Dermatology 1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
List 5 pathophysiological mechanisms leading to blister formation
1. Spongiosis
2. Acantholysis
3. Cytolysis
4. Subepidermal blister formation
5. Mechanical blister formation
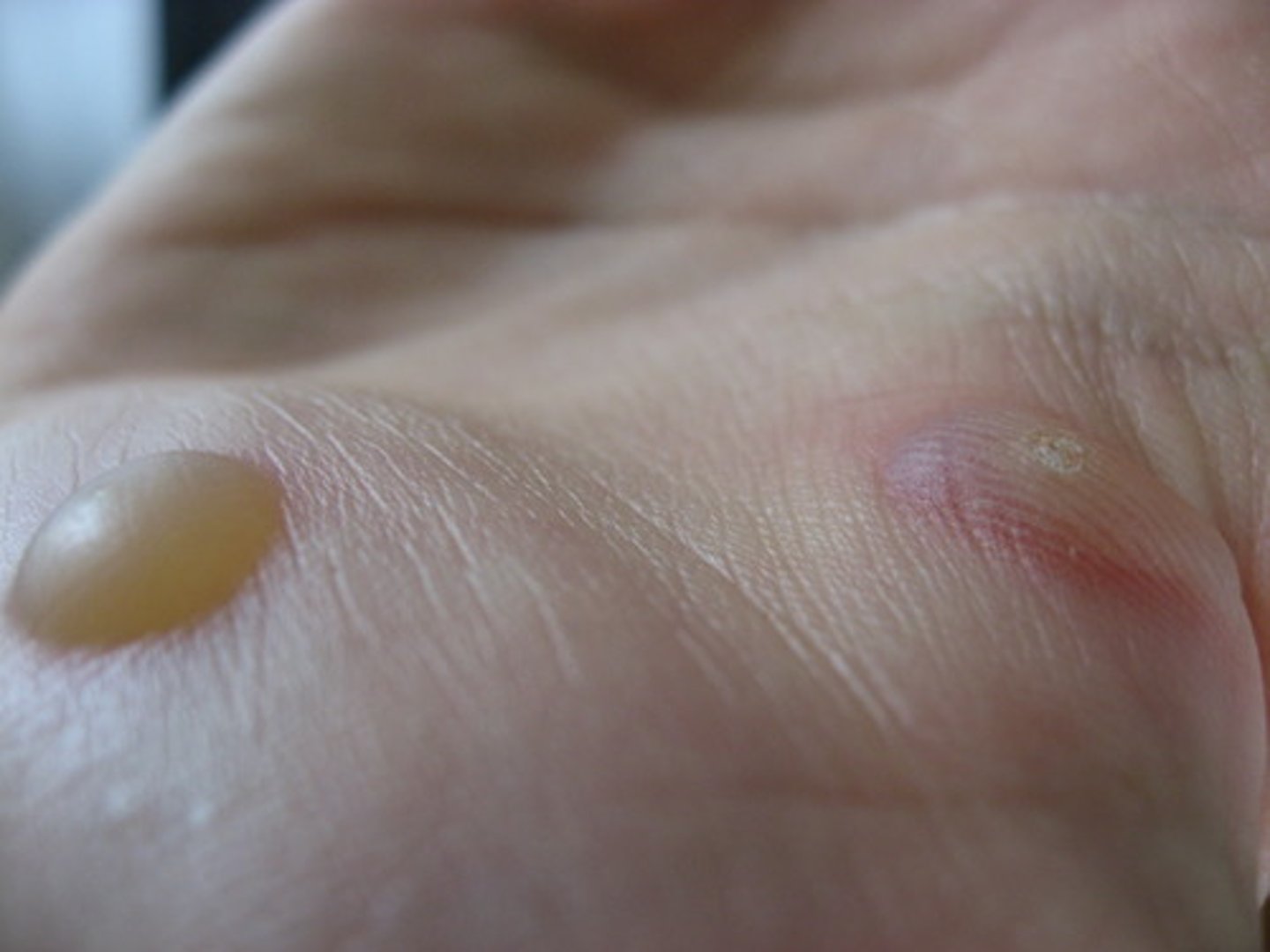
Name at least 2 microbial cofactors in acne rosacea
