Lecture 13: Bacteria structure, growth and taxonomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are bacteria
Unicellular, free-living microorganisms
Taxonomically in bacterial domain: prokaryotes, unpaired chromosome with no nucleus, opposed to eukaryotes
Kingdom - Protista
Taxonomic ranks of procaryotae (kingdom) to species
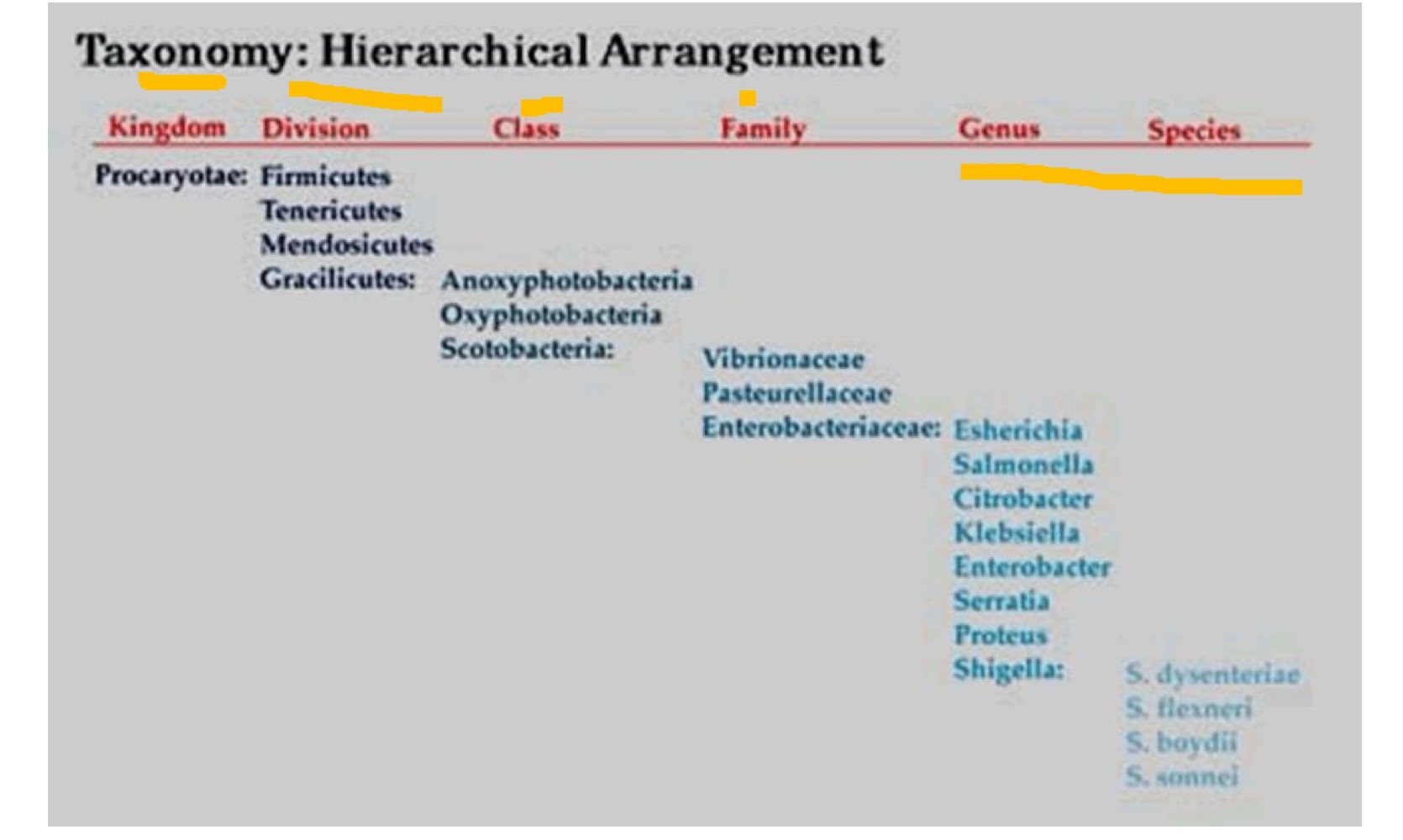
Binomial system of bacteria
Genus + Species
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphule (bunch of grapes)
