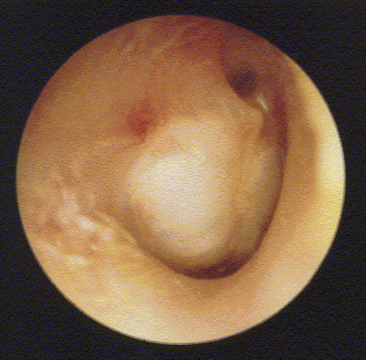
disordered otoscopy: middle ear
cholesteatoma
middle ear growth: invasive, benign progressively enlarging tumor
starts at TM where layer is pinched and forms a pocket in middle ear where things get stuck and lead to cholesteatoma
needs to get surgically removed
conductive HL
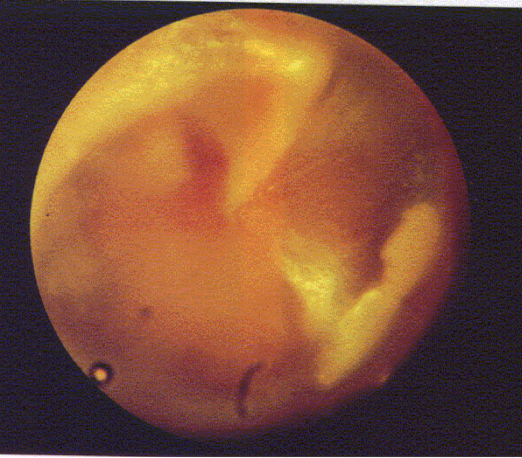
disordered otoscopy: middle ear
otosclerosis
middle ear growth: abnormal bone grows over 3 middle ear bones
looks like: reddish blue tinge from behind TM
often in pregnancy
treated surgically - could grow back or use H.A.
conductive HL
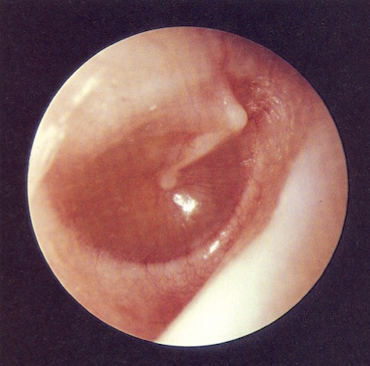
disordered otoscopy: middle ear
otitis media
middle ear infection; inflammation with accumulation of infected fluid in middle ear; bulging TM; pain; drainage of pus into ear canal
conductive HL
disordered otoscopy: middle ear
disarticulation of the ossicles
breakage of the ossicles or their attachments; due to physical trauma
audiometry
within what range of frequencies are octaves tested with an audiometer
250 - 8000 Hz
audiometry
should the patient be able to see you
should you see them
no
yes
audiometry
what is the name of the ASHA Cstandardized procedure for a hearing test
Modified Hughson-Westlake Procedure
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
you change dB by how much when testing hearing thresholds
if patient responds:
if patient does not respond:
if patient responds: down 10
if patient does not respond: up 5
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
when testing thresholds: vary dB level until you find lowest where patient responds correctly ___% or _____ times
50% or 2/3 times
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
start at what frequency and dB level?
1000 Hz, 30 dB
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
what ear do you start in
the better ear
if no better ear = right ear
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
once you reach 8000 Hz, where do you go next?
1000 Hz
then 500 Hz, then 250 Hz
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
if there is ___ dB between adjacent frequencies, test inter-octaves (750, 1500, 3000, 6000 Hz)
20 or greater
audiometry: modified hughson-westlake procedure
do you test one ear at a time?
yes
audiometry
0 dB HL
not the absence of sound; equal to lowest amount of sound pressure
threshold for young, healthy adults
audiometry
minimal hearing curve
done on best hearing young adults to find normal thresholds and convert dB HL to dB SPL
extreme frequencies take more sound pressure than the best threshold of hearing (our hearing range)
audiogram
symbol for: right ear, air conduction
red circle
audiogram
symbol for: left ear, air conduction
blue X