Demodex folliculorum; Helicobacter pylori
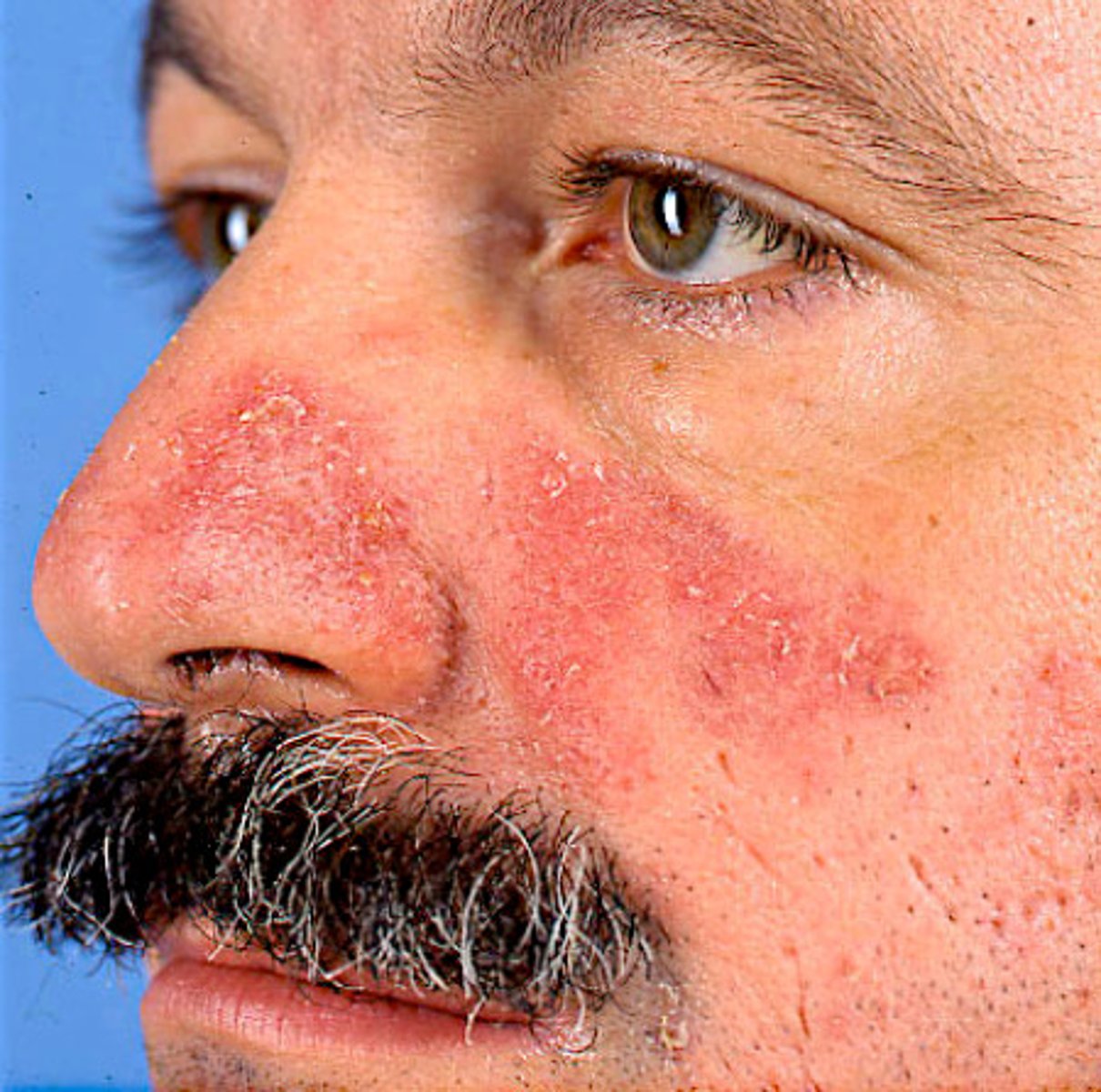
Name the two most commonly used Severity Score indices for psoriasis
PASI (Psoriasis Area Severity Index) and BSA (Body Surface Area)
What are the main risk factors for developing cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma?