Kokkos (berry)
Aureus (golden)
Why is bacterial taxonomy important?
Handling information - storage and retrieval
Learning - diverse organisms
Communication - of information about bacteria
Identification - of unknown bacteria
Evolution - allows epidemiological data to be understood
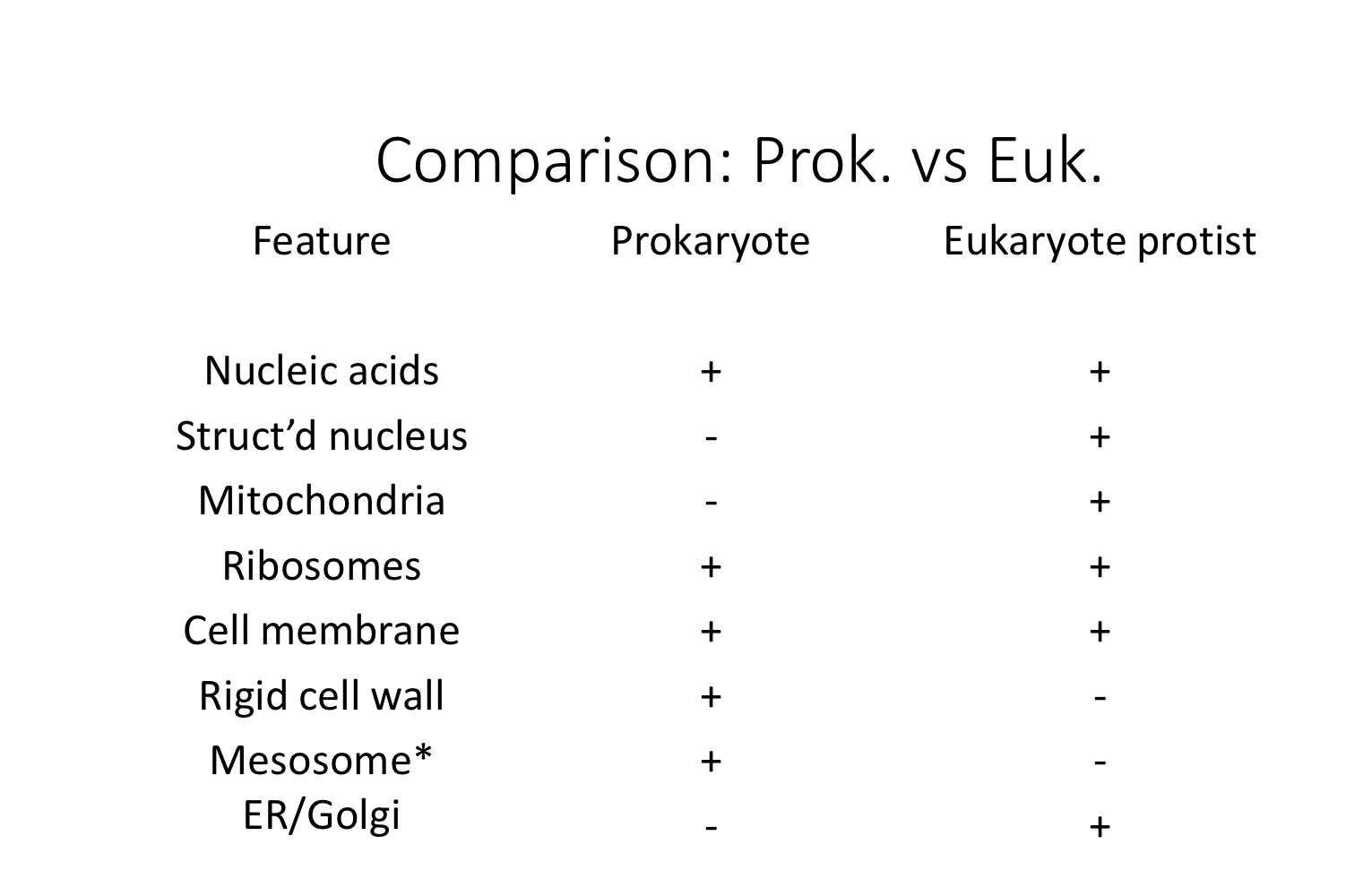
Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote protist
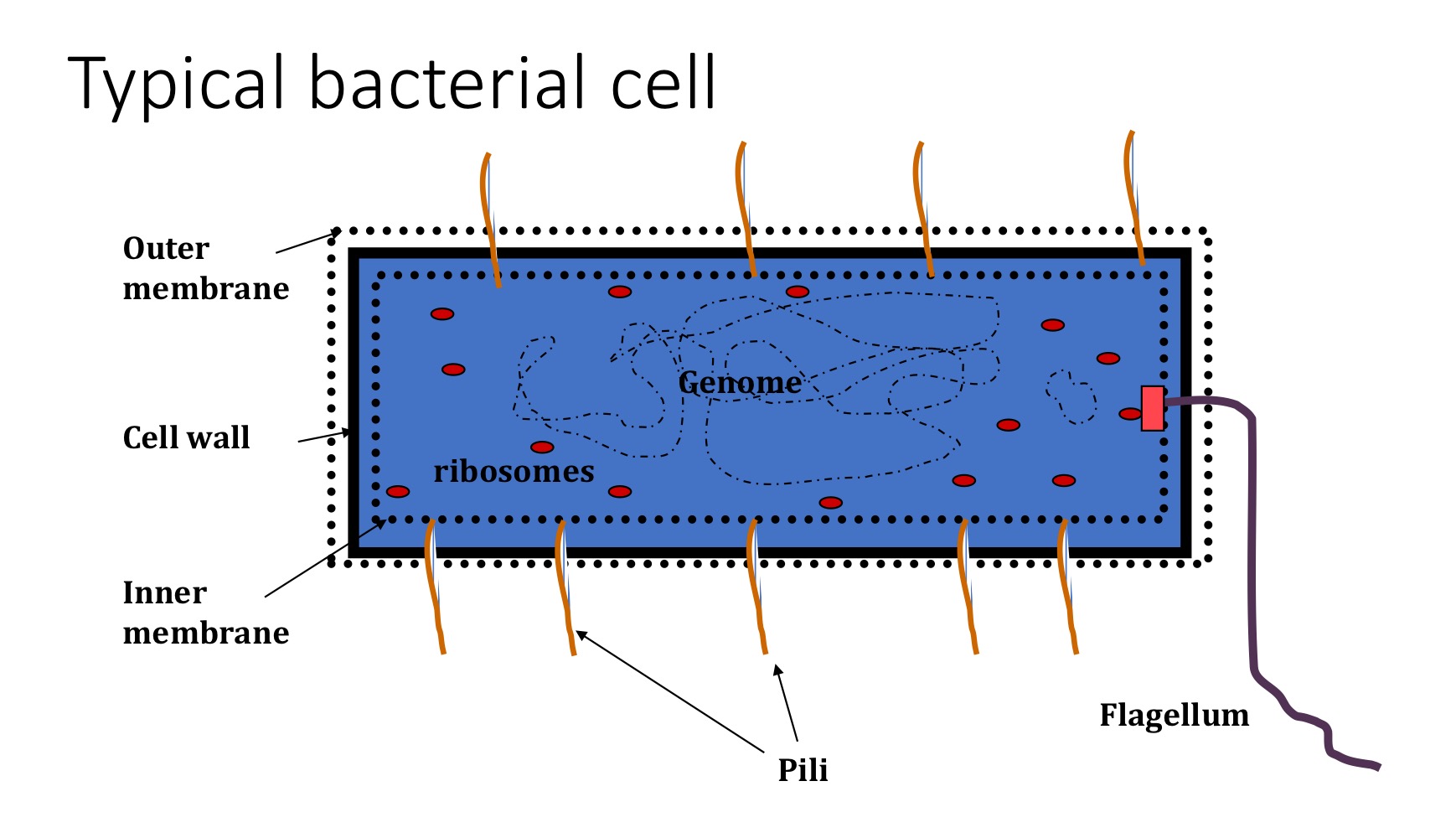
Typical bacterial cell
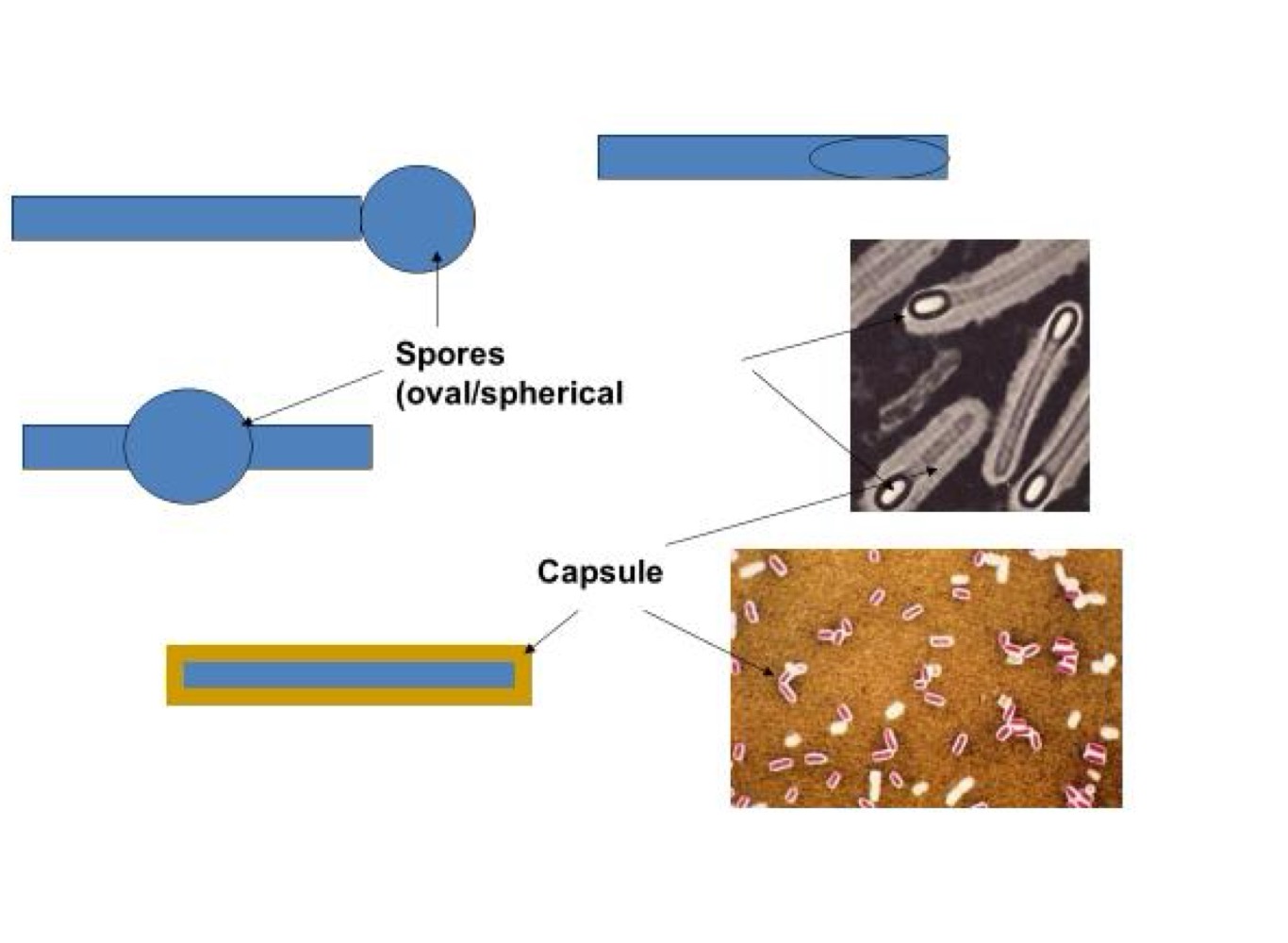
