Chemistry -Chap. 1 States of matter
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.1-1.4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Solid
Arrangement: Particles are close together and regularly packed.
Movement: Particles vibrate around a fixed point.
Energy: Particles have less kinetic energy than both liquids and gasses.

Liquid
Arrangement: Particles are close together but irregular.
Movement: Particles are free to move.
Energy: Particles have less kinetic energy than gasses but more than solids.

Gas
Arrangement: Particles are far apart and there are no forces between them.
Movement: Particles are free to move.
Energy: Particles have more kinetic energy than liquids and solids.
Melting
Solid —> Liquid
When a solid is heated, the energy makes the particles vibrate fast enough so that the forces of attraction between the particles break.
Freezing
Liquid —> Solid
When a liquid is cooled, the particles move slow enough so that the forces of attraction between them will hold them into a solid.
Boiling
Liquid —> Gas
When a liquid is heated strongly, the energy makes the particles move fast enough so that all forces of attraction are broken.
Condensing
Gas —> Liquid
When a gas is cooled, the particles move slow enough so that the forces of attraction between them will hold them as a liquid.
Sublimation
Solid —> Gas
A small number of substances have the ability to change directly from a solid to a gas when heated.
Diffusion
The net movement of particles from areas of a high concentration to areas of low concentration.
Dilution of coloured solutions
Dissolving potassium manganate(VII) in water demonstrates that the diffusion in liquids is very slow because there are only small gaps between the liquid particles into which other particles diffuse.
The random motion of particles cause the purple colour to eventually be evenly spread out throughout the water.
Adding more water to the solution causes the potassium manganate(VII) particles to spread out further apart therefore the solutions becomes less purple. This is called dilution.
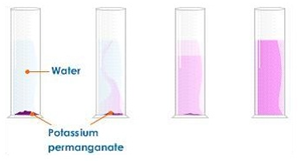
Diffusion expermiment
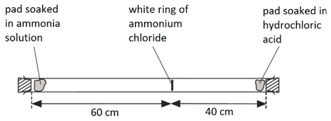
When ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride gas mix, they react together to form a white solid called ammonium chloride.
ammonia + hydrogen chloride –> ammonium chloride
NH3(g) + HCl(g) –> NH4Cl(s)
A cotton wool pad was soaked in ammonia solution and another was soaked in hydrogen chloride solution. The two pads were then put into opposite ends of a dry glass tube at the same time.
The white ring of ammonium chloride forms closer to the hydrochloric acid end because ammonia particles are lighter than hydrogen chloride particles and therefore travel faster.
Even though these particles travel at several hundred metres per second, it takes about 5 min for the ring to form. This is because the particles move in random directions and will collide with air particles in the tube.
What is a solute?
the substance that dissolves
What is a solvent?
the liquid in which it dissolves
What is a solution?
the liquid formed
What is a saturated solution?
a solution into which no more solute can be dissolved