1. Chronic UV exposure
2. Fair skin (Fitzpatrick 1 and 2)
3. HPV infection (16 and 18)
4. Immunosuppression (e.g. organ-transplanted patients)
5. Chronic wounds or scars (Marjolin ulcer)
6. Tobacco and alcohol use
7. Arsenic exposure
8. Genetic disorders (e.g. xeroderma pigmentosum).
Which are the topical antifungals used in seborrheic dermatitis?
Ketoconazole and ciclopirox
A 17-year-old boy presents with a 6-month history of small, itchy wheals appearing within minutes of exercise or hot showers. They resolve within an hour. He occasionally feels flushed and lightheaded during episodes. What is the most likely diagnosis, and how would you confirm it?
Cholinergic urticaria; clinical observation and provocation tests.
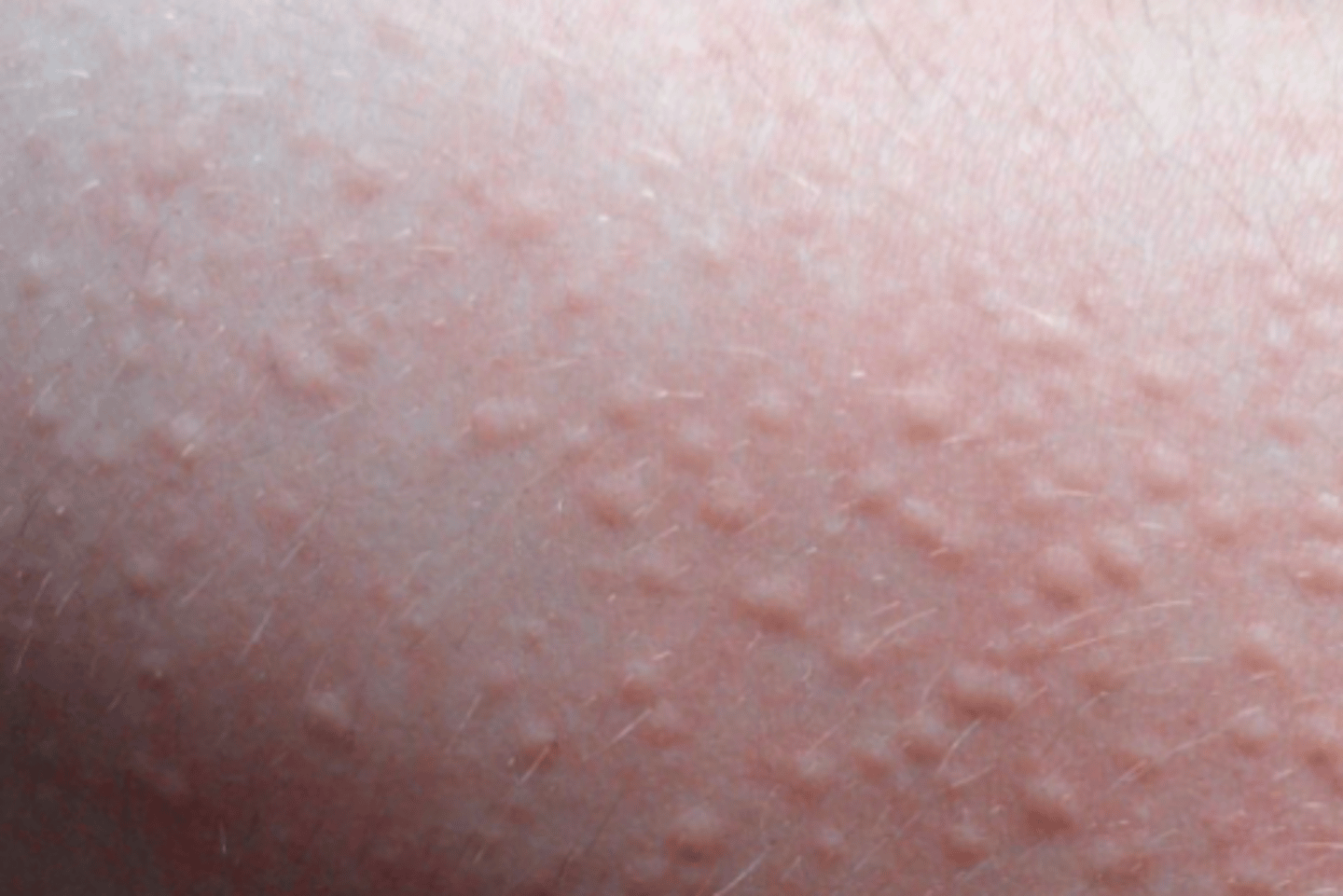
Give the 2 main nail signs of psoriasis
Onycholysis; Irregular pitting.