Morphological features of Clostridium difficile
Cell survival in adverse conditions
Desiccation, heat, starvation
Gram +ve bacteria
Capsule/ glycocalyx (loosely bound and amorphous)
Features of flagella
Cell motility
1-20, can be peritrichous or polar
Coiled in structure
Protein (flagellin)
Anchored in bacterial membranes
Chemotaxis
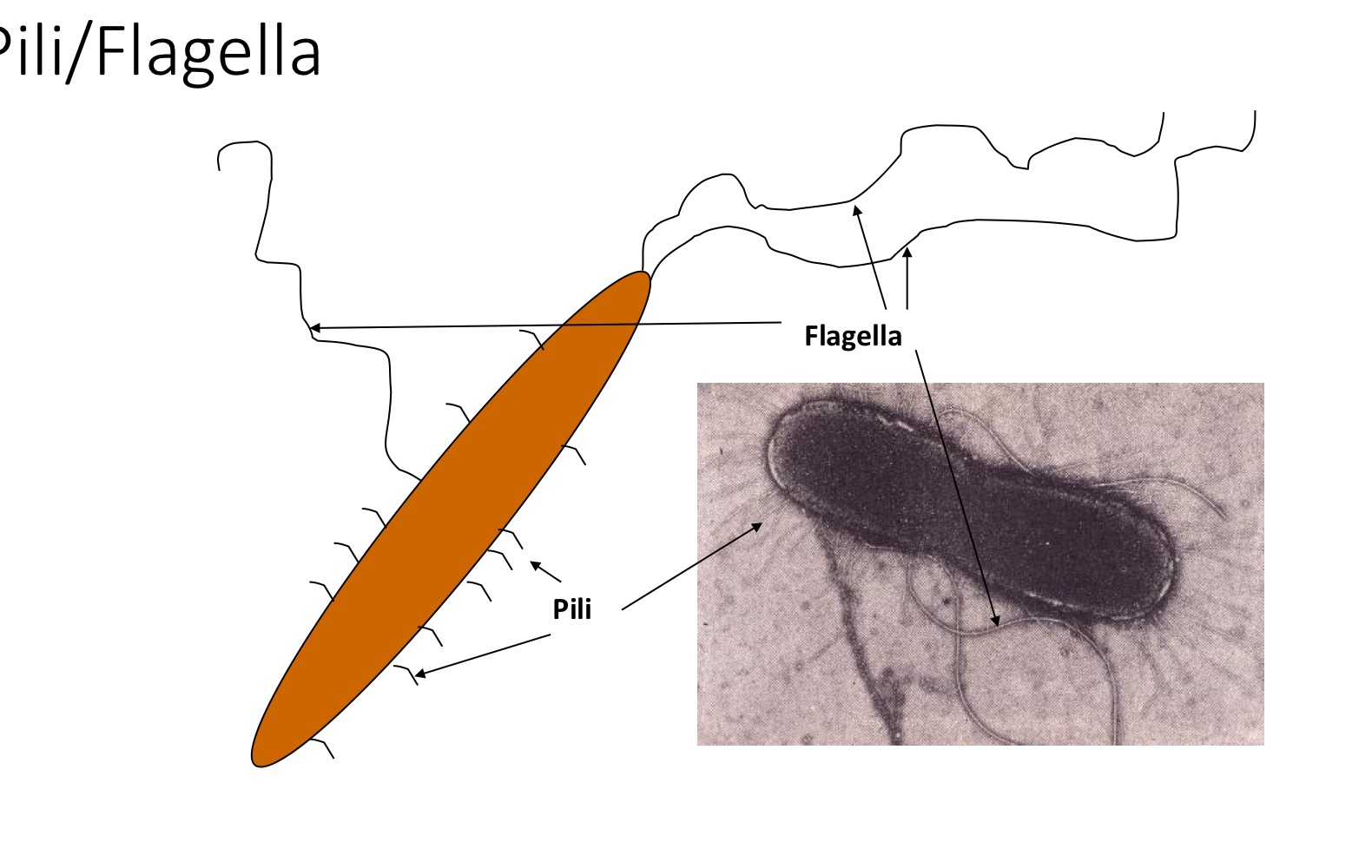
Fimbriae (pili) features
Up to 100+
Perithrichous
Not coiled
Protein (pilin)
Adherence
