Posterior Tibialis Tendinopathy
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
posterior tibialis insertion
tarsals and metatarsals (navicular)
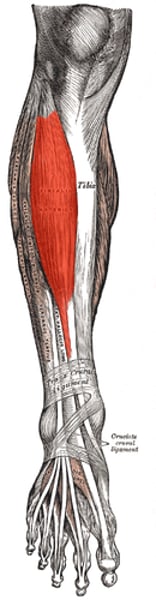
what does the posterior tibialis tendon do
-plantarflexor and invertor
-adductor of the forefoot
-primary dynamic stabilizer of the medial longitudinal arch
posterior tibialis tendon and medial longitudinal arch
primary dynamic stabilizer
-works with osteoligamentous structures and spring ligament
-elongation of posterior tibialis tendon by as little as 1 cm can reduce its efficiency as a stabilizer
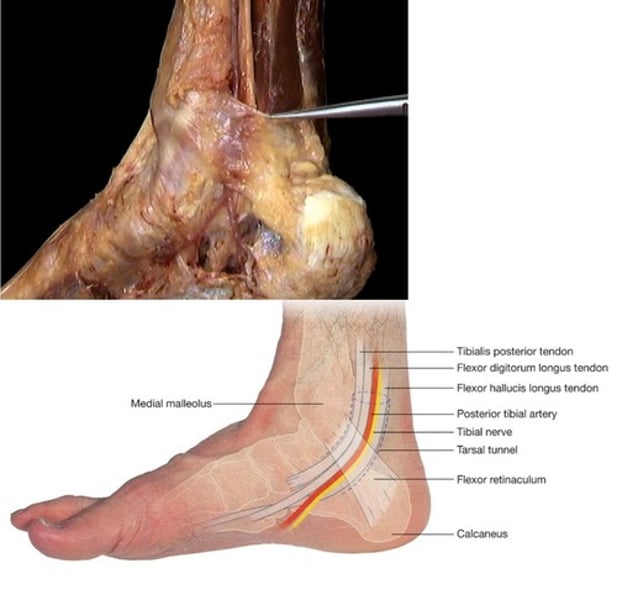
structures that run by medial malleoli
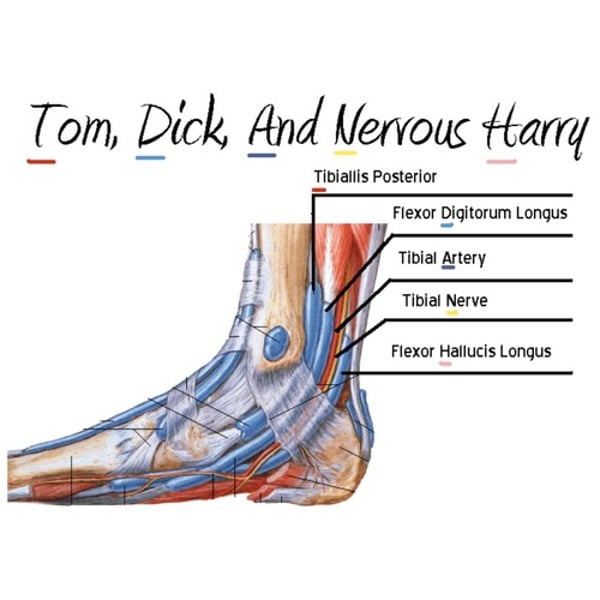
posterior tibialis tendon's role in gait
-controls rearfoot eversion during LR (eccentric contraction)
-stabilizes transverse tarsal joints during midstance through STJ supination (concentric)
-assists in heel rise and weight shift in late stance
posterior tibialis during midstance
stabilizes transverse tarsal joint through ST supination
-minimal tendon gliding
-midfoto locks
-gastroc complex at a mechanical advantage for propulsion
-assists in maintaining the integrity of the longitudinal arch
posterior tibialis tendon during weight shift
lateral to medial shift of body weight due to balanced activity of posterior tibialis and peroneals
etiology of posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-congenital pes planus (flat foot)
-age related degeneration
-systemic inflammatory diseases (RA, lupus)
-chronic microtrauma/increases mechanical stress
-anatomic anomalies
-increased local mechanical stress from adjacent structures
chronic microtrauma etiology of posterior tibialis tendinopathy
combined repetitive mechanical stress and poor blood supply
anatomical anomalies leading to posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-accessory naviclar bone
-prominent navicular tuberosity
what structure can increase local mechanical stress on posterior tibialis tendon
tight flexor retinaculum leading to tendon constriction posterior to medial malleolus
onset of posterior tibialis tendinopathy
insidious onset is most common
-symptoms can be present for months or years
early symptoms with posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-swelling medially (everywhere)
-pain in medial plantar arch
-heel rise if painful and difficult
-usually unilateral but can be bilateral
-gradual worsening with eventual collapse of medial longitudinal arch
