biol 117 – ch 18: cardiovascular system: blood
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
blood
a fluid connective tissue composed of formed elements and plasma that’s transported through the cardiovascular system
functions of blood
transports nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases
regulates body temp, pH, and fluid levels
protects body against activities of pathogens
physical characteristics of blood
color, volume, viscosity, plasma concentration, temp, pH
color of oxygen-rich blood
this type of blood is bright red or almost scarlet
color of oxygen-poor blood
this type of blood is dark red
5 L (but can range from 4-6 L)
average volume of blood in an adult
viscosity
thickness of a solution; provides resistance to fluid flow
blood is about 4-5 times more viscous than water
comparison of viscosity between blood and water
plasma concentration
the relative concentration of solutes in plasma
typically 0.9% concentration
temperature of blood
the temp of blood is almost 1 degree C (or 2 degrees F) higher than measured body temp —> blood warms areas through which it travels
ex: if your body temp is 37 degrees C, your blood temp is 38 degrees C
7.35-7.45
normal pH for blood
erythrocytes, buffy coat, and plasma
centrifugation separates blood into these 3 components
buffy coat
composed of leukocytes and platelets
hematocrit
represents the percentage of formed elements in blood
males typically have higher hematocrits than females
this gender typically have higher hematocrits than the other
formed elements
this type of elements in blood can be viewed in a blood smear
formed elements
consists of buffy coat + erythrocytes
blood plasma
a mixture of water, plasma proteins, and other solutes
about 55% of whole blood
blood plasma forms about this percent of whole blood
whole blood
both plasma and formed elements
plasma is similar in composition to interstitial fluid, except it contains proteins
what’s the difference between plasma and interstitial fluid?
albumin
~58% of plasma proteins
exerts osmotic force to retain fluid within the blood
contributes to blood’s viscosity
transport selected molecules (ex: ions, lipids, hormones)
globulins
~37% of plasma proteins
alpha-”[term]” transport lipids and some metal ions (ex: copper)
beta-”[term]” transport lipids and iron ions
gamma-”[term]” are antibodies that immobilize pathogens
fibrinogen
~4% of plasma proteins
participates in blood coagulation (clotting)
regulatory proteins
<1% of plasma proteins
consists of enzymes and hormones
plasma proteins
~7% of plasma
all of these buffer against pH changes
albumin; globulins; fibrinogen and other clotting proteins; and regulatory proteins
other solutes in blood plasma
~1% of blood plasma
electrolytes, nutrients, respiratory gases, wastes
electrolytes
other solutes of blood plasma
help establish, maintain, and change membrane potentials, maintain pH balance, and regulate osmosis
ex: sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, iron, bicarbonate, hydrogen
nutrients
other solutes of blood plasma
energy source; precursor for synthesizing other molecules
ex: amino acids, glucose, cholesterol, vitamins, fatty acids
respiratory gases
other solutes of blood plasma
oxygen is needed for aerobic cellular respiration
CO2 is a waste product produced by cells during this process
wastes
other solutes of blood plasma
serve no function in the blood plasma
they merely are being transported to the liver and kidneys, where they can be removed from the blood
ex: breakdown products of metabolism, such as lactate, creatinine, urea, bilirubin, ammonia
erythrocytes
transport respiratory gases
biconcave disc structure
leukocytes
serve some roles in protecting the body from harmful substances
platelets
participate in hemostasis
hematopoeisis
the process by which formed elements develop
red bone marrow
hematopoeisis takes place here
hemocytoblasts
hematopoiesis starts with these hematopoietic stem cells
multipotent
multipotent cells
can differentiate and develop into many different kinds of cells
myeloid line
forms erythrocytes, all leukocytes except lymphocytes, and megakaryocytes (produce platelets)
lymphoid line
forms only lymphocytes
hemoglobin
a pigmented protein within mature erythrocytes
transports oxygen and CO2
120 days
aged erythrocytes are broken down and their components recycled after about this many days in the blood
surface antigens on the erythrocytes
blood type is determined by this
erythropoiesis
erythrocyte production
leukopoiesis
leukocyte production
thrombopoiesis
production of platelets
megakaryoblast
a committed cell from the myeloid stem cell
BEFORE megakaryocyte (think b before c)
erythropoietin (EPO)
hormone that controls erythropoiesis
kidneys
organ that is primary producers of EPO
liver
this organ secretes a small amount of EPO
decrease in blood oxygen levels
this is the initial stimulus for EPO release
how erythropoietin (EPO) regulates erythrocyte production
stimulus: decreased blood oxygen levels
receptor: kidney detects decreased blood O2
control center: kidney cells release EPO into blood
effector: EPO stimulates red bone marrow to increase the rate of production of erythrocytes
net effect: increased #’s of erythrocytes enter circulation —> the erythrocytes are oxygenated and blood O2 levels increase
increased blood O2 levels are detected by the kidney —> inhibits EPO release by negative feedback
type A blood
erythrocytes have surface antigen A
plasma has anti-B antibodies
type B blood
erythrocytes have surface antigen B
plasma has anti-A antibodies
type AB blood
erythrocytes have surface antigens A and B
plasma has NEITHER anti-A not anti-B antibodies
type O blood
erythrocytes don’t have surface antigen A or B
plasma has BOTH anti-A and anti-B antibodies
Rh positive
erythrocytes have surface antigen D
plasma has NO anti-D antibodies
Rh negative
erythrocytes have no surface antigen D
plasma has NO anti-D antibodies unless exposed to Rh positive blood
agglutination
process by which cells clump due to cross-linking by antibodies
happens if a person is transfused with blood of an incompatible type
diapedesis
passage of leukocytes through the intact blood vessel wall
chemotaxis
a process in which leukocytes are attracted to a site of infection by the presence of molecules released by damaged cells, dead cells, or invading pathogens
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
3 types of granulocytes
lymphocytes and monocytes
2 types of agranulocytes
neutrophils characteristics
granulocyte with multilobed nucleus (as many as 5)
cytosol contains neutral, or pale, specific granules
neutrophils functions
phagocytize pathogens, especially bacteria
release enzymes that target pathogens
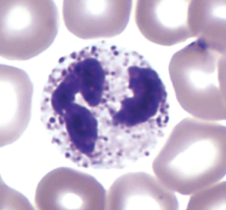
neutrophils approximate percentage
50-70% of total leukocytes (1800-7800 cells per microliter)
eosinophils characteristics
granulocyte with bilobed nucleus
cytosol contains reddish or pink-orange specific granules
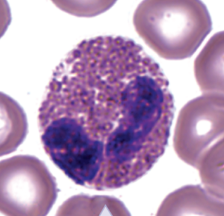
eosinophils functions
phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes and allergens
release chemical mediators to destroy parasitic worms
eosinophils approximate %
1-4% of total leukocytes (100-400 cells per microliter)