Bacterial growth requirements
Physical characteristics - Sensitive to gas/ temp./ water/ pH/ light/ osmolarity
Nutritional requirements - carbon source, nitrogen source, inorganic salts, organic compounds
Phenotypic characteristics of bacteria
Macroscopic/ microscopic
Biotyping vs serotyping
Categorising organisms by the way they respond to biochemical tests, grouping by the presence of a specific set of antigens
Antibiogram patterns
Categorise by response to antibiotics (Abx)
Pyocin vs Phage
Pyocin - toxins produced
Phage - ability to be infected by virus (typing)
Macroscopic (growth on agar medium)

Macroscopic : texture, appearance, pigmentation and optical density

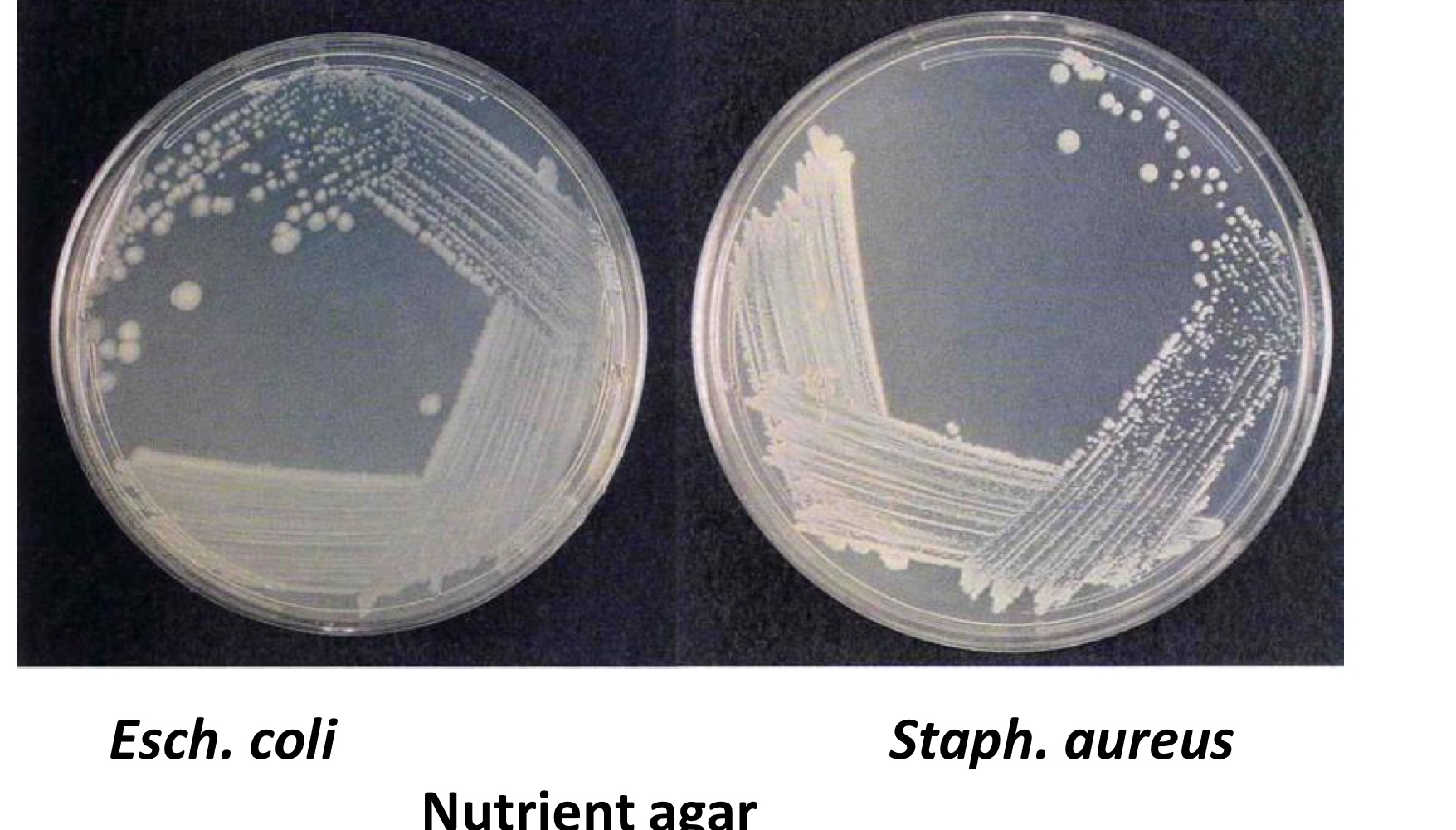
Nutrient agar colony morphology
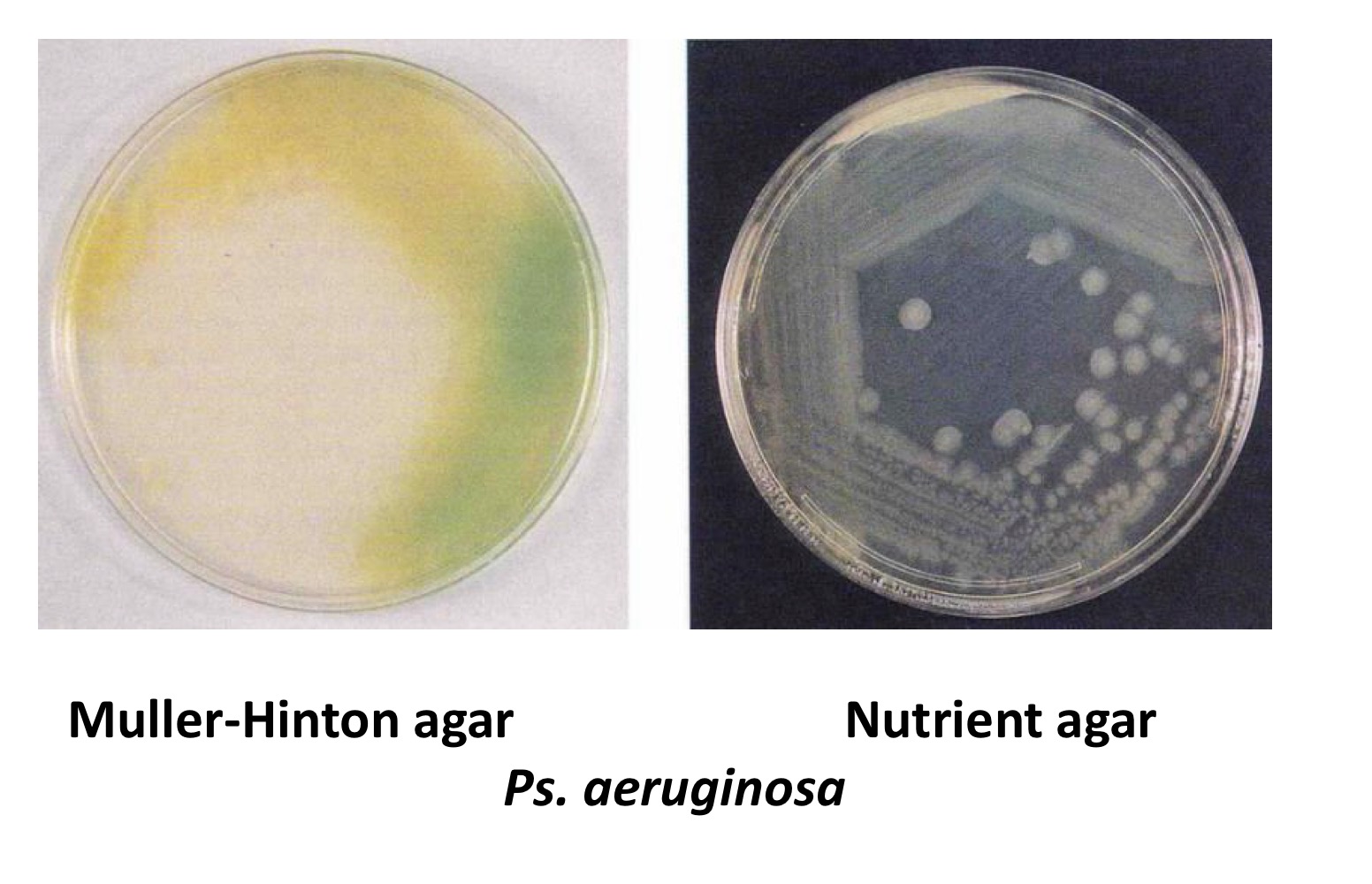
Muller-Hinton agar
Haemolysis on blood agar
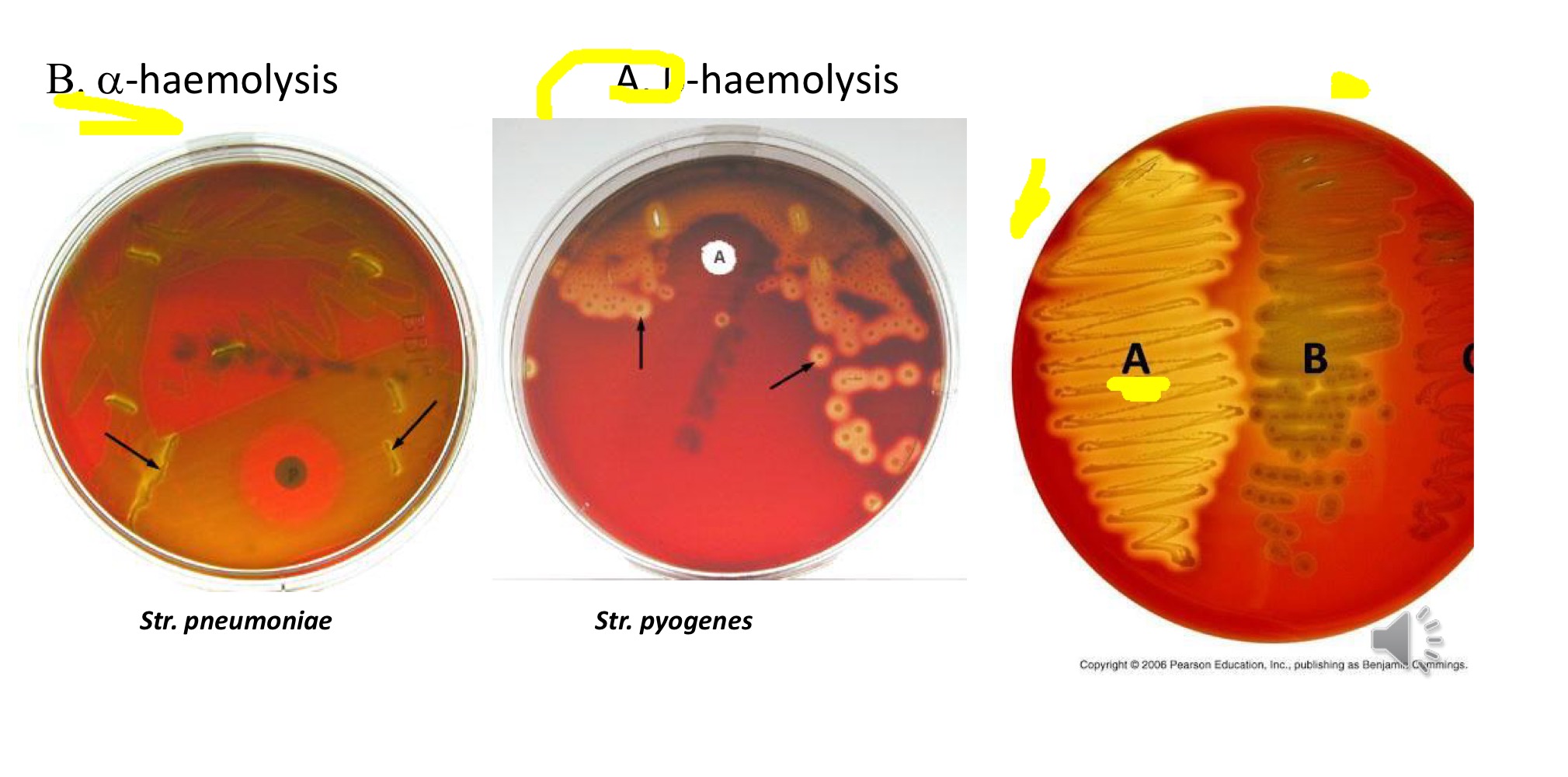
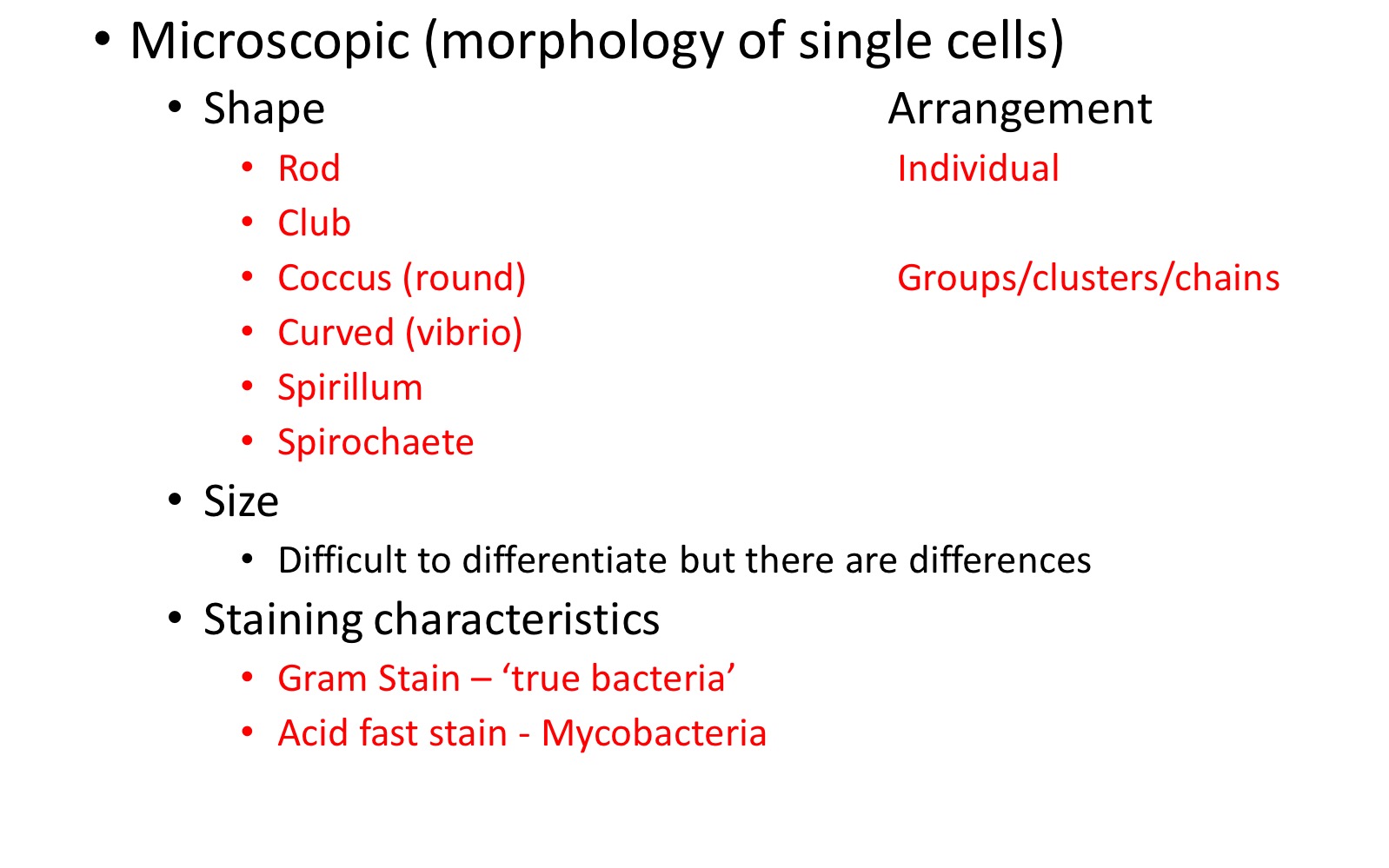
Microscopic: Shape/ arrangement/ size and staining characteristics