signs of posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-increased heel valgus
-PF of talus
-flattening of medial longitudinal arch
-abduction of forefoot
test/measures for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-too many toes sign
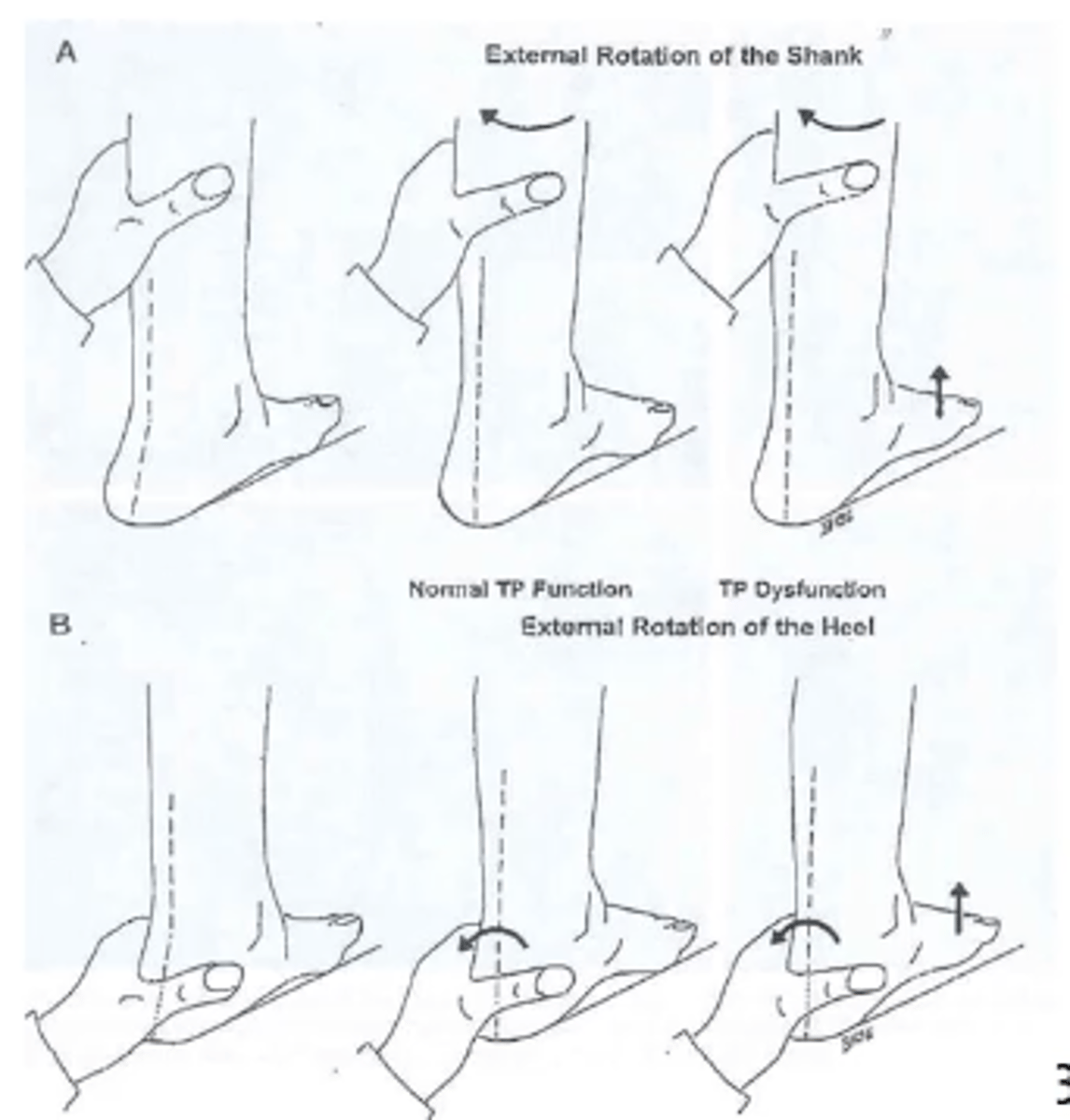
-first metatarsal rise sign (sensitive at early stage)
-B limb heel rise (assess for inversion of calcaneus)
-single limb heel rise (
first metatarsal rise sign
positive result is first ray rises with tib fib external rotation
imaging for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
MRI is gold standard
-CT is used if MRI is contraindicated
stage 1 PTTD: posterior tib condition
peritendinitis and/or tendon degeneration
stage 1 PTTD: hindfoot
mobile, normal alignment
stage 1 PTTD: pain
medial: focal
-mild to moderate
stage 1 PTTD: too many toes sign
normal
stage 1 PTTD: pathology
synovial proliferation, degeneration
stage 1 PTTD: treatment
conservative
-3 months with synovectomy, tendon debridement, rest
stage 2 PTTD: posterior tib condition
elongation
stage 2 PTTD: hindfoot
mobile
-valgus position
stage 2 PTTD: pain
medial: along posterior tibialis tendon
-moderate
stage 2 PTTD: too many toes sign
positive
stage 2 PTTD: pathology
marked degeneration
stage 2 PTTD: treatment
-conservative
-transfer flexor digitorum longus for posterior tibialis tendon
stage 3 PTTD: posterior tib condition
elongation
stage 3 PTTD: hindfoot
fixed
-valgus position
stage 3 PTTD: pain
medial, possibly lateral
-moderate
stage 3 PTTD: too many toes sign
positive
stage 3 PTTD: pathology
marked degeneration
stage 3 PTTD: treatment
subtalar arthrodesis-> fusion
conservative treatment for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-elevate medial arch
-orthotic in neutral
-education (shoes)
-reduce swelling
orthotic in stage 3 posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-can give an orthotic to prevent progression but it will not reverse damage because it is fixed
stage 4 posterior tibialis tendinopathy
fixed valgus tilt of the talus in the ankle mortise
-leads to lateral tibiotalar degeneration/arthritis
modalities to NOT use for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
lack of evidence to support the use of US, deep transverse friction massage, massage/mobilization, extracorporeal shock wave therapy
modalities that can be used for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
acute stage can be used to decrease inflammation
-iontophoresis
-cryotherapy