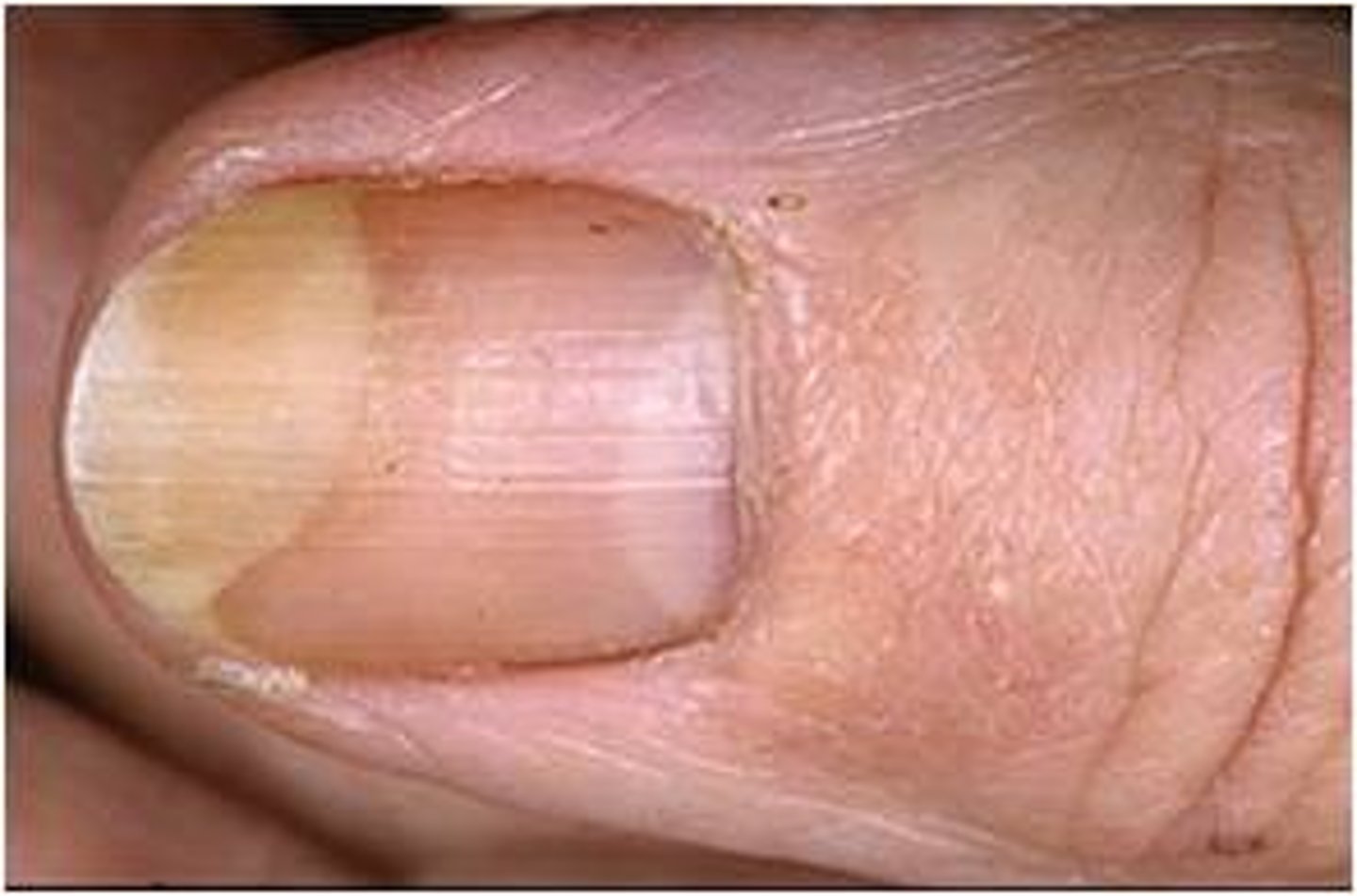
What are the worst complications in women affected by Chlamydia?
