Cog Neuro Lec 2 - Fundamentals of neurotransmission, neuroanatomy
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
astrocytes
BBB
respond to brain injury
neuro development (building the bridges for the neurons)
oligodendrocytes
collect waste (dead and dying cells)
important after brain injury
only brain and spinal cord
schwann cells
found in arms, legs (periphery)
insulate neuro signals
development
maintenance
function
regeneration of peripheral nerves.
same as oligodendrocytes but for the peripheral nervous system
what are the three classes of neurons?
motor neurons
sensory neurons
interneurons
overwhelming number of our neurons
complex types of information
integration across brain regions and within them
not just motor or sensory, more complex
what is the all-or-none principle
whether a neuron sends or does not send a signal based on threshold
does it matter how stimulated a neuron is for the action potential spikes to vary
no, the neuron will send the same action potential, however if there is more stimulation, it will send more signals
what does the axon hillock do?
it decides if there is enough action potential
which glial cell speeds the signal of a neuron up through insulation/ where do myelin sheaths come from?
oligodendrocytes
what is saltatory conduction?
the jumping of the signal from each node of ranvier
which disease has different symptoms depending on the place of origin
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
what causes the MS?
the immune system attacking the myelin in the brain
where is MS more common and what is it correlation?
north western areas (canada, england) correlated with vitamin D among other things
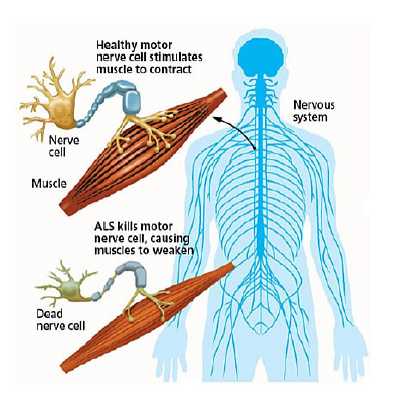
what is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
specific to motor neurons
fast development of paralysis
can cause you to stop breathing
what is excitotoxicity? and how did they find that this was what ALS was?
increased neural activity
found due to the fact if you give someone with ALS reducing neural activity drugs, it slows the progression
Ischemia
when parts of the body do not get enough oxygen to perform tasks
what causes neural failure
when the neuron does not get enough oxygen to perform its task (neural ischemia)
what kind of stroke is most common?
ischemic stroke
blood clot to an area of the brain
associated with diet and overall health
if treatment for a ischemic stroke is performed in how x number of minutes, what can happen to the neurons?
if within 90 minutes, there is treatment, then the neuron can come back to life
what are the signs of a stroke
facial drooping on one side
muscle weakness of legs or arms on one side
slurred speech
how much oxygen does the brain use up?
25% of our oxygen
what causes presynaptic neurons to release neurotransmitters into postsynaptic neurons
the influx of Ca2+ into the cell binds to the vesicles to release at the synapse
where is dopamine produced
in the brainstem in the substantia nigra
ventral tegmental area (decision making)
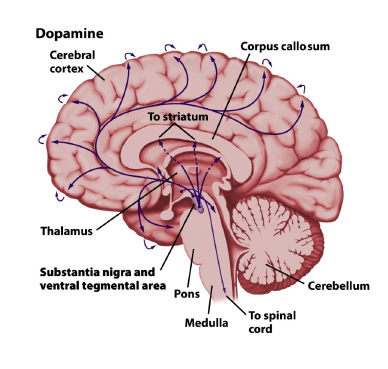
what is dopamine good for?
Higher-order cognition
moment-moment consciousness
used to not loose train of thought
Voluntary movement
in other areas such as the basil ganglia
Reward/reinforcement learning
operant conditioning
addiction
what happens to the substantia nigra when you have parkinson’s disease
90% of substantia nigra has died
what are some diseases associated with dopamine
Parkinson’s disease (decrease)
psychotic thoughts/behaviours
addiction
where is norepinephrine produced
locus coeruleus
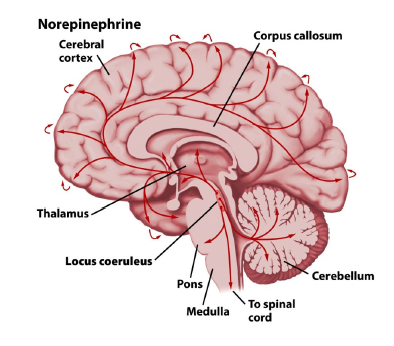
what causes cognitive arousal/ attention
norepinepherine
what is norepinephrine used for?
cognitive arousal/attention
memory and mental flexibility
being open to changing how you think about something
mood
Dysfunctional levels associated with norepinephrine
Alzheimer’s disease
reduction in consciousness, loss of memory, mood changes
Mood disorders
Visuospatial neglect
where is serotonin produced?
raphe nucleus
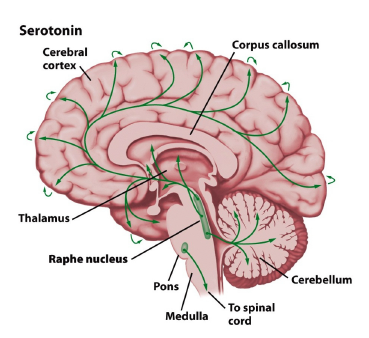
what is serotonin used for?
mood
Dysfunctional levels associated with serotonin
mood disorders
psychotic thoughts/behaviours
where is acetylcholine (Ach) produced
basal forebrain
what is acetylcholine used for?
Sensory processing/attention
Learning and short-term memory
Movement (peripheral nervous system - PNS)
Dysfunctional levels associated with
Alzheimer’s disease
Myasthenia gravis (PNS)
lack of muscle movement
what is the yerkes-dodson curve?
An individual’s baseline level of a neurotransmitter
what’s of challenge of psychopharmacology?
effecting one hormone may effect the yerkes-dodson curve of another hormone/neurotransmitter
what is the corticospinal tract/pyramidal tract for and where does it extent from
it is there for voluntary movement
path: motor cortex → midbrain → medulla → switch sides (medullary pyramids) → spinal cord
what does the medial lemniscal tract carry
carries touch information and proprioception information
what is proprioception?
knowing where your body is in space without vision
what does the lateral spinothalamic tract carry?
pain and temperature information
what two tracts terminate in the parietal lobe?
the medial lemniscal tract and the lateral spinothalamic tract
whats the difference between ventral and dorsal information?
dorsal is sensory (dorSal → SenSory)
ventral is motor
what is a dermatome map?
map of the human body where parts of the spinal cord control
what does the frontal lobe do?
higher order cognition
advanced thinking
movement/motor control
speeking/language production
where does broca’s aphasia take place
frontal lobe
parietal lobe fucntion
crucial for attention
somata sensation (spacial awareness on your body
occipital lobe function
visual processing
temporal lobe function
hugely involved in memory
dementia is here
hearing
language comprehension
wernike’s area is here
where is the motor cortex?
frontal lobe
where is the somatosensory cortex?
parietal lobe
what is the brain mostly composed of in terms of cortex?
association cortex
what do primary, secondary, and association cortex’s do?
primary and secondary only focus on one or two input/output functions but most of the brain processes multiple functions at a time
what is the lymbic system involved in?
emotion and memory
amygdala
processing of emotion
almond-shaped structure
end of hippocampus
what is the role of the hippocampus?
creation new conscious or declarative memories
thalamus
large nucleus that helps transmit sensory information
important in consciousness
every sense except for olfaction synapses in the thalamus
corpus collosum
white matter tract that connects the left and right hemispheres
what sense does not get relayed/synapsed in the thalamus?
olfaction
basil ganglia
procedural learning (ex. shooting basketball, bike)
routine/autopilot (ex. driving)
what are the three parts of the basil ganglia?
caudate nucleus
putamen
globus pallidus
cerebellum
thought it was only for motor coordination (smooth, continuous, accurate movement)
language and memory
executive function
how can we detect meningitis or other neural ailments in the brain?
taking the fluid from the spine
what are the roles of the ventricular system
to keep the brain stationary so that it doesn’t move around and bruise the brain (buoyancy)
eliminates waste from nervous system
what arteries bring blood to the brain and to where?
through the vertebral artery (back) and the common carotid artery (front) to the circle of willis
what are the three major arteries of the brain
anterior cerebral artery, middle cerebral artery, posterior cerebral artery
what is the middle cerebral artery distribution?
frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes (lateral surface of the cortex)
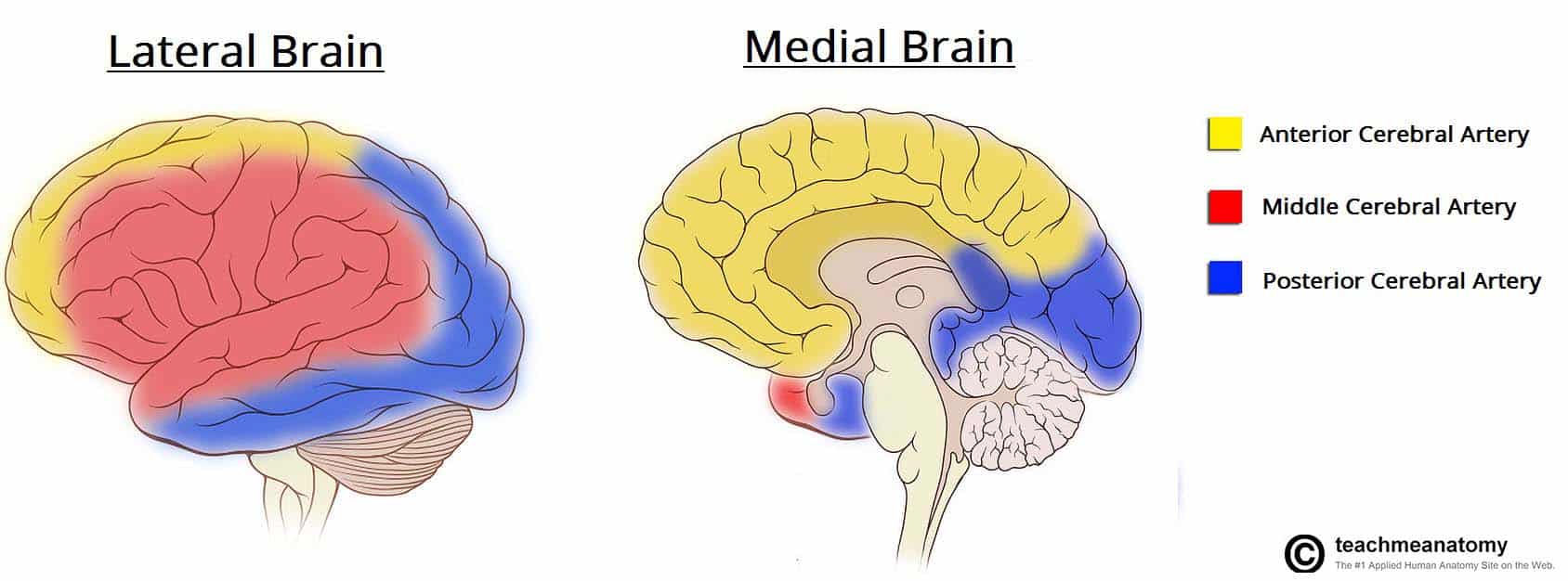
anterior cerebral artery distribution
the medial portions of the frontal and parietal lobes
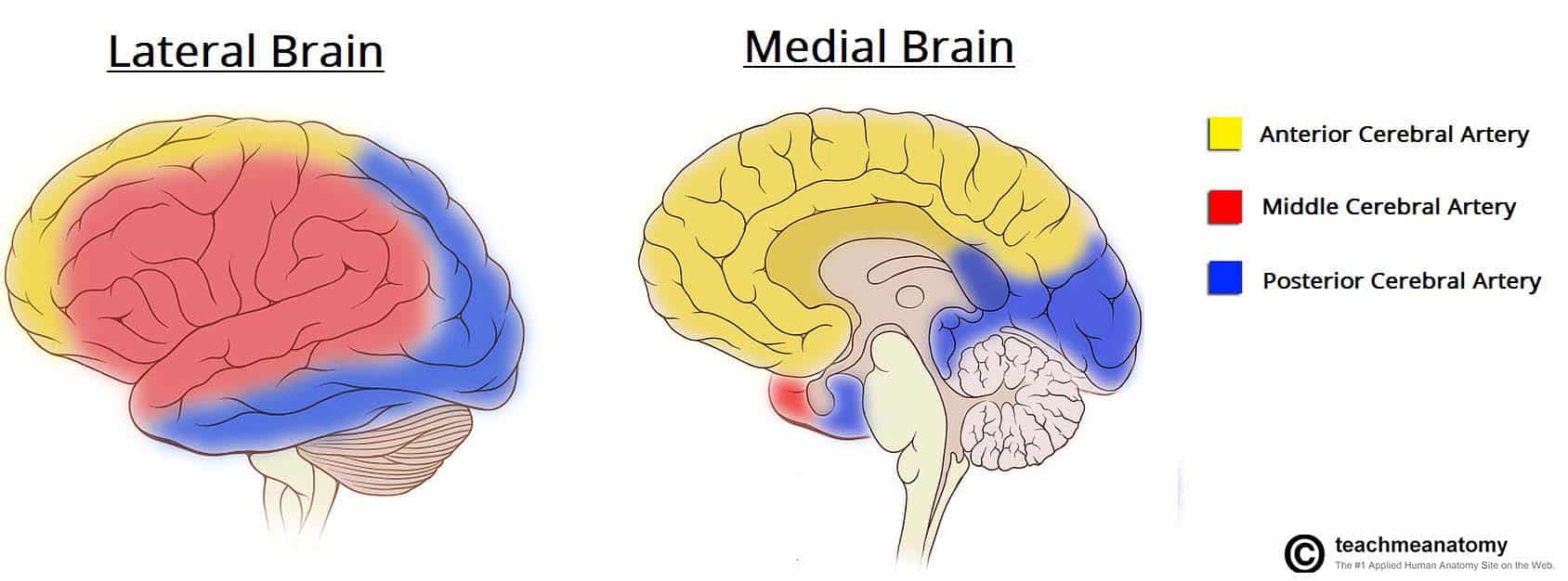
posterior cerebral artery distribution
ventral part of the temporal lobe and all of the occipital lobe
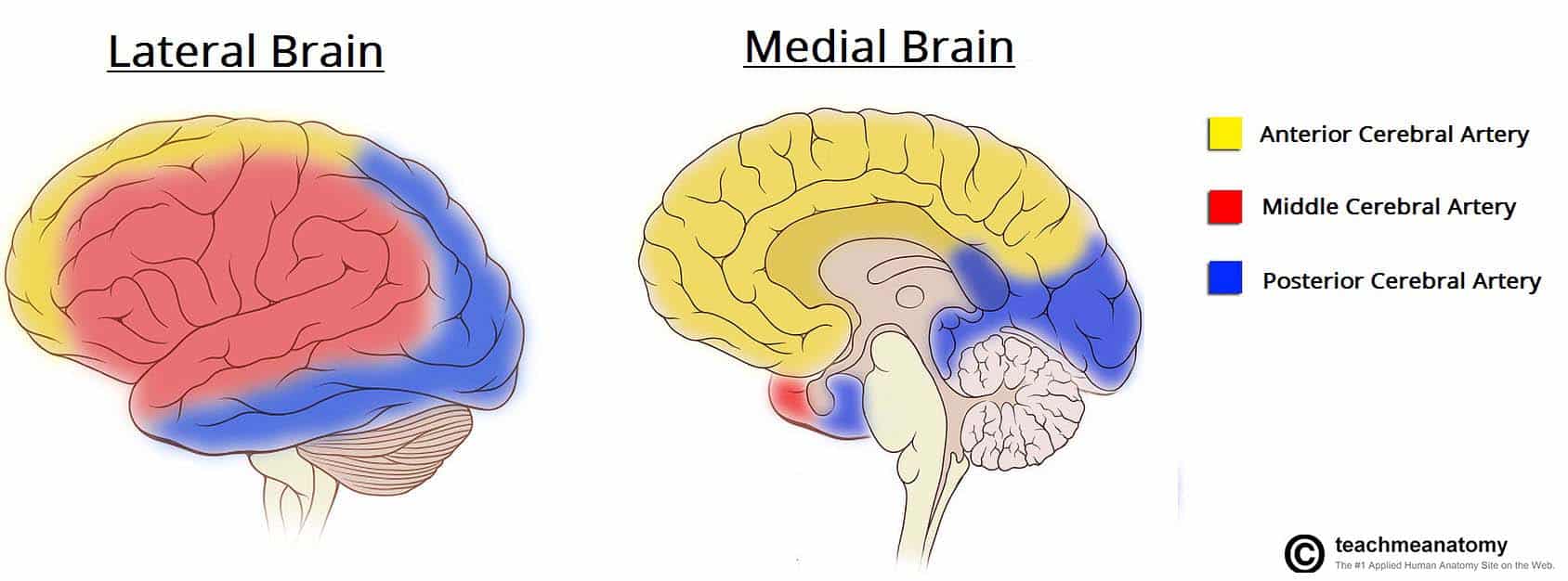
neuropsychological conditions caused by stroke are caused by damage to what?
the middle cerebral artery distribution