-US
low level laser therapy for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
can reduce pain in chronic tendinopathy
-but not sure exactly for posterior tibialis
non surgical interventions for stage 1 and 2 posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-immobilization for tenosynovitis
-orthosis in neutral
-achilles tendon stretching
-posterior tibialis strengthening
goals of nonsurgical interventions for stage 1 and 2
-elimination of clinical symptoms
-improvement of hindfoot alignment
-prevention of progressive foot deformity
non surgical interventions for stage 3 posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-not passively correctable
-must accommodate deformity
goal of nonsurgical intervention for stage 3 posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-alleviate pain
-slow progression
exercise for conservative posterior tibialis tendinopathy
-gastrocsoleus stretching commonly recommended
-foot adduction in neutral position (orthosis, shoes or taping) more effective
-eccentric strengthening more effective than concentric or orthosis alone
-tendon itself is not getting better (no neovascularization) but pain and function improves
orthotics for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
need to address
-hindfoot eversion
-depressed MLA
-FF abduction
immobilization with posterior tibialis tendinopathy
CAM boots used in highly symptomatic pts
-limit sagittal and frontal plane motion
taping for posterior tibialis tendinopathy
used to assess appropriateness of an orthotic
EdUReP model for tendinopathy
for nonsurgical management of tendinopathy
-Education
-Unloading
-Reloading
-Prevention
education in EdUReP model
-assess
-advise
-agree
-assist
-arrange
unloading in EdUReP model
identification of tendon unloading strategies through behavioral and mechanical methods
-vary general workload tasks
-use of orthoses
-appropriate exercise interventions for surrounding tissues
reloading in EdUReP model
-follows physical stress theory
-12 weeks in duration
-psychoeducational interventions that help modify the volume and technique of an activity
-mechanical loading through orthoses and body weight supported activities
-eccentric reloading at slow speeds and sufficient loads
prevention in EdUReP model
-optimal secondary prevention programs have yet to be determined
-continuation of prior education and unloading/reloading phases
-independence in self-management of residual symptoms and impairments after return to activities