Urogenital complications, meaning pelvic inflammatory diseases which lead to ectopic pregnancies, chronic pelvic pain and infertility.
30-year-old man has recurrent blistering lesions located on both elbows and knees, persistent for around 2 years. He has T1DM and autoimmune thyroiditis. He hates hospitals since his childhood diagnosis of diabetes, and avoids medical facilities unless absolutely necessary. He sought medical attention due to intense pruritus which was intolerable and which is significantly affecting his daily activities. Family history: his grandfather was probably diagnosed with lymphoma (though the patient is unsure of the specific type). On examination, he appears pale, of short stature, and has a lean build. Nikolsky sign is negative. Multiple erythematous vesicles are observed in a symmetrical pattern on the medial aspects of his buttocks. Direct immunofluorescence testing reveals granular IgA deposits along the apical part of papillae at dermoepidermal junction. Most likely diagnosis?
DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS, a cutaneous manifestation of Celiac Disease
How is Breslow thickness measured and what is its significance in melanoma diagnosis?
Breslow thickness is reported to the nearest 0.1 mm. It is measured vertically in millimeters from the granular layer (or base of superficial ulceration) to the deepest point of tumor involvement. It is important because it is a prognostic factor: the thicker the melanoma, the worst the outcome 8= more likely to metastasize).
List the 4 conditions that all share nail curvature alterations
Parrot beak nails
Tile-shaped nails
Pincer nails
Clubbed nails.
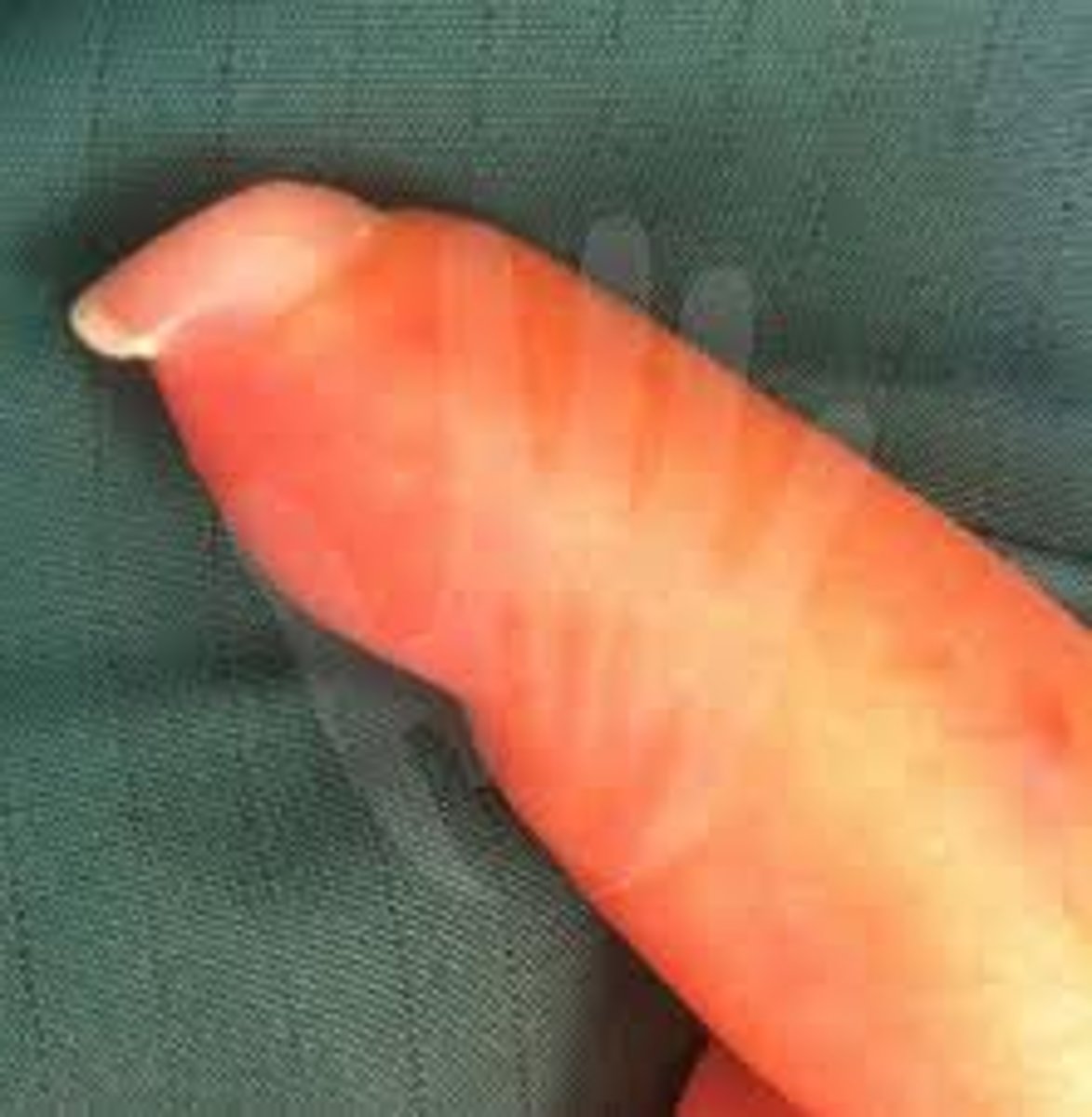