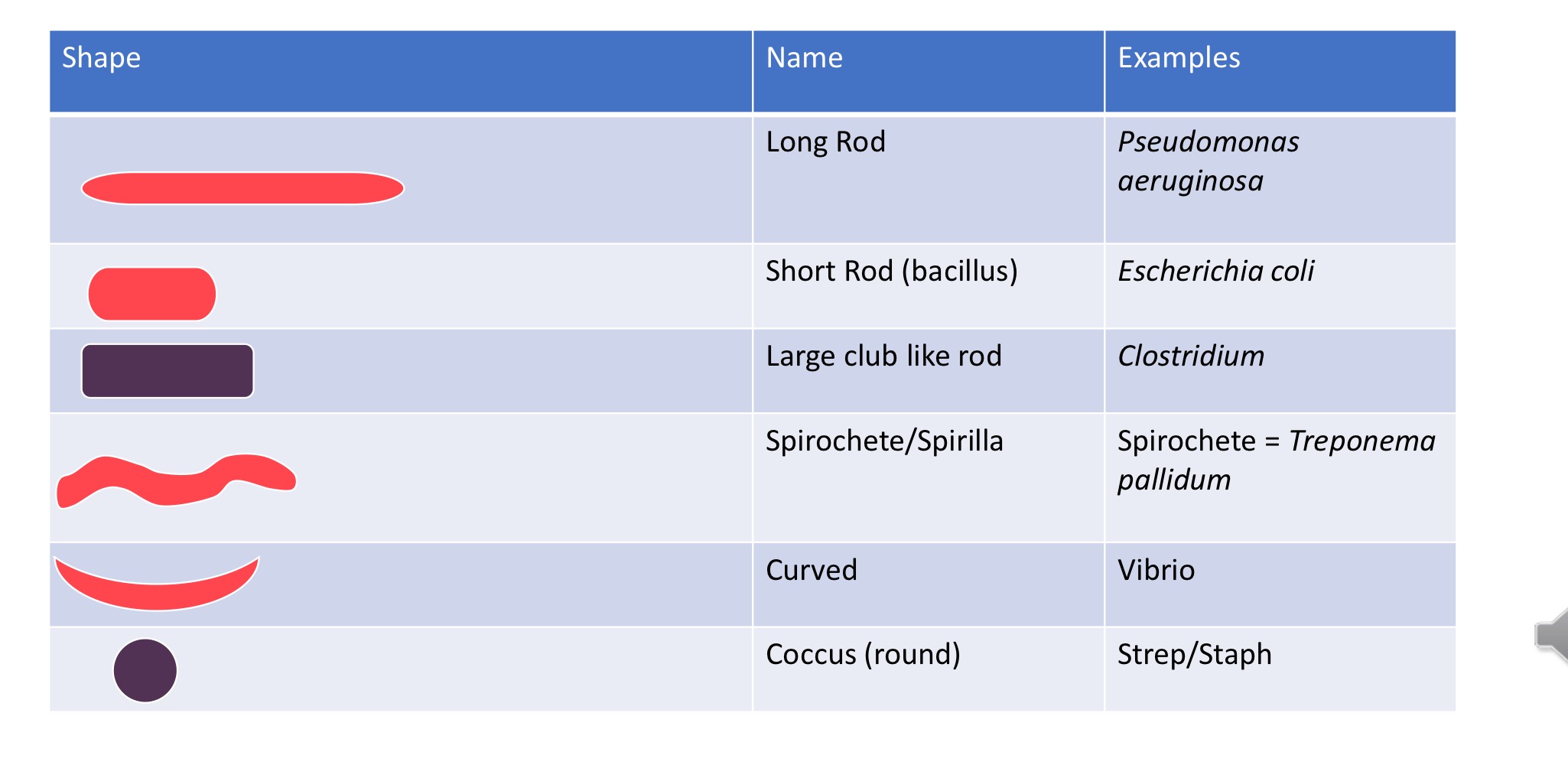
Shape + Examples
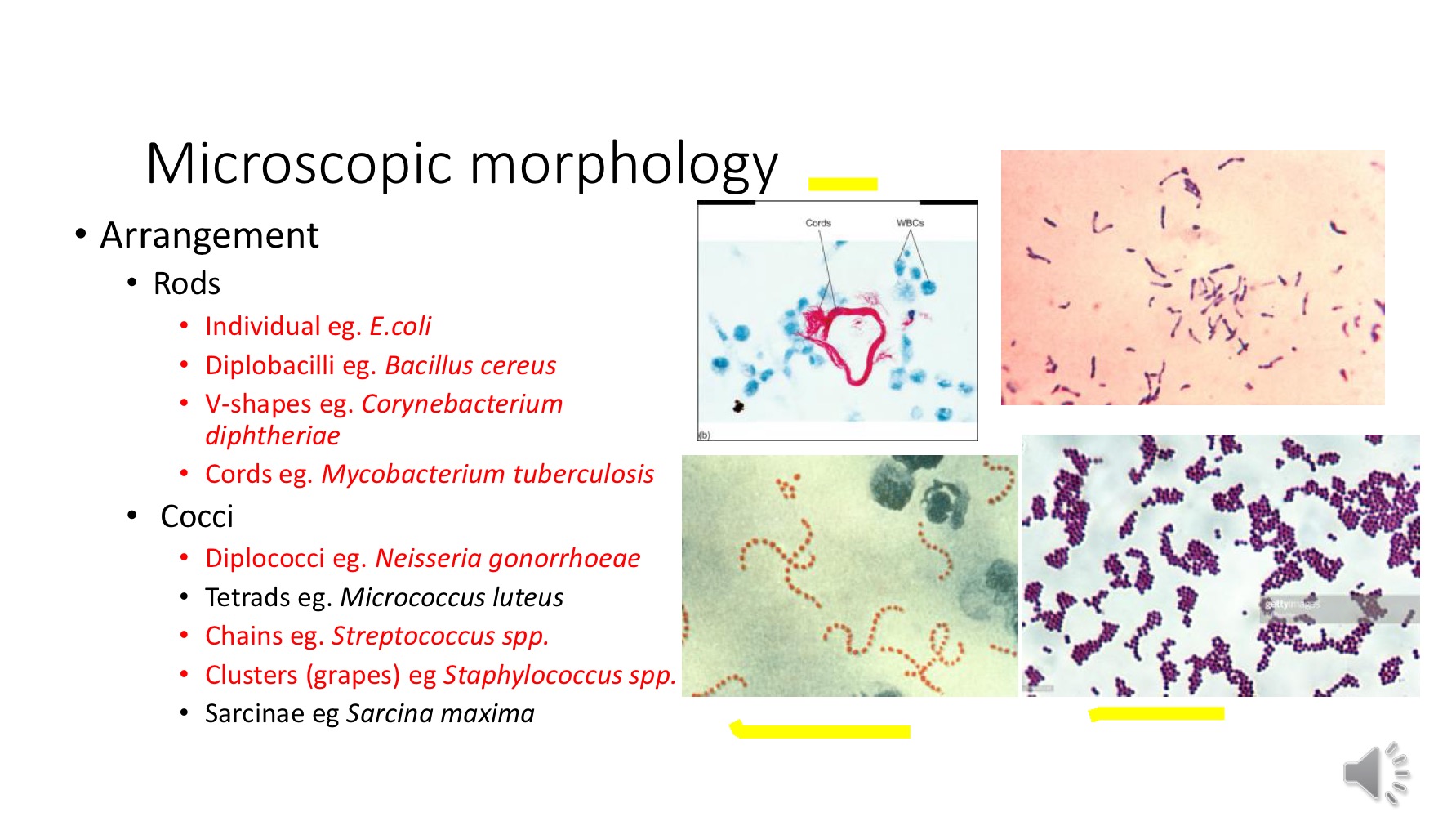
Microscopic morphology - arrangement
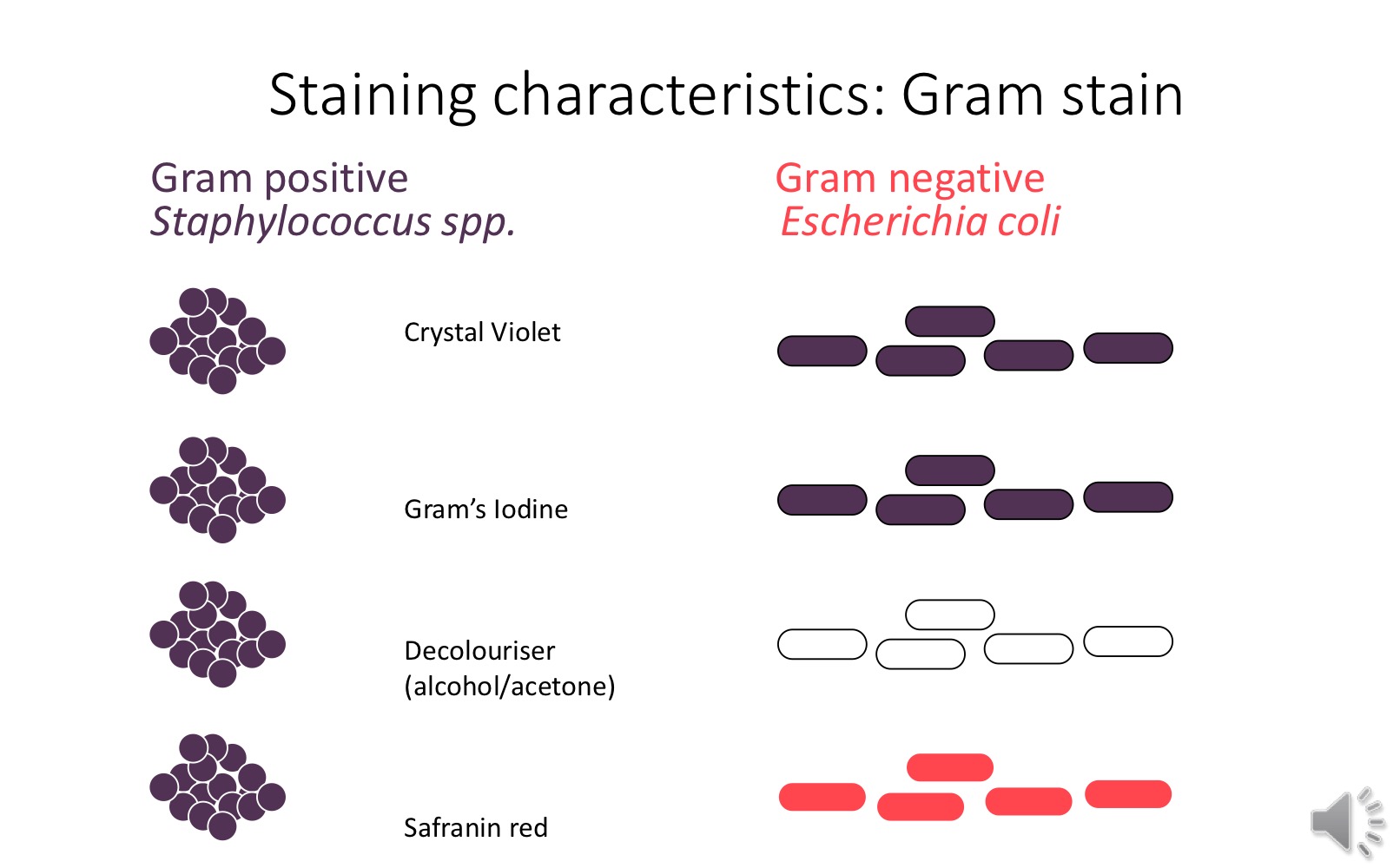
Gram staining
Differentiates bacteria on basis of their cell wall structure
Positive - thick cell wall
Negative - thin cell wall
Gram positive vs negative stages
Crystal violet
Grams Iodine
Decolouriser
Safranin red
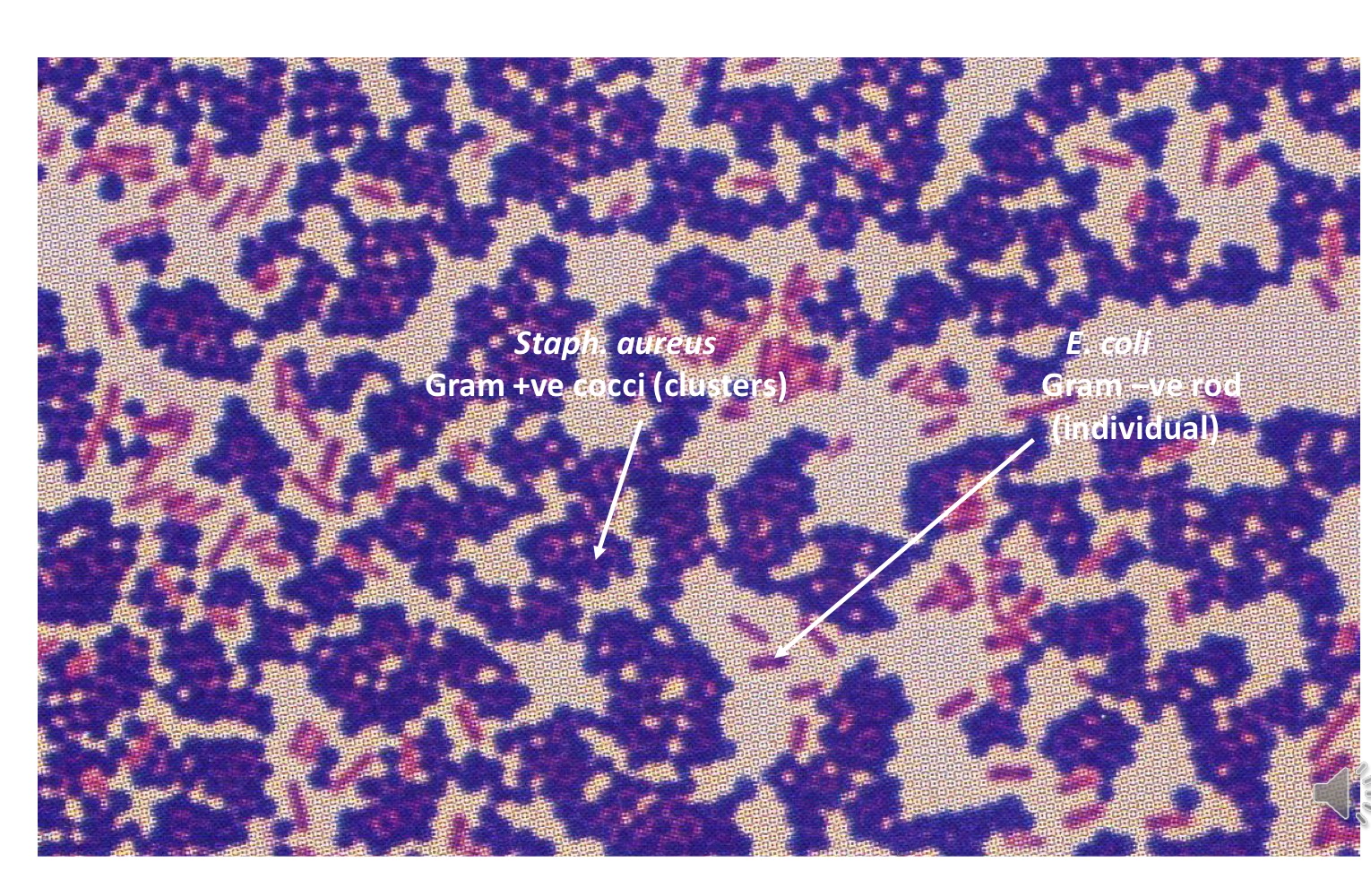
Staph aureus vs E.coli, which is Gram+ve and -ve?
