TOPIC 5: POVERTY AND INEQUALITY
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Which groups are most likely to be placed in the low poverty groups
Those living in rural areas
Women
Ethnic minorities and indigenous populations
What are the properties that we want in a good measure of poverty
Anonymity principle: The measure should not depend on who has the higher income
Population independence principle: An inequality measure should not be based on the number of income residents
Monotonicity principle: If you add income to someone below the poverty line with all other incomes held constant poverty should fall.
Distributional sensitivity principle: If you transfer income from someone who is poorer to someone who is richer the economy is deemed poorer.
What are the headcount measures of poverty
Poverty headcount: The number of individuals falling below a pre specified poverty level
The headcount ratio: The number of people that are poor as a fraction of the population
What are the problems with the headcount and the headcount ratio
The poverty headcount fails to satisfy the population independence principle
The headcount ration fails to satisfy the monotonicity principle and distributional sensitivity, but satisfies anonymity and population independence.
What incentives are created by measuring poverty through headcount or fractions
Governments are pushed to show improvements in poverty measures.
Focus shifts to helping those just above or near the poverty line not ust the poorest
The MDG’s reinforce this focus
What is the equation for Total Poverty Gap
H= Total number of poor people
Yp= The poverty line income
Yi= The actual income of poor person
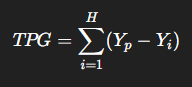
What is the equation for average poverty gap
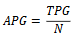
What is the equation for poverty gap index
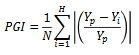
What are the strengths of the Total Poverty Gap
TPG is sensitive to the changes below the poverty line
TPG satisfies the monotonicity principle
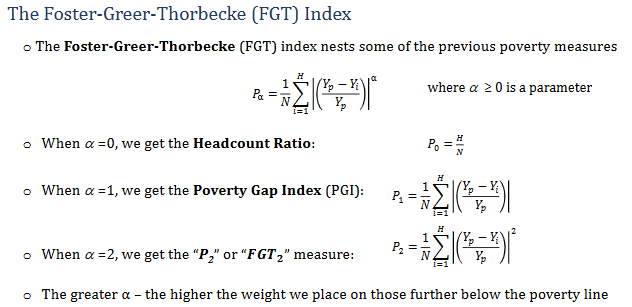
What is the Foster Greer Thorbecke index
it's a family of poverty measures used in development economics, that incorporates other poverty measures
Why can high inequality be harmful for economic development
Low overall savings rate from those of poorer background (S) is apart of AD
Rich gain excessive bargaining power influencing policies in their favour
Inefficient land use
Corruption issues
This cycle continues reinforcing these negative factors.
What is the Kuznets curve
The curve shows the relationship between economic development and income inequality
At first in early stages of development income is concentrated within a few groups but as the economy develops in factors like education and urbanization and technological progress there is more equal distribution of income.
What properties are in a good measure of inequality
Scale independence: Inequality measures should not depend on the size of the economy
Transfer principle: All other incomes constant if we transfer income from a richer to a poorer person the resulting new income distribution is more equal.
What is the Lorenz curve
The curve shows a country’s distribution of income shares relative to population shares.
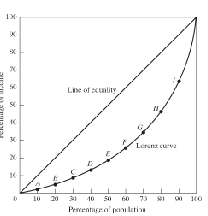
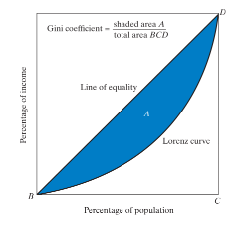
What is the Gini coefficient
Summarises the relationship between the Lorenz curve and the line of Equality
What are some of the policies that can be introduced to reduce inequality
Progressive redistribution of asset ownership
Progressive taxation
Transfer payments and public provision of goods and services.
Programmes aimed at creating Jobs when employment is scarce
Why might workfare programs be preferred over welfare programs in developing countries?
Hard to screen the poor without a work requirement.
Poor workers have low opportunity cost of time (little economic loss if they work in the program).
Non-poor workers have high opportunity cost of time (less likely to participate).
Example: Food for Work programs.