What's the clinical sign that helps differentiating Pemphigus Vulgaris from Bullous Pemphigoid? Explain how it is elicited
The clinical sign is Nikolsky sign, which is elicited by applying lateral pressure in the perilesional or affected skin area.
If the sign is positive, the lesion should spread when pressure is applied; this occurs in intraepidermal blisters —> sign is positive in Pemphigus Vulgaris.
The sign is negative in subepidermal blisters --> negative in Bullous Pemphigoid.
Briefly explain what (1) pale (scar-like) areas and (2) nodular appearance refer to in the setting of Superficial Spreading Melanoma?
Pale (scar-like) areas refer to remission of the lesion (with the risk of underestimating the Breslow thickness);
The nodular appearance is a sign of deeper invasion (= progression to the vertical growth phase).
What are the two main classes of Epidermolysis Bullosa?
Acquired AND Inherited. Inherited further subdivided into simplex, junctional and dystrophic.
A 32-year-old male presents with a sudden onset of numerous small, droplet-shaped, erythematous papules and plaques on his trunk and proximal extremities. He reports a recent history of a streptococcal throat infection two weeks prior. He has no significant past medical history and no family history of psoriasis. The lesions are mildly pruritic but not painful. He denies any joint pain or other systemic symptoms. On physical examination, the patient has multiple small, erythematous, scaly papules and plaques distributed primarily on his trunk and proximal limbs. The lesions are well-demarcated and measure 1-10 mm in diameter. There is no evidence of nail involvement or joint swelling. Which type of psoriasis is presented in this case?