Common gram negative bacillus
Escherichia Coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Haemophilus influenzae
Gram positive coccus
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram negative diplococcus
Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria gonorrhea
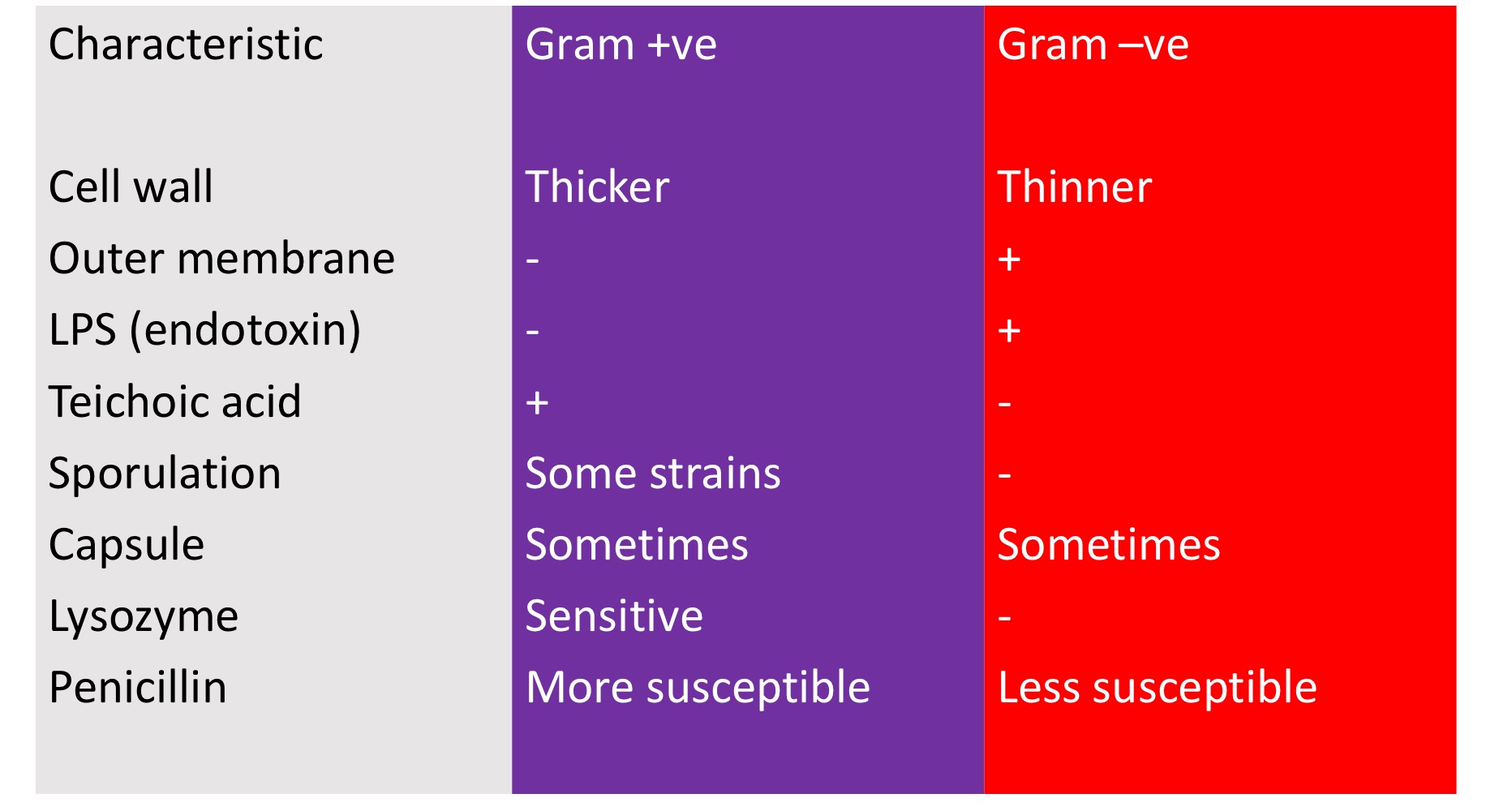
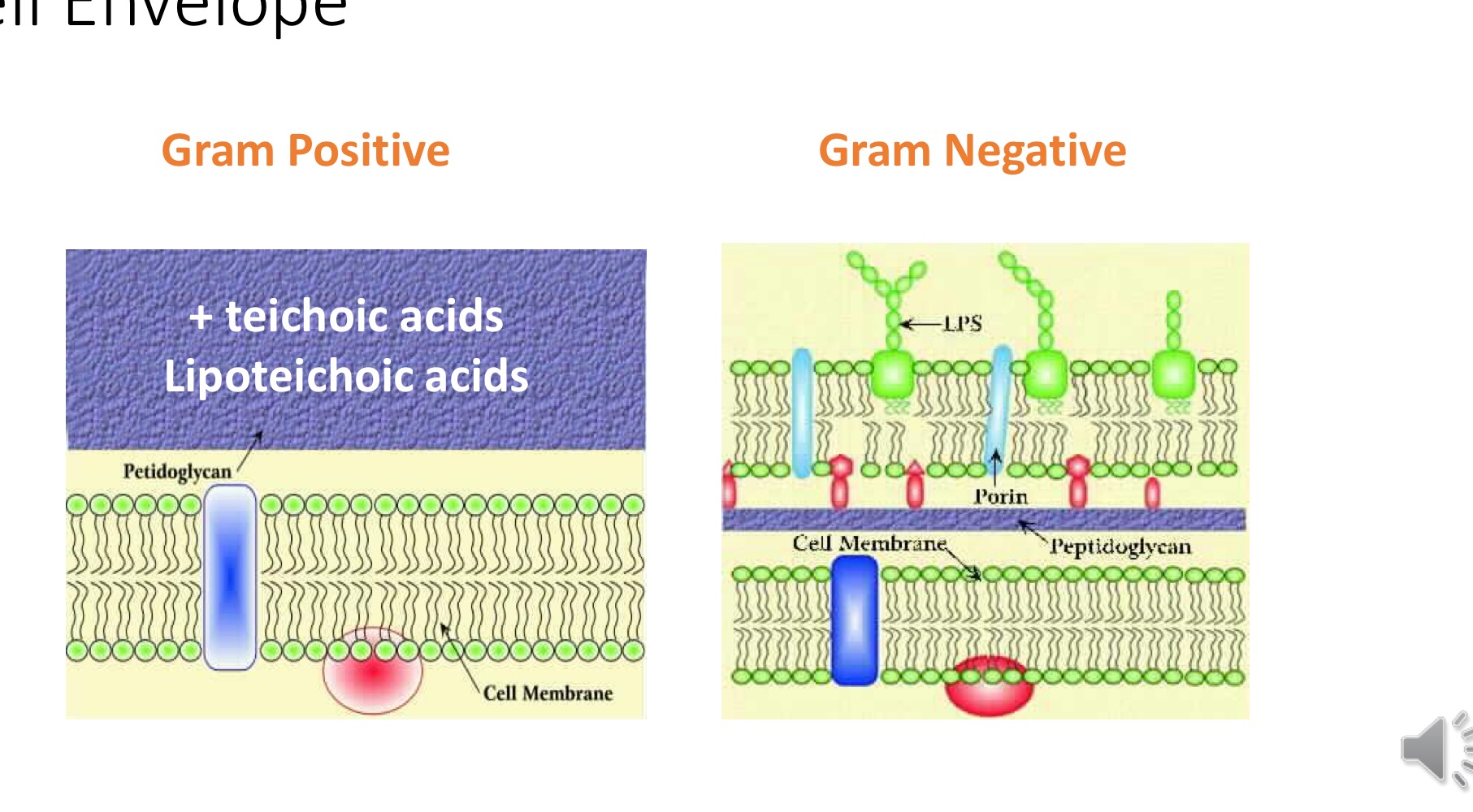
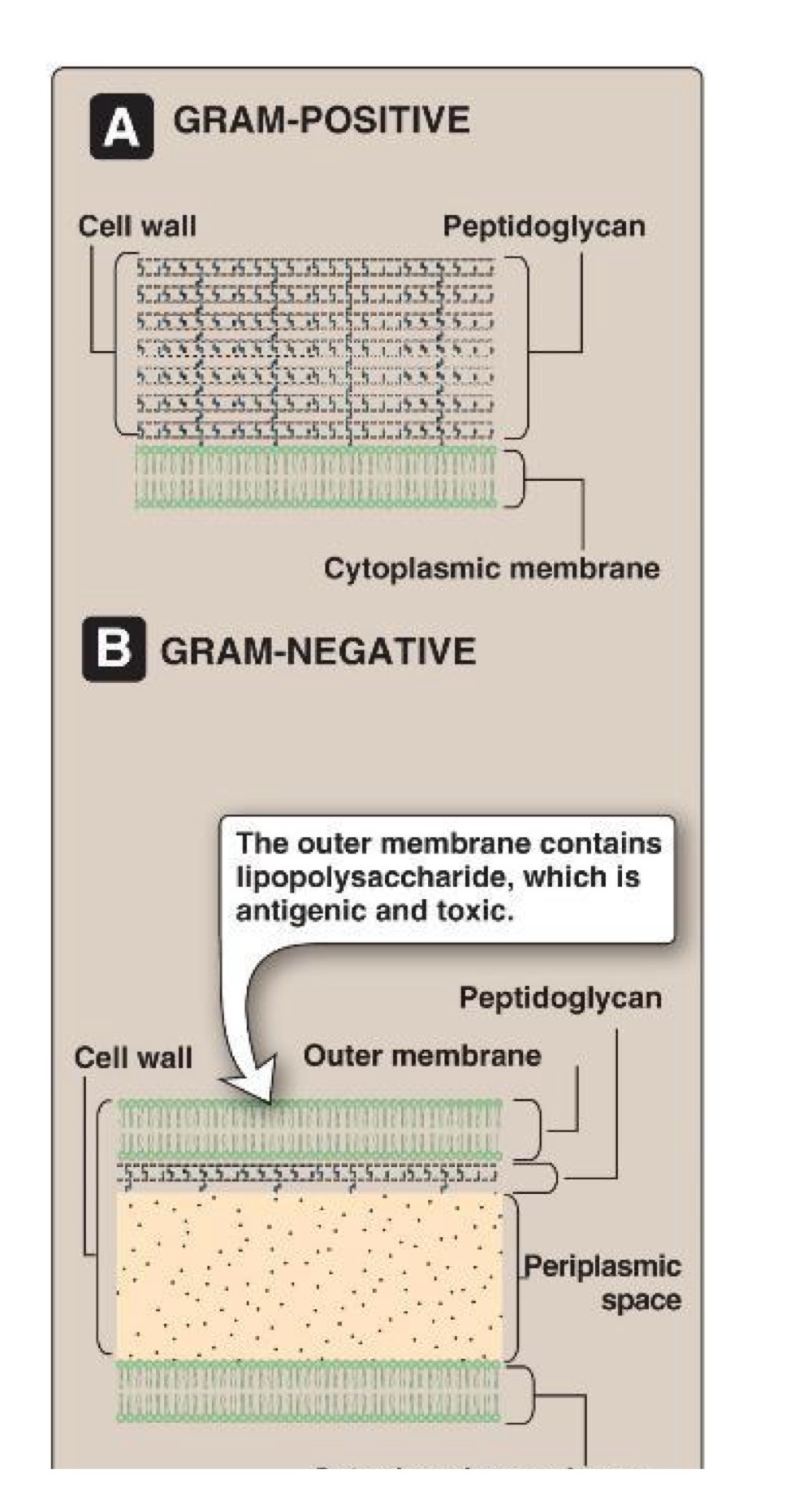
Gram +ve vs Gram -ve cell envelope
Lipid bilayer
Two parallel phospholipid cell membranes → lipid bilayer, polar phosphate groups are on outisde, non polar lipid chains on inside
Gram +ve vs Gram -ve cell envelope image
What are the functions of the cell wall?