Guttate psoriasis
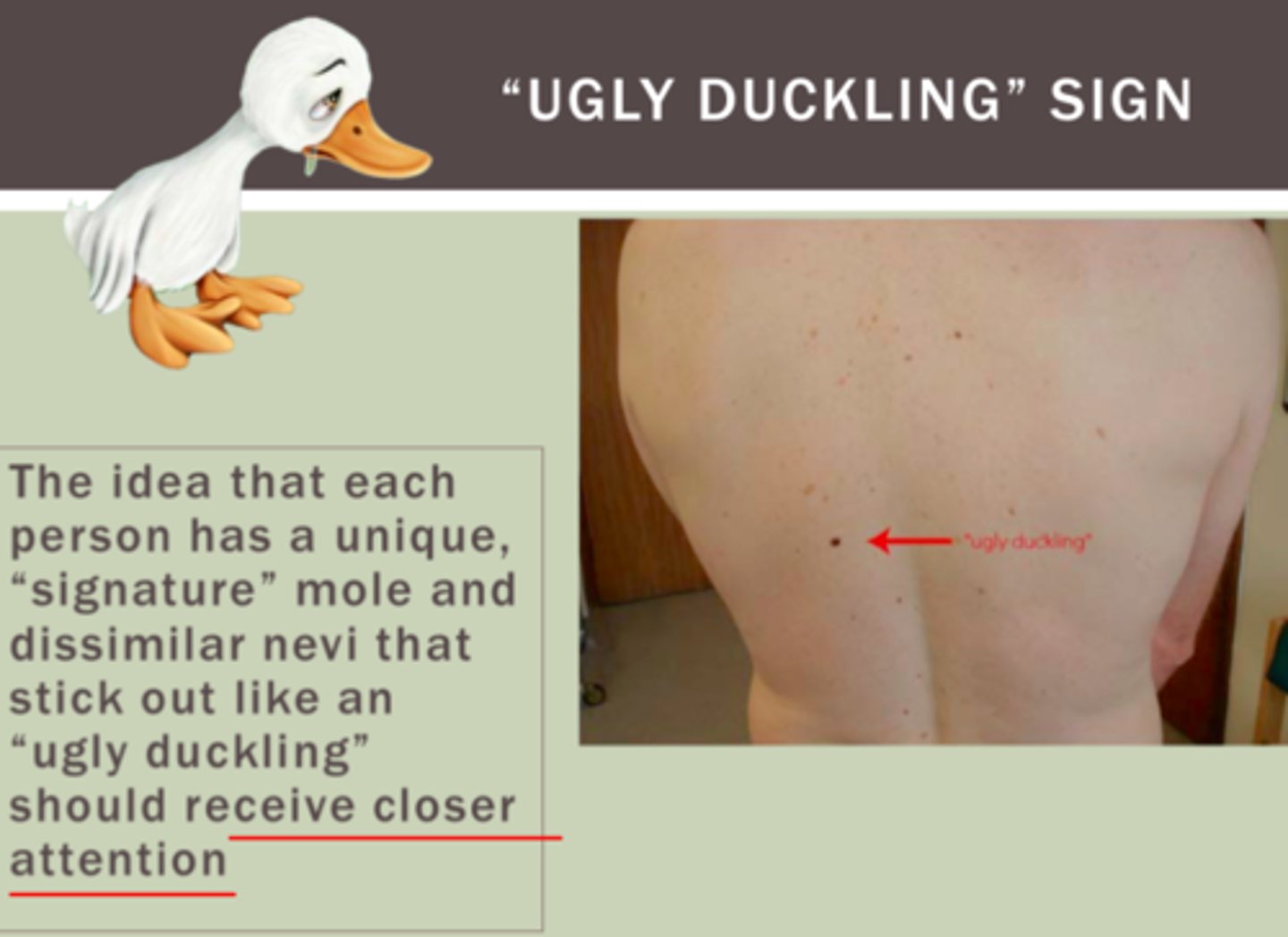
Please define the ugly duckling sign and what it is used for
The ugly duckling sign refers to a nevus that stands out and looks different from all the other nevi on the body of a person. It should be approached with a high index of suspicion. It is used as a clinical feature indicative of malignancy in a nevus.
State how blister location differs in the mucosal-dominant PV versus the mucocutaneous type PV. Which autoantibodies profile do you expect in these two subtypes?
In the mucosal-dominant PV, we find blisters and erosions in the deep layers of the mucosae, especially the oral mucosa. We expect positivity to anti-Desmoglein 3 IgG, since this glycoprotein is most abundantly expressed at this level.
In the mucocutaneous type of PV we find blisters in the deep layers of the mucosa and also in the epidermis; since it is an overlap between the mucosal type and the cutaneous type PV, in this case we have autoantibodies against both desmoglein 1 and 3.
What is the treatment of choice for urticaria? Give examples of some common side effects.
2nd generation H1 antihistamines; corticosteroids;
2nd line: Cyclosporin;
3rd line: Omalizumab.
List at least 5 triggers of thermal urticaria.
Warm or cold environmental temperature;
Hot or cold water temperature when bathing or showering;
Hot or cold drinks or foods;
Fever;
Warm sunlight;
Local warming of the skin (heating pads);
Generalized overheating
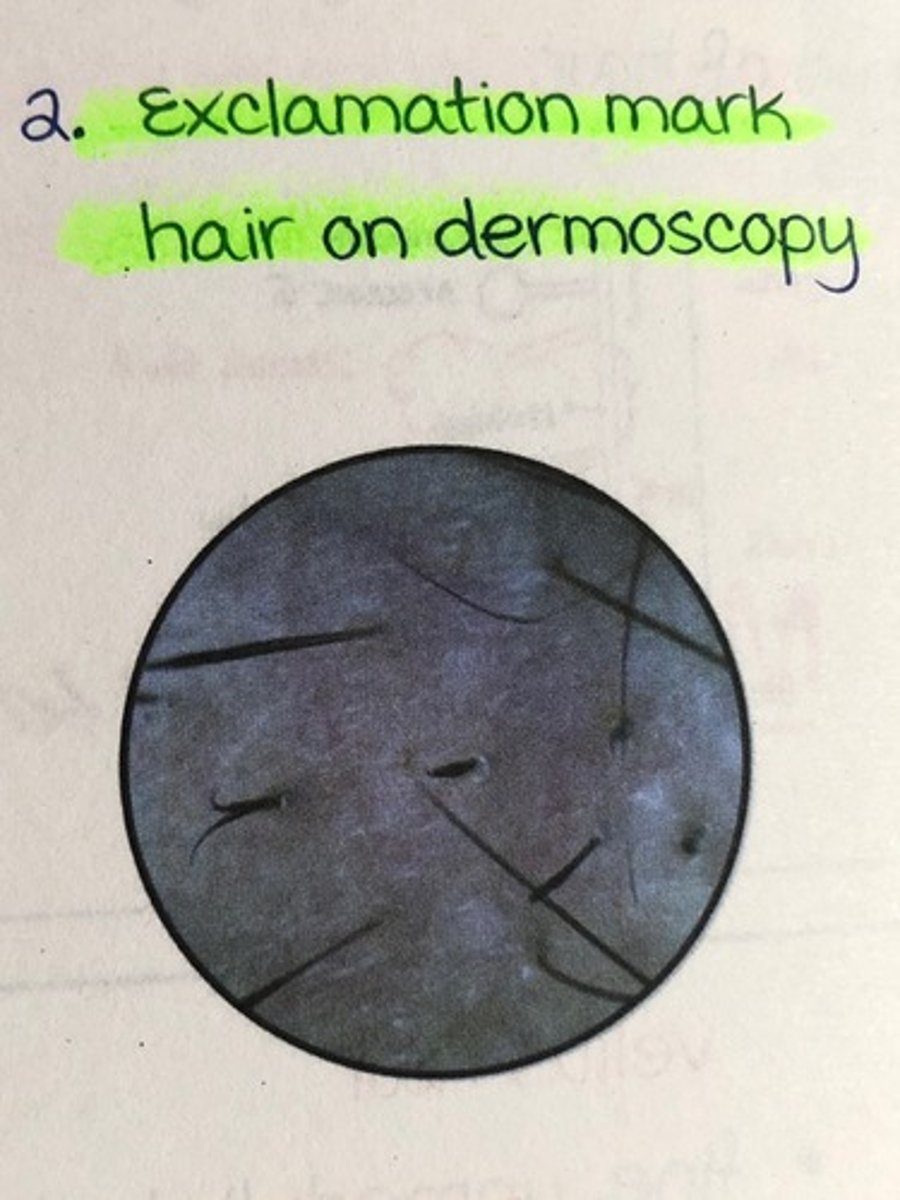
What is a typical clinical finding in alopecia areata?
Exclamation point hair + yellow dots