Maintain rigidity and cell shape/ structure
Maintain osmoalroty
Survival
Cell division
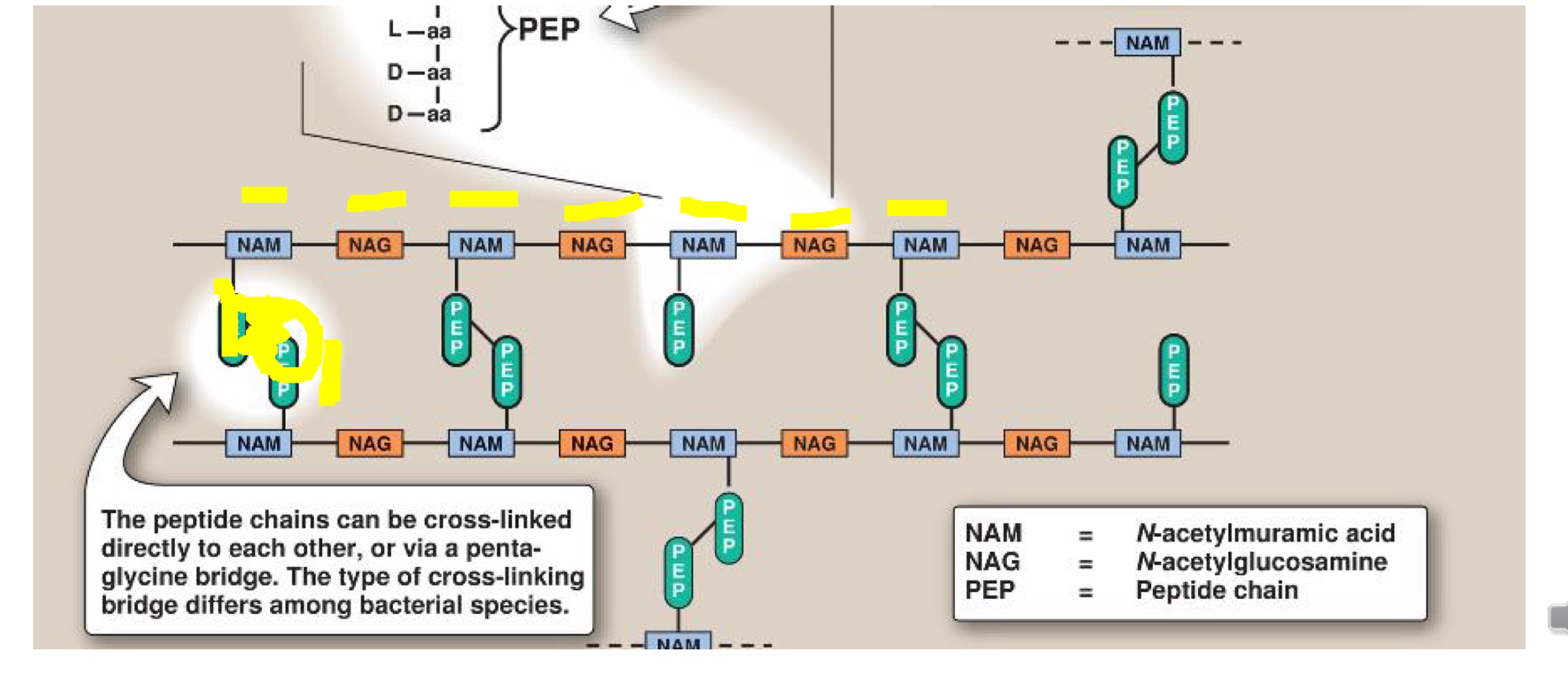
Bacterial cell wall synthesis
Peptidoglycan precursor synthesised inside cell
Exported across cell membrane (blocked by Abx bacitracin)
A site is created in the existing wall by enzymes action
Cell grows
Cell wall structure
Mycobacterium cell wall
Covalently attached to arabinogalactan polymer
Mycolic acid waxy coat - lipids
Poor gram stain
Acid fast (zeihl-Neelsen stain) - carbolfuchsin
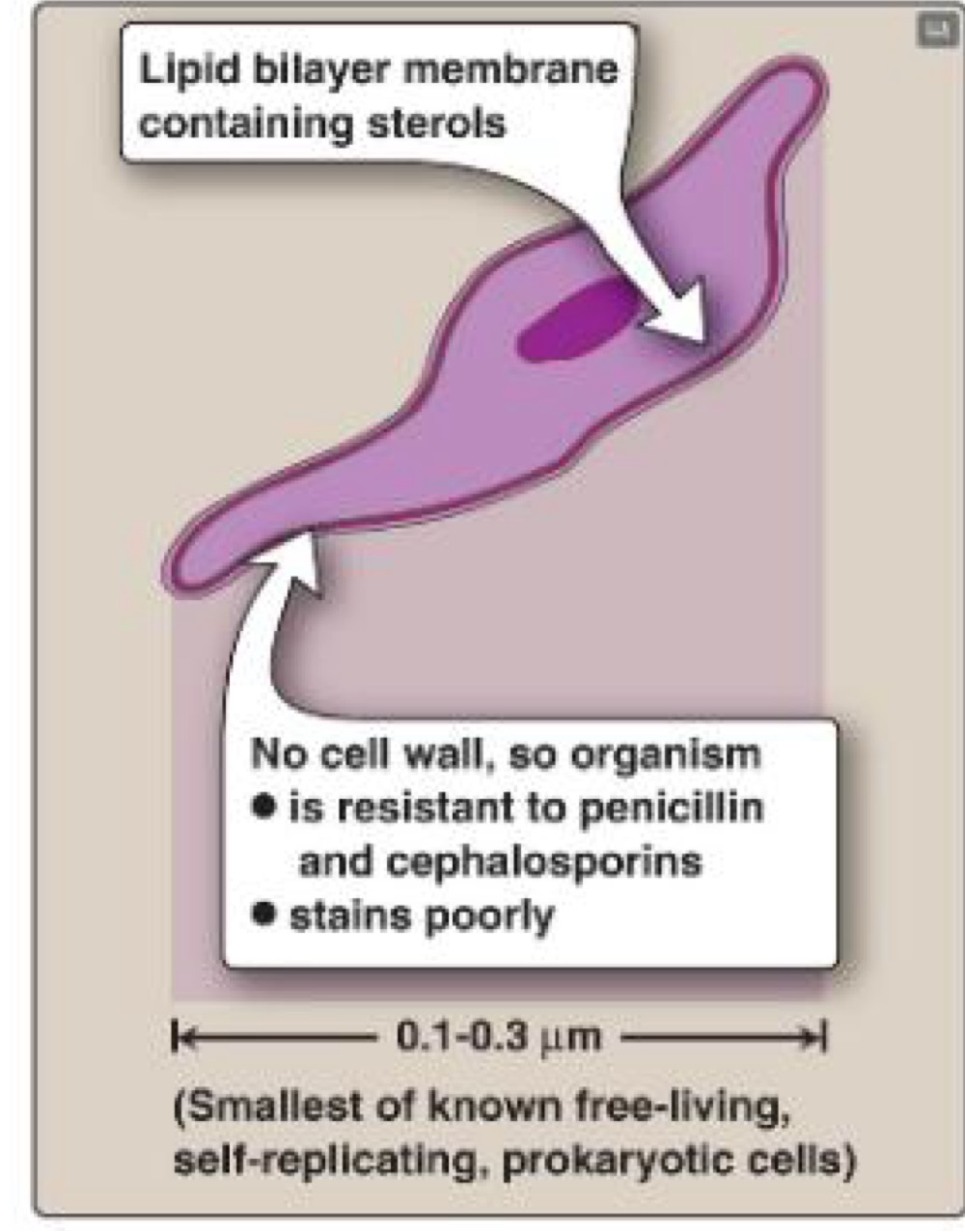
Mycoplasma cell wall
No cell wall
Cell membrane contains steroids
Cell wall synthesis
Antibiotics such as penicillin, vancomycin
Capsules
Vaccines eg strep. Pneumoniae
Cell membranes
Antibiotics such as polymoxin and vaccines
Ribosomes
Antibiotics eg gentamicin/